Inspiratory Muscle Training Improves Respiratory Muscle Strength and Cardiovascular Autonomic Regulation in Obese Young Men
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Inspiratory Muscle Training Program
2.4. Respiratory Muscle Strength Test
2.5. Heart Rate and Blood Pressure Test
2.6. Heart Rate Variability Test
2.7. Data and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
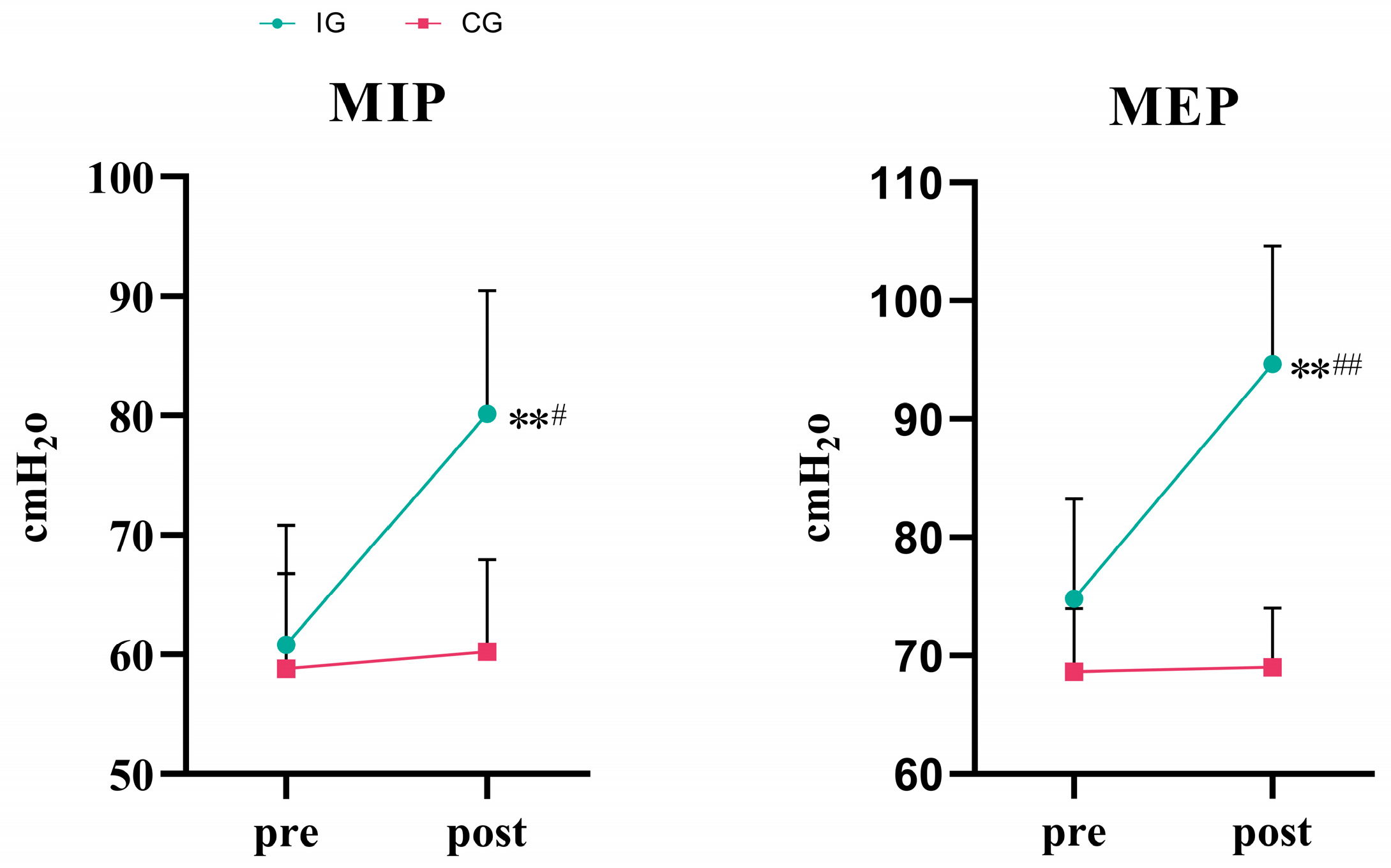
3.1. Respiratory Muscle Strength
3.2. Cardiovascular Function
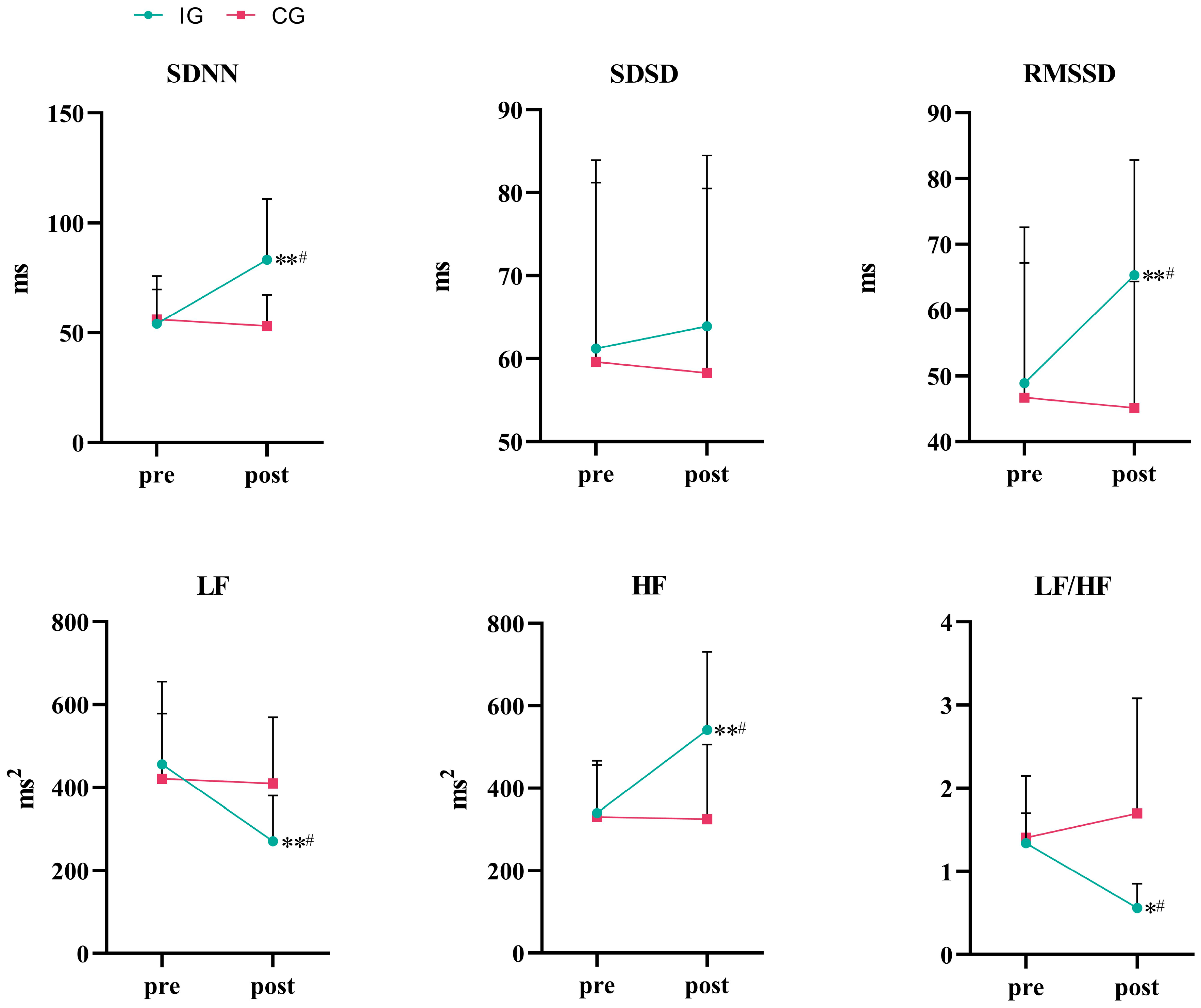
3.3. Autonomic Function
4. Discussion
4.1. Effect of 8 Weeks of IMT on Respiratory Muscle Strength
4.2. Effects of 8-Week IMT on Cardiovascular Function
4.3. Effects of 8-Week IMT on Autonomic Function
4.4. Limitations of the Study
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pan, X.-F.; Wang, L.; Pan, A. Epidemiology and Determinants of Obesity in China. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2021, 9, 373–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wharton, S.; Lau, D.C.W.; Vallis, M.; Sharma, A.M.; Biertho, L.; Campbell-Scherer, D.; Adamo, K.; Alberga, A.; Bell, R.; Boulé, N.; et al. Obesity in Adults: A Clinical Practice Guideline. CMAJ 2020, 192, E875–E891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, C.D.; de Abreu, R.M.; Rehder-Santos, P.; De Noronha, M.; Catai, A.M. Can Respiratory Muscle Training Change the Blood Pressure Levels in Hypertension? A Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2021, 31, 1384–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, I.; Briggs, R.; Spengler, C.M. Respiratory Muscles, Exercise Performance, and Health in Overweight and Obese Subjects. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2011, 43, 714–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caicedo-Trujillo, S.; Torres-Castro, R.; Vasconcello-Castillo, L.; Solis-Navarro, L.; Sanchez-Ramirez, D.; Núñez-Cortés, R.; Vera-Uribe, R.; Muñoz-Muñoz, I.; Barros-Poblete, M.; Romero, J.E.; et al. Inspiratory Muscle Training in Patients with Obesity: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Med. 2023, 10, 1284689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turcu, A.; Ilie, A.; Ștefăniu, R.; Țăranu, S.; Sandu, I.; Alexa-Stratulat, T.; Pîslaru, A.; Alexa, I. The Impact of Heart Rate Variability Monitoring on Preventing Severe Cardiovascular Events. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 2382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voulgari, C.; Pagoni, S.; Vinik, A.; Poirier, P. Exercise Improves Cardiac Autonomic Function in Obesity and Diabetes. Metab.-Clin. Exp. 2013, 62, 609–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alugubelli, N.; Abuissa, H.; Roka, A. Wearable Devices for Remote Monitoring of Heart Rate and Heart Rate Variability-What We Know and What Is Coming. Sensors 2022, 22, 8903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tung, J.Y.L.; Poon, G.W.K.; Du, J.; Wong, K.K.Y. Obesity in Children and Adolescents: Overview of the Diagnosis and Management. Chronic Dis. Transl. Med. 2023, 9, 122–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlos de Medeiros, A.I.; Bastos Fuzari, H.K.; Rattes, C.; Brandao, D.C.; de Melo Marinho, P.E. Inspiratory Muscle Training Improves Respiratory Muscle Strength, Functional Capacity and Quality of Life in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease: A Systematic Review. J. Physiother. 2017, 63, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cipriano, G.F.; Cipriano Jr, G.; Santos, F.V.; Güntzel Chiappa, A.M.; Pires, L.; Cahalin, L.P.; Chiappa, G.R. Current Insights of Inspiratory Muscle Training on the Cardiovascular System: A Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis. Integr. Blood Press. Control 2019, 12, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witt, J.D.; Guenette, J.A.; Rupert, J.L.; McKenzie, D.C.; Sheel, A.W. Inspiratory Muscle Training Attenuates the Human Respiratory Muscle Metaboreflex: Cardiovascular Effects of Training Respiratory Muscle. J. Physiol. 2007, 584, 1019–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callegaro, C.C.; Ribeiro, J.P.; Tan, C.O.; Taylor, J.A. Attenuated Inspiratory Muscle Metaboreflex in Endurance-Trained Individuals. Respir. Physiol. Neurobiol. 2011, 177, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalski, T.; Klusiewicz, A.; Rębiś, K.; Wilk, A.; Starczewski, M. Comparative Study of Different Respiratory Muscle Training Methods: Effects on Cardiopulmonary Indices and Athletic Performance in Elite Short-Track Speedskaters. Life 2024, 14, 1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, J.B.; Plentz, R.D.M.; Stein, C.; Casali, K.R.; Arena, R.; Dal Lago, P. Inspiratory Muscle Training Reduces Blood Pressure and Sympathetic Activity in Hypertensive Patients: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Int. J. Cardiol. 2013, 166, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Abreu, R.M.; Rehder-Santos, P.; Minatel, V.; dos Santos, G.L.; Catai, A.M. Effects of Inspiratory Muscle Training on Cardiovascular Autonomic Control: A Systematic Review. Auton. Neurosci. 2017, 208, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Hu, D.; Zhang, W.; Cui, L.; Jia, X.; Yang, D.; Liu, S.; Deng, F.; Liu, J.; Guo, X. Effect of Short-Term Exposure to Particulate Air Pollution on Heart Rate Variability in Normal-Weight and Obese Adults. Environ. Health 2021, 20, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, L.; Shamseer, L.; Altman, D.G.; Schulz, K.F.; Moher, D. Does Use of the CONSORT Statement Impact the Completeness of Reporting of Randomised Controlled Trials Published in Medical Journals? A Cochrane Reviewa. Syst. Rev. 2012, 1, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z.; Guo, J.; He, Y.; Luo, Y.; Wu, H. Effects of Inspiratory Muscle Training on Respiratory Muscle Strength, Lactate Accumulation and Exercise Tolerance in Amateur Runners: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Life 2025, 15, 705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Almeida, L.B.; Seixas, M.B.; Trevizan, P.F.; CamarotiLaterza, M.; da Silva, L.P.; Martinez, D.G. Effects of Inspiratory Muscle Training on Autonomic Control: Systematic Review. Fisioter. Pesqui. 2018, 25, 345–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Xian, H.; Guo, J.; Li, W.; Wang, J.; Chen, Q.; Fu, X.; Li, H.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, W.; et al. A Novel Blood Pressure Monitoring Technique by Smart HUAWEI WATCH: A Validation Study According to the ANSI/AAMI/ISO 81060-2:2018 Guidelines. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 9, 923655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, L.; Li, J. Research on Effect of Load Stimulation Change on Heart Rate Variability of Women Volleyball Athletes. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2022, 2022, 3917415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pałac, M.; Rutka, M.; Wolny, T.; Podgórski, M.; Linek, P. Ultrasonography in Assessment of Respiratory Muscles Function: A Systematic Review. Respiration 2022, 101, 878–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Álvarez, E.D.; Guzmán-David, C.A.; Ruiz-González, J.C.; Ortega-Hernández, A.M.; Ortiz-González, D.C. Effect of a Respiratory Muscle Training Program on Lung Function, Respiratory Muscle Strength and Resting Oxygen Consumption in Sedentary Young People. Rev. Fac. Med. 2018, 66, 605–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craighead, D.H.; Freeberg, K.A.; Maurer, G.S.; Myers, V.H.; Seals, D.R. Translational Potential of High-Resistance Inspiratory Muscle Strength Training. Exerc. Sport. Sci. Rev. 2022, 50, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enright, S.J.; Unnithan, V.B. Effect of Inspiratory Muscle Training Intensities on Pulmonary Function and Work Capacity in People Who Are Healthy: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Phys. Ther. 2011, 91, 894–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K. Correlation between Respiratory Muscle Strength and Pulmonary Function with Respiratory Muscle Length Increase in Healthy Adults. Phys. Ther. Rehabil. Sci. 2021, 10, 398–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Notter, D.A.; Verges, S.; Renggli, A.S.; Beltrami, F.G.; Spengler, C.M. Similar Effects on Exercise Performance Following Different Respiratory Muscle Training Programs in Healthy Young Men. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 16135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muntner, P.; Shimbo, D.; Carey, R.M.; Charleston, J.B.; Gaillard, T.; Misra, S.; Myers, M.G.; Ogedegbe, G.; Schwartz, J.E.; Townsend, R.R.; et al. Measurement of Blood Pressure in Humans: A Scientific Statement From the American Heart Association. Hypertension 2019, 73, e35–e66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Bonito, P.; Valerio, G.; Pacifico, L.; Chiesa, C.; Invitti, C.; Morandi, A.; Licenziati, M.R.; Manco, M.; Giudice, E.M.; Baroni, M.G.; et al. Impact of the 2017 Blood Pressure Guidelines by the American Academy of Pediatrics in overweight/obese youth. J. Hypertens. 2019, 37, 732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.-A.; Mao, S.-T.; Lin, H.-C.; Liu, W.-T.; Tam, K.-W.; Tsai, C.-Y.; Kuan, Y.-C. Effects of Inspiratory Muscle Training on Blood Pressure- and Sleep-Related Outcomes in Patients with Obstructive Sleep Apnea: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Sleep Breath. 2023, 27, 1953–1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Posser, S.R.; Callegaro, C.C.; Beltrami-Moreira, M.; Moreira, L.B. Effect of Inspiratory Muscle Training with Load Compared with Sham Training on Blood Pressure in Individuals with Hypertension: Study Protocol of a Double-Blind Randomized Clinical Trial. Trials 2016, 17, 382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos-Barrera, G.E.; DeLucia, C.M.; Bailey, E.F. Inspiratory Muscle Strength Training Lowers Blood Pressure and Sympathetic Activity in Older Adults with OSA: A Randomized Controlled Pilot Trial. J. Appl. Physiol. 2020, 129, 449–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeLucia, C.M.; De Asis, R.M.; Bailey, E.F. Six Weeks Inspiratory Muscle Strength Training Lowers Blood Pressure but Does Not Affect Baroreflex Sensitivity or Cardiac Output in Active Young Adults. FASEB J. 2017, 31, 724.5–724.5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wei, F.-F.; Wang, S.; Cheng, Y.-B.; Wang, J.-G. Cardiovascular Risks Associated With Diastolic Blood Pressure and Isolated Diastolic Hypertension. Curr. Hypertens. Rep. 2014, 16, 489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bersten, A.D.; Holt, A.W.; Vedig, A.E.; Skowronski, G.A.; Baggoley, C.J. Treatment of Severe Cardiogenic Pulmonary Edema with Continuous Positive Airway Pressure Delivered by Face Mask. N. Engl. J. Med. 1991, 325, 1825–1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvadego, D.; Tringali, G.; De Micheli, R.; Sartorio, A. Respiratory Muscle Interval Training Improves Exercise Capacity in Obese Adolescents during a 3-Week In-Hospital Multidisciplinary Body Weight Reduction Program. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.-G. The Role of Heart Rate Variability in Sports Physiology. Exp. Ther. Med. 2016, 11, 1531–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granero-Gallegos, A.; González-Quílez, A.; Plews, D.; Carrasco-Poyatos, M. HRV-Based Training for Improving VO2max in Endurance Athletes. A Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 7999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiss, O.; Sydó, N.; Vargha, P.; Vágó, H.; Czimbalmos, C.; Édes, E.; Zima, E.; Apponyi, G.; Merkely, G.; Sydó, T.; et al. Detailed Heart Rate Variability Analysis in Athletes. Clin. Auton. Res. 2016, 26, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrasco-Poyatos, M.; González-Quílez, A.; Martínez-González-Moro, I.; Granero-Gallegos, A. HRV-Guided Training for Professional Endurance Athletes: A Protocol for a Cluster-Randomized Controlled Trial. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 5465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalski, T.; Obmiński, Z.; Waleriańczyk, W.; Klusiewicz, A. The Acute Effect of Respiratory Muscle Training on Cortisol, Testosterone, and Testosterone-to-Cortisol Ratio in Well-Trained Triathletes—Exploratory Study. Respir. Physiol. Neurobiol. 2025, 331, 104353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shei, R.J. Recent Advancements in Our Understanding of the Ergogenic Effect of Respiratory Muscle Training in Healthy Humans: A Systematic Review. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2018, 32, 2665–2676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amann, M. Pulmonary System Limitations to Endurance Exercise Performance in Humans: Pulmonary System and Exercise Performance. Exp. Physiol. 2012, 97, 311–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, G.D.; Dal Lago, P.; Soares, P.P.d.S. Time-Dependent Effects of Inspiratory Muscle Training and Detraining on Cardiac Autonomic Control in Older Women. Exp. Gerontol. 2021, 150, 111357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaenisch, R.B.; Quagliotto, E.; Chechi, C.; Calegari, L.; dos Santos, F.; Borghi-Silva, A.; Dal Lago, P. Respiratory Muscle Training Improves Chemoreflex Response, Heart Rate Variability, and Respiratory Mechanics in Rats With Heart Failure. Can. J. Cardiol. 2017, 33, 508–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mello, P.R.; Guerra, G.M.; Borile, S.; Rondon, M.U.; Alves, M.J.; Negrão, C.E.; Dal Lago, P.; Mostarda, C.; Irigoyen, M.C.; Consolim-Colombo, F.M. Inspiratory Muscle Training Reduces Sympathetic Nervous Activity and Improves Inspiratory Muscle Weakness and Quality of Life in Patients With Chronic Heart Failure: A CLINICAL TRIAL. J. Cardiopulm. Rehabil. Prev. 2012, 32, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
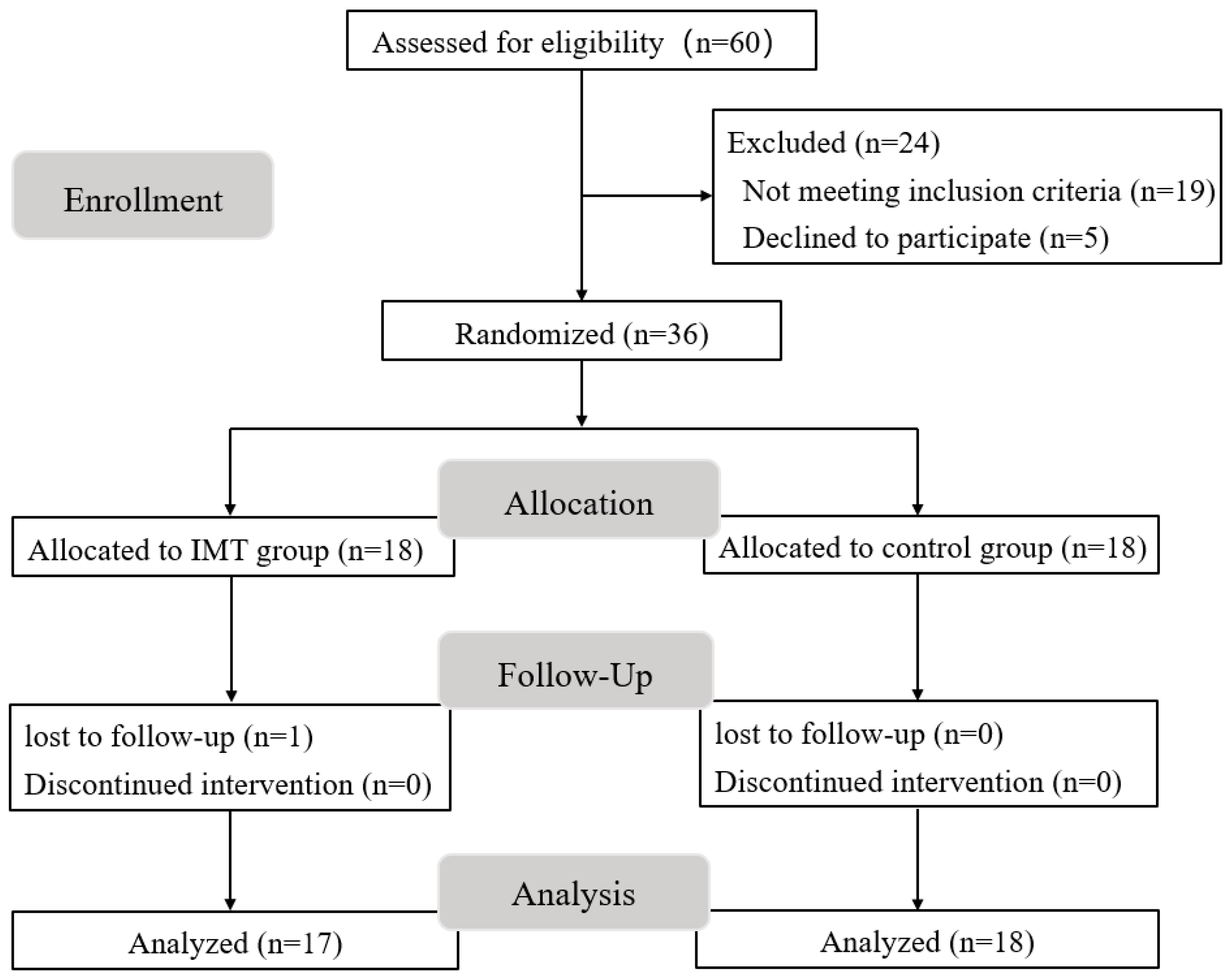

| Group | IG (n = 17) | CG (n = 18) | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 21.1 ± 1.79 | 21.0 ± 2.06 | 0.909 |
| Height (cm) | 175.31 ± 4.48 | 176.48 ± 5.15 | 0.524 |
| Weight (kg) | 90.10 ± 5.82 | 89.50 ± 5.14 | 0.810 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 29.3 ± 0.96 | 28.7 ± 1.00 | 0.219 |
| MIP (cmH2O) | 60.83 ± 9.98 | 58.82 ± 7.96 | 0.624 |
| MEP (cmH2O) | 74.81 ± 8.43 | 68.63 ± 5.33 | 0.066 |
| SBP (mmHg) | 126.30 ± 1.34 | 126.00 ± 2.26 | 0.722 |
| DBP (mmHg) | 87.50 ± 1.84 | 87.80 ± 2.04 | 0.734 |
| HR (bpm) | 75.30 ± 1.25 | 75.00 ± 1.25 | 0.598 |
| Variables | Group | Pre | Post | Mean Difference (95% CI) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MIP (cmH2O) | IG (n = 17) | 60.83 ± 9.98 | 80.16 ± 10.30 **# | −19.33[−28.82,−9.85] | <0.001 |
| CG (n = 18) | 58.82 ± 7.96 | 60.24 ± 7.69 | −1.42[−8.06,10.92] | 0.755 | |
| MEP (cmH2O) | IG (n = 17) | 74.81 ± 8.43 | 94.63 ± 10.01 **## | −19.82[−22.77,−16.87] | <0.001 |
| CG (n = 18) | 68.63 ± 5.33 | 69.01 ± 5.01 | −0.38[−3.33,2.58] | 0.792 |
| Variables | Group | Pre | Post | Mean Difference (95% CI) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SBP (mmHg) | IG (n = 17) | 126.30 ± 1.34 | 123.50 ± 2.59 **# | 2.80[1.70,3.99] | <0.001 |
| CG (n = 18) | 126.00 ± 2.26 | 125.80 ± 2.10 | 0.20[−0.90,1.30] | 0.707 | |
| DBP (mmHg) | IG (n = 17) | 87.50 ± 1.84 | 84.70 ± 1.25 **## | 2.80[1.95,3.65] | <0.001 |
| CG (n = 18) | 87.80 ± 2.04 | 87.50 ± 1.90 | 0.30[−0.55,1.15] | 0.470 | |
| HR | IG (n = 17) | 75.30 ± 1.25 | 73.70 ± 1.42 **# | 1.60[0.99,2.21] | <0.001 |
| (bpm) | CG (n = 18) | 75.00 ± 1.25 | 75.10 ± 0.99 | −0.10[0.74,−0.71] | 0.736 |
| Variables | Group | Pre | Post | Mean Difference (95% CI) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SDNN (ms) | IG (n = 17) | 54.00 ± 15.69 | 83.20 ± 27.73 **# | −29.20[−47.69,−10.71] | 0.004 |
| CG (n = 18) | 56.00 ± 19.78 | 53.10 ± 14.08 | 2.90[−15.59,21.39] | 0.746 | |
| SDSD (ms) | IG (n = 17) | 61.20 ± 22.70 | 63.90 ± 20.57 | −2.70[−15.54,10.14] | 0.664 |
| CG (n = 18) | 59.60 ± 21.60 | 58.30 ± 22.23 | 1.30[−11.54,14.14] | 0.834 | |
| RMSSD (ms) | IG (n = 17) | 48.90 ± 23.73 | 65.30 ± 17.51 **# | −16.40[−22.31,−10.49] | <0.001 |
| CG (n = 18) | 46.70 ± 20.48 | 45.10 ± 19.27 | −1.60[−7.51,4.31] | 0.577 | |
| LF (ms2) | IG (n = 17) | 455.40 ± 199.87 | 270.80 ± 109.77 **# | 184.60[73.53,295.66] | 0.003 |
| CG (n = 18) | 420.80 ± 157.00 | 409.40 ± 159.63 | 11.40[−99.67,122.47] | 0.832 | |
| HF (ms2) | IG (n = 17) | 339.50 ± 116.89 | 541.10 ± 188.95 **# | −201.60[−316.28,−86.92] | 0.002 |
| CG (n = 18) | 330.50 ± 135.94 | 324.90 ± 189.72 | 5.60[−1.9.08,120.28] | 0.919 | |
| LF/HF | IG (n = 17) | 1.34 ± 0.36 | 0.56 ± 0.29 *# | 0.78[0.09,1.47] | 0.029 |
| CG (n = 18) | 1.41 ± 0.74 | 1.70 ± 1.38 | −2.90[−0.98,0.40] | 0.33 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ren, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Yang, J.; Wei, D.; Wu, H. Inspiratory Muscle Training Improves Respiratory Muscle Strength and Cardiovascular Autonomic Regulation in Obese Young Men. Life 2025, 15, 1191. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15081191
Ren Z, Zhou Z, Yang J, Wei D, Wu H. Inspiratory Muscle Training Improves Respiratory Muscle Strength and Cardiovascular Autonomic Regulation in Obese Young Men. Life. 2025; 15(8):1191. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15081191
Chicago/Turabian StyleRen, Zhe, Zeyu Zhou, Jikai Yang, Dongyue Wei, and Hao Wu. 2025. "Inspiratory Muscle Training Improves Respiratory Muscle Strength and Cardiovascular Autonomic Regulation in Obese Young Men" Life 15, no. 8: 1191. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15081191
APA StyleRen, Z., Zhou, Z., Yang, J., Wei, D., & Wu, H. (2025). Inspiratory Muscle Training Improves Respiratory Muscle Strength and Cardiovascular Autonomic Regulation in Obese Young Men. Life, 15(8), 1191. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15081191







