Postbiotics: A Promising Approach to Combat Age-Related Diseases
Abstract
1. Introduction
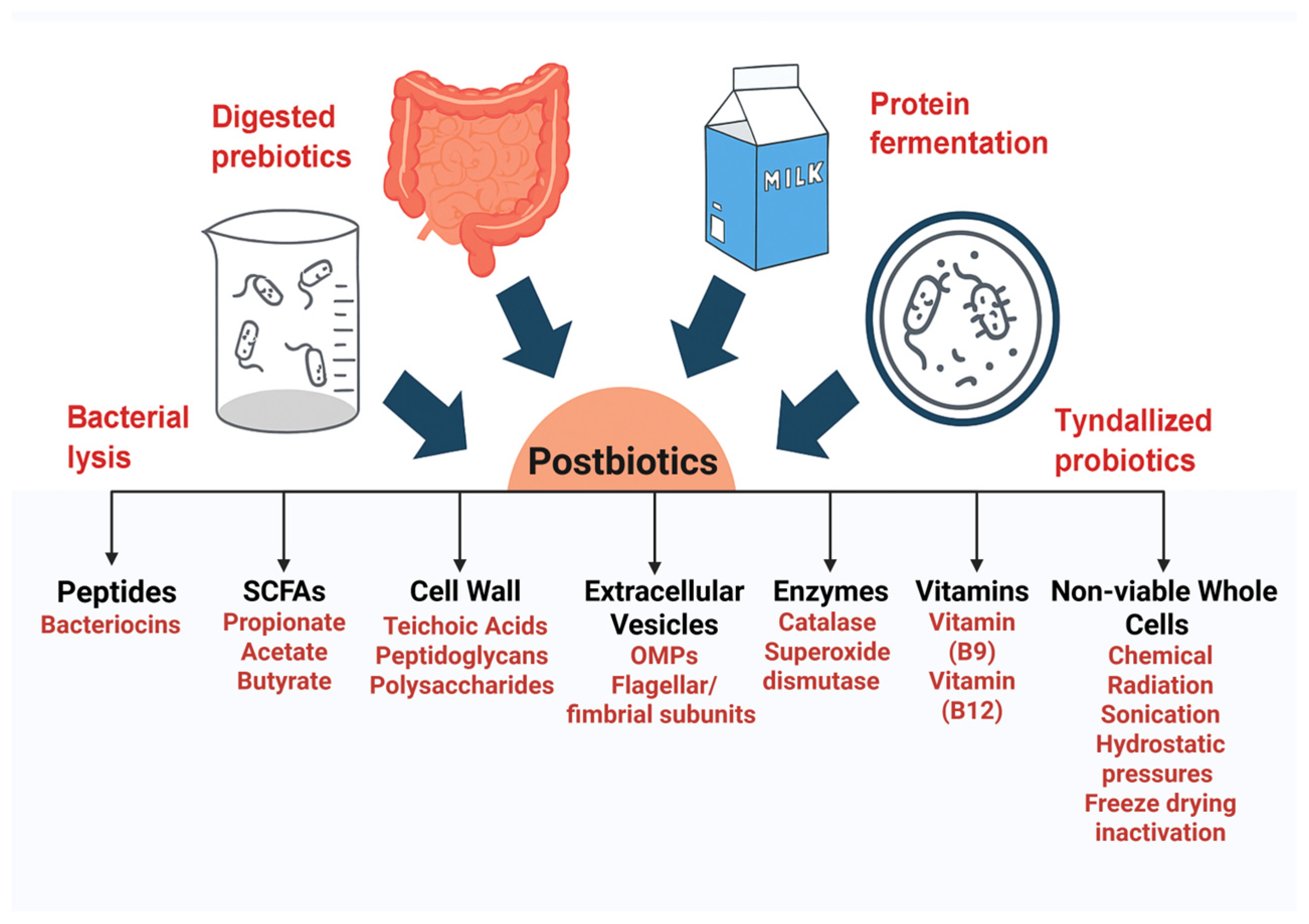
2. Key Components of Postbiotics
2.1. Non-Viable Whole Cells
2.2. Bacteriocins
2.3. Short Chain Fatty Acids
2.4. Extracellular Vesicles
2.5. Peptidoglycans as Bacterial Cell Wall-Derived Postbiotics
2.6. Teichoic Acids
2.7. Polysaccharides
2.8. Enzymes
2.9. Vitamins
3. Advantages of Postbiotics over Probiotics
4. The Role of Postbiotics in Healthy Ageing and Age-Related Diseases
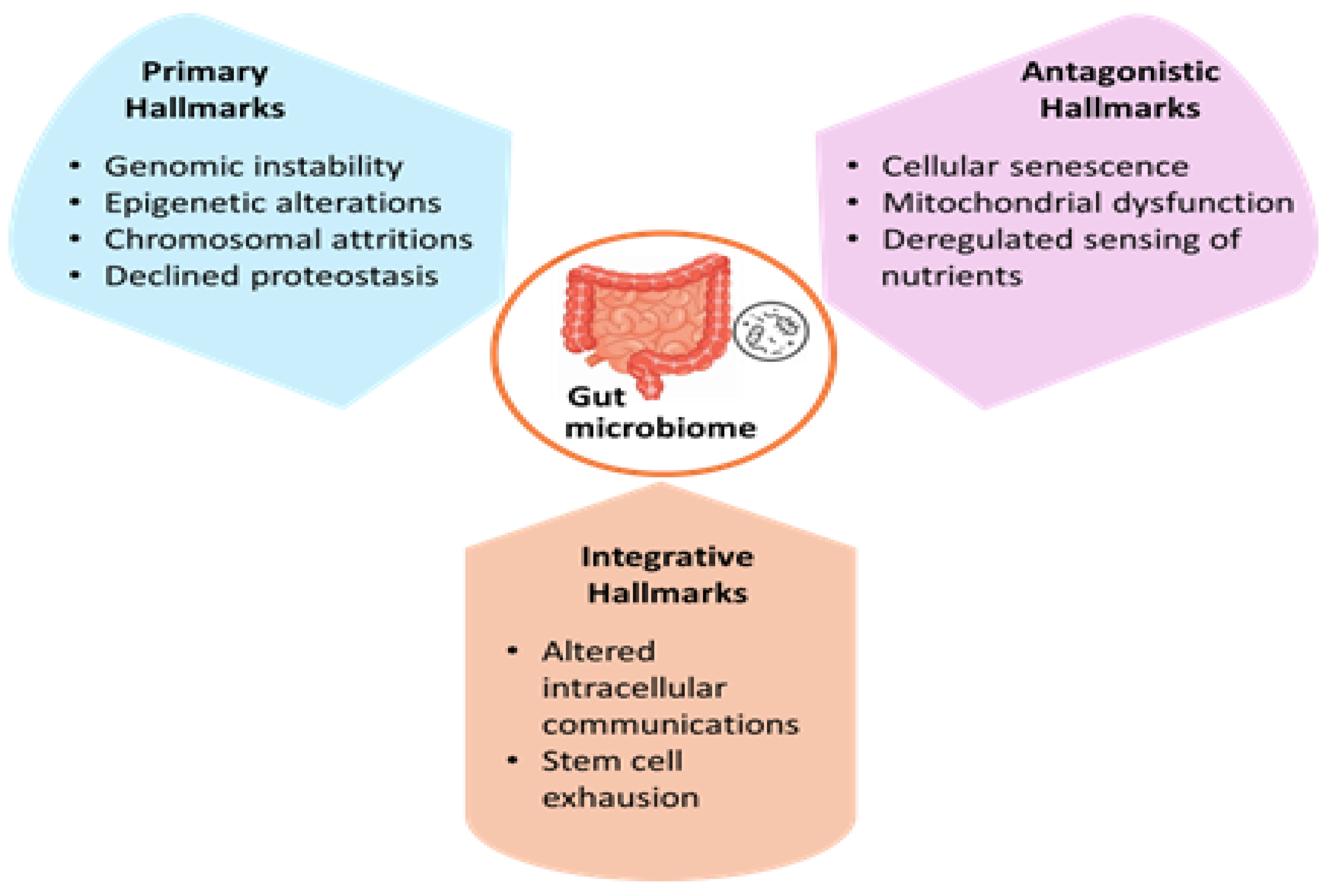
4.1. Gut Microbiota Dysbiosis as a Hallmark of Ageing and the Role of Postbiotics in Healthy Ageing
4.2. Current Understanding of Postbiotic Mechanism of Action
4.2.1. Antioxidant Effects and Oxidative Stress Mitigation
4.2.2. Anti-Inflammatory and Immunomodulatory Properties
4.2.3. Postbiotics and Gut Barrier Integrity: Mechanisms and Protective Role
5. Gut Microbiome Signatures in Ageing and the Role of Postbiotics in Age-Related Disease Mitigation
5.1. Age-Related Changes in Gut Microbiome Signatures and Their Health Implications
5.2. Microbiome Signatures in Healthy vs. Unhealthy Ageing
5.3. Clinical Evidence of Postbiotics in Modulating Gut Microbiota and Promoting Healthy Ageing
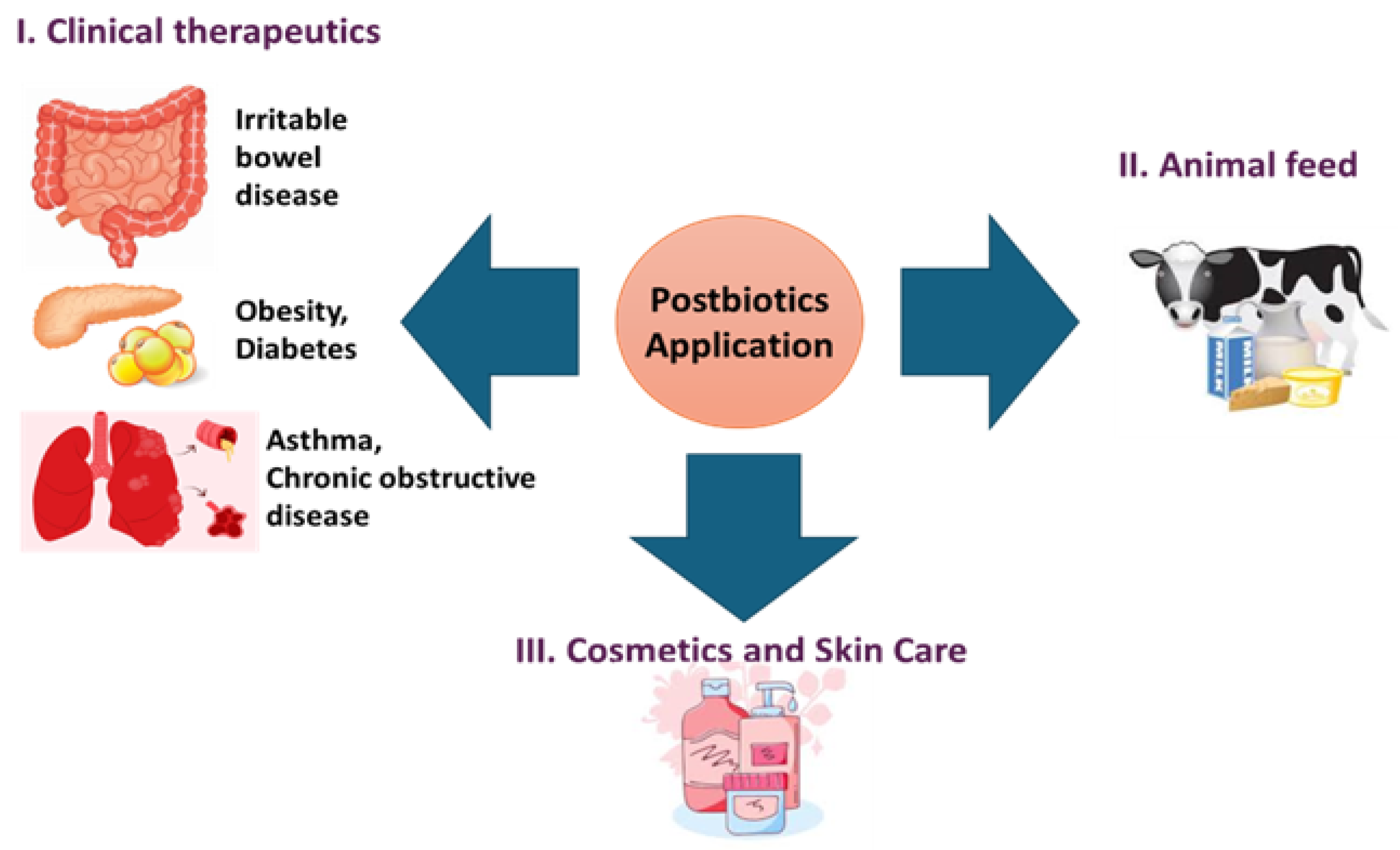
6. Specific Age-Related Diseases and Postbiotic Interventions
6.1. Cardiovascular Diseases and Metabolic Disorders
6.2. Neurodegenerative Disorders
6.3. Bone Health and Osteoporosis
7. Economic Potential and Regulatory Outlook of Postbiotics
8. Challenges and Future Directions in Postbiotic Research and Therapeutic Applications
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. Ageing and Health. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/ageing-and-health (accessed on 23 July 2025).
- United Nations (Department of Economic and Social Affairs, Population Division). World Population Prospects 2022: Summary of Results; Report No.: UN DESA/POP/2022/TR/NO.3; Department of Economic and Social Affairs, Population Division: New York, NY, USA, 2022.
- Australian Bureau of Statistics. Population Projections, Australia; Cat. no. 3222.0; Australian Bureau of Statistics: Canberra, Australia, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Kirkwood, T.B. Evolution of ageing. Nature 1977, 270, 301–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garmany, A.; Yamada, S.; Terzic, A. Longevity leap: Mind the healthspan gap. NPJ Regen. Med. 2021, 6, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maynard, S.; Fang, E.F.; Scheibye-Knudsen, M.; Croteau, D.L.; Bohr, V.A. DNA Damage, DNA Repair, Aging, and Neurodegeneration. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2015, 5, a025130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gladyshev, V.N. Aging: Progressive decline in fitness due to the rising deleteriome adjusted by genetic, environmental, and stochastic processes. Aging Cell 2016, 15, 594–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clegg, A.; Young, J.; Iliffe, S.; Rikkert, M.O.; Rockwood, K. Frailty in elderly people. Lancet 2013, 381, 752–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.H.; Glynn, R.J.; Avorn, J.; Lipsitz, L.A.; Rockwood, K.; Pawar, A.; Schneeweiss, S. Validation of a Claims-Based Frailty Index Against Physical Performance and Adverse Health Outcomes in the Health and Retirement Study. J. Gerontol. Ser. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2019, 74, 1271–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fore, D.; Leibfritz, W.; Roseveare, D.; Wurzel, E. Ageing Populations, Pension Systems and Government Budgets: Simulations for 20 OECD Countries; OECD Publishing: Paris, France, 1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breyer, F.; Felder, S. Ageing, health, and health care. Oxf. Rev. Econ. Policy 2011, 26, 674–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosch-Farré, C.; Garre-Olmo, J.; Bonmatí-Tomàs, A.; Malagón-Aguilera, M.C.; Gelabert-Vilella, S.; Fuentes-Pumarola, C.; Juvinyà-Canal, D. Prevalence and related factors of Active and Healthy Ageing in Europe according to two models: Results from the Survey of Health, Ageing and Retirement in Europe (SHARE). PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0206353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garibaldi, P.; Oliveira Martins, J.; Ours, J. Ageing, Health, and Productivity: The Economics of Increased Life Expectancy; OUP Oxford: Oxford, UK, 2010; pp. 1–280. [Google Scholar]
- Sharpe, A. Is ageing a drag on productivity growth? A review article on ageing, health and productivity: The economics of increased life expectancy. Int. Product. Monit. 2011, 21, 82. [Google Scholar]
- Harris, A.; Sharma, A. Estimating the future health and aged care expenditure in Australia with changes in morbidity. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0201697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menassa, M.; Stronks, K.; Khatmi, F.; Roa Díaz, Z.M.; Espinola, O.P.; Gamba, M.; Itodo, O.A.; Buttia, C.; Wehrli, F.; Minder, B.; et al. Concepts and definitions of healthy ageing: A systematic review and synthesis of theoretical models. EClinicalMedicine 2023, 56, 101821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Neill, D. Brocklehurst’s textbook of geriatric medicine and gerontology. In Age Ageing, 7th ed.; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2011; Volume 40, p. 409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelaiditi, E.; van Kan, G.A.; Cesari, M. Frailty: Role of nutrition and exercise. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2014, 17, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hurez, V.; Dao, V.; Liu, A.; Pandeswara, S.; Gelfond, J.; Sun, L.; Bergman, M.; Orihuela, C.J.; Galvan, V.; Padrón, Á.; et al. Chronic mTOR inhibition in mice with rapamycin alters T, B, myeloid, and innate lymphoid cells and gut flora and prolongs life of immune-deficient mice. Aging Cell 2015, 14, 945–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, S.C.; Rabinovitch, P.S.; Kaeberlein, M. mTOR is a key modulator of ageing and age-related disease. Nature 2013, 493, 338–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stallone, G.; Infante, B.; Prisciandaro, C.; Grandaliano, G. mTOR and Aging: An Old Fashioned Dress. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, A.W.; Uit de Bos, J.; Sterken, M.G.; Kammenga, J.E.; Smith, R.L.; Houtkooper, R.H. Forward and reverse genetics approaches to uncover metabolic aging pathways in Caenorhabditis elegans. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2018, 1864, 2697–2706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, H.G.; Altintas, O.; Kim, E.J.E.; Kwon, S.; Lee, S.V. Age-dependent changes and biomarkers of aging in Caenorhabditis elegans. Aging Cell 2019, 18, e12853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Ou, Y.; Li, Y.; Hu, S.; Shao, L.W.; Liu, Y. Metformin extends C. elegans lifespan through lysosomal pathway. eLife 2017, 6, e31268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin-Montalvo, A.; Mercken, E.M.; Mitchell, S.J.; Palacios, H.H.; Mote, P.L.; Scheibye-Knudsen, M.; Gomes, A.P.; Ward, T.M.; Minor, R.K.; Blouin, M.J.; et al. Metformin improves healthspan and lifespan in mice. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salmon, A.B. About-face on the metabolic side effects of rapamycin. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 2585–2586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlender, L.; Martinez, Y.V.; Adeniji, C.; Reeves, D.; Faller, B.; Sommerauer, C.; Al Qur’an, T.; Woodham, A.; Kunnamo, I.; Sönnichsen, A.; et al. Efficacy and safety of metformin in the management of type 2 diabetes mellitus in older adults: A systematic review for the development of recommendations to reduce potentially inappropriate prescribing. BMC Geriatr. 2017, 17, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govindaraju, T.; Sahle, B.W.; McCaffrey, T.A.; McNeil, J.J.; Owen, A.J. Dietary Patterns and Quality of Life in Older Adults: A Systematic Review. Nutrients 2018, 10, 971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bojang, K.P.; Manchana, V. Nutrition and Healthy Aging: A Review. Curr. Nutr. Rep. 2023, 12, 369–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koutnikova, H.B.; Genser, M.; Monteiro-Sepulveda, J.; Faurie, M.; Rizkalla, S.; Schrezenmeir, J.; Clément, K. Impact of Bacterial Probiotics on Obesity, Diabetes and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Related Variables: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomised Controlled Trials. BMJ Open 2019, 9, e017995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eloe-Fadrosh, E.A.; Brady, A.; Crabtree, J.; Drabek, E.F.; Ma, B.; Mahurkar, A.; Ravel, J.; Haverkamp, M.; Fiorino, A.M.; Botelho, C.; et al. Functional Dynamics of the Gut Microbiome in Elderly People during Probiotic Consumption. mBio 2015, 6, 10–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, B.; Sivaramakrishnan, P.; Lin, C.J.; Neve, I.A.A.; He, J.; Tay, L.W.R.; Sowa, J.N.; Sizovs, A.; Du, G.; Wang, J.; et al. Microbial Genetic Composition Tunes Host Longevity. Cell 2017, 169, 1249–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leulier, F.; MacNeil, L.T.; Lee, W.J.; Rawls, J.F.; Cani, P.D.; Schwarzer, M.; Zhao, L.; Simpson, S.J. Integrative Physiology: At the Crossroads of Nutrition, Microbiota, Animal Physiology, and Human Health. Cell Metab. 2017, 25, 522–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimidi, E.; Christodoulides, S.; Scott, S.M.; Whelan, K. Mechanisms of Action of Probiotics and the Gastrointestinal Microbiota on Gut Motility and Constipation. Adv. Nutr. 2017, 8, 484–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doron, S.; Snydman, D.R. Risk and safety of probiotics. Clin. Infect. Dis. Off. Publ. Infect. Dis. Soc. Am. 2015, 60 (Suppl. S2), S129–S134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davani-Davari, D.; Negahdaripour, M.; Karimzadeh, I.; Seifan, M.; Mohkam, M.; Masoumi, S.J.; Berenjian, A.; Ghasemi, Y. Prebiotics: Definition, Types, Sources, Mechanisms, and Clinical Applications. Foods 2019, 8, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salminen, S.; Collado, M.C.; Endo, A.; Hill, C.; Lebeer, S.; Quigley, E.M.M.; Sanders, M.E.; Shamir, R.; Swann, J.R.; Szajewska, H.; et al. The International Scientific Association of Probiotics and Prebiotics (ISAPP) consensus statement on the definition and scope of postbiotics. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 18, 649–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Żółkiewicz, J.; Marzec, A.; Ruszczyński, M.; Feleszko, W. Postbiotics-A Step Beyond Pre- and Probiotics. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vinderola, G.; Sanders, M.E.; Salminen, S. The Concept of Postbiotics. Foods 2022, 11, 1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wegh, C.A.M.; Geerlings, S.Y.; Knol, J.; Roeselers, G.; Belzer, C. Postbiotics and Their Potential Applications in Early Life Nutrition and Beyond. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rafique, N.; Jan, S.Y.; Dar, A.H.; Dash, K.K.; Sarkar, A.; Shams, R.; Pandey, V.K.; Khan, S.A.; Amin, Q.A.; Hussain, S.Z. Promising bioactivities of postbiotics: A comprehensive review. J. Agric. Food Res. 2023, 14, 100708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurkiewicz, D.; Zielnik-Jurkiewicz, B. Bacterial lysates in the prevention of respiratory tract infections. Pol. J. Otolaryngol. 2018, 72, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopetuso, L.; Graziani, C.; Guarino, A.; Lamborghini, A.; Masi, S.; Stanghellini, V. Gelatin tannate and tyndallized probiotics: A novel approach for treatment of diarrhea. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2017, 21, 873–883. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.H.; Yoon, J.M.; Kim, Y.H.; Jeong, D.G.; Park, S.; Kang, D.J. Therapeutic effect of tyndallized Lactobacillus rhamnosus IDCC 3201 on atopic dermatitis mediated by down-regulation of immunoglobulin E in NC/Nga mice. Microbiol. Immunol. 2016, 60, 468–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar-Toalá, J.E.; Arioli, S.; Behare, P.; Belzer, C.; Berni Canani, R.; Chatel, J.M.; D’Auria, E.; de Freitas, M.Q.; Elinav, E.; Esmerino, E.A.; et al. Postbiotics—When simplification fails to clarify. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 18, 825–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, M.S.; Ijssennagger, N.; Kies, A.K.; van Mil, S.W.C. Protein fermentation in the gut; implications for intestinal dysfunction in humans, pigs, and poultry. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2018, 315, G159–G170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeşilyurt, N.; Yılmaz, B.; Ağagündüz, D.; Capasso, R. Involvement of Probiotics and Postbiotics in the Immune System Modulation. Biologics 2021, 1, 89–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, J.; Wu, C. Modulation of Gut Microbiota and Immune System by Probiotics, Pre-biotics, and Post-biotics. Front. Nutr. 2022, 8, 634897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mi, X.-J.; Tran, T.H.M.; Park, H.-R.; Xu, X.Y.; Subramaniyam, S.; Choi, H.S.; Kim, J.; Koh, S.C.; Kim, Y.J. Immune-enhancing effects of postbiotic produced by Bacillus velezensis Kh2-2 isolated from Korea Foods. Food Res. Int. 2022, 152, 110911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, X.; Rodriguez, J.; Wee, J. Dietary Postbiotics Reduce Cytotoxicity and Inflammation Induced by Crystalline Silica in an In Vitro RAW 264.7 Macrophage Model. Foods 2022, 11, 877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurunathan, S.; Thangaraj, P.; Kim, J.-H. Postbiotics: Functional Food Materials and Therapeutic Agents for Cancer, Diabetes, and Inflammatory Diseases. Foods 2024, 13, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salminen, S.; Collado, M.C.; Endo, A.; Hill, C.; Lebeer, S.; Quigley, E.M.M.; Sanders, M.E.; Shamir, R.; Swann, J.R.; Szajewska, H.; et al. Reply to: Postbiotics—When simplification fails to clarify. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 18, 827–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuevas-González, P.F.; Liceaga, A.M.; Aguilar-Toalá, J.E. Postbiotics and paraprobiotics: From concepts to applications. Food Res. Int. 2020, 136, 109502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miettinen, M.; Vuopio-Varkila, J.; Varkila, K. Production of human tumor necrosis factor alpha, interleukin-6, and interleukin-10 is induced by lactic acid bacteria. Infect. Immun. 1996, 64, 5403–5405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastrangeli, G.; Corinti, S.; Butteroni, C.; Afferni, C.; Bonura, A.; Boirivant, M.; Colombo, P.; Di Felice, G. Effects of live and inactivated VSL#3 probiotic preparations in the modulation of in vitro and in vivo allergen-induced Th2 responses. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2009, 150, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugahara, H.; Yao, R.; Odamaki, T.; Xiao, J.Z. Differences between live and heat-killed bifidobacteria in the regulation of immune function and the intestinal environment. Benef. Microbes 2017, 8, 463–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarrerias, A.L.; Costil, V.; Vicari, F.; Létard, J.C.; Adenis-Lamarre, P.; Aisène, A.; Batistelli, D.; Bonnaud, G.; Carpentier, S.; Dalbiès, P.; et al. The effect of inactivated Lactobacillus LB fermented culture medium on symptom severity: Observational investigation in 297 patients with diarrhea-predominant irritable bowel syndrome. Dig. Dis. 2011, 29, 588–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aiba, Y.; Ishikawa, H.; Tokunaga, M.; Komatsu, Y. Anti-Helicobacter pylori activity of non-living, heat-killed form of lactobacilli including Lactobacillus johnsonii No.1088. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2017, 364, fnx102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehling, H.; Busjahn, A. Non-viable Lactobacillus reuteri DSMZ 17648 (Pylopass™) as a new approach to Helicobacter pylori control in humans. Nutrients 2013, 5, 3062–3073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumariya, R.; Garsa, A.K.; Rajput, Y.S.; Sood, S.K.; Akhtar, N.; Patel, S. Bacteriocins: Classification, synthesis, mechanism of action and resistance development in food spoilage causing bacteria. Microb. Pathog. 2019, 128, 171–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khorshidian, N.; Khanniri, E.; Mohammadi, M.; Mortazavian, A.M.; Yousefi, M. Antibacterial Activity of Pediocin and Pediocin-Producing Bacteria Against Listeria monocytogenes in Meat Products. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 709959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez, R.C.R.; Alvarenga, V.O.; Thomazini, M.; Fávaro-Trindade, C.S.; de Souza Sant’Ana, A. Assessment of the inhibitory effect of free and encapsulated commercial nisin (Nisaplin®), tested alone and in combination, on Listeria monocytogenes and Bacillus cereus in refrigerated milk. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 68, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Ramos, A.; Madi-Moussa, D.; Coucheney, F.; Drider, D. Current Knowledge of the Mode of Action and Immunity Mechanisms of LAB-Bacteriocins. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 2107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, R.; Dicks, L.M. Mode of action of lipid II-targeting lantibiotics. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2005, 101, 201–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.T.; Ding, X.L.; Li, N.; Zhang, X.Y.; Zeng, X.F.; Wang, S.; Liu, H.B.; Wang, Y.M.; Jia, H.M.; Qiao, S.Y. Dietary supplemented antimicrobial peptide microcin J25 improves the growth performance, apparent total tract digestibility, fecal microbiota, and intestinal barrier function of weaned pigs. J. Anim. Sci. 2017, 95, 5064–5076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loh, T.C.; Foo, H.L. Monogastric Animal Feed. U.S. Patent 9,271,518, 1 March 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Rescigno, M.; Penna, G. Postbiotic-Based Composition for Treatment of Ocular Inflammation. U.S. Patent 16/322,394, 13 June 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Bu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, S.; Liu, Q.; Hao, H.; Yi, H. Screening and Probiotic Potential Evaluation of Bacteriocin-Producing Lactiplantibacillus plantarum In Vitro. Foods 2022, 11, 1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerry, R.G.; Patra, J.K.; Gouda, S.; Park, Y.; Shin, H.-S.; Das, G. Benefaction of probiotics for human health: A review. J. Food Drug Anal. 2018, 26, 927–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gill, P.A.; van Zelm, M.C.; Muir, J.G.; Gibson, P.R. Review Article: Short Chain Fatty Acids as Potential Therapeutic Agents in Human Gastrointestinal and Inflammatory Disorders. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2018, 48, 15–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Vadder, F.; Kovatcheva-Datchary, P.; Zitoun, C.; Duchampt, A.; Bäckhed, F.; Mithieux, G. Microbiota-Produced Succinate Improves Glucose Homeostasis Via Intestinal Gluconeogenesis. Cell Metab. 2016, 24, 151–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouter, K.; Bakker, G.J.; Levin, E.; Hartstra, A.V.; Kootte, R.S.; Udayappan, S.D.; Katiraei, S.; Bahler, L.; Gilijamse, P.W.; Tremaroli, V.; et al. Differential metabolic effects of oral butyrate treatment in lean versus metabolic syndrome subjects. Clin. Transl. Gastroenterol. 2018, 9, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- den Besten, G.; Bleeker, A.; Gerding, A.; van Eunen, K.; Havinga, R.; van Dijk, T.H.; Oosterveer, M.H.; Jonker, J.W.; Groen, A.K.; Reijngoud, D.J.; et al. Short-Chain Fatty Acids Protect Against High-Fat Diet-Induced Obesity via a PPARγ-Dependent Switch From Lipogenesis to Fat Oxidation. Diabetes 2015, 64, 2398–2408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjbar, R.; Vahdati, S.N.; Tavakoli, S.; Khodaie, R.; Behboudi, H. Immunomodulatory roles of microbiota-derived short-chain fatty acids in bacterial infections. Biomed. Pharmacother 2021, 141, 111817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivaprakasam, S.; Gurav, A.; Paschall, A.V.; Coe, G.L.; Chaudhary, K.; Cai, Y.; Kolhe, R.; Martin, P.; Browning, D.; Huang, L.; et al. An essential role of Ffar2 (Gpr43) in dietary fibre-mediated promotion of healthy composition of gut microbiota and suppression of intestinal carcinogenesis. Oncogenesis 2016, 5, e238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.; McKenzie, C.; Vuillermin, P.J.; Goverse, G.; Vinuesa, C.G.; Mebius, R.E.; Macia, L.; Mackay, C.R. Dietary Fiber and Bacterial SCFA Enhance Oral Tolerance and Protect against Food Allergy through Diverse Cellular Pathways. Cell Rep. 2016, 15, 2809–2824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Qian, J.; Wang, Q.; Wang, F.; Ma, Z.; Qiao, Y. Butyrate protects rat liver against total hepatic ischemia reperfusion injury with bowel congestion. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e106184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krzyżek, P.; Marinacci, B.; Vitale, I.; Grande, R. Extracellular Vesicles of Probiotics: Shedding Light on the Biological Activity and Future Applications. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avila-Calderón, E.D.; Ruiz-Palma, M.D.S.; Aguilera-Arreola, M.G.; Velázquez-Guadarrama, N.; Ruiz, E.A.; Gomez-Lunar, Z.; Witonsky, S.; Contreras-Rodríguez, A. Outer Membrane Vesicles of Gram-Negative Bacteria: An Outlook on Biogenesis. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 557902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, A.J. The “hole” story of predatory outer-membrane vesicles. Can. J. Microbiol. 2018, 64, 589–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvarez, C.S.; Giménez, R.; Cañas, M.A.; Vera, R.; Díaz-Garrido, N.; Badia, J.; Baldomà, L. Extracellular vesicles and soluble factors secreted by Escherichia coli Nissle 1917 and ECOR63 protect against enteropathogenic E. coli-induced intestinal epithelial barrier dysfunction. BMC Microbiol. 2019, 19, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cañas, M.A.; Fábrega, M.J.; Giménez, R.; Badia, J.; Baldomà, L. Outer Membrane Vesicles From Probiotic and Commensal Escherichia coli Activate NOD1-Mediated Immune Responses in Intestinal Epithelial Cells. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Díaz-Garrido, N.; Bonnin, S.; Riera, M.; Gíménez, R.; Badia, J.; Baldomà, L. Transcriptomic microRNA Profiling of Dendritic Cells in Response to Gut Microbiota-Secreted Vesicles. Cells 2020, 9, 1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashrafian, F.; Behrouzi, A.; Shahriary, A.; Ahmadi Badi, S.; Davari, M.; Khatami, S.; Rahimi Jamnani, F.; Fateh, A.; Vaziri, F.; Siadat, S.D. Comparative study of effect of Akkermansia muciniphila and its extracellular vesicles on toll-like receptors and tight junction. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. Bed Bench 2019, 12, 163–168. [Google Scholar]
- Keshavarz Azizi Raftar, S.; Ashrafian, F.; Yadegar, A.; Lari, A.; Moradi, H.R.; Shahriary, A.; Azimirad, M.; Alavifard, H.; Mohsenifar, Z.; Davari, M.; et al. The Protective Effects of Live and Pasteurized Akkermansia muciniphila and Its Extracellular Vesicles against HFD/CCl4-Induced Liver Injury. Microbiol. Spectr. 2021, 9, e0048421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chelakkot, C.; Choi, Y.; Kim, D.K.; Park, H.T.; Ghim, J.; Kwon, Y.; Jeon, J.; Kim, M.S.; Jee, Y.K.; Gho, Y.S.; et al. Akkermansia muciniphila-derived extracellular vesicles influence gut permeability through the regulation of tight junctions. Exp. Mol. Med. 2018, 50, e450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Lee, K.; Hsu, M.; Nau, G.; Mylonakis, E.; Ramratnam, B. Lactobacillus-derived extracellular vesicles enhance host immune responses against vancomycin-resistant enterococci. BMC Microbiol. 2017, 17, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, H.; Zhang, X.; Tong, L.; Liu, Q.; Liang, X.; Bu, Y.; Gong, P.; Liu, T.; Zhang, L.; Xia, Y.; et al. Effect of Extracellular Vesicles Derived From Lactobacillus plantarum Q7 on Gut Microbiota and Ulcerative Colitis in Mice. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 777147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, E.A.; Choi, H.I.; Hong, S.W.; Kang, S.; Jegal, H.Y.; Choi, E.W.; Park, B.S.; Kim, J.S. Extracellular Vesicles Derived from Kefir Grain Lactobacillus Ameliorate Intestinal Inflammation via Regulation of Proinflammatory Pathway and Tight Junction Integrity. Biomedicines 2020, 8, 522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Shen, Q.; Lyu, W.; Lv, L.; Wang, W.; Yu, M.; Yang, H.; Tao, S.; Xiao, Y. Clostridium butyricum and Its Derived Extracellular Vesicles Modulate Gut Homeostasis and Ameliorate Acute Experimental Colitis. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e0136822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, L.; Yang, C.; Liu, L.; Mai, G.; Li, H.; Wu, L.; Jin, M.; Chen, Y. Commensal bacteria-derived extracellular vesicles suppress ulcerative colitis through regulating the macrophages polarization and remodeling the gut microbiota. Microb. Cell Factories 2022, 21, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jo, C.S.; Myung, C.H.; Yoon, Y.C.; Ahn, B.H.; Min, J.W.; Seo, W.S.; Lee, D.H.; Kang, H.C.; Heo, Y.H.; Choi, H.; et al. The Effect of Lactobacillus plantarum Extracellular Vesicles from Korean Women in Their 20s on Skin Aging. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2022, 44, 526–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aintablian, A.; Jaber, D.; Jallad, M.-A.; Abdelnoor, A. The Effect of Lactobacillus Plantarum and Bacterial Peptidoglycan on the Growth of Mouse Tumors in vivo and in vitro. Am. J. Immunol. 2017, 13, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Han, X.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Li, H.; Jiao, Y. Whole Peptidoglycan Extracts from the Lactobacillus paracasei subsp. paracasei M5 Strain Exert Anticancer Activity In Vitro. BioMed Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 2871710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shida, K.; Kiyoshima-Shibata, J.; Kaji, R.; Nagaoka, M.; Nanno, M. Peptidoglycan from lactobacilli inhibits interleukin-12 production by macrophages induced by Lactobacillus casei through Toll-like receptor 2-dependent and independent mechanisms. Immunology 2009, 128, e858–e869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavallari, J.F.; Fullerton, M.D.; Duggan, B.M.; Foley, K.P.; Denou, E.; Smith, B.K.; Desjardins, E.M.; Henriksbo, B.D.; Kim, K.J.; Tuinema, B.R.; et al. Muramyl Dipeptide-Based Postbiotics Mitigate Obesity-Induced Insulin Resistance via IRF4. Cell Metab. 2017, 25, 1063–1074.e1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, F.; Cao, H.; Cover, T.L.; Whitehead, R.; Washington, M.K.; Polk, D.B. Soluble proteins produced by probiotic bacteria regulate intestinal epithelial cell survival and growth. Gastroenterology 2007, 132, 562–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaefer, A.K.; Melnyk, J.E.; He, Z.; Del Rosario, F.; Grimes, C.L. Chapter 14—Pathogen- and Microbial- Associated Molecular Patterns (PAMPs/MAMPs) and the Innate Immune Response in Crohn’s Disease. In Immunity and Inflammation in Health and Disease; Chatterjee, S., Jungraithmayr, W., Bagchi, D., Eds.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 175–187. [Google Scholar]
- Szydłowska, A.; Sionek, B. Probiotics and Postbiotics as the Functional Food Components Affecting the Immune Response. Microorganisms 2022, 11, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Granados, M.J.; Franco-Robles, E. Postbiotics in human health: Possible new functional ingredients? Food Res. Int. 2020, 137, 109660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorakkattu, P.; Khanashyam, A.C.; Shah, K.; Babu, K.S.; Mundanat, A.S.; Deliephan, A.; Deokar, G.S.; Santivarangkna, C.; Nirmal, N.P. Postbiotics: Current Trends in Food and Pharmaceutical Industry. Foods 2022, 11, 3094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamann, L.; El-Samalouti, V.; Ulmer, A.J.; Flad, H.D.; Rietschel, E.T. Components of gut bacteria as immunomodulators. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 1998, 41, 141–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, B.; Xie, N.; Wang, Y. Cooperative effect of Bifidobacteria lipoteichoic acid combined with 5-fluorouracil on hepatoma-22 cells growth and apoptosis. Bull. Cancer 2015, 102, 204–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Ahmadi, S.; Nagpal, R.; Jain, S.; Mishra, S.P.; Kavanagh, K.; Zhu, X.; Wang, Z.; McClain, D.A.; Kritchevsky, S.B.; et al. Lipoteichoic acid from the cell wall of a heat killed Lactobacillus paracasei D3-5 ameliorates aging-related leaky gut, inflammation and improves physical and cognitive functions: From C. elegans to mice. GeroScience 2020, 42, 333–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Souza, L.F.; Jardim, F.R.; Sauter, I.P.; de Souza, M.M.; Bernard, E.A. High glucose increases RAW 264.7 macrophages activation by lipoteichoic acid from Staphylococcus aureus. Clin. Chim. Acta 2008, 398, 130–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zadeh, M.; Khan, M.W.; Goh, Y.J.; Selle, K.; Owen, J.L.; Klaenhammer, T.; Mohamadzadeh, M. Induction of intestinal pro-inflammatory immune responses by lipoteichoic acid. J. Inflamm. 2012, 9, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badel, S.; Bernardi, T.; Michaud, P. New perspectives for Lactobacilli exopolysaccharides. Biotechnol. Adv. 2011, 29, 54–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diao, Y.; Xin, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Li, N.; Pan, X.; Qi, S.; Qi, Z.; Xu, Y.; Luo, L.; Wan, H.; et al. Extracellular polysaccharide from Bacillus sp. strain LBP32 prevents LPS-induced inflammation in RAW 264.7 macrophages by inhibiting NF-κB and MAPKs activation and ROS production. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2014, 18, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adebayo-Tayo, B.; Fashogbon, R. In vitro antioxidant, antibacterial, in vivo immunomodulatory, antitumor and hematological potential of exopolysaccharide produced by wild type and mutant Lactobacillus delbureckii subsp. bulgaricus. Heliyon 2020, 6, e03268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Niu, M.; Song, D.; Song, X.; Zhao, J.; Wu, Y.; Lu, B.; Niu, G. Preparation, partial characterization and biological activity of exopolysaccharides produced from Lactobacillus fermentum S1. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2020, 129, 206–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, R.; Aruhan; Xiu, L.; Sheng, S.; Liang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Y.; Tong, H.; Du, R.; Wang, X. Exopolysaccharides from Lactobacillus buchneri TCP016 Attenuate LPS- and d-GalN-Induced Liver Injury by Modulating the Gut Microbiota. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 11627–11637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Beilen, J.B.; Li, Z. Enzyme technology: An overview. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2002, 13, 338–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amaretti, A.; di Nunzio, M.; Pompei, A.; Raimondi, S.; Rossi, M.; Bordoni, A. Antioxidant properties of potentially probiotic bacteria: In vitro and in vivo activities. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2013, 97, 809–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomusiak-Plebanek, A.; Heczko, P.; Skowron, B.; Baranowska, A.; Okoń, K.; Thor, P.J.; Strus, M. Lactobacilli with superoxide dismutase-like or catalase activity are more effective in alleviating inflammation in an inflammatory bowel disease mouse model. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2018, 12, 3221–3233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimamura, S.; Abe, F.; Ishibashi, N.; Miyakawa, H.; Yaeshima, T.; Araya, T.; Tomita, M. Relationship between oxygen sensitivity and oxygen metabolism of Bifidobacterium species. J. Dairy Sci. 1992, 75, 3296–3306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Wu, J.; Cao, P.; Jin, Y.; Pan, D.; Zeng, X.; Guo, Y. Characterization of probiotic bacteria involved in fermented milk processing enriched with folic acid. J. Dairy Sci. 2017, 100, 4223–4229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutavdzin, S.; Gopcevic, K.; Stankovic, S.; Jakovljevic Uzelac, J.; Labudovic Borovic, M.; Djuric, D. The Effects of Folic Acid Administration on Cardiac Oxidative Stress and Cardiovascular Biomarkers in Diabetic Rats. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2019, 2019, 1342549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, M.; Amaretti, A.; Raimondi, S. Folate production by probiotic bacteria. Nutrients 2011, 3, 118–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pompei, A.; Cordisco, L.; Amaretti, A.; Zanoni, S.; Matteuzzi, D.; Rossi, M. Folate production by bifidobacteria as a potential probiotic property. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karamshetty, V.; Acharya, J.D.; Ghaskadbi, S.; Goel, P. Mathematical Modeling of Glutathione Status in Type 2 Diabetics with Vitamin B12 Deficiency. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2016, 4, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleerebezem, M.; Hugenholtz, J. Metabolic pathway engineering in lactic acid bacteria. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2003, 14, 232–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, B.; Xing, D. The Current and Future Perspectives of Postbiotics. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2023, 15, 1626–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, C.A. The probiotic paradox: Live and dead cells are biological response modifiers. Nutr. Res. Rev. 2010, 23, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sreeja, V.; Prajapati, J.B. Probiotic Formulations: Application and Status as Pharmaceuticals-A Review. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2013, 5, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imperial, I.C.; Ibana, J.A. Addressing the Antibiotic Resistance Problem with Probiotics: Reducing the Risk of Its Double-Edged Sword Effect. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, C.S. A “Gut Feeling” to Create a 10th Hallmark of Aging. J. Gerontol. Ser. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2021, 76, 1891–1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerville, F.; De Souto Barreto, P.; Ader, I.; Andrieu, S.; Casteilla, L.; Dray, C.; Fazilleau, N.; Guyonnet, S.; Langin, D.; Liblau, R.; et al. Revisiting the Hallmarks of Aging to Identify Markers of Biological Age. J. Prev. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2020, 7, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bana, B.; Cabreiro, F. The Microbiome and Aging. Annu. Rev. Genet. 2019, 53, 239–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Otín, C.; Blasco, M.A.; Partridge, L.; Serrano, M.; Kroemer, G. The hallmarks of aging. Cell 2013, 153, 1194–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ovadya, Y.; Landsberger, T.; Leins, H.; Vadai, E.; Gal, H.; Biran, A.; Yosef, R.; Sagiv, A.; Agrawal, A.; Shapira, A.; et al. Impaired immune surveillance accelerates accumulation of senescent cells and aging. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 5435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragonnaud, E.; Biragyn, A. Gut microbiota as the key controllers of “healthy” aging of elderly people. Immun. Ageing 2021, 18, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.; Benayoun, B.A. The microbiome: An emerging key player in aging and longevity. Transl. Med. Aging 2020, 4, 103–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.; Jazwinski, S.M. The Gut Microbiota and Healthy Aging: A Mini-Review. Gerontology 2018, 64, 513–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rampelli, S.; Candela, M.; Turroni, S.; Biagi, E.; Collino, S.; Franceschi, C.; O’Toole, P.W.; Brigidi, P. Functional metagenomic profiling of intestinal microbiome in extreme ageing. Aging 2013, 5, 902–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collino, S.; Montoliu, I.; Martin, F.P.; Scherer, M.; Mari, D.; Salvioli, S.; Bucci, L.; Ostan, R.; Monti, D.; Biagi, E.; et al. Metabolic signatures of extreme longevity in northern Italian centenarians reveal a complex remodeling of lipids, amino acids, and gut microbiota metabolism. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e56564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, P.; Willemsen, D.; Popkes, M.; Metge, F.; Gandiwa, E.; Reichard, M.; Valenzano, D.R. Regulation of life span by the gut microbiota in the short-lived African turquoise killifish. eLife 2017, 6, e27014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bárcena, C.; Valdés-Mas, R.; Mayoral, P.; Garabaya, C.; Durand, S.; Rodríguez, F.; Fernández-García, M.T.; Salazar, N.; Nogacka, A.M.; Garatachea, N.; et al. Healthspan and lifespan extension by fecal microbiota transplantation into progeroid mice. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 1234–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Zhang, W.; Feng, C.; Kwok, L.Y.; He, Q.; Sun, Z. Stronger gut microbiome modulatory effects by postbiotics than probiotics in a mouse colitis model. NPJ Sci. Food 2022, 6, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peluzio, M.d.C.G.; Martinez, J.A.; Milagro, F.I. Postbiotics: Metabolites and mechanisms involved in microbiota-host interactions. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 108, 11–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozma, M.A.; Abbasi, A.; Akrami, S.; Lahouty, M.; Shahbazi, N.; Ganbarov, K.; Pagliano, P.; Sabahi, S.; Köse, Ş.; Yousefi, M.; et al. Postbiotics as the key mediators of the gut microbiota-host interactions. Infez. Med. 2022, 30, 180–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arasu, K.A.; Rajasekar, T. Immunomodulatory Activity of Postbiotics from Lactobacillus. In Postbiotics; Dharumadurai, D., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2024; pp. 181–186. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, C.N.; Kogut, M.H.; Genovese, K.; He, H.; Kazemi, S.; Arsenault, R.J. Administration of a Postbiotic Causes Immunomodulatory Responses in Broiler Gut and Reduces Disease Pathogenesis Following Challenge. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lü, J.M.; Lin, P.H.; Yao, Q.; Chen, C. Chemical and molecular mechanisms of antioxidants: Experimental approaches and model systems. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2010, 14, 840–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liguori, I.; Russo, G.; Curcio, F.; Bulli, G.; Aran, L.; Della-Morte, D.; Gargiulo, G.; Testa, G.; Cacciatore, F.; Bonaduce, D.; et al. Oxidative stress, aging, and diseases. Clin. Interv. Aging 2018, 13, 757–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martorell, P.; Alvarez, B.; Llopis, S.; Navarro, V.; Ortiz, P.; Gonzalez, N.; Balaguer, F.; Rojas, A.; Chenoll, E.; Ramón, D.; et al. Heat-Treated Bifidobacterium longum CECT-7347: A Whole-Cell Postbiotic with Antioxidant, Anti-Inflammatory, and Gut-Barrier Protection Properties. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humam, A.M.; Loh, T.C.; Foo, H.L.; Izuddin, W.I.; Zulkifli, I.; Samsudin, A.A.; Mustapha, N.M. Supplementation of postbiotic RI11 improves antioxidant enzyme activity, upregulated gut barrier genes, and reduced cytokine, acute phase protein, and heat shock protein 70 gene expression levels in heat-stressed broilers. Poult. Sci. 2021, 100, 100908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izuddin, W.I.; Humam, A.M.; Loh, T.C.; Foo, H.L.; Samsudin, A.A. Dietary Postbiotic Lactobacillus plantarum Improves Serum and Ruminal Antioxidant Activity and Upregulates Hepatic Antioxidant Enzymes and Ruminal Barrier Function in Post-Weaning Lambs. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, Y.; Guo, H.n.; Abbas, Z.; Zhang, J.; Wang, J.; Cheng, Q.; Peng, S.; Yang, T.; Bai, T.; Zhou, Y.; et al. Optimizing postbiotic production through solid-state fermentation with Bacillus amyloliquefaciens J and Lactiplantibacillus plantarum SN4 enhances antibacterial, antioxidant, and anti-inflammatory activities. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1229952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Marco, S.; Sichetti, M.; Muradyan, D.; Piccioni, M.; Traina, G.; Pagiotti, R.; Pietrella, D. Probiotic Cell-Free Supernatants Exhibited Anti-Inflammatory and Antioxidant Activity on Human Gut Epithelial Cells and Macrophages Stimulated with LPS. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2018, 2018, 1756308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, T.W.; Tseng, S.C.; Wang, S.L. Production and Characterization of Antioxidant Properties of Exopolysaccharide(s) from Peanibacillus mucilaginosus TKU032. Mar. Drugs 2016, 14, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Niu, M.; Yao, D.; Zhao, J.; Wu, Y.; Lu, B.; Zheng, X. Physicochemical characteristics and in vitro and in vivo antioxidant activity of a cell-bound exopolysaccharide produced by Lactobacillus fermentum S1. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 139, 252–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, T.; Wu, P.; Zhan, J.; Wang, W.; Shen, J.; Wang, M.; Ho, C.-T.; Li, S. Structure variety and its potential effects on biological activity of tea polysaccharides. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2022, 11, 587–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alan, Y.; Savcı, A.; Koçpınar, E.F.; Ertaş, M. Postbiotic metabolites, antioxidant and anticancer activities of probiotic Leuconostoc pseudomesenteroides strains in natural pickles. Arch. Microbiol. 2022, 204, 571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerrero-Encinas, I.; González-González, J.N.; Santiago-López, L.; Muhlia-Almazán, A.; Garcia, H.S.; Mazorra-Manzano, M.A.; Vallejo-Cordoba, B.; González-Córdova, A.F.; Hernández-Mendoza, A. Protective Effect of Lacticaseibacillus casei CRL 431 Postbiotics on Mitochondrial Function and Oxidative Status in Rats with Aflatoxin B1–Induced Oxidative Stress. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2021, 13, 1033–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schöpping, M.; Vesth, T.; Jensen, K.; Franzén, C.J.; Zeidan, A.A. Genome-Wide Assessment of Stress-Associated Genes in Bifidobacteria. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2022, 88, e0225121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noori, S.M.A.; Behfar, A.; Saadat, A.; Ameri, A.; Atashi Yazdi, S.S.; Siahpoosh, A. Antimicrobial and Antioxidant Properties of Natural Postbiotics Derived from Five Lactic Acid Bacteria. Jundishapur J. Nat. Pharm. Prod. 2022, 18, e130785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrew, M.; Jayaraman, G. Structural features of microbial exopolysaccharides in relation to their antioxidant activity. Carbohydr. Res. 2020, 487, 107881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furman, D.; Campisi, J.; Verdin, E.; Carrera-Bastos, P.; Targ, S.; Franceschi, C.; Ferrucci, L.; Gilroy, D.W.; Fasano, A.; Miller, G.W.; et al. Chronic inflammation in the etiology of disease across the life span. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 1822–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khani, N.; Abedi Soleimani, R.; Noorkhajavi, G.; Abedi Soleimani, A.; Abbasi, A.; Homayouni Rad, A. Postbiotics as potential promising tools for SARS-CoV-2 disease adjuvant therapy. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2022, 132, 4097–4111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Małaczewska, J.; Kaczorek-Łukowska, E.; Wójcik, R.; Rękawek, W.; Siwicki, A.K. In vitro immunomodulatory effect of nisin on porcine leucocytes. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2019, 103, 882–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouritzen, M.V.; Andrea, A.; Qvist, K.; Poulsen, S.S.; Jenssen, H. Immunomodulatory potential of Nisin A with application in wound healing. Wound Repair Regen. 2019, 27, 650–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Z.; He, M.; Wang, C.; Chen, A.; Zhang, X.; Xu, J.; Fu, H.; Liu, B. Nisin reduces uterine inflammation in rats by modulating concentrations of pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines. Am. J. Reprod. Immunol. 2019, 81, e13096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heeney, D.D.; Zhai, Z.; Bendiks, Z.; Barouei, J.; Martinic, A.; Slupsky, C.; Marco, M.L. Lactobacillus plantarum bacteriocin is associated with intestinal and systemic improvements in diet-induced obese mice and maintains epithelial barrier integrity in vitro. Gut Microbes 2019, 10, 382–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tejada-Simon, M.V.; Pestka, J.J. Proinflammatory cytokine and nitric oxide induction in murine macrophages by cell wall and cytoplasmic extracts of lactic acid bacteria. J. Food Prot. 1999, 62, 1435–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kieser, K.J.; Kagan, J.C. Multi-receptor detection of individual bacterial products by the innate immune system. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2017, 17, 376–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shigwedha, N.; Sichel, L.; Jia, l.; Zhang, L. Probiotical Cell Fragments (PCFs) as “Novel Nutraceutical Ingredients”. J. Biosci. Med. 2014, 2, 43–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedrich, A.D.; Campo, V.E.; Cela, E.M.; Morelli, A.E.; Shufesky, W.J.; Tckacheva, O.A.; Leoni, J.; Paz, M.L.; Larregina, A.T.; González Maglio, D.H. Oral administration of lipoteichoic acid from Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG overcomes UVB-induced immunosuppression and impairs skin tumor growth in mice. Eur. J. Immunol. 2019, 49, 2095–2102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clua, P.; Kanmani, P.; Zelaya, H.; Tada, A.; Kober, A.; Salva, S.; Alvarez, S.; Kitazawa, H.; Villena, J. Peptidoglycan from Immunobiotic Lactobacillus rhamnosus Improves Resistance of Infant Mice to Respiratory Syncytial Viral Infection and Secondary Pneumococcal Pneumonia. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanmani, P.; Albarracin, L.; Kobayashi, H.; Iida, H.; Komatsu, R.; Humayun Kober, A.K.M.; Ikeda-Ohtsubo, W.; Suda, Y.; Aso, H.; Makino, S.; et al. Exopolysaccharides from Lactobacillus delbrueckii OLL1073R-1 modulate innate antiviral immune response in porcine intestinal epithelial cells. Mol. Immunol. 2018, 93, 253–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Małaczewska, J.; Kaczorek-Łukowska, E.; Wójcik, R.; Siwicki, A.K. Antiviral effects of nisin, lysozyme, lactoferrin and their mixtures against bovine viral diarrhoea virus. BMC Vet. Res. 2019, 15, 318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philpott, D.J.; Girardin, S.E. The role of Toll-like receptors and Nod proteins in bacterial infection. Mol. Immunol. 2004, 41, 1099–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frece, J.; Kos, B.; Svetec, I.K.; Zgaga, Z.; Mrsa, V.; Susković, J. Importance of S-layer proteins in probiotic activity of Lactobacillus acidophilus M92. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2005, 98, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konstantinov, S.R.; Smidt, H.; de Vos, W.M.; Bruijns, S.C.; Singh, S.K.; Valence, F.; Molle, D.; Lortal, S.; Altermann, E.; Klaenhammer, T.R.; et al. S layer protein A of Lactobacillus acidophilus NCFM regulates immature dendritic cell and T cell functions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2008, 105, 19474–19479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jastrząb, R.; Graczyk, D.; Siedlecki, P. Molecular and Cellular Mechanisms Influenced by Postbiotics. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 13475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Cui, Y.; Qu, X. Exopolysaccharides of lactic acid bacteria: Structure, bioactivity and associations: A review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 207, 317–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makino, S.; Sato, A.; Goto, A.; Nakamura, M.; Ogawa, M.; Chiba, Y.; Hemmi, J.; Kano, H.; Takeda, K.; Okumura, K.; et al. Enhanced natural killer cell activation by exopolysaccharides derived from yogurt fermented with Lactobacillus delbrueckii ssp. bulgaricus OLL1073R-1. J. Dairy Sci. 2016, 99, 915–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagai, T.; Makino, S.; Ikegami, S.; Itoh, H.; Yamada, H. Effects of oral administration of yogurt fermented with Lactobacillus delbrueckii ssp. bulgaricus OLL1073R-1 and its exopolysaccharides against influenza virus infection in mice. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2011, 11, 2246–2250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morita, N.; Umemoto, E.; Fujita, S.; Hayashi, A.; Kikuta, J.; Kimura, I.; Haneda, T.; Imai, T.; Inoue, A.; Mimuro, H.; et al. GPR31-dependent dendrite protrusion of intestinal CX3CR1+ cells by bacterial metabolites. Nature 2019, 566, 110–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Almada, C.N.; Almada, C.N.; Martinez, R.C.R.; Sant’Ana, A.S. Paraprobiotics: Evidences on their ability to modify biological responses, inactivation methods and perspectives on their application in foods. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 58, 96–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xie, J.; Wang, N.; Li, Y.; Sun, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, H. Lactobacillus casei Zhang modulate cytokine and toll-like receptor expression and beneficially regulate poly I:C-induced immune responses in RAW264.7 macrophages. Microbiol. Immunol. 2013, 57, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamilya, D.; Baruah, A.; Sangma, T.; Chowdhury, S.; Pal, P. Inactivated Probiotic Bacteria Stimulate Cellular Immune Responses of Catla, Catla catla (Hamilton) In Vitro. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2015, 7, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, L.; Wu, K.G.; Pai, C.; Hsieh, P.S.; Tsai, J.J.; Yen, J.H.; Lin, M.Y. Heat-killed cells of lactobacilli skew the immune response toward T helper 1 polarization in mouse splenocytes and dendritic cell-treated T cells. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 11080–11086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Liu, S.; Li, S.; Jiang, W.; Wang, J.; Xiao, J.; Chen, T.; Ma, J.; Khan, M.Z.; Wang, W.; et al. Unlocking the power of postbiotics: A revolutionary approach to nutrition for humans and animals. Cell Metab. 2024, 36, 725–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyauchi, E.; Morita, H.; Tanabe, S. Lactobacillus rhamnosus alleviates intestinal barrier dysfunction in part by increasing expression of zonula occludens-1 and myosin light-chain kinase in vivo. J. Dairy Sci. 2009, 92, 2400–2408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Y.; Huang, N.; Ye, X.; Liu, M.; Wei, M.; Huang, Y. The postbiotic of hawthorn-probiotic ameliorating constipation caused by loperamide in elderly mice by regulating intestinal microecology. Front. Nutr. 2023, 10, 1103463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pradhan, D.; Gulati, G.; Avadhani, R.; HM, R.; Soumya, K.; Kumari, A.; Gupta, A.; Dwivedi, D.; Kaushik, J.K.; Grover, S. Postbiotic Lipoteichoic acid of probiotic Lactobacillus origin ameliorates inflammation in HT-29 cells and colitis mice. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 236, 123962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izuddin, W.I.; Loh, T.C.; Foo, H.L.; Samsudin, A.A.; Humam, A.M.; Postbiotic, L. plantarum RG14 improves ruminal epithelium growth, immune status and upregulates the intestinal barrier function in post-weaning lambs. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 9938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cicenia, A.; Santangelo, F.; Gambardella, L.; Pallotta, L.; Iebba, V.; Scirocco, A.; Marignani, M.; Tellan, G.; Carabotti, M.; Corazziari, E.S.; et al. Protective Role of Postbiotic Mediators Secreted by Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG Versus Lipopolysaccharide-induced Damage in Human Colonic Smooth Muscle Cells. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2016, 50 (Suppl. S2), S140–S144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Servi, B.; Ranzini, F. Protective efficacy of antidiarrheal agents in a permeability model of Escherichia coli-infected CacoGoblet® cells. Future Microbiol. 2017, 12, 1449–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariadason, J.M.; Catto-Smith, A.; Gibson, P.R. Modulation of distal colonic epithelial barrier function by dietary fibre in normal rats. Gut 1999, 44, 394–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Kelly, C.J.; Battista, K.D.; Schaefer, R.; Lanis, J.M.; Alexeev, E.E.; Wang, R.X.; Onyiah, J.C.; Kominsky, D.J.; Colgan, S.P. Microbial-Derived Butyrate Promotes Epithelial Barrier Function through IL-10 Receptor-Dependent Repression of Claudin-2. J. Immunol. 2017, 199, 2976–2984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, L.; Li, Z.R.; Green, R.S.; Holzman, I.R.; Lin, J. Butyrate enhances the intestinal barrier by facilitating tight junction assembly via activation of AMP-activated protein kinase in Caco-2 cell monolayers. J. Nutr. 2009, 139, 1619–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almeida, A.; Mitchell, A.L.; Boland, M.; Forster, S.C.; Gloor, G.B.; Tarkowska, A.; Lawley, T.D.; Finn, R.D. A new genomic blueprint of the human gut microbiota. Nature 2019, 568, 499–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ley, R.E.; Hamady, M.; Lozupone, C.; Turnbaugh, P.J.; Ramey, R.R.; Bircher, J.S.; Schlegel, M.L.; Tucker, T.A.; Schrenzel, M.D.; Knight, R.; et al. Evolution of mammals and their gut microbes. Science 2008, 320, 1647–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, T.S.; Shanahan, F.; O’Toole, P.W. The gut microbiome as a modulator of healthy ageing. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 19, 565–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flint, H.J.; Scott, K.P.; Louis, P.; Duncan, S.H. The role of the gut microbiota in nutrition and health. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2012, 9, 577–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheithauer, T.P.; Rampanelli, E.; Nieuwdorp, M.; Vallance, B.A.; Verchere, C.B.; Van Raalte, D.H.; Herrema, H. Gut microbiota as a trigger for metabolic inflammation in obesity and type 2 diabetes. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 571731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, H.K.; Gudmundsdottir, V.; Nielsen, H.B.; Hyotylainen, T.; Nielsen, T.; Jensen, B.A.; Forslund, K.; Hildebrand, F.; Prifti, E.; Falony, G. Human gut microbes impact host serum metabolome and insulin sensitivity. Nature 2016, 535, 376–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischbach, M.A.; Segre, J.A. Signaling in host-associated microbial communities. Cell 2016, 164, 1288–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiavi, E.; Gleinser, M.; Molloy, E.; Groeger, D.; Frei, R.; Ferstl, R.; Rodriguez-Perez, N.; Ziegler, M.; Grant, R.; Moriarty, T.F.; et al. The surface-associated exopolysaccharide of Bifidobacterium longum 35624 plays an essential role in dampening host proinflammatory responses and repressing local TH17 responses. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 82, 7185–7196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couto, M.R.; Gonçalves, P.; Magro, F.; Martel, F. Microbiota-derived butyrate regulates intestinal inflammation: Focus on inflammatory bowel disease. Pharmacol. Res. 2020, 159, 104947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Braun, C.; Murphy, E.F.; Enck, P. Bifidobacterium longum 1714™ strain modulates brain activity of healthy volunteers during social stress. Off. J. Am. Coll. Gastroenterol. Enck ACG 2019, 114, 1152–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burokas, A.; Moloney, R.D.; Dinan, T.G.; Cryan, J.F. Microbiota regulation of the mammalian gut–brain axis. Adv. Appl. Microbiol. 2015, 91, 1–62. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pellanda, P.; Ghosh, T.S.; O’Toole, P.W. Understanding the impact of age-related changes in the gut microbiome on chronic diseases and the prospect of elderly-specific dietary interventions. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2021, 70, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claesson, M.J.; Jeffery, I.B.; Conde, S.; Power, S.E.; O’connor, E.M.; Cusack, S.; Harris, H.M.; Coakley, M.; Lakshminarayanan, B.; O’sullivan, O.; et al. Gut microbiota composition correlates with diet and health in the elderly. Nature 2012, 488, 178–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, A.; Harty, S.; Johnson, K.V.-A.; Moeller, A.H.; Archie, E.A.; Schell, L.D.; Carmody, R.N.; Clutton-Brock, T.H.; Dunbar, R.I.M.; Burnet, P.W.J. Microbial transmission in animal social networks and the social microbiome. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2020, 4, 1020–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeffery, I.B.; Lynch, D.B.; O’Toole, P.W. Composition and temporal stability of the gut microbiota in older persons. ISME J. 2016, 10, 170–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, T.S.; Das, M.; Jeffery, I.B.; O’Toole, P.W. Adjusting for age improves identification of gut microbiome alterations in multiple diseases. eLife 2020, 9, e50240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langsetmo, L.; Johnson, A.; Demmer, R.T.; Fino, N.; Orwoll, E.S.; Ensrud, K.E.; Hoffman, A.R.; Cauley, J.A.; Shmagel, A.; Meyer, K.; et al. The Association between Objectively Measured Physical Activity and the Gut Microbiome among Older Community Dwelling Men. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2019, 23, 538–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fart, F.; Rajan, S.K.; Wall, R.; Rangel, I.; Ganda-Mall, J.P.; Tingö, L.; Brummer, R.J.; Repsilber, D.; Schoultz, I.; Lindqvist, C.M. Differences in Gut Microbiome Composition between Senior Orienteering Athletes and Community-Dwelling Older Adults. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, J.R.; Carroll, I.; Azcarate-Peril, M.A.; Rochette, A.D.; Heinberg, L.J.; Peat, C.; Steffen, K.; Manderino, L.M.; Mitchell, J.; Gunstad, J. A preliminary examination of gut microbiota, sleep, and cognitive flexibility in healthy older adults. Sleep Med. 2017, 38, 104–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haran, J.P.; Bhattarai, S.K.; Foley, S.E.; Dutta, P.; Ward, D.V.; Bucci, V.; McCormick, B.A. Alzheimer’s Disease Microbiome Is Associated with Dysregulation of the Anti-Inflammatory P-Glycoprotein Pathway. mBio 2019, 10, 619–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, M.; Cronin, O.; Keohane, D.M.; Cormac, E.M.; Nugent, H.; Nugent, M.; Molloy, C.; O’Toole, P.W.; Shanahan, F.; Molloy, M.G.; et al. Gut microbiota alterations associated with reduced bone mineral density in older adults. Rheumatology 2019, 58, 2295–2304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Margiotta, E.; Miragoli, F.; Callegari, M.L.; Vettoretti, S.; Caldiroli, L.; Meneghini, M.; Zanoni, F.; Messa, P. Gut microbiota composition and frailty in elderly patients with Chronic Kidney Disease. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0228530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, X.; Harrington, J.M.; Millar, S.R.; Perry, I.J.; O’Toole, P.W.; Phillips, C.M. Gut Microbiota Associations with Metabolic Health and Obesity Status in Older Adults. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Teame, T.; Hao, Q.; Ding, Q.; Liu, H.; Ran, C.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Duan, M.; et al. Use of a paraprobiotic and postbiotic feed supplement (HWF™) improves the growth performance, composition and function of gut microbiota in hybrid sturgeon (Acipenser baerii x Acipenser schrenckii). Fish. Shellfish Immunol. 2020, 104, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinu, L.D.; Avram, I.; Pelinescu, D.R.; Vamanu, E. Mineral-Enriched Postbiotics: A New Perspective for Microbial Therapy to Prevent and Treat Gut Dysbiosis. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 2392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Shi, C.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, S.; Ismael, M.; Zhang, J.; Wang, X.; Lü, X. Protective effects of Companilactobacillus crustorum MN047 against dextran sulfate sodium-induced ulcerative colitis: A fecal microbiota transplantation study. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 1547–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.-Y.; Wu, Y.-P.; Jia, X.-Z.; Lin, J.; Xiao, L.-F.; Liu, D.-M.; Liang, M.-H. Lactiplantibacillus plantarum DMDL 9010 alleviates dextran sodium sulfate (DSS)-induced colitis and behavioral disorders by facilitating microbiota-gut-brain axis balance. Food Funct. 2022, 13, 411–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Din, A.U.; Hassan, A.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, K.; Wang, Y.; Li, T.; Wang, Y.; Wang, G. Inhibitory effect of Bifidobacterium bifidum ATCC 29521 on colitis and its mechanism. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2020, 79, 108353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-Y.; Lee, B.-H.; Park, J.-H.; Park, M.-S.; Ji, G.-E.; Sung, M.-K. Bifidobacterium bifidum BGN4 paraprobiotic supplementation alleviates experimental colitis by maintaining gut barrier and suppressing nuclear factor kappa B activation signaling molecules. J. Med. Food 2022, 25, 146–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braido, F.; Melioli, G.; Candoli, P.; Cavalot, A.; Di Gioacchino, M.; Ferrero, V.; Incorvaia, C.; Mereu, C.; Ridolo, E.; Rolla, G.; et al. The bacterial lysate Lantigen B reduces the number of acute episodes in patients with recurrent infections of the respiratory tract: The results of a double blind, placebo controlled, multicenter clinical trial. Immunol. Lett. 2014, 162, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braido, F.; Melioli, G.; Cazzola, M.; Fabbri, L.; Blasi, F.; Moretta, L.; Canonica, G.W. Sub-lingual administration of a polyvalent mechanical bacterial lysate (PMBL) in patients with moderate, severe, or very severe chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) according to the GOLD spirometric classification: A multicentre, double-blind, randomised, controlled, phase IV study (AIACE study: Advanced Immunological Approach in COPD Exacerbation). Pulm. Pharmacol. Ther. 2015, 33, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montané, E.; Barriocanal, A.M.; Arellano, A.L.; Valderrama, A.; Sanz, Y.; Perez-Alvarez, N.; Cardona, P.; Vilaplana, C.; Cardona, P.J. Pilot, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trial of the supplement food Nyaditum resae® in adults with or without latent TB infection: Safety and immunogenicity. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0171294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Ma, W.; Ma, C.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, J. An emerging strategy: Probiotics enhance the effectiveness of tumor immunotherapy via mediating the gut microbiome. Gut Microbes 2024, 16, 2341717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, W.; Liang, H.; Bugno, J.; Xu, Q.; Ding, X.; Yang, K.; Fu, Y.; Weichselbaum, R.R.; Zhao, X.; Wang, L. Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG induces cGAS/STING- dependent type I interferon and improves response to immune checkpoint blockade. Gut 2022, 71, 521–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krusteva, E.; Hristova, S.; Damyanov, D.; Bogdanov, A.; Altaparmakov, I.; Pacelli, E. Clinical study of the effect of the preparation DEODAN on leukopenia, induced by cytostatics. Int. J. Immunopharmacol. 1997, 19, 487–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodgers, J.L.; Jones, J.; Bolleddu, S.I.; Vanthenapalli, S.; Rodgers, L.E.; Shah, K.; Karia, K.; Panguluri, S.K. Cardiovascular Risks Associated with Gender and Aging. J. Cardiovasc. Dev. Dis. 2019, 6, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grundy, S.M.; Cleeman, J.I.; Daniels, S.R.; Donato, K.A.; Eckel, R.H.; Franklin, B.A.; Gordon, D.J.; Krauss, R.M.; Savage, P.J.; Smith, S.C., Jr.; et al. Diagnosis and management of the metabolic syndrome: An American Heart Association/National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute Scientific Statement. Circulation 2005, 112, 2735–2752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M.; Joung, M.; Park, J.H.; Ha, S.K.; Park, H.Y. Role of Postbiotics in Diet-Induced Metabolic Disorders. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdollahi, S.; Ghahremani, M.H.; Setayesh, N.; Samadi, N. Listeria monocytogenes and Salmonella enterica affect the expression of nisin gene and its production by Lactococcus lactis. Microb. Pathog. 2018, 123, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Davis, B.; Zhu, W.; Zheng, N.; Meng, D.; Walker, W.A. Short-chain fatty acid butyrate, a breast milk metabolite, enhances immature intestinal barrier function genes in response to inflammation in vitro and in vivo. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2021, 320, G521–G530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerdes, V.; Gueimonde, M.; Pajunen, L.; Nieuwdorp, M.; Laitinen, K. How strong is the evidence that gut microbiota composition can be influenced by lifestyle interventions in a cardio-protective way? Atherosclerosis 2020, 311, 124–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tani, M.; Tanaka, S.; Takamiya, K.; Kato, Y.; Harata, G.; He, F.; Sakaue, M.; Ito, M. Effects of dietary fiber on vascular calcification by repetitive diet-induced fluctuations in plasma phosphorus in early-stage chronic kidney disease rats. J. Clin. Biochem. Nutr. 2020, 67, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.S.; Wang, G.; Lobaton, G.; Li, E.; Yang, T.; Raizada, M. OS 05-10 the microbial metabolite, butyrate attenuates Angiotensin II-induced hypertension and dysbiosis. J. Hypertens. 2016, 34, e60–e61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pluznick, J. A novel SCFA receptor, the microbiota, and blood pressure regulation. Gut Microbes 2014, 5, 202–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.U.; In, H.J.; Kwon, M.S.; Park, B.O.; Jo, M.; Kim, M.O.; Cho, S.; Lee, S.; Lee, H.J.; Kwak, Y.S.; et al. β-Arrestin 2 mediates G protein-coupled receptor 43 signals to nuclear factor-κB. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2013, 36, 1754–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lymperopoulos, A.; Suster, M.S.; Borges, J.I. Short-Chain Fatty Acid Receptors and Cardiovascular Function. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knock, G.; Psaroudakis, D.; Abbot, S.; Aaronson, P.I. Propionate-induced relaxation in rat mesenteric arteries: A role for endothelium-derived hyperpolarising factor. J. Physiol. 2002, 538, 879–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robles-Vera, I.; Toral, M.; de la Visitación, N.; Sánchez, M.; Gómez-Guzmán, M.; Romero, M.; Yang, T.; Izquierdo-Garcia, J.L.; Jiménez, R.; Ruiz-Cabello, J.; et al. Probiotics Prevent Dysbiosis and the Rise in Blood Pressure in Genetic Hypertension: Role of Short-Chain Fatty Acids. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2020, 64, e1900616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Pan, Y.; Shao, W.; Wang, C.; Wang, R.; He, Y.; Zhang, M.; Wang, Y.; Li, T.; Wang, Z.; et al. Beneficial effect of the short-chain fatty acid propionate on vascular calcification through intestinal microbiota remodelling. Microbiome 2022, 10, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moleón, J.; González-Correa, C.; Miñano, S.; Robles-Vera, I.; de la Visitación, N.; Barranco, A.M.; Gómez-Guzmán, M.; Sánchez, M.; Riesco, P.; Guerra-Hernández, E.; et al. Protective effect of microbiota-derived short chain fatty acids on vascular dysfunction in mice with systemic lupus erythematosus induced by toll like receptor 7 activation. Pharmacol. Res. 2023, 198, 106997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartolomaeus, H.; Balogh, A.; Yakoub, M.; Homann, S.; Markó, L.; Höges, S.; Tsvetkov, D.; Krannich, A.; Wundersitz, S.; Avery, E.G.; et al. Short-Chain Fatty Acid Propionate Protects From Hypertensive Cardiovascular Damage. Circulation 2019, 139, 1407–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haghikia, A.; Zimmermann, F.; Schumann, P.; Jasina, A.; Roessler, J.; Schmidt, D.; Heinze, P.; Kaisler, J.; Nageswaran, V.; Aigner, A.; et al. Propionate attenuates atherosclerosis by immune-dependent regulation of intestinal cholesterol metabolism. Eur. Heart J. 2022, 43, 518–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onyszkiewicz, M.; Gawrys-Kopczynska, M.; Konopelski, P.; Aleksandrowicz, M.; Sawicka, A.; Koźniewska, E.; Samborowska, E.; Ufnal, M. Butyric acid, a gut bacteria metabolite, lowers arterial blood pressure via colon-vagus nerve signaling and GPR41/43 receptors. Pflug. Arch. 2019, 471, 1441–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.; Goel, R.; Kumar, A.; Qi, Y.; Lobaton, G.; Hosaka, K.; Mohammed, M.; Handberg, E.M.; Richards, E.M.; Pepine, C.J.; et al. Imbalance of gut microbiome and intestinal epithelial barrier dysfunction in patients with high blood pressure. Clin. Sci. 2018, 132, 701–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flori, L.; Benedetti, G.; Martelli, A.; Calderone, V. Microbiota alterations associated with vascular diseases: Postbiotics as a next-generation magic bullet for gut-vascular axis. Pharmacol. Res. 2024, 207, 107334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Pan, D.; Li, H.; Sun, Y.; Zeng, X.; Yan, B. Antioxidant and immunomodulatory activity of selenium exopolysaccharide produced by Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis. Food Chem. 2013, 138, 84–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, H.; Zhu, X.; Omura, K.; Suzuki, S.; Kitamura, S. Effects of an exopolysaccharide (kefiran) on lipids, blood pressure, blood glucose, and constipation. Biofactors 2004, 22, 197–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.Y.; Kim, H.; Jung, B.J.; Kim, N.R.; Park, J.E.; Chung, D.K. Lipoteichoic acid isolated from Lactobacillus plantarum suppresses LPS-mediated atherosclerotic plaque inflammation. Mol. Cells 2013, 35, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Yan, L.; Chen, H.; Wu, N.; Wang, W.; Wang, D. Cyclocarya paliurus polysaccharides alleviate type 2 diabetic symptoms by modulating gut microbiota and short-chain fatty acids. Phytomedicine 2020, 77, 153268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Zhao, J.; Xie, F.; He, H.; Johnston, L.J.; Dai, X.; Wu, C.; Ma, X. Dietary fiber-derived short-chain fatty acids: A potential therapeutic target to alleviate obesity-related nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Obes. Rev. 2021, 22, e13316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, L. Alterations of Gut Microbiota by Overnutrition Impact Gluconeogenic Gene Expression and Insulin Signaling. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salazar, N.; Neyrinck, A.M.; Bindels, L.B.; Druart, C.; Ruas-Madiedo, P.; Cani, P.D.; de Los Reyes-Gavilán, C.G.; Delzenne, N.M. Functional Effects of EPS-Producing Bifidobacterium Administration on Energy Metabolic Alterations of Diet-Induced Obese Mice. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, X.; Yue, M.; Wei, J.; Wang, Y.; Hong, D.; Wang, B.; Zhou, X.; Chen, T. Evaluation of the Anti-Aging Effects of a Probiotic Combination Isolated From Centenarians in a SAMP8 Mouse Model. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 792746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, S.M.; Mohajeri, M.H. The Role of Gut Bacterial Metabolites in Brain Development, Aging and Disease. Nutrients 2021, 13, 732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, R.; Padwad, Y. Probiotic bacteria as modulators of cellular senescence: Emerging concepts and opportunities. Gut Microbes 2020, 11, 335–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, A.; Fonseca, S.; Carding, S.R. Gut microbes and metabolites as modulators of blood-brain barrier integrity and brain health. Gut Microbes 2020, 11, 135–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knox, E.G.; Aburto, M.R.; Clarke, G.; Cryan, J.F.; O’Driscoll, C.M. The blood-brain barrier in aging and neurodegeneration. Mol. Psychiatry 2022, 27, 2659–2673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.; Busetti, A.; Fotiadou, P.; Vincy Jose, N.; Reid, S.; Georgieva, M.; Brown, S.; Dunbar, H.; Beurket-Ascencio, G.; Delday, M.I.; et al. In vitro Characterization of Gut Microbiota-Derived Bacterial Strains with Neuroprotective Properties. Front. Cell Neurosci. 2019, 13, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, G.H.; Bock, H.J.; Lee, N.K.; Paik, H.D. Soy yogurt using Lactobacillus plantarum 200655 and fructooligosaccharides: Neuroprotective effects against oxidative stress. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 59, 4870–4879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.K.; Kim, D.H. Lactobacillus mucosae and Bifidobacterium longum Synergistically Alleviate Immobilization Stress-Induced Anxiety/Depression in Mice by Suppressing Gut Dysbiosis. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 29, 1369–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Xie, L.; Schröder, J.; Schuster, I.S.; Nakai, M.; Sun, G.; Sun, Y.B.Y.; Mariño, E.; Degli-Esposti, M.A.; Marques, F.Z.; et al. Dietary Fiber and Microbiota Metabolite Receptors Enhance Cognition and Alleviate Disease in the 5xFAD Mouse Model of Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Neurosci. 2023, 43, 6460–6475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bull-Larsen, S.; Mohajeri, M.H. The Potential Influence of the Bacterial Microbiome on the Development and Progression of ADHD. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.C.; Bogale, T.A.; Koistinaho, J.; Pizzi, M.; Rolova, T.; Bellucci, A. The contribution of β-amyloid, Tau and α-synuclein to blood-brain barrier damage in neurodegenerative disorders. Acta Neuropathol. 2024, 147, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fock, E.; Parnova, R. Mechanisms of Blood-Brain Barrier Protection by Microbiota-Derived Short-Chain Fatty Acids. Cells 2023, 12, 657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirin, S.; Aslim, B. Protective effect of exopolysaccharides from lactic acid bacteria against amyloid beta1-42induced oxidative stress in SH-SY5Y cells: Involvement of the AKT, MAPK, and NF-κB signaling pathway. Process Biochem. 2021, 106, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.Y.; Jin, M.M.; Meng, J.; Gao, S.M.; Lu, R.R. Exopolysaccharide from Lactobacillus planterum LP6: Antioxidation and the effect on oxidative stress. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 98, 1147–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.; Kim, Y.K.; Han, P.L. Extracellular Vesicles Derived from Lactobacillus plantarum Increase BDNF Expression in Cultured Hippocampal Neurons and Produce Antidepressant-like Effects in Mice. Exp. Neurobiol. 2019, 28, 158–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Li, N.; Gao, Y.; Xu, F.; Chen, H.; Zhang, C.; Ni, X. The activation impact of lactobacillus-derived extracellular vesicles on lipopolysaccharide-induced microglial cell. BMC Microbiol. 2024, 24, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, H.; Lee, E.H.; Park, S.Y.; Park, J.Y.; Hong, J.H.; Kim, E.K.; Shin, T.S.; Kim, Y.K.; Han, P.L. Lactobacillus-derived extracellular vesicles counteract Aβ42-induced abnormal transcriptional changes through the upregulation of MeCP2 and Sirt1 and improve Aβ pathology in Tg-APP/PS1 mice. Exp. Mol. Med. 2023, 55, 2067–2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobbs, M.B.; Buckwalter, J.; Saltzman, C. Osteoporosis: The increasing role of the orthopaedist. Iowa Orthop. J. 1999, 19, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zaiss, M.M.; Axmann, R.; Zwerina, J.; Polzer, K.; Gückel, E.; Skapenko, A.; Schulze-Koops, H.; Horwood, N.; Cope, A.; Schett, G. Treg cells suppress osteoclast formation: A new link between the immune system and bone. Arthritis Rheum. 2007, 56, 4104–4112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.G.; Lee, C.K.; Nah, S.S.; Mun, S.H.; Yoo, B.; Moon, H.B. Human CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells inhibit the differentiation of osteoclasts from peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2007, 357, 1046–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapra, L.; Bhardwaj, A.; Mishra, P.K.; Garg, B.; Verma, B.; Mishra, G.C.; Srivastava, R.K. Regulatory B Cells (Bregs) Inhibit Osteoclastogenesis and Play a Potential Role in Ameliorating Ovariectomy-Induced Bone Loss. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 691081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhardwaj, A.; Sapra, L.; Tiwari, A.; Mishra, P.K.; Sharma, S.; Srivastava, R.K. “Osteomicrobiology”: The Nexus Between Bone and Bugs. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 812466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myeong, J.-Y.; Jung, H.-Y.; Chae, H.-S.; Cho, H.H.; Kim, D.-K.; Jang, Y.-J.; Park, J.-I. Protective Effects of the Postbiotic Lactobacillus plantarum MD35 on Bone Loss in an Ovariectomized Mice Model. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2024, 16, 541–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzoli, R.; Biver, E.; Brennan-Speranza, T.C. Nutritional intake and bone health. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2021, 9, 606–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, A.R.; Park, J.S.; Kim, D.K.; Park, J.Y.; Ahn, J.H.; Kim, D.Y.; Lee, T.S.; Chang, J.Y.; Choi, J.H.; Park, J.H. Cell-free culture supernatant of Lactobacillus curvatus Wikim38 inhibits RANKL-induced osteoclast differentiation and ameliorates bone loss in ovariectomized mice. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2021, 73, 383–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, J.I.; Baek, S.M.; Nguyen, T.H.; Kim, J.W.; Kang, C.H.; Kim, S.; Imm, J.Y. Effects of Probiotic Culture Supernatant on Cariogenic Biofilm Formation and RANKL-Induced Osteoclastogenesis in RAW 264.7 Macrophages. Molecules 2021, 26, 733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, F.L.; Rios-Arce, N.D.; Schepper, J.D.; Jones, A.D.; Schaefer, L.; Britton, R.A.; McCabe, L.R.; Parameswaran, N. Beneficial effects of Lactobacillus reuteri 6475 on bone density in male mice is dependent on lymphocytes. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 14708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, S.; Omata, Y.; Hofmann, J.; Böttcher, M.; Iljazovic, A.; Sarter, K.; Albrecht, O.; Schulz, O.; Krishnacoumar, B.; Krönke, G.; et al. Short-chain fatty acids regulate systemic bone mass and protect from pathological bone loss. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rad, A.H.; Abbasi, A.; Kafil, H.S.; Ganbarov, K. Potential Pharmaceutical and Food Applications of Postbiotics: A Review. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2020, 21, 1576–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nataraj, B.H.; Ali, S.A.; Behare, P.V.; Yadav, H. Postbiotics-parabiotics: The new horizons in microbial biotherapy and functional foods. Microb. Cell Factories 2020, 19, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, J.; Xu, B.; Zeng, X.; Shen, K. Broncho-Vaxom in pediatric recurrent respiratory tract infections: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2018, 54, 198–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, J.; Jin, W.; Liu, S.J.; Jiao, Z.; Li, X. Probiotics, prebiotics, and postbiotics in health and disease. MedComm (2020) 2023, 4, e420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaji, R.; Kiyoshima-Shibata, J.; Nagaoka, M.; Nanno, M.; Shida, K. Bacterial teichoic acids reverse predominant IL-12 production induced by certain lactobacillus strains into predominant IL-10 production via TLR2-dependent ERK activation in macrophages. J. Immunol. 2010, 184, 3505–3513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.S.; Sim, J.R.; Yun, C.H.; Han, S.H. Lipoteichoic acids as a major virulence factor causing inflammatory responses via Toll-like receptor 2. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2016, 39, 1519–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bourebaba, Y.; Marycz, K.; Mularczyk, M.; Bourebaba, L. Postbiotics as potential new therapeutic agents for metabolic disorders management. Biomed. Pharmacother 2022, 153, 113138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balthazar, C.F.; Guimarães, J.F.; Coutinho, N.M.; Pimentel, T.C.; Ranadheera, C.S.; Santillo, A.; Albenzio, M.; Cruz, A.G.; Sant’Ana, A.S. The future of functional food: Emerging technologies application on prebiotics, probiotics and postbiotics. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2022, 21, 2560–2586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, K.; Wang, X.; Huang, R.; Wang, H.; Lan, P.; Zhao, Y. Prebiotics and Postbiotics Synergistic Delivery Microcapsules from Microfluidics for Treating Colitis. Adv. Sci. 2022, 9, 2104089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, E.; De Paepe, K.; Van de Wiele, T. Postbiotics and Their Health Modulatory Biomolecules. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradi, M.; Kousheh, S.A.; Almasi, H.; Alizadeh, A.; Guimarães, J.T.; Yılmaz, N.; Lotfi, A. Postbiotics produced by lactic acid bacteria: The next frontier in food safety. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2020, 19, 3390–3415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zmora, N.; Zeevi, D.; Korem, T.; Segal, E.; Elinav, E. Taking it Personally: Personalized Utilization of the Human Microbiome in Health and Disease. Cell Host Microbe 2016, 19, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Postbiotics Component | Isolation Characteristics from Probiotic Strain | Key Study Findings | Mechanistic Aspects | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Heat-treated, non-viable | Heat-treated Bifidobacterium longum CECT-7347 by autoclaving for 20 min at 121 °C, 1 atm pressure. | Increased Caenorhabditis elegans survival rates after oxidative stress. | Activated DAF-16 (worm homolog of FOXO transcription factor), decreased IL-8, and suppressed NF-κB signalling. | [145] |
| Cell-free supernatant | Lactiplantibacillus plantarum RI11 grown in MRS broth at 37 °C for 48 h. | Increased IL-10; reduced IL-8, HSP70, TNF-α, and α1-acid glycoprotein. | Elevated serum glutathione peroxidase and Zn/Cu superoxide dismutase levels. | [146] |
| L. plantarum RG11, RG14, and TL1 cultured in MRS broth at 30 °C for 10 h. | Improved antioxidant activity and regulation of rumen barrier function in postbiotic-treated animals. | Elevated serum glutathione peroxidases and Zn/Cu superoxide dismutases. | [147] | |
| L. plantarum SN4 and Bacillus amyloliquefaciens J cultured in LB or MRS broth at 37 °C for 10 h. | Demonstrated broad-spectrum antibacterial effects, strong antioxidant activity, anti-inflammatory effects, and intestinal wound healing. | Inhibited nitric oxide (NO) production. | [148] | |
| Lactobacillus spp. (L. acidophilus, L. casei, L. lactis, L. reuteri), and Saccharomyces boulardii cultured in RPMI 1640 at 37 °C for 24 h. | Reduced oxidative damage and exhibited strong free radical scavenging. | Downregulated PGE-2, IL-8, IL-1β, IL-6, TNF-α; upregulated IL-10 production by human macrophages. | [149] | |
| Exopolysaccharides | Lactobacillus fermentum S1 grown in fermentation broth at 37 °C for 10 h under aerobic conditions; proteins removed with trichloroacetic acid. | Exhibited in vitro antioxidant activity against free radicals. | [110] | |
| Paenibacillus mucilaginosus TKU032 grown in SPP-treated medium at 37 °C for 6 days aerobically with agitation; exopolysaccharides precipitated with ethanol. | Demonstrated in vitro antioxidant activity and reactive oxygen species (ROS) scavenging. | [150] | ||
| L. helveticus MB2-1 cultured in fermentation broth at 33 °C for 24 h aerobically; precipitated with 0.9% NaCl, sonicated, and reprecipitated with 75% ethanol. | Showed in vitro antioxidant and ROS scavenging activity; enhanced total antioxidant capacity and superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity, and reduced malondialdehyde in rats. | Activity attributed to uronic acid polysaccharide binding ferrous iron, similar to green tea. | [151,152] | |
| Cellular isolates | Leuconostoc pseudomesenteroides processed via enzymatic lysis and sonication. | Exhibited in vitro antioxidant and ROS scavenging activity. | Demonstrated higher antioxidant activity than controls. | [153] |
| Lysates | L. casei CRL431 lysed via enzymatic treatment and sonication. | Exhibited in vitro antioxidant and ROS scavenging activity. | Modulated antioxidant response under aflatoxin B1-induced oxidative stress. | [154] |
| Postbiotics Component | Isolation Characteristics from Probiotic Strains | Key Study Findings | Mechanistic Aspects | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lipoteichoic acid | Extracted from Lactobacillus rhamnosus using butanol/phenol-based solvent from cell-free supernatant. | Reversed UV-induced immunosuppression in skin hypersensitivity. | Activated dendritic cells and T-lymphocytes in the skin. | [167] |
| Peptidoglycans | Lipid removed from L. rhamnosus via organic solvent extraction following sonication to disrupt the cell wall. | Reversed polyinosinic:polycytidylic acid (poly I:C)-induced lung injuries. | Increased IL-α, IL-β, IL-γ, IL-6, and IL-10 levels via TLR-3 activation. | [168] |
| Exopolysaccharides | Extracted from Lactobacillus delbrueckii using protein precipitation with trichloroacetic acid followed by ethanol precipitation at 4 °C overnight. | Improved gut health and inhibited viral replication. | Balanced pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokine responses. | [169] |
| Short-chain fatty acids (acetate, propionate, butyrate) | Isolated via liquid-liquid extraction using water:acetonitrile, followed by vortexing and filtration. | Maintained colon health by restoring gut microbiome balance. | Activated GPCR-43, promoting beneficial bacterial growth and inhibiting pathogenic bacteria. | [75] |
| Bacteriocin | Harvested from Lactococcus lactis through cell collection and solvent extraction using chloroform. | Promoted differentiation and proliferation of B- and T-lymphocytes. | Increased IL-1β and IL-6 levels. | [170] |
| Postbiotics Component | Study Description | Findings | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Propionic acid, Butyric acid, Acetic acid | 1 g/kg parenteral administration in C57BL/6 mice. | Reduced heart rate and mean arterial pressure. | [239] |
| 13-week oral supplementation (0.5 mg/kg/day) in spontaneously hypertensive rats. | Reduced blood pressure. | [240] | |
| Observational clinical cohort study of 92 patients; SCFA levels measured in faecal and blood samples and correlated with vascular calcification scores. | Inverse correlation between SCFA levels and vascular calcification and lipid profiles. | [241] | |
| Butyric acid Acetic acid | 8-week oral supplementation (68 mM acetate; 40 mM butyrate) in TLRY264H lupus-prone mice. | Enhanced endothelial-dependent vasodilation, reduced blood pressure and left ventricular hypertrophy, and improved gut barrier integrity. | [242] |
| Propionic acid | Oral administration (200 mmol/L) in angiotensin II-infused wild-type and ApoE–/– mice. | Decreased systolic and diastolic blood pressure. | [243] |
| 4-week oral supplementation (200 mg/kg) in high-fat diet-fed ApoE–/– mice. | Reduced plasma LDL, VLDL, total cholesterol, and atherosclerotic lesion size. | [244] | |
| 8-week oral supplementation (500 mg, BID) in hypercholesterolemic patients. | Decreased plasma lipid concentrations. | ||
| 6-week oral or rectal administration (200 mM) in a vitamin D3/nicotine-induced vascular calcification rat model. | 59% reduction in aortic calcium content; decreased TNFα, IL-1β, and IL-6 expression; reduced vascular macrophage infiltration; improved gut dysbiosis and barrier integrity. | [241] | |
| Butyric acid | IV administration (0.14–5.6 mmol/kg) in rats. | Lowered blood pressure. | [245] |
| 28-day parenteral administration (1 g/kg) in angiotensin II-infused mice. | Improved vasodilation response in pre-contracted aortic rings. | [246] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hamdi, A.; Lloyd, C.; Eri, R.; Van, T.T.H. Postbiotics: A Promising Approach to Combat Age-Related Diseases. Life 2025, 15, 1190. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15081190
Hamdi A, Lloyd C, Eri R, Van TTH. Postbiotics: A Promising Approach to Combat Age-Related Diseases. Life. 2025; 15(8):1190. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15081190
Chicago/Turabian StyleHamdi, Adel, Charmaine Lloyd, Rajaraman Eri, and Thi Thu Hao Van. 2025. "Postbiotics: A Promising Approach to Combat Age-Related Diseases" Life 15, no. 8: 1190. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15081190
APA StyleHamdi, A., Lloyd, C., Eri, R., & Van, T. T. H. (2025). Postbiotics: A Promising Approach to Combat Age-Related Diseases. Life, 15(8), 1190. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15081190







