Cost Consequences for the NHS of Using a Two-Step Testing Method for the Detection of Clostridium difficile with a Point of Care, Polymerase Chain Reaction Test as the First Step
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
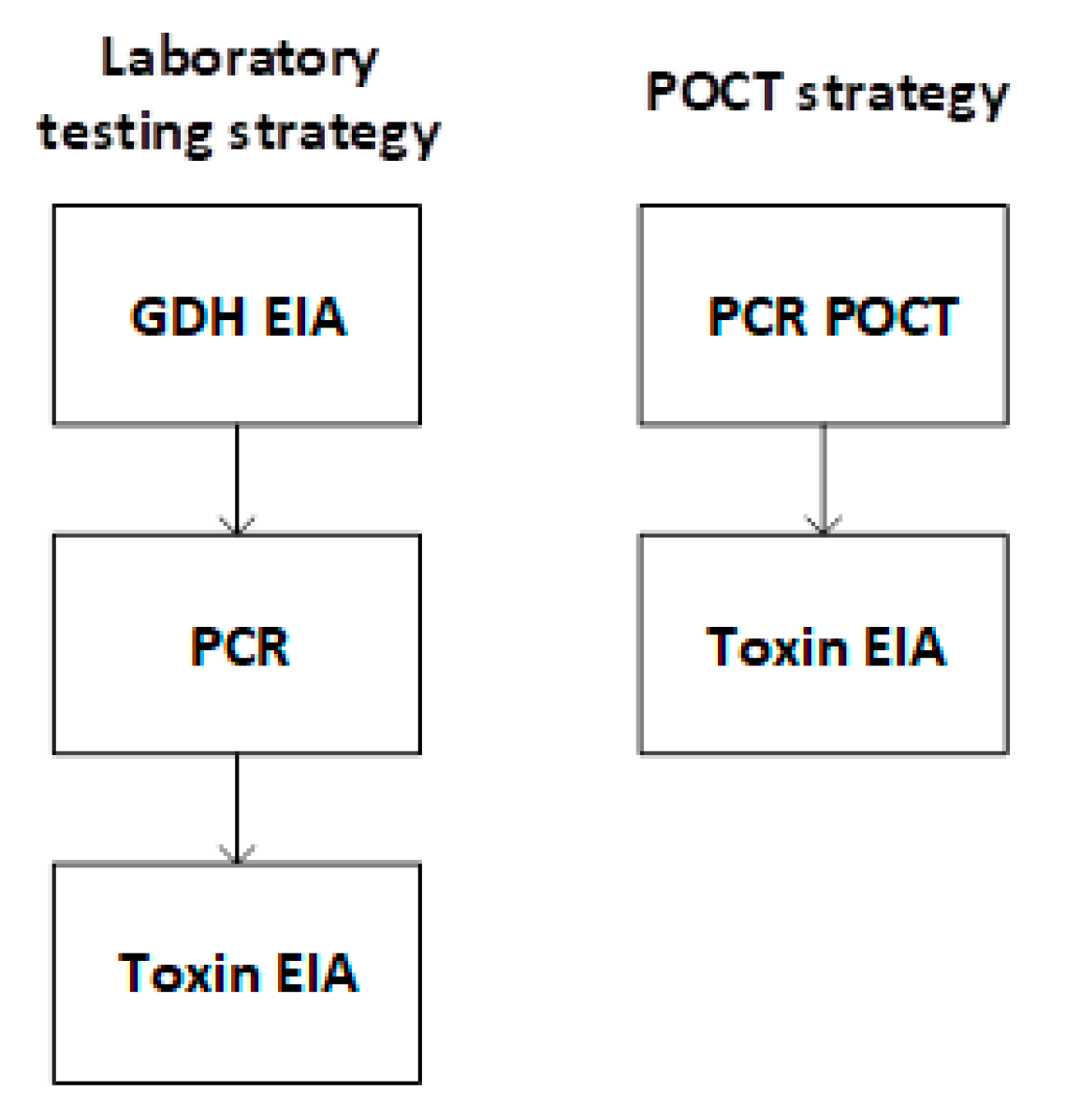
2.1. Diagnostic Strategies
2.2. Analysis
2.3. Model Parameters
2.4. Exploring Uncertainties in Model Outputs
3. Results
3.1. Systematic Search for Previous Health Economic Models
3.2. Accuracy of Test Strategies
3.3. Time Outcomes
3.4. Cost Outcomes
4. Discussion
Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- DH/HCAI/ Infectious Disease. Updated Guidance on the Diagnosis and Reporting of Clostridium Difficile 2012; Department of Health and Social Care: London, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Crobach, M.; Planche, T.; Eckert, C.; Barbut, F.; Terveer, E.M.; Dekkers, O.; Wilcox, M.; Kuijper, E.J. European Society of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases: Update of the diagnostic guidance document for Clostridium difficile infection. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2016, 22, S63–S81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Crobach, M.J.T.; Dekkers, O.M.; Wilcox, M.H.; Kuijper, E.J. European Society of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases (ESCMID): Data review and recommendations for diagnosing Clostridium difficile-infection (CDI). Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2009, 15, 1053–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nguyen, T.; Chidambara, V.A.; Andreasen, S.Z.; Golabi, M.; Huynh, V.N.; Linh, Q.T.; Bang, D.D.; Wolff, A. Point-of-care devices for pathogen detections: The three most important factors to realise towards commercialization. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2020, 131, 116004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewar, S.; Vass, D.; MacKenzie, F.; Parcell, B. Point-of-care testing by healthcare workers for detection of meticillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, Clostridioides difficile, and norovirus. J. Hosp. Infect. 2019, 103, 447–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- CADTH Database Search Filters. Available online: https://www.cadth.ca/resources/finding-evidence. (accessed on 22 October 2018).
- GenePOCTM. Available online: https://www.meridianbioscience.com/human-condition/gastrointestinal/c-difficile/revogene-c-difficile/?country=GB (accessed on 13 October 2020).
- Department of Health. NHS Reference Costs 2014–2015. Available online: https://www.gov.uk/government/publications/nhs-reference-costs-2014-to-2015 (accessed on 22 October 2018).
- Bank of England Inflation Calculator. Available online: https://www.bankofengland.co.uk/monetary-policy/inflation/inflation-calculator (accessed on 20 October 2018).
- National Services Scotland, NHS Scotland MRSA Screening Pathfinder Programme-Final Report Volume 2: An Assessment of the Economics, Implementation and Modelling of Universal Screening; Health Protection Scotland: Glasgow, UK, 2011.
- TreeAge Pro 2016. TreeAge Software, Williamstown, MA, USA. Available online: http://www.treeage.com (accessed on 11 January 2016).
- Freeman, K.; Mistry, H.; Tsertsvadze, A.; Royle, P.; McCarthy, N.; Philips, S.T.; Manuel, R.; Mason, J. Multiplex tests to identify gastrointestinal bacteria, viruses and parasites in people with suspected infectious gastroenteritis: A systematic review and economic analysis. Heal. Technol. Assess. 2017, 21, 1–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Laboratory Testing Strategy (Days) | POCT Strategy (Days) | Incremental Time (Laboratory Testing Strategy—POCT Strategy) (Days) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Patients Starting out in an Isolation Bed (n = 511) | |||
| Time in isolation bed | 1.33 | 0.80 | 0.53 |
| Total length of stay | 1.37 | 1.16 | 0.21 |
| Patients initially admitted to a general bed (n = 489) | |||
| Time in isolation bed | 0.62 | 0.64 | −0.02 |
| Total length of stay | 1.32 | 1.11 | 0.21 |
| Cost of… | Laboratory Testing Strategy | POCT Strategy | Incremental Cost(Laboratory Testing Strategy—POCT Strategy) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Patients starting out in an isolation bed (n = 511) | |||
| Total bed days (isolation + general) | £909,845.72 | £734,674.92 | £175,170.80 |
| Diagnostic testing costs | £6372.17 | £11,589.48 | −£5217.31 |
| Treatment | £5329.73 | £5610.78 | −£281.05 |
| Total costs | £919,728.46 | £751,864.96 | £167,863.50 |
| Patients starting out in a general bed (n = 489) | |||
| Total bed days (isolation + general) | £804,004.02 | £690,375.09 | £113,628.93 |
| Diagnostic testing costs | £15,393.72 | £11,085.63 | £4308.09 |
| Treatment | £5100.27 | £5369.22 | −£268.95 |
| Total costs | £825,236.40 | £709,817.73 | £115418.67 |
| Total cost for cohort | £1,744,964.86 | £1,461,682.90 | £283,282.17 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jones, W.S.; Rice, S.; Power, H.M.; Maniatopoulos, G.; Suklan, J.; Beyer, F.; Wilcox, M.H.; Permain, M.; Simpson, A.J.; Price, D.A.; et al. Cost Consequences for the NHS of Using a Two-Step Testing Method for the Detection of Clostridium difficile with a Point of Care, Polymerase Chain Reaction Test as the First Step. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 819. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10100819
Jones WS, Rice S, Power HM, Maniatopoulos G, Suklan J, Beyer F, Wilcox MH, Permain M, Simpson AJ, Price DA, et al. Cost Consequences for the NHS of Using a Two-Step Testing Method for the Detection of Clostridium difficile with a Point of Care, Polymerase Chain Reaction Test as the First Step. Diagnostics. 2020; 10(10):819. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10100819
Chicago/Turabian StyleJones, William S., Stephen Rice, H. Michael Power, Gregory Maniatopoulos, Jana Suklan, Fiona Beyer, Mark H. Wilcox, Michelle Permain, A. John Simpson, D. Ashley Price, and et al. 2020. "Cost Consequences for the NHS of Using a Two-Step Testing Method for the Detection of Clostridium difficile with a Point of Care, Polymerase Chain Reaction Test as the First Step" Diagnostics 10, no. 10: 819. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10100819
APA StyleJones, W. S., Rice, S., Power, H. M., Maniatopoulos, G., Suklan, J., Beyer, F., Wilcox, M. H., Permain, M., Simpson, A. J., Price, D. A., & Allen, A. J. (2020). Cost Consequences for the NHS of Using a Two-Step Testing Method for the Detection of Clostridium difficile with a Point of Care, Polymerase Chain Reaction Test as the First Step. Diagnostics, 10(10), 819. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10100819





