CSID: A Novel Multimodal Image Fusion Algorithm for Enhanced Clinical Diagnosis
Abstract
1. Introduction
- We employ contrast stretching and the spatial gradient method to extract edges from the input source images.
- We propose the use of the cartoon-texture decomposition that creates an over-complete dictionary.
- We propose a modified Convolutional Sparse Coding (CSC) method.
- Finally, our proposed algorithm uses enhanced decision maps and a fusion rule to obtain the fused image.
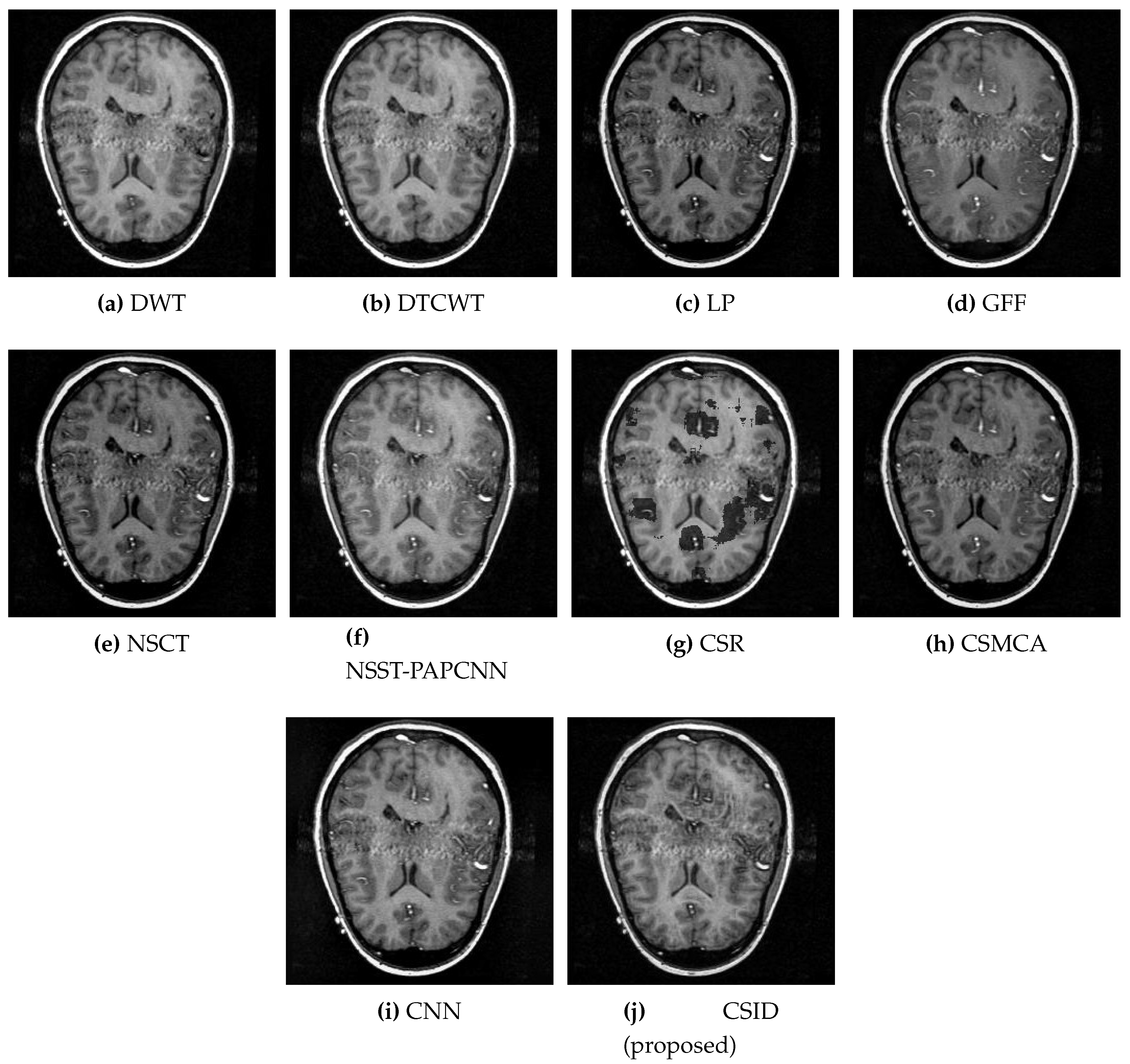
- Additionally, this simulation study reveals that the CSID algorithm achieves superior performance, in terms of visual quality and enriched information extraction, in comparison with other image fusion algorithms, as it will be discussed in Section 5.
2. Related Work
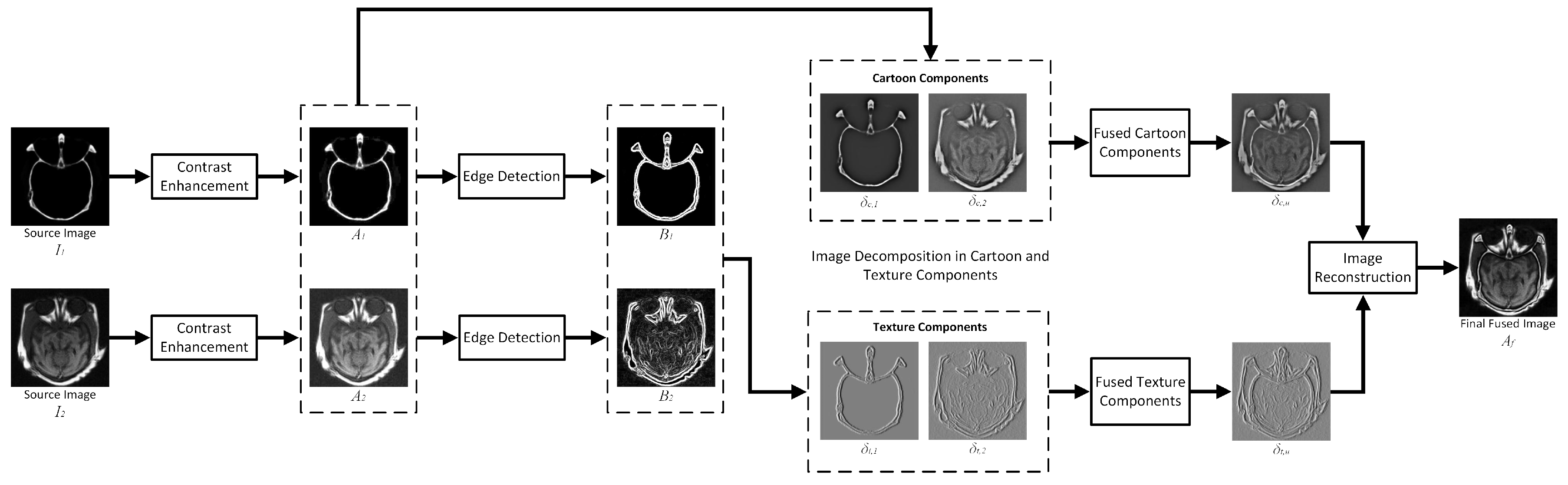
3. The Proposed Convolutional Sparse Image Decomposition (CSID) Algorithm
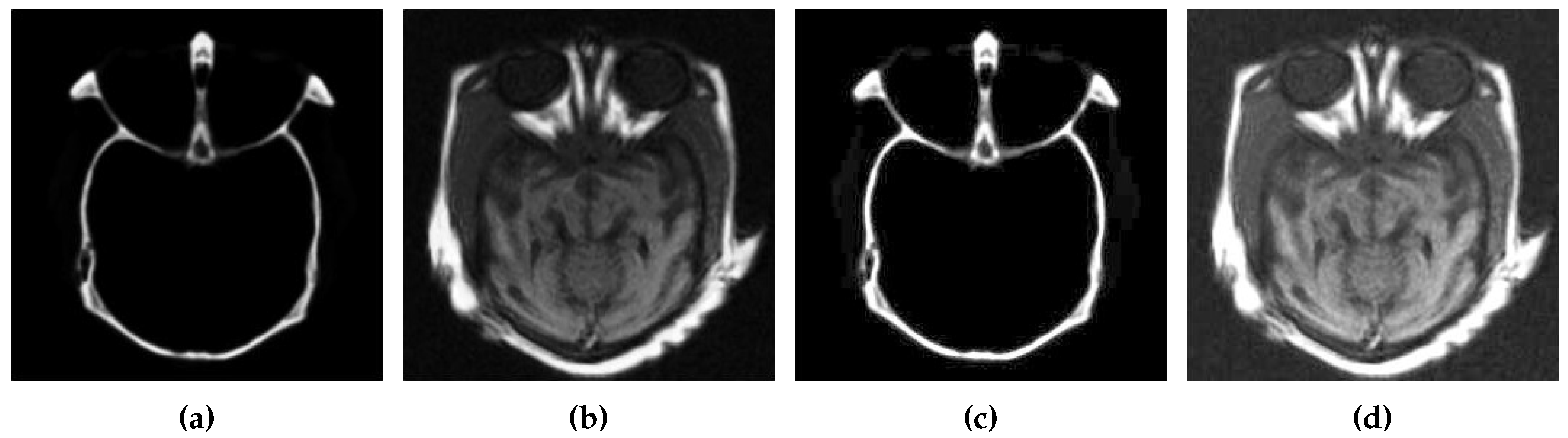
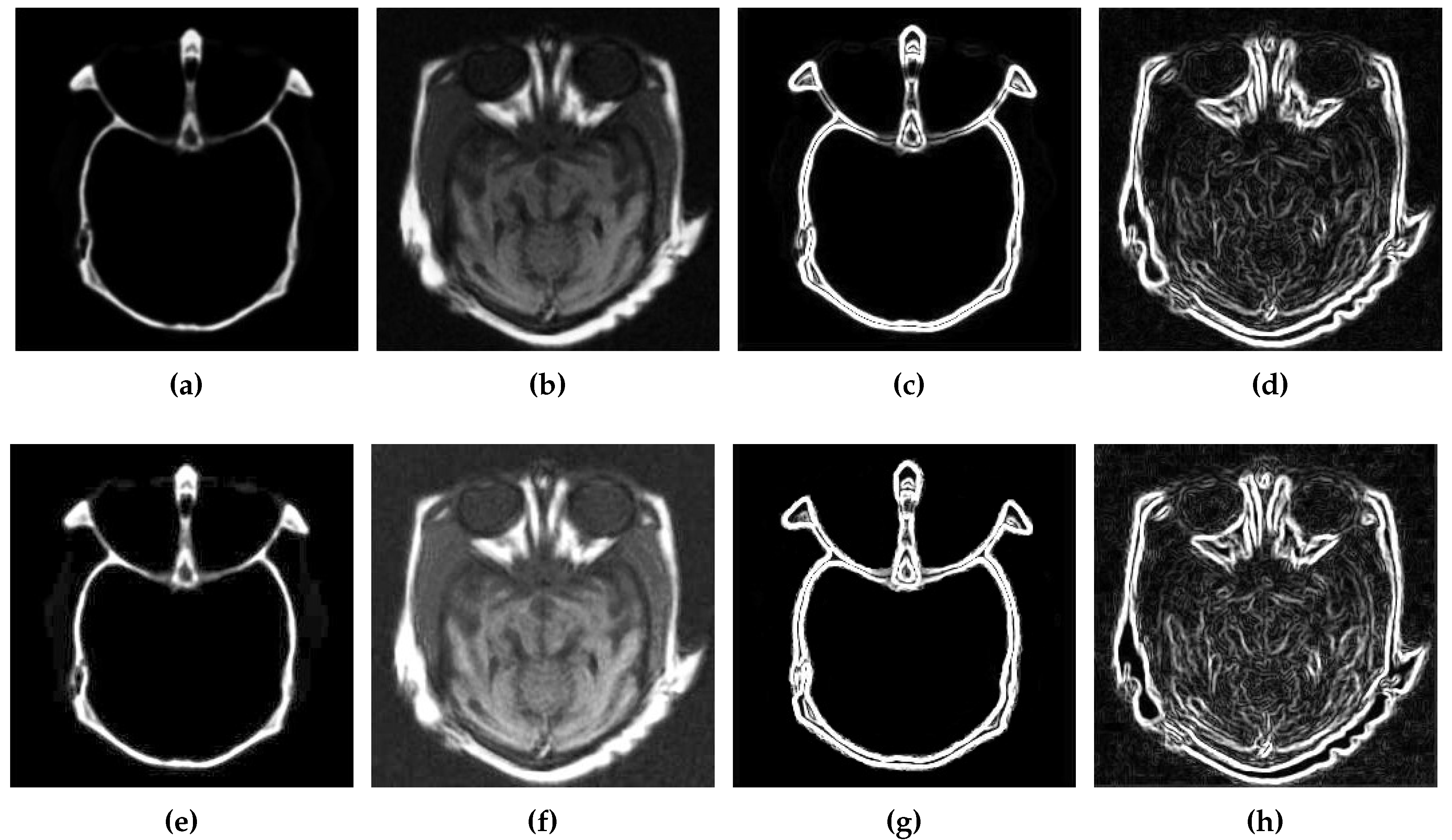
3.1. Contrast Enhancement
3.2. Edge Detection
3.3. Cartoon and Texture Decomposition
3.4. Enhanced CSC-Based Sparse Coding
3.5. Sparse Coefficient Maps Fusion
3.6. Fused Image Reconstruction
4. Objective Evaluation Metrics
4.1. Mutual Information (MI)
4.2. Entropy (EN)
4.3. Feature Mutual Information (FMI)
4.4. Spatial Structural Similarity (SSS)
4.5. Visual Information Fidelity (VIF)
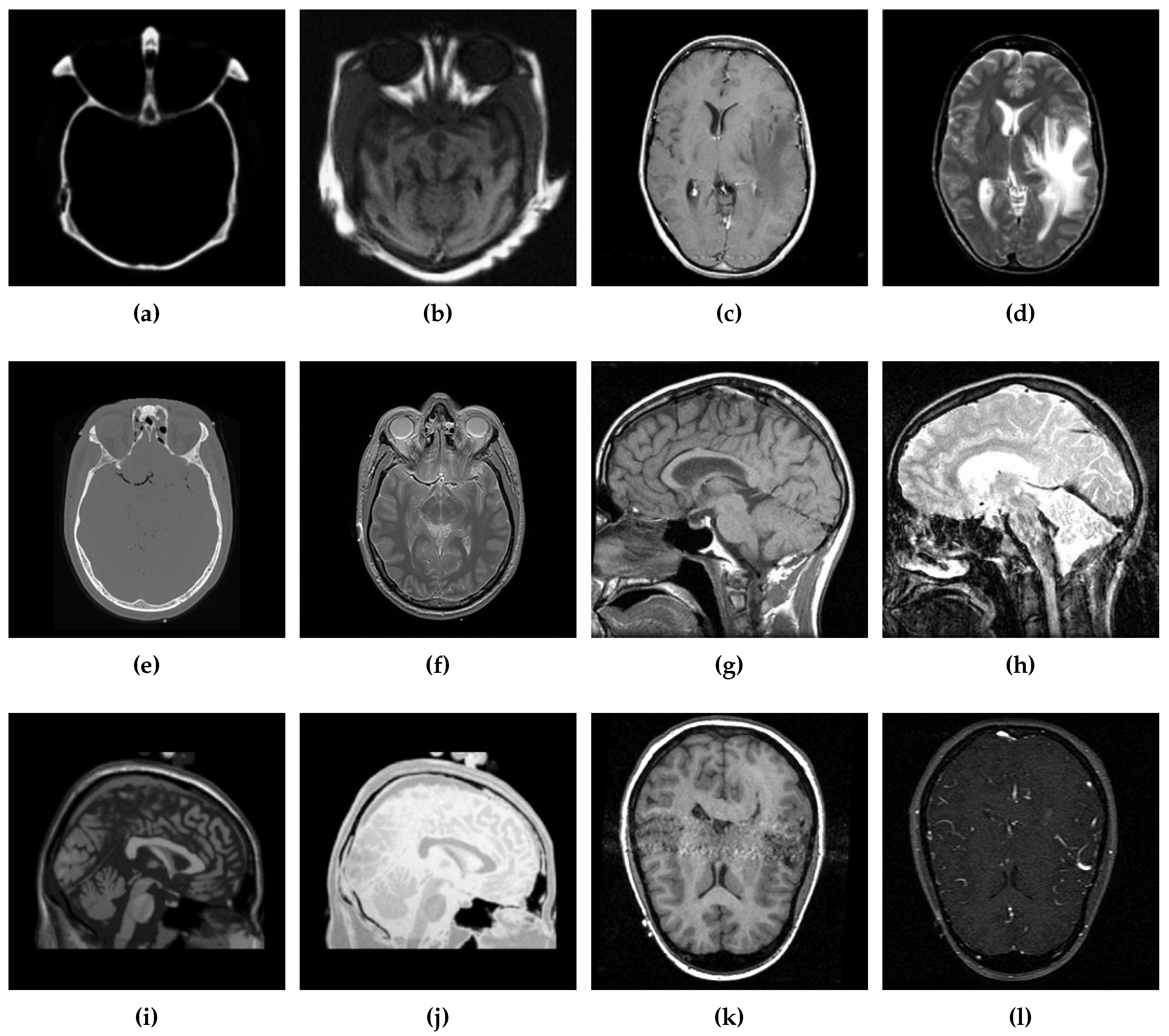
5. Performance Evaluation
5.1. Simulation Setup
5.2. Results and Discussion
5.2.1. Qualitative Analysis of the Given Set of Algorithms for Multimodal Fusion
5.2.2. Quantitative Analysis of the Given Set of Algorithms for Multimodal Fusion
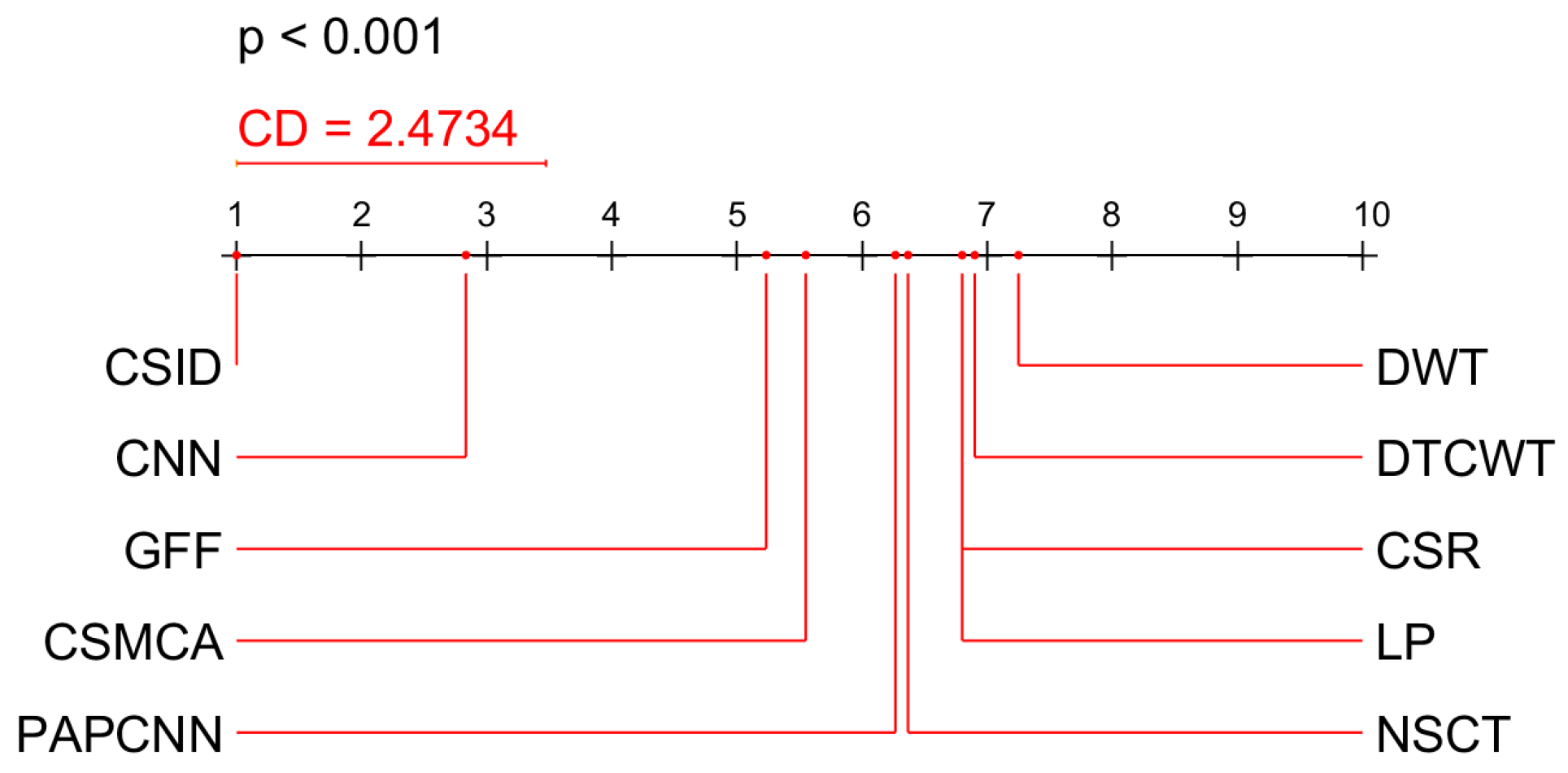
5.2.3. Statistical Analysis of the Results
5.2.4. Computational Efficiency
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, X.; Liu, Q.; Wang, Y. Remote sensing image fusion based on two-stream fusion network. Inf. Fusion 2020, 55, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maqsood, S.; Javed, U. Biomedical Signal Processing and Control Multi-modal Medical Image Fusion based on Two-scale Image Decomposition and Sparse Representation. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2020, 57, 101810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Li, C.; Wei, W.; Jing, W.; Woźniak, M.; Blažauskas, T.; Damaševičius, R. Fully convolutional neural network with augmented atrous spatial pyramid pool and fully connected fusion path for high resolution remote sensing image segmentation. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nisa, M.; Shah, J.H.; Kanwal, S.; Raza, M.; Khan, M.A.; Damaševičius, R.; Blažauskas, T. Hybrid malware classification method using segmentation-based fractal texture analysis and deep convolution neural network features. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 4966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardo, L.S.; Quezada, A.; Muñoz, R.; Maia, F.M.; Pereira, C.R.; Wu, W.; de Albuquerque, V.H.C. Handwritten pattern recognition for early Parkinson’s disease diagnosis. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2019, 125, 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gambhir, D.; Manchanda, M. Waveatom transform-based multimodal medical image fusion. Signal Image Video Process. 2019, 13, 321–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manchanda, M.; Sharma, R. An improved multimodal medical image fusion algorithm based on fuzzy transform. J. Vis. Commun. Image Represent. 2018, 51, 76–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, Q.; Zhang, J.; Wei, W.; Damaševičius, R.; Woźniak, M. Adaptive independent subspace analysis of brain magnetic resonance imaging data. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 12252–12261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.; Zhou, B.; Polap, D.; Wozniak, M. A regional adaptive variational PDE model for computed tomography image reconstruction. Pattern Recognit. 2019, 92, 64–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Li, X.; Huang, H.; Guo, N.; Li, Q. Deep Learning-Based Image Segmentation on Multimodal Medical Imaging. IEEE Trans. Radiat. Plasma Med. Sci. 2019, 3, 162–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.A.; Ashraf, I.; Alhaisoni, M.; Damaševičius, R.; Scherer, R.; Rehman, A.; Bukhari, S.A.C. Multimodal Brain Tumor Classification Using Deep Learning and Robust Feature Selection: A Machine Learning Application for Radiologists. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maqsood, S.; Javed, U.; Riaz, M.M.; Muzammil, M.; Muhammad, F.; Kim, S. Multiscale Image Matting Based Multi-Focus Image Fusion Technique. Electronics 2020, 9, 472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, A.P.; Dasarathy, B.V. Medical image fusion: A survey of the state of the art. Inf. Fusion 2014, 19, 4–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermessi, H.; Mourali, O.; Zagrouba, E. Convolutional neural network-based multimodal image fusion via similarity learning in the shearlet domain. Neural Comput. Appl. 2018, 30, 2029–2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Li, B.; Tian, L.F. Multi-modal medical image fusion using the inter-scale and intra-scale dependencies between image shift-invariant shearlet coefficients. Inf. Fusion 2014, 19, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Qiu, H.; Yu, Z.; Li, B. Multifocus image fusion via fixed window technique of multiscale images and non-local means filtering. Signal Process. 2017, 138, 71–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Wang, M.; Jiao, L.; Wu, R.; Wang, Z. Image fusion based on a new contourlet packet. Inf. Fusion 2010, 11, 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y. A novel DWT based multi-focus image fusion method. Procedia Eng. 2011, 24, 177–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Qiu, H.; Yu, Z.; Zhang, Y. Infrared and visible image fusion scheme based on NSCT and low-level visual features. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2016, 76, 174–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nencini, F.; Garzelli, A.; Baronti, S.; Alparone, L. Remote sensing image fusion using the curvelet transform. Inf. Fusion 2007, 8, 143–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Li, W.; Xiao, B. Union laplacian pyramid with multiple features for medical image fusion. Neurocomputing 2016, 194, 326–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Kang, X.; Hu, J. Image fusion with guided filtering. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2013, 22, 2864–2875. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, X.; Ward, R.K.; Wang, Z.J. Image Fusion With Convolutional Sparse Representation. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2016, 23, 1882–1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, X.; Ward, R.K.; Wang, Z.J. Medical Image Fusion via Convolutional Sparsity Based Morphological Component Analysis. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2019, 26, 485–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, X.; Cheng, J.; Peng, H. A medical image fusion method based on convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the 2017 20th International Conference on Information Fusion (Fusion), Xi’an, China, 10–13 July 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, B.; Li, S. Visual attention guided image fusion with sparse representation. Optik (Stuttg). 2014, 125, 4881–4888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, S.; Wang, Z. A general framework for image fusion based on multi-scale transform and sparse representation. Inf. Fusion 2015, 24, 147–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Yin, H.; Fang, L. Group-sparse representation with dictionary learning for medical image denoising and fusion. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2012, 59, 3450–3459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Han, D.K.; Ko, H. Joint patch clustering-based dictionary learning for multimodal image fusion. Inf. Fusion 2016, 27, 198–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basar, S.; Adnan, A.; Khan, N.H.; Haider, S. Color image segmentation using K-mean classification on RGB histrogram. In Proceedings of the Recent Advances In Telecommunications, Informatics And Educational Technologies, Istanbul, Turkey, 15–17 December 2014; pp. 257–262. [Google Scholar]
- Litjens, G.; Kooi, T.; Bejnordi, B.E.; Setio, A.; Ciompi, F.; Ghafoorian, M. A survey on deep learning in medical image analysis. Med. Image Anal. 2017, 42, 60–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Zheng, M.; Wei, H.; Qi, G.; Li, Y. Multi-modality medical image fusion using convolutional neural network and contrast pyramid. Sensors 2020, 20, 2169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Levine, M.D. Robust multi-focus image fusion using multi-task sparse representation and spatial context. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2016, 25, 2045–2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, C.; Wang, M.; Dong, C.; Duan, C.; Wang, Z. Using Taylor Expansion and Convolutional Sparse Representation for Image Fusion. Neurocomputing 2020, 402, 437–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Sun, Y.; Huang, X.; Qi, G.; Zheng, M.; Zhu, Z. An image fusion method based on sparse representation and Sum Modified-Laplacian in NSCT Domain. Entropy 2018, 20, 522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Jia, L.; Du, J. Multi-Modal Sensor Medical Image Fusion Based on Multiple Salient Features with Guided Image Filter. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 173019–173033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arif, M.; Wang, G. Fast curvelet transform through genetic algorithm for multimodal medical image fusion. Soft Comput. 2020, 24, 1815–1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, M.; Singh, D. Fusion of medical images using deep belief network. Cluster Comput. 2020, 23, 1439–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahdoosti, H.R.; Mehrabi, A. Multimodal image fusion using sparse representation classification in tetrolet domain. Digital Signal Process. 2018, 79, 9–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, Z.; Li, G.; Gao, W. A Bio-Inspired Multi-Exposure Fusion Framework for Low-light Image Enhancement. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1711.00591. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, J.; Li, J.; Fu, X. No-Reference Quality Assessment of Contrast-Distorted Images using Contrast Enhancement. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1904.08879. [Google Scholar]
- Poddar, S.; Tewary, S.; Sharma, D.; Karar, V.; Ghosh, A.; Pal, S.K. Non-parametric modified histogram equalisation for contrast enhancement. IET Image Process. 2013, 7, 641–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schindelin, J.; Rueden, C.T.; Hiner, M.C.; Eliceiri, K.W. The ImageJ ecosystem: An open platform for biomedical image analysis. Mol. Reprod. Dev. 2015, 82, 518–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinheiro, P.O.; Collobert, R. From image-level to pixel-level labeling with convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the 28th IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, CVPR 2015, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 1713–1721. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, W.; Zhang, X.; Yang, L.; Liu, H. An improved Sobel edge detection. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Computer Science and Information Technology, Chengdu, China, 9–11 July 2010; pp. 67–71. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Patel, V.M. Convolutional sparse and low-rank coding-based image decomposition. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2017, 27, 2121–2133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wohlberg, B. Efficient algorithms for convolutional sparse representation. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2016, 25, 301–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, B.; Li, S. Pixel-level image fusion with simultaneous orthogonal matching pursuit. Inf. Fusion 2012, 13, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Wang, M. Image fusion with morphological component analysis. Inf. Fusion 2014, 18, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossny, M.; Nahavandi, S.; Vreighton, D. Comments on information measure for performance of image fusion. Electron. Lett. 2008, 44, 1066–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haghighat, M.B.A.; Aghagolzadeh, A.; Seyedarabi, H. A non-reference image fusion metric based on mutual information of image features. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2011, 37, 744–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrovi, V.S.; Xydeas, C.S. Sensor noise effects on signal-level image fusion performance. Inf. Fusion 2003, 4, 167–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Cai, Y.; Cao, Y.; Xu, X. A new image fusion performance metric based on visual information fidelity. Inf. Fusion 2013, 14, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B.; Jia, B.; Ding, L.; Cai, Z.; Wu, Q. Hybrid dual-tree complex wavelet transform and support vector machine for digital multi-focus image fusion. Neurocomputing 2016, 182, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, M.; Liu, X.; Liu, Y.; Chen, X. Medical Image Fusion With Parameter-Adaptive Pulse Coupled-Neural Network in Nonsubsampled Shearlet Transform Domain. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Measur. 2019, 68, 49–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Chai, Y.; Yin, H.; Li, Y.; Liu, Z. A novel dictionary learning approach for multi-modality medical image fusion. Neurocomputing 2016, 214, 471–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madanagopal, R. Medical fusion imaging: Paving the way for better diagnosis of tumours. Health Manag. 2014, 1–3. Available online: https://healthmanagement.org/c/healthmanagement/issuearticle/medical-fusionimaging-paving-the-way-\for-better-diagnosis-of-tumours (accessed on 1 September 2020).
- Amini, N.; Fatemizadeh, E.; Behnam, H. MRI-PET image fusion based on NSCT transform using local energy and local variance fusion rules. J. Med. Eng. Technol. 2014, 38, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demsar, J. Statistical comparisons of classifiers over multiple data sets. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2006, 7, 1–30. [Google Scholar]
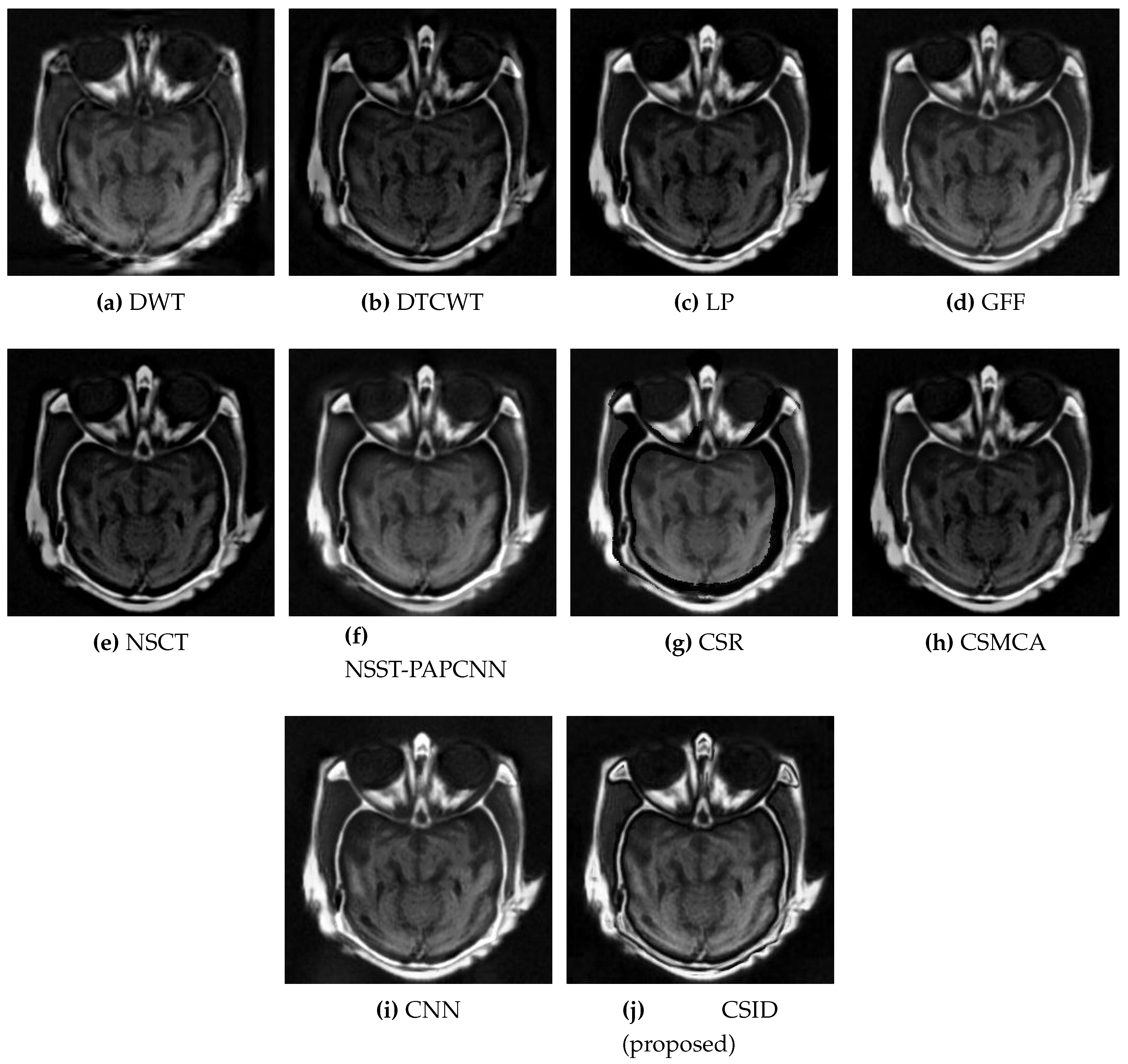
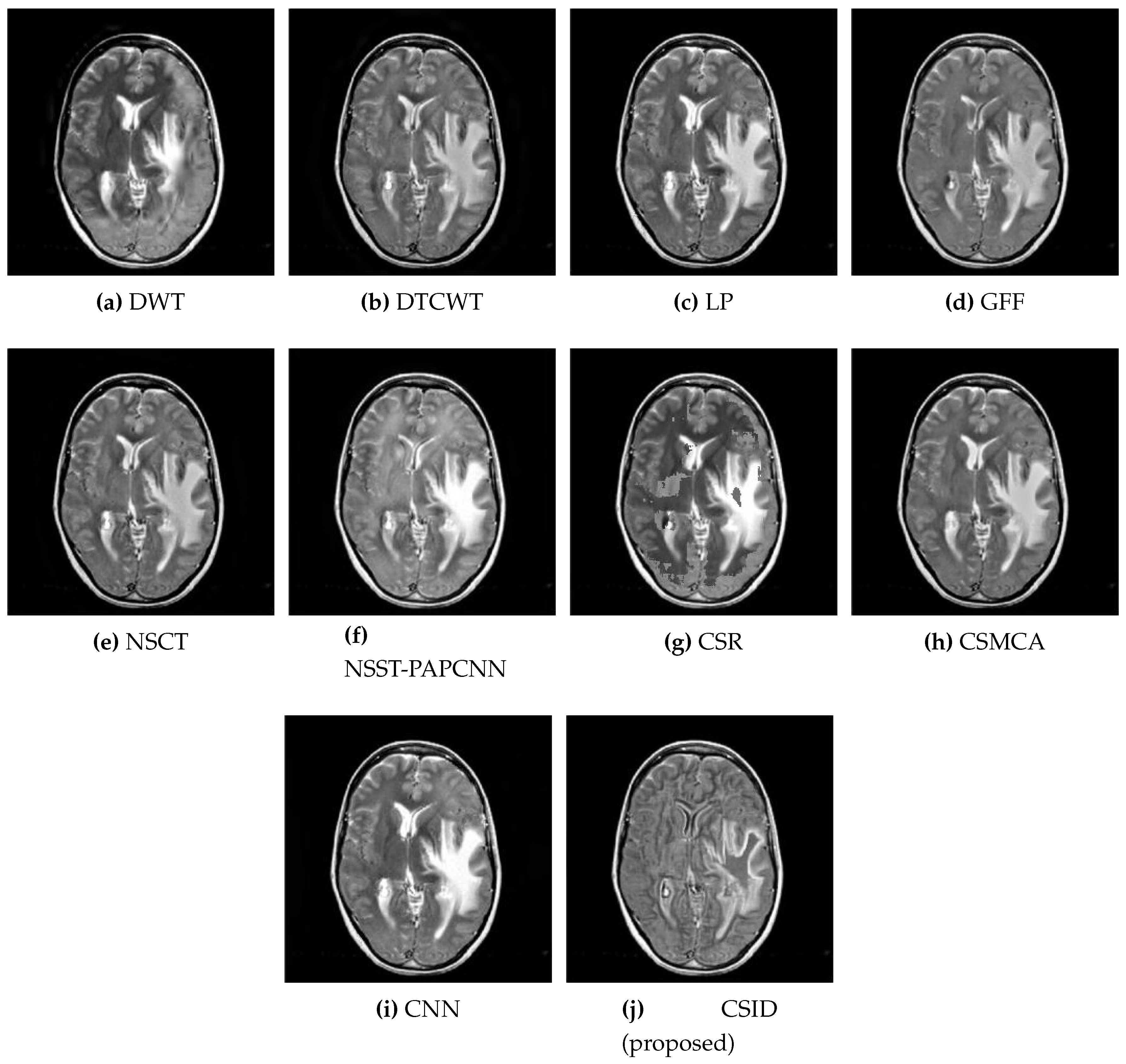

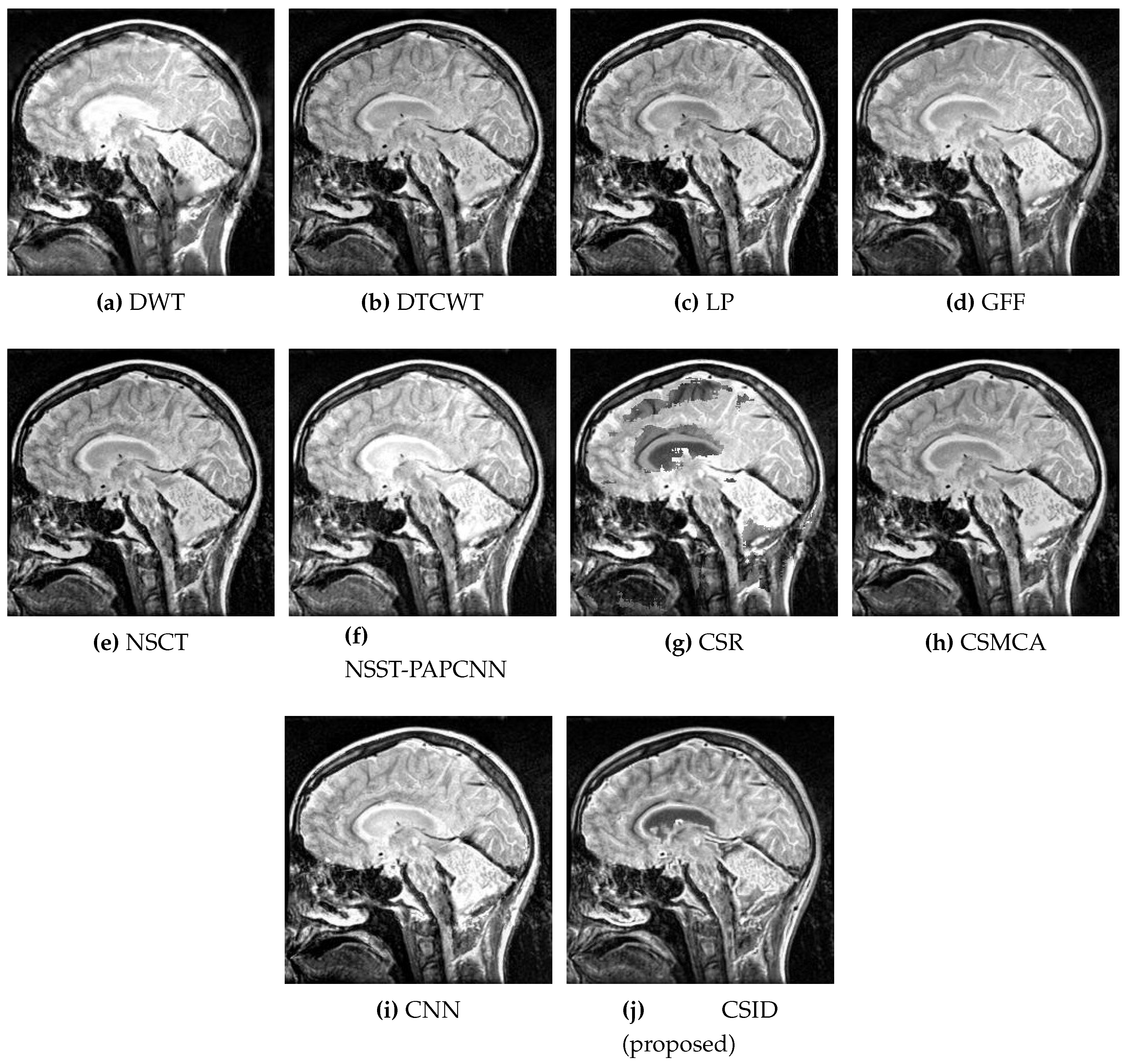
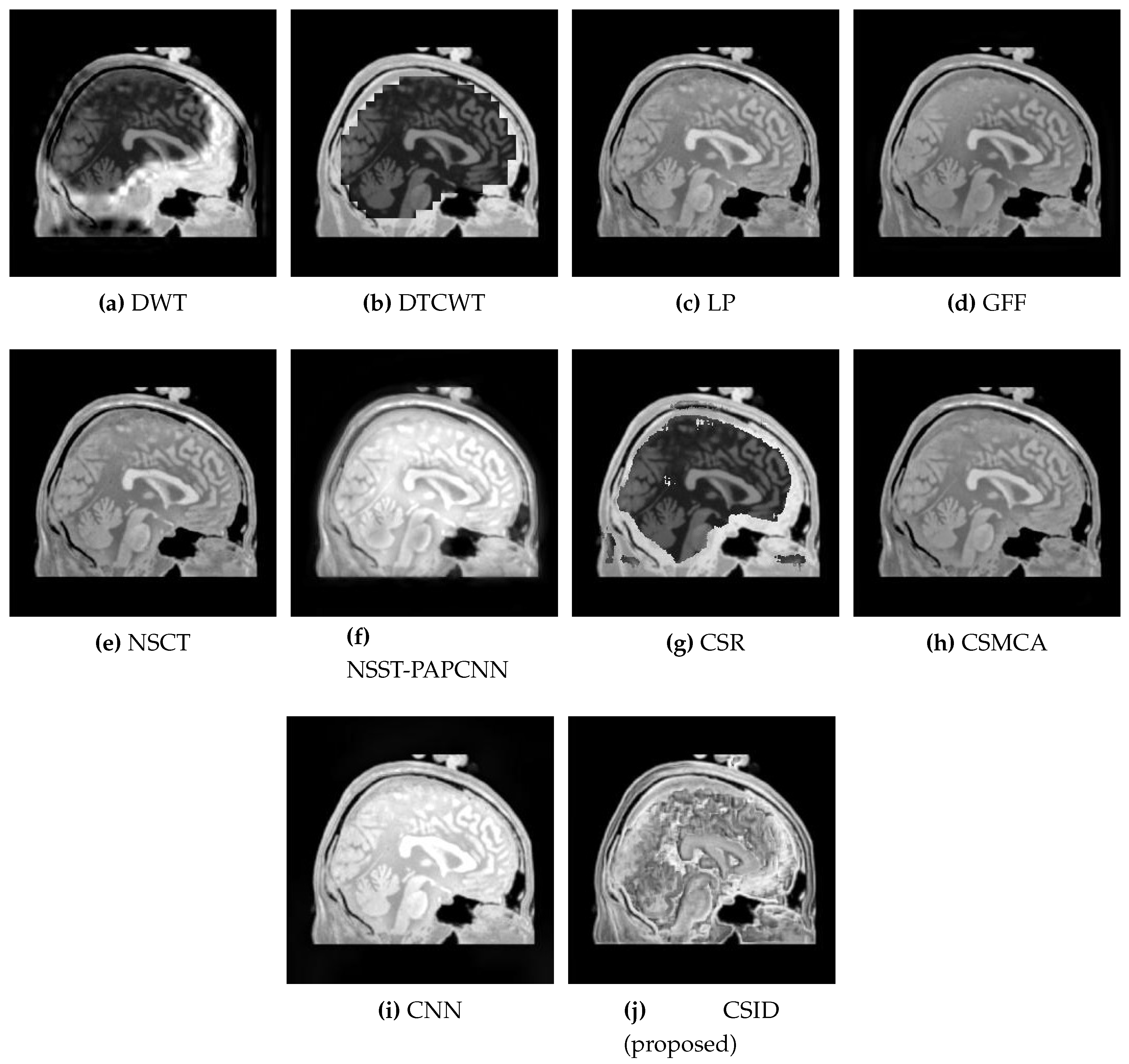
| Images | Fusion Methods | MI [50] | EN [27] | [51] | [52] | VIF [53] | Time (s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DWT [18] | 2.1141 | 6.1512 | 0.7654 | 0.6656 | 0.4065 | 3.644 | |
| Data-1 | DTCWT [54] | 2.1044 | 6.2074 | 0.8341 | 0.6454 | 0.3976 | 6.645 |
| LP [21] | 2.5508 | 6.2724 | 0.7412 | 0.6321 | 0.4141 | 1.699 | |
| GFF [22] | 3.4313 | 6.7971 | 0.9032 | 0.7849 | 0.4864 | 3.004 | |
| NSCT [19] | 2.2087 | 6.1488 | 0.7612 | 0.6872 | 0.3864 | 2.100 | |
| NSST-PAPCNN [55] | 2.4665 | 6.9551 | 0.4559 | 0.6968 | 0.9015 | 5.083 | |
| CSR [23] | 2.087 | 6.4871 | 0.3712 | 0.6327 | 0.8041 | 24.037 | |
| CSMCA [24] | 2.5863 | 6.3274 | 0.4751 | 0.7373 | 0.9088 | 76.700 | |
| CNN [25] | 3.5248 | 6.7541 | 0.7712 | 0.7992 | 0.8991 | 10.696 | |
| Proposed CSID | 3.9649 | 6.9971 | 0.9781 | 0.8021 | 0.9897 | 4.065 | |
| DWT [18] | 3.5472 | 5.5481 | 0.8493 | 0.6922 | 0.5593 | 3.649 | |
| Data-2 | DTCWT [54] | 3.5201 | 6.2074 | 0.8341 | 0.6756 | 0.5521 | 6.544 |
| LP [21] | 3.5908 | 5.6692 | 0.8568 | 0.6571 | 0.4352 | 1.783 | |
| GFF [22] | 3.8595 | 5.8459 | 0.8596 | 0.5919 | 0.4295 | 3.024 | |
| NSCT [19] | 3.5110 | 5.5703 | 0.8498 | 0.6837 | 0.5435 | 2.112 | |
| NSST-PAPCNN [55] | 3.5462 | 7.7278 | 0.5597 | 0.5136 | 0.8393 | 5.144 | |
| CSR [23] | 3.8744 | 6.0867 | 0.5614 | 0.6667 | 0.4715 | 23.441 | |
| CSMCA [24] | 3.5008 | 7.6182 | 0.5728 | 0.5772 | 0.8615 | 74.994 | |
| CNN [25] | 4.2014 | 7.8421 | 0.7458 | 0.6969 | 0.8015 | 10.447 | |
| Proposed CSID | 4.8821 | 8.0142 | 0.8850 | 0.7199 | 0.8715 | 4.051 | |
| DWT [18] | 3.0523 | 7.1581 | 0.9438 | 0.7542 | 0.5369 | 3.702 | |
| Data-3 | DTCWT [54] | 3.0871 | 7.1287 | 0.9361 | 0.7414 | 0.5348 | 6.414 |
| LP [21] | 3.1847 | 7.0536 | 0.8914 | 0.7499 | 0.4832 | 1.955 | |
| GFF [22] | 4.0609 | 5.2463 | 0.9013 | 0.6788 | 0.4486 | 3.287 | |
| NSCT [19] | 3.7394 | 7.1873 | 0.9197 | 0.7101 | 0.5132 | 2.089 | |
| NSST-PAPCNN [55] | 3.7147 | 5.3329 | 0.5536 | 0.5956 | 0.8825 | 5.090 | |
| CSR [23] | 3.9478 | 5.0398 | 0.8657 | 0.6342 | 0.7226 | 23.339 | |
| CSMCA [24] | 3.3098 | 5.0064 | 0.4679 | 0.6397 | 0.9048 | 76.018 | |
| CNN [25] | 4.0183 | 6.9420 | 0.9224 | 0.7301 | 0.9755 | 9.581 | |
| Proposed CSID | 4.4388 | 7.5970 | 0.9744 | 0.7842 | 0.9891 | 4.049 |
| Images | Fusion Methods | MI [50] | EN [27] | [51] | [52] | VIF [53] | Time (s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DWT [18] | 3.5962 | 4.7393 | 0.3823 | 0.5835 | 0.9027 | 3.645 | |
| Data-4 | DTCWT [54] | 3.6632 | 4.8551 | 0.8339 | 0.6921 | 0.6679 | 6.643 |
| LP [21] | 3.4733 | 4.6547 | 0.7690 | 0.6391 | 0.9255 | 1.774 | |
| GFF [22] | 3.4514 | 4.4081 | 0.9047 | 0.6470 | 0.4961 | 3.132 | |
| NSCT [19] | 3.8544 | 4.5360 | 0.8395 | 0.7093 | 0.7769 | 2.143 | |
| NSST-PAPCNN [55] | 3.3372 | 5.0598 | 0.5401 | 0.6076 | 0.8960 | 5.232 | |
| CSR [23] | 3.6584 | 4.7695 | 0.8471 | 0.6655 | 0.8467 | 22.998 | |
| CSMCA [24] | 3.4007 | 4.3896 | 0.4939 | 0.6601 | 0.9027 | 75.802 | |
| CNN [25] | 4.2540 | 5.1748 | 0.8421 | 0.7441 | 0.9408 | 10.113 | |
| Proposed CSID | 4.6987 | 5.9459 | 0.9814 | 0.8023 | 0.9947 | 4.122 | |
| DWT [18] | 4.0214 | 4.6386 | 0.4777 | 0.5782 | 0.7592 | 3.650 | |
| Data-5 | DTCWT [54] | 4.2985 | 4.7687 | 0.4885 | 0.6257 | 0.5573 | 6.625 |
| LP [21] | 4.4128 | 4.8825 | 0.5241 | 0.6825 | 0.5826 | 1.874 | |
| GFF [22] | 4.7093 | 5.2982 | 0.7849 | 0.7259 | 0.7928 | 3.332 | |
| NSCT [19] | 3.9309 | 4.9304 | 0.6908 | 0.6827 | 0.7469 | 2.139 | |
| NSST-PAPCNN [55] | 4.1937 | 4.9809 | 0.7360 | 0.6887 | 0.6993 | 5.403 | |
| CSR [23] | 4.5094 | 5.0297 | 0.6997 | 0.6259 | 0.5067 | 23.422 | |
| CSMCA [24] | 5.0924 | 5.9330 | 0.7485 | 0.7759 | 0.8257 | 76.112 | |
| CNN [25] | 5.1118 | 5.9989 | 0.8697 | 0.8267 | 0.8881 | 10.691 | |
| Proposed CSID | 5.2471 | 6.2874 | 0.8847 | 0.8728 | 0.8971 | 4.041 | |
| DWT [18] | 3.6877 | 4.8474 | 0.5570 | 0.4938 | 0.5551 | 3.647 | |
| Data-6 | DTCWT [54] | 3.6439 | 4.8839 | 0.5683 | 0.5097 | 0.6086 | 6.245 |
| LP [21] | 3.9482 | 4.9029 | 0.6019 | 0.6287 | 0.6239 | 1.963 | |
| GFF [22] | 4.1675 | 5.0098 | 0.7829 | 0.6876 | 0.7452 | 3.504 | |
| NSCT [19] | 3.8888 | 4.8729 | 0.7067 | 0.6431 | 0.7884 | 2.146 | |
| NSST-PAPCNN [55] | 4.0671 | 4.9038 | 0.7149 | 0.6835 | 0.7763 | 5.113 | |
| CSR [23] | 3.7432 | 4.4597 | 0.6839 | 0.5334 | 0.6720 | 23.483 | |
| CSMCA [24] | 4.5810 | 4.9997 | 0.8097 | 0.7482 | 0.8027 | 76.772 | |
| CNN [25] | 4.6744 | 5.2779 | 0.8527 | 0.7983 | 0.8341 | 10.834 | |
| Proposed CSID | 4.8887 | 5.8209 | 0.8817 | 0.8497 | 0.8748 | 4.047 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Muzammil, S.R.; Maqsood, S.; Haider, S.; Damaševičius, R. CSID: A Novel Multimodal Image Fusion Algorithm for Enhanced Clinical Diagnosis. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 904. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10110904
Muzammil SR, Maqsood S, Haider S, Damaševičius R. CSID: A Novel Multimodal Image Fusion Algorithm for Enhanced Clinical Diagnosis. Diagnostics. 2020; 10(11):904. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10110904
Chicago/Turabian StyleMuzammil, Shah Rukh, Sarmad Maqsood, Shahab Haider, and Robertas Damaševičius. 2020. "CSID: A Novel Multimodal Image Fusion Algorithm for Enhanced Clinical Diagnosis" Diagnostics 10, no. 11: 904. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10110904
APA StyleMuzammil, S. R., Maqsood, S., Haider, S., & Damaševičius, R. (2020). CSID: A Novel Multimodal Image Fusion Algorithm for Enhanced Clinical Diagnosis. Diagnostics, 10(11), 904. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10110904





