Olfactory Network Functional Connectivity as a Marker for Parkinson’s Disease Severity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Study Subjects
2.2. PDAR and PDT Classification
2.3. MRI Imaging
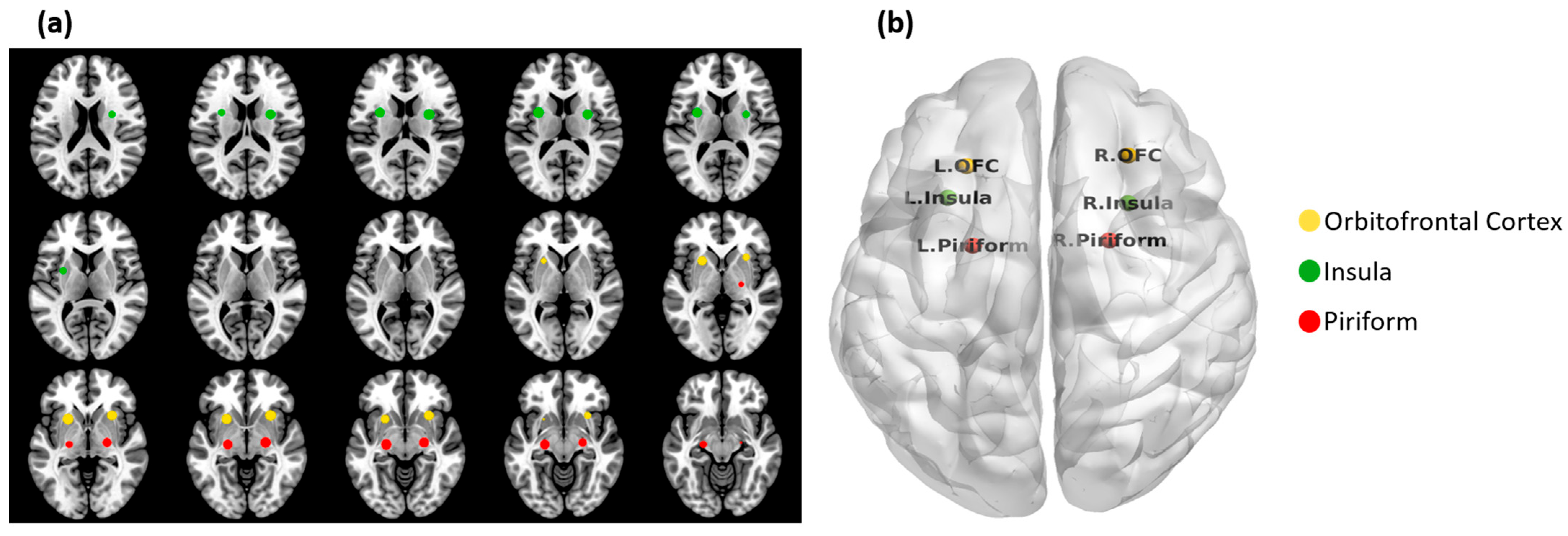
2.4. Olfactory Network
2.5. Functional Connectivity Analysis
2.6. Voxel-Based Morphometry
2.7. Statistical Analysis
2.8. Multivariate Classification of ON FC Values
2.9. Data Availability
3. Results
3.1. Demographic and Cognitive Comparisons
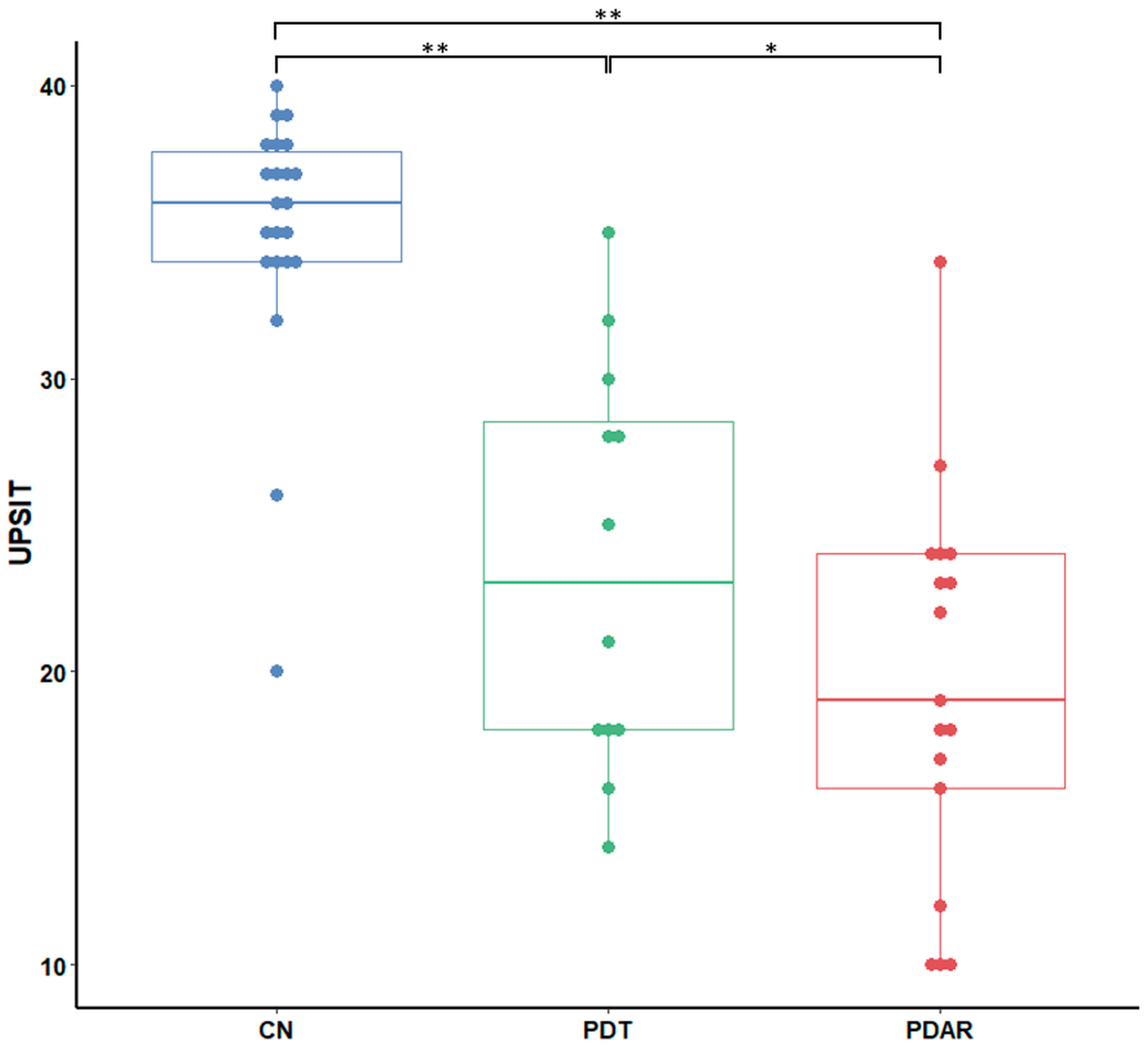
3.2. UPSIT Group Differences
3.3. Volume Differences
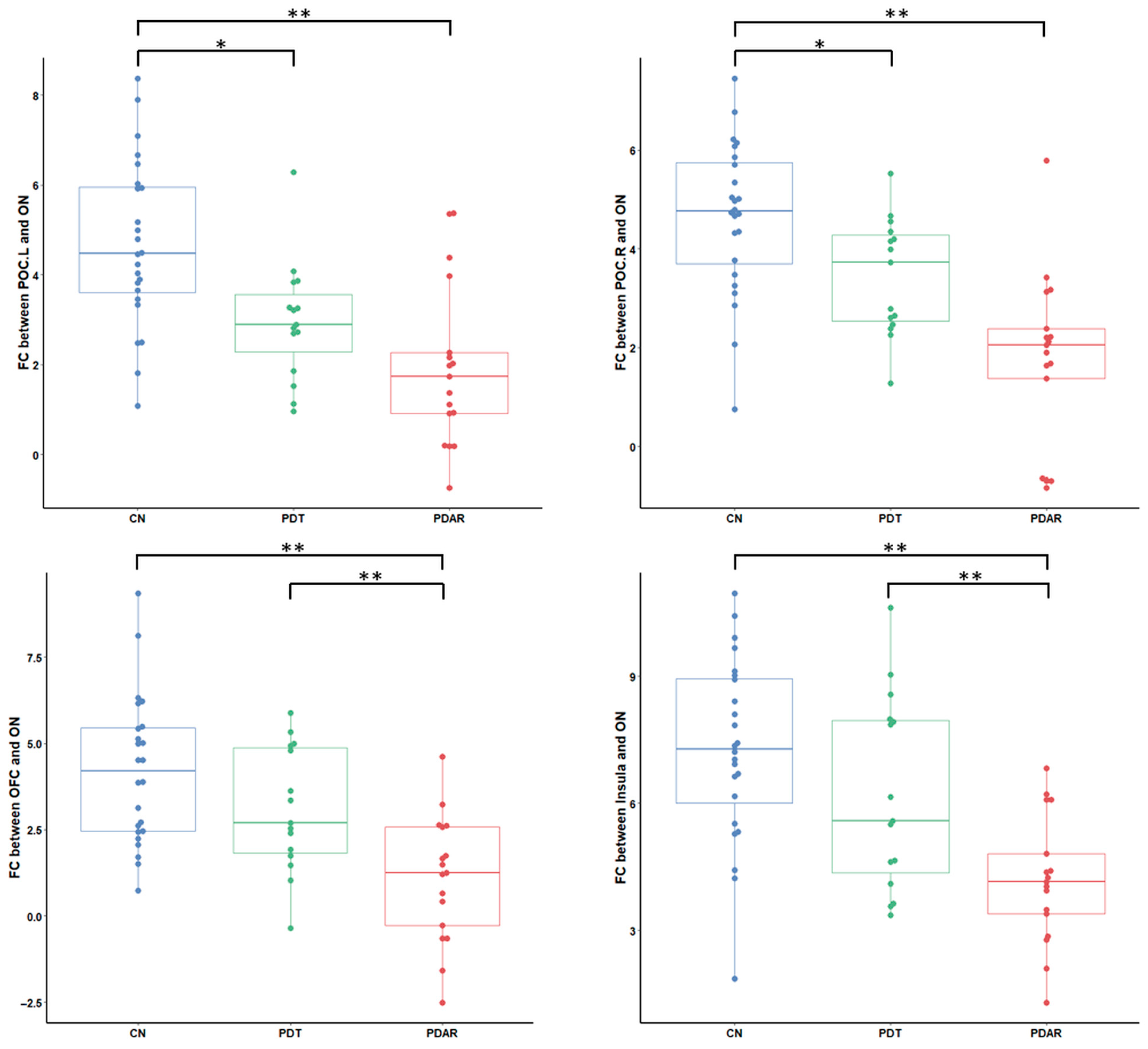
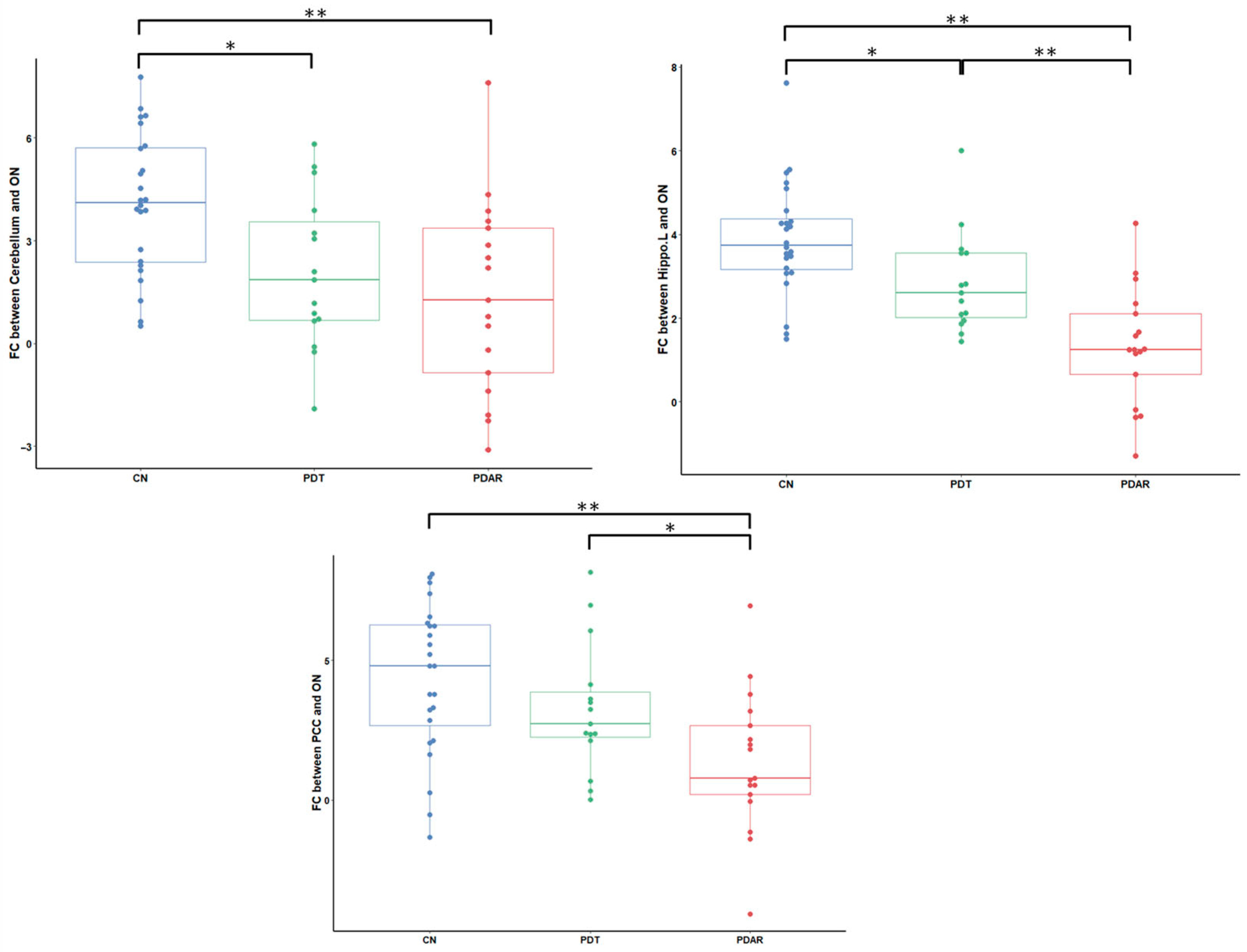
3.4. ON FC Group Differences
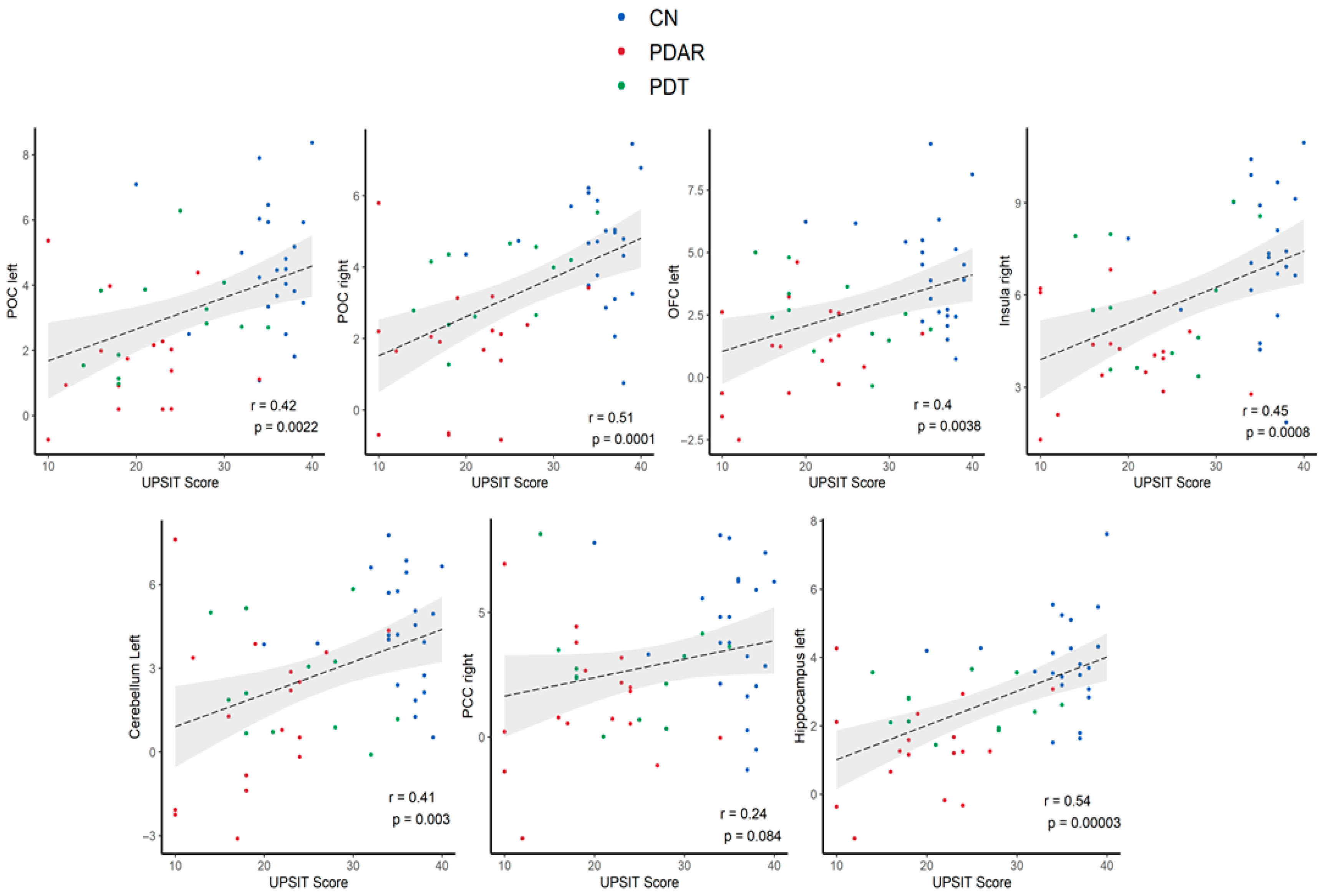
3.5. Correlations Between ON FC and UPSIT Scores
3.6. Multivariate Classification of ON FC
4. Discussion
4.1. Impact of Non-Olfactory Cognitive Scores on UPSIT
4.2. ON FC Distribution
4.3. Network Perspective of Olfactory Function in PD
4.4. Resting-State fMRI
4.5. Gray Matter Comparison
4.6. Multivariate ON FC
4.7. Study Limitations and Future Directions
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Martí, M.J.; Tolosa, E. New Guidelines for Diagnosis of Parkinson Disease. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2013, 9, 190–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lees, A.J.; Hardy, J.; Revesz, T. Parkinson’s Disease. Lancet 2009, 373, 2055–2066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zetusky, W.J.; Jankovic, J.; Pirozzolo, F.J. The Heterogeneity of Parkinson’s Disease: Clinical and Prognostic Implications. Neurology 1985, 35, 522–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jankovic, J.; McDermott, M.; Carter, J.; Gauthier, S.; Goetz, C.; Golbe, L.; Huber, S.; Koller, W.; Olanow, C.; Shoulson, I.; et al. Variable Expression of Parkinson’s Disease: A Base-Line Analysis of the Datatop Cohort. The Parkinson Study Group. Neurology 1990, 40, 1529–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, S.; Foltynie, T.; Blackwell, A.D.; Robbins, T.W.; Owen, A.M.; Barker, R.A. Heterogeneity of Parkinson’s Disease in the Early Clinical Stages Using a Data Driven Approach. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2005, 76, 343–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eggers, C.; Pedrosa, D.J.; Kahraman, D.; Maier, F.; Lewis, C.J.; Fink, G.R.; Schmidt, M.; Timmermann, L. Parkinson Subtypes Progress Differently in Clinical Course and Imaging Pattern. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e46813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helmich, R.C.; Hallett, M.; Deuschl, G.; Toni, I.; Bloem, B.R. Cerebral Causes and Consequences of Parkinsonian Resting Tremor: A Tale of Two Circuits? Brain 2012, 135, 3206–3226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, M.M.; Du, G.; Sen, S.; Kawaguchi, A.; Truong, Y.; Lee, S.; Mailman, R.B.; Huang, X. Differential Involvement of Striato- and Cerebello-Thalamo-Cortical Pathways in Tremor- and Akinetic/Rigid-Predominant Parkinson’s Disease. Neuroscience 2011, 177, 230–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaidel, A.; Arkadir, D.; Israel, Z.; Bergman, H. Akineto-Rigid Vs. Tremor Syndromes in Parkinsonism. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2009, 22, 387–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schapira, A.H.; Chaudhuri, K.R.; Jenner, P. Non-Motor Features of Parkinson Disease. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2017, 18, 435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solla, P.; Wang, Q.; Frau, C.; Floris, V.; Loy, F.; Sechi, L.A.; Masala, C. Olfactory Impairment Is the Main Predictor of Higher Scores at Rem Sleep Behavior Disorder (Rbd) Screening Questionnaire in Parkinson’s Disease Patients. Brain Sci. 2023, 13, 599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doty, R.L. Olfactory Dysfunction in Parkinson Disease. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2012, 8, 329–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siderowf, A.; Jennings, D.; Eberly, S.; Oakes, D.; Hawkins, K.A.; Ascherio, A.; Stern, M.B.; Marek, K.; Investigators, P. Impaired Olfaction and Other Prodromal Features in the Parkinson at-Risk Syndrome Study. Mov. Disord. 2012, 27, 406–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Postuma, R.; Gagnon, J.-F. Cognition and Olfaction in Parkinson’s Disease. Brain 2010, 133, e160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fullard, M.E.; Tran, B.; Xie, S.X.; Toledo, J.B.; Scordia, C.; Linder, C.; Purri, R.; Weintraub, D.; Duda, J.E.; Chahine, L.M. Olfactory Impairment Predicts Cognitive Decline in Early Parkinson’s Disease. Park. Relat. Disord. 2016, 25, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helmich, R.C.; Janssen, M.J.; Oyen, W.J.; Bloem, B.R.; Toni, I. Pallidal Dysfunction Drives a Cerebellothalamic Circuit into Parkinson Tremor. Ann. Neurol. 2011, 69, 269–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponsen, M.M.; Stoffers, D.; Booij, J.; van Eck-Smit, B.L.; Wolters, E.C.; Berendse, H.W. Idiopathic Hyposmia as a Preclinical Sign of Parkinson’s Disease. Ann. Neurol. 2004, 56, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tissingh, G.; Berendse, H.; Bergmans, P.; DeWaard, R.; Drukarch, B.; Stoof, J.; Wolters, E.C. Loss of Olfaction in De Novo and Treated Parkinson’s Disease: Possible Implications for Early Diagnosis. Mov. Disord. 2001, 16, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poewe, W.; Seppi, K.; Tanner, C.M.; Halliday, G.M.; Brundin, P.; Volkmann, J.; Schrag, A.-E.; Lang, A.E. Parkinson Disease. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2017, 3, 17013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solla, P.; Masala, C.; Ercoli, T.; Orofino, G.; Loy, F.; Pinna, I.; Fadda, L.; Defazio, G. Olfactory Impairment in Parkinson’s Disease Patients with Tremor Dominant Subtype Compared to Those with Akinetic Rigid Dominant Subtype: A Pilot Study. Brain Sci. 2022, 12, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stern, M.B.; Doty, R.; Dotti, M.; Corcoran, P.; Crawford, D.; McKeown, D.; Adler, C.; Gollomp, S.; Hurtig, H. Olfactory Function in Parkinson’s Disease Subtypes. Neurology 1994, 44, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karunanayaka, P.R.; Lee, E.Y.; Lewis, M.M.; Sen, S.; Eslinger, P.J.; Yang, Q.X.; Huang, X. Default Mode Network Differences between Rigidity- and Tremor-Predominant Parkinson’s Disease. Cortex 2016, 81, 239–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cieri, F.; Giriprakash, P.; Nandy, R.; Zhuang, X.; Caldwell, J.Z.K.; Cordes, D. Functional Connectivity Differences of the Olfactory Network in Parkinson’s Disease, Mild Cognitive Impairment and Cognitively Normal Individuals: A Resting-State Fmri Study. Neuroscience 2024, 559, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yahiaoui-Doktor, M.; Luck, T.; Riedel-Heller, S.G.; Loeffler, M.; Wirkner, K.; Engel, C. Olfactory Function Is Associated with Cognitive Performance: Results from the Population-Based Life-Adult-Study. Alzheimers Res. Ther. 2019, 11, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchida, S.; Shimada, C.; Sakuma, N.; Kagitani, F.; Kan, A.; Awata, S. The Relationship between Olfaction and Cognitive Function in the Elderly. J. Physiol. Sci. 2020, 70, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hummel, T.; Fliessbach, K.; Abele, M.; Okulla, T.; Reden, J.; Reichmann, H.; Wüllner, U.; Haehner, A. Olfactory Fmri in Patients with Parkinson’s Disease. Front. Integr. Neurosci. 2010, 4, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doty, R.L.; Shaman, P.; Dann, M. Development of the University of Pennsylvania Smell Identification Test: A Standardized Microencapsulated Test of Olfactory Function. Physiol. Behav. 1984, 32, 489–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodyear, M.D.; Krleza-Jeric, K.; Lemmens, T. The Declaration of Helsinki. BMJ 2007, 335, 624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calne, D.; Snow, B.; Lee, C. Criteria for Diagnosing Parkinson’s Disease. Ann. Neurol. 1992, 32, S125–S127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiess, M.C.; Zheng, H.; Soukup, V.M.; Bonnen, J.G.; Nauta, H.J. Parkinson’s Disease Subtypes: Clinical Classification and Ventricular Cerebrospinal Fluid Analysis. Park. Relat. Disord. 2000, 6, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seubert, J.; Freiherr, J.; Djordjevic, J.; Lundström, J.N. Statistical Localization of Human Olfactory Cortex. NeuroImage 2013, 66, 333–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobia, M.J.; Yang, Q.X.; Karunanayaka, P. Intrinsic Intranasal Chemosensory Brain Networks Shown by Resting-State Functional Mri. Neuroreport 2016, 27, 527–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, J.; Testa, N.; Jordan, R.; Elyan, R.; Kanekar, S.; Wang, J.; Eslinger, P.; Yang, Q.X.; Zhang, B.; Karunanayaka, P.R. Functional Connectivity between the Resting-State Olfactory Network and the Hippocampus in Alzheimer’s Disease. Brain Sci. 2019, 9, 338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, E.-Y.; Sen, S.; Eslinger, P.J.; Wagner, D.; Shaffer, M.L.; Kong, L.; Lewis, M.M.; Du, G.; Huang, X. Early Cortical Gray Matter Loss and Cognitive Correlates in Non-Demented Parkinson’s Patients. Park. Relat. Disord. 2013, 19, 1088–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brodersen, K.H.; Schofield, T.M.; Leff, A.P.; Ong, C.S.; Lomakina, E.I.; Buhmann, J.M.; Stephan, K.E. Generative Embedding for Model-Based Classification of Fmri Data. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2011, 7, e1002079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braak, H.; Del Tredici, K.; Rüb, U.; De Vos, R.A.; Steur, E.N.J.; Braak, E. Staging of Brain Pathology Related to Sporadic Parkinson’s Disease. Neurobiol. Aging 2003, 24, 197–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attems, J.; Walker, L.; Jellinger, K.A. Olfactory Bulb Involvement in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Acta Neuropathol. 2014, 127, 459–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beach, T.G.; White, C.L.; Hamilton, R.L.; Duda, J.E.; Iwatsubo, T.; Dickson, D.W.; Leverenz, J.B.; Roncaroli, F.; Buttini, M.; Hladik, C.L. Evaluation of A-Synuclein Immunohistochemical Methods Used by Invited Experts. Acta Neuropathol. 2008, 116, 277–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Den Heuvel, M.P.; Pol, H.E.H. Exploring the Brain Network: A Review on Resting-State Fmri Functional Connectivity. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2010, 20, 519–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fishman, P.S. Paradoxical Aspects of Parkinsonian Tremor. Mov. Disord. 2008, 23, 168–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottfried, J.A. Central Mechanisms of Odour Object Perception. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2010, 11, 628–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostka, J.K.; Bitzenhofer, S.H. How the Sense of Smell Influences Cognition Throughout Life. Neuroforum 2022, 28, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ercoli, T.; Masala, C.; Cadeddu, G.; Mascia, M.M.; Orofino, G.; Gigante, A.F.; Solla, P.; Defazio, G.; Rocchi, L. Does Olfactory Dysfunction Correlate with Disease Progression in Parkinson’s Disease? A Systematic Review of the Current Literature. Brain Sci. 2022, 12, 513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witt, M.; Bormann, K.; Gudziol, V.; Pehlke, K.; Barth, K.; Minovi, A.; Hähner, A.; Reichmann, H.; Hummel, T. Biopsies of Olfactory Epithelium in Patients with Parkinson’s Disease. Mov. Disord. 2009, 24, 906–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haehner, A.; Schöpf, V.; Loureiro, A.; Linn, J.; Reichmann, H.; Hummel, T.; Kitzler, H.H. Substantia Nigra Fractional Anisotropy Changes Confirm the Pd at-Risk Status of Patients with Idiopathic Smell Loss. Park. Relat. Disord. 2018, 50, 113–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domellöf, M.E.; Lundin, K.-F.; Edström, M.; Forsgren, L. Olfactory Dysfunction and Dementia in Newly Diagnosed Patients with Parkinson’s Disease. Park. Relat. Disord. 2017, 38, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marin, C.; Vilas, D.; Langdon, C.; Alobid, I.; López-Chacón, M.; Haehner, A.; Hummel, T.; Mullol, J. Olfactory Dysfunction in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Curr. Allergy Asthma Rep. 2018, 18, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, T.L.; Sadikot, A.F.; Djordjevic, J. Metacognitive Knowledge of Olfactory Dysfunction in Parkinson’s Disease. Brain Cogn. 2016, 104, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dirkx, M.F.; den Ouden, H.; Aarts, E.; Timmer, M.; Bloem, B.R.; Toni, I.; Helmich, R.C. The Cerebral Network of Parkinson’s Tremor: An Effective Connectivity Fmri Study. J. Neurosci. 2016, 36, 5362–5372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mundinano, I.-C.; Caballero, M.-C.; Ordóñez, C.; Hernandez, M.; DiCaudo, C.; Marcilla, I.; Erro, M.-E.; Tunon, M.-T.; Luquin, M.-R. Increased Dopaminergic Cells and Protein Aggregates in the Olfactory Bulb of Patients with Neurodegenerative Disorders. Acta Neuropathol. 2011, 122, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Lane, G.; Cooper, S.L.; Kahnt, T.; Zelano, C. Characterizing Functional Pathways of the Human Olfactory System. eLife 2019, 8, e47177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, M.W.; Bassett, D.S.; Power, J.D.; Braver, T.S.; Petersen, S.E. Intrinsic and Task-Evoked Network Architectures of the Human Brain. Neuron 2014, 83, 238–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braak, H.; Braak, E. Evolution of Neuronal Changes in the Course of Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Neural. Transm. Suppl. 1998, 53, 127–140. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Braak, H.; Rub, U.; Jansen Steur, E.N.; Del Tredici, K.; de Vos, R.A. Cognitive Status Correlates with Neuropathologic Stage in Parkinson Disease. Neurology 2005, 64, 1404–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; You, H.; Liu, J.-F.; Ni, D.-F.; Zhang, Z.-X.; Guan, J. Association of Olfactory Bulb Volume and Olfactory Sulcus Depth with Olfactory Function in Patients with Parkinson Disease. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2011, 32, 677–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deco, G.; Jirsa, V.K.; McIntosh, A.R. Emerging Concepts for the Dynamical Organization of Resting-State Activity in the Brain. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2011, 12, 43–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honey, C.J.; Kötter, R.; Breakspear, M.; Sporns, O. Network Structure of Cerebral Cortex Shapes Functional Connectivity on Multiple Time Scales. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 10240–10245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westermann, B.; Wattendorf, E.; Schwerdtfeger, U.; Husner, A.; Fuhr, P.; Gratzl, O.; Hummel, T.; Bilecen, D.; Welge-Lüssen, A. Functional Imaging of the Cerebral Olfactory System in Patients with Parkinson’s Disease. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2008, 79, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parkkinen, L.; Silveira-Moriyama, L.; Holton, J.L.; Lees, A.J.; Revesz, T. Can Olfactory Bulb Biopsy Be Justified for the Diagnosis of Parkinson’s Disease? Comments on “Olfactory Bulb [Alpha]-Synucleinopathy Has High Specificity and Sensitivity for Lewy Body Disorders”. Acta Neuropathol. 2009, 117, 213–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brodoehl, S.; Klingner, C.; Volk, G.F.; Bitter, T.; Witte, O.W.; Redecker, C. Decreased Olfactory Bulb Volume in Idiopathic Parkinson’s Disease Detected by 3.0-Tesla Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Mov. Disord. 2012, 27, 1019–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wattendorf, E.; Welge-Lüssen, A.; Fiedler, K.; Bilecen, D.; Wolfensberger, M.; Fuhr, P.; Hummel, T.; Westermann, B. Olfactory Impairment Predicts Brain Atrophy in Parkinson’s Disease. J. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 15410–15413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Yu, C.; Fan, F.; Zhang, K.; Zhu, C.; Wu, T.; Li, K.; Chan, P. Correlation between Progressive Changes in Piriform Cortex and Olfactory Performance in Early Parkinson’s Disease. Eur. Neurol. 2011, 66, 98–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.E.; Cho, K.H.; Ham, J.H.; Song, S.K.; Sohn, Y.H.; Lee, P.H. Olfactory Performance Acts as a Cognitive Reserve in Non-Demented Patients with Parkinson’s Disease. Park. Relat. Disord. 2014, 20, 186–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tessitore, A.; Amboni, M.; Esposito, F.; Russo, A.; Picillo, M.; Marcuccio, L.; Pellecchia, M.T.; Vitale, C.; Cirillo, M.; Tedeschi, G.; et al. Resting-State Brain Connectivity in Patients with Parkinson’s Disease and Freezing of Gait. Park. Relat. Disord. 2012, 18, 781–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karunanayaka, P.R.; Wilson, D.A.; Tobia, M.J.; Martinez, B.E.; Meadowcroft, M.D.; Eslinger, P.J.; Yang, Q.X. Default Mode Network Deactivation During Odor–Visual Association. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2017, 38, 1125–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doty, R.L. Olfaction in Parkinson’s Disease and Related Disorders. Neurobiol. Dis. 2012, 46, 527–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barone, D.A.; Henchcliffe, C. Rapid Eye Movement Sleep Behavior Disorder and the Link to Alpha-Synucleinopathies. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2018, 129, 1551–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawasaki, I.; Baba, T.; Takeda, A.; Mori, E. Loss of Awareness of Hyposmia Is Associated with Mild Cognitive Impairment in Parkinson’s Disease. Park. Relat. Disord. 2016, 22, 74–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aarsland, D.; Creese, B.; Politis, M.; Chaudhuri, K.R.; Weintraub, D.; Ballard, C. Cognitive Decline in Parkinson Disease. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2017, 13, 217–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Cleene, N.; Schwarzová, K.; Labrecque, S.; Cerejo, C.; Djamshidian, A.; Seppi, K.; Heim, B. Olfactory Dysfunction as Potential Biomarker in Neurodegenerative Diseases: A Narrative Review. Front. Neurosci. 2025, 18, 1505029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| CN (n = 24) | PDAR (n = 17) | PDT (n = 15) | p-Value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN vs. PDAR | CN vs. PDT | PDAR vs. PDT | ||||
| Age (yrs.) | 57.8 ± 7.4 | 59.1 ± 7.4 | 61.7 ± 6.7 | 0.836 | 0.236 | 0.569 |
| Gender (M:F) | 11:13 | 9:8 | 6:9 | 0.876 | 0.423 | 0.724 |
| Education (yrs.) | 15.8 ± 2.4 | 13.9 ± 2.1 | 15.2 ± 3.2 | 0.068 | 0.795 | 0.329 |
| MMSE | 29.6 ± 0.9 | 29.1 ±1.2 | 29.7 ± 0.5 | 0.257 | 0.959 | 0.221 |
| HAM-D Scale | 4.2± 2.7 | 7.2 ± 3.3 | 6.9 ± 4.0 | 0.0003 * | 0.078 * | 0.215 |
| Disease duration (yrs.) | NA. | 3.7 ± 4.6 | 3.5 ± 3.5 | NA. | NA. | 0.91 |
| UPDRS III | 1.2 ± 2.6 | 20.8 ± 12.9 | 17.1 ± 9.5 | <0.0001 * | <0.0001 * | 0.48 |
| T/AR | NA. | 0.18 ± 0.22 | 2.63 ± 1.77 | NA. | NA. | <0.0001 * |
| H&Y stage | NA. | 1.7 ± 0.6 | 1.7 ± 0.6 | NA. | NA. | 0.06 |
| LEDD (mg/day) | NA. | 366 ± 229 | 354 ± 282 | NA. | NA. | 0.88 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Peiris, S.; Ekanayake, A.; Lu, J.; Elyan, R.; Geesey, K.; Cottrill, R.; Eslinger, P.; Huang, X.; Karunanayaka, P. Olfactory Network Functional Connectivity as a Marker for Parkinson’s Disease Severity. Life 2025, 15, 1324. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15081324
Peiris S, Ekanayake A, Lu J, Elyan R, Geesey K, Cottrill R, Eslinger P, Huang X, Karunanayaka P. Olfactory Network Functional Connectivity as a Marker for Parkinson’s Disease Severity. Life. 2025; 15(8):1324. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15081324
Chicago/Turabian StylePeiris, Senal, Anupa Ekanayake, Jiaming Lu, Rommy Elyan, Katie Geesey, Ross Cottrill, Paul Eslinger, Xuemei Huang, and Prasanna Karunanayaka. 2025. "Olfactory Network Functional Connectivity as a Marker for Parkinson’s Disease Severity" Life 15, no. 8: 1324. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15081324
APA StylePeiris, S., Ekanayake, A., Lu, J., Elyan, R., Geesey, K., Cottrill, R., Eslinger, P., Huang, X., & Karunanayaka, P. (2025). Olfactory Network Functional Connectivity as a Marker for Parkinson’s Disease Severity. Life, 15(8), 1324. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15081324






