Risk Factors for Endoscopic Gastric Mucosal Lesions: Analysis of Lifestyle, Dietary, and Clinical Determinants in 361 Patients
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Method
2.1. Study Design and Participants
2.2. Clinical Data Collection
2.3. Laboratory Assessments
2.4. Dietary Assessment
2.5. Endoscopic Assessment
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Participant Characteristics
| Endoscopic Severity | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Characteristic | All Patients (n = 361) 1 | Normal n = 35 1 | Edema/Erythema n = 163 1 | Erosions n = 87 1 | Ulcer/Bleeding n = 76 1 | p Value 2 |
| Age, years | 65.0 (55.0, 73.0) | 64.0 (53.0, 77.0) | 64.0 (53.0, 70.0) | 66.0 (57.0, 72.0) | 70.0 (58.0, 77.5) | 0.015 |
| Sex | 0.242 | |||||
| Female | 193 (53) | 22 (63) | 91 (56) | 39 (45) | 41 (54) | |
| Male | 168 (47) | 13 (37) | 72 (44) | 48 (55) | 35 (46) | |
| NSAIDs use | 59 (16) | 4 (11) | 21 (13) | 19 (22) | 15 (20) | 0.207 |
| PPI | 194 (54) | 17 (49) | 91 (56) | 40 (46) | 46 (61) | 0.245 |
| H. pylori infection | 0.198 | |||||
| Negative | 247 (68) | 19 (54) | 118 (72) | 60 (69) | 50 (66) | |
| Positive | 114 (32) | 16 (46) | 45 (28) | 27 (31) | 26 (34) | |
| Smoking status | 0.097 | |||||
| Never smoker | 225 (62) | 29 (83) | 101 (62) | 44 (51) | 51 (67) | |
| Former smoker > 10 y | 45 (12) | 5 (14) | 19 (12) | 13 (15) | 8 (11) | |
| Former smoker < 10 y | 36 (10) | 0 (0) | 18 (11) | 12 (14) | 6 (8) | |
| Current smoker > 10 y | 49 (14) | 1 (3) | 21 (13) | 17 (20) | 10 (13) | |
| Current smoker < 10 y | 6 (2) | 0 (0) | 4 (2) | 1 (1) | 1 (1) | |
| Alcohol consumption, units/week | 0.0 (0.0, 2.0) | 0.0 (0.0, 1.0) | 0.0 (0.0, 4.0) | 0.0 (0.0, 4.0) | 0.0 (0.0, 2.0) | 0.389 |
| Hemoglobin, g/dL | 12.2 (2.7) | 10.6 (2.8) | 12.5 (2.5) | 12.6 (2.8) | 11.7 (2.9) | <0.001 |
| Mean corpuscular volume, fL | 87 (9) | 89 (11) | 86 (10) | 87 (7) | 87 (10) | 0.555 |
| Pro-inflammatory diet score | 11.7 (8.4, 15.1) | 13.0 (9.4, 14.3) | 11.7 (8.2, 15.3) | 12.2 (7.4, 16.3) | 11.0 (8.3, 13.9) | 0.559 |
| Protective diet score | 26.2 (20.8, 31.0) | 26.2 (20.8, 31.5) | 25.6 (20.8, 31.0) | 26.8 (20.8, 31.0) | 25.6 (20.8, 31.5) | 0.996 |
3.2. Smoking as an Independent Risk Factor
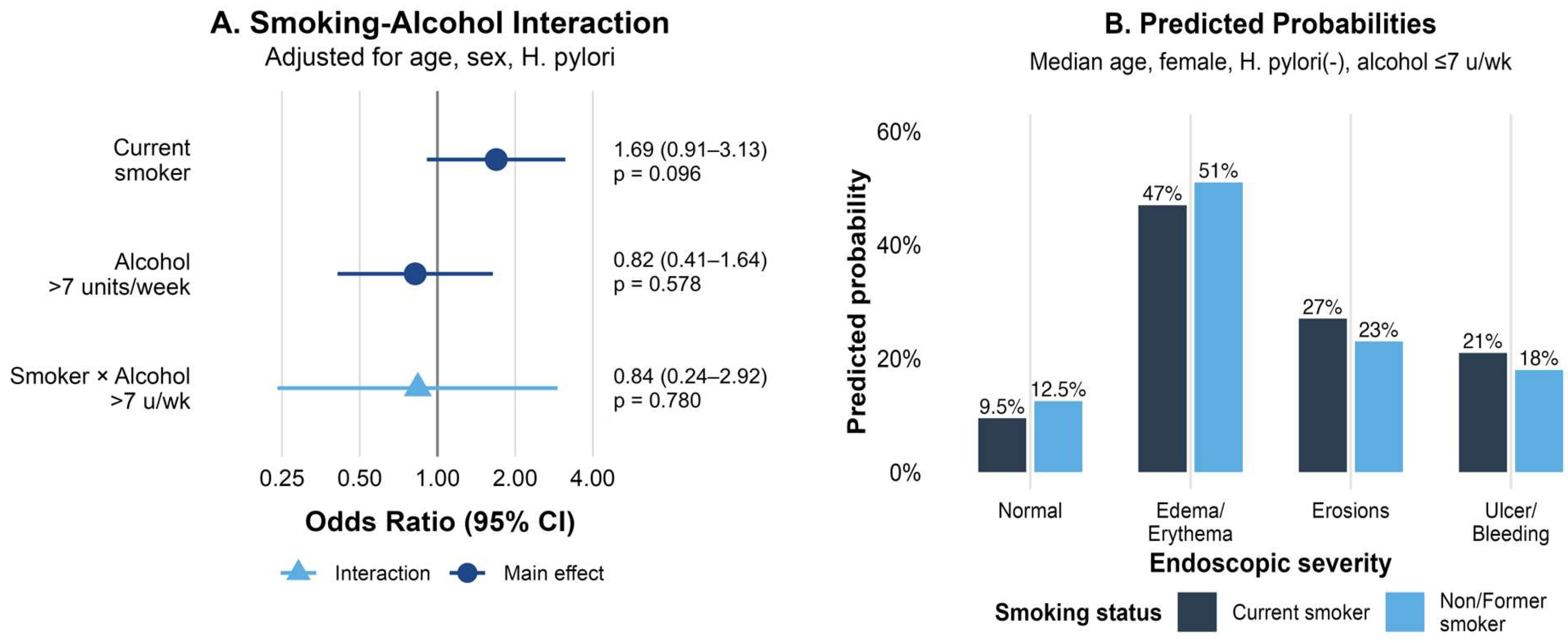
3.3. Interaction Between Smoking and Alcohol Consumption
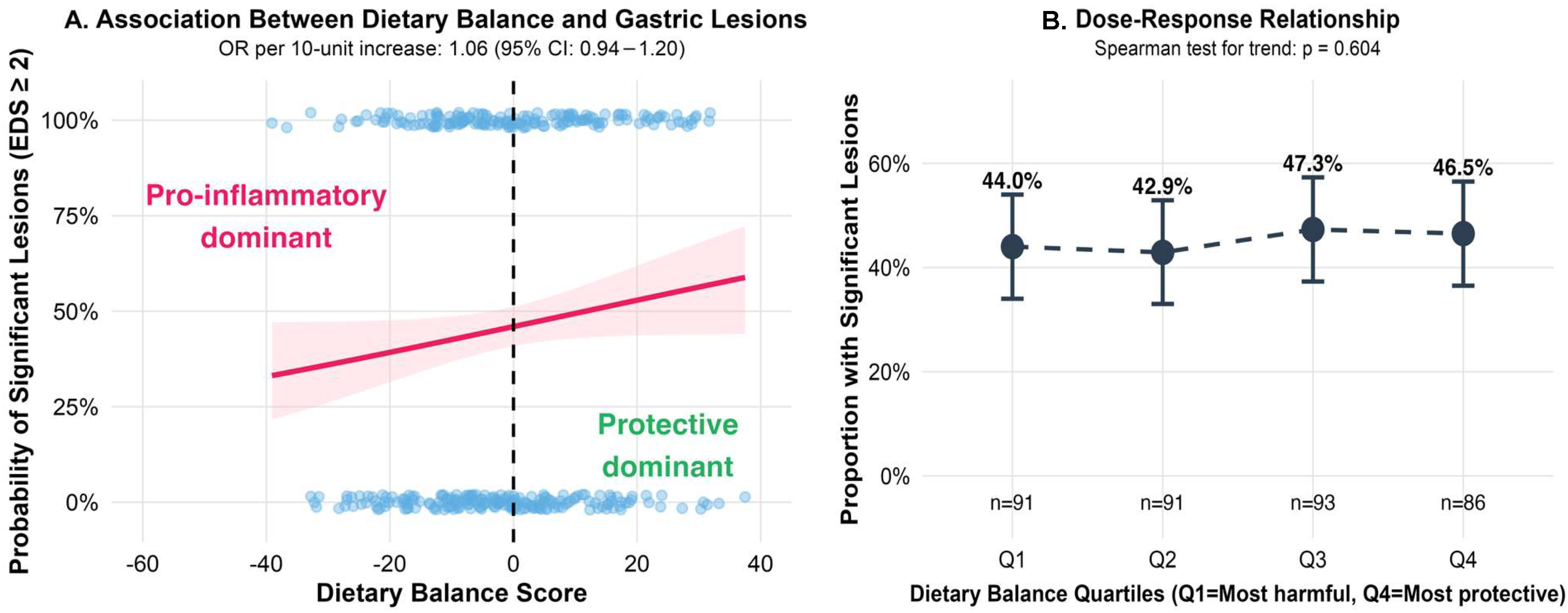
3.4. Dietary Balance and the Severity of Gastric Lesions
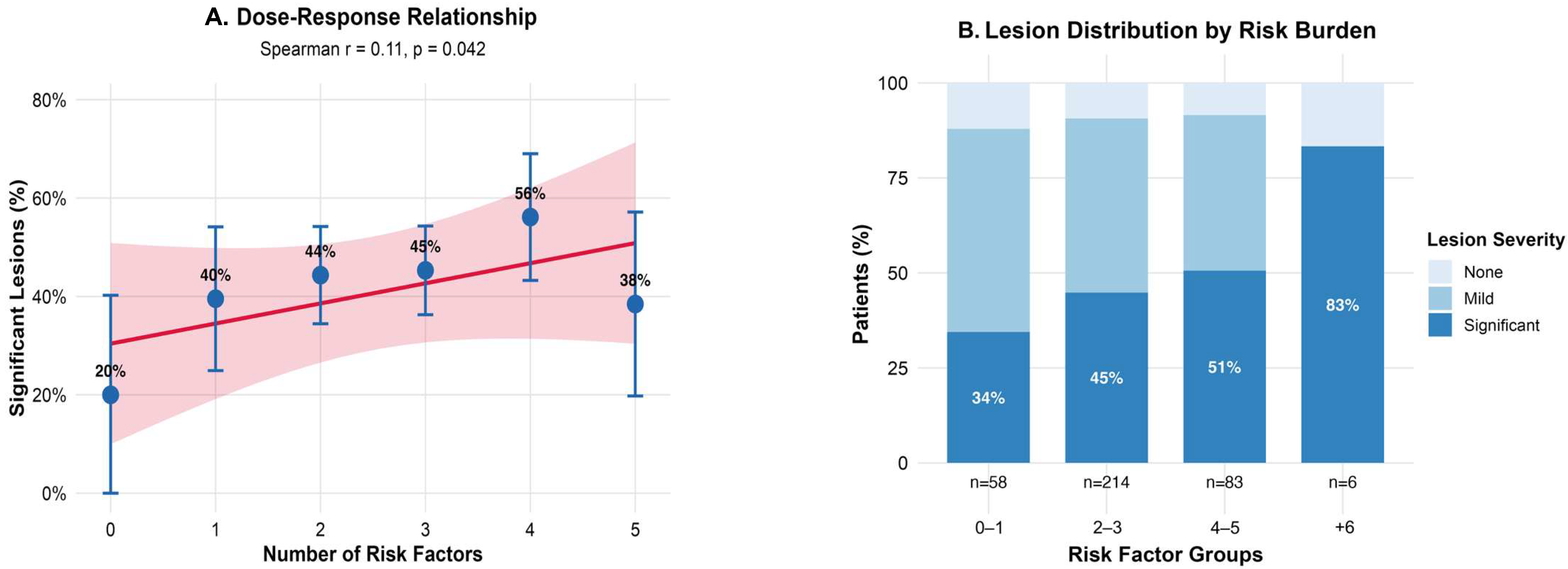
3.5. Cumulative Risk Factors and Dose–Response Relationship
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| H. pylori | Helicobacter pylori |
| NSAID | Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drug |
| MCV | Mean Corpuscular Volume |
| OR | Odds Ratio |
| CI | Confidence Interval |
| NNH | Number Needed to Harm |
| IQR | Interquartile Range |
References
- Marino, P.; Mininni, M.; Deiana, G.; Marino, G.; Divella, R.; Bochicchio, I.; Giuliano, A.; Lapadula, S.; Lettini, A.R.; Sanseverino, F. Healthy Lifestyle and Cancer Risk: Modifiable Risk Factors to Prevent Cancer. Nutrients 2024, 16, 800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugano, K.; Tack, J.; Kuipers, E.J.; Graham, D.Y.; El-Omar, E.M.; Miura, S.; Haruma, K.; Asaka, M.; Uemura, N.; Malfertheiner, P. Kyoto Global Consensus Report on Helicobacter pylori Gastritis. Gut 2015, 64, 1353–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Choi, H.; Leung, K.; Jiang, F.; Graham, D.Y.; Leung, W.K. Global Prevalence of Helicobacter pylori Infection between 1980 and 2022: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2023, 8, 553–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corojan, A.L.; Dumitrașcu, D.-L.; Ciobanca, P.; Leucuta, D.-C. Prevalence of Helicobacter pylori Infection among Dyspeptic Patients in Northwestern Romania: A Decreasing Epidemiological Trend in the Last 30 Years. Exp. Ther. Med. 2020, 20, 3488–3492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inoue, M. Epidemiology of Gastric Cancer—Changing Trends and Global Disparities. Cancers 2024, 16, 2948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balendra, V.; Amoroso, C.; Galassi, B.; Esposto, J.; Bareggi, C.; Luu, J.; Scaramella, L.; Ghidini, M. High-Salt Diet Exacerbates H. pylori Infection and Increases Gastric Cancer Risks. J. Pers. Med. 2023, 13, 1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Chen, L.; Cheng, J.; Qian, J.; Fang, Z.; Wu, J. Effect of Dietary Salt Intake on Risk of Gastric Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Case-Control Studies. Nutrients 2022, 14, 4260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Yang, X.; Zhang, C.; Zhu, C.; Tao, G.; Zhao, L.; Tang, S.; Shu, Z.; Cai, J.; Dai, S.; et al. Red and Processed Meat Intake Is Associated with Higher Gastric Cancer Risk: A Meta-Analysis of Epidemiological Observational Studies. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e70955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsson, S.C.; Orsini, N.; Wolk, A. Processed Meat Consumption and Stomach Cancer Risk: A Meta-Analysis. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2006, 98, 1078–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.R.; Kim, K.; Lee, S.A.; Kwon, S.O.; Lee, J.-K.; Keum, N.; Park, S.M. Effect of Red, Processed, and White Meat Consumption on the Risk of Gastric Cancer: An Overall and Dose–Response Meta-Analysis. Nutrients 2019, 11, 826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raei, N.; Behrouz, B.; Zahri, S.; Latifi-Navid, S. Helicobacter pylori Infection and Dietary Factors Act Synergistically to Promote Gastric Cancer. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. APJCP 2016, 17, 917–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagiou, P.; Samoli, E.; Lagiou, A.; Peterson, J.; Tzonou, A.; Dwyer, J.; Trichopoulos, D. Flavonoids, Vitamin C and Adenocarcinoma of the Stomach. Cancer Causes Control 2004, 15, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reytor-González, C.; Zambrano, A.K.; Montalvan, M.; Frias-Toral, E.; Simancas-Racines, A.; Simancas-Racines, D. Adherence to the Mediterranean Diet and Its Association with Gastric Cancer: Health Benefits from a Planeterranean Perspective. J. Transl. Med. 2024, 22, 483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Read, N.W.; Grech, P. Effect of Cigarette Smoking on Competence of the Pylorus: Preliminary Study. Br. Med. J. 1973, 3, 313–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Yuan, S.; Chen, J.; Ruan, X.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, K.; Wang, X.; Li, X.; Gill, D.; Burgess, S.; Giovannucci, E.; et al. Smoking, Alcohol Consumption, and 24 Gastrointestinal Diseases: Mendelian Randomization Analysis. eLife 2023, 12, e84051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.K.K.; Cho, C.H. The Pharmacological Actions of Nicotine on the Gastrointestinal Tract. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2004, 94, 348–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, R.E.; Levine, R.A.; Nandi, J.; Schwartzel, E.H.; Beach, D.H.; Borer, P.N.; Levy, G.C. Effects of Ethanol on Gastric Epithelial Cell Phospholipid Dynamics and Cellular Function. Am. J. Physiol. 1987, 252, G237–G243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guslandi, M. Effects of Ethanol on the Gastric Mucosa. Dig. Dis. Basel Switz. 1987, 5, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Romania: Alcohol Consumption Country Profile 2019; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2019; Available online: https://cdn.who.int/media/docs/default-source/country-profiles/substances-abuse/rou.pdf (accessed on 13 August 2025).
- Szőke, A.; Mocan, S.; Negovan, A. Helicobacter pylori Infection over Bile Reflux: No Influence on the Severity of Endoscopic or Premalignant Gastric Lesion Development. Exp. Ther. Med. 2021, 22, 766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Yang, S.; Wang, S.; Li, H.; Li, R.; Li, H.; Shi, Y.; Yang, J.; Bao, Y.; Du, S.; et al. Smoking Cessation and Mortality Risk Reduction in Older Adults with Long-Term Smoking History. BMC Public Health 2024, 24, 2821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Guide for Monitoring Alcohol Consumption and Related Harm. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/international-guide-for-monitoring-alcohol-consumption-and-related-harm (accessed on 12 August 2025).
- Roman, G.; Craciun, A.; Rusu, A.; Craciun, C.; Ananie, B.; Bala, C. Validation of the romanian version of a self-administered food frequency questionnaire. Romanian J. Diabetes Nutr. Metab. Dis. 2019, 26, 117–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.W.; Liu, S.Z.; Zhang, M.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, S.K.; Sun, X.B. Multivariate analysis of the association between consumption of fried food and gastric cancer and precancerous lesions. Zhonghua Yu Fang Yi Xue Za Zhi 2018, 52, 170–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, M.; He, F.J.; Ding, J.; Li, Y.; Zhang, P.; MacGregor, G.A. Salt Content of Sauces in the UK and China: Cross-Sectional Surveys. BMJ Open 2019, 9, e025623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, J.; Gul, P.; Rashid, M.T.; Li, Q.; Liu, K. Composition of Whole Grain Dietary Fiber and Phenolics and Their Impact on Markers of Inflammation. Nutrients 2024, 16, 1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatun, S.; Mollah, M.I. Analysis of Black Rice and Some Other Cereal Grains for Protein, Sugar, Polyphenols, Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Properties. J. Agric. Food Res. 2024, 16, 101121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milesi, G.; Rangan, A.; Grafenauer, S. Whole Grain Consumption and Inflammatory Markers: A Systematic Literature Review of Randomized Control Trials. Nutrients 2022, 14, 374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanza, F.L.; Collaku, A.; Liu, D.J. Endoscopic Comparison of Gastroduodenal Injury with Over-the-Counter Doses of New Fast-Dissolving Ibuprofen and Paracetamol Formulations: A Randomized, Placebo-Controlled, 4-Way Crossover Clinical Trial. Clin. Exp. Gastroenterol. 2018, 11, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatta, W.; Koike, T.; Asonuma, S.; Okata, H.; Uno, K.; Oikawa, T.; Iwai, W.; Yonechi, M.; Fukushi, D.; Kayaba, S.; et al. Smoking History and Severe Atrophic Gastritis Assessed by Pepsinogen Are Risk Factors for the Prevalence of Synchronous Gastric Cancers in Patients with Gastric Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection: A Multicenter Prospective Cohort Study. J. Gastroenterol. 2023, 58, 433–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Torre, G.; Chiaradia, G.; Gianfagna, F.; De Lauretis, A.; Boccia, S.; Mannocci, A.; Ricciardi, W. Smoking Status and Gastric Cancer Risk: An Updated Meta-Analysis of Case-Control Studies Published in the Past Ten Years. Tumori 2009, 95, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rota, M.; Possenti, I.; Valsassina, V.; Santucci, C.; Bagnardi, V.; Corrao, G.; Bosetti, C.; Specchia, C.; Gallus, S.; Lugo, A. Dose-Response Association between Cigarette Smoking and Gastric Cancer Risk: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. ResearchGate 2025, 27, 197–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poorolajal, J.; Moradi, L.; Mohammadi, Y.; Cheraghi, Z.; Gohari-Ensaf, F. Risk Factors for Stomach Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Epidemiol. Health 2020, 42, e2020004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, J.Y.C.; Ma, L.; Cho, C.H. Effect of Cigarette Smoke on Ethanol-Induced Gastric Mucosal Lesions: The Role of Nitric Oxide and Neutrophils. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1998, 342, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, I.B.; Jørgensen, T.; Bonnevie, O.; Grønbaek, M.; Sørensen, T.I. Smoking and Alcohol Intake as Risk Factors for Bleeding and Perforated Peptic Ulcers: A Population-Based Cohort Study. Epidemiol. Camb. Mass 2000, 11, 434–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, J.K.; Cho, C.H. Alcohol Drinking and Cigarette Smoking: A “Partner” for Gastric Ulceration. Chin. Med. J. 2000, 63, 845–854. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chow, J.Y.; Ma, L.; Zhu, M.; Cho, C.H. The Potentiating Actions of Cigarette Smoking on Ethanol-Induced Gastric Mucosal Damage in Rats. Gastroenterology 1997, 113, 1188–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Global Status Report on Alcohol and Health 2018; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018; Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789241565639 (accessed on 13 August 2025).
- Piper, D.W.; McIntosh, J.H.; Greig, M.; Shy, C.M. Environmental Factors and Chronic Gastric Ulcer. A Case Control Study of the Association of Smoking, Alcohol, and Heavy Analgesic Ingestion with the Exacerbation of Chronic Gastric Ulcer. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 1982, 17, 721–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjarnason, I.; Scarpignato, C.; Holmgren, E.; Olszewski, M.; Rainsford, K.D.; Lanas, A. Mechanisms of Damage to the Gastrointestinal Tract From Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs. Gastroenterology 2018, 154, 500–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allison, M.C.; Howatson, A.G.; Torrance, C.J.; Lee, F.D.; Russell, R.I. Gastrointestinal Damage Associated with the Use of Nonsteroidal Antiinflammatory Drugs. N. Engl. J. Med. 1992, 327, 749–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papatheodoridis, G.V.; Sougioultzis, S.; Archimandritis, A.J. Effects of Helicobacter pylori and Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs on Peptic Ulcer Disease: A Systematic Review. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2006, 4, 130–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, S.; Fowora, M.; Pellicano, R. Infections with Helicobacter pylori and Challenges Encountered in Africa. World J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 25, 3183–3195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chiciudean, P.-L.-D.; Filip, A.-M.; Munteanu, S.-N.; Cîmpian, C.-I.; Mocan, S.; Pantea, M.; Negovan, A.E. Risk Factors for Endoscopic Gastric Mucosal Lesions: Analysis of Lifestyle, Dietary, and Clinical Determinants in 361 Patients. Life 2025, 15, 1474. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15091474
Chiciudean P-L-D, Filip A-M, Munteanu S-N, Cîmpian C-I, Mocan S, Pantea M, Negovan AE. Risk Factors for Endoscopic Gastric Mucosal Lesions: Analysis of Lifestyle, Dietary, and Clinical Determinants in 361 Patients. Life. 2025; 15(9):1474. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15091474
Chicago/Turabian StyleChiciudean, Patrick-Lazăr-Dominik, Ana-Maria Filip, Sabrina-Nicoleta Munteanu, Cristian-Ioan Cîmpian, Simona Mocan, Monica Pantea, and Anca Elena Negovan. 2025. "Risk Factors for Endoscopic Gastric Mucosal Lesions: Analysis of Lifestyle, Dietary, and Clinical Determinants in 361 Patients" Life 15, no. 9: 1474. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15091474
APA StyleChiciudean, P.-L.-D., Filip, A.-M., Munteanu, S.-N., Cîmpian, C.-I., Mocan, S., Pantea, M., & Negovan, A. E. (2025). Risk Factors for Endoscopic Gastric Mucosal Lesions: Analysis of Lifestyle, Dietary, and Clinical Determinants in 361 Patients. Life, 15(9), 1474. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15091474







