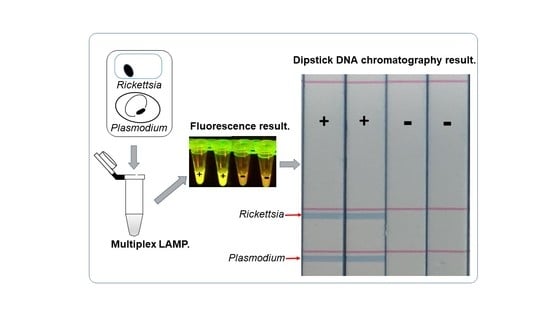
Development of a Multiplex Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification (LAMP) Method for Simultaneous Detection of Spotted Fever Group Rickettsiae and Malaria Parasites by Dipstick DNA Chromatography
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Multiplex LAMP
2.2. Visualization of Multiplex Amplified Products by Dipstick DNA Chromatography C-PAS
2.3. The Determination of the Sensitivity of Multiplex LAMP Assay Using Synthetic Genes
2.4. The Determination of the Sensitivity of Multiplex LAMP Assay Using Genomic DNA from In Vitro Cultured R. monacensis or P. falciparum
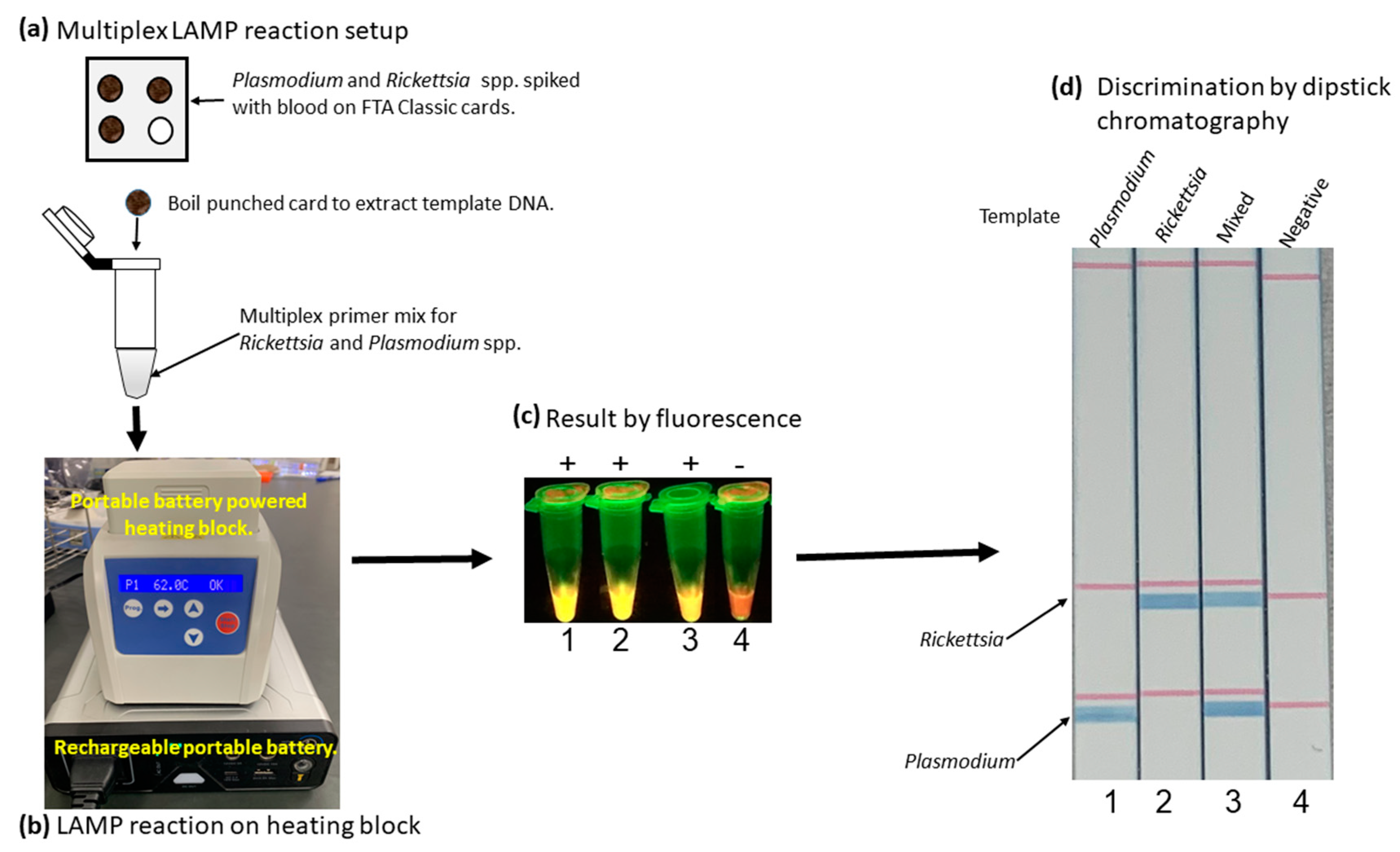
2.5. Detection of R. monacensis and P. falciparum Spiked with Human Blood from DNA Card Using Heating Block and Dipstick Chromatography
3. Results
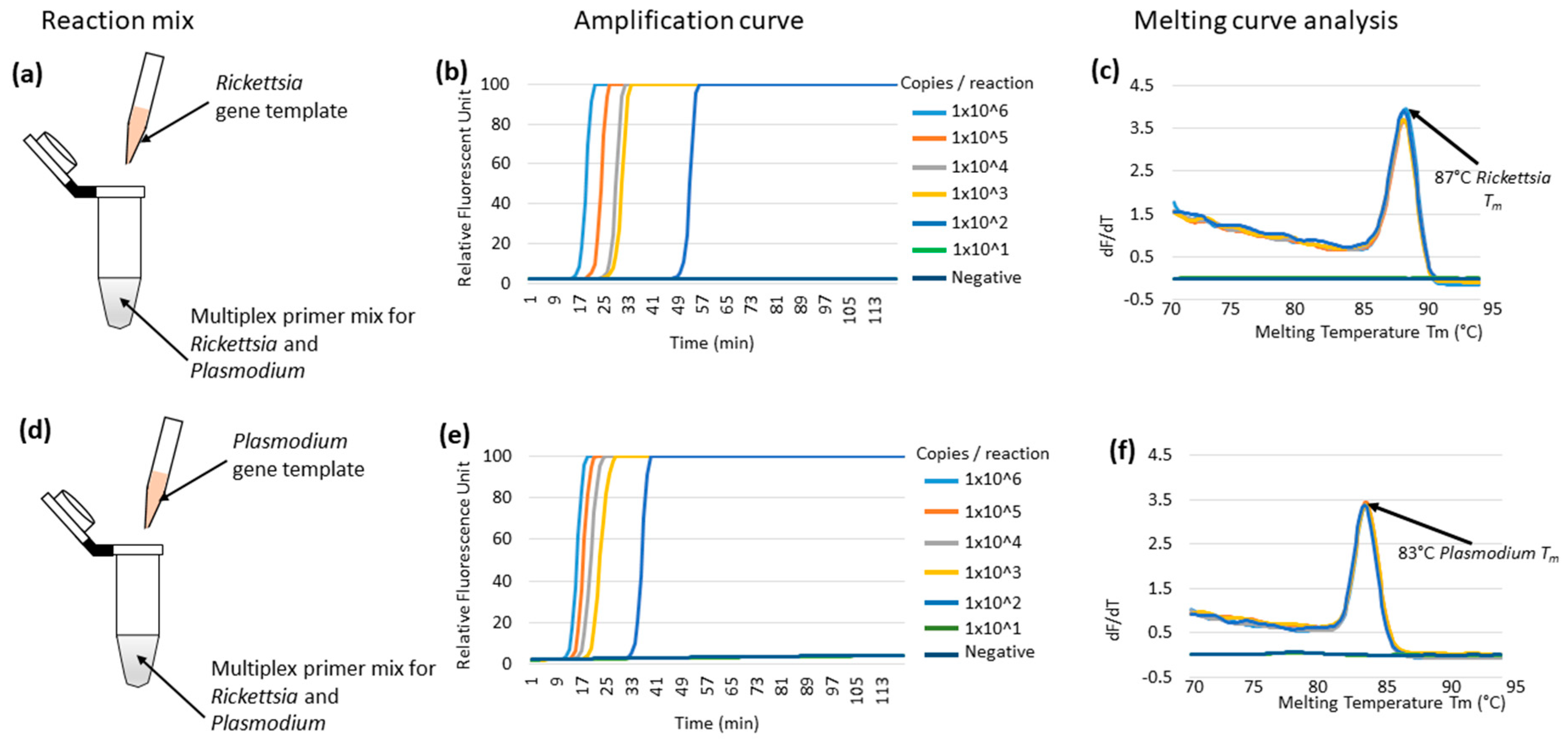
3.1. Multiplex LAMP Using Individual Synthetic Templates of Rickettsia or Plasmodium Genes in Plasmids
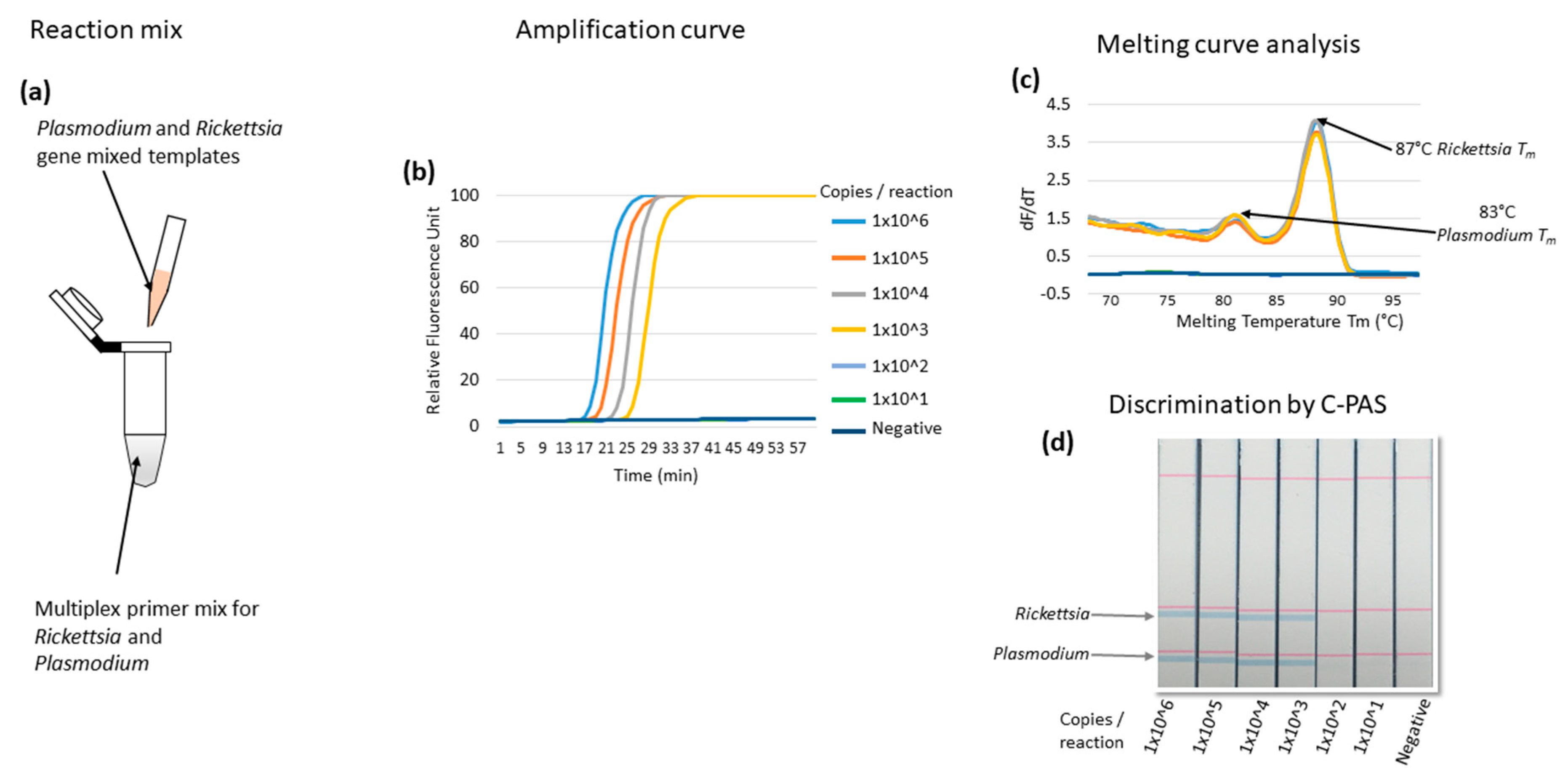
3.2. Optimization of Multiplex LAMP Using Mixed Synthetic Templates of Rickettsia and Plasmodium Gene, and Discrimination by C-PAS
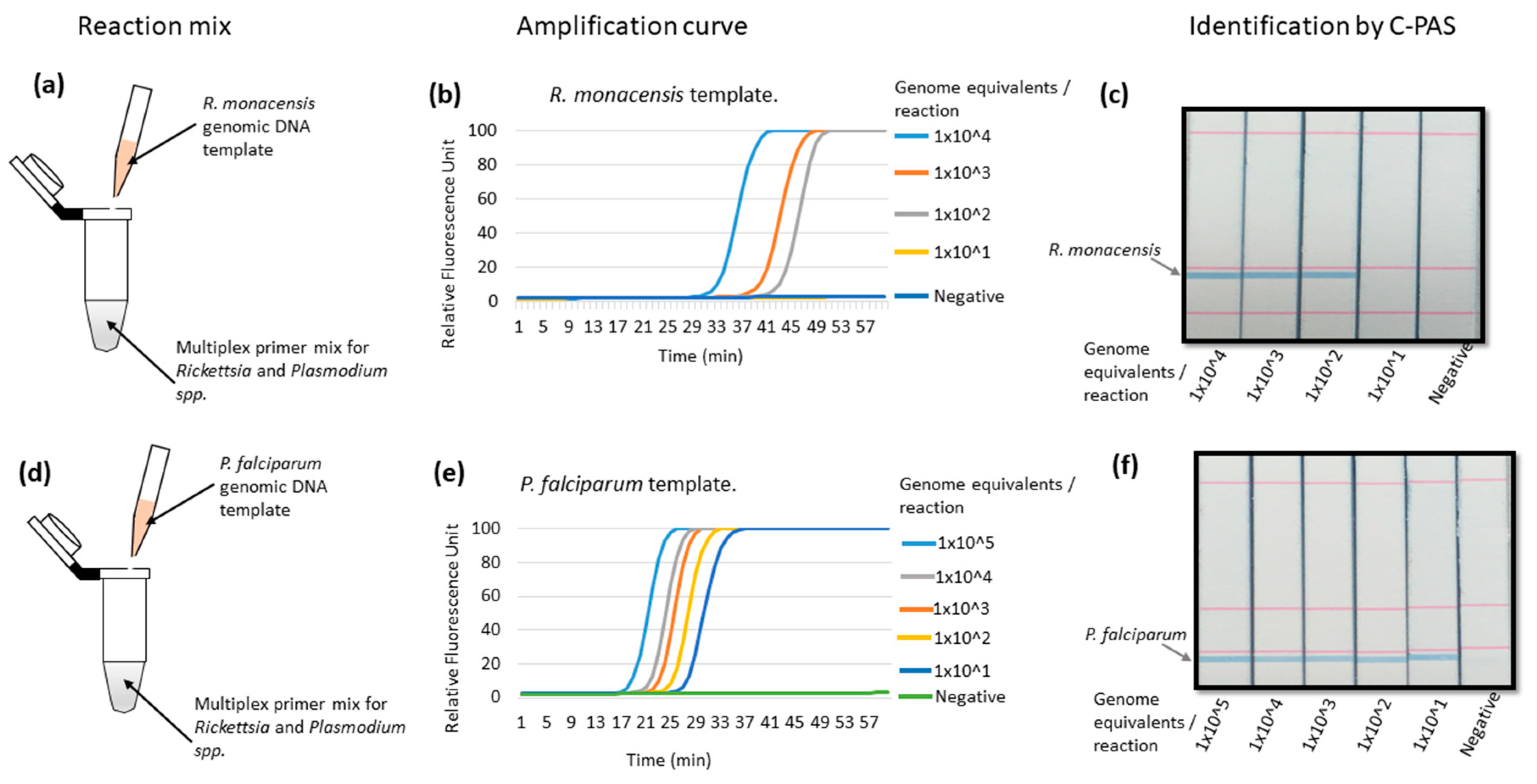
3.3. Validation of Multiplex LAMP Using Genomic DNA from In Vitro Cultured R. monacensis or P. falciparum Organisms
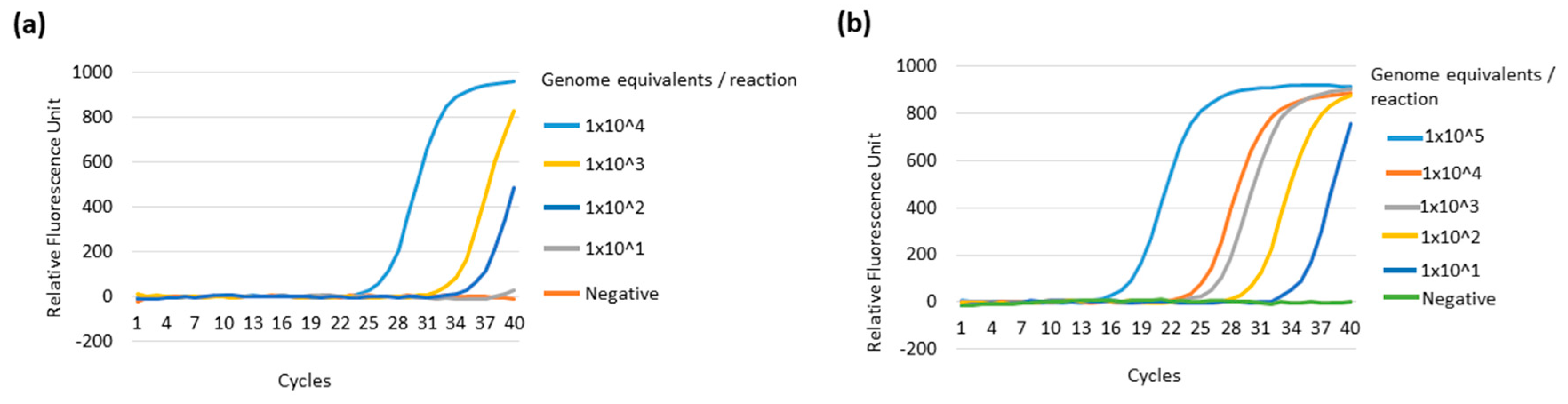
3.4. Comparative Sensitivity of the Multiplex LAMP System against the Real-Time qPCR System
3.5. Simplified LAMP Reaction Using Human Blood Spiked Samples and Field-Deployable Amplification Methods
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Petit:, P.L.; van Ginneken, J.K. Analysis of hospital records in four African countries, 1975-1990, with emphasis on infectious diseases. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1995, 98, 217–227. [Google Scholar]
- Prasad, N.; Murdoch, D.R.; Reyburn, H.; Crump, J.A. Etiology of severe febrile illness in low- and middle-income countries: A systematic review. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamau, A.; Mogeni, P.; Okiro, E.A.; Snow, R.W.; Bejon, P. A systematic review of changing malaria disease burden in sub-Saharan Africa since 2000: Comparing model predictions and empirical observations. BMC Med. 2020, 18, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reyburn, H.; Mbatia, R.; Drakeley, C.; Carneiro, I.; Mwakasungula, E.; Mwerinde, O.; Saganda, K.; Shao, J.; Kitua, A.; Olomi, R.; et al. Overdiagnosis of malaria in patients with severe febrile illness in Tanzania: A prospective study. Br. Med. J. 2004, 329, 1212–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brah, S.; Daou, M.; Salissou, L.; Mahaman, S.; Alhousseini, D.; Iroungou, A.; Moussa, S.; Malam-Abdou, B.; Adamou, H.; Adehossi, E. Fever of Unknown Origin in Africa: The Causes Are Often Determined! Health Sci. Dis. 2015, 16, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Wangdi, K.; Kasturiaratchi, K.; Nery, S.V.; Lau, C.L.; Gray, D.J.; Clements, A.C.A. Diversity of infectious aetiologies of acute undifferentiated febrile illnesses in south and Southeast Asia: A systematic review. BMC Infect. Dis. 2019, 19, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mediannikov, O.; Socolovschi, C.; Edouard, S.; Fenollar, F.; Mouffok, N.; Bassene, H.; Diatta, G.; Tall, A.; Niangaly, H.; Doumbo, O.; et al. Common epidemiology of Rickettsia felis infection and malaria, Africa. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2013, 19, 1775–1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amexo, M.; Tolhurst, R.; Barnish, G.; Bates, I. Malaria misdiagnosis: Effects on the poor and vulnerable. Lancet 2004, 364, 1896–1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raoult, D.; Fournier, P.E.; Fenollar, F.; Jensenius, M.; Prioe, T.; De Pina, J.J.; Caruso, G.; Jones, N.; Laferl, H.; Rosenblatt, J.E.; et al. Rickettsia africae, a tick-borne pathogen in travelers to sub-Saharan Africa. N. Engl. J. Med. 2001, 344, 1504–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mediannikov, O.; Diatta, G.; Fenollar, F.; Sokhna, C.; Trape, J.F.; Raoult, D. Tick-borne rickettsioses, neglected emerging diseases in rural Senegal. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2010, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, M.T.; Satjanadumrong, J.; Hughes, T.; Stenos, J.; Blacksell, S.D. Diagnosis of spotted fever group Rickettsia infections: The Asian perspective. Epidemiol. Infect. 2019, 147, e286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santibáñez, S.; Portillo, A.; Santibáñez, P.; Palomar, A.M.; Oteo, J.A. Usefulness of rickettsial PCR assays for the molecular diagnosis of human rickettsioses. Enferm. Infecc. Microbiol. Clin. 2013, 31, 283–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crump, J.A.; Morrissey, A.B.; Nicholson, W.L.; Massung, R.F.; Stoddard, R.A.; Galloway, R.L.; Ooi, E.E.; Maro, V.P.; Saganda, W.; Kinabo, G.D.; et al. Etiology of Severe Non-malaria Febrile Illness in Northern Tanzania: A Prospective Cohort Study. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2013, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Punjabi, N.H.; Taylor, W.R.J.; Murphy, G.S.; Purwaningsih, S.; Picarima, H.; Sisson, J.; Olson, J.G.; Baso, S.; Wangsasaputra, F.; Lesmana, M.; et al. Etiology of acute, non-malaria, febrile illnesses in Jayapura, Northeastern Papua, Indonesia. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2012, 86, 46–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinheirob, V.E.; Thaithongc, S.; Browna, K.N. High sensitivity of detection of human malaria parasites by the use of nested polymerase chain reaction. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 1993, 61, 315–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cnops, L.; Jacobs, J.; Van Esbroeck, M. Validation of a four-primer real-time PCR as a diagnostic tool for single and mixed Plasmodium infections. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2011, 17, 1101–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.J.; Lee, S.H.; Park, K.H.; Koh, Y.S.; Lee, K.H.; Baik, H.S.; Choi, M.S.; Kim, I.S.; Jang, W.J. Evaluation of PCR-based assay for diagnosis of spotted fever group rickettsiosis in human serum samples. Clin. Diagn. Lab. Immunol. 2005, 12, 759–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Renvoisé, A.; Rolain, J.M.; Socolovschi, C.; Raoult, D. Widespread use of real-time PCR for rickettsial diagnosis. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 2012, 64, 126–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Notomi, T.; Okayama, H.; Masubuchi, H.; Yonekawa, T.; Watanabe, K.; Amino, N.; Hase, T. Loop-mediated isothermal amplification of DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, e63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashida, K.; Kajino, K.; Simukoko, H.; Simuunza, M.; Ndebe, J.; Chota, A.; Namangala, B.; Sugimoto, C. Direct detection of falciparum and non-falciparum malaria DNA from a drop of blood with high sensitivity by the dried-LAMP system. Parasites Vectors 2017, 10, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, E.T.; Watanabe, R.; Sattabongkot, J.; Khuntirat, B.; Sirichaisinthop, J.; Iriko, H.; Jin, L.; Takeo, S.; Tsuboi, T. Detection of four Plasmodium species by genus- and species-specific loop-mediated isothermal amplification for clinical diagnosis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2007, 45, 2521–2528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polley, S.D.; Mori, Y.; Watson, J.; Perkins, M.D.; González, I.J.; Notomi, T.; Chiodini, P.L.; Sutherland, C.J. Mitochondrial DNA targets increase sensitivity of malaria detection using loop-mediated isothermal amplification. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2010, 48, 2866–2871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noden, B.H.; Martin, J.; Carrillo, Y.; Talley, J.L.; Ochoa-Corona, F.M. Development of a loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) assay for rapid screening of ticks and fleas for spotted fever group rickettsia. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, L.; Zhang, L.; Wang, G.; Liu, Q. Rapid, simple, and sensitive detection of the ompB gene of spotted fever group rickettsiae by loop-mediated isothermal amplification. BMC Infect. Dis. 2012, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, Y.; Kitao, M.; Tomita, N.; Notomi, T. Real-time turbidimetry of LAMP reaction for quantifying template DNA. J. Biochem. Biophys. Methods 2004, 59, 145–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, N.; Zou, D.; Dong, D.; Yang, Z.; Ao, D.; Liu, W.; Huang, L. Development of a multiplex loop-mediated isothermal amplification method for the simultaneous detection of Salmonella spp. and Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takabatake, R.; Kagiya, Y.; Minegishi, Y.; Futo, S.; Soga, K.; Nakamura, K.; Kondo, K.; Mano, J.; Kitta, K. Rapid Screening Detection of Genetically Modified Crops by Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification with a Lateral Flow Dipstick. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 7839–7845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanner, N.A.; Zhang, Y.; Evans, T.C. Simultaneous multiple target detection in real-time loop-mediated isothermal amplification. Biotechniques 2012, 53, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Lan, R.; Xu, H.; Ma, A.; Li, D.; Dai, H.; Yuan, X.; Xu, J.; Ye, C. Multiple endonuclease restriction real-time loop-mediated isothermal amplification: A novel analytically rapid, sensitive, multiplex loop-mediated isothermal amplification detection technique. J. Mol. Diagnostics 2015, 17, 392–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ball, C.S.; Light, Y.K.; Koh, C.Y.; Wheeler, S.S.; Coffey, L.L.; Meagher, R.J. Quenching of Unincorporated Amplification Signal Reporters in Reverse-Transcription Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification Enabling Bright, Single-Step, Closed-Tube, and Multiplexed Detection of RNA Viruses. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 3562–3568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monden, Y.; Takasaki, K.; Futo, S.; Niwa, K.; Kawase, M.; Akitake, H.; Tahara, M. A rapid and enhanced DNA detection method for crop cultivar discrimination. J. Biotechnol. 2014, 185, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanmugakani, R.K.; Akeda, Y.; Yamamoto, N.; Sakamoto, N.; Hagiya, H.; Yoshida, H.; Takeuchi, D.; Sugawara, Y.; Kodera, T.; Kawase, M.; et al. PCR-dipstick chromatography for differential detection of carbapenemase genes directly in stool specimens. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2017, 61, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niwa, K.; Oribe, A.; Okumura, H.; Shimono, M.; Nagai, K.; Hirota, T.; Yasue, H.; Kawase, M. Tag/hybridization-based sensitive detection of polymerase chain reaction products. Anal. Biochem. 2014, 464, 12–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, L.; Sato, T.; Niwa, K.; Kawase, M.; Mayanagi, G.; Washio, J.; Takahashi, N. PCR-dipstick DNA chromatography for profiling of a subgroup of caries associated bacterial species in plaque from healthy coronal surfaces and periodontal pockets. Biomed. Res. 2016, 37, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugita-Konishi, Y.; Kobayashi, N.; Takasaki, K.; Kanno, T.; Itoh, M.; Riztyan; Futo, S.; Asakura, H.; Taira, K.; Kawakami, Y. Detection of Sarcocystis spp. and Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli in Japanese sika deer meat using a loop-mediated isothermal amplification-lateral flow strip. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2019, 81, 586–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashida, K.; Kajino, K.; Hachaambwa, L.; Namangala, B.; Sugimoto, C. Direct Blood Dry LAMP: A Rapid, Stable, and Easy Diagnostic Tool for Human African Trypanosomiasis. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2015, 9, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashida, K.; Orba, Y.; Sequeira, P.C.; Sugimoto, C.; Hall, W.W.; Eshita, Y.; Suzuki, Y.; Runtuwene, L.; Brasil, P.; Calvet, G.; et al. Field diagnosis and genotyping of chikungunya virus using a dried reverse transcription loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) assay and MinION sequencing. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2019, 13, e0007480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thu, M.J.; Qiu, Y.; Kataoka-Nakamura, C.; Sugimoto, C.; Katakura, K.; Isoda, N.; Nakao, R. Isolation of Rickettsia, Rickettsiella, and Spiroplasma from Questing Ticks in Japan Using Arthropod Cells. Vector-Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2019, 19, 474–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moonga, L.C.; Hayashida, K.; Nakao, R.; Lisulo, M.; Kaneko, C.; Nakamura, I.; Eshita, Y.; Mweene, A.S.; Namangala, B.; Sugimoto, C.; et al. Molecular detection of Rickettsia felis in dogs, rodents and cat fleas in Zambia. Parasites Vectors 2019, 12, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trager, W.; Jensen, J.B. Human malaria parasites in continuous culture. Science (80-. ) 1976, 193, 673–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefterova, M.I.; Budvytiene, I.; Sandlund, J.; Färnert, A.; Banaei, N. Simple real-time PCR and amplicon sequencing method for identification of Plasmodium species in human whole blood. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2015, 53, 2251–2257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, E.H.; Lee, S.K.; Ihm, C.; Sohn, Y.H.; Kwang, S.; Ihm, C.; Sohn, Y.H. Rapid DNA Extraction from Dried Blood Spots on Filter Paper: Potential Applications in Biobanking. Osong Public Health Res. Perspect. 2014, 5, 351–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rolando, J.C.; Jue, E.; Barlow, J.T.; Ismagilov, R.F. Real-time kinetics and high-resolution melt curves in single-molecule digital LAMP to differentiate and study specific and nonspecific amplification. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, e42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, C.; Id, H.; Kristine, M.; Elizabeth, G.; Str, A.; Langeland, N.; Hanevik, K.; Mohn, S.C. Assessment of malaria real-time PCR methods and application with focus on low- level parasitemia. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0218982. [Google Scholar]
- Mandage, R.; Kaur, C.; Pramanik, A.; Kumar, V.; Kodan, P.; Singh, A.; Saha, S.; Pandey, S.; Wig, N.; Pandey, R.M.; et al. Association of Dengue Virus and Leptospira Co-Infections with Malaria Severity. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2020, 26, 1645–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGready, R.; Blacksell, S.D.; Luksameetanasan, R.; Wuthiekanun, V.; Jedsadapanpong, W.; Day, N.P.J.; Nosten, F. First report of an orientia tsutsugamushi type TA716-related scrub typhus infection in Thailand. Vector-Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2010, 10, 191–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watt, G.; Parola, P. Scrub typhus and tropical rickettsioses. Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 2003, 16, 429–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rolain, J.M.; Gouriet, F.; Brouqui, P.; Larrey, D.; Janbon, F.; Vene, S.; Jarnestrom, V.; Raoult, D. Concomitant or consecutive infection with Coxiella burnetti, tickborne diseases. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2005, 40, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phimda, K.; Hoontrakul, S.; Suttinont, C.; Chareonwat, S.; Losuwanaluk, K.; Chueasuwanchai, S.; Chierakul, W.; Suwancharoen, D.; Silpasakorn, S.; Saisongkorh, W.; et al. Doxycycline versus azithromycin for treatment of leptospirosis and scrub typhus. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2007, 51, 3259–3263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haanshuus, C.G.; Mohn, S.C.; Mørch, K.; Langeland, N.; Blomberg, B.; Hanevik, K. A novel, single-amplification PCR targeting mitochondrial genome highly sensitive and specific in diagnosing malaria among returned travelers in Bergen, Norway. Malar. J. 2013, 12, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandasegui, J.; Fernández-Soto, P.; Muro, A.; Simões Barbosa, C.; Lopes de Melo, F.; Loyo, R.; de Souza Gomes, E.C. A field survey using LAMP assay for detection of Schistosoma mansoni in a low-transmission area of schistosomiasis in Umbuzeiro, Brazil: Assessment in human and snail samples. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2018, 12, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oriero, E.C.; Van Geertruyden, J.P.; Nwakanma, D.C.; Dalessandro, U.; Jacobs, J. Novel techniques and future directions in molecular diagnosis of malaria in resource-limited settings. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2015, 15, 1419–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinko, B.; Oguike, M.C.; Larbi, J.A.; Bousema, T.; Sutherland, C.J. Persistent detection of Plasmodium falciparum, P. malariae, P. ovale curtisi and P. ovale wallikeri after ACT treatment of asymptomatic Ghanaian school-children. Int. J. Parasitol. Drugs Drug Resist. 2013, 3, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imwong, M.; Woodrow, C.J.; Hendriksen, I.C.E.; Veenemans, J.; Verhoef, H.; Faiz, M.A.; Mohanty, S.; Mishra, S.; Mtove, G.; Gesase, S.; et al. Plasma concentration of parasite DNA as a measure of disease severity in falciparum malaria. J. Infect. Dis. 2015, 211, 1128–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, C.; Chung, I.; Paddock, C. Estimation of Rickettsia rickettsii copy number in the blood of patients with Rocky Mountain spotted fever suggests cyclic diurnal trends in bacteremia. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2016, 22, 394–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Target Pathogen | Target Gene Name | Primer Name [Reference] | Primer Sequence Name | Primer Sequence |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spotted fever and Transitional group rickettsiae | 17 kDa protein-encoding (htrA) gene | 17 kDA [23] | Rr17F3 | 5′-TGTTACAAGCCTGTAACGG-3′ |
| Rr17B3 | 5′-TCCTGTTCATCCATACCTG-3′ | |||
| Rr17FIP | 5′-GAGAACCAAGTAATGCGCCGGGCGGTATGAATAAACAAGG-3′ | |||
| Rr17BIP | 5′-AATTCGGTAAGGGCAAAGGACCACCGATTTGTCCACCAA-3′ | |||
| Rr17LoopF | 5′-F1-X-CCGCCAAGAAGTGTTCCTGTA-3′ | |||
| Rr17LoopB | 5′-Biotin-AGCTTGTTGGAGTAGGTGTAGGTG-3′ | |||
| Plasmodium spp. | Mitochondrial Cytochrome b (cytb) gene | PgMt19 [22] | PgMt19-F3 | 5′-TCGCTTCTAACGGTGAAC-3′ |
| PgMt19-B3 | 5′-AATTGATAGTATCAGCTATCCATAG-3′ | |||
| PgMt19-FIP | 5′-GGTGGAACACATTGTTTCATTTGATCTCATTCCAATGGAACCTTG-3′ | |||
| PgMt19-BIP | 5′-Biotin-GTTTGCTTCTAACATTCCACTTGCCCGTTTTGACCGGTCATT-3′ | |||
| PgMt19-LF | 5′-F4-X-CACTATACCTTACCAATCTATTTGAACTTG-3′ | |||
| PgMt19-LB | 5′-TGGACGTAACCTCCAGGC-3′ |
| Copy Number Per Reaction | 1,000,000 | 100,000 | 10,000 | 1000 | 100 | 10 | NTC | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Melting peak analysis result | Plasmodium gene | 5/5 (100%) | 5/5 (100%) | 5/5 (100%) | 5/5 (100%) | 3/5 (60%) | 1/5 (20%) | 0/5 (0%) |
| Rickettsia gene | 5/5 (100%) | 5/5 (100%) | 5/5 (100%) | 5/5 (100%) | 0/5 (0%) | 0/5 (0%) | 0/5 (0%) | |
| C-PAS result | Plasmodium gene | 5/5 (100%) | 5/5 (100%) | 5/5 (100%) | 5/5 (100%) | 3/5 (60%) | 1/5 (20%) | 0/5 (0%) |
| Rickettsia gene | 5/5 (100%) | 5/5 (100%) | 5/5 (100%) | 5/5 (100%) | 0/5 (0%) | 0/5 (0%) | 0/5 (0%) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Moonga, L.C.; Hayashida, K.; Kawai, N.; Nakao, R.; Sugimoto, C.; Namangala, B.; Yamagishi, J. Development of a Multiplex Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification (LAMP) Method for Simultaneous Detection of Spotted Fever Group Rickettsiae and Malaria Parasites by Dipstick DNA Chromatography. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 897. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10110897
Moonga LC, Hayashida K, Kawai N, Nakao R, Sugimoto C, Namangala B, Yamagishi J. Development of a Multiplex Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification (LAMP) Method for Simultaneous Detection of Spotted Fever Group Rickettsiae and Malaria Parasites by Dipstick DNA Chromatography. Diagnostics. 2020; 10(11):897. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10110897
Chicago/Turabian StyleMoonga, Lavel Chinyama, Kyoko Hayashida, Naoko Kawai, Ryo Nakao, Chihiro Sugimoto, Boniface Namangala, and Junya Yamagishi. 2020. "Development of a Multiplex Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification (LAMP) Method for Simultaneous Detection of Spotted Fever Group Rickettsiae and Malaria Parasites by Dipstick DNA Chromatography" Diagnostics 10, no. 11: 897. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10110897
APA StyleMoonga, L. C., Hayashida, K., Kawai, N., Nakao, R., Sugimoto, C., Namangala, B., & Yamagishi, J. (2020). Development of a Multiplex Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification (LAMP) Method for Simultaneous Detection of Spotted Fever Group Rickettsiae and Malaria Parasites by Dipstick DNA Chromatography. Diagnostics, 10(11), 897. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10110897