Comparative Cranial and Postcranial Osteology of Blanus Species (Squamata: Amphisbaenia) from Türkiye: Insights from Morphological Evolution and Phylogeny
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling
2.2. Osteological Study
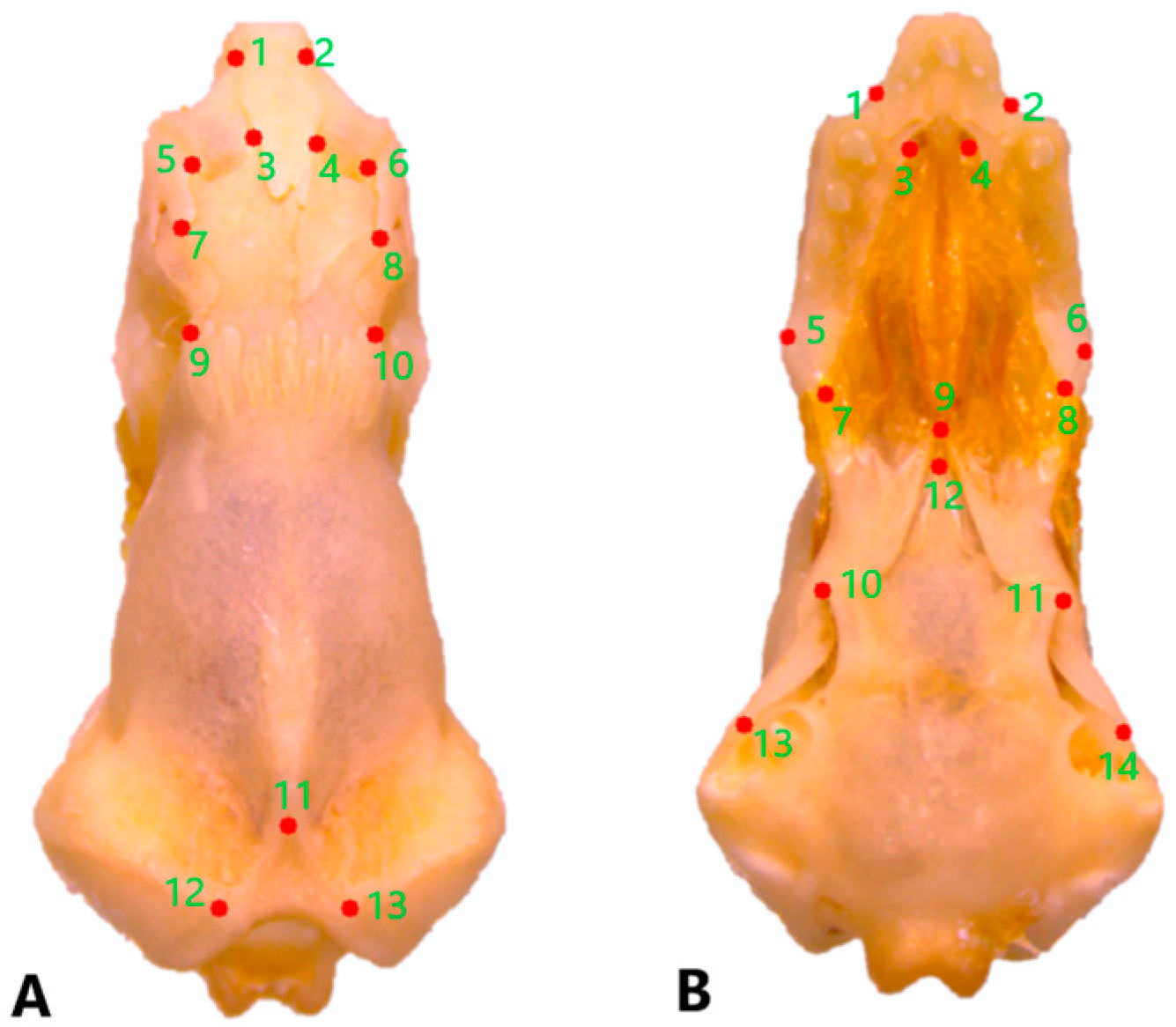
2.3. Geometric Morphometric Analysis
2.4. Phylogenetic Reconstruction
3. Results
3.1. Comparative Cranial Osteology
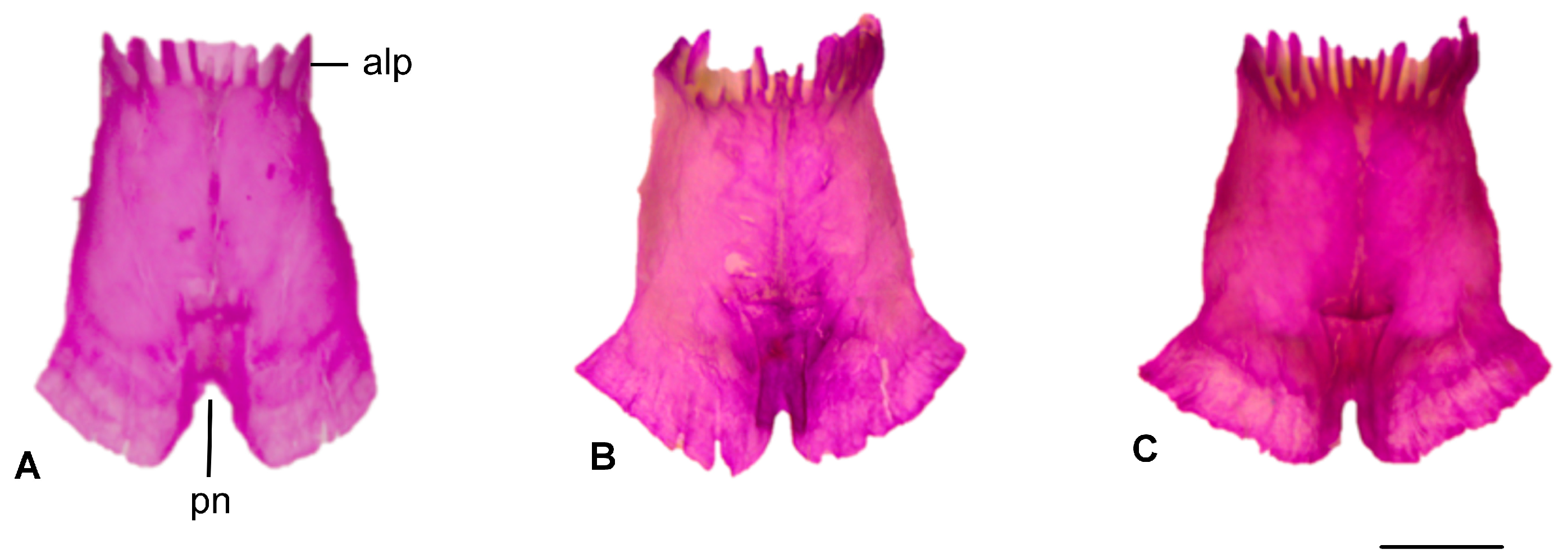
3.1.1. Nasal
3.1.2. Maxilla
3.1.3. Parietal
3.1.4. Prefrontal
3.1.5. Squamosal
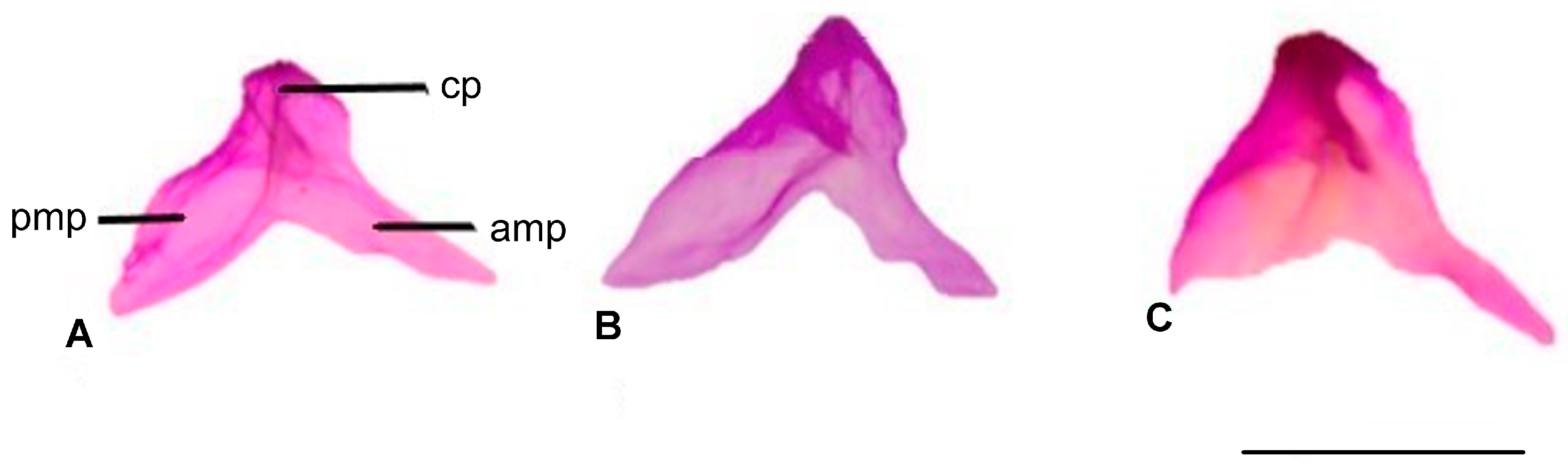
3.1.6. Vomer
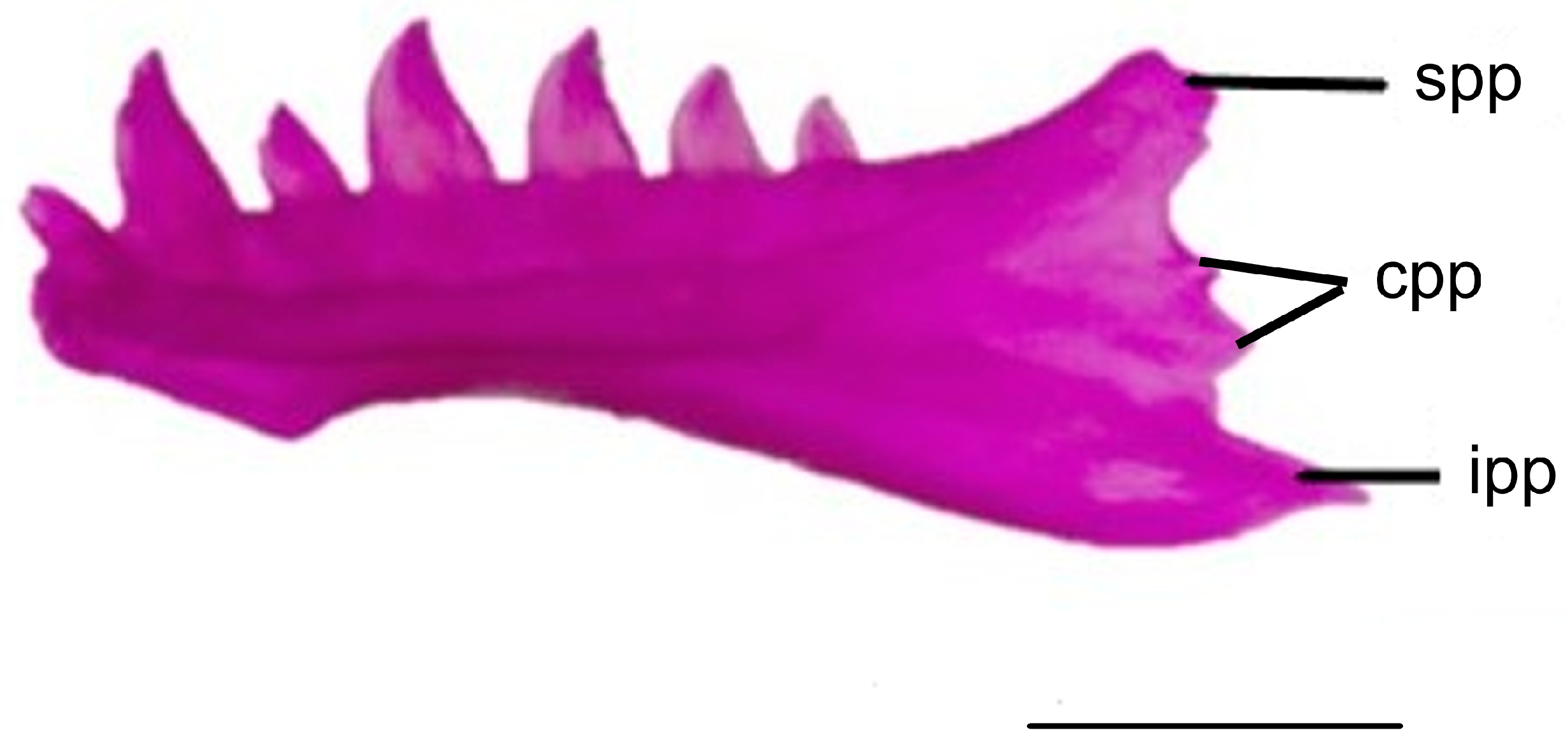
3.1.7. Dentary
3.1.8. Coronoid
3.2. Osteological Characters Exhibiting Variation Among Blanus Species and Related Taxa
3.3. General Postcranial Shape of Blanus Species
3.3.1. The Vertebral Column
3.3.2. Pelvic and Pectoral Girdles
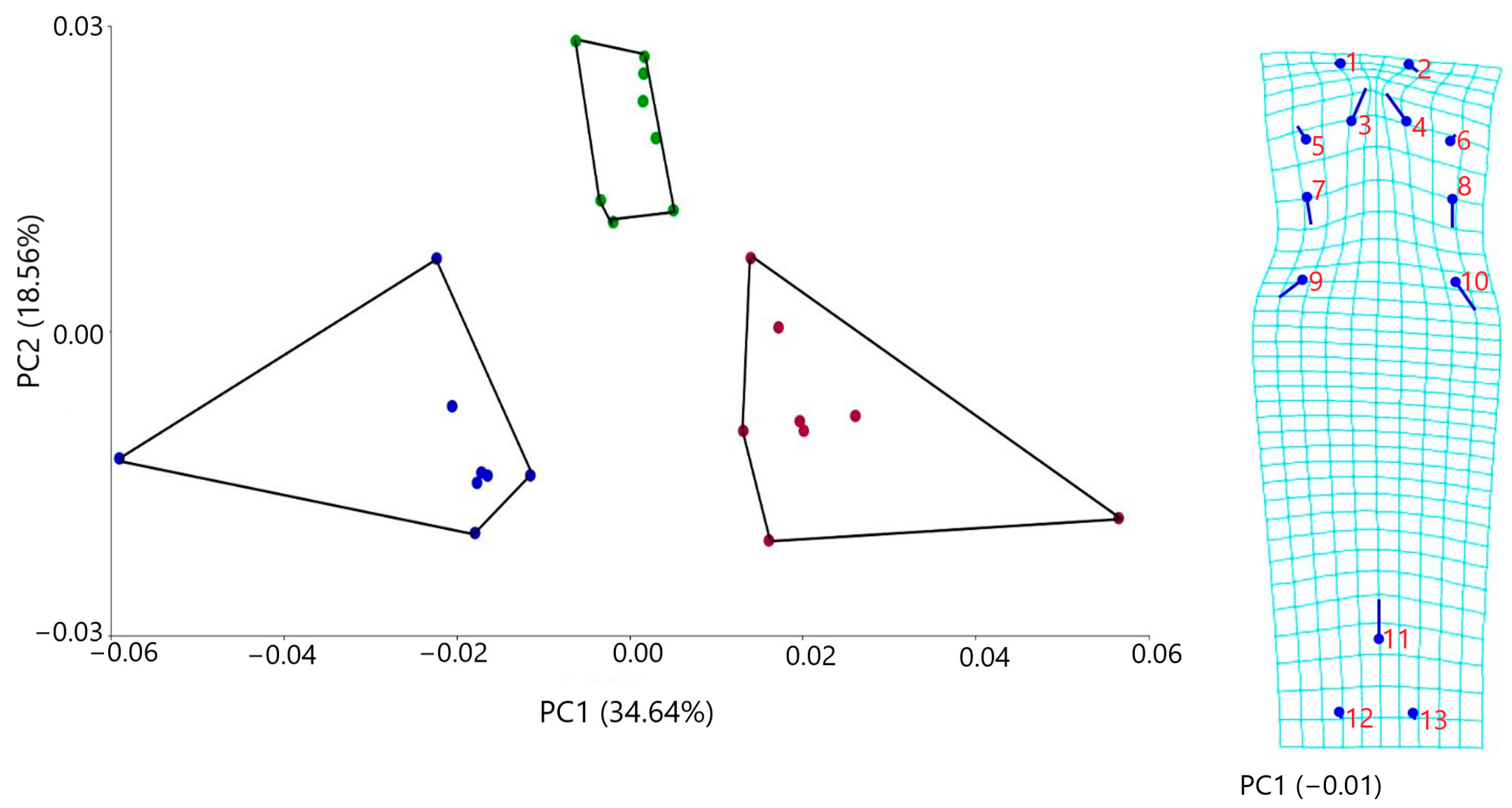
3.4. Geometric Morphometric Analyses
3.4.1. Dorsal Cranial Morphometrics
3.4.2. Ventral Cranial Morphometrics
3.5. Parsimony Reconstruction
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Species | Osteological Data | Source |
|---|---|---|
| Amphisbaenian sp. | Postcranial osteology | [26] |
| Amphisbaenian sp. | Postcranial osteology | [26] |
| Amphisbaenian sp. | Postcranial osteology | [27] |
| Slavoia darevskii (extinct sp.) | Postcranial osteology | [29] |
| Zygaspis quadrifrons | Postcranial osteology | [57] |
| Blanus sp. | Cranial osteology | [28] |
| Blanus mendezi sp. Nov. (extict sp.) | Cranial osteology | [32] |
| Amphisbaenian sp. | Cranial osteology | [36] |
| Zygaspis quadrifrons | Cranial osteology | [41] |
| Amphisbaenia alba | Cranial osteology | [42] |
| Diplometopon zarudnyi | Cranial osteology | [43] |
| Rhineura hatcherii (extinct sp.) | Cranial osteology | [44] |
| Spathorhynchus fossorium (extinct sp.) | Cranial osteology | [46] |
| Amphisbaenian sp. | Cranial osteology | [58] |
| Diplometalon zarudnyi | Cranial osteology | [59] |
| Genus Zygaspis | Cranial osteology | [60] |
| Diplometopon zarudnyi | Cranial osteology | [61] |
| Amphisbaenian sp. | Cranial osteology | [62] |
Appendix B
- Premaxilla: the number of teeth: (0) 3, (1) 7.
- Premaxilla: rostrol process: (0) absent, (1) present.
- Premaxilla: ascending nasal process: (0) tapers posteriorly with a slight projection, (1) tapers posteriorly with a slight depression, (2) narrows towards the truncated or pointed dorsal end, (3) tapers with an arrow shaped*, (4) narrow and elongated end*, (5) appears to be short and peg-like, (6) tapers posteriorly with rounded end.
- Premaxilla: ascending nasal process contacts to: (0) anteromedial process of the frontal, (1) nasal.
- Maxilla: The number of teeth: (0) 3, (1) 4, (2) 5, (3) 6, (4) 7.
- Maxilla: the larger teeth: (0) first teeth, (1) second teeth.
- Maxilla: facial process: (0) wider, (1) taller.
- Maxilla: the number of the projection from the dorsal end of the facial process: (0) 1, (1) 2, (2) 3.
- Maxilla: the number of labial foramen: (0) 1, (1) 2, (2) more than two, (3) variable, (4) more than two and each side variable.
- Nasal: the posterior process of the nasal: (0) the posterior process of the nasal bone is shorter than the length of the distal portion of the ascending nasal process of the premaxilla, (1) the posterior process of the nasal bone is approximately equal in length to the distal portion of the ascending nasal process of the premaxilla. (2) the posterior process of the nasal bone is longer than the length of the distal portion of the ascending nasal process of the premaxilla.
- Frontal: suture between the frontals: (0) straight articulation, (1) tongue-and-groove articulation.
- Frontal: number of maximum finger-like projections on the posterior margin of each frontal bone: (0) 3, (1) 4, (2) 5, (3) 6, (4) 7.
- Parietal: number of maximum finger-like projections on the anterior margin of the parietal bone: (0) 5, (1) 6, (2) 7, (3) 8, (4) 9, (5) 10, (6) 11.
- Parietal: parietal notch: (0) narrow, (1) wide.
- Parietal: the lateralmost finger-like projection touches the prefrontal: (0) yes, (1) no, (2) both, (3) approach but not contact.
- Parietal: parietal (pineal) foramen: (0) present, (1) absent.
- Parietal: sagittal crest; (0) distinct, (1) indistinct, (3) absent.
- Parietal: otic-occipital lappet; (0) wide, (1) narrow.
- Parietal: the length of the finger-like projection; (0) relatively equal, (1) not equal.
- Prefrontal: (0) present, (1) absent.
- Squamosal: the length of the bone: (0) present, (1) absent, (2) fused with the otic-occipital complex.
- Quadrate: the projection of the posteromedial part of the pillar: (0) distinct, (1) thin, (2) poor development.
- Quadrate: quadrate foramen; (0) present and one, (1) absent, (2) present and more than one.
- Epipterygoid: (0) present, (1) absent, (2) both.
- Vomer: rostral process: (0) bifurcated, (1) long and slender, (2) wide and triangular-shaped posteriorly.
- Vomer: posterior process: (0) long and narrow with an acute end, (1) long and slender.
- Vomer: lateral wings: (0) slender and anteriorly directed, (1) posteriorly directed and then tapers, (2) posteriorly directed and widens, (3) widens laterally at approximately its midpoint, (4) widens and anteriorly directed, (5) slender and posteriorly directed.
- Palatine: the laminar expansion of the lateral margin of the bone: (0) long, (1) short, (2) poor development, (3) absent.
- Palatine: anterior processes: (0) the length of the vomerine process > the maxillar process, (1) the length of the vomerine process < the maxillar process, (2) the length of the vomerine process = the maxillar process, (3) absent.
- Palatine: pterygoid process: (0) laterally oriented, long, and pointed, (1) flat and ends in a pointed tip, (2) projects posteriorly, (3) posteriorly directed and further tapers.
- Palatine: palatine foramen: (0) present, (1) absent.
- Pterygoid recess: (0) straight, (1) wide angle, (2) narrow angle, (3) absent.
- Pterygoid: teeth: (1) present, (2) absent.
- Dentary: the longest tooth of the dentary: (0) first, (1) second, (2) third, (3) first and forth.
- Dentary: the number of ventral posterior process of the dentary: (0) 0, (1) 1, (2) 2, (3) 3.
- Dentary: the first foramen of the dentary: (0) the level of the 2–3 teeth, (1) the level of the 1–2 teeth, (2) the level of the 1 teeth, (3) on the 2th teeth, (4) mental foramina are variable on the left and right sides.
- Dentary: The second foramen of the dentary: (0) the level of the 3–4 teeth, (1) the level of the 2–3 teeth, (2) on the 2nd teeth, (3) on the 4th teeth, (4) mental foramina are variable on the left and right sides.
- Dentary: The third foramen of the dentary: (0) the level of the 6–7 teeth, (1) the level of the 5–6 teeth, (2) the level of 3–4 teeth, (3) the level of 4–5 teeth, (4) on the 5th teeth, (5) mental foramina are variable on the left and right sides.
- Dentary: the number of teeth: (0) 6, (1) 7, (2) 8, (3) 7 or 8.
- Presacral vertebra: the average number of the presacral vertebrae: (0) 118, (1) 123, (2) 128.
Appendix C
| Species | Data Matrix | Reference | Citations |
| Blanus alexandri | 1100100310135111100001020001001112330031 | Present Study | |
| Blanus aporus | 1110100310125111100000020001001112315030 | Present Study | |
| Blanus strauchi | 1110100240136131100010220001001112310032 | Present Study | |
| Blanus cineraus | 112010012011301100000100000100111233003? | Villa et al., 2019 | [28] |
| Blanus tingitanus | 112010012012311100001101000100111231002? | Villa et al., 2019 | [28] |
| Blanus mettatali | 11201001301131?100000200000100111231003? | Villa et al., 2019 | [28] |
| Blanus vandelli | 112010012011301100000200000100111231003? | Villa et al., 2019 | [28] |
| Amphisbaena alba | 10402000221120210100?20?002???111230302? | Montero & Gans, 1999 | [42] |
| Amphisbaena arda | 10401000311120210000??0?102?021?1224451? | Paiva et al., 2024 | [45] |
| Amphisbaena vermicularis | 10401000311100210000??0?102?021?1224451? | Paiva et al., 2024 | [45] |
| Zygaspis quadrifrons | 11160100210430111000?10?005300011222233? | Bell et al., 2023 | [41] |
| Diplometopon zarudyni | 01300011210151110011001?004302031003110? | Maisano et al., 2006 | [43] |
| Rhineura hatcherii | 01513100211??0010110221?003302121331141? | Kearney et al., 2005 | [44] |
| Spathorhychus fossorium | 0?614100221???010??0211?201?230?1332222? | Müller et al., 2016 | [46] |
References
- Albert, E.M.; Fernández, A. Evidence of cryptic speciation in a fossorial reptile: Description of a new species of Blanus (Squamata: Amphisbaenia: Blanidae) from the Iberian Peninsula. Zootaxa 2009, 2234, 56–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sindaco, R.; Kornilios, P.; Sacchi, R.; Lymberakis, P. Taxonomic reassessment of Blanus strauchi (Bedriaga, 1884) (Squamata: Amphisbaenia: Blanidae), with the description of a new species from southeast Anatolia (Turkey). Zootaxa 2014, 3795, 311–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceríaco, L.M.P.; Bauer, A.M. An integrative approach to the nomenclature and taxonomic status of the genus Blanus Wagler, 1830 (Squamata: Blanidae) from the Iberian Peninsula. J. Nat. Hist. 2018, 52, 849–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baran, İ.; Avcı, A.; Kumlutaş, Y.; Olgun, K.; Ilgaz, Ç. Türkiye Amfibi ve Sürüngenleri; Palme: Ankara, Turkey, 2021; p. 223. [Google Scholar]
- von Bedriaga, J. Amphisbaena cinerea und A. strauchi v. Bedr. Erster Beitrag zur Kenntniss der Deppelscleichen. Arch. Für Naturgeschicte 1884, 50, 23–77. [Google Scholar]
- Werner, F. Über einige neue Reptilien und einen neuen Frosch aus dem cilicischen Taurus. Zool. Anz. 1898, 21, 217–223. [Google Scholar]
- Busack, S.D. Biochemical and morphological differentiation in Spanish and Moroccan populations of Blanus and the description of a new species from northern Morocco (Reptilia, Amphisbaenia, Amphisbaenidae). Copeia 1988, 1988, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampaio, F.L.; Harris, D.J.; Perera, A.; Salvi, D. Phylogenetic and diversity patterns of Blanus worm lizards (Squamata: Amphisbaenia): Insights from mitochondrial and nuclear gene genealogies and species tree. J. Zool. Syst. Evol. Res. 2015, 53, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hipsley, C.A.; Rentinck, M.N.; Röder, M.O.; Müller, J. Ontogenetic allometry constrains cranial shape of the head-first burrowing worm lizard Cynisca leucura (Squamata: Amphisbaenidae). J. Morphol. 2016, 277, 1159–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hohl, L.S.L.; Barros-Filho, J.D.; Rocha-Barbosa, O. Skull variation in a shovel-headed amphisbaenian genus, inferred from the geometric morphometric analysis of five South American Leposternon species. J. Morphol. 2018, 279, 1665–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hohl, L.S.L.; Azorit, C.; Vassallo, A.I.; Casinos, A.; Machado, A.S.; Lopes, R.T.; Rocha-Barbosa, O. Ontogenetic skull variation in a shovel-headed amphisbaenian species. J. Morphol. 2023, 284, e21643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gans, C.; Wever, E.G. The Amphisbaenian Ear: Blanus cinereus and Diplometopon zarudnyi. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1975, 72, 1487–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martín, J.; López, P.; Salvador, A. Microhabitat selection of the Amphisbaenian Blanus cinereus. Copeia 1991, 1991, 1142–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-Paniagua, C.; Blázoquez, M.C.; Keller, C.; Andreu, A.C.; Olmedo, G.; Mateo, J.A. Observations on seasonal and diel surface activity of the amphisbaenian Blanus cinereus in South-Western Spain. Herpetol. J. 1995, 5, 217–220. [Google Scholar]
- Vaconcelos, R.; Carretero, M.A.; Harris, D.J. Phylogeography of the genus Blanus (worm lizards) in Iberia and Morocco based on mitochondrial and nuclear markers—Preliminary analysis. Amphib.-Reptilia 2006, 27, 339–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albert, E.M.; Zardoya, R.; García-París, M. Phylogeographical and speciation patterns in subterranean worm lizards of the genus Blanus (Amphisbaenia: Blanidae). Mol. Ecol. 2007, 16, 1519–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yıldırımhan, H.S.; Yılmaz, N.; İncedoğan, S. Helminth Fauna of the Anatolian Worm Lizard, Blanus strauchi (Bedriaga, 1884) From Hatay. Türkiye Parazitoloji Dergisi. 2009, 33, 327–329. [Google Scholar]
- Yıldız, M.Z.; Akman, B.; Göçmen, B.; Yalçınkaya, D. New locality records for the Turkish worm lizard, Blanus strauchi aporus (Werner, 1898) (Sauria: Amphisbaenidae) in Southeast Anatolia, Turkey. North-West. J. Zool. 2009, 5, 379–385. [Google Scholar]
- Düşen, S.; Uğurtaş, İ.H.; Aydoğdu, A. Nematode parasites of the two limbless lizards: Turkish worm lizard, Blanus strauchi (Bedriaga, 1884) (Squamata: Amphisbaenidae), and slow worm, Anguis fragilis Linnaeus 1758 (Squamata: Anguidae), from Turkey. Helminthologia 2010, 47, 158–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tok, C.V.; Tosunoğlu, M.; Ayaz, D.; Çiçek, K.; Mutlu, H.S. New records of the Anatolian Worm Lizard, Blanus strauchi (Bedriaga, 1884), from Turkey. Herpetozoa 2012, 24, 107–111. [Google Scholar]
- Jablonski, D.; Sadek, R.A. The species identity and biogeography of Blanus (Amphisbaenia: Blanidae) in Lebanon. Zool. Middle East. 2019, 65, 208–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gervais, P. Recherches sur l’osteologie de plusieurs especes d’Amphisbenes, et remarques sur la classification de ces reptiles. Ann. Sci. Naturelles 1853, 20, 293–312. [Google Scholar]
- Fürbringer, M. Die Knochen und Muskeln der Extremitaten bei den Schlangenahnlichen Sauriern: Vergleichend-Anatomische Abhandlung; W. Engelmann: Leipzig, Germany, 1869; p. 135. [Google Scholar]
- Fürbringer, M. Zur vergleichenden Anatomie des Brustschulterapparates und der Schultermuskeln. Jenaische Z. Für Naturwissenschaft 1900, 34, 215–718. [Google Scholar]
- Cope, E.D. The osteology of the Lacertilia. Proc. Am. Philos. Soc. 1892, 30, 185–221. [Google Scholar]
- Zangerl, R. Contributions to the osteology of the post-cranial skeleton of the Amphisbaenidae. Am. Midl. Nat. 1945, 33, 764–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kearney, M. Appendicular skeleton in Amphisbaenians (Reptilia: Squamata). Copeia 2002, 2002, 719–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villa, A.; Kirchner, M.; Alba, D.M.; Bernardini, F.; Bolet, A.; Lujan, A.H.; Fortuny, J.; Hipsley, A.C.; Müller, J.; Sindaco, R.; et al. Comparative cranial osteology of Blanus (Squamata: Amphisbaenia). Zool. J. Linn. Soc. 2019, 185, 693–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talanta, M. Evolution of postcranial skeleton in worm lizards inferred from its status in the Cretaceous stem-amphisbaenian Slavoia darevskii. Acta Palaeontol. Pol. 2017, 62, 9–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delfino, M. Blanus from the Early Pleistocene of Southern Italy: Another small tessera from a big mosaic. In Herpetologia Bonnensis; Böhme, W., Bischoff, W., Ziegler, T., Eds.; Societas Europae Herpetologica: Bonn, Germany, 1997; pp. 89–97. [Google Scholar]
- Čerňanskỳ, A.; Venczel, M. An amphisbaenid reptile (Squamata, Amphisbaenidae) from the Lower Miocene of Northwest Bohemia (MN 3, Czech Republic). Neues Jahrb. Fur Geol. Und Palaontol. Abhandlungen 2011, 260, 73–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolet, A.; Delfino, M.; Fortuny, J.; Almécija, S.; Robles, J.M.; Alba, D.M.; Rook, L. An amphisbaenian skull from the European Miocene and the evolution of Mediterranean worm lizards. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e98082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgalis, G.L.; Halaçlar, K.; Mayda, S.; Kaya, T.; Ayaz, D. First fossil find of the Blanus strauchi complex (Amphisbaenia, Blanidae) from the Miocene of Anatolia. J. Vertebr. Paleontol. 2018, 38, e1437044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syromyatnikova, E.V.; Kovalenko, E.S.; Kaloyan, A.A. A fossil record of the Eastern clade of Blanus (Amphisbaenia: Blanidae) from the late Miocene of Ukraine. Geobios 2021, 69, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wassersug, R. A procedure for differential staining of cartilage and bone in whole formalin fixed vertebrates. Stain Technol. 1976, 51, 131–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gans, C.; Montero, R. An atlas of amphisbaenian skull anatomy. In Biology of the Reptilia: Morphology I. The skull and Appendicular Locomotor Apparatus of Lepidosauria; Gans, C., Gaunt, A., Adler, K., Eds.; Society for the Study of Amphibians and Reptiles: Ithaca, Greece, 2008; pp. 621–738. [Google Scholar]
- Rohlf, F.J. tpsDig; SUNY at Stony Brook Department of Ecology and Evolution, State University of New York, Stony Brook: New York, NY, USA, 2010; 11794–524. [Google Scholar]
- Goloboff, P.A.; Farris, J.S.; Nixon, K.C. TNT, a free program for phylogenetic analysis. Cladistics 2008, 24, 774–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goloboff, P.A.; Catalano, S.A. TNT version 1.5, including a full implementation of phylogenetic morphometrics. Cladistics 2016, 32, 221–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uetz, P.; Freed, P.; Aguliar, R.; Reyes, F.; Kudera, J.; Hošek, J. The Reptile Database. Available online: http://reptile-database.org (accessed on 11 June 2025).
- Bell, C.J.; Cadena, C.; Meza, A.; Rudie, L.; Lewis, P.J. Cranial anatomy of the “round-headed” Amphisbaenian Zygaspis quadrifrons (Squamata, Amphisbaenia) based on high-resolution x-ray computed tomography. Anat. Rec. 2023, 307, 495–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montero, R.; Gans, C. The head skeleton of Amphisbaenia alba Linneaus. Ann. Carnegie Mus. 1999, 68, 15–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maisano, J.A.; Kearney, M.; Rowe, T. Cranial anatomy of the spade-headed Amphisbaenian Diplometopon zarudnyi (Squamata, Amphisbaenia) based on high-resolution X-ray Ccmputed tomography. J. Morphol. 2006, 267, 70–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kearney, M.; Maisano, J.A.; Rowe, T. Cranial anatomy of the extinct amphisbaenian Rhineura hatcherii (Squamata, Amphisbaenia) based on high-resolution X-ray computed tomography. J. Morphol. 2005, 264, 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paiva, C.L.; Hipsley, C.A.; Müller, J.; Zaher, H.; Costa, H.C. Comparative skull osteology of Amphisbaena arda and Amphisbaena vermicularis (Squamata: Amphisbaenidae). J. Morphol. 2024, 285, e21702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, J.; Hipsley, C.A.; Maisano, J.A. Skull osteology of the Eocene amphisbaenian Spathorhynchus fossorium (Reptilia, Squamata) suggests convergent evolution and reversals of fossorial adaptations in worm lizards. J. Anat. 2016, 229, 615–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gans, C. Tetrapod limblessness: Evolution and functional corollaries. Am. Zool. 1975, 15, 455–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.S.Y. Convergent evolution and character correlation in burrowing reptiles: Towards a resolution of squamate relationships. Biol. J. Linn. Soc. 1998, 65, 369–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiens, J.J.; Brandley, M.C.; Reeder, T.W. Why does a trait evolve multiple times within a clade? Repeated evolution of snake-like body form in squamate reptiles. Evolution 2006, 60, 123–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camaiti, M.; Evans, A.R.; Hipsley, C.A.; Chapple, D.G. A fare-well to arms and legs: A review of limb reduction in squamates. Biol. Rev. 2021, 96, 1035–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayne, B.C. Comparative morphology of the semispinalisspinalis muscle of snakes and correlations with locomotion and constriction. J. Morphol. 1982, 172, 83–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayne, B.C. Swimming in constricting (Elaphe g. guttata) and nonconstricting (Nerodia fasciata pictiventris) colubroid snakes. Copeia 1985, 1985, 195–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasc, J.P.; Gans, C. Tests on locomotion of the elongate and limbless lizard Anguis fragilis (Squamata: Anguidae). Copeia 1990, 1990, 1055–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, K.C.; Arnold, S.J.; Gladstone, J. The effect of substrate and vertebral number on locomotion in the garter snake Thamnophis elegans. Funct. Ecol. 1997, 11, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, E.N. Structural niche, limb morphology and locomotion in lacertid lizards (Squamata Lacertidae); a preliminary survey. Bull. Br. Mus. (Nat. Hist.) Zool. 1998, 64, 63–89. [Google Scholar]
- Arnold, E.N. Osteology, genitalia and the relationships of Acanthodactylus (Reptilia: Lacertidae). Bull. Br. Mus. (Nat. Hist.) Zool. 1983, 44, 291–339. [Google Scholar]
- Urben, C.C.; Daza, J.D.; Cadena, C.; Lewis, P.J.; Thies, M.L. The Homology of the Pelvic Elements of Zygaspis quadrifrons (Squamata: Amphisbaenia). Anat. Rec. 2014, 297, 1407–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gans, C. The characteristics and affinities of the Amphisbaenia. Trans. Zool. Soc. Lond. 1978, 34, 347–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawkins, R.; Bell, C.; Olori, J.C.; Stocker, M.R. Intraspecific variation in the cranial osteology of Diplometopon zarudnyi (Squamata: Amphisbaenia: Trogonophidae). J. Morphol. 2022, 283, 1359–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meza, A.; Bell, C.J.; Daza, J.D.; Thies, M.L.; Lewis, P.J. Variation in the cranial osteology of the amphisbaenian genus Zygaspis based on high-resolution x-ray computed tomography. Anat. Rec. 2023, 307, 475–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abo-Eleneen, R.E.; Othman, S.I.; Al-Harbi, H.M.; Abdeen, A.M.; Allam, A.A. Anatomical study of the skull of amphisbaenian Diplometopon zarudnyi (Squamata, Amphisbaenia). Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2019, 26, 503–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zangerl, R. Contributions to the osteology of the skull of the Amphisbaenidae. Am. Midl. Nat. 1944, 31, 417–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Species | Region (City of Türkiye) | Number of Sample |
|---|---|---|
| Blanus alexandri | Adıyaman | 3 |
| Mardin | 2 | |
| Urfa | 3 | |
| Blanus aporus | Antalya | 2 |
| Adana | 2 | |
| Mersin | 2 | |
| Hatay | 2 | |
| Blanus strauchi | Marmaris (Muğla) | 3 |
| Fethiye (Muğla) | 3 | |
| Muğla | 2 |
| Species | Cervical Vertebrae | Thoracic Vertebra | Lumbar Vertebrae | Caudal Vertebrae |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| B. aporus | 2 (atlas and axis) | 98 | 2 | 16 |
| B. alexandri | 2 (atlas and axis) | 100 | 2 | 19 |
| B. strauchi | 2 (atlas and axis) | 105 | 2 | 19 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yıldırım Caynak, E.; Candan, K.; Kumlutaş, Y.; Ilgaz, Ç.; Korkmaz, A.G.; Yazar, E.B.; Şen, E.; Hastürk, E.B.; Birlik, S.; Akat Çömden, E.; et al. Comparative Cranial and Postcranial Osteology of Blanus Species (Squamata: Amphisbaenia) from Türkiye: Insights from Morphological Evolution and Phylogeny. Life 2025, 15, 1263. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15081263
Yıldırım Caynak E, Candan K, Kumlutaş Y, Ilgaz Ç, Korkmaz AG, Yazar EB, Şen E, Hastürk EB, Birlik S, Akat Çömden E, et al. Comparative Cranial and Postcranial Osteology of Blanus Species (Squamata: Amphisbaenia) from Türkiye: Insights from Morphological Evolution and Phylogeny. Life. 2025; 15(8):1263. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15081263
Chicago/Turabian StyleYıldırım Caynak, Elif, Kamil Candan, Yusuf Kumlutaş, Çetin Ilgaz, Ahmet Gökay Korkmaz, Emine Beyza Yazar, Eda Şen, Ecem Büşra Hastürk, Sezen Birlik, Esra Akat Çömden, and et al. 2025. "Comparative Cranial and Postcranial Osteology of Blanus Species (Squamata: Amphisbaenia) from Türkiye: Insights from Morphological Evolution and Phylogeny" Life 15, no. 8: 1263. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15081263
APA StyleYıldırım Caynak, E., Candan, K., Kumlutaş, Y., Ilgaz, Ç., Korkmaz, A. G., Yazar, E. B., Şen, E., Hastürk, E. B., Birlik, S., Akat Çömden, E., & Gül, S. (2025). Comparative Cranial and Postcranial Osteology of Blanus Species (Squamata: Amphisbaenia) from Türkiye: Insights from Morphological Evolution and Phylogeny. Life, 15(8), 1263. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15081263






