Genetic Variants in Cytokines IL-10 and IL-17A Are Associated with the Risk and Severity of Sporadic Parkinson’s Disease in Mexican Patients
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Molecular Analysis
2.2. Biochemical Analysis
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Clinical and Biochemical Parameters in Patients and Controls
3.2. Distribution of Genetic Variants in the Participants
3.3. Association Analysis of Genetic Variants and Clinical and Biochemical Parameters
3.4. Haplotype Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kouli, A.; Torsney, K.M.; Kuan, W.L. Parkinson’s Disease: Etiology, Neuropathology, and Pathogenesis. In Parkinson’s Disease: Pathogenesis and Clinical Aspects; Stoker, T.B., Greenland, J.C., Eds.; Codon Publications: Singapore, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lees, A.J.; Hardy, J.; Revesz, T. Parkinson’s disease. Lancet 2009, 373, 2055–2066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pajares, M.; IRojo, A.; Manda, G.; Boscá, L.; Cuadrado, A. Inflammation in Parkinson’s Disease: Mechanisms and Therapeutic Implications. Cells 2020, 9, 1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tansey, M.G.; Wallings, R.L.; Houser, M.C.; Herrick, M.K.; Keating, C.E.; Joers, V. Inflammation and immune dysfunction in Parkinson disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2022, 22, 657–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Ke, B.; Chen, J.; Xiao, Y.; Wang, S.; Jiang, R.; Zheng, X.; Lin, J.; Huang, J.; Shang, H. Systemic inflammation and risk of Parkinson’s disease: A prospective cohort study and genetic analysis. Brain Behav. Immun. 2024, 117, 447–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.W.; Chen, C.M.; Chang, K.H. Biomarker of Neuroinflammation in Parkinson’s Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 4148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommer, A.; Marxreiter, F.; Krach, F.; Fadler, T.; Grosch, J.; Maroni, M.; Graef, D.; Eberhardt, E.; Riemenschneider, M.J.; Yeo, G.W.; et al. Th17 Lymphocytes Induce Neuronal Cell Death in a Human iPSC-Based Model of Parkinson’s Disease. Cell Stem Cell 2019, 24, 1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Qi, B.; Xu, W.; Ma, B.; Li, L.; Chen, Q.; Qian, W.; Liu, X.; Qu, H. Clinical correlation of peripheral CD4+-cell sub-sets, their imbalance and Parkinson’s disease. Mol. Med. Rep. 2015, 12, 6105–6111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kustrimovic, N.; Comi, C.; Magistrelli, L.; Rasini, E.; Legnaro, M.; Bombelli, R.; Aleksic, I.; Blandini, F.; Minafra, B.; Riboldazzi, G.; et al. Parkinson’s disease patients have a complex phenotypic and functional Th1 bias: Cross-sectional studies of CD4+ Th1/Th2/T17 and Treg in drug-naïve and drug-treated patients. J. Neuroinflamm. 2018, 15, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, X.Y.; Zhang, S.P.; Cao, C.; Loh, Y.P.; Cheng, Y. Aberrations in Peripheral Inflammatory Cytokine Levels in Parkinson Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. JAMA Neurol. 2016, 73, 1316–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koziorowski, D.; Tomasiuk, R.; Szlufik, S.; Friedman, A. Inflammatory cytokines and NT-proCNP in Parkinson’s disease patients. Cytokine 2012, 60, 762–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rota, E.; Bellone, G.; Rocca, P.; Bergamasco, B.; Emanuelli, G.; Ferrero, P. Increased intrathecal TGF-beta1, but not IL-12, IFN-gamma and IL-10 levels in Alzheimer’s disease patients. Neurol. Sci. Off. J. Ital. Neurol. Soc. Ital. Soc. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2006, 27, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bialecka, M.; Klodowska-Duda, G.; Kurzawski, M.; Slawek, J.; Opala, G.; Bialecki, P.; Safranow, K.; Droździk, M. Interleukin-10 gene polymorphism in Parkinson’s disease patients. Arch. Med. Res. 2007, 38, 858–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bialecka, M.; Klodowska-Duda, G.; Kurzawski, M.; Slawek, J.; Gorzkowska, A.; Opala, G.; Bialecki, P.; Sagan, L.; Droździk, M. Interleukin-10 (IL10) and tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF) gene polymorphisms in Parkinson’s disease patients. Park. Relat. Disord. 2008, 14, 636–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; He, Q.; Li, R.; Xu, X.; Chen, B.; Xie, A. Interleukin-10 promoter polymorphisms in Chinese patients with Parkinson’s disease. Neurosci. Lett. 2012, 513, 183–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, L.; Liang, D.; Pan, H.; Xu, Q.; Yan, X.; Tang, B.; Sun, Q. Gastrointestinal Dysfunctions Are Associated with IL-10 Variants in Parkinson’s Disease. Park. Dis. 2018, 2018, 5908359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascale, E.; Passarelli, E.; Purcaro, C.; Vestri, A.R.; Fakeri, A.; Guglielmi, R.; Passarelli, F.; Meco, G. Lack of association between IL-1β, TNF-α, and IL-10 gene polymorphisms and sporadic Parkinson’s disease in an Italian cohort. Acta Neurol. Scand. 2011, 124, 176–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.; Wu, P.; Li, W.; Shi, J.; Chen, J.; Li, R.; Tan, S. Interleukin-10-1082A/G and -592C/A polymorphisms with risk of Parkinson’s disease: A meta-analysis. Int. J. Neurosci. 2014, 124, 852–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Guo, J.; Wang, Y.; Li, K.; Kang, J.; Wei, Y.; Sun, Q.; Xu, Q.; Xu, C.; Yan, X.; et al. Lack of association between IL-10 and IL-18 gene promoter polymorphisms and Parkinson’s disease with cognitive impairment in a Chinese population. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 19021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, Y.; Jiang, S.; Cai, L.; Guan, X.; Hou, S.; Wang, Z.; Lu, Q.; Liu, J. Identification of Functional Genetic Polymorphisms at IL-10 Promoter Region and their Association with Risk of Ischemic Stroke in Chinese Han Population. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2018, 22, 779–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Gu, R.; Bai, J. Differentiation and regulation of CD4+ T cell subsets in Parkinson’s disease. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. CMLS 2024, 81, 352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mori, S.; Maher, P.; Conti, B. Neuroimmunology of the Interleukins 13 and 4. Brain Sci. 2016, 6, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Huang, Y.; Cao, B.B.; Qiu, Y.H.; Peng, Y.P. Th17 Cells Induce Dopaminergic Neuronal Death via LFA-1/ICAM-1 Interaction in a Mouse Model of Parkinson’s Disease. Mol. Neurobiol. 2017, 54, 7762–7776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Qiu, A.W.; Huang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Chen, J.N.; Gu, T.T.; Cao, B.B.; Qiu, Y.H.; Peng, Y.P. IL-17A exacerbates neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration by activating microglia in rodent models of Parkinson’s disease. Brain Behav. Immun. 2019, 81, 630–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Liu, X.; Zhong, Y. Interleukin-17A: The Key Cytokine in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2020, 12, 566922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez-Luquín, D.D.; Arce-Sillas, A.; Leyva-Hernández, J.; Sevilla-Reyes, E.; Boll, M.C.; Montes-Moratilla, E.; Vivas-Almazán, V.; Pérez-Correa, C.; Rodríguez-Ortiz, U.; Espinoza-Cárdenas, R.; et al. Regulatory impairment in untreated Parkinson’s disease is not restricted to Tregs: Other regulatory populations are also involved. J. Neuroinflamm. 2019, 16, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, N.P.; Assis, F.; Scalzo, P.L.; Vieira, É.L.M.; Barbosa, I.G.; de Souza, M.S.; Christo, P.P.; Reis, H.J.; Teixeira, A.L. Reduced Activated T Lymphocytes (CD4+CD25+) and Plasma Levels of Cytokines in Parkinson’s Disease. Mol. Neurobiol. 2018, 55, 1488–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Deng, G.; Zhang, G.; Yu, Z.; Yang, F.; Chen, J.; Cai, Y.; Werz, O.; Chen, X. Genetic polymorphism rs8193036 of IL17A is associated with increased susceptibility to pulmonary tuberculosis in Chinese Han population. Cytokine 2020, 127, 154956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, H.; Wang, N.; Li, H.; Bian, Y.; Wen, W.; Kong, X.; Wang, F. The dynamic shifts of IL-10-producing Th17 and IL-17-producing Treg in health and disease: A crosstalk between ancient “Yin-Yang” theory and modern immunology. Cell Commun. Signal. CCS 2024, 22, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newcomb, D.C.; Boswell, M.G.; Huckabee, M.M.; Goleniewska, K.; Dulek, D.E.; Reiss, S.; Lukacs, N.W.; Kolls, J.K.; Peebles, R.S., Jr. IL-13 regulates Th17 secretion of IL-17A in an IL-10-dependent manner. J. Immunol. 2012, 188, 1027–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Álvarez-Luquín, D.D.; Guevara-Salinas, A.; Arce-Sillas, A.; Espinosa-Cárdenas, R.; Leyva-Hernández, J.; Montes-Moratilla, E.U.; Adalid-Peralta, L. Increased Tc17 cell levels and imbalance of naïve/effector immune response in Parkinson’s disease patients in a two-year follow-up: A case control study. J. Transl. Med. 2021, 19, 378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhang, X.; Guo, N.; Tian, D.; Zhang, C.; Mu, C.; Han, C.; Zhu, R.; Zhang, J.; Liu, X. Genetically Predicted Levels of Circulating Inflammatory Cytokines and the Risk and Age at Onset of Parkinson’s Disease: A Two-Sample Mendelian Randomization Study. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2022, 14, 811059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas-Alarcon, G.; Ramírez-Bello, J.; Juárez-Cedillo, T.; Ramírez-Fuentes, S.; Carrillo-Sánchez, S.; Fragoso, J.M. Distribution of the IL-1RN, IL-6, IL-10, INF-γ, and TNF-α Gene Polymorphisms in the Mexican Population. Genet. Test. Mol. Biomark. 2012, 16, 1246–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villarreal-Martínez, A.; Gallardo-Blanco, H.; Cerda-Flores, R.; Torres-Muñoz, I.; Gómez-Flores, M.; Salas-Alanís, J.; Ocampo-Candiani, J.; Martínez-Garza, L. Candidate gene polymorphisms and risk of psoriasis: A pilot study. Exp. Ther. Med. 2016, 11, 1217–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Ambrocio-Ortiz, E.; Galicia-Negrete, G.; Pérez-Rubio, G.; Escobar-Morales, A.J.; Abarca-Rojano, E.; Del Angel-Pablo, A.D.; Castillejos-López, M.D.J.; Falfán-Valencia, R. Single Nucleotide and Copy-Number Variants in IL4 and IL13 Are Not Associated with Asthma Susceptibility or Inflammatory Markers: A Case-Control Study in a Mexican-Mestizo Population. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas-Alarcón, G.; Angeles-Martínez, J.; Villarreal-Molina, T.; Alvarez-León, E.; Posadas-Sánchez, R.; Cardoso-Saldaña, G.; Ramírez-Bello, J.; Pérez-Hernández, N.; Juárez-Rojas, J.G.; Rodríguez-Pérez, J.M.; et al. Interleukin-17A gene haplotypes are associated with risk of premature coronary artery disease in Mexican patients from the Genetics of Atherosclerotic Disease (GEA) study. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0114943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponce-Gallegos, M.A.; Pérez-Rubio, G.; Ambrocio-Ortiz, E.; Partida-Zavala, N.; Hernández-Zenteno, R.; Flores-Trujillo, F.; García-Gómez, L.; Hernández-Pérez, A.; Ramírez-Venegas, A.; Falfán-Valencia, R. Genetic variants in IL17A and serum levels of IL-17A are associated with COPD related to tobacco smoking and biomass burning. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavarria-Buenrostro, L.E.; Hernandez-Bello, J.; Muñoz-Valle, J.F.; Macias-Barragan, J.; Hernandez-Carrillo, L.B.; Topete-Reyes, J.F.; Parra-Michel, R.; Ramirez-Dueñas, M.G.; Sanchez-Hernandez, P.E.; Pereira-Suarez, A.L.; et al. IL10 haplotypes are associated with diabetic nephropathy susceptibility in patients from western Mexico. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2019, 33, e22691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Postuma, R.B.; Berg, D.; Stern, M.; Poewe, W.; Olanow, C.W.; Oertel, W.; Obeso, J.; Marek, K.; Litvan, I.; Lang, A.E.; et al. MDS clinical diagnostic criteria for Parkinson’s disease. Mov. Disord. Off. J. Mov. Disord. Soc. 2015, 30, 1591–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrett, J.C.; Fry, B.; Maller, J.; Daly, M.J. Haploview: Analysis and visualization of LD and haplotype maps. Bioinformatics 2005, 21, 263–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortega-Vázquez, A.; Sánchez-Badajos, S.; Ramírez-García, M.Á.; Alvarez-Luquín, D.; López-López, M.; Adalid-Peralta, L.V.; Monroy-Jaramillo, N. Longitudinal Changes in Mitochondrial DNA Copy Number and Telomere Length in Patients with Parkinson’s Disease. Genes 2023, 14, 1913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickham, H.; Chang, W.; Henry, L.; Pedersen, T.L.; Takahashi, K.; Wilke, C.; Woo, K.; Yutani, H.; Dunnington, D.; van den Brand, T.; et al. ggplot2: Create Elegant Data Visualisations Using the Grammar of Graphics [Internet]. 2024. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/ggplot2/index.html (accessed on 19 November 2024).
- Guevara-Salinas, A.; Netzahualcoyotzi, C.; Álvarez-Luquín, D.D.; Pérez-Figueroa, E.; Sevilla-Reyes, E.E.; Castellanos-Barba, C.; Vega-Ángeles, V.T.; Terán-Dávila, E.; Estudillo, E.; Velasco, I.; et al. Treating activated regulatory T cells with pramipexole protects human dopaminergic neurons from 6-OHDA-induced degeneration. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2024, 30, e14883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suárez, A.; Castro, P.; Alonso, R.; Mozo, L.; Gutiérrez, C. Interindividual variations in constitutive interleukin-10 messenger RNA and protein levels and their association with genetic polymorphisms. Transplantation 2003, 75, 711–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavón-Romero, G.F.; Pérez-Rubio, G.; Ramírez-Jiménez, F.; Ambrocio-Ortiz, E.; Merino-Camacho, C.R.; Falfán-Valencia, R.; Teran, L.M. IL10 rs1800872 Is Associated with Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs Exacerbated Respiratory Disease in Mexican-Mestizo Patients. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasvenskaite, A.; Liutkeviciene, R.; Gedvilaite, G.; Vilkeviciute, A.; Liutkevicius, V.; Uloza, V. Impact of IL-10 Promoter Polymorphisms and IL-10 Serum Levels on Advanced Laryngeal Squamous Cell Carcinoma and Survival Rate. Cancer Genom. Proteom. 2021, 18, 53–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Gómez, L.E.; Oropeza-Vélez, C.I.; Almonte-Becerril, M.; Chavez-Galan, L.; Martinez-Armenta, C.; Vidal-Vázquez, R.P.; Ramírez-Hinojosa, J.P.; Vázquez-Cárdenas, P.; Gómez-Martín, D.; Vargas-Alarcón, G.; et al. Association of pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory cytokine polymorphisms with COVID-19 severity in unvaccinated patients. Front. Immunol. 2025, 16, 1641285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dzamko, N. Cytokine activity in Parkinson’s disease. Neuronal Signal. 2023, 7, NS20220063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Lu, H.; Tao, F.; Guo, T.; Liu, C.; Cui, B.; Ning, G. An association of interleukin-10 gene polymorphisms with Graves’ disease in two Chinese populations. Endocrine 2011, 40, 90–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Posadas-Sánchez, R.; Angeles-Martínez, J.; Pérez-Hernández, N.; Rodríguez-Pérez, J.M.; López-Bautista, F.; Flores-Dominguez, C.; Fragoso, J.M.; Posadas-Romero, C.; Vargas-Alarcón, G. The IL-10-1082 (rs1800896) G allele is associated with a decreased risk of developing premature coronary artery disease and some IL-10 polymorphisms were associated with clinical and metabolic parameters. The GEA study. Cytokine 2018, 106, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Garduño, T.C.; Padilla-Gutiérrez, J.R.; Aceves-Ramírez, M.; Parra-Reyna, B.; Flores-Salinas, H.E.; Valdes-Alvarado, E.; Becerra-Loaiza, D.S.; Quintero-Ramos, A.; Roa-Bruzón, I.Y.; de la Cruz, A.; et al. IL10 promoter variants are associated with gene expression but they are not markers of susceptibility to acute coronary syndrome. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 13196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, K.; Zhou, X.; Luo, B.Y. Cytokine gene polymorphisms and Parkinson’s disease: A meta-analysis. Can. J. Neurol. Sci. 2012, 39, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porro, C.; Cianciulli, A.; Panaro, M.A. The Regulatory Role of IL-10 in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruddy, M.J.; Wong, G.C.; Liu, X.K.; Yamamoto, H.; Kasayama, S.; Kirkwood, K.L.; Gaffen, S.L. Functional cooperation between interleukin-17 and tumor necrosis factor-alpha is mediated by CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein family members. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 2559–2567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.T.; Lu, Y.L.; Wang, R.; Qin, H.M.; Wang, C.F.; Wang, J.L.; Xiang, Y.; Guo, J.; Lan, Y.; Wei, Y.S. The association of IL-17A polymorphisms with IL-17A serum levels and risk of ischemic stroke. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 103499–103508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, H.; Pei, H.; Xia, Q.; Tang, Y.; Huang, J.; Huang, J.; Pei, F. Role of gene polymorphisms/haplotypes and serum levels of interleukin-17A in susceptibility to viral myocarditis. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2018, 104, 140–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, X.; Liu, W.; Hou, Y.; Zhao, W.; Yang, X.; Chen, L.; Yan, Q.; Cheng, W. IL-17A polymorphism (rs2275913) and levels are associated with preeclampsia pathogenesis in Chinese patients. BMC Med. Genom. 2021, 14, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguirre, C.A.; Concetta Morale, M.; Peng, Q.; Sanchez-Alavez, M.; Cintrón-Colón, R.; Feng, K.; Fazelpour, S.; Maher, P.; Conti, B. Two single nucleotide polymorphisms in IL13 and IL13RA1 from individuals with idiopathic Parkinson’s disease increase cellular susceptibility to oxidative stress. Brain Behav. Immun. 2020, 88, 920–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez-Rodríguez, L.; López-Hoyos, M.; Carrasco-Marín, E.; Mata, C.; Calvo-Alén, J.; Aurrecoechea, E.; Blanco, R.; Ruiz, T.; Muñoz Cacho, P.; Villa, I.; et al. Analysis of the rs20541 (R130Q) polymorphism in the IL-13 gene in patients with elderly-associated chronic inflammatory diseases. Reumatol. Clin. 2012, 8, 321–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Lazzaro, G.; Picca, A.; Boldrini, S.; Bove, F.; Marzetti, E.; Petracca, M.; Piano, C.; Bentivoglio, A.R.; Calabresi, P. Differential profiles of serum cytokines in Parkinson’s disease according to disease duration. Neurobiol. Dis. 2024, 190, 106371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouli, A.; Williams-Gray, C.H. Timing Is Everything: The T-Cell Response to α-Synuclein Is Maximal in Early Parkinson’s. Mov. Disord. Off. J. Mov. Disord. Soc. 2020, 35, 1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindestam Arlehamn, C.S.; Dhanwani, R.; Pham, J.; Kuan, R.; Frazier, A.; Rezende Dutra, J.; Phillips, E.; Mallal, S.; Roederer, M.; Marder, K.S.; et al. α-Synuclein-specific T cell reactivity is associated with preclinical and early Parkinson’s disease. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, J. Neuroinflammation in Parkinson’s disease and its potential as therapeutic target. Transl. Neurodegener. 2015, 4, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.J.; Rodriguez-Salgado, A.M.; Llibre-Rodriguez, J.J.; Acosta, I.; Sosa, A.L.; Acosta, D.; Jimenez-Velasquez, I.Z.; Guerra, M.; Salas, A.; Jeyachandran, C.; et al. Burden of Parkinsonism and Parkinson’s Disease on Health Service Use and Outcomes in Latin America. J. Park. Dis. 2023, 13, 1199–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juárez-Cedillo, T.; Zuñiga, J.; Acuña-Alonzo, V.; Pérez-Hernández, N.; Rodríguez-Pérez, J.M.; Barquera, R.; Gallardo, G.J.; Sánchez-Arenas, R.; García-Peña, M.d.e.l.C.; Granados, J.; et al. Genetic admixture and diversity estimations in the Mexican Mestizo population from Mexico City using 15 STR polymorphic markers. Forensic Sci. Int. Genet. 2008, 2, e37–e39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iyer, S.S.; Cheng, G. Role of interleukin 10 transcriptional regulation in inflammation and autoimmune disease. Crit. Rev. Immunol. 2012, 32, 23–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdalla, M.A.; Hamdan, H.Z. IL13 gene polymorphisms among Sudanese patients with bronchial asthma: A case-control study. Mol. Biol. Res. Commun. 2025, 14, 27–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grunwald, C.; Adamska-Patruno, E.; Wawrusiewicz-Kurylonek, N.; Czarnowska, A.; Snarska, K.; Dardzińska-Głębocka, A.; Kapica-Topczewska, K.; Mirończuk, A.; Bazylewicz, M.; Kochanowicz, J.; et al. Multiple sclerosis susceptibility may be associated with the coding rs20541 (R130Q) IL-13 gene polymorphism in the Polish population. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 22083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.; Ding, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, M. The rs2275913 polymorphism of the interleukin-17A gene is associated with the risk of ovarian endometriosis. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. 2023, 43, 2199852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinoza, J.L.; Takami, A.; Nakata, K.; Onizuka, M.; Kawase, T.; Akiyama, H.; Miyamura, K.; Morishima, Y.; Fukuda, T.; Kodera, Y.; et al. A genetic variant in the IL-17 promoter is functionally associated with acute graft-versus-host disease after unrelated bone marrow transplantation. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e26229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borilova Linhartova, P.; Kastovsky, J.; Lucanova, S.; Bartova, J.; Poskerova, H.; Vokurka, J.; Fassmann, A.; Kankova, K.; Izakovicova Holla, L. Interleukin-17A Gene Variability in Patients with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus and Chronic Periodontitis: Its Correlation with IL-17 Levels and the Occurrence of Periodontopathic Bacteria. Mediat. Inflamm. 2016, 2016, 2979846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nie, K.; Zhang, Y.; Gan, R.; Wang, L.; Zhao, J.; Huang, Z.; Tang, H.; Wang, L. Polymorphisms in immune/inflammatory cytokine genes are related to Parkinson’s disease with cognitive impairment in the Han Chinese population. Neurosci. Lett. 2013, 541, 111–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Yang, L.; Lv, X.; Zuo, C.; Jia, C.; Yang, Z.; Fan, C.; Chen, H. Cumulative evidence for associations between genetic variants in interleukin 17 family gene and risk of human diseases. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1008184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

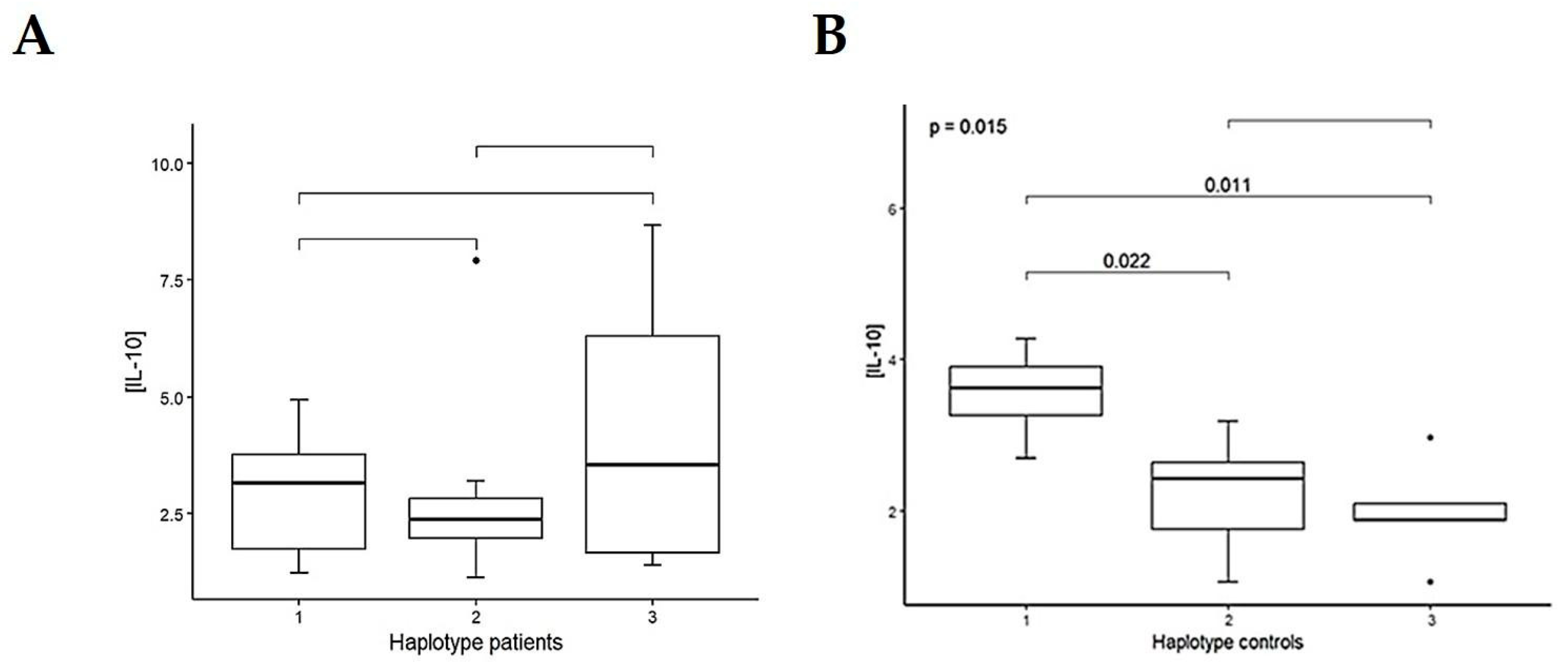
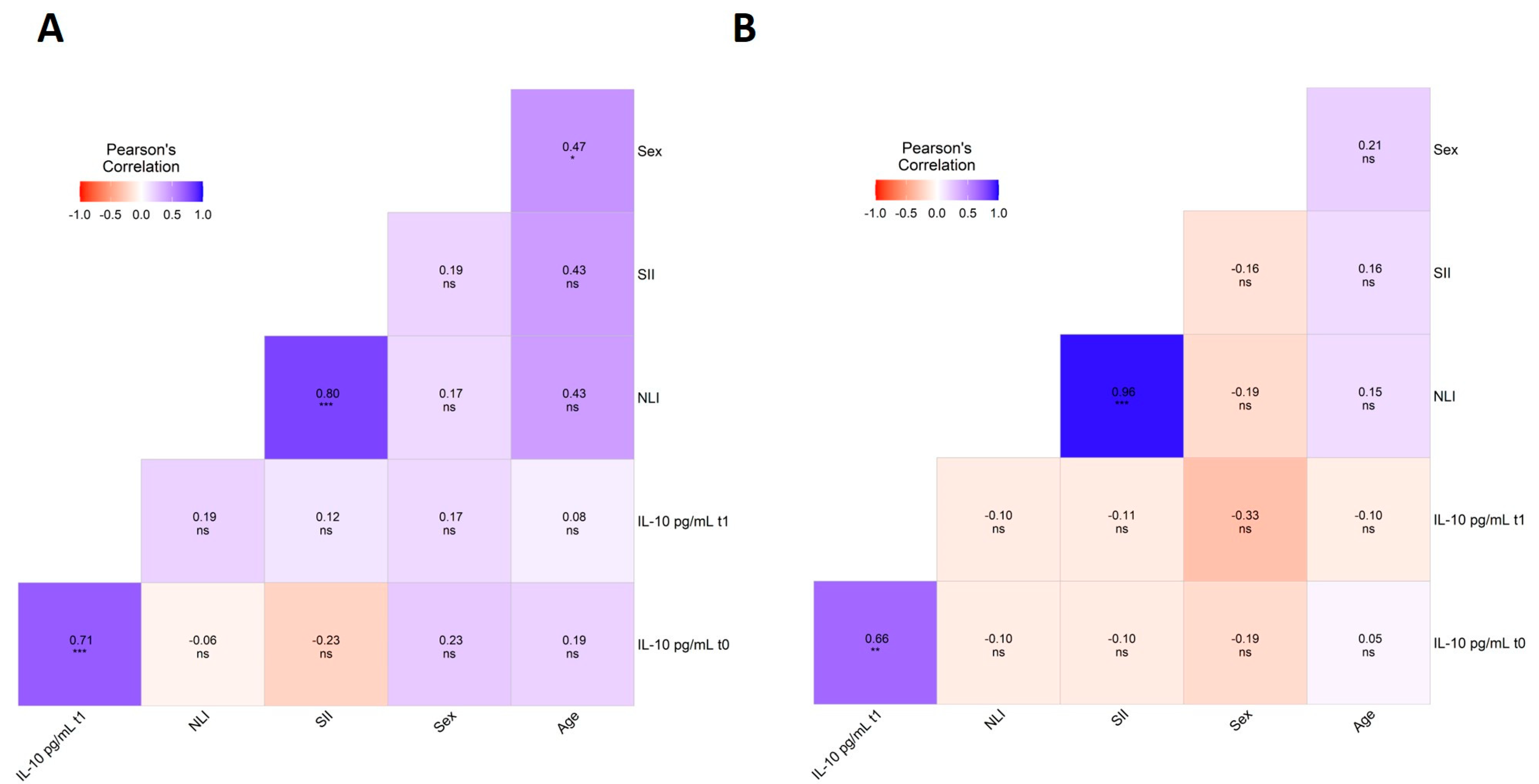
| Characteristics | Treated PD Patients (n = 239) | Controls (n = 84) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total (n = 239) | Male (n = 127) | Female (n = 112) | Total (n = 84) | Male (n = 38) | Female (n = 46) | |
| Sex (%) | 100 | 53.16 | 46.84 | 100 | 45.45 | 54.54 |
| Age in years, mean ± SD (range) | 59.15 ± 12.63 (23–88) | 58.4 ± 12.24 (23–84) | 60.05 ± 13.05 (29–88) | 47.87 ± 18.54 (21–71) | 45.21 ± 17.91 (21–69) | 44.68 ± 18.79 (19–83) |
| Untreated PD Patients in the Clinical Group | Controls in the Clinical Group | |||||
| Total (n = 26) | Male (n = 16) | Female (n = 10) | Total (n = 21) | Male (n = 11) | Female (n = 10) | |
| Sex (%) | 100 | 61 | 39 | 100 | 52 | 48 |
| Age in years, mean ± SD (range) | 60.93 ± 10.60 (38–85) | 59.56 ± 10.53 (38–85) | 63.00 ± 10.82 (41–81) | 55.73 ± 10.20 (34–81) | 54.58 ± 8.39 (40–60) | 57.00 ± 12.38 (34–81) |
| Weight (Kg), mean ± SD (range) | 70.71 ± 13.13 (48–97) | 75.82 ± 12.07 (54–97) | 62.36 ± 10.55 (48–81) | 69.21 ± 8.96 (54–90) | 70.62 ± 7.17 (59–81.5) | 67.52 ± 10.90 (54–90) |
| Height (cm), mean ± SD (range) | 160.07 ± 11.29 (138–180) | 166.11 ± 7.53 (150–180) | 150.18 ± 9.36 (138–169) | 159.77 ± 8.60 (143–176) | 165.08 ± 6.17 (154–176) | 153.4 ± 6.58 (143–167) |
| BMI, mean ± SD (range) | 27.55 ± 4.74 (20.61–37.4) | 27.26 ± 13.02 (26.61–33.20) | 28.02 ± 6.36 (21.69–37.40) | 26.85± 3.89 (20.7–36.4) | 26.13 ± 3.21 (20.7–32.91) | 27.72 ± 4.60 (22.5–36.4) |
| Cholesterol (mg/dL), mean ± SD (range) | 189.24 ± 34.35 (122.1–266.6) | 176.36 ± 32.75 (122.10–236.15) | 209.87 ± 26.88 (185.18–266.60) | 217.35 ± 55.95 (139.94–377) | 213.07 ± 49.05 (139.94–309) | 222.49 ± 65.65 (154–377) |
| Triglycerides (mg/dL), mean ± SD (range) | 140.23 ± 55.02 (47.35–293.4) | 127.17 ± 46.25 (47.35–216.6) | 162.42 ± 63.83 (77.5–293.4) | 162.17 ± 63.02 (74.5–318.52) | 166.11 ± 73.31 (89.27–318.52) | 157.45 ± 51.51 (74.5–229.1) |
| Smokers, n (%) | 3 (10) | 3 (16.7) | 0 | 9 (40.9) | 8 (66.7) | 1 (10) |
| Alcohol consumers, n (%) | 10 (33.3) | 9 (50) | 1 (8.3) | 10 (45.5) | 8 (66.7) | 2 (20) |
| Uric acid (mg/dL), mean ± SD (range) | 5.77 ± 1.37 (3.7–9.18) | 6.40 ± 1.30 (4.51–9.18) | 4.70 ± 0.60 (3.7–5.8) | 6.13 ± 1.50 (4.01–9.35) | 6.69 ± 1.46 (4.8–9.35) | 5.47 ± 1.31 (4.01–7.95) |
| IL-10 (pg/mL), mean ± SD (range) | 2.95 ± 2.02 (0–8.67) | 2.44 ± 1.79 (0–7.91) | 3.71 ± 2.18 (1.44–8.67) | 2.68 ± 2.54 (0.08–13.02) | 3.12 ± 3.27 (0.41–13.02) | 2.17 ± 1.20 (0.08–3.78) |
| IL-13 (pg/mL), mean ± SD (range) | 4.38 ± 7.34 (0–31.67) | 3.74 ± 5.30 (0–17.10) | 5.86 ± 8.99 (0–31.67) | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| IL-17A (pg/mL), mean ± SD (range) | 1341.87 ± 1365.9 (73.4–3904.4) | 1363.9 ± 1424.55 (73.4–3904.4) | 1308.81 ± 1334.30 (77.4–3888.4) | 2250.71 ± 1365.93 (6.4–3937.4) | 2354.57 ± 1370.27 (6.4–3937.4) | 2126.1 ± 1423.70 (515.4–3898.4) |
| NLI, mean ± SD (range) | 1.68 ± 0.46 (0.71–3.05) | 1.71 ± 0.50 (0.71–3.05) | 1.63 ± 0.41 (1.05–2.17) | 1.99 ± 1.56 (0.53–8.44) | 1.81 ± 0.58 (1.27–2.96) | 2.26 ± 2.22 (0.53–8.44) |
| SII, mean ± SD (range) | 399.31 ± 176.35 (78.1–883.89) | 387.82 ± 154.33 (78.1–671.04) | 418.11 ± 214.38 (203.49–883.89) | 492.84 ± 454.88 (108.36–2447.31) | 415.91 ± 186.73 (108.36–777.02) | 554.47 ± 688.78 (110.76–2447.31) |
| Clinical Scales for the Staging of the Functional Disability of Patients | ||||||
| HOEN and YAHR scale, median (range) | 2 (1–4) | 2 (1–3) | 2 (1–4) | NA | NA | NA |
| MDS-UPDRS I, mode (range) | 4 (0–6) | 4 (0–6) | 4 (0–4) | NA | NA | NA |
| MDS-UPDRS II, mode (range) | 10 (3–25) | 10 (3–25) | 15 (5–25) | NA | NA | NA |
| MDS-UPDRS III, mode (range) | 38 (4–72) | 38 (4–60.5) | 13 (13–72) | NA | NA | NA |
| MDS-UPDRS IV | 0 | 0 | 0 | NA | NA | NA |
| MDS-UPDRS Total, mode (range) | 52 (8–93) | 47 (8–88) | 52 (21–93) | NA | NA | NA |
| Schwab and England scale, mode (range) | 90 (20–100) | 90 (50–100) | 90 (20–90) | 100 (90–100) | 100 (100–100) | 100 (90–100) |
| Beck’s Depression Inventory, mode (range) | 10 (0–30) | 10 (0–23) | 10 (2–30) | 2.5 (0–21) | 1.5 (0–13) | 7 (0–21) |
| Genetic Characteristic | Total Group of PD Patients (n = 239 and 478 Alleles) | Total Group of Controls (n = 84 and 168 Alleles) | p-Values | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gene | Variant ID | Genotype/Allele | n | Frequency | CI95% | n | Frequency | CI95% | p 1 | p 2 | p 3 |
| IL-10 | rs1800896 | TT | 118 | 0.54 | 0.43–0.56 | 42 | 0.50 | 0.39–0.61 | 1.00 | 0.22 | 0.18 |
| TC | 93 | 0.39 | 0.33–0.45 | 34 | 0.40 | 0.30–0.52 | 0.79 | 0.83 | 0.65 | ||
| CC | 18 | 0.08 | 0.05–0.12 | 8 | 0.10 | 0.04–0.18 | 0.64 | 0.24 | 0.19 | ||
| T | 349 | 0.73 | 0.69–0.77 | 118 | 0.70 | 0.63–0.77 | 0.48 | 0.18 | 0.14 | ||
| C | 129 | 0.27 | 0.23–0.31 | 50 | 0.30 | 0.23–0.37 | |||||
| rs1800872 | TT | 45 | 0.19 | 0.14–0.24 | 13 | 0.15 | 0.09–0.25 | 0.62 | <0.01 | <0.01 | |
| TG | 103 | 0.43 | 0.37–0.50 | 46 | 0.55 | 0.44–0.66 | 0.07 | <0.01 | <0.01 | ||
| GG | 91 | 0.38 | 0.32–0.45 | 25 | 0.30 | 0.20–0.41 | 0.18 | 0.29 | 1.00 | ||
| T | 193 | 0.40 | 0.36–0.45 | 72 | 0.43 | 0.35–0.51 | 0.58 | <0.01 | <0.01 | ||
| G | 285 | 0.60 | 0.55–0.64 | 96 | 0.57 | 0.49–0.65 | |||||
| IL-13 | rs20541 | AA | 82 | 0.34 | 0.28–0.41 | 24 | 0.29 | 0.19–0.39 | 0.35 | 0.13 | 0.06 |
| AG | 110 | 0.46 | 0.40–0.53 | 42 | 0.50 | 0.39–0.61 | 0.61 | 0.84 | 0.51 | ||
| GG | 47 | 0.20 | 0.15–0.25 | 18 | 0.21 | 0.13–0.32 | 0.75 | 0.18 | 0.15 | ||
| A | 278 | 0.58 | 0.54–0.63 | 90 | 0.54 | 0.46–0.61 | 0.32 | 0.05 | 0.03 | ||
| G | 210 | 0.42 | 0.39–0.49 | 78 | 0.46 | 0.39–0.54 | |||||
| IL-17A | rs2275913 | GG | 162 | 0.68 | 0.61–0.74 | 58 | 0.69 | 0.58–0.79 | 0.89 | 0.83 | 0.81 |
| GA | 66 | 0.28 | 0.22–0.34 | 23 | 0.27 | 0.18–0.38 | 1.00 | 0.82 | 0.80 | ||
| AA | 11 | 0.04 | 0.02–0.08 | 3 | 0.04 | 0.01–0.10 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | ||
| G | 390 | 0.82 | 0.78–0.85 | 139 | 0.83 | 0.76–0.88 | 0.82 | 0.85 | 0.84 | ||
| A | 88 | 0.18 | 0.15–0.22 | 29 | 0.17 | 0.12–0.24 | |||||
| rs8193036 | CC | 33 | 0.14 | 0.10–0.19 | 3 | 0.04 | 0.01–0.10 | <0.01 | 1.00 | 0.16 | |
| CT | 70 | 0.29 | 0.24–0.36 | 23 | 0.27 | 0.18–0.38 | 0.78 | 0.65 | 0.47 | ||
| TT | 136 | 0.57 | 0.50–0.63 | 58 | 0.69 | 0.58–0.79 | 0.05 | 0.87 | 0.36 | ||
| C | 136 | 0.28 | 0.24–0.33 | 29 | 0.17 | 0.12–0.24 | <0.01 | 1.00 | 0.08 | ||
| T | 342 | 0.72 | 0.67–0.76 | 139 | 0.83 | 0.76–0.88 | |||||
| Genetic Characteristic | Untreated PD Patients in the Clinical Group (n = 26) | Controls in the Clinical Group (n = 21) | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gene | Variant ID | Genotype | n | NLI | SII | † IL Plasma Levels | ‡ IL Plasma Levels | n | NLI | SII | † IL Plasma Levels | ‡ IL Plasma Levels |
| IL-10 | rs1800896 | TT | 17 | 2.26 (0.96) | 479.57 (203.30) | 2.79 (1.84) | 2.87 (1.97) | 8 | 2.2 (2.51) | 538.62 (775.43) | 2.55 (1.37) | 2.41 (0.77) |
| TC | 9 | 1.56 (0.20) | 409.23 (181.18) | 3.72 (2.58) | 3.51 (2.23) | 8 | 2.08 (0.56) | 540.96 (114.32) | 3.31 (4.059) | 4.39 (4.01) | ||
| CC | 0 | --- | --- | --- | — | 5 | 1.2 (0.44) | 349.33 (152.05) | 1.98 (0.68) | 2.24 (0.58) | ||
| rs1800872 | TT | 15 | 2.12 (0.98) | 491.62 (216.80) | 2.84 (1.08) | 2.99 (1.84) | 5 | 2.79 (3.16) | 743.09 (955.73) | 2.86 (1.65) | 2.46 (0.86) | |
| TG | 4 | 1.79 (0.33) | 337.34 (68.99) | 7.913 | 5.47 | 10 | 1.93 (0.60) | 449.77 (196.00) | 1.96 (0.94) | 4.52 (3.91) | ||
| GG | 7 | 2.07 (0.85) | 437.23 (173.47) | 3.64 (3.262) | 2.64 (2.57) | 6 | 1.27 (0.39) | 361.71 (139.34) | 3.82 (4.55) | 2.06 (0.68) | ||
| Diplotype | TT-TT | 12 | 2.22 (1.04) | 500.32 (231.23) | 2.88 (1.18) | 3.02 (2.02) | 4 | 3.10 (3.6) | 273.89 (20.34) | 3.55 (0.66) | 3.19 | |
| TT-TG | 2 | 1.79 | 337.34 | 4.79 | 4.027 | 4 | 1.38 (0.23) | 259.99 (121.59) | 1.55 (1.12) | 2.03 (0.63) | ||
| TT-GG | 3 | 2.9 | 518.08 | 1.13 (1.13) | 1.58 (1.68) | 0 | NA | NA | NA | NA | ||
| TC-TT | 3 | 1.62 | 448.10 | 2.68 (0.44) | 2.81 | 1 | 1.54 | 446.45 | 0.08 | 1.74 | ||
| TC-TG | 2 | ND | ND | 1.66 | ND | 6 | 2.29 (0.47) | 576.28 (110.71) | 2.22 (0.78) | 3.87 (3.48) | ||
| TC-GG | 4 | 1.52 (0.12) | 383.32 (217.95) | 5.52 (3.07) | 4.22 | 1 | 1.37 | 423.61 | 13.02 | 10.78 | ||
| CC-GG | 0 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 5 | 1.25 (0.44) | 349.33 (152.05) | 1.978 (0.68) | 2.24 (0.58) | ||
| IL-13 | rs20541 | AA | 13 | 1.76 (0.49) | 356.92 (103.36) | 5.13 (5.16) | 0 | 8 | 2.43 (2.45) | 667.99 (725.51) | 0 | 10.42 (16.14) |
| AG | 11 | 2.19 (0.82) | 465.45 (99.94) | 0 | 3.556 (7.951) | 8 | 1.60 (1.39) | 385.54 (195.94) | 0 | 15.54 (22.19) | ||
| GG | 2 | 0.98 | 320.59 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 1.73 (0.94) | 391.03 (217.12) | 0 | 0 | ||
| IL-17A | rs2275913 | GG | 17 | 2.08 (0.87) | 516.03 (142.19) | 1218.34 (1382.52) | 1741.95 (1119.02) | 2 | 1.41 (0.11) | 323.90 (12.48) | 3472.9 (522.55) | ND |
| GA | 8 | 2.12 (1.01) | 446.78 (221.42) | 1932.28 (1191.93) | 1446.14 (1766.87) | 6 | 1.71 (0.33) | 444.97 (89.57) | 1494.23 (1257.09) | ND | ||
| AA | 1 | 1.61 | 233.36 | 383.4 | 585.40 | 13 | 2.14 (2.01) | 543.52 (604.62) | 2412.55 (1421.42) | ND | ||
| rs8193036 | CC | 3 | 2.75 (1.38) | 516.51 (192.01) | 1267.07 (661.61) | 2294.73 (1590.42) | 2 | 1.77 (0.65) | 439.43 (102.58) | 2269.4 (1854.03) | ND | |
| CT | 9 | 2.39 (1.06) | 523.60 (285.52) | 1456.29 (1797.25) | 1706.57 (1738.23) | 5 | 1.53 (0.41) | 382.43 (182.24) | 1066.8 (1016.43) | ND | ||
| TT | 14 | 1.68 (0.46) | 406.91 (126.26) | 1381.11 (1186.82) | 1274.62 (1050.33) | 14 | 2.12 (1.92) | 542.3 (574.26) | 2671.54 (1304.51) | ND | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Monroy-Jaramillo, N.; Ortega-Vázquez, A.; López-López, M.; Adalid-Peralta, L.V. Genetic Variants in Cytokines IL-10 and IL-17A Are Associated with the Risk and Severity of Sporadic Parkinson’s Disease in Mexican Patients. Life 2025, 15, 1480. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15091480
Monroy-Jaramillo N, Ortega-Vázquez A, López-López M, Adalid-Peralta LV. Genetic Variants in Cytokines IL-10 and IL-17A Are Associated with the Risk and Severity of Sporadic Parkinson’s Disease in Mexican Patients. Life. 2025; 15(9):1480. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15091480
Chicago/Turabian StyleMonroy-Jaramillo, Nancy, Alberto Ortega-Vázquez, Marisol López-López, and Laura Virginia Adalid-Peralta. 2025. "Genetic Variants in Cytokines IL-10 and IL-17A Are Associated with the Risk and Severity of Sporadic Parkinson’s Disease in Mexican Patients" Life 15, no. 9: 1480. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15091480
APA StyleMonroy-Jaramillo, N., Ortega-Vázquez, A., López-López, M., & Adalid-Peralta, L. V. (2025). Genetic Variants in Cytokines IL-10 and IL-17A Are Associated with the Risk and Severity of Sporadic Parkinson’s Disease in Mexican Patients. Life, 15(9), 1480. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15091480







