Effects of Different Types of High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT) on Physical Performance in Female Basketball Players—A Systematic Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
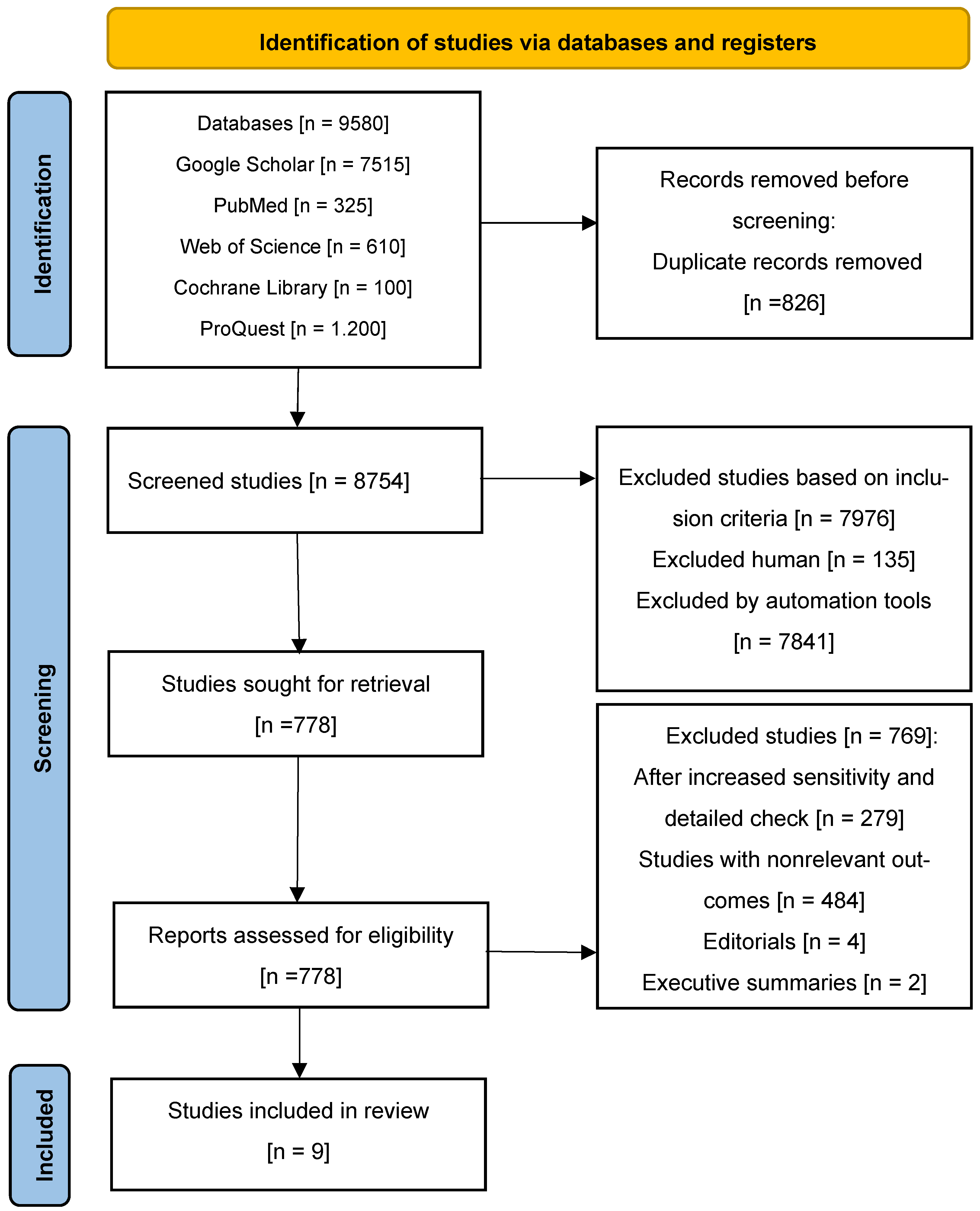
2.1. Literature Identification
2.2. Eligibility Criteria
2.3. Data Extraction
3. Results
3.1. Study Selection and Characteristics
3.2. Study Quality
3.3. Effects of HIIT on Body Composition
3.4. Effects of HIIT on Aerobic and Anaerobic Capacity
3.5. Effects of HIIT on Physical Fitness
4. Discussion
5. Practical Applications
6. Limitations
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Popescu, S.; Stănilă, A.M.; Grădinaru, C. Gender equality in basketball payments: The case for pay parity. Timis. Phys. Educ. Rehabil. J. 2023, 16, 38–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radu, A. The Science of Basketball; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Mancha-Triguero, D.; García-Rubio, J.; Calleja-González, J.; Ibáñez, S. Physical fitness in basketball players: A systematic review. J. Sports Med. Phys. Fitness 2019, 59, 1513–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zarić, I.; Kukić, F.; Jovićević, N.; Zarić, M.; Toskić, L.; Đurić, S.; Markovic, M.; Dopsaj, M.M. Body height of female basketball players: Association with ranking at the Women’s World Basketball Cup. Anthr. Noteb. 2020, 26, 88–102. [Google Scholar]
- Bishop, D.; Wright, C. A time-motion analysis of professional basketball to determine the relationship between three activity profiles: High, medium and low intensity and the length of the time spent on court. Int. J. Perform. Anal. Sport 2006, 6, 130–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stojanović, E.; Stojiljković, N.; Scanlan, A.T.; Dalbo, V.J.; Berkelmans, D.M.; Milanović, Z. The activity demands and physiological responses encountered during basketball match-play: A systematic review. Sports Med. 2018, 48, 111–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laursen, P.; Buchheit, M. Science and Application of High-Intensity Interval Training; Human Kinetics: Champaign, IL, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Andreyo, E.; Unverzagt, C.; Tompkins, J.; Dawes, J.J.; Croll, S. A Needs Analysis and Training Considerations for Female Adolescent Basketball Players. Strength Cond. J. 2024, 46, 320–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sansone, P.; Makivic, B.; Csapo, R.; Hume, P.; Martínez-Rodríguez, A.; Bauer, P. Body fat of basketball players: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sports Med. Open 2022, 8, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reina, M.; García-Rubio, J.; Ibáñez, S.J. Training and competition load in female basketball: A systematic review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public. Health 2020, 17, 2639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, G.; Li, H. High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT): Impacts on Cardiovascular Fitness and Muscle Development. Rev. Psicol. Deporte (J. Sport Psychol.) 2024, 33, 210–219. [Google Scholar]
- Batacan, R.B.; Duncan, M.J.; Dalbo, V.J.; Tucker, P.S.; Fenning, A.S. Effects of high-intensity interval training on cardiometabolic health: A systematic review and meta-analysis of intervention studies. Br. J. Sports Med. 2017, 51, 494–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buchheit, M.; Laursen, P.B. High-intensity interval training, solutions to the programming puzzle: Part I: Cardiopulmonary emphasis. Sports Med. 2013, 43, 313–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, S.; Liu, J.; Wang, Z.; Geok, S.K. The effects of functional training on physical fitness and skill-related performance among basketball players: A systematic review. Front. Physiol. 2024, 15, 1391394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deepika, V.; Rathod, L.L. A Study on the Co-Relation of Basketball Playing Ability with Motor Fitness and Health Related Fitness of Female Basketball Players: Ashok Yakkaldevi; Lulu Publication: Raleigh, NC, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, Y.; Soh, K.G.; Qi, F.; Bashir, M.; Zhao, N. Effects of high-intensity interval training on selected indicators of physical fitness among male team-sport athletes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0310955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henrique, J.R.; Ramirez-Campillo, R.; Fernandez, F.T.G.; Castillo, D.; Raya-González, J.; Zmijewski, P.; Silva, R.M.; Clemente, F.M. High-intensity interval training programs and their impact on endurance performance in handball players: A systematic review. Biomed. Hum. Kinet. 2024, 16, 113–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manuel Clemente, F.; Couceiro, M.; MLMartins, F.; Mendes, R. The usefulness of small-sided games on soccer training. J. Phys. Educ. Sport 2019, 12, 93–102. [Google Scholar]
- Meignié, A.; Duclos, M.; Carling, C.; Orhant, E.; Provost, P.; Toussaint, J.-F.; Antero, J. The effects of menstrual cycle phase on elite athlete performance: A critical and systematic review. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 654585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edwards, T.; Spiteri, T.; Piggott, B.; Bonhotal, J.; Haff, G.G.; Joyce, C. Monitoring and managing fatigue in basketball. Sports 2018, 6, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravé, G.; Granacher, U.; Boullosa, D.; Hackney, A.C.; Zouhal, H. How to use global positioning systems (GPS) data to monitor training load in the “real world” of elite soccer. Front. Physiol. 2020, 11, 944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tornero-Aguilera, J.F.; Jimenez-Morcillo, J.; Rubio-Zarapuz, A.; Clemente-Suárez, V.J. Central and peripheral fatigue in physical exercise explained: A narrative review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public. Health 2022, 19, 3909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, S.; Geok, S.K.; Roslan, S.; Sun, H.; Lam, S.K.; Qian, S. Mental fatigue and basketball performance: A systematic review. Front. Psychol. 2022, 12, 819081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abate, M.; Salini, V. Oxidative stress, testosterone, cortisol, and vitamin d: Differences in professional soccer players of African and Caucasian origin. Med. Princ. Pract. 2022, 31, 352–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stanković, M.; Čaprić, I.; Katanić, B.; Špirtović, O.; Maljanović, D.; Nailović, H.; Muković, I.; Jelaska, I.; Trajković, N. Proprioceptive training methods (PTM) in female soccer players–a systematic review. BMC Sports Sci. Med. Rehabil. 2024, 16, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, S.; Li, Z.; Wang, Z.; Geok, S.K.; Liu, J. The Effects of High-Intensity Interval Training on Basketball Players: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Sports Sci. Med. 2025, 24, 31–51. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schmitz, B.; Niehues, H.; Thorwesten, L.; Klose, A.; Krüger, M.; Brand, S.-M. Sex differences in high-intensity interval training–are HIIT protocols interchangeable between females and males? Front. Physiol. 2020, 11, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rethlefsen, M.L.; Kirtley, S.; Waffenschmidt, S.; Ayala, A.P.; Moher, D.; Page, M.J.; Koffel, J.B. PRISMA-S: An extension to the PRISMA statement for reporting literature searches in systematic reviews. Syst. Rev. 2021, 10, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prictor, M.; Hill, S. Cochrane Consumers and Communication Review Group: Leading the field on health communication evidence. J. Evid. Based Med. 2013, 6, 216–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maher, C.G.; Sherrington, C.; Herbert, R.D.; Moseley, A.M.; Elkins, M. Reliability of the PEDro scale for rating quality of randomized controlled trials. Phys. Ther. 2003, 83, 713–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasanzade Maha, M.; Nemati, N. The Effect of High Intensity Interval Training and Medium Continuous Training on Visfatin Plasma Levels, Anaerobic and Aerobic Power Female Basketball Players. J. Chem. Health Risks 2018, 5, 313–322. [Google Scholar]
- Sanchez-Sanchez, J.; Carretero, M.; Ramirez-Campillo, R.; Petisco, C.; Diego, M.; Gonzalo-Skok, O.; Nakamura, F.Y. Effects of high-intensity training with one versus three changes of direction on youth female basketball players’ performance. Kinesiology 2018, 50, 117–125. [Google Scholar]
- Aschendorf, P.F.; Zinner, C.; Delextrat, A.; Engelmeyer, E.; Mester, J. Effects of basketball-specific high-intensity interval training on aerobic performance and physical capacities in youth female basketball players. Physician Sportsmed. 2019, 47, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, J.; Xu, J.; Xu, Y.; Zhou, W.; Xu, F. Effects of 4-week small-sided games vs. high-intensity interval training with changes of direction in female collegiate basketball players. Int. J. Sports Sci. Coach. 2022, 17, 366–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Fernández, A.; Lago, Á.; Ramirez-Campillo, R.; Sánchez, M.; Sánchez-Sánchez, J. Cardiopulmonary-versus neuromuscular-based high-intensity interval training during a pre-season in youth female basketball players. Hum. Mov. 2023, 24, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apaydın, M.B.; Şengür, E.; Turasan, İ. Investigation of the effect of HITT training applied to basketball players on sportive performance: Basketbolculara uygulanan HITT antrenmanların sportif performansa etkisinin incelenmesi. J. Hum. Sci. 2023, 20, 584–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mourgan, F.; Almatar, N.; Al-Shamli, A.; Al-Kitani, M.; Al-Yaaribi, A.; Albarri, O. The Effect of Specific High-intensity Exercises on Cardiovascular Balance, Vascularity, and Performance in Female Youth Basketball Players. Open Biochem. J. 2024, 18, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haghighi, A.H.; Hosseini, S.B.; Askari, R.; Shahrabadi, H.; Ramirez-Campillo, R. Effects of plyometric compared to high-intensity interval training on youth female basketball player’s athletic performance. Sport. Sci. Health 2024, 20, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, K.; Jiang, H. Gender-specific effects of short sprint interval training on aerobic and anaerobic capacities in basketball players: A randomized controlled trial. J. Sports Sci. Med. 2024, 23, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eken, Ö.; Kafkas, M.E. Effects of low and high intensity interval training exercises on VO2max and components of neuromuscular and vascular system in male volunteers. J. Musculoskelet Neuronal Interact. 2022, 22, 352. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Boullosa, D.; Dragutinovic, B.; Feuerbacher, J.F.; Benítez-Flores, S.; Coyle, E.F.; Schumann, M. Effects of short sprint interval training on aerobic and anaerobic indices: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2022, 32, 810–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subekti, N.; Raihan, A.A.D.A.; Hafif, M.; Syaukani, A.A. The Effect of the High-Intensity Interval Training Program in Increasing VO2max Capacity and Heart Rate Recovery. J. Sport Sci. Educ. 2022, 7, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edge, J.; Bishop, D.; Goodman, C.; Dawson, B. Effects of high-and moderate-intensity training on metabolism and repeated sprints. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2005, 37, 1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franchini, E.; Cormack, S.; Takito, M.Y. Effects of high-intensity interval training on olympic combat sports athletes’ performance and physiological adaptation: A systematic review. J. Strength Cond Res. 2019, 33, 242–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delextrat, A.; Martinez, A. Small-sided game training improves aerobic capacity and technical skills in basketball players. Int. J. Sports Med. 2014, 35, 385–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buchheit, M. The 30–15 intermittent fitness test: 10 year review. Myorobie J. 2010, 1, 278. [Google Scholar]
- Bishop, D.; Girard, O.; Mendez-Villanueva, A. Repeated-sprint ability—Part II: Recommendations for training. Sports Med. 2011, 41, 741–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bravo, D.F.; Impellizzeri, F.M.; Rampinini, E.; Castagna, C.; Bishop, D.; Wisloff, U. Sprint vs. interval training in football. Int. J. Sports Med. 2008, 29, 668–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clemente, F.M.; Ramirez-Campillo, R.; Afonso, J.; Sarmento, H. Effects of small-sided games vs. running-based high-intensity interval training on physical performance in soccer players: A meta-analytical comparison. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 642703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bickham, D.; Le Rossignol, P. Effects of high-intensity interval training on the accumulated oxygen deficit of endurance-trained runners. Prof. Exerc. Physiol. 2004, 7. [Google Scholar]
- Burgomaster, K.A.; Cermak, N.M.; Phillips, S.M.; Benton, C.R.; Bonen, A.; Gibala, M.J. Divergent response of metabolite transport proteins in human skeletal muscle after sprint interval training and detraining. Am. J. Physiol.Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2007, 292, R1970–R1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esfarjani, F.; Laursen, P.B. Manipulating high-intensity interval training: Effects on V˙ O2max, the lactate threshold and 3000 m running performance in moderately trained males. J. Sci. Med. Sport 2007, 10, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibala, M.J.; Little, J.P.; Van Essen, M.; Wilkin, G.P.; Burgomaster, K.A.; Safdar, A.; Raha, S.; Tarnopolsky, M.A. Short-term sprint interval versus traditional endurance training: Similar initial adaptations in human skeletal muscle and exercise performance. J. Physiol. 2006, 575, 901–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dudley, G.A.; Djamil, R. Incompatibility of endurance-and strength-training modes of exercise. J. Appl. Physiol. 1985, 59, 1446–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helgerud, J.; Engen, L.C.; Wisløff, U.; Hoff, J. Aerobic endurance training improves soccer performance. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2001, 33, 1925–1931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mcmillan, K.; Helgerud, J.; Macdonald, R.; Hoff, J. Physiological adaptations to soccer specific endurance training in professional youth soccer players. Br. J. Sports Med. 2005, 39, 273–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buchheit, M.; Laursen, P.; Kuhnle, J.; Ruch, D.; Renaud, C.; Ahmaidi, S. Game-based training in young elite handball players. Int. J. Sports Med. 2009, 30, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Purkhús, E.; Krustrup, P.; Mohr, M. High-intensity training improves exercise performance in elite women volleyball players during a competitive season. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2016, 30, 3066–3072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sperlich, B.; De Marées, M.; Koehler, K.; Linville, J.; Holmberg, H.C.; Mester, J. Effects of 5 weeks of high-intensity interval training vs. volume training in 14-year-old soccer players. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2011, 25, 1271–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iacono, A.D.; Eliakim, A.; Meckel, Y. Improving fitness of elite handball players: Small-sided games vs. high-intensity intermittent training. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2015, 29, 835–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stankovic, M.; Djordjevic, D.; Trajkovic, N.; Milanovic, Z. Effects of high-intensity interval training (HIIT) on physical performance in female team sports: A systematic review. Sports Med. Open 2023, 9, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Räntilä, A.; Ahtiainen, J.P.; Häkkinen, K. Effects of acute loading induced fatigability, acute serum hormone responses and training volume to individual hypertrophy and maximal strength during 10 weeks of strength training. J. Sports Sci. Med. 2023, 22, 559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calleja-Gonzalez, J.; Marques-Jimenez, D.; Jones, M.; Huyghe, T.; Navarro, F.; Delextrat, A.; Jukic, I.; Ostojic, S.M.; Sampaio, J.E.; Schelling, X.; et al. What are we doing wrong when athletes report higher levels of fatigue from traveling than from training or competition? Front. Psychol. 2020, 11, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alonso-Fernández, D.; Lima-Correa, F.; Gutierrez-Sánchez, Á.; de Vicuña, O.A.G. Effects of a high-intensity interval training protocol based on functional exercises on performance and body composition in handball female players. J. Hum. Sport Exerc. 2017, 12, 1186–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| PICOS | Inclusion Criteria |
|---|---|
| Population | Female basketball players competing at elite, sub-elite, or collegiate levels |
| Intervention | HIIT programs lasting at least 2 weeks with exercise intensity 80–100% HRmax |
| Comparison | Control group or other training interventions (when applicable) |
| Outcome | VO2max, RSA, change-of-direction speed, linear speed, explosive power, body composition |
| Study Design | Longitudinal, randomized, controlled trials; no date restriction |
| Study: | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | ∑ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Maha et al. (2015) [31] | Y | Y | N | Y | N | N | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | 7 |
| Sanchez-Sanchez et al. (2018) [32] | Y | Y | Y | Y | N | N | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | 7 |
| Aschendorf et al. (2019) [33] | Y | Y | N | Y | N | N | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | 6 |
| Zeng et al. (2022) [34] | Y | Y | Y | Y | N | N | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | 7 |
| Rodríguez-Fernández et al. (2023) [35] | Y | Y | Y | Y | N | N | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | 7 |
| Apaydın et al. (2023) [36] | Y | Y | N | Y | N | N | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | 6 |
| Mourgan et al. (2024) [37] | Y | Y | Y | Y | N | N | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | 7 |
| Haghighi et al. (2024) [38] | Y | Y | N | Y | N | N | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | 6 |
| Fang et al. (2024) [39] | Y | Y | Y | Y | N | N | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | 7 |
| Study | Age [Years] | Number and Groups | Duration [Weeks] Sessions [Per Week] | Program (Type, Intensity Frequency, Training Duration) | Measured Outcomes | Results | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E Group | C Group | Body Composition | Physical Fitness | VO2max | ||||||
| Maha et al. (2015) [31] | __ | N-20 HIIT-10, MCT-10 | 6 week 3 sessions | HIIT, 85–95% HRmax | MCT, 60–70% HRmax | __ | __ | VO2max VT 3000-m race PPO MPO | HIIT: VO2max ↑ * VT↑ 3000 mr↑ * PPO ↑ * MPO↑ | MCT: VO2max ↑ * VT↑ 3000 mr↓ PPO ↓ MPO↓ |
| Sanchez-Sanchez et al. (2018) [32] | 17.2 ± 1.1 | N-12 HITCOD1–6, HITCOD3–6 | 6 weeks 2 sessions | COD1- HIIT (1 COD), 90%, (+6 regular practices), 2 × 6 min | COD3- HIIT (3 CODs), 90%, 2 × per week (+6 regular practices), 2 × 6 min | __ | V-cut RSA | VIFT | HITCOD1 V-cut ↑ RSA- ↑ VIFT- ↑ | HITCOD3 MAT  V-cut ↑ * RSA- ↑ * VIFT- ↑ * |
| Aschendorf et al. (2019) [33] | 15.1 ± 1.1 | N-24, TG-11, CG-13 | 5 weeks 2 sessions | Specific basketball practices HIIT, 90–90% HRmax; 25 min | Regular field practices | BF FFM | CMJ CMJa SJ COD | YYIR1 Shuttle run 20 m | TG: COD180 ↑ CMJ  CMJa  SJ  YYIR ↑ BF  FFM  | CG: COD180 ↓ * CMJ  CMJa  SJ  YYIR1  BF  FFM  |
| Zeng et al. (2022) [34] | 19.9 ± 1.1 | N-19 SSG-9, HITCOD -10 | 4 weeks 3 sessions | HIITCOD: 3 × (6 min od 15″-15″ 90% VIFT) | SSG: 3 × (2 × 2 min 45), 2 min passive rest | __ | MAT CMJ SAT RSA | 30-15 IFT Shuttle run 20 m | SSG: 30-15 IFT↓ RSA↑ MAT↑ * CMJ↓ | HIIT: 30-15 IFT↓ RSA↑ MAT↑ CMJ↓ |
| Rodríguez-Fernández, et al. (2023) [35] | 17.9 ± 0.6 | N-16 C-HIIT-8 N-HIIT-8 | 6 weeks 2 sessions | HIIT 30 s/30 s (passive) 90% 40 m 2 × 12 min [3 min] | HIIT 15 s/15 s (passive) 100% 40 m 2 × 6 min (6 min) | __ | __ | 30-15 VIFT RSA | C-HIIT: 30-15 IFT↑ * RSA  | N-HIIT: 30-15 IFT ↑ RSA  |
| Apaydın, et al. (2023) [36] | 15.7 ± 0.93 | N-20 | 8 weeks 2 sessions | 90–95% HRmax | Regular field practices | BMI | VJ 10 m 20 m | __ | HIIT BMI  VJ↑ 10m↑ * 20m↑ * | CG: BMI  VJ  10m  20m↑ * |
| Mourgan, et al. (2024) [37] | 15.1 ± 1.1 | N-24 TG-12 CG-12 | 5 weeks 2 h | HIIT 90–95% HRmax; 25 min, 4 min HIIT 3 min rest | Regular field practices | __ | CMJ SJ COD20 | VO2max VCO2 VEGF | TG: CMJ↑ SJ↑ VO2max ↑ * VCO2↑ * VEGF ↑ COD20↑ * | CG: |
| Haghighi, et al. (2024) [38] | 14–16 | N-24 HIIT-8 PT-8 CG-8 | 6 weeks 2 sessions | HIIT: 90–95% HRmax, 2 × per week, 30–60 min | Plyometric sessions, 2 × per week, 30–60 min | __ | CMJ SJ 20m | RSA VO2max 30-15 IFT | PT | HIIT |
| Fang et al. (2024) [39] | 23.1 ± 1.5 | N-20 CG-10 TG-10 | 6 weeks 2 sessions | SIT 3 sets of 10 repetitions | Regular field practices | __ | VJ 20m Illionois T test | YYIR1 VO2max | VJ↑ * 20m↑ * Illionois↑ T test↑ * YYIR1↑ * VO2max↑ * | VJ 20m  Illionois  T test  YYIR1  VO2max  |
 —no statistically significant change; E group—experimental group; TG—training group; CG—control group; HIIT—high-intensity interval training; MCT—medium continuous training; VO2max—maximal oxygen uptake; PPO—peak power output; MPO—mean power output; V-cut—25 m maximal running test with four directional changes (around four cones); RST—repeated sprint test; VIFT—velocity at the last completed stage of the intermittent fitness test; MAT—modified agility test; CMJ—countermovement jump; CMJa—countermovement jump with arm swing; SJ—squat jump; YYIR1—Yo-Yo intermittent recovery test level 1; COD—change-of-direction test; 20/40 m Shuttle Run—test for evaluating agility; BF—body fat percentage; FFM—fat-free mass; COD180—change-of-direction test with a 180° turn; VT—ventilatory threshold; SAT—shooting accuracy test; RSA—repeated sprint ability; 30-15 IFT—30-15 intermittent fitness test; 3000 m race—3000 mr; SSG—small-sided games; HR—heart rate *.
—no statistically significant change; E group—experimental group; TG—training group; CG—control group; HIIT—high-intensity interval training; MCT—medium continuous training; VO2max—maximal oxygen uptake; PPO—peak power output; MPO—mean power output; V-cut—25 m maximal running test with four directional changes (around four cones); RST—repeated sprint test; VIFT—velocity at the last completed stage of the intermittent fitness test; MAT—modified agility test; CMJ—countermovement jump; CMJa—countermovement jump with arm swing; SJ—squat jump; YYIR1—Yo-Yo intermittent recovery test level 1; COD—change-of-direction test; 20/40 m Shuttle Run—test for evaluating agility; BF—body fat percentage; FFM—fat-free mass; COD180—change-of-direction test with a 180° turn; VT—ventilatory threshold; SAT—shooting accuracy test; RSA—repeated sprint ability; 30-15 IFT—30-15 intermittent fitness test; 3000 m race—3000 mr; SSG—small-sided games; HR—heart rate *.Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Čaprić, I.; Stanković, M.; Bojić, I.; Katanić, B.; Jelaska, I.; Pezelj, L.; Masanovic, B.; Stefanica, V.; Govindasamy, K. Effects of Different Types of High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT) on Physical Performance in Female Basketball Players—A Systematic Review. Life 2025, 15, 1180. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15081180
Čaprić I, Stanković M, Bojić I, Katanić B, Jelaska I, Pezelj L, Masanovic B, Stefanica V, Govindasamy K. Effects of Different Types of High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT) on Physical Performance in Female Basketball Players—A Systematic Review. Life. 2025; 15(8):1180. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15081180
Chicago/Turabian StyleČaprić, Ilma, Mima Stanković, Ivana Bojić, Borko Katanić, Igor Jelaska, Luka Pezelj, Bojan Masanovic, Valentina Stefanica, and Karuppasamy Govindasamy. 2025. "Effects of Different Types of High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT) on Physical Performance in Female Basketball Players—A Systematic Review" Life 15, no. 8: 1180. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15081180
APA StyleČaprić, I., Stanković, M., Bojić, I., Katanić, B., Jelaska, I., Pezelj, L., Masanovic, B., Stefanica, V., & Govindasamy, K. (2025). Effects of Different Types of High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT) on Physical Performance in Female Basketball Players—A Systematic Review. Life, 15(8), 1180. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15081180










