Is It Possible to Analyze Kidney Functions, Electrolytes and Volemia Using Artificial Intelligence?
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Measuring Data
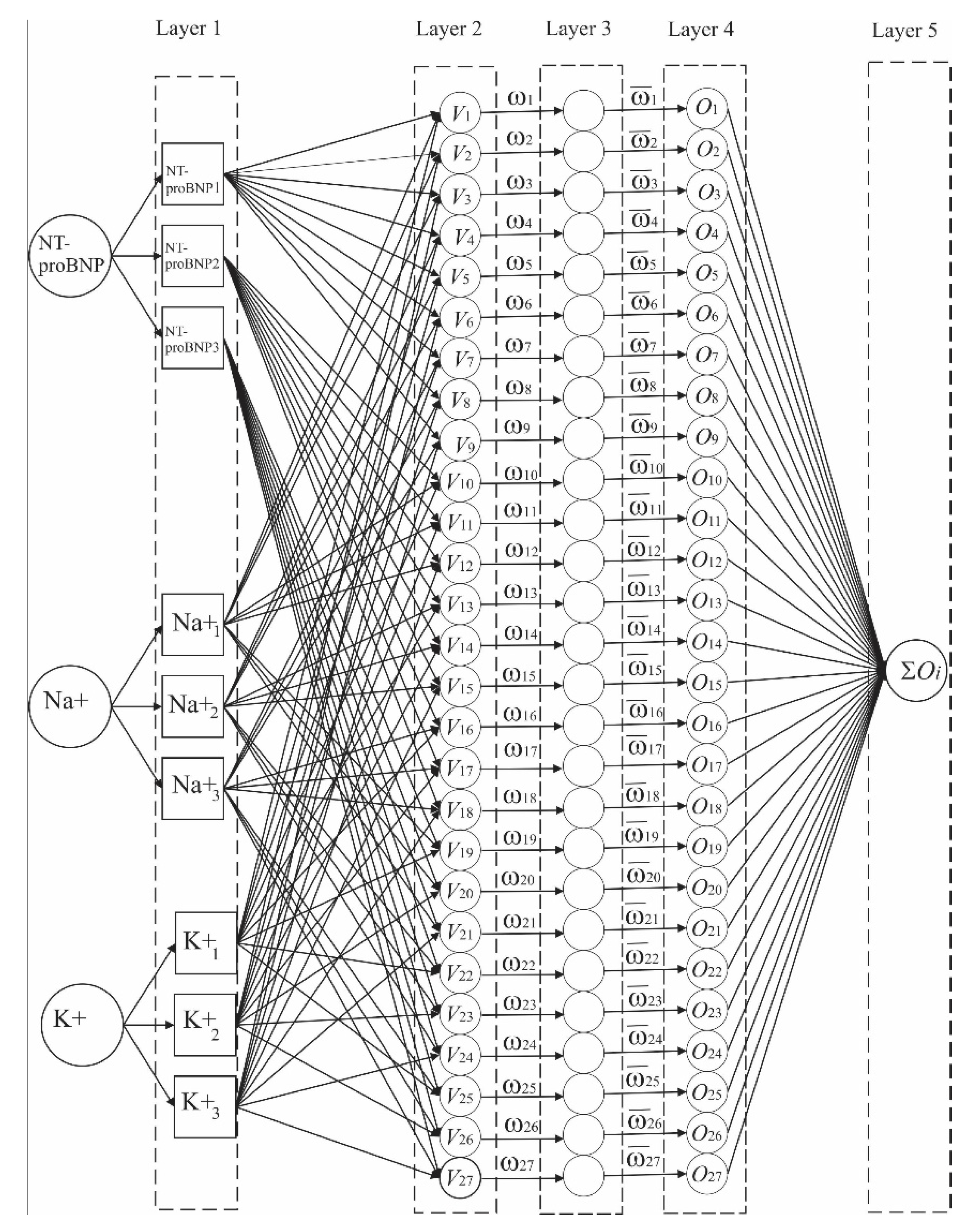
2.2. Neuro-Fuzzy Method
2.3. Model Description
3. Results
3.1. Implementing the Model
3.2. Characteristics of the Respondents
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ronco, C.; Cicoira, M.; McCullough, P.A. Cardiorenal Syndrome Type 1: Pathophysiological crosstalk leading to combined heart and kidney dysfunction in the setting of acutely decompensated heart failure. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2012, 60, 1031–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zannad, F.; Rossignol, P. Cardiorenal Syndrome Revisited. Circulation 2018, 138, 929–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, S.; Graham, M.M.; Lecamwasam, A.; Romanovsky, A.; Duggan, S.; Bagshaw, S.; Senaratne, J.M. Cardiorenal Interactions: A Review. CJC Open 2022, 4, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agewall, S. Adherence to guidelines and registry data. Eur. Heart J.-Cardiovasc. Pharmacother. 2017, 3, 183–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambrosy, A.P.; Gheorghiade, M. Real-world dosing of evidence-based medications for heart failure: Embracing guideline recommendations and clinical judgement. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2017, 19, 1424–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tate, S.; Griem, A.; Durbin-Johnson, B.; Watt, C.; Schaefer, S. Marked elevation of B-type natriuretic peptide in patients with heart failure and preserved ejection fraction. J. Biomed Res. 2014, 28, 255–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, A. The real-world evidence of heart failure co-morbidities. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2017, 19, 434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunalp, M.E.; Hauptman, P.J.; Amin, A.N.; Chase, S.L.; Chiodoll, J.A.; Chiong, J.R.; Dasta, J. Current management of Hyponatremia in Acute heart Failure: A report from the Hyponatremia registry for patients With Euvolemic and Hypovolemic Hyponatremia. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2017, 6, e005261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polson, M.; Lord, T.C.; Kangethe, A.; Speicher, L.; Farnum, C.; Brenner, M.; Oestreicher, N.; Alvarez, P. Clinical and Economic Impact of Hyperkalemia in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease and Heart Failure. J. Manag. Care Spéc. Pharm. 2017, 23 (Suppl. 4), S2–S9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tromp, J.; Ter Maaten, J.M.; Damman, K.; O’Connor, C.M.; Metra, M.; Dittrich, H.C.; Ponikowski, P.; Teerlink, J.R.; Cotter, G.; Davison, B.; et al. Serum Potassium Levels and Outcome in Acute Heart Failure (Data from the PROTECT and COACH Trials). Am. J. Cardiol. 2017, 119, 290–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossignol, P.; Legrand, M.; Kosiborod, M.; Hollenberg, S.M.; Peacock, W.F.; Emmett, M.; Epstein, M.; Kovesdy, C.P.; Yilmaz, M.B.; Stough, W.G.; et al. Emergency management of severe hyperkalemia: Guideline for best practice and opportunities for the future. Pharmacol. Res. 2016, 113, 585–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kervella, D.; Lemoine, S.; Sens, F.; Dubourg, L.; Sebbag, L.; Guebre-Egziabher, F.; Bonnefoy, E.; Juillard, L. Cystatin C Versus Creatinine for GFR Estimation in CKD Due to Heart Failure. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2017, 69, 321–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stevens, L.A.; Levey, A.S. Measured GFR as a Confirmatory Test for Estimated GFR. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2009, 20, 2305–2313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- DuPont, M.; Wu, Y.; Hazen, L.S.; Tang, W.H.W. Cystatin C Identifies Patients With Stable Chronic Heart Failure at Increased Risk for Adverse Cardiovascular Events. Circ. Heart Fail. 2012, 5, 602–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martens, P.; Mullens, W. Spot Urinary Sodium in Decompensated Heart Failure as a Prognostic Metric for Successful Ambulatory Decongestion. J. Card. Fail. 2018, 24, 355–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chioncel, O.; Mebazaa, A.; Maggioni, A.P.; Harjola, V.P.; Rosano, G.; Laroche, C.; Piepoli, M.F.; Seferovic, P.; Lund, L.H. on Behalf on the ESC-EORP HFA Heart Failure Long-term Registry Investigators. Acute heart fail-ure congestion and perfusion status-impact of the clinical classification on in-hospital and long-term out-comes;insights from the ESC-EORP HFA Heart Failure Long-Term Registry. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2019, 21, 1338–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horii, M.; Matsumoto, T.; Uemura, S.; Sugawara, Y.; Takitsume, A.; Ueda, T.; Nakagawa, H.; Nishida, T.; Soeda, T.; Okayama, S.; et al. Prognostic value of B-type natriuretic peptide and its amino-terminal proBNP fragment for cardiovascular events with stratification by renal function. J. Cardiol. 2013, 61, 410–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Takase, H.; Dohi, Y.; Toriyama, T.; Okado, T.; Tanaka, S.; Shinbo, H.; Kimura, G. B-type natriuretic peptide levels and cardiovascular risk in patients with diastolic dysfunction on chronic haemodialysis: Cross-sectional and observational studies. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2011, 26, 683–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Seino, Y.; Ogawa, A.; Yamashita, T.; Fukushima, M.; Ogata, K.-I.; Fukumoto, H.; Takano, T. Application of NT-proBNP and BNP measurements in cardiac care: A more discerning marker for the detection and evaluation of heart failure. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2004, 6, 295–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, M.; Troughton, R.W. NT-proBNP in heart failure: Therapy decisions and monitoring. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2004, 6, 351–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, C. NT-ProBNP: The Mechanism Behind the Marker. J. Card. Fail. 2005, 11, S81–S83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadollahpour, A.; Nourozi, J.; Mirbagheri, S.A.; Simancas-Acevedo, E.; Trejo-Macotela, F.R. Designing and Implementing an ANFIS Based Medical Decision Support System to Predict Chronic Kidney Disease Progression. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subhashini, R.; Jeyakumar, M. E-Anfis to diagnose the progression of chronic kidney disease. Clin. Pract. 2019, 16, 1235–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Akgundogdu, A.; Kurt, S.; Kilic, N.; Ucan, O.N.; Akalin, N. Diagnosis of Renal Failure Disease Using Adaptive Neuro-Fuzzy Inference System. J. Med. Syst. 2010, 34, 1003–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kannathal, N.; Lim, C.; Acharya, U.R.; Sadasivan, P. Cardiac state diagnosis using adaptive neuro-fuzzy technique. Med. Eng. Phys. 2006, 28, 809–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Available online: http://www.kidney.org/professionals/KDOQI/gfr_calculator (accessed on 10 January 2012).
- Boyer, N.M.; Laskey, W.K.; Cox, M.; Hernandez, A.F.; Peterson, E.D.; Bhatt, D.L.; Cannon, C.P.; Fonarow, G.C. Trends in Clinical, Demographic, and Biochemical Characteristics of Patients With Acute Myocardial Infarction From 2003 to 2008: A Report From the American Heart Association Get With The Guidelines Coronary Artery Disease Program. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2012, 1, e001206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wandt, B.; Bojo, L.; Tolagen, K.; Wranne, B. Echocardiographic assessment of ejection fraction in left ventricular hypertrophy. Heart 1999, 82, 192–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shahjalal, M.; Mitra, D.J.; Sulta, A.; Mitra, N.K.; Khodadad Khan, A.F.M. Measuring Risk of Diabetic: A Fuzzy Logic Approach. Prog. Nonlinear Dyn. Chaos 2016, 4, 23–33. [Google Scholar]
- Katigari, M.R.; Ayatollahi, H.; Malek, M.; Haghighi, M.K. Fuzzy expert system for diagnosing diabetic neuropathy. World J. Diabetes 2017, 8, 80–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vosoulipour, A.; Teshnehlab, M.; Moghadam, H.A. Classification on Diabetes Mellitus Data-set Based-on Artificial Neural Networks and ANFIS. In Proceedings of the 4th Kuala Lumpur International Conference on Biomedical Engineering, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 25–28 June 2008; pp. 27–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bressan, G.M.; De Azevedo, B.C.F.; De Souza, R.M. A Fuzzy Approach for Diabetes Mellitus Type 2 Classification. Braz. Arch. Biol. Technol. 2020, 63, e20180742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, J.-S.R. ANFIS: Adaptive-Network-Based Fuzzy Inference System. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 1993, 23, 665–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furundzic, D.; Djordjevic, M.; Bekic, A.J. Neural networks approach to early breast cancer detection. J. Syst. Arch. 1998, 44, 617–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furundzic, D.; Stankovic, S.; Jovicic, S.; Punisic, S.; Subotic, M. Distance based resampling of imbalanced classes: With an application example of speech quality assessment. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2017, 64, 440–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tasic, D. Markers of the progression of kidney damage analyzed by soft computing approach. Sens. Rev. 2018, 38, 74–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tasic, D.; Djordjevic, K.; Galovic, S.; Milovancevic, M.; Kocic, G.; Radenković, S.; Dimitrijevic, Z.; Jancic, N.; Vrecic, T.; Jovanovic, A. Prediction of cardiorenal syndrome by artifitial intelligence. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2021, 36, M0475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tasic, D.; Milovancevic, M.; Djordjevic, K.; Galovic, S.; Dimitrijevic, Z.; Mitic, B.; Glogovac, S. History of artificial intelligence and its application in nephrology. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2020, 35, iii2157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado-Fragua, M.D.; Landré, B.; Chen, M.; Fayosse, A.; Dugravot, A.; Kivimaki, M.; Sabia, S.; Singh-Manoux, A. Circulating serum metabolites as predictors of dementia: A machine learning approach in a 21-year follow-up of the Whitehall II cohort study. BMC Med. 2022, 20, 334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, G.; Roy, S.; Merdji, A. A proposed health monitoring system using fuzzy inference system. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part H J. Eng. Med. 2020, 234, 562–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dogantekin, E.; Dogantekin, A.; Avci, D.; Avci, L. An intelligent diagnosis system for diabetes on Linear Discriminant Analysis and Adaptive Network Based Fuzzy Inference System: LDA-ANFIS. Digit. Signal Process. 2010, 20, 1248–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karabpour, S.; Jafarian, A. A New Artificial Intelligence Method for Prediction of Diabetes Type2. Bull. De La Société R. Des Sci. De Liège 2016, 85, 376–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamedan, F.; Orooji, A.; Sanadgol, H.; Sheikhtaheri, A. Clinical decision support system to predict chronic kidney disease: A fuzzy expert system approach. Int. J. Med. Inform. 2020, 138, 104134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naumovic, R.; Furuncic, D.; Jovanovic, D.; Stosovic, M.; Basta-Jovanovic, G.; Lezaic, V. Application of artificial neural networks in estimating predictive factors and therapeutic efficacy in idiopathic membranous nephropathy. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2010, 64, 633–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogrizović-Simić, S.; Furundzić, D.; Lezaić, V.; Radivojević, D.; Blagojević, R.; Djukanović, L.j. Using ANN in Selection of the Most Important Variables in Prediction of Chronic Renal Allograft Rejection Progression. Transpl. Proc. 1999, 31, 368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gnanaraj, J.F.; von Haehling, S.; Anker, S.D.; Raj, D.S.; Radhakrishnan, J. The relevance of congestion in the cardio-renal syndrome. Kidney Int. 2013, 83, 384–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rubio-Gracia, J.; Giménez-López, I.; Sánchez-Marteles, M.; Josa-Laorden, C.; Pérez-Calvo, J.I. Intra-abdominal pressure and its relationship with markers of congestion in patients admitted for acute decompensated heart failure. Heart Vessel. 2020, 35, 1545–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.Y.; Kim, S. Pathophysiology of Cardiorenal Syndrome and Use of Diuretics and Ultrafiltration as Volume Control. Korean Circ. J. 2021, 51, 656–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamoto, R.; Ali, Y.; Hashizume, R.; Suzuki, N.; Ito, M. BNP as a Major Player in the Heart-Kidney Connection. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Epstein, F.H.; Levin, E.R.; Gardner, D.G.; Samson, W.K. Natriuretic Peptides. N. Engl. J. Med. 1998, 339, 321–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastural-Thaunat, M.; Ecochard, R.; Boumendjel, N.; Abdullah, E.; Cardozo, C.; Lenz, A.; M’Pio, I.; Szelag, J.; Fouque, D.; Walid, A.; et al. Relative Change in NT-proBNP Level: An Important Risk Predictor of Cardiovascular Congestion in Haemodialysis Patients. Nephron Extra 2012, 2, 311–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parcha, V.; Patel, N.; Gutierrez, O.M.; Li, P.; Gamble, K.L.; Musunuru, K.; Margulies, K.B.; Cappola, T.P.; Wang, T.J.; Arora, G.; et al. Chronobiology of Natriuretic Peptides and Blood Pressure in Lean and Obese Individuals. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2021, 77, 2291–2303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aimo, A.; Gaggin, H.K.; Barison, A.; Emdin, M.; Januzzi, J.L. Imaging, Biomarker, and Clinical Predictors of Cardiac Remodeling in Heart Failure With Reduced Ejection Fraction. JACC Heart Fail. 2019, 7, 782–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daubert, M.A.; Adams, K.; Yow, E.; Barnhart, H.X.; Douglas, P.S.; Rimmer, S.; Norris, C.; Cooper, L.; Leifer, E.; Desvigne-Nickens, P.; et al. NT-proBNP Goal Achievement Is Associated With Significant Reverse Remodeling and Improved Clinical Outcomes in HFrEF. JACC Heart Fail. 2019, 7, 158–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goetze, J.P.; Bruneau, B.G.; Ramos, H.R.; Ogawa, T.; de Bold, M.K.; de Bold, A.J. Cardiac natriuretic peptides. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2020, 17, 698–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cunningham, J.W.; Claggett, B.L.; O’Meara, E.; Prescott, M.F.; Pfeffer, M.A.; Shah, S.J.; Redfield, M.M.; Zannad, F.; Chiang, L.-M.; Rizkala, A.R.; et al. Effect of Sacubitril/Valsartan on Biomarkers of Extracellular Matrix Regulation in Patients With HFpEF. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2020, 76, 503–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossignol, P.; Coats, A.J.; Chioncel, O.; Spoletini, I.; Rosano, G. Renal function, electrolytes, and congestion monitoring in heart failure. Eur. Heart J. Suppl. 2019, 21, M25–M31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Husain-Syed, F.; Gröne, H.; Assmus, B.; Bauer, P.; Gall, H.; Seeger, W.; Ghofrani, A.; Ronco, C.; Birk, H. Congestive nephropathy: A neglected entity? Proposal for diagnostic criteria and future perspectives. ESC Heart Fail. 2021, 8, 183–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferro, M.; de Cobelli, O.; Musi, G.; del Giudice, F.; Carrieri, G.; Busetto, G.M.; Falagario, U.G.; Sciarra, A.; Maggi, M.; Crocetto, F.; et al. Radiomics in prostate cancer: An up-to-date review. Ther. Adv. Urol. 2022, 14, 1–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Parameters | Na (mmol/L) | K (mmol/L) | NT-pro BNP (pg/mL) | CystatinC (mg/L) | Age (Years) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Min. value | 123.00 | 2.40 | 10.00 | 1.73 | 18.00 |
| Max. value | 150.00 | 7.80 | 5000.00 | 0.21 | 88.00 |
| Mean | 137.90 | 4.84 | 1275.77 | 3.33 | 65.98 |
| SD | 4.57 | 0.97 | 1533.89 | 0.825 | 15.74 |
| Parameters | Min. Value | Max. Value | Mean | SD |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Na(mmol/L) | 123 | 150 | 138 | 4.12 |
| K(mmol/L) | 2.4 | 7.8 | 4.85 | 0.88 |
| NT-pro BNP (pg/mL) | 10 | 5000 | 1292.10 | 252.00 |
| EF% | 12 | 75 | 72.8 | 15.04 |
| EPI cystatin C(mL/min/1.73 m2) | 14 | 146 | 50.20 | 37.88 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tasić, D.; Đorđević, K.; Galović, S.; Furundžić, D.; Dimitrijević, Z.; Radenković, S. Is It Possible to Analyze Kidney Functions, Electrolytes and Volemia Using Artificial Intelligence? Diagnostics 2022, 12, 3131. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12123131
Tasić D, Đorđević K, Galović S, Furundžić D, Dimitrijević Z, Radenković S. Is It Possible to Analyze Kidney Functions, Electrolytes and Volemia Using Artificial Intelligence? Diagnostics. 2022; 12(12):3131. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12123131
Chicago/Turabian StyleTasić, Danijela, Katarina Đorđević, Slobodanka Galović, Draško Furundžić, Zorica Dimitrijević, and Sonja Radenković. 2022. "Is It Possible to Analyze Kidney Functions, Electrolytes and Volemia Using Artificial Intelligence?" Diagnostics 12, no. 12: 3131. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12123131
APA StyleTasić, D., Đorđević, K., Galović, S., Furundžić, D., Dimitrijević, Z., & Radenković, S. (2022). Is It Possible to Analyze Kidney Functions, Electrolytes and Volemia Using Artificial Intelligence? Diagnostics, 12(12), 3131. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12123131








