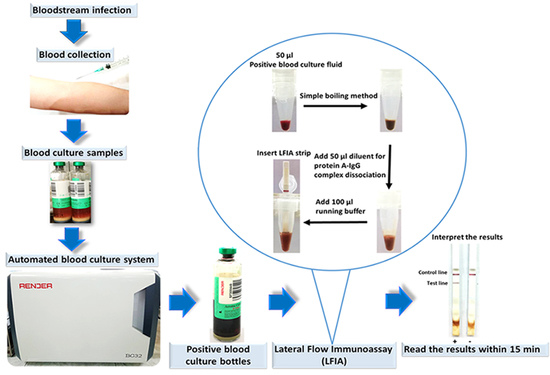
Development of a Prototype Lateral Flow Immunoassay for Rapid Detection of Staphylococcal Protein A in Positive Blood Culture Samples
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Strains
2.2. Establishment and Assembly of the LFIA
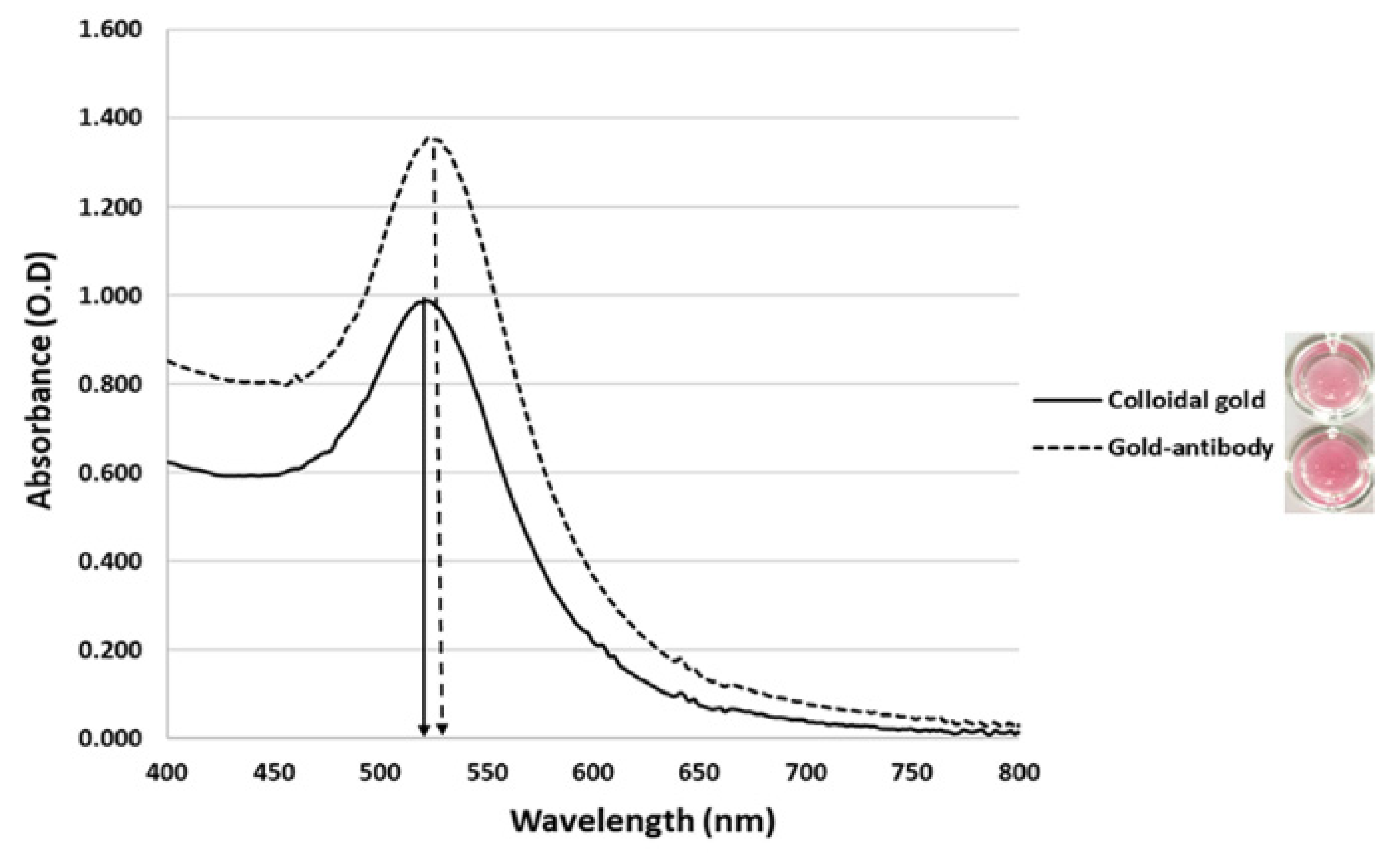
2.2.1. Preparation of Gold Nanoparticles
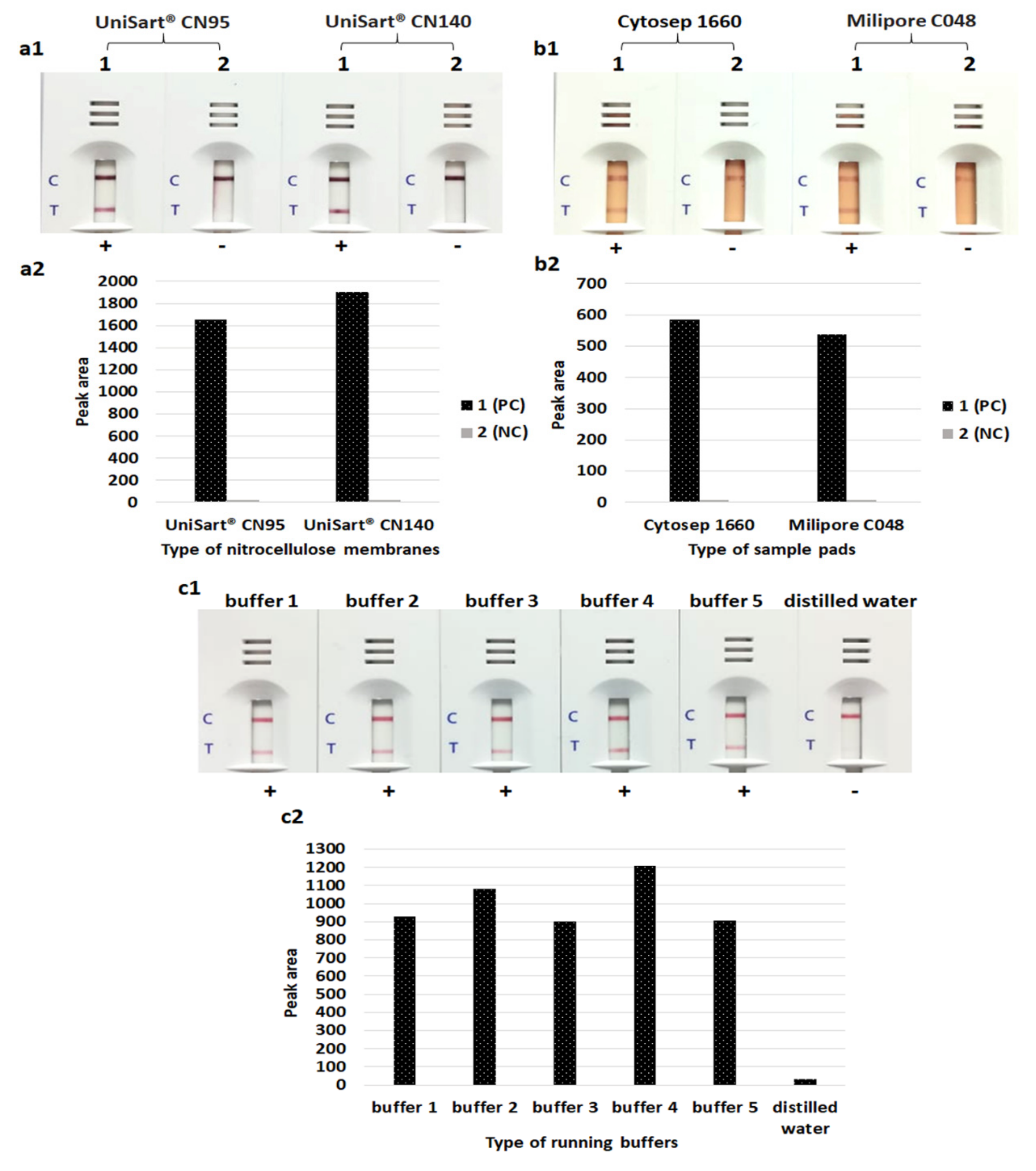
2.2.2. Optimization of Gold Nanoparticle Conjugation
2.2.3. Preparation of Gold Nanoparticle Conjugate Antibody
2.2.4. Preparation of LFIA Strips
2.3. PCR-Based Identification of S. aureus by Amplification of the nuc Gene
2.4. Detection Limit of the LFIA
2.5. Detection of S. aureus Directly from Bacterial Colonies and Spiked Blood Culture Samples
2.5.1. Testing with Bacterial Colonies
2.5.2. Testing with Spiked Blood Culture Samples
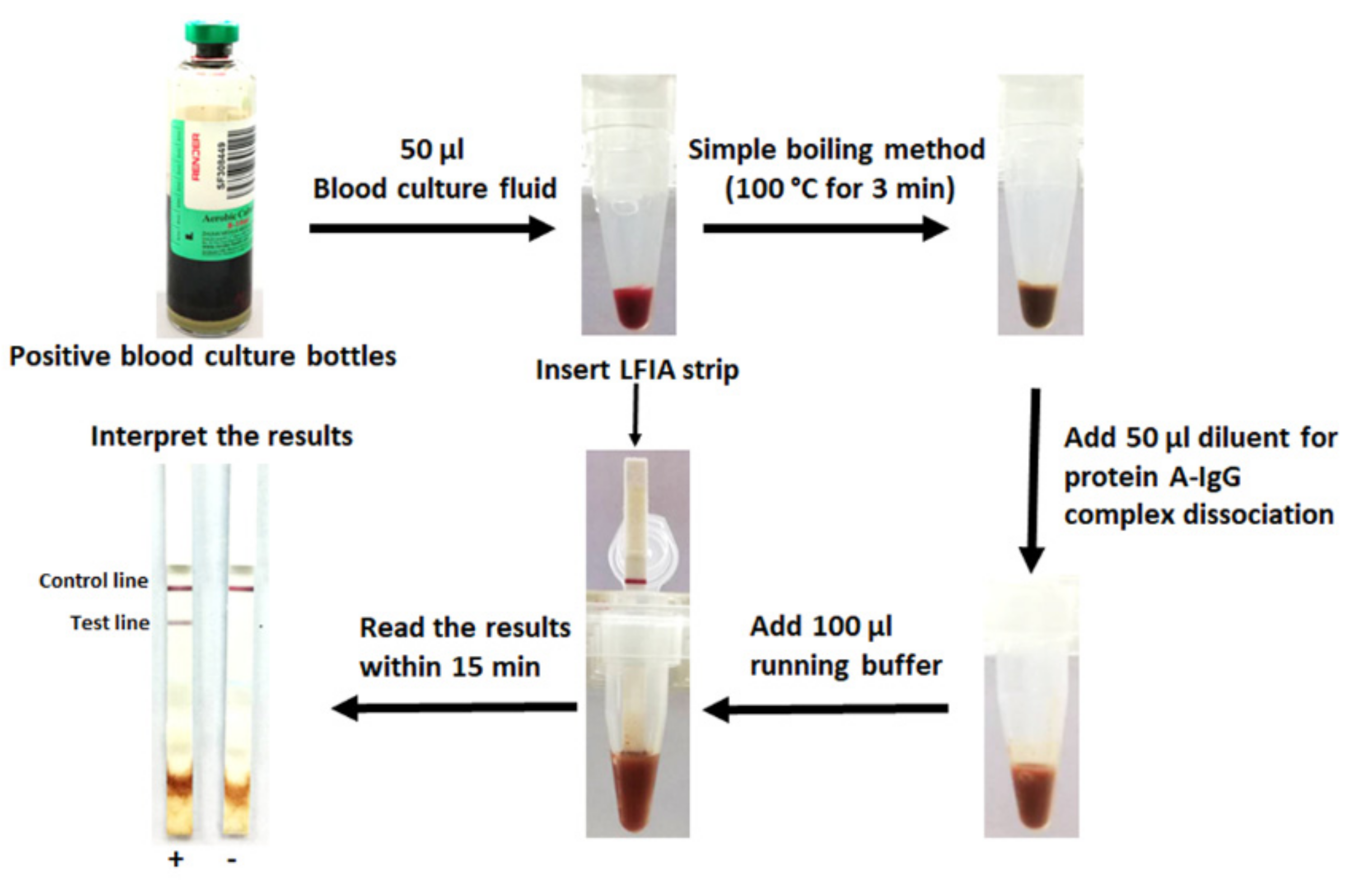
2.6. Evaluation of the LFIA for Direct Detection in Positive Blood Culture Bottles from the Hospital
2.7. LFIA Imaging and Quantitative Analysis of Signal
2.8. Stability of the LFIA Strip
3. Results
3.1. Gold Nanoparticle Preparation and Optimization of the LFIA
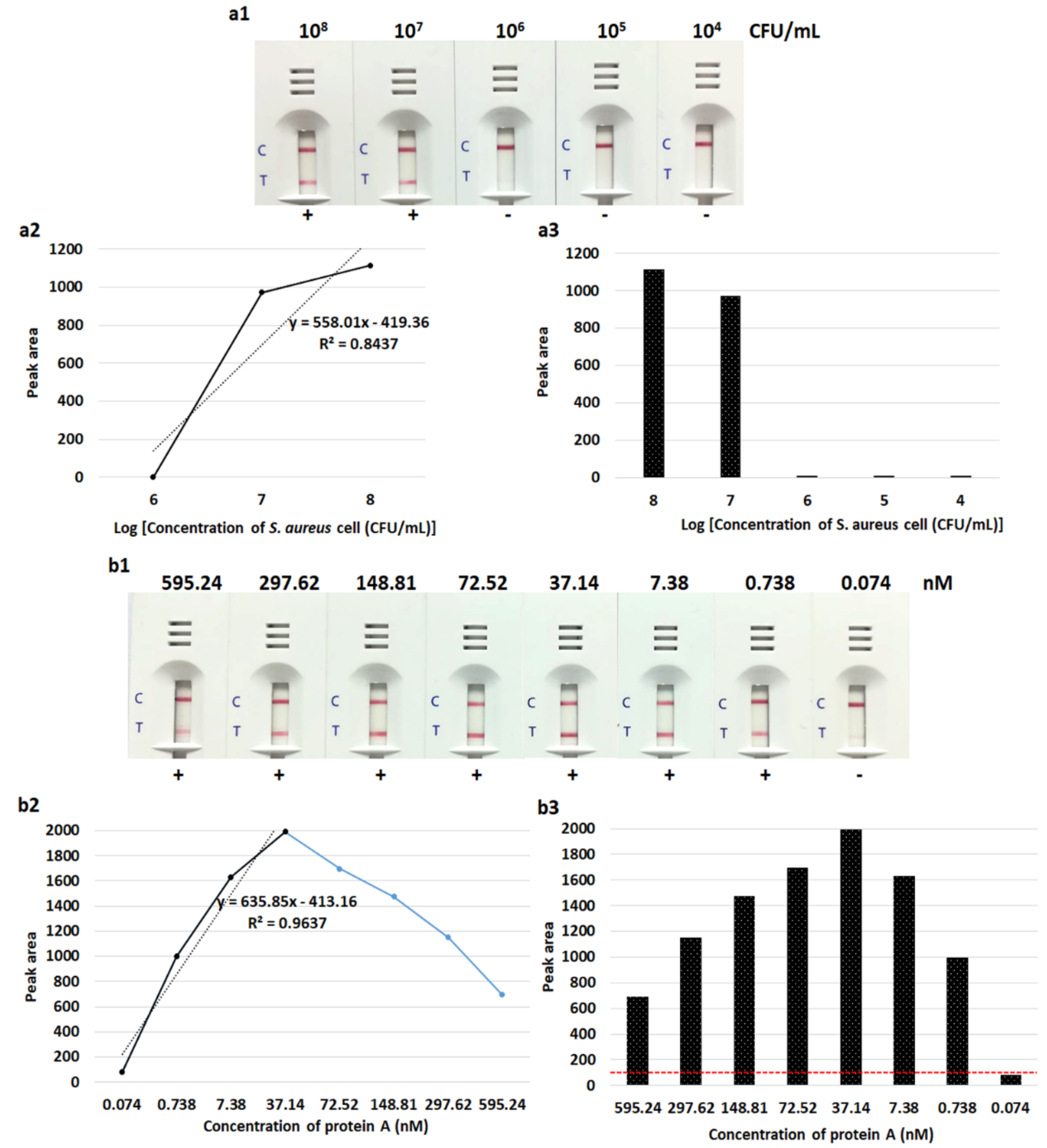
3.2. Detection Limit of the LFIA Strip
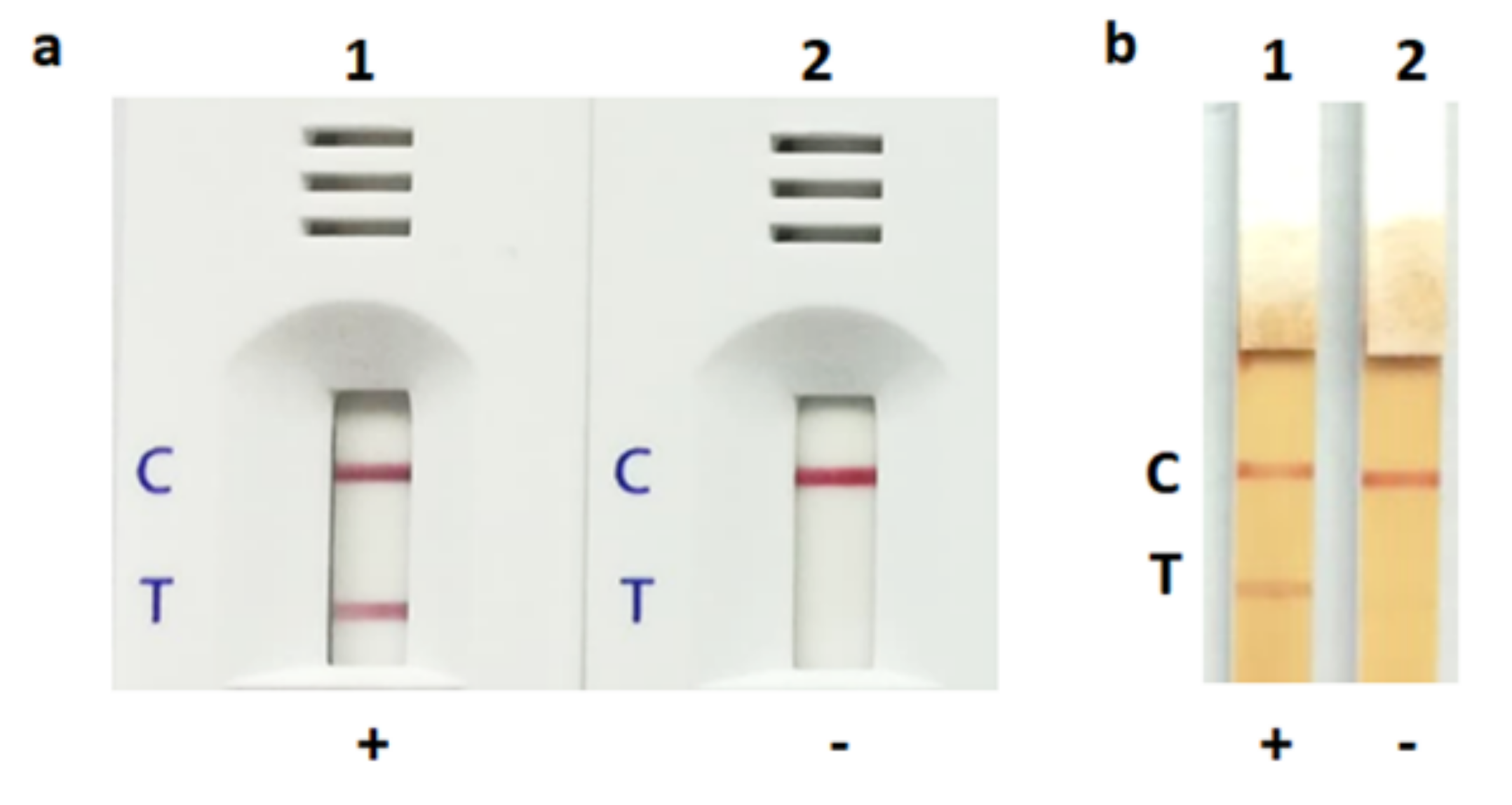
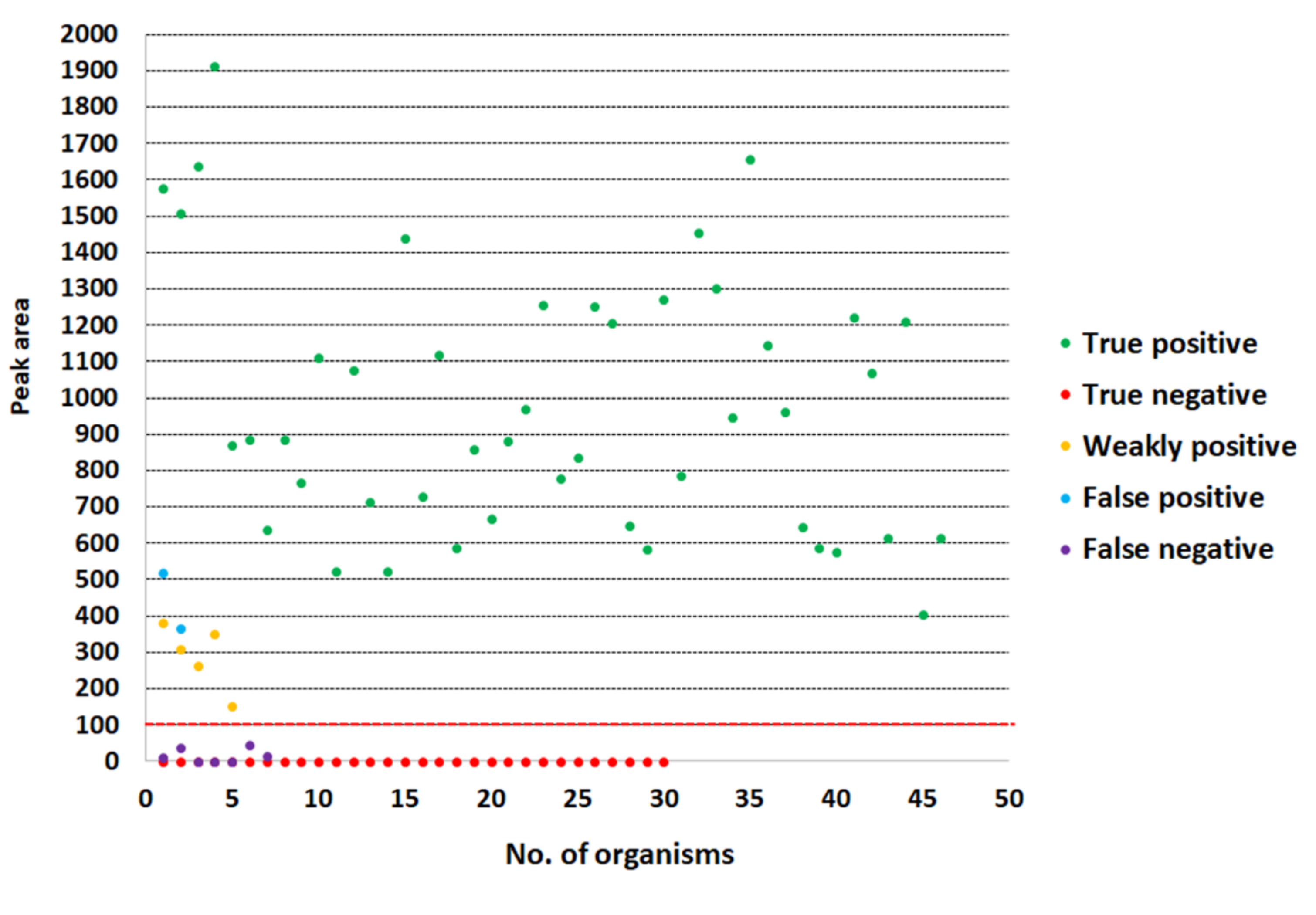
3.3. Detection of S. aureus by LFIA Using Bacterial Colonies and Spiked Blood Culture Samples
3.4. Evaluation of the LFIA for Direct Detection in Positive Blood Culture Bottles from Hospital
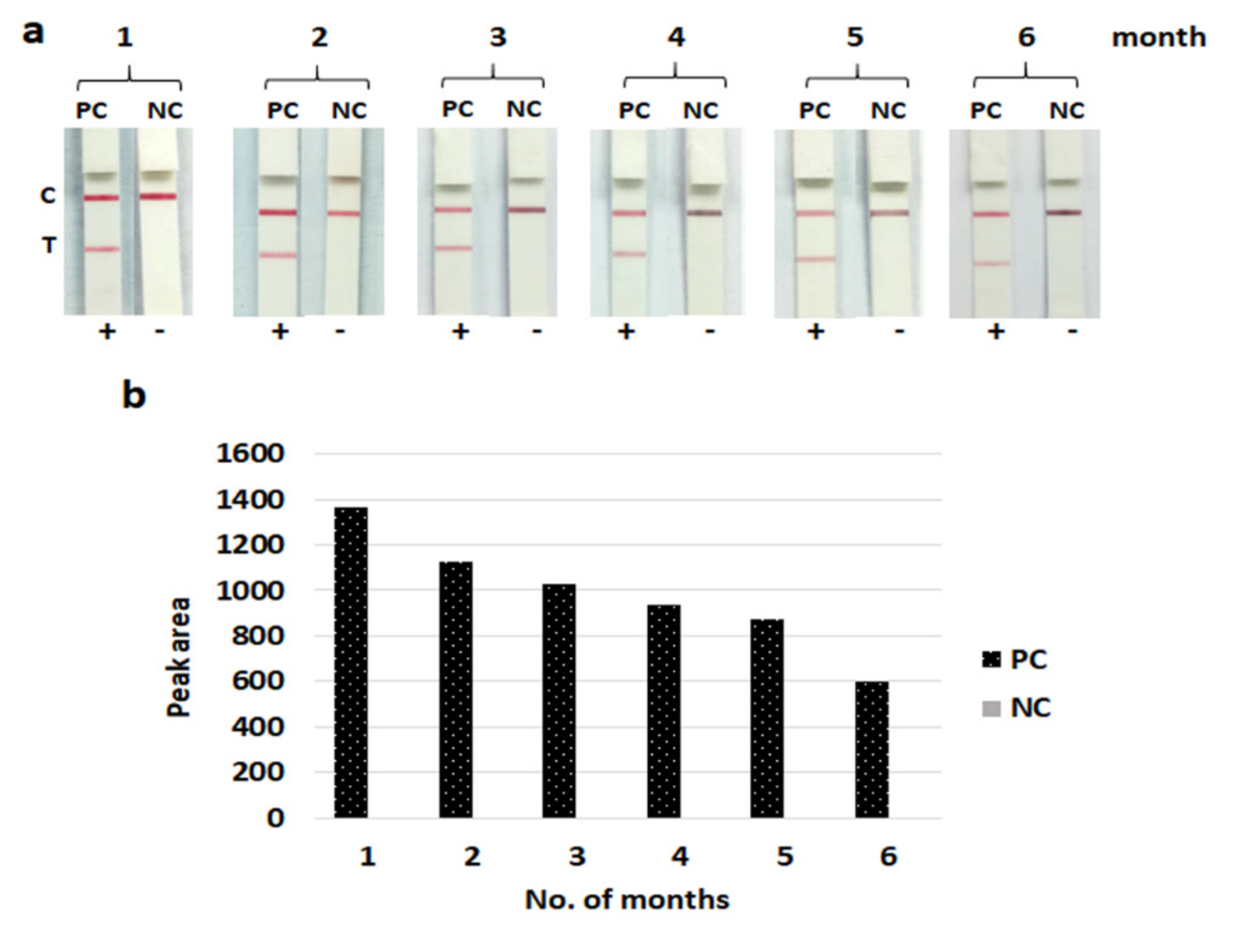
3.5. Stability of the LFIA Strip
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Opota, O.; Croxatto, A.; Prod’Hom, G.; Greub, G. Blood culture-based diagnosis of bacteraemia: State of the art. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2015, 21, 313–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, S.Y.C.; Davis, J.S.; Eichenberger, E.; Holland, T.L.; Fowler, V.G. Staphylococcus aureus Infections: Epidemiology, Pathophysiology, Clinical Manifestations, and Management. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2015, 28, 603–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulane, A.; Hoosen, A. Use of matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionisation-time of flight mass spectrometry analyser in a diagnostic microbiology laboratory in a developing country. Afr. J. Lab. Med. 2017, 6, 598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gherardi, G.; Angeletti, S.; Panitti, M.; Pompilio, A.; Di Bonaventura, G.; Crea, F.; Avola, A.; Fico, L.; Palazzo, C.; Sapia, G.F.; et al. Comparative evaluation of the Vitek-2 Compact and Phoenix systems for rapid identification and antibiotic susceptibility testing directly from blood cultures of Gram-negative and Gram-positive isolates. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2012, 72, 20–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- La Scola, B.; Raoult, D. Direct Identification of Bacteria in Positive Blood Culture Bottles by Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption Ionisation Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e8041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocchetti, T.T.; Martins, K.B.; Martins, P.Y.F.; Oliveira, R.A.; Mondelli, A.L.; Fortaleza, C.M.C.B.; Cunha, M.D.L.R.D. Detection of the mecA gene and identification of Staphylococcus directly from blood culture bottles by multiplex polymerase chain reaction. Braz. J. Infect. Dis. 2018, 22, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Won, H.; Rothman, R.; Ramachandran, P.; Hsieh, Y.-H.; Kecojevic, A.; Carroll, K.C.; Aird, D.; Gaydos, C.; Yang, S. Rapid Identification of Bacterial Pathogens in Positive Blood Culture Bottles by Use of a Broad-Based PCR Assay Coupled with High-Resolution Melt Analysis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2010, 48, 3410–3413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andriesse, G.I.; Elberts, S.; Vrolijk, A.; Verhulst, C.; Kluytmans, J.A.J.W. Evaluation of a fourth-generation latex agglutination test for the identification of Staphylococcus aureus. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2010, 30, 259–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsson, M.C.; Karlsson, E.; Woksepp, H.; Frölander, K.; Mårtensson, A.; Rashed, F.; Annika, W.; Schön, T.; Serrander, L. Rapid identification of pneumococci, enterococci, beta-haemolytic streptococci and S. aureus from positive blood cultures enabling early reports. BMC Infect. Dis. 2014, 14, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Halloran, D.P.; Wynne, K.; Geoghegan, J.A. Protein A is Released into the Staphylococcus aureus Culture Supernatant with an Unprocessed Sorting Signal. Infect. Immun. 2015, 83, 1598–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakeri, F.; Shojai, A.; Golalipour, M.; Alang, S.R.; Vaez, H.; Ghaemi, E.A. SpaDiversity among MRSA and MSSA Strains of Staphylococcus aureus in North of Iran. Int. J. Microbiol. 2010, 2010, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bosi, E.; Monk, J.; Aziz, R.K.; Fondi, M.; Nizet, V.; Palsson, B.Ø. Comparative genome-scale modelling of Staphylococcus aureus strains identifies strain-specific metabolic capabilities linked to pathogenicity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, E3801–E3809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stieber, B.; Monecke, S.; Müller, E.; Büchler, J.; Ehricht, R. Direct, Specific and Rapid Detection of Staphylococcal Proteins and Exotoxins Using a Multiplex Antibody Microarray. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0143246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marquez, S.; Morales-Narváez, E. Nanoplasmonics in Paper-Based Analytical Devices. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2019, 7, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yetisen, A.K.; Akram, M.S.; Lowe, C. Paper-based microfluidic point-of-care diagnostic devices. Lab Chip 2013, 13, 2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, T.-T.; Huang, T.-H.; Chen, C.-A.; Ho, N.Y.-J.; Chou, Y.-J.; Chen, C.-F. Development a stacking pad design for enhancing the sensitivity of lateral flow immunoassay. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 17319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koczula, K.M.; Gallotta, A. Lateral flow assays. Essays Biochem. 2016, 60, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Wang, K.; Yang, J.; Xu, H.; Cao, B.; Wo, Y.; Jin, Q.-H.; Cui, D. Algorithms for immunochromatographic assay: Review and impact on future application. Analyst 2019, 144, 5659–5676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.-H. Gold nanoparticle-based immunochromatographic test for identification of Staphylococcus aureus from clinical specimens. Clin. Chim. Acta 2006, 373, 139–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.-H.; Wei, H.-C.; Lee, Y.-C. One-step immunochromatographic assay for the detection of Staphylococcus aureus. Food Control. 2007, 18, 893–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, H.D.; A Mirkin, C. The bio-barcode assay for the detection of protein and nucleic acid targets using DTT-induced ligand exchange. Nat. Protoc. 2006, 1, 324–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kestrel BioSciences Thailand Co. Ltd. Lateral-Flow Optimization: Materials, Methods, Protocols. Available online: http://kestrelthailand.com (accessed on 21 July 2019).
- Shittu, A.; Lin, J.; Morrison, D.; Kolawole, D. Isolation and molecular characterization of multi resistant Staphylococcus sciuri and Staphylococcus haemolyticus associated with skin and soft-tissue infections. J. Med. Microbiol. 2004, 53, 51–55. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dortet, L.; Tande, D.; De Briel, D.; Bernabeu, S.; Lasserre, C.; Gregorowicz, G.; Jousset, A.B.; Naas, T. MALDI-TOF for the rapid detection of carbapenemase-producing Enterobacteriaceae: Comparison of the commercialized MBT STAR®-Carba IVD Kit with two in-house MALDI-TOF techniques and the RAPIDEC® CARBA NP. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2018, 73, 2352–2359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landis, J.R.; Koch, G.G. The Measurement of Observer Agreement for Categorical Data. Biomatrics 1977, 33, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yrad, F.; Castañares, J.M.; Alocilja, E.C. Visual Detection of Dengue-1 RNA Using Gold Nanoparticle-Based Lateral Flow Biosensor. Diagnostics 2019, 9, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilecky, M.; Schildberger, A.; Knabl, L.; Orth-Höller, D.; Weber, V. Influence of antibiotic treatment on the detection of S. aureus in whole blood following pathogen enrichment. BMC Microbiol. 2019, 19, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balachandran, M.; Bemis, D.A.; Kania, S.A. Expression and function of protein A in Staphylococcus pseudintermedius. Virulence 2018, 9, 390–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.H.; Chang, T.C.; Kao, E.-F.; Chou, C. Detection of Protein A Produced by Staphylococcus aureus with a Fiber-optic-based Biosensor. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 1996, 60, 1571–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Movitz, J. Formation of Extracellular Protein A by Staphylococcus aureus. JBIC J. Boil. Inorg. Chem. 1976, 68, 291–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varley, C. Development of methods for the detection Staphylococcal protein A in ICU patient urine. Master’s Thesis, Lancaster University, Lancaster, UK, 2016. Available online: https://eprints.lancs.ac.uk/id/eprint/81893/ (accessed on 20 May 2020).
- Nilsson, R.; Davidsson, B. Quantitation of protein A in human plasma is possible after heat inactivation of the samples. J. Immunol. Methods 1990, 135, 77–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arakawa, T.; Philo, J.S.; Tsumoto, K.; Yumioka, R.; Ejima, D. Elution of antibodies from a protein-A column by aqueous arginine solutions. Protein Expr. Purif. 2004, 36, 244–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ejima, D.; Yumioka, R.; Tsumoto, K.; Arakawa, T. Effective elution of antibodies by arginine and arginine derivatives in affinity column chromatography. Anal. Biochem. 2005, 345, 250–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shukla, D.; Zamolo, L.; Cavallotti, C.; Trout, B.L. Understanding the Role of Arginine as an Eluent in Affinity Chromatography via Molecular Computations. J. Phys. Chem. B 2011, 115, 2645–2654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, T.C.; Huang, S.H. An Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay for the Rapid Detection of Staphylococcus aureus in Processed Foods. J. Food Prot. 1994, 57, 184–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tate, J.; Ward, G. Interferences in Immunoassay. Clin. Biochem. Rev. 2004, 25, 105–120. [Google Scholar]
- Templier, V.; Livache, T.; Boisset, S.; Maurin, M.; Slimani, S.; Mathey, R.; Roupioz, Y. Biochips for Direct Detection and Identification of Bacteria in Blood Culture-Like Conditions. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 9457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peeters, M.; Chung, P.; Lin, H.; Mortelmans, K.; Phe, C.; San, C.; Kuijpers, L.M.F.; Teav, S.; Phe, T.; Jacobs, J. Diagnostic accuracy of the InBiOS AMD rapid diagnostic test for the detection of Burkholderia pseudomallei antigen in grown blood culture broth. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2018, 37, 1169–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rey, E.G.; O’Dell, D.; Mehta, S.; Erickson, D. Mitigating the Hook Effect in Lateral Flow Sandwich Immunoassays Using Real-Time Reaction Kinetics. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 5095–5100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiriyachaiporn, S.; Howarth, P.; Bruce, K.D.; Dailey, L.A. Evaluation of a rapid lateral flow immunoassay for Staphylococcus aureus detection in respiratory samples. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2013, 75, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, T.V.; Do, B.N.; Nguyen, T.P.T.; Tran, T.T.; Tran, S.C.; Nguyen, B.V.; Nguyen, C.V.; Le, H.Q. Development of an IgY-based lateral flow immunoassay for detection of fumonisin B in maize. F1000Research 2019, 8, 1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’farrell, B. Evolution in Lateral Flow–Based Immunoassay Systems. Lateral Flow Immunoass. 2008, 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; McMillan, D.; Macdonald, J. Enhancing the signal of lateral flow immunoassays by using different developing methods. Sens. Mater. 2015, 27, 549–561. [Google Scholar]
- Anfossi, L.; Di Nardo, F.; Giovannoli, C.; Passini, C.; Baggiani, C. Increased sensitivity of lateral flow immunoassay for ochratoxin A through silver enhancement. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2013, 405, 9859–9867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saisin, L.; Amarit, R.; Somboonkaew, A.; Gajanandana, O.; Himananto, O.; Sutapun, B. Significant Sensitivity Improvement for Camera-Based Lateral Flow Immunoassay Readers. Sensors 2018, 18, 4026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urusov, A.Е.; Zherdev, A.V.; Dzantiev, B.B. Towards Lateral Flow Quantitative Assays: Detection Approaches. Biosensors 2019, 9, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhiman, N.; Trienski, T.L.; DiPersio, L.P.; DiPersio, J.R. Evaluation of the BinaxNOW Staphylococcus aureus Test for Rapid Identification of Gram-Positive Cocci from VersaTREK Blood Culture Bottles. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2013, 51, 2939–2942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heraud, S.; Freydière, A.-M.; Doléans-Jordheim, A.; Bes, M.; Tristan, A.; Vandenesch, F.; Laurent, F.; Dauwalder, O. Direct Identification of Staphylococcus aureus and Determination of Methicillin Susceptibility From Positive Blood-Culture Bottles in a Bact/ALERT System Using Binax Now S. aureus and PBP2a Tests. Ann. Lab. Med. 2015, 35, 454–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, H.; Tong, L.; Zhang, W.; Fu, Y.; Li, X. Combined use of the BinaxNOW Staphylococcus aureus test with the Clearview PBP2a assay for the early detection of methicillin-resistant S. aureus from positive blood cultures. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2014, 78, 226–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, T.C.; Huang, S.H. Evaluation of Coagulase Activity and Protein A Production for the Identification of Staphylococcus aureus. J. Food Prot. 1995, 58, 858–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneewind, O.; Missiakas, D. Sortases, Surface proteins, and their roles in Staphylococcus aureus disease and vaccine development. Microbiol Spectr. 2019, 7, 10. [Google Scholar]
| Organisms (n) | No. Isolates Positive by PCR | No. Isolates Tested by LFIA in | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bacterial Colonies | Spiked Blood Cultures | ||||||
| Positive | Weakly Positive | Negative | Positive | Weakly Positive | Negative | ||
| Gram-positive bacteria (76) | |||||||
| S. aureus (58) | |||||||
| S. aureus (54) | 54 | 47 | 4 | 3 | 42 | 5 | 7 |
| S. aureus (NCTC10442) (1) | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| S. aureus SCCmec II (1) | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| S. aureus SCCmec III (2) | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 |
| Coagulase-negative staphylococci (14) | |||||||
| S. sciuri (4) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 4 |
| S. haemolyticus (2) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 2 |
| S. saprophyticus (2) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 0 |
| S. caprae (1) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| S. chromogenes (1) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| S. cohnii spp. urealyticus (1) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| S. hyicus (1) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| S. vitulinus (1) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| S. xylosus (1) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| Aerococcus viridans (1) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| Enterococcus spp. (3) | |||||||
| E. faecalis (2) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 2 |
| E. faecium (1) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| Gram-negative bacteria (12) | |||||||
| A. baumannii (4) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 4 |
| P. aeruginosa (3) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 3 |
| Enterobacter spp. (1) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| E. coli ATCC 25922 (1) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| E. coli (1) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| K. pneumoniae ATCC BAA-1705 (1) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| K. pneumoniae (1) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| Yeast (2) | |||||||
| C. albicans (1) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| C. tropicalis (1) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| Number of Samples | Routine Methods a | LFIA for S. aureus |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Staphylococcus aureus | + |
| 2 | Staphylococcus aureus | + |
| 3 | Staphylococcus aureus | + |
| 4 | Staphylococcus aureus | + |
| 5 | Staphylococcus aureus | + |
| 6 | Staphylococcus aureus | + |
| 7 | Staphylococcus aureus | + |
| 8 | Staphylococcus aureus | - |
| 9 | Micrococcus spp. | - |
| 10 | Micrococcus spp. | - |
| 11 | Staphylococcus epidermidis | - |
| 12 | Aerococcus viridans | - |
| 13 | Bacillus spp. | - |
| 14 | Corynebacterium spp. | - |
| 15 | Escherichia coli | - |
| 16 | Klebsiella pneumoniae | - |
| 17 | Salmonella spp. | - |
| 18 | Acinetobacter baumannii | - |
| 19 | Pseudomonas aeruginosa | - |
| 20 | Cryptococcus neoformans | - |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Srisrattakarn, A.; Tippayawat, P.; Chanawong, A.; Tavichakorntrakool, R.; Daduang, J.; Wonglakorn, L.; Lulitanond, A. Development of a Prototype Lateral Flow Immunoassay for Rapid Detection of Staphylococcal Protein A in Positive Blood Culture Samples. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 794. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10100794
Srisrattakarn A, Tippayawat P, Chanawong A, Tavichakorntrakool R, Daduang J, Wonglakorn L, Lulitanond A. Development of a Prototype Lateral Flow Immunoassay for Rapid Detection of Staphylococcal Protein A in Positive Blood Culture Samples. Diagnostics. 2020; 10(10):794. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10100794
Chicago/Turabian StyleSrisrattakarn, Arpasiri, Patcharaporn Tippayawat, Aroonwadee Chanawong, Ratree Tavichakorntrakool, Jureerut Daduang, Lumyai Wonglakorn, and Aroonlug Lulitanond. 2020. "Development of a Prototype Lateral Flow Immunoassay for Rapid Detection of Staphylococcal Protein A in Positive Blood Culture Samples" Diagnostics 10, no. 10: 794. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10100794
APA StyleSrisrattakarn, A., Tippayawat, P., Chanawong, A., Tavichakorntrakool, R., Daduang, J., Wonglakorn, L., & Lulitanond, A. (2020). Development of a Prototype Lateral Flow Immunoassay for Rapid Detection of Staphylococcal Protein A in Positive Blood Culture Samples. Diagnostics, 10(10), 794. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10100794