Movement-Evoked Pain and Temporal Summation in Individuals with Symptomatic Rotator Cuff Tears: A Cross-Sectional Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Study Population
2.3. Procedure
2.4. Temporal Summation
2.5. Movement-Evoked Pain
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Study Limitations
4.2. Implications
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data availability statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MEP | Movement-Evoked Pain |
| RC | Rotator Cuff |
| TS | Temporal Summation |
| RCRSP | Rotator Cuff Related Shoulder Pain |
| ARCR | Arthroscopic Rotator Cuff Repair |
| NRS | Numerical Pain Rating Scale |
References
- Hinsley, H.; Ganderton, C.; Arden, N.K.; Carr, A.J. Prevalence of rotator cuff tendon tears and symptoms in a Chingford general population cohort, and the resultant impact on UK health services: A cross-sectional observational study. BMJ Open 2022, 12, e059175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abate, M.; Di Carlo, L.; Salini, V.; Schiavone, C. Risk factors associated with bilateral rotator cuff tears. Orthop. Traumatol. Surg. Res. 2017, 103, 841–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minagawa, H.; Yamamoto, N.; Abe, H.; Fukuda, M.; Seki, N.; Kikuchi, K.; Kijima, H.; Itoi, E. Prevalence of symptomatic and asymptomatic rotator cuff tears in the general population: From mass-screening in one village. J. Orthop. 2013, 10, 8–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, R.; Yang, R.; Ning, N. Central sensitization syndrome in patients with rotator cuff tear: Prevalence and associated factors. Postgrad. Med. 2023, 135, 593–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haik, M.N.; Evans, K.; Smith, A.; Henríquez, L.; Bisset, L. People with musculoskeletal shoulder pain demonstrate no signs of altered pain processing. Musculoskelet. Sci. Pract. 2019, 39, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, D.C.; Jafarian Tangrood, Z.; Wilson, R.; Sole, G.; Abbott, J.H. Tailored exercise and manual therapy versus standardized exercise for patients with shoulder subacromial pain: A feasibility randomized controlled trial (the Otago MASTER trial). BMJ Open 2022, 12, e053572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leemans, L.; Polli, A.; Nijs, J.; Wideman, T.; den Bandt, H.; Beckwée, D. It hurts to move! Intervention effects and assessment methods for movement-evoked pain in patients with musculoskeletal pain: A systematic review with meta-analysis. J. Orthop. Sports Phys. Ther. 2022, 52, 345–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobkin, P.L.; Da Costa, D.; Abrahamowicz, M.; Dritsa, M.; Du Berger, R.; Fitzcharles, M.A.; Lowensteyn, I. Adherence during an individualized home based 12-week exercise program in women with fibromyalgia. J. Rheumatol. 2006, 33, 333–341. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lima, L.V.; Abner, T.S.S.; Sluka, K.A. Does exercise increase or decrease pain? Central mechanisms underlying these two phenomena. J. Physiol. 2017, 595, 4141–4150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butera, K.A.; Chimenti, R.L.; Alsouhibani, A.M.; Berardi, G.; Booker, S.Q.; Knox, P.J.; Post, A.A.; Merriwether, E.N.; Wilson, A.T.; Simon, C.B. Through the lens of movement-evoked pain: A theoretical framework of the “Pain-Movement Interface” to guide research and clinical care for musculoskeletal pain conditions. J. Pain 2024, 25, 104486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fullwood, D.; Means, S.; Merriwether, E.N.; Chimenti, R.L.; Ahluwalia, S.; Booker, S.Q. Toward understanding movement-evoked pain (MEP) and its measurement: A scoping review. Clin. J. Pain 2021, 37, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, A.K.; Rainville, P.; O’Leary, S.; Elphinston, R.A.; Sterling, M.; Larivière, C.; Sullivan, M.J. Validation of an index of sensitivity to movement-evoked pain in patients with whiplash injuries. Pain Rep. 2018, 3, e661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alaiti, R.K.; Caneiro, J.P.; Gasparin, J.T.; Chaves, T.C.; Malavolta, E.A.; Gracitelli, M.E.; Meulders, A.; da Costa, M.F. Shoulder pain across more movements is not related to more rotator cuff tendon findings in people with chronic shoulder pain diagnosed with subacromial pain syndrome. Pain Rep. 2021, 6, e980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunn, W.R.; Kuhn, J.E.; Sanders, R.; An, Q.; Baumgarten, K.M.; Bishop, J.Y.; Brophy, R.H.; Carey, J.L.; Holloway, G.B.; Jones, G.L.; et al. Symptoms of pain do not correlate with rotator cuff tear severity: A cross-sectional study of 393 patients with a symptomatic atraumatic full-thickness rotator cuff tear. J. Bone Joint Surg. Am. 2014, 96, 793–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staud, R.; Vierck, C.J.; Cannon, R.L.; Mauderli, A.P.; Price, D.D. Abnormal sensitization and temporal summation of second pain (wind-up) in patients with fibromyalgia syndrome. Pain 2001, 91, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Overstreet, D.S.; Michl, A.N.; Penn, T.M.; Rumble, D.D.; Aroke, E.N.; Sims, A.M.; King, A.L.; Hasan, F.N.; Quinn, T.L.; Long, D.L.; et al. Temporal summation of mechanical pain prospectively predicts movement-evoked pain severity in adults with chronic low back pain. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2021, 22, 429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, J.T.; You, D.S.; Law, C.S.W.; Darnall, B.D.; Gross, J.J.; Manber, R.; Mackey, S. Association between temporal summation and conditioned pain modulation in chronic low back pain: Baseline results from two clinical trials. Pain Rep. 2021, 6, e975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uszynski, M.; Purtill, H.; Coote, S. Interrater Reliability of Four Sensory Measures in People with Multiple Sclerosis. Int. J. MS Care 2016, 18, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreuders, T.A.; Selles, R.W.; van Ginneken, B.T.; Janssen, W.G.; Stam, H.J. Sensory evaluation of the hands in patients with Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease using Semmes-Weinstein monofilaments. J. Hand Ther. 2008, 21, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mailloux, C.; Beaulieu, L.D.; Wideman, T.H.; Massé-Alarie, H. Within-session test-retest reliability of pressure pain threshold and mechanical temporal summation in healthy subjects. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0245278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozano-Meca, J.A.; Gacto-Sánchez, M.; Montilla-Herrador, J. Movement-evoked pain is not associated with pain at rest or physical function in knee osteoarthritis. Eur. J. Pain 2024, 28, 987–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Mani, R.; Zeng, J.; Chapple, C.M.; Ribeiro, D.C. Test-retest reliability of movement-evoked pain and sensitivity to movement-evoked pain in patients with rotator cuff-related shoulder pain. Braz. J. Phys. Ther. 2023, 27, 100535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hinkle, D.E.; Wiersma, W.; Jurs, S.G. Applied Statistics for the Behavioral Sciences; Houghton Mifflin College Division: Boston, MA, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Simon, C.B.; Lentz, T.A.; Ellis, L.; Bishop, M.D.; Fillingim, R.B.; Riley, J.L., III; George, S.Z. Static and dynamic pain sensitivity in adults with persistent low back pain: Comparison to healthy controls and associations with movement-evoked pain versus traditional clinical pain measures. Clin. J. Pain 2021, 37, 494–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wideman, T.H.; Finan, P.H.; Edwards, R.R.; Quartana, P.J.; Buenaver, L.F.; Haythornthwaite, J.A.; Smith, M.T. Increased sensitivity to physical activity among individuals with knee osteoarthritis: Relation to pain outcomes, psychological factors, and responses to quantitative sensory testing. Pain 2014, 155, 703–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butera, K.A.; Fox, E.J.; George, S.Z. Toward a transformed understanding: From pain and movement to pain with movement. Phys. Ther. 2016, 96, 1503–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Owens, M.A.; Bulls, H.W.; Trost, Z.; Terry, S.C.; Gossett, E.W.; Wesson-Sides, K.M.; Goodin, B.R. An examination of pain catastrophizing and endogenous pain modulatory processes in adults with chronic low back pain. Pain Med. 2016, 17, 1452–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corbett, D.B.; Simon, C.B.; Manini, T.M.; George, S.Z.; Riley, J.L., III; Fillingim, R.B. Movement-evoked pain: Transforming the way we understand and measure pain. Pain 2019, 160, 757–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iio, R.; Manaka, T.; Nakazawa, K.; Hirakawa, Y.; Ito, Y.; Ogura, A.; Nakamura, H. Assessment of Prevalence and Risk Factors for Central Sensitization Related to Shoulder Osteoarthritis and Rotator Cuff Tears Using the Central Sensitization Inventory: A Cross-Sectional Study in Shoulder Surgery Patients. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 5633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woolf, C.J. Central sensitization: Implications for the diagnosis and treatment of pain. Pain 2011, 152, 2–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, M.J.; Thorn, B.; Haythornthwaite, J.A.; Keefe, F.; Martin, M.; Bradley, L.A.; Lefebvre, J.C. Theoretical perspectives on the relation between catastrophizing and pain. Clin. J. Pain 2001, 17, 52–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Characteristics | Median (IQR) |
|---|---|
| Age (Years) | 55 (9) |
| Height (cm) | 161 (14) |
| Weight (kg) | 70 (13) |
| Pain at rest | 3 (4) |
| MEP | 7 (3) |
| TS1 | 1 (1) |
| TS10 | 5 (3) |
| TSD | 3 (3) |
| Duration of symptoms (Months) | 3 (5) |
| Gender (Male/Female) | 54 (63.5%)/31 (36.5%) |
| Affected side (R/L) | 46 (54.1%)/39 (45.9%) |
| Dominant side (R/L) | 85 (100%)/0 (0%) |
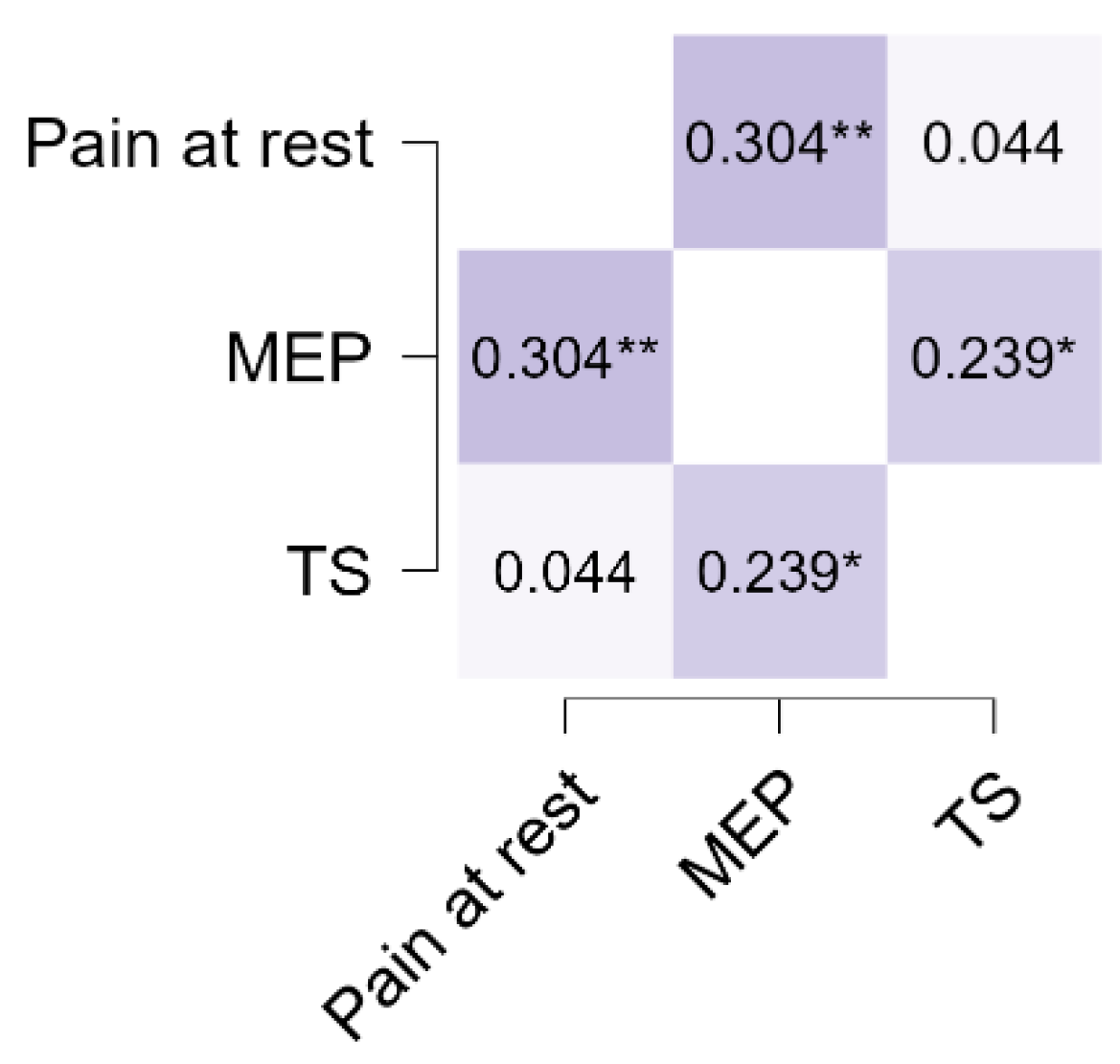
| Variable | Pain at Rest | MEP | TS | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pain at rest | Spearman’s rho | |||||
| p value | ||||||
| Upper 95% CI | ||||||
| Lower 95% CI | — | |||||
| Effect size (Fisher’s z) | — | |||||
| SE Effect size | — | |||||
| MEP | Spearman’s rho | 0.304 | ** | — | ||
| p value | 0.005 | — | ||||
| Upper 95% CI | 0.486 | — | ||||
| Lower 95% CI | 0.098 | — | ||||
| Effect size (Fisher’s z) | 0.314 | — | ||||
| SE Effect size | 0.112 | — | ||||
| TS | Spearman’s rho | 0.044 | 0.239 | * | — | |
| p value | 0.688 | 0.028 | — | |||
| Upper 95% CI | 0.255 | 0.430 | — | |||
| Lower 95% CI | −0.171 | 0.027 | — | |||
| Effect size (Fisher’s z) | 0.044 | 0.244 | — | |||
| SE Effect size | 0.110 | 0.112 | — | |||
| Group | N | Mean | SD | Statistic | p | 95% Confidence Interval | Effect Size | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pain at rest | Chronic | 45 | 2.56 | 2.14 | 836 | 0.560 | −0.00000388 | 1.000 | 0.0717 |
| Acute | 40 | 2.33 | 2.19 | ||||||
| MEP | Chronic | 45 | 7.09 | 1.92 | 700 | 0.075 | −0.00000129 | 2.000 | 0.2228 |
| Acute | 40 | 6.30 | 2.00 | ||||||
| TS | Chronic | 45 | 3.04 | 1.99 | 843 | 0.612 | −1.00 | 1.000 | 0.0639 |
| Acute | 40 | 3.27 | 1.81 | ||||||
| Predictor | Estimate | SE | Z | p | Odds Ratio | 95% Confidence Interval | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower | Upper | ||||||
| Pain at rest | 0.018 | 0.111 | 0.163 | 0.871 | 1.018 | 0.82 | 1.264 |
| MEP | −0.2571 | 0.13 | −1.978 | 0.048 | 0.773 | 0.599 | 0.998 |
| TS | 0.1421 | 0.126 | 1.132 | 0.258 | 1.153 | 0.901 | 1.475 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Prabhu B, A.; Maiya, A.G.; Pandey, V.; Acharya, K.K.V.; Jaganathan, V.; Elliott, J.M.; Meeus, M. Movement-Evoked Pain and Temporal Summation in Individuals with Symptomatic Rotator Cuff Tears: A Cross-Sectional Study. Life 2025, 15, 1394. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15091394
Prabhu B A, Maiya AG, Pandey V, Acharya KKV, Jaganathan V, Elliott JM, Meeus M. Movement-Evoked Pain and Temporal Summation in Individuals with Symptomatic Rotator Cuff Tears: A Cross-Sectional Study. Life. 2025; 15(9):1394. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15091394
Chicago/Turabian StylePrabhu B, Anupama, Arun G. Maiya, Vivek Pandey, Kiran K. V. Acharya, Vennila Jaganathan, James M. Elliott, and Mira Meeus. 2025. "Movement-Evoked Pain and Temporal Summation in Individuals with Symptomatic Rotator Cuff Tears: A Cross-Sectional Study" Life 15, no. 9: 1394. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15091394
APA StylePrabhu B, A., Maiya, A. G., Pandey, V., Acharya, K. K. V., Jaganathan, V., Elliott, J. M., & Meeus, M. (2025). Movement-Evoked Pain and Temporal Summation in Individuals with Symptomatic Rotator Cuff Tears: A Cross-Sectional Study. Life, 15(9), 1394. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15091394






