A Programmable Finite-Replicated Organism Framework for Balanced Safety and Functionality
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Strains and Culture Conditions
2.2. Plasmid Construction
2.3. Quantitative Detection of Aminoacyl-tRNA Synthetase Efficiency
2.4. Flow-Cytometry (FCM) Measurement
2.5. Strain Construction of Essential Gene Editing in E. coli Genome
2.6. Solid Media Escape Frequency
2.7. Observation of Bacterial Growth with Suicide Module—Toxin Expression
2.8. Quantification and Observation of Bacterial Viability After Cl2Y Removal
2.9. Growth Dynamics Quantification of FROs
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
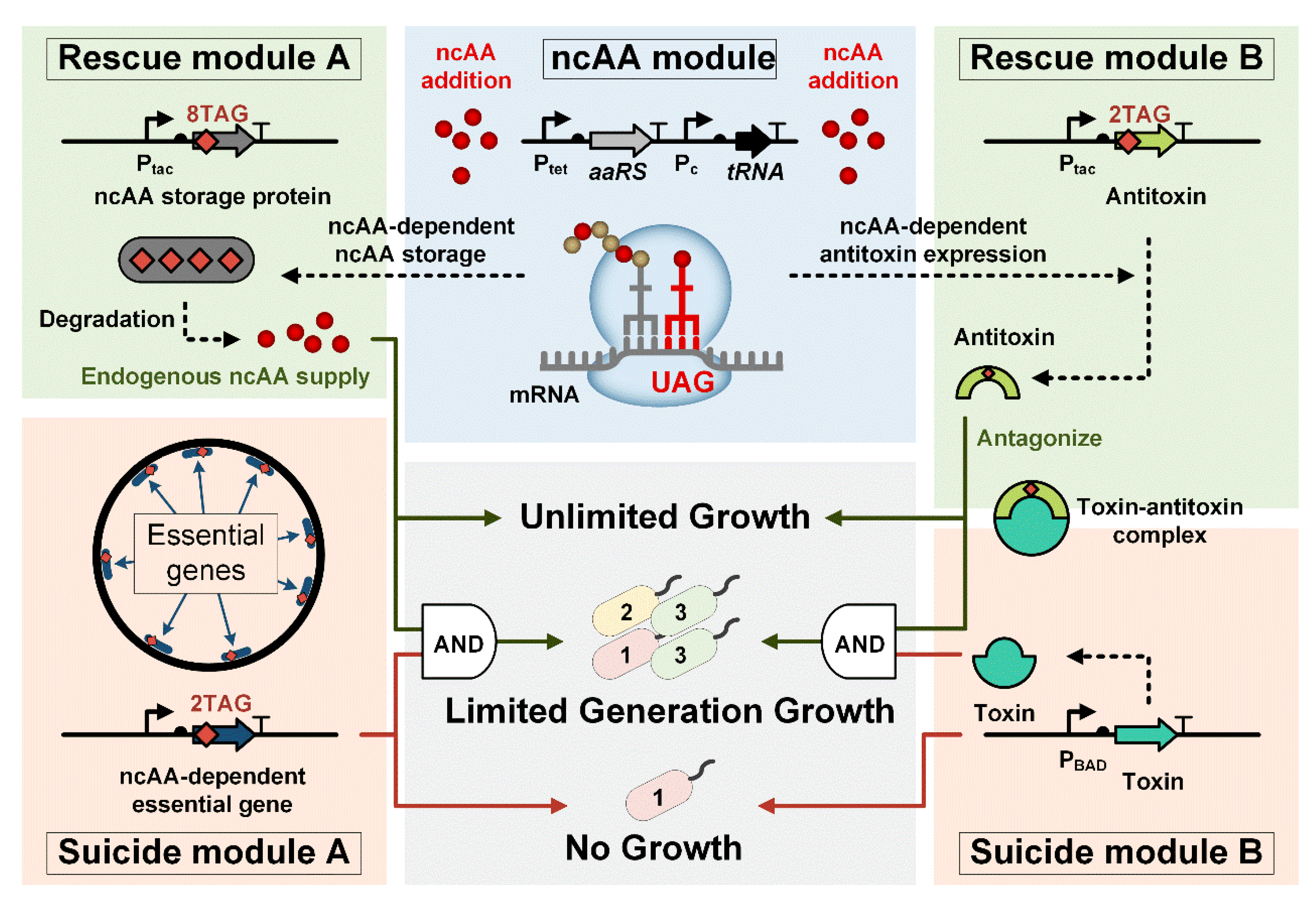
3.1. Design of the Finite-Replicated Organism (FRO)
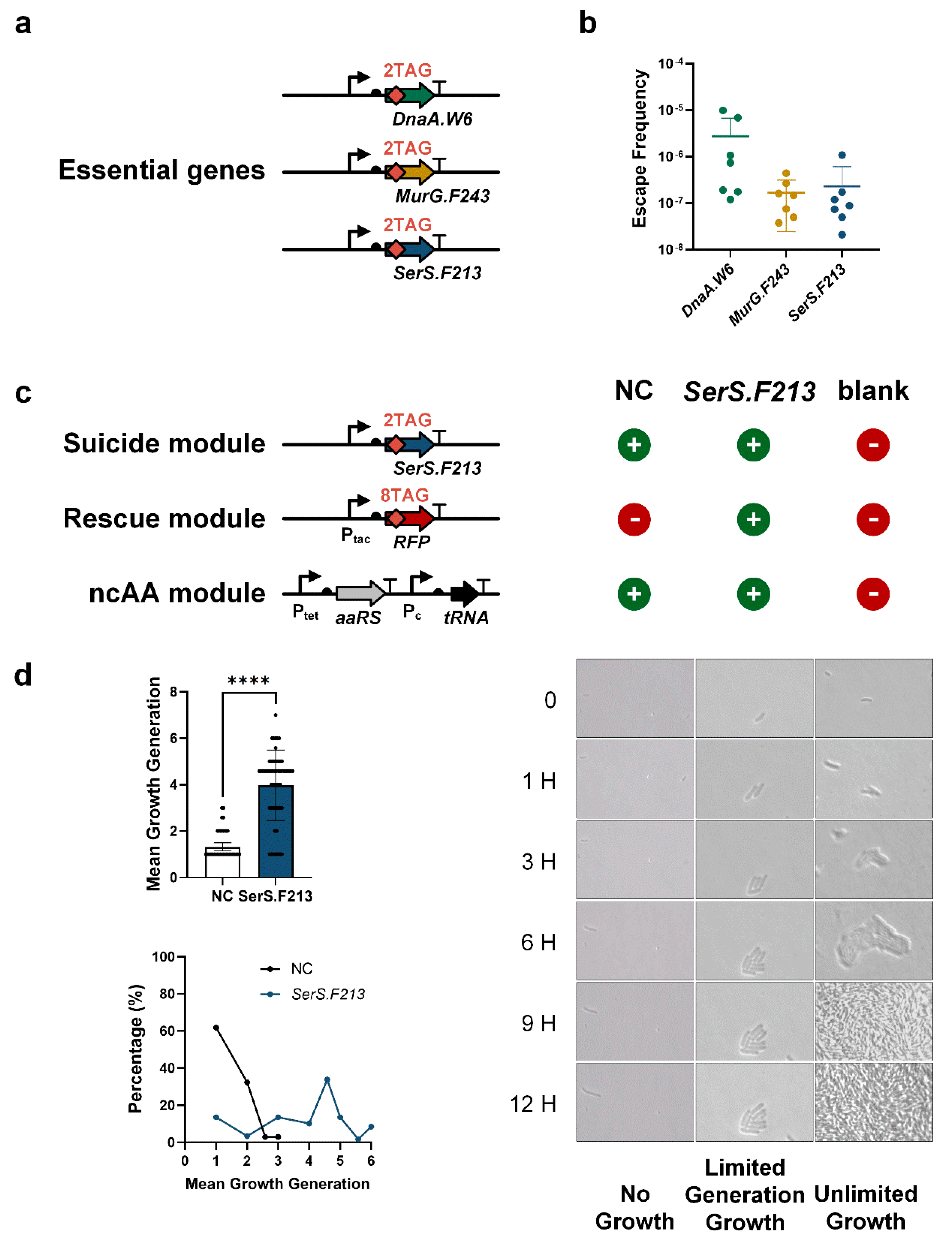
3.2. Finite Replication by FROs Based on Essential Gene Strategy
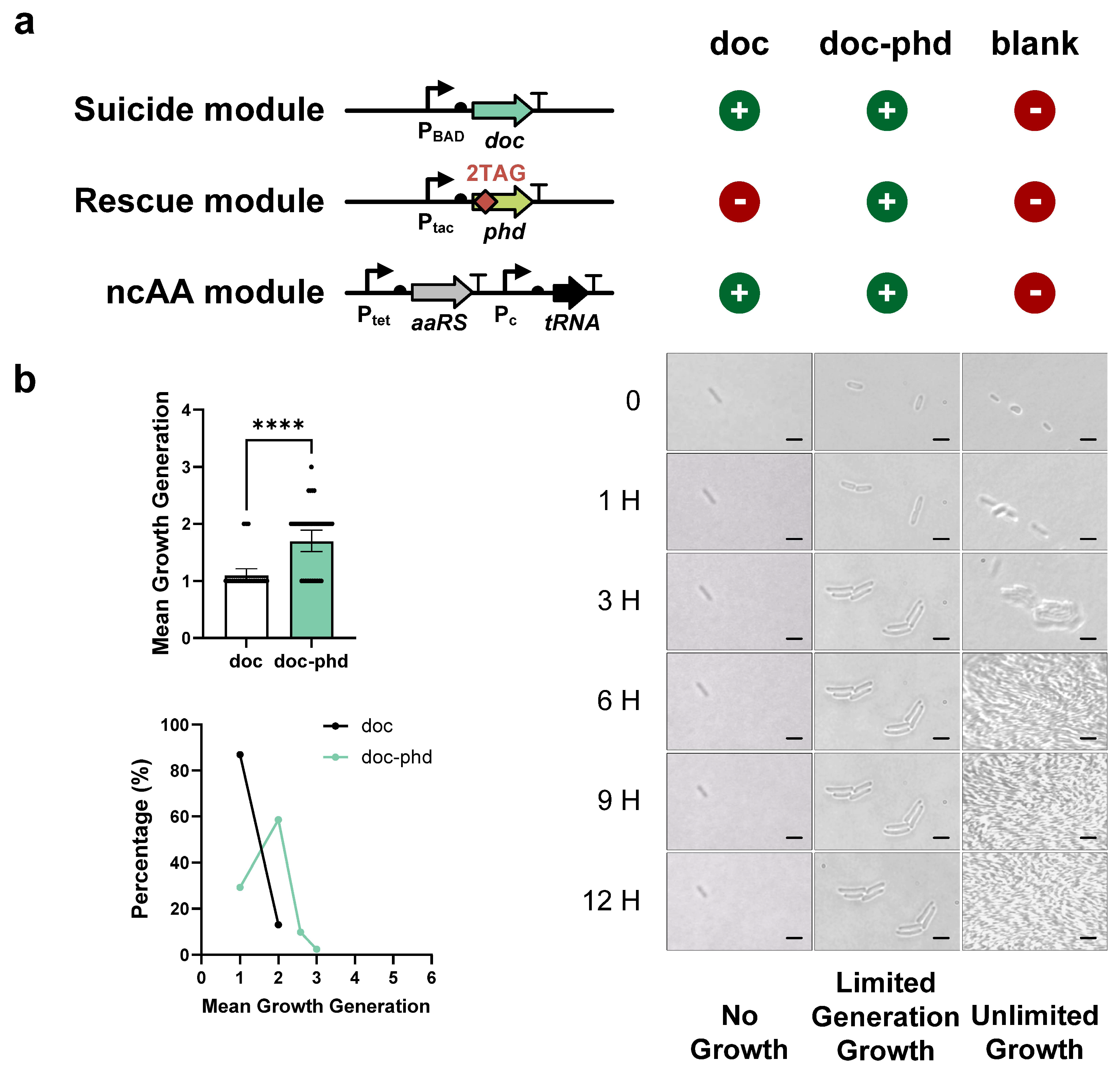
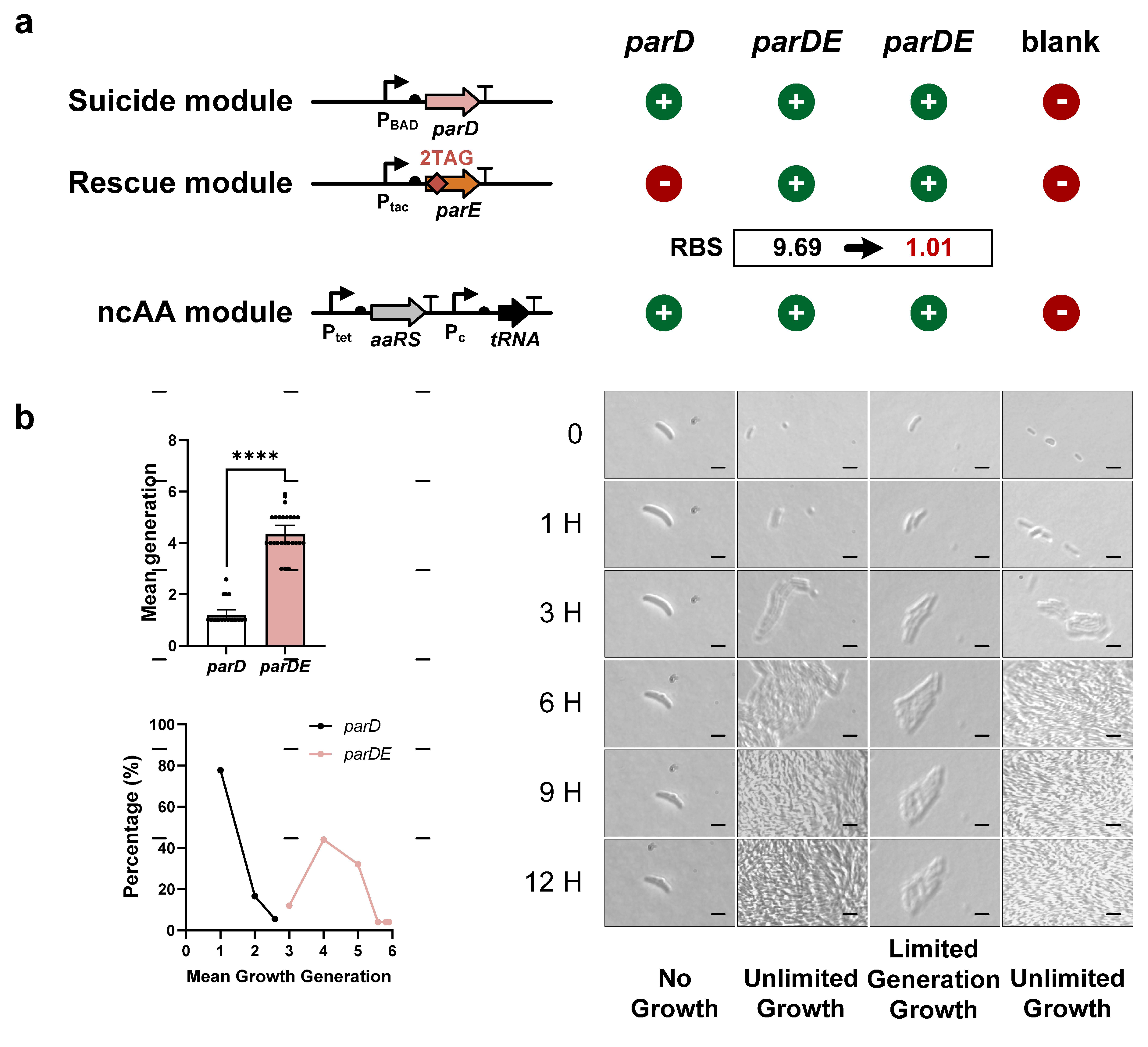
3.3. Finite Replication by FROs Based on Type II TA Systems
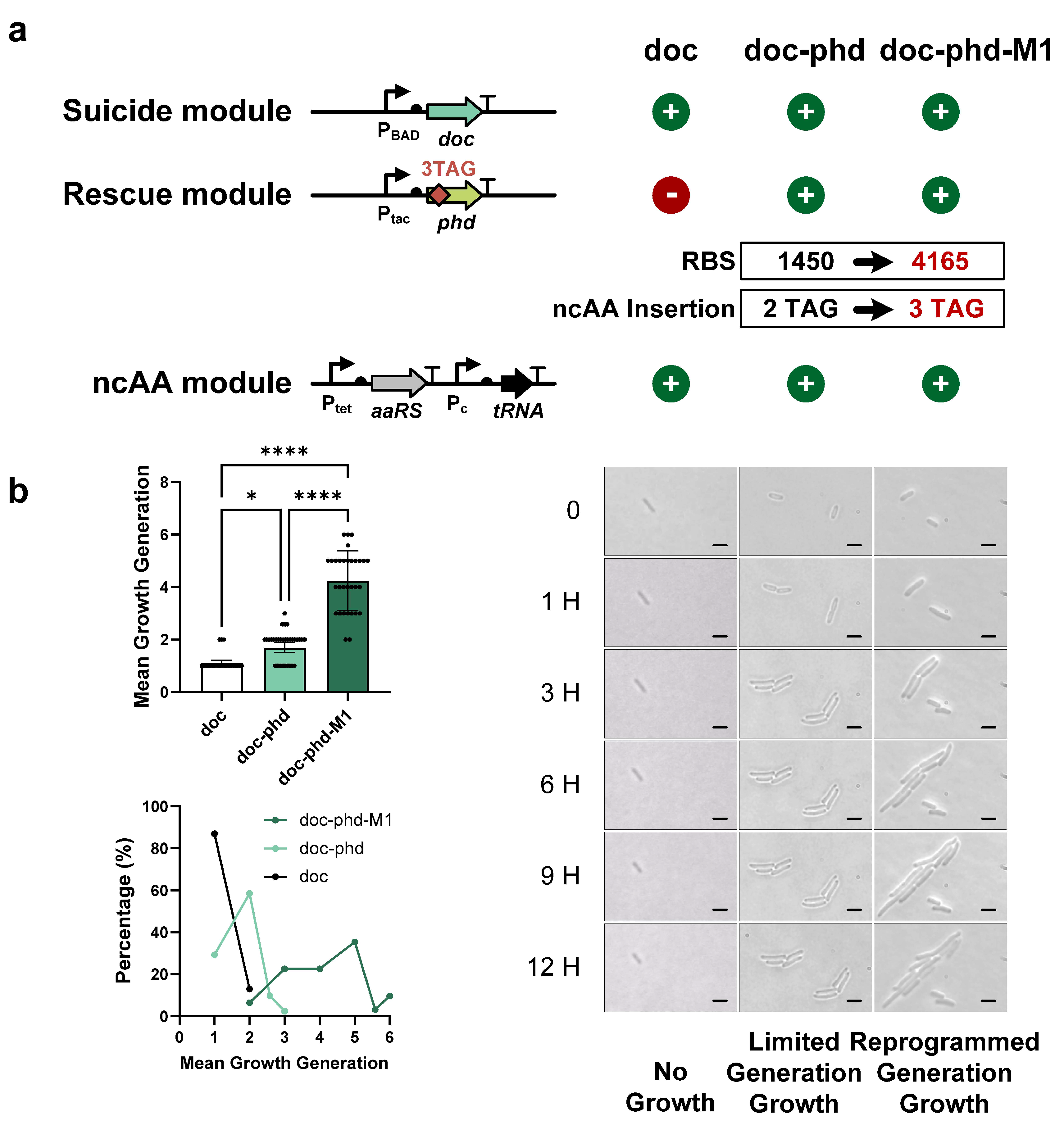
3.4. Modulation of the Growth Generation of FROs
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gruzdev, N.; Pitcovski, J.; Katz, C.; Ruimi, N.; Eliahu, D.; Noach, C.; Rosenzweig, E.; Finger, A.; Shahar, E. Development of toxin-antitoxin self-destructive bacteria, aimed for salmonella vaccination. Vaccine 2023, 41, 4918–4925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagasawa, Y.; Nakayama, M.; Kato, Y.; Ogawa, Y.; Aribam, S.D.; Tsugami, Y.; Iwata, T.; Mikami, O.; Sugiyama, A.; Onishi, M.; et al. A novel vaccine strategy using quick and easy conversion of bacterial pathogens to unnatural amino acid-auxotrophic suicide derivatives. Microbiol. Spectr. 2024, 12, e03557-23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauch, S.; Jasny, E.; Schmidt, K.E.; Petsch, B. New Vaccine Technologies to Combat Outbreak Situations. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brisse, M.; Vrba, S.M.; Kirk, N.; Liang, Y.; Ly, H. Emerging Concepts and Technologies in Vaccine Development. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 58307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, S.; Gyles, C.; Wilkie, B. Evaluation of an aroA mutant Salmonella typhimurium vaccine in chickens using modified semisolid Rappaport Vassiliadis medium to monitor faecal shedding. Veter. Microbiol. 1997, 54, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nan, W.; Qin, L.; Wang, Y.; Yhang, Y.; Tan, P.; Chen, Y.; Mao, K.; Chen, Y. A rapid minor groove binder PCRmethod for distinguishing the vaccine strain Brucella abortus, 1.0.4.M. BMC Vet. Res. 2018, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, H.; Liu, X.; Peng, Q. The advances in brucellosis vaccines. Vaccine 2019, 37, 3981–3988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandell, D.J.; Lajoie, M.J.; Mee, M.T.; Takeuchi, R.; Kuznetsov, G.; Norville, J.E.; Gregg, C.J.; Stoddard, B.L.; Church, G.M. Biocontainment of genetically modified organisms by synthetic protein design. Nature 2015, 518, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lajoie, M.J.; Rovner, A.J.; Goodman, D.B.; Aerni, H.R.; Haimovich, A.D.; Kuznetsov, G.; Mercer, J.A.; Wang, H.H.; Carr, P.A.; Mosberg, J.A.; et al. Genomically recoded organisms expand biological functions. Science 2013, 342, 357–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abe, Y.; Jo, T.; Matsuda, Y.; Matsunaga, C.; Katayama, T.; Ueda, T. Structure function of DnaAN-terminal domains: Specific sites mechanisms in inter-DnaA interaction in DnaB helicase loading on oriC. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 17816–17827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, Y. An engineered bacterium auxotrophic for an unnatural amino acid: A novel biological containment system. PeerJ 2015, 3, e1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jurėnas, D.; Fraikin, N.; Goormaghtigh, F.; Van Melderen, L. Biology and evolution of bacterial toxin–antitoxin systems. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2022, 20, 335–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuster, C.F.; Bertram, R. Toxin-antitoxin systems are ubiquitous and versatile modulators of prokaryotic cell fate. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2013, 340, 73–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Jiang, L.; Li, J.; Wang, L.; Yu, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Lv, X.; Gong, W.; Lu, Y.; Wang, J. Significant Expansion of Fluorescent Protein Sensing Ability through the Genetic Incorporation of Superior Photo-Induced Electron-Transfer Quenchers. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 13094–13097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salis, H.M. The Ribosome Binding Site Calculator, in Synthetic Biology, Part B-Computer Aided Design and DNA Assembly; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2011; pp. 19–42. [Google Scholar]
- Ao, X.; Yao, Y.; Li, T.; Yang, T.-T.; Dong, X.; Zheng, Z.-T.; Chen, G.-Q.; Wu, Q.; Guo, Y. A Multiplex Genome Editing Method for Escherichia coli Based on CRISPR-Cas12a. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Chen, B.; Duan, C.; Sun, B.; Yang, J.; Yang, S.; Kelly, R.M. Multigene Editing in the Escherichia coli Genome via the CRISPR-Cas9 System. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 81, 2506–2514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Lin, Z.; Huang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Tang, Y.-J.; Chen, T.; Zhao, X. Metabolic engineering of Escherichia coli using CRISPR–Cas9 meditated genome editing. Metab. Eng. 2015, 31, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cha, J.S.; Pujol, C.; I Kado, C. Identification and characterization of a Pantoea citrea gene encoding glucose dehydrogenase that is essential for causing pink disease of pineapple. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1997, 63, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pujol, C.J.; Kado, C.I. Genetic and Biochemical Characterization of the Pathway in Pantoea citrea Leading to Pink Disease of Pineapple. J. Bacteriol. 2000, 182, 2230–2237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharan, S.K.; Thomason, L.C.; Kuznetsov, S.G.; Court, D.L. Recombineering: A homologous recombination-based method of genetic engineering. Nat. Protoc. 2009, 4, 206–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rovner, A.J.; Haimovich, A.D.; Katz, S.R.; Li, Z.; Grome, M.W.; Gassaway, B.M.; Amiram, M.; Patel, J.R.; Gallagher, R.R.; Rinehart, J.; et al. Recoded organisms engineered to depend on synthetic amino acids. Nature 2015, 518, 89–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lajoie, M.J.; Kosuri, S.; Mosberg, J.A.; Gregg, C.J.; Zhang, D.; Church, G.M. Probing the Limits of Genetic Recoding in Essential Genes. Science 2013, 342, 361–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, S.; Gross, B.; Walker, S.E. Coli MurG: A Paradigm for a Superfamily of Glycosyltransferases. Curr. Drug Targets Infect. Disord. 2001, 1, 201–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galindo-Feria, A.S.; Notarnicola, A.; Lundberg, I.E.; Horuluoglu, B. Aminoacyl-tRNA Synthetases: On Anti-Synthetase Syndrome and Beyond. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 866087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, F.; Van Melderen, L. Toxins-antitoxins: Diversity, evolution and function. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2011, 46, 386–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guglielmini, J.; Van Melderen, L. Bacterial toxin-antitoxin systems. Mob. Genet. Elem. 2014, 1, 283–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leplae, R.; Geeraerts, D.; Hallez, R.; Guglielmini, J.; Drèze, P.; Van Melderen, L. Diversity of bacterial type II toxin–antitoxin systems: A comprehensive search and functional analysis of novel families. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, 5513–5525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro-Roa, D.; Garcia-Pino, A.; De Gieter, S.; van Nuland, N.A.J.; Loris, R.; Zenkin, N. The Fic protein Doc uses an inverted substrate to phosphorylate and inactivate EF-Tu. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2013, 9, 811–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hallez, R.; Geeraerts, D.; Sterckx, Y.; Mine, N.; Loris, R.; Van Melderen, L. New toxins homologous to ParE belonging to three-component toxin-antitoxin systems in Escherichia coli O157:H7. Mol. Microbiol. 2010, 76, 719–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamphuis, M.B.; Monti, M.C.; Heuvel, R.H.H.v.D.; Lopez-Villarejo, J.; Diaz-Orejas, R.; Boelens, R. Structure and Function of Bacterial Kid-Kis and Related Toxin-Antitoxin Systems. Protein Pept. Lett. 2007, 14, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Critchlow, S.E.; O’Dea, M.H.; Howells, A.J.; Couturier, M.; Gellert, M.; Maxwell, A. The interaction of the F plasmid killer protein, CcdB, with DNA gyrase: Induction of DNA cleavage and blocking of transcription. J. Mol. Biol. 1997, 273, 826–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poria, R.; Kala, D.; Nagraik, R.; Dhir, Y.; Dhir, S.; Singh, B.; Kaushik, N.K.; Noorani, S.; Kaushal, A.; Gupta, S. Vaccine development: Current trends and technologies. Life Sci. 2023, 336, 122331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grome, M.W.; Nguyen, M.T.A.; Moonan, D.W.; Mohler, K.; Gurara, K.; Wang, S.; Hemez, C.; Stenton, B.J.; Cao, Y.; Radford, F.; et al. Engineering a genomically recoded organism with one stop codon. Nature 2025, 639, 512–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, M.; Du, P.; Meng, F.; Zhang, W.; Xiang, Y.; Wu, Q.; Lou, C. A Programmable Finite-Replicated Organism Framework for Balanced Safety and Functionality. Life 2025, 15, 1381. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15091381
Wang M, Du P, Meng F, Zhang W, Xiang Y, Wu Q, Lou C. A Programmable Finite-Replicated Organism Framework for Balanced Safety and Functionality. Life. 2025; 15(9):1381. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15091381
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Mengyuan, Pei Du, Fankang Meng, Wenhui Zhang, Yanhui Xiang, Qiong Wu, and Chunbo Lou. 2025. "A Programmable Finite-Replicated Organism Framework for Balanced Safety and Functionality" Life 15, no. 9: 1381. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15091381
APA StyleWang, M., Du, P., Meng, F., Zhang, W., Xiang, Y., Wu, Q., & Lou, C. (2025). A Programmable Finite-Replicated Organism Framework for Balanced Safety and Functionality. Life, 15(9), 1381. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15091381







