Jinyuan 601 a Novel High-Protein Soybean Variety with Improved Agronomic Traits and Nutritional Quality
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
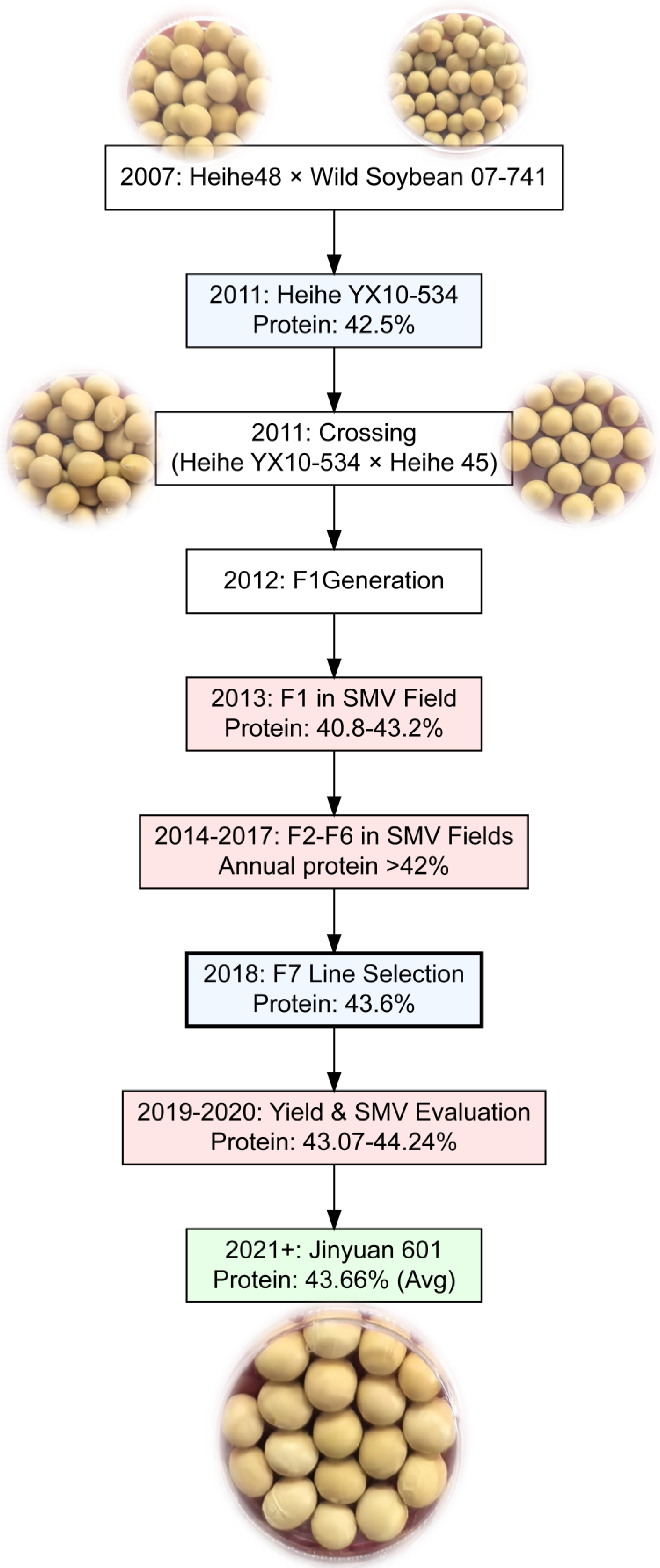
2.1. Plant Material and Breeding Program
2.2. Breeding Methodology and Cultivar Development
2.3. Experimental Sites and Environmental Conditions
2.4. Seed Composition Analysis
2.4.1. Protein Content Determination
2.4.2. Determination of Soybean Seed Oil Content
2.5. Soybean Mosaic Virus Resistance Evaluation
2.6. Agronomic Evaluation
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Analysis of Variance for Soybean Yield Across Environments and Seasons
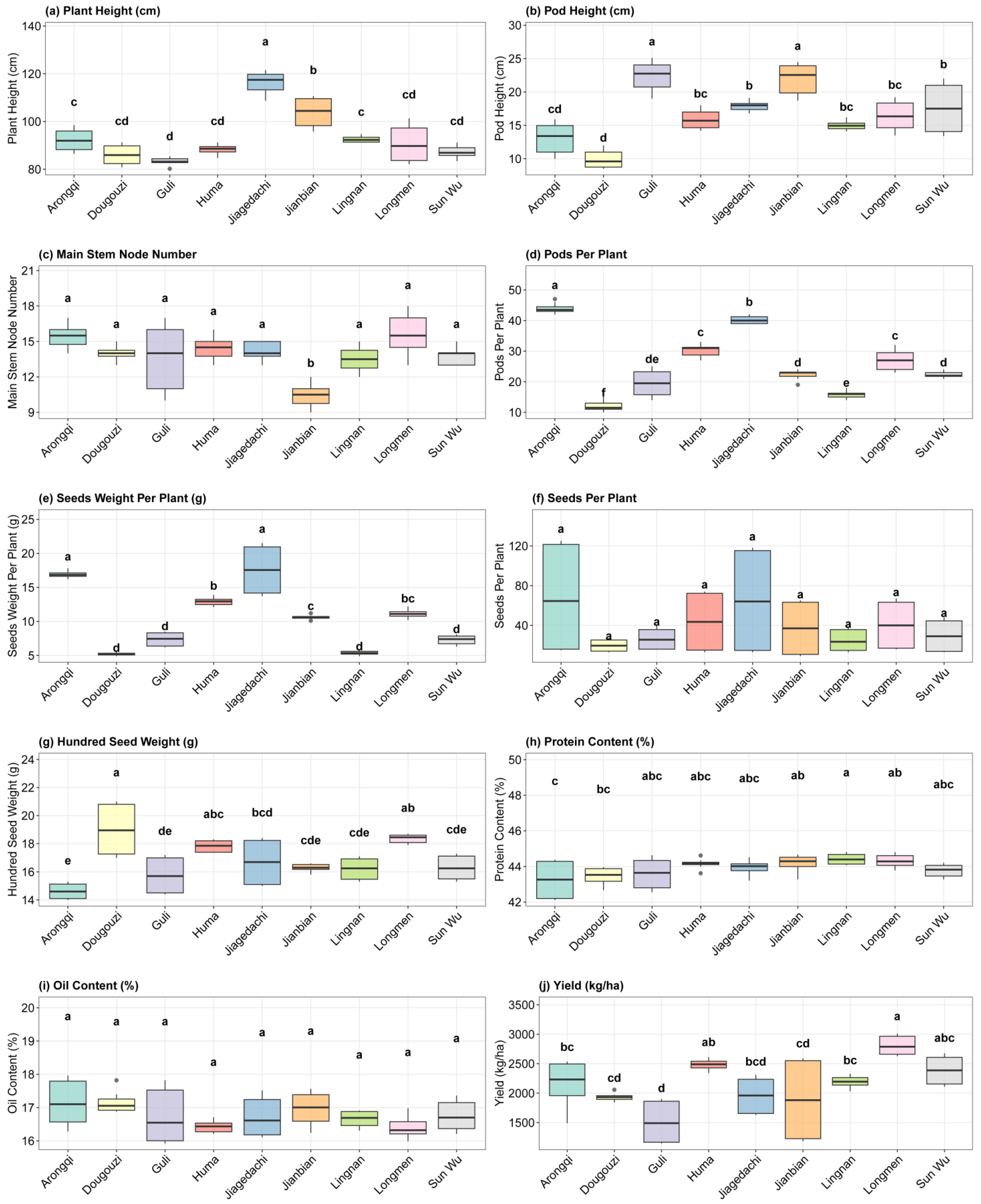
3.2. Variability in Agronomic and Quality Traits of Soybean Cultivars
3.3. Phenological Development and Yield Performance of Jinyuan 601 Soybean Cultivar Across Different Geographical Locations
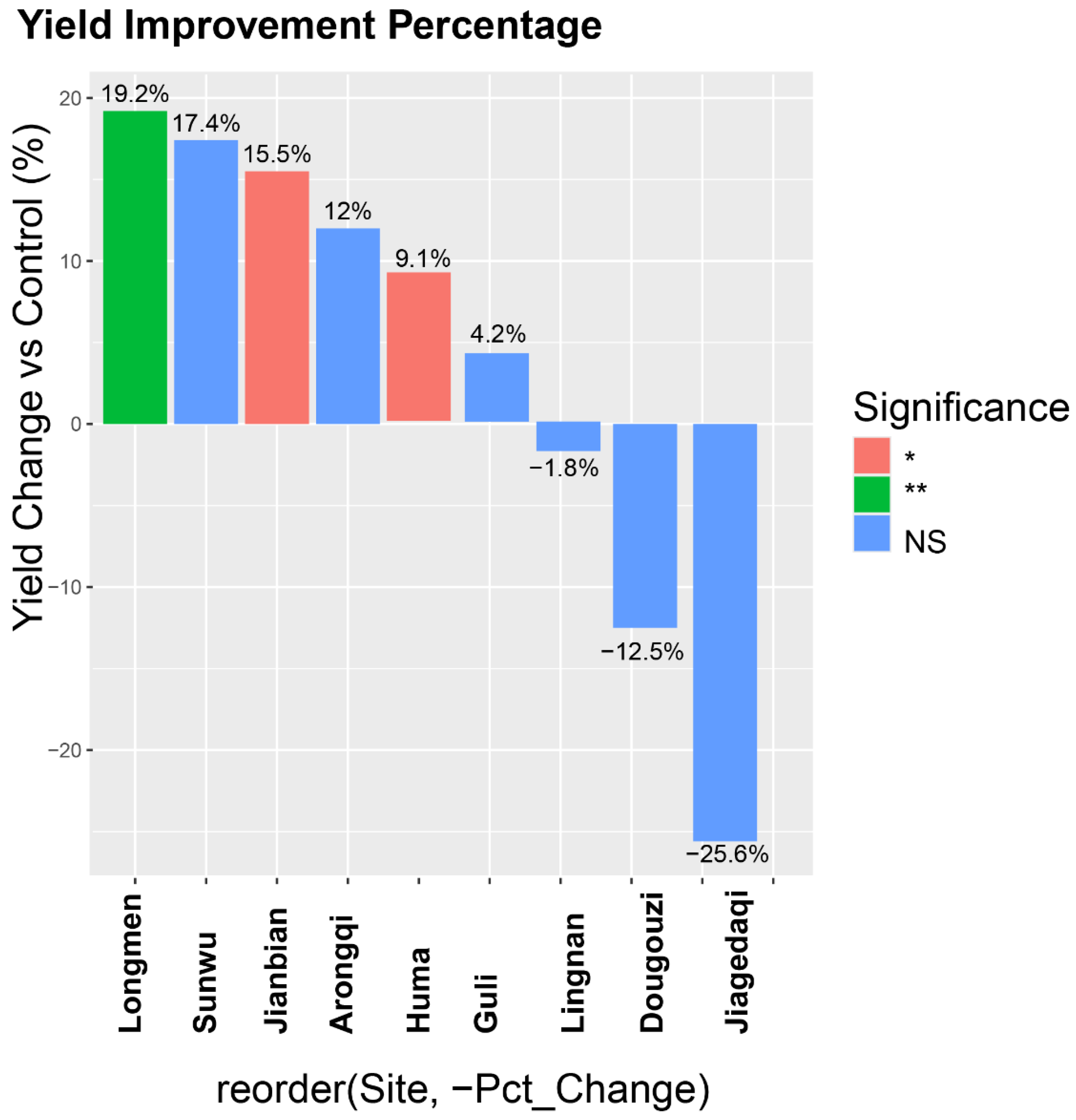
3.4. Multi-Location Yield Performance and Environmental Adaptation
3.5. Seed Quality and Morphological Traits in Jinyuan 601 Soybean Across Production Locations
3.6. Agronomic Trait Variability and Seed Quality Stability Across Environments
3.7. Disease Resistance Evaluation of Jinyuan 601 Soybean Cultivar
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kim, M.Y.; Van, K.; Kang, Y.J.; Kim, K.H.; Lee, S.-H. Tracing soybean domestication history: From nucleotide to genome. Breed. Sci. 2012, 61, 445–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamlom, S.F.; Zhang, Y.; Su, B.; Wu, H.; Zhang, X.; Fu, J.; Zhang, B.; Qiu, L.-J. Map-based cloning of a novel QTL qBN-1 influencing branch number in soybean [Glycine max (L.) Merr.]. Crop J. 2020, 8, 793–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartman, G.L.; West, E.D.; Herman, T.K. Crops that feed the World 2. Soybean—Worldwide production, use, and constraints caused by pathogens and pests. Food Secur. 2011, 3, 5–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Chen, J.; Hao, X.; Ji, X.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, X.; Yao, Y. A systematic review of black soybean (Glycine max (L.) Merr.): Nutritional composition, bioactive compounds, health benefits, and processing to application. Food Front. 2024, 5, 1188–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voora, V.; Bermúdez, J.; Le, H.; Larrea, C.; Luna, E. Soybean prices and sustainability. IISD Mark. Rep. 2024, 2. Available online: https://www.iisd.org/publications/report/2024-global-market-report-soybean (accessed on 21 June 2025).
- Zha, B.; Zhang, C.; Yuan, R.; Zhao, K.; Sun, J.; Liu, X.; Wang, X.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, B.; Lamlom, S.F. Integrative QTL mapping and candidate gene analysis for main stem node number in soybean. BMC Plant Biol. 2025, 25, 422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Zhao, K.; Ren, H.; Lamlom, S.F.; Liu, X.; Wang, X.; Zhang, F.; Yuan, R.; Wang, J. Comparative study of isoflavone synthesis genes in two wild soybean varieties using transcriptomic analysis. Agriculture 2023, 13, 1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zha, B.; Yuan, R.; Zhao, K.; Sun, J.; Liu, X.; Wang, X.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, B.; Lamlom, S.F. Identification of Quantitative Trait Loci for Node Number, Pod Number, and Seed Number in Soybean. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 2300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lassaletta, L.; Billen, G.; Garnier, J.; Bouwman, L.; Velazquez, E.; Mueller, N.D.; Gerber, J.S. Nitrogen use in the global food system: Past trends and future trajectories of agronomic performance, pollution, trade, and dietary demand. Environ. Res. Lett. 2016, 11, 095007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, C.; Yuan, R.; Liu, X.; Zhang, F.; Zhao, K.; Zhang, M.; Abdelghany, A.M.; Lamlom, S.F.; Zhang, B. Transcriptome profiling uncovers differentially expressed genes linked to nutritional quality in vegetable soybean. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0313632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, H.; Zhao, K.; Zhang, C.; Lamlom, S.F.; Liu, X.; Wang, X.; Zhang, F.; Yuan, R.; Gao, Y.; Cao, B. Genetic analysis and QTL mapping of seed hardness trait in a soybean (Glycine max) recombinant inbred line (RIL) population. Gene 2024, 905, 148238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banaszkiewicz, T. Nutritional value of soybean meal. Soybean Nutr. 2011, 2011, 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Florou-Paneri, P.; Christaki, E.; Giannenas, I.; Bonos, E.; Skoufos, I.; Tsinas, A.; Tzora, A.; Peng, J. Alternative protein sources to soybean meal in pig diets. J. Food Agric. Env. 2014, 12, 655–660. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, P.; Wang, T.; Luo, Y. A review on plant-based proteins from soybean: Health benefits and soy product development. J. Agric. Food Res. 2022, 7, 100265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, H.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, C.; Liu, X.; Wang, X.; Zhang, F.; Zhao, K.; Yuan, R.; Abdelghany, A.M.; Lamlom, S.F. Uncovering molecular mechanisms of soybean response to 12C6+ heavy ion irradiation through integrated transcriptomic and metabolomic profiling. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2025, 289, 117689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dilawari, R.; Kaur, N.; Priyadarshi, N.; Prakash, I.; Patra, A.; Mehta, S.; Singh, B.; Jain, P.; Islam, M.A. Soybean: A key player for global food security. In Soybean Improvement: Physiological, Molecular and Genetic Perspectives; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; pp. 1–46. [Google Scholar]
- Gulkirpik, E. Development and Evaluation of Processing Technologies to Improve the Utilization of Soybean Products and Enhance the Nutritional Value of Foods in Sub-Saharan Africa. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, Champaign, IL, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Leamy, L.J.; Zhang, H.; Li, C.; Chen, C.Y.; Song, B.-H. A genome-wide association study of seed composition traits in wild soybean (Glycine soja). BMC Genom. 2017, 18, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudełka, W.; Kowalska, M.; Popis, M. Quality of soybean products in terms of essential amino acids composition. Molecules 2021, 26, 5071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boerma, H.R.; Specht, J.E. Soybeans: Improvement, Production, and Uses; American Society of Agronomy, Crop Science Society of America, Soil Science Society of America: Madison, WI, USA, 2004; pp. 621–677. [Google Scholar]
- Stevenson, S.E.; Woods, C.A.; Hong, B.; Kong, X.; Thelen, J.J.; Ladics, G.S. Environmental effects on allergen levels in commercially grown non-genetically modified soybeans: Assessing variation across North America. Front. Plant Sci. 2012, 3, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotundo, J.L.; Westgate, M.E. Meta-analysis of environmental effects on soybean seed composition. Field Crops Res. 2009, 110, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotundo, J.L.; Miller-Garvin, J.E.; Naeve, S.L. Regional and temporal variation in soybean seed protein and oil across the United States. Crop Sci. 2016, 56, 797–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.; Yang, X.; Zhao, H.; Song, X.; Tsvetkov, Y.D.; Wu, Y.; Gao, Q.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, J. Genetic analysis of protein content and oil content in soybean by genome-wide association study. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1182771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Sun, S.; Wu, T.; Yang, R.; Tian, S.; Xu, C.; Jiang, B.; Yuan, S.; Hou, W.; Wu, C. Geographic distributions and the regionalization of soybean seed compositions across China. Food Res. Int. 2023, 164, 112364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, M.; Li, F.; Liu, X.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, F.; Zhao, K.; Yuan, R.; Lamlom, S.F.; Ren, H.; et al. Genome-Wide Association Study Reveals Key Genetic Loci Controlling Oil Content in Soybean Seeds. Agronomy 2025, 15, 1889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Yang, Y.; Xie, H.; Zhang, Y.; He, H.; Zhang, X.; Sun, S. Enhancing sustainable agriculture in China: A meta-analysis of the impact of straw and manure on crop yield and soil fertility. Agriculture 2024, 14, 480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, H.; Qu, X.; Hong, H.; Sun, L.; Lamlom, S.F.; Liu, Z.; Lu, W. Multi-environment QTL mapping identifies major genetic loci influencing soybean main stem node architecture. PeerJ 2024, 12, e18539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Tang, H.; Niu, D.; Lv, M. Study on Meteorological Forecasting Method of Key Quality Components in Soybean. Soybean Sci. 2021, 40, 112–121. [Google Scholar]
- Bosaz, L.B.; Gerde, J.A.; Borrás, L.; Cipriotti, P.A.; Ascheri, L.; Campos, M.; Gallo, S.; Rotundo, J.L. Management and environmental factors explaining soybean seed protein variability in central Argentina. Field Crops Res. 2019, 240, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vital, R.G.; Müller, C.; Freire, F.B.S.; Silva, F.B.; Batista, P.F.; Fuentes, D.; Rodrigues, A.A.; Moura, L.M.F.; Daloso, D.M.; Silva, A.A. Metabolic, physiological and anatomical responses of soybean plants under water deficit and high temperature condition. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 16467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrera, C.; Martínez, M.J.; Dardanelli, J.; Balzarini, M. Environmental variation and correlation of seed components in nontransgenic soybeans: Protein, oil, unsaturated fatty acids, tocopherols, and isoflavones. Crop Sci. 2011, 51, 800–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Hong, H.; Liu, X.; Wang, X.; Zhang, C.; Zhao, K.; Yuan, R.; Abdelghany, A.M.; Zhang, B.; Lamlom, S.F. Large-scale evaluation of soybean germplasm reveals geographic patterns in shade tolerance and identifies elite genotypes for intercropping systems. BMC Plant Biol. 2025, 25, 1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diers, B.W.; Specht, J.; Rainey, K.M.; Cregan, P.; Song, Q.; Ramasubramanian, V.; Graef, G.; Nelson, R.; Schapaugh, W.; Wang, D. Genetic architecture of soybean yield and agronomic traits. G3 Genes Genomes Genet. 2018, 8, 3367–3375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cober, E.; D Voldeng, H. Developing high-protein, high-yield soybean populations and lines. Crop Sci. 2000, 40, 39–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCleary, B.V. Measurement of dietary fiber: Which AOAC Official Method of Analysis SM to use. J. AOAC Int. 2023, 106, 917–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachkar, C.; Balgude, Y.; Shinde, P.; Deokar, C. Screening of soybean genotypes against soybean mosaic virus under natural and glass house conditions. Int. J. Commun. Syst. 2019, 7, 2267–2269. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, M.; Liu, S.; Wang, Z.; Yuan, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Liang, Q.; Yang, X.; Duan, Z.; Liu, Y.; Kong, F. Progress in soybean functional genomics over the past decade. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2022, 20, 256–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Liu, K. Chemistry and nutritional value of soybean components. In Soybeans: Chemistry, Technology, and Utilization; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1997; pp. 25–113. [Google Scholar]
- Galiyeva, A. Nutritional Value Assessment of Different Soy Beans Genotypes Screened via Biotechnology Methods. Master’s Thesis, Vytautas Magnus University, Kaunas, Lithuania, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- GC, M. Preparation and Quality Evaluation of Protein-Rich Concentrate Using Buffalo (Bubalus bubalis) Liver and Germinated Soybean (Glycine max). Ph.D. Thesis, Department of Food Technology Central Campus of Technology Institute of Science and Technology Tribhuvan University, Kirtipur, Nepal, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Abrams, J.S. Identification and Confirmation of Quantitative Trait Loci for Protein Concentration and Improved Amino Acid Composition in Glycine max. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Tennessee, Knoxville, TN, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Arora, B.; Babita, G.M.; Bhardwaj, N. Transgenic Approaches in the Improvement of Seed Oil and Quality in Oil Seed Crops. Int. J. Multidiscip. Res. 2023, 5, 1–26. [Google Scholar]
- Bekhit, A.E.-D.A.; Riley, W.W.; Hussain, M.A. Alternative Proteins: Safety and Food Security Considerations; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Sau, F. Theoretical description of the motion of soybean seeds in coaxially positioned cylinders. Sustain. Dev. 2015, 8, 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Karikari, B.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, C.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, T.; Feng, J. Comprehensive identification of main, environment interaction and epistasis quantitative trait nucleotides for 100-seed weight in soybean (Glycine max (L.) Merr.). Agronomy 2024, 14, 483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rani, R.; Raza, G.; Ashfaq, H.; Rizwan, M.; Shimelis, H.; Tung, M.H.; Arif, M. Analysis of genotype× environment interactions for agronomic traits of soybean (Glycine max [L.] Merr.) using association mapping. Front. Genet. 2023, 13, 1090994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotundo, J.L.; Rech, R.; Cardoso, M.M.; Fang, Y.; Tang, T.; Olson, N.; Pyrik, B.; Conrad, G.; Borras, L.; Mihura, E. Development of a decision-making application for optimum soybean and maize fertilization strategies in Mato Grosso. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2022, 193, 106659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, E.; Alvarez Prado, S.; Rotundo, J.L.; Gerde, J.A. Unravelling the environmental drivers determining the residual fraction of soybean seed. Crop Sci. 2025, 65, e21406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, X.; Feng, F.; Li, D.; Herbert, S.J.; Liao, Y.; Siddique, K.H. Changes in yield and agronomic traits of soybean cultivars released in China in the last 60 years. Crop Pasture Sci. 2017, 68, 973–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zheng, H.; Li, W.; Olesen, J.E.; Harrison, M.T.; Bai, Z.; Zou, J.; Zheng, A.; Bernacchi, C.; Xu, X. Genetic progress battles climate variability: Drivers of soybean yield gains in China from 2006 to 2020. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2023, 43, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilcox, J. Sixty years of improvement in publicly developedelite gation and soil water-deficit. Field Crops Res. 1991, 27, 71–82. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, W.; Hou, J.; Hu, Q.; An, J.; Zhang, Y.; Han, Q.; Li, X.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, D.; Wang, J. Pedigree-based genetic dissection of quantitative loci for seed quality and yield characters in improved soybean. Mol. Breed. 2021, 41, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grieshop, C.M.; Fahey, G.C. Comparison of quality characteristics of soybeans from Brazil, China, and the United States. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2001, 49, 2669–2673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prenger, E.M.; Ostezan, A.; Mian, M.R.; Stupar, R.M.; Glenn, T.; Li, Z. Identification and characterization of a fast-neutron-induced mutant with elevated seed protein content in soybean. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2019, 132, 2965–2983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Location | Province | Soil Type | Temp. Range (°C) | Mean Temp. (°C) | Precipitation (mm, Growing Season) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sunwu County (Heihe) | Heilongjiang | Black soil | 8–28 | ~17.5 | 420–440 |
| Longmen (Heihe) | Heilongjiang | Dark loam | 9–29 | ~18.0 | 430–440 |
| Lingnan (Daxing’anling) | Heilongjiang | Sandy loam | 10–30 | ~19.2 | 400–420 |
| Jiagedaqi (Daxing’anling) | Heilongjiang | Meadow soil | 7–27 | ~17.8 | 410–430 |
| Jianbian (Heihe) | Heilongjiang | Loamy black soil | 8–29 | ~18.4 | 420–435 |
| Dougouzi (Heihe) | Heilongjiang | Sandy clay loam | 10–31 | ~19.0 | 430–450 |
| Huma (Daxing’anling) | Heilongjiang | Black soil | 6–26 | ~16.9 | 410–440 |
| Oroqen Banner (Hulunbuir) | Inner Mongolia | Meadow–chernozem soil | 9–28 | ~18.6 | 420–440 |
| Guli (Hulunbuir) | Inner Mongolia | Sandy loam | 10–30 | ~19.1 | 410–425 |
| Source | Df | Sum Sq | Mean Sq | F Value | Pr(>F) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ENV | 8.00 | 1.81 × 104 | 2.27 × 103 | 815 *** | <0.001 |
| REP(ENV) | 81 | 225 | 2.78 | 1.22 NS | 0.184 |
| Seasons | 1.00 | 2.69 | 2.69 | 0.0393 NS | 0.848 |
| Seasons: ENV | 8.00 | 547 | 68.4 | 30.1 *** | <0.001 |
| ENV/Seasons | 16 | 1.87 × 104 | 1.17 × 103 | 513 *** | <0.001 |
| ENV/2022 | 8.00 | 1.01 × 104 | 1.26 × 103 | 554 *** | <0.001 |
| ENV/2023 | 8.00 | 8.59 × 103 | 1.07 × 103 | 472 *** | <0.001 |
| Residuals | 81 | 184 | 2.28 | ||
| CV(%) | 5.87 | ||||
| MSR+/MSR− | 2.69 | ||||
| OV mean | 25.7 |
| Variable | CV | Max | Mean | Median | Min | SD. Amo | SE | CI.T |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HSW | 9.81 | 21 | 16.8 | 16.9 | 14 | 1.65 | 0.123 | 0.243 |
| MSNN | 14.4 | 18 | 13.8 | 14 | 9.00 | 1.99 | 0.149 | 0.293 |
| PH | 11.6 | 124 | 93.4 | 90.1 | 80.1 | 10.8 | 0.804 | 1.59 |
| PODH | 24.8 | 25.3 | 16.5 | 16.1 | 8.20 | 4.10 | 0.306 | 0.603 |
| PPP | 40.2 | 47 | 25.7 | 24 | 9.00 | 10.3 | 0.77 | 1.52 |
| SPP | 85.4 | 125 | 39.3 | 20.5 | 9.00 | 33.5 | 2.50 | 4.93 |
| SWP | 43.4 | 21.5 | 10.5 | 10.5 | 4.80 | 4.54 | 0.339 | 0.668 |
| oil | 3.24 | 18 | 16.8 | 16.7 | 15.9 | 0.543 | 0.0405 | 0.0799 |
| protein | 1.54 | 44.8 | 43.9 | 44.1 | 42.1 | 0.677 | 0.0505 | 0.0996 |
| Locations | Sowing Period | Seedling Period | Maturity Period | Growing Days (d) | Days Longer or Shorter than the Control (d) | Yield per ha (kg) | Yield Increase or Decrease Compared to the Control (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jianbian | 05/08 | 05/24 | 09/10 | 110 | 3 | 2452.5 | 9.0 |
| Longmen | 05/21 | 06/03 | 09/07 | 97 | 2 | 2587.5 | 15.0 |
| Jiagedaqi | 05/24 | 06/09 | 09/28 | 112 | 7 | 1402.5 | −16.4 |
| Lingnan | 05/27 | 06/08 | 09/26 | 111 | 2 | 2269.5 | 5.1 |
| Guri | 05/17 | 05/29 | 09/17 | 112 | 4 | 2434.5 | 4.4 |
| Dougouzi | 05/21 | 06/08 | 09/18 | 103 | 3 | 1987.5 | 8.0 |
| Huma | 05/20 | 06/05 | 09/30 | 118 | 2 | 2287.5 | 10.5 |
| Arongqi | 05/19 | 06/01 | 09/20 | 112 | −2 | 2592 | 3.2 |
| Sunwu | 05/20 | 06/01 | 09/11 | 103 | 1 | 2547 | 3.3 |
| Locations | Intact Grain Rate (%) | Purple Spot Rate (%) | Brown Spots Grain Rate (%) | Insect Food Grain Rate (%) | Others Particle Rate (%) | Seed Coat Color | Umbilical Color (Hilum Color) | Seed Shape | Brightness |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sun Wu | 98.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | yellow | yellow | round | Faint light |
| Longmen | 98.2 | 0.0 | 1.8 | 0.0 | 0.0 | yellow | yellow | round | Faint light |
| Lingnan | 97.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 1.0 | 2.0 | yellow | light yellow | round | Strong light |
| Jiagedachi | 90.0 | 1.0 | 0.0 | 1.0 | 8.0 | yellow | light yellow | oblate | Strong light |
| Jianbian | 98.4 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 1.6 | yellow | yellow | round | No light |
| Dougouzi | 98.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 2.0 | yellow | yellow | round | Faint light |
| Huma | 97.6 | 0.0 | 0.8 | 1.4 | 0.2 | yellow | yellow | round | Faint light |
| Arongqi | 96.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 4.0 | 0.0 | yellow | yellow | round | Faint light |
| Guli | 96.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.7 | 3.3 | yellow | light yellow | round | Faint light |
| Average | 96.6 | 0.1 | 0.3 | 1.0 | 2.0 | yellow | light yellow | round | Faint light |
| Variety | Year | SMV1 Disease Index (%) | SMV1 Resistance | SMV3 Disease Index (%) | SMV3 Resistance | SCSH Weighted Value | SCSH Resistance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Huajiang No. 2 | 2021 | 36.67 | Medium | 46.67 | Medium | 1.2 | Disease resistant |
| Huajiang No. 2 | 2022 | 35.50 | Moderate | 50.00 | Medium | 1.0 | Disease resistant |
| Jinyuan 601 | 2021 | 34.29 | Moderate | 45.71 | Medium | 0.00 | Highly resistant |
| Jinyuan 601 | 2022 | 30.00 | Moderate | 50.00 | Medium | 1.50 | Disease resistant |
| Jinyuan 601 | 2021–2022 | 34.29 | Moderate | 50.00 | Medium | 1.50 | Disease resistant |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wei, X.; Yu, X.; Chen, X.; Cui, S.; Cui, J.; Wei, R.; Diao, H.; Ren, H.; Lu, W.; Tang, X. Jinyuan 601 a Novel High-Protein Soybean Variety with Improved Agronomic Traits and Nutritional Quality. Life 2025, 15, 1414. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15091414
Wei X, Yu X, Chen X, Cui S, Cui J, Wei R, Diao H, Ren H, Lu W, Tang X. Jinyuan 601 a Novel High-Protein Soybean Variety with Improved Agronomic Traits and Nutritional Quality. Life. 2025; 15(9):1414. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15091414
Chicago/Turabian StyleWei, Xinyu, Xiaoguang Yu, Xiangjin Chen, Shaobin Cui, Jieyin Cui, Ran Wei, Henan Diao, Honglei Ren, Wencheng Lu, and Xiaodong Tang. 2025. "Jinyuan 601 a Novel High-Protein Soybean Variety with Improved Agronomic Traits and Nutritional Quality" Life 15, no. 9: 1414. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15091414
APA StyleWei, X., Yu, X., Chen, X., Cui, S., Cui, J., Wei, R., Diao, H., Ren, H., Lu, W., & Tang, X. (2025). Jinyuan 601 a Novel High-Protein Soybean Variety with Improved Agronomic Traits and Nutritional Quality. Life, 15(9), 1414. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15091414






