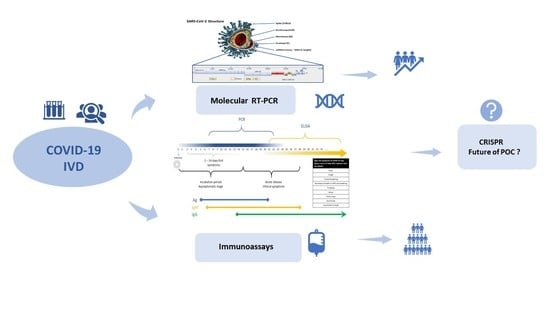
Molecular and Serological Tests for COVID-19. A Comparative Review of SARS-CoV-2 Coronavirus Laboratory and Point-of-Care Diagnostics
Abstract
1. Introduction
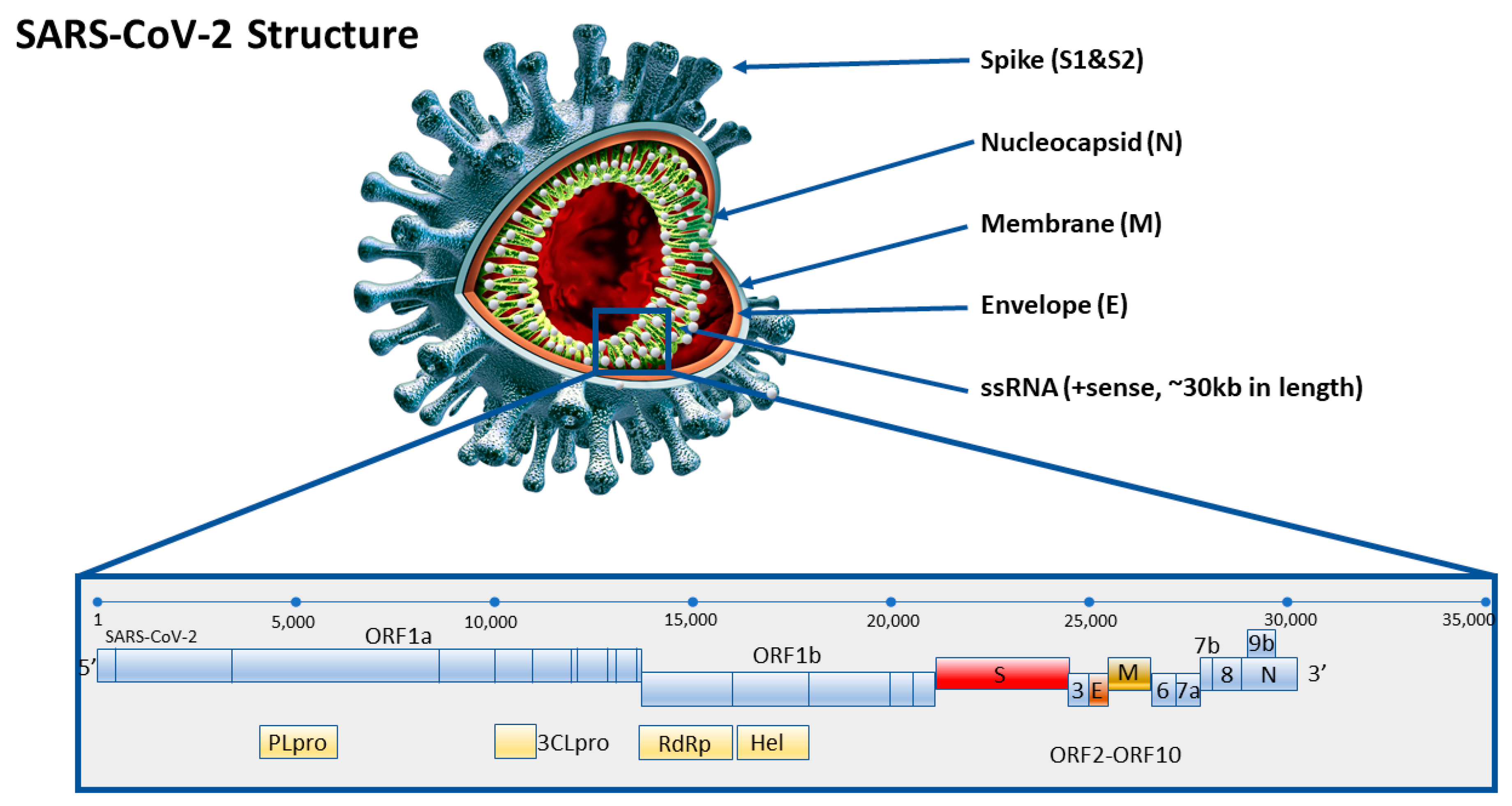
2. Reference Molecular RT-qPCR Assay for Validated COVID-19 Diagnosis
Evaluation of Molecular RT-qPCR Tests that Detect the RNA Nucleic Acid of SARS-CoV-2
3. Emerged Rapid Immunodiagnostic (Serology Immunoassays) Tests
3.1. Lateral Flow Immunoassay
3.2. Immunoenzymatic and Immunofluorimetric Assays
3.3. Protein Microarray Method (PMM)
4. The Currently Developing Concepts of COVID-19 Diagnostics
4.1. Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats (CRISPR/Cas13) Technology
4.2. Exhaled Breath Condensate (EBC)
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lau, S.K.P.; Woo, P.C.Y.; Yip, C.C.Y.; Tse, H.; Tsoi, H.; Cheng, V.C.C.; Lee, P.; Tang, B.S.F.; Cheung, C.H.Y.; Lee, R.A.; et al. Coronavirus HKU1 and Other Coronavirus Infections in Hong Kong. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2006, 44, 2063–2071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singhal, T. A Review of Coronavirus Disease-2019 (COVID-19). Indian J. Pediatr. 2020, 87, 281–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- COVID-19 Dashboard by the Center for Systems Science and Engineering (CSSE) at Johns Hopkins University (JHU). Available online: https://coronavirus.jhu.edu/map.html (accessed on 13 June 2020).
- World Health Organization. Advice on the Use of Point-Of-Care Immunodiagnostic Tests for COVID-19. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/commentaries/detail/advice-on-the-use-of-point-of-care-immunodiagnostic-tests-for-covid-19 (accessed on 13 June 2020).
- Corman, V.; Bleicker, T.; Brünink, S.; Drosten, C.; Landt, O.; Koopmans, M.; Zambon, M. Diagnostic Detection of 2019-nCoV by Real-Time RT-PCR. Protocol and Preliminary Evaluationas of 17 January 2020. Available online: https://www.who.int/docs/default-source/coronaviruse/protocol-v2-1.pdf?sfvrsn=a9ef618c_2. (accessed on 23 June 2020).
- Lu, X.; Chen, Y.; Bai, B.; Hu, H.; Tao, L.; Yang, J.; Chen, J.; Chen, Z.; Hu, Z.; Wang, H. Immune responses against severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus induced by virus-like particles in mice. Immunology 2007, 122, 496–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Liu, L.; Kou, G.; Zheng, Y.; Ding, Y.; Ni, W.; Wang, Q.; Tan, L.; Wu, W.; Tang, S.; et al. Evaluation of Nucleocapsid and Spike Protein-based ELISAs for detecting antibodies against SARS-CoV-2. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2020, 58, e00461-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corman, V.M.; Landt, O.; Kaiser, M.; Molenkamp, R.; Meijer, A.; Chu, D.K.W.; Bleicker, T.; Brünink, S.; Schneider, J.; Schmidt, M.L.; et al. Detection of 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) by real-time RT-PCR. Eurosurveillance 2020, 25, 2000045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vashist, S.K. In Vitro Diagnostic Assays for COVID-19: Recent Advances and Emerging Trends. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shereen, M.A.; Khan, S.; Kazmi, A.; Bashir, N.; Siddique, R. COVID-19 infection: Origin, transmission, and characteristics of human coronaviruses. J. Adv. Res. 2020, 24, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diagnostic Detection of Wuhan Coronavirus 2019 by Real-Time RT-PCR. Available online: https://www.who.int/docs/default-source/coronaviruse/wuhan-virus-assay-v1991527e5122341d99287a1b17c111902.pdf (accessed on 13 June 2020).
- COVID-19 Diagnostics Resource Centre. Available online: https://www.finddx.org/covid-19/ (accessed on 13 June 2020).
- Deepak, S.A.; Kottapalli, K.R.; Rakwal, R.; Oros, G.; Rangappa, K.S.; Iwahashi, H.; Masuo, Y.; Agrawal, G.K. Real-Time PCR: Revolutionizing Detection and Expression Analysis of Genes. Curr. Genom. 2007, 8, 234–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rapid Test for COVID-19 (SARS-CoV-2). Available online: https://www.bosch-vivalytic.com/en/product/vivalytic-tests/vri-multiplex-test/ (accessed on 9 May 2020).
- SARS-CoV-2 Real Time PCR LAB-KIT™. Available online: https://www.biomaxima.com/736-koronawirus-sars-cov-2.html (accessed on 28 April 2020).
- Novel Corona Virus SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19). Available online: http://www.ox.ac.uk/news/2020-03-18-oxford-scientists-develop-rapid-testing-technology-covid-19 (accessed on 9 May 2020).
- Huang, W.E.; Lim, B.; Hsu, C.C.; Xiong, D.; Wu, W.; Yu, Y.; Jia, H.; Wang, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Ji, M.; et al. RT-LAMP for rapid diagnosis of coronavirus SARS-CoV-2. Microb. Biotechnol. 2020, 13, 950–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Z.; Chang, H.; Wang, H.; Lim, B.; Hsu, C.C.; Yu, Y.; Jia, H.; Wang, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Ji, M.; et al. Development of a rapid test kit for SARS-CoV-2: An example of product design. Biodes. Manuf. 2020, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moran, A.; Beavis, K.G.; Matushek, S.M.; Ciaglia, C.; Francois, N.; Tesic, V.; Love, N. The Detection of SARS-CoV-2 using the Cepheid Xpert Xpress SARS-CoV-2 and Roche cobas SARS-CoV-2 Assays. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watson, J.; Whiting, P.F.; Brush, J.E. Interpreting a covid-19 test result. BMJ 2020, 369, m1808. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- West, C.P.; Montori, V.M.; Sampathkumar, P. COVID-19 Testing: TheThreat of False-Negative Results. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lippi, G.; Salvagno, G.L.; Pegoraro, M.; Militello, V.; Caloi, C.; Peretti, A.; Gaino, S.; Bassi, A.; Bovo, C.; Lo Cascio, G. Assessment of immune response to SARS-CoV-2 with fully automated MAGLUMI 2019-nCoV IgG and IgM chemiluminescence immunoassays. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsueh, P.R.; Huang, L.M.; Chen, P.J.; Kao, C.L.; Yang, P.C. Chronological evolution of IgM, IgA, IgG and neutralisation antibodies after infection with SARS-associated coronavirus. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2004, 10, 1062–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, M.; Chen, H.Y.; Foo, S.Y.; Tan, Y.J.; Goh, P.Y.; Wee, S.H. Recombinant protein-based enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and immunochromatographic tests for detection of immunoglobulin G antibodies to severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) coronavirus in SARS patients. Clin. Diagnost. Lab. Immunol. 2004, 11, 287–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kogaki, H.; Uchida, Y.; Fujii, N.; Kurano, Y.; Miyake, K.; Kido, Y.; Kariwa, H.; Takashima, I.; Tamashiro, H.; Ling, A.-E.; et al. Novel rapid immunochromatographic test based on an enzyme immunoassay for detecting nucleocapsid antigen in SARS-associated coronavirus. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2005, 19, 150–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koczula, K.M.; Gallotta, A. Lateral flow assays. Essays Biochem. 2016, 60, 111–120. [Google Scholar]
- Oh, J.-S.; Ha, G.-W.; Cho, Y.-S.; Kim, M.J.; An, D.J.; Hwang, K.K.; Lim, Y.K.; Park, B.K.; Kang, B.; Song, D.S. One Step Immunochromatography Assay Kit for Detecting Antibodies to Canine Parvovirus. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2006, 13, 520–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Posthuma-Trumpie, G.A.; Korf, J.; van Amerongen, A. Lateral flow (immuno)assay: Its strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats. A literature survey. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2009, 393, 569–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stürenburg, E.; Junker, R. Point-of-care testing in microbiology: The advantages and disadvantages of immunochromatographic test strips. Dtsch. Arztebl. Int. 2009, 106, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Yi, Y.; Luo, X.; Xiong, N.; Liu, Y.; Li, S.; Sun, R.; Wang, Y.; Hu, B.; Chen, W.; et al. Development and clinical application of a rapid IgM-IgG combined antibody test for SARS-CoV-2 infection diagnosis. J. Med. Virol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Independent Evaluations of COVID-19 Serological Tests. Available online: https://open.fda.gov/apis/device/covid19serology/ (accessed on 13 June 2020).
- Lauer, S.A.; Grantz, K.H.; Bi, Q.; Jones, F.K.; Zheng, Q.; Meredith, H.R.; Azman, A.S.; Reich, N.G.; Lessler, J. The Incubation Period of Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) From Publicly Reported Confirmed Cases: Estimation and Application. Ann. Intern. Med. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melton, L. Protein arrays: Proteomics in multiplex. Nature 2004, 429, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, D.A.; Ptacek, J.; Snyder, M. Protein microarray technology. Mech. Ageing. Dev. 2007, 128, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, H.; Hu, S.; Jona, G.; Zhu, X.; Kreiswirth, N.; Willey, B.M.; Mazzulli, T.; Liu, G.; Song, Q.; Chen, P.; et al. Severe acute respiratory syndrome diagnostics using a coronavirus protein microarray. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 4011–4016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molecular and Antibody Point-Of-Care Tests to Support the Screening, Diagnosis and Monitoring of COVID-19. Available online: https://www.cebm.net/covid-19/molecular-and-antibody-point-of-care-tests-to-support-the-screening-diagnosis-and-monitoring-of-covid-19/ (accessed on 13 June 2020).
- Wang, X.; Zhong, M.; Liu, Y.; Ma, P.; Dang, L.; Meng, Q.; Wan, W.; Ma, X.; Liu, J.; Yang, G.; et al. Rapid and Sensitive Detection of COVID-19 Using CRISPR/Cas12a-based Detection with Naked Eye Readout, CRISPR/Cas12a-NER. Sci. Bull. (Beijing) 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoubnasabjafari, M.; Jouyban-Gharamaleki, V.; Ghanbari, R.; Jouyban, A. Exhaled breath condensate as a potential specimen for diagnosing COVID-19. Bioanalysis 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jerzyńska, J.; Brzozowska, A.; Bobrowska-Korzeniowska, M.; Grzelewski, T.; Stelmach, I. Usefulness of exhaled breath condensate for evaluation of markers of airway inflammation in children with asthma. Pediatr. Pol. 2009, 84, 437–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Developer | Name of the Kit | Gene | Regulatory | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ORF1a | ORF1ab | RdRP | E | N | S | |||
| Manual test | ||||||||
| 1drop Inc. | 1copy™ COVID-19 qPCR Kit | CE-IVD | ||||||
| AB ANALITICA srl | REALQUALITY RQ-2019-nCoV | CE-IVD | ||||||
| ADT Biotech | LyteStar 2019-nCoV RT-PCR Kit 1.0 | RUO | ||||||
| altona Diagnostics | RealStar® SARS-CoV-2 RT-PCR Kit | USA EUA; CE-IVD | ||||||
| Atila Biosystems Inc. | Atila iAMP® COVID Detection Kit | USA EUA | ||||||
| BIOMAXIMA S.A. | SARS-CoV-2 Real Time PCR LAB-KIT™ | CE-IVD | ||||||
| bioMérieux | SARS-COV-2 R-GENE® | USA EUA; CE-IVD; RUO | ||||||
| Bioneer | AccuPower® SARS-CoV-2 Real-Time RT-PCR | CE-IVD | ||||||
| BGI Health (HK) | Real-time fluorescent RT-PCR kit 2019-nCoV | USA EUA; CE-IVD; Canada | ||||||
| CerTest Biotec, S.L | VIASURE SARS-CoV-2 Real Time PCR Kit | CE-IVD | ||||||
| CerTest Biotec, S.L | VIASURE SARS-CoV-2 S gene Real Time PCR Kit | CE-IVD | ||||||
| Co-diagnostics | Logix Smart Coronavirus disease 2019 | CE-IVD | ||||||
| CTK Biotech, Inc. | Aridia COVID-19 Real Time PCR Test | CE-IVD | ||||||
| DAAN Gene Co | Detection Kit for 2019 Novel Coronavirus | CE-IVD; China | ||||||
| Edinburgh Genetics | COVID-19 Real-time PCR Testing Kit | CE-IVD; China FDA | ||||||
| Gencurix Inc. | GenePro COVID-19 Detection Test | CE-IVD | ||||||
| Genomictree, Inc. | AccuraTect RT-qPCR SARS-CoV-2 | CE-IVD | ||||||
| KH Medical | RADI COVID-19 Detection Kit | CE-IVD | ||||||
| KRISHGEN | SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) Real-Time PCR Kit | RUO | ||||||
| Liming Bio-Products | SrongStep® Novel Coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) | CE-IVD | ||||||
| PerkinElmer Inc. | PerkinElmer® SARS-CoV-2 Realtime RT-PCR | CE-IVD; WHO-EUL | ||||||
| Primerdesign Ltd. | COVID-19 genesig Real-Time PCR assay | CE-IVD; USA EUA;WHO EUL | ||||||
| R-Biopharm AG | RIDA® GENE SARS-CoV-2 RUO (PG6815RUO) | RUO | ||||||
| SD BIOSENSOR Inc. | STANDARD M nCoV Real-Time Detection Kit | CE-IVD; USA EUA; Brazil | ||||||
| TIB/Roche Diagn. | LightMix Modular SARS-CoV-2 (COVID19) | RUO | ||||||
| TIB/Roche Diagn | LightMix Modular SARS-CoV-2 (COVID19) | RUO | ||||||
| TIB/Roche Diagn | LightMix Modular SARS-CoV-2 (COVID19) | RUO | ||||||
| SD BIOSENSOR | STANDARD M nCoV Real-Time Detection kit | USA EUA; CE-IVD; Brazil | ||||||
| Seegene, Inc. | Allplex 2019-nCoV assay | USA EUA; CE-IVD; Canada | ||||||
| Sansure Biotech Inc | Novel Coronavirus (2019-nCoV) Nucleic Acid | USA EUA; CE-IVD; China | ||||||
| Sente Biolab Sentelig | COVID-19 qRT PCR Detection Kit | CE-IVD | ||||||
| Shanghai ZJ Bio-Tech | Liferiver Novel Coronavirus Multiplex RT-PCR | CE-IVD, China FDA | ||||||
| Thermo Fisher | TaqPath™ COVID-19 CE-IVD RT-PCR Kit | CE-IVD | ||||||
| Automated Lab-based, near-POC NAT or POC NAT | ||||||||
| 3D Biomedicine | DMed 2019-nCoV RT-qPCR Detection Kit | US FDA—CE-IVD | ||||||
| Abbott Molecular Inc. | Abbott RealTime SARS-CoV-2 EUA test | US FDA—CE-IVD | ||||||
| Cepheid | Xpert Xpress SARS-CoV-2 | US FDA-EUA | ||||||
| Roche Molecular Dia | cobas® SARS-CoV-2 | US FDA—WHO EUL | ||||||
| Sente Biolab | Senteligo COVID-19 qRT PCR Detection Kit | CE-IVD | ||||||
| Solgent Co.Ltd | DiaPlexQ™ Novel Coronavirus (2019-nCoV) | CE-IVD | ||||||
| Star Array Ptd. Ltd. | 8-min RT-qPCR direct PCR testing | RUO | ||||||
| Veredus Laboratories | VereCoV™ Detection Kit and VerePLEX™ | CE-IVD | ||||||
| Developer | Name of the Kit | Gene | Clinical Sensitivity | Clinical Specificity | Limit of Detection LOD (Copies/Reaction) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| altona Diagnostics | RealStar® SARS-CoV-2 RT-PCR Kit 1.0 | E | 92% | 100% | 1–10 |
| S | 92% | 100% | 1–10 | ||
| Atila BioSystems Inc. | Atila iAMP COVID-19 Detection (isothermal detection) | ORF1ab | 100% | 99% | 20–100 |
| N | 100% | 100% | 1–10 | ||
| BGI Health (HK) Co. Ltd. | Real-time Fluorescent RT-PCR kit for detection 2019-nCOV (CE-IVD) | ORF1 | 100% | 99% | 1–10 |
| bioMérieux | ARGENE® SARS-COV-2 R-GENE® | N | 100% | 100% | 10–50 |
| RdRP | 96% | 100% | 10–50 | ||
| BIONEER | AccuPower® SARS-CoV-2 Real-Time RT-PCR Kit | E | 100% | 100% | 10–50 |
| RdRP | 100% | 100% | 10–50 | ||
| Boditech Med. Inc. | ExAmplar COVID-19 real-time PCR kit (L) | E | 100% | 100% | 10–50 |
| RdRP | 90% | 100% | 50–100 | ||
| CerTest Biotec | VIASURE SARS-CoV-2 Real Time PCR Detection Kit | ORF1ab | 98% | 100% | 10–50 |
| N | 100% | 100% | 1–10 | ||
| DAAN Gene Co. Ltd. | Detection Kit for 2019 Novel Coronavirus (2019-nCoV) RNA (PCR-Fluorescence Probing) | ORF1 | 100% | 96% | 1–10 |
| N | 100% | 98% | 1–10 | ||
| EUROIMMUN | EURORealTime SARS-CoV-2 | ORF1ab/N | 100% | 98% | 1–10 |
| GeneFirst Ltd. | The Novel Coronavirus (2019-nCoV) Nucleic Acid Test Kit | ORF1 | 100% | 99% | 1–10 |
| N | 98% | 100% | 1–10 | ||
| KH Medical Co. Ltd. | RADI COVID-19 Detection Kit | S | 100% | 100% | 1–10 |
| RdRP | 100% | 100% | 10–50 | ||
| Primerdesign Ltd. | Coronavirus COVID-19 genesig® Real-Time PCR assay | RdRP | 100% | 100% | 1–10 |
| R-Biopharm AG | RIDA® GENE SARS-CoV-2 RUO | E | 100% | 100% | 1–10 |
| SD Biosensor Inc. | STANDARD M nCoV Real-Time Detection Kit | E | 100% | 97% | 1–10 |
| ORF1 | 100% | 99% | 1–10 | ||
| Seegene Inc. | Allplex™ 2019-nCoV Assay | E | 100% | 100% | 1–10 |
| N | 100% | 100% | 1–10 | ||
| RdRP | 100% | 100% | 1–10 | ||
| Shanghai Kehua Bio-Engineering | KHB Diagnostic kit for SARS-CoV-2 Nucleic Acid (Real-time PCR) | ORF1 | 100% | 100% | 1–10 |
| N | 100% | 100% | 1–10 | ||
| E | 100% | 100% | 1–10 | ||
| Tib Molbiol | ModularDx Kit SARS-CoV (COVID19) E-gene (Tib Molbiol) + LightCycler Multiplex RNA Virus Master (Roche) | E | 100% | 100% | 1–10 |
| Vela Diagnostics | ViroKey™ SARS-CoV-2 RT-PCR Test | RdRP | 94% | 100% | 10–50 |
| ORF1 | 100% | 100% | 1–10 |
| Microorganism | Name of Test | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1drop Inc. 1copy™ COVID-19 qPCR Kit | Altona Diagnostics RealStar® SARS-CoV-2 RT-PCR Kit | Atila iAMP® COVID Detection Kit | CerTest Biotec, S.L VIASURE SARS-CoV-2 | Co-diagnostics Logix Smart Coronavirus Disease 2019 | Edinburgh Genetics COVID-19 Real-time PCR Testing Kit | Liming Bio-Products SrongStep® Novel Coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) | PerkinElmer® SARS-CoV-2 Realtime RT-PCR | SD BIOSENSOR Inc. STANDARD M nCoV Real-Time Detection Kit | Seegene, Inc. Allplex 2019-nCoV Assay | Thermo Fisher Scientific TaqPath COVID-19 Combo Kit | Abbott RealTime SARS-CoV-2 EUA test | Cepheid Xpert Xpress SARS-CoV-2 | |
| Human coronavirus NL 63 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| Human coronavirus OC229E | nd | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Human coronavirus OC43 | - | - | - | - | - | - | nd | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Human coronavirus HKU1 | - | nd | - | - | - | - | - | nd | - | - | - | - | - |
| Human Metapneumovirus (hMPV) | - | - | - | - | - | nd | nd | nd | nd | - | - | - | - |
| SARS-coronavirus | - | - | - | - | - | nd | nd | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| MERS-coronavirus | - | - | - | - | - | nd | nd | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Parainfluenza virus 1 | - | - | - | - | - | nd | nd | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Parainfluenza virus 2 | - | - | - | - | - | nd | nd | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Parainfluenza virus 3 | - | - | - | - | - | nd | nd | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Parainfluenza virus 4 | - | - | - | nd | - | nd | nd | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Influenza A virus | - | - | nd | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Influenza B Virus | nd | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Adenovirus | nd | - | nd | - | - | - | nd | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Enterovirus (e.g., EV68) | - | - | - | nd | - | nd | nd | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Respiratory syncytial virus A | nd | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Respiratory syncytial virus B | nd | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Rhinovirus | - | - | - | - | - | nd | nd | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Chlamydia pneumoniae | - | - | - | - | - | nd | nd | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Hemophilus influenzae | - | - | nd | - | - | nd | nd | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Legionella pneumophila | - | - | nd | - | - | nd | nd | nd | - | - | - | - | - |
| Mycobacterium tuberculosis | - | nd | nd | - | - | nd | nd | nd | - | - | - | - | - |
| Streptococcus pneumoniae | - | - | nd | - | - | nd | - | nd | - | - | - | - | - |
| Streptococcus pyogenes | - | - | nd | nd | - | nd | nd | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Bordetella parapertussis | nd | nd | nd | - | nd | nd | nd | nd | nd | nd | nd | nd | nd |
| Bordetella bronchiseptica | nd | nd | nd | - | nd | nd | nd | nd | nd | nd | nd | nd | nd |
| Bordetella pertussis | - | - | - | - | - | nd | nd | nd | - | - | - | - | - |
| Mycoplasma pneumoniae | - | - | nd | - | - | - | nd | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Pneumocystis jirovecii (PJP) | - | - | nd | - | - | nd | nd | nd | - | - | - | - | - |
| Candida albicans | - | - | nd | nd | - | nd | nd | nd | nd | - | - | - | - |
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa | - | - | - | nd | - | nd | nd | nd | - | - | - | - | - |
| Staphylococcus epidermis | - | nd | nd | nd | - | nd | nd | nd | - | - | - | - | - |
| Staphylococcus salivarius | - | nd | - | nd | - | nd | nd | nd | - | - | - | - | - |
| Staphylococcus aureus | nd | nd | nd | - | - | nd | nd | - | nd | nd | - | nd | - |
| Human immunodeficiency virus type 1,2 | nd | nd | nd | nd | nd | nd | nd | - | nd | nd | nd | nd | nd |
| Hepatitis virus (A, B, C) | nd | nd | nd | nd | nd | nd | nd | - | nd | nd | nd | nd | nd |
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Short reaction time for most tests, amounting to 5–20 min | Suboptimal sensitivity, results often false negative, particularly during enhanced activity of the virus |
| Simple and comfortable to use and perform. Some tests may be performed in outpatient clinics or at patient’s bed. | Despite substantial specificity sometimes the results are false negative, particularly when the virus is not much active. |
| Reading most often possible with ‘naked eye’. | It is necessary to verify positive or doubtful results. |
| Small amount of material to be collected, variety of material. | Increased risk of operator becoming infected |
| “best before” date distant (usually 18 months from manufacturing date) |
| Phase of Infection | Type of Test | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| PCR | IgM | IgG | |
| The window period for a test designed to detect a specific disease | P(+) | N(−) | N(−) |
| Early stage of infection | P(+) | P(+) | N(−) |
| Active phase of infection | P(+) | P(+) | P(+) |
| Late or recurrent stage of infection | P(+) | N(−) | P(+) |
| Early stage of infection. PCR result may be false negative * | N(−) | P(+) | N(−) |
| Past infection (recover) * | N(−) | N(−) | P(+) |
| The recovery stage of infection, or PCR result may be false negative * | N(−) | P(+) | P(+) |
| No infection and no special symptoms | N(−) | N(−) | N(−) |
| Test Name | Euroimmun SARS-COV-2 ELISA (IgG) | Healgen COVID-19 IgG/IgM Rapid Test Cassette | Biomedomics COVID-19 IgM-IgG Rapid Test kit | Phamatech COVID19 RAPID TEST | Tianjin Beroni Biotechnology SARS-COV-2 IgG/IgM Antibody Detection Kit |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clinical Sensitivity IgM | 100% | 86.7% | 26.7% | 83.3% | |
| Clinical Specificity IgM | 100% | 97.1% | 97.5% | 100% | |
| Clinical Sensitivity IgG | 90% | 96.7% | 73.3% | 86.7% | 30% |
| Clinical Specificity IgG | 100% | 97.5% | 100% | 96.2% | 100% |
| Clinical Sensitivity IgM+IgG | 100% | 96.7% | 86.7% | 90% | |
| Clinical Specificity IgM+IgG | 97.5% | 97.1% | 93.8% | 100% | |
| Positive Predictive Value at prevalence = 5% (IgM+IgG or IgG) | 100% | 67.8% | 63.7% | 42.4% | 100% |
| Negative Predictive Value at prevalence = 5% (IgM+IgG or IgG) | 99.5% | 100% | 99.8% | 99.3% | 99.5% |
 | |||||
| Developer | Test | Sensitivity: | Specificity: | Sample Size | Time (min) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AccuBioTech Co. Ltd. | Accu-Tell COVID-19 IgG/IgM Rapid Test Cassette | IgG 97.4% IgM 86.8% | IgG 99.3% IgM 98.6% | 10 μL of whole blood, serum or plasma | 10 |
| AllTest Biotech Hangzhou | 2019-nCoV IgG/IgM Rapid Test Cassette | IgG 100% IgM 85% | IgG 98% IgM 96% | 10 μL of serum or plasma 20 μL of fingertip blood or whole blood | 10 |
| Aytu Bioscience | COVID-19 IgG/IgM Rapid Tes | lgM 89.2% lgG 91.9% | IgM 100% IgG 100% | 5 μL of serum or plasma 10 μL of whole blood | 2–10 |
| BIOMAXIMA S.A. | 2019-nCoV IgG/IgM Rapid Test Cassette | IgG100% IgM 85% | IgG 98% IgM 96% | 10–20 μL whole blood, serum or plasma | 10–15 |
| BioMedomics, Inc | COVID-19 IgM-IgG Dual Antibody Rapid Test | 89% | 91% | 10–20 μL whole blood, serum or plasma | 10–15 |
| Cellex Inc. | Cellex qSARS-CoV-2 IgG/IgM Cassette Rapid Test | 93.8% | 96.0% | 10 μL whole blood, serum or plasma | 15–20 |
| Changsha Sinocare Inc. | SARS-CoV-2 Antibody Test Strip (Colloidal Gold Method) | 96.3% Serum/Plasma 95.0% Whole blood | 99.6% Serum/Plasma 99.2% Whole blood | 10 μL of whole blood, serum or plasma | 15–20 |
| CTK Biotech | OnSite COVID-19 IgG/IgM Rapid Tes | 96.9% | 99.4% | 10–15 μL of serum or plasma | 10–15 |
| Edinburgh Genetics Limited | Watmind 2019 nCoV novel coronavirus antibody detection reagent | - | - | 10 μL of serum or plasma; 20 μL of fingertip blood or whole blood | 15 |
| Getein Biotech, Inc. | One Step Test for Novel Coronavirus (2019-nCoV) IgM/IgG Antibody | 94.1% | 95.1% | 10 μL of serum or plasma; 20 μL of fingertip blood or whole blood | 10–20 |
| Goldsite Diagnostics Inc. | SARS-CoV-2 IgG/IgM Kit | - | - | 30 μL of whole blood | 12 |
| Hangzhou Biotest Biotech | COVID-19 IgG/IgM Rapid Test Cassette | IgM 91.8% IgG 100% | IgM 99.2% IgG 99.5% | 10 μL of whole blood, serum or plasma | 10 |
| Hunan Lituo Biotechnology | COVID-19 IgG/IgM Detection Kit | - | - | - | 15 |
| InTec Products, Inc. | Rapid SARS-CoV-2 Antibody Test IgG or Ig Mor IgG/IgM | 94.4% | 98% | 10 μL of sample | 15–20 |
| Liming Bio-Products Co., Ltd. | COVID-19 IgG/IgM Combo Rapid Test Device | IgG 93.1% IgM 64.7% | IgG 100% IgM 100% | 10 μL of serum or plasma; 20 μL of whole blood | 15 |
| Livzon Diagnostic | Diagnostic Kit for IgM/IgG Antibody to Coronavirus (SARSCoV-2) | 90.6% | 99.2% | 10 μL of serum or plasma; 20 μL of whole blood | 15 |
| nal von minden GmbH | NADAL® COVID-19 IgG/IgM Test | 94.1% | 99.2% | 10 μL of whole blood, serum or plasma | 10 |
| Nanjing Vazyme Medical Tech. | 2019-nCoV IgG/IgM Detection Kit | 91.54% | 97.02% | 20 μL of whole blood, serum or plasma | 15 |
| PRIMA Lab S.A. | PRIMA COVID-19 IgG/IgM Rapid Test (For Professional Use) | - | - | 10 μL of serum or plasma; 20 μL of fingertip blood or whole blood | 20 |
| Sugentech, Inc | SGTi-flex COVID-19 IgM/IgG | 90%-92% | 96%-98% | 10 μL whole blood | 10 |
| Sensing Self, | COVID-19 Rapid IgG/IgM combined Antibody assay | IgM 92% IgG 100% | IgM 97.58% IgG 99.31% | 20 μL of fingertip blood or whole blood | 10 |
| Xiamen AmonMed Biotechnology | COVID-19 IgM/IgG test kit | IgM 78.43% IgG 84.31% | IgM 98.40% IgG 99.20% | - | 15 |
| Coris BioConcept | COVID-19 Ag Respi-Strip | 60% | 98–100% | 100 μL extract | 15 |
| RapiGEN, Inc. | BIOCREDIT COVID-19 Ag | 89.4 | 98% | 90–150 μL extract | 5–8 |
| SD BIOSENSOR, | STANDARD Q COVID-19 Ag Test | 84% | 100% | 10 μL extract | 15–30 |
| VivaChek Laboratories, | VivaDiagTM COVID-19 IgM/IgG Rapid Test | 100% | IgM and IgG: 97.1% | 10 μL of whole blood, serum or plasma | 15 |
| Qingdao Hightop Biotech | SARS-CoV-2 IgM/IgG Antibody Rapid Test | IgG 93% IgM 82% | IgG 97.5% IgM 96% | 10 μL of serum or plasma 20 μL of whole blood | 15–20 |
| Novazym | Wuhan Coronavirus Rapid Test (2019-nCoV, COVID-19) IgG/IgM | IgG 91.8% IgM 95.7% | IgG 96.4% IgM 97.3% | 5 μL of serum or plasma 10 μL of whole blood | 15 |
| Test Type | Developer | Test | Molecule | Materials | Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Immunochromatographic | AccuBioTech Co. Ltd. | Accu-Tell COVID-19 IgG/IgM Rapid Test Cassette | IgG or IgM or both | Whole blood/serum/plasma | CE |
| BIOMAXIMA S.A. | 2019-nCoV IgG/IgM Rapid Test Cassette | CE-IVD | |||
| BioMedomics, Inc | COVID-19 IgM-IgG Dual Antibody Rapid Test | CE-IVD; India | |||
| Cellex Inc. | Cellex qSARS-CoV-2 IgG/IgM Cassette Rapid Test | CE-IVD; USA; Australia; Brazil | |||
| Changsha Sinocare Inc. | SARS-CoV-2 Antibody Test Strip (Colloidal Gold Method) | CE-IVD | |||
| Edinburgh Genetics Limited | Watmind 2019 nCoV novel coronavirus antibody detection reagent | CE-IVD | |||
| Getein Biotech, Inc. | One Step Test for Novel Coronavirus (2019-nCoV) IgM/IgG Antibody | CE | |||
| Goldsite Diagnostics Inc. | SARS-CoV-2 IgG/IgM Kit | - | |||
| Hunan Lituo Biotechnology | COVID-19 IgG/IgM Detection Kit | - | |||
| Innovita Biological Technology | 2019-nCoV Ab Test (Colloidal Gold) IgM/IgG | CE-IVD; China, Brazil | |||
| InTec Products, Inc. | Rapid SARS-CoV-2 Antibody Test IgG or Ig Mor IgG/IgM | CE-IVD | |||
| Liming Bio-Products Co., Ltd. | COVID-19 IgG/IgM Combo Rapid Test Device | - | |||
| nal von minden GmbH | NADAL® COVID-19 IgG/IgM Test | - | |||
| PRIMA Lab S.A. | PRIMA COVID-19 IgG/IgM Rapid Test (For Professional Use) | CE | |||
| Dynamiker Biotechnology (Tianjin) Co., Ltd. | 2019 nCOV IgG/IgM Rapid Test | CE-IVD | |||
| Coris BioConcept | COVID-19 Ag Respi-Strip | Antigen | Nasopharyngeal secretions/swab | CE-IVD | |
| RapiGEN, Inc. | BIOCREDIT COVID-19 Ag | CE-IVD | |||
| SD BIOSENSOR, Inc. | STANDARD Q COVID-19 Ag Test | CE-IVD, Brasil | |||
| ELISA | DRG International, Inc. | COVID-19 lgG, EIA-6146 | IgG | Serum | - |
| Epitope Diagnostics, Inc. | EDI™ Novel Coronavirus COVID-19 IgG ELISA Kit | CE-IVD | |||
| EUROIMMUN AG | Anti-SARS-CoV-2 ELISA (IgG) | CE-IVD; Brazil; USA | |||
| DRG International, Inc. | COVID-19 lgM, EIA-6147 | IgM | - | ||
| Epitope Diagnostics, Inc. | EDI™ Novel Coronavirus COVID-19 IgM ELISA Kit | CE-IVD | |||
| EUROIMMUN AG | Anti-SARS-CoV-2 ELISA (IgA) | IgA | CE-IVD; Brazil | ||
| immunofluorescent | SD BIOSENSOR, Inc. | STANDARD F COVID-19 Ag FIA | Antigen | Nasopharyngeal swab | CE-IVD, Brasil |
| Shenzhen Bioeasy Biotechnology Co., Ltd. | Bioeasy 2019-nCoV Ag Fluorescence Rapid Test Kit | CE-IVD | |||
| Mokobio Biotechnology R&D Center | SARS-CoV-2 IgM & IgG Quantum Dot Immunoassay | IgG/IgM | serum, plasma, whole blood | - | |
| Proteome Microarray | PEPperPRINT GmbH | PEPperCHIP® SARS-CoV-2 Proteome Microarray (manual) | Proteome | Serum | - |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kubina, R.; Dziedzic, A. Molecular and Serological Tests for COVID-19. A Comparative Review of SARS-CoV-2 Coronavirus Laboratory and Point-of-Care Diagnostics. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 434. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10060434
Kubina R, Dziedzic A. Molecular and Serological Tests for COVID-19. A Comparative Review of SARS-CoV-2 Coronavirus Laboratory and Point-of-Care Diagnostics. Diagnostics. 2020; 10(6):434. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10060434
Chicago/Turabian StyleKubina, Robert, and Arkadiusz Dziedzic. 2020. "Molecular and Serological Tests for COVID-19. A Comparative Review of SARS-CoV-2 Coronavirus Laboratory and Point-of-Care Diagnostics" Diagnostics 10, no. 6: 434. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10060434
APA StyleKubina, R., & Dziedzic, A. (2020). Molecular and Serological Tests for COVID-19. A Comparative Review of SARS-CoV-2 Coronavirus Laboratory and Point-of-Care Diagnostics. Diagnostics, 10(6), 434. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10060434