Predictive Performance of SAPS-3, SOFA Score, and Procalcitonin for Hospital Mortality in COVID-19 Viral Sepsis: A Cohort Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Study Design, Setting, and Ethics
2.2. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
2.3. Outcome
2.4. Data Collection and Variables
2.5. Statistical Analysis
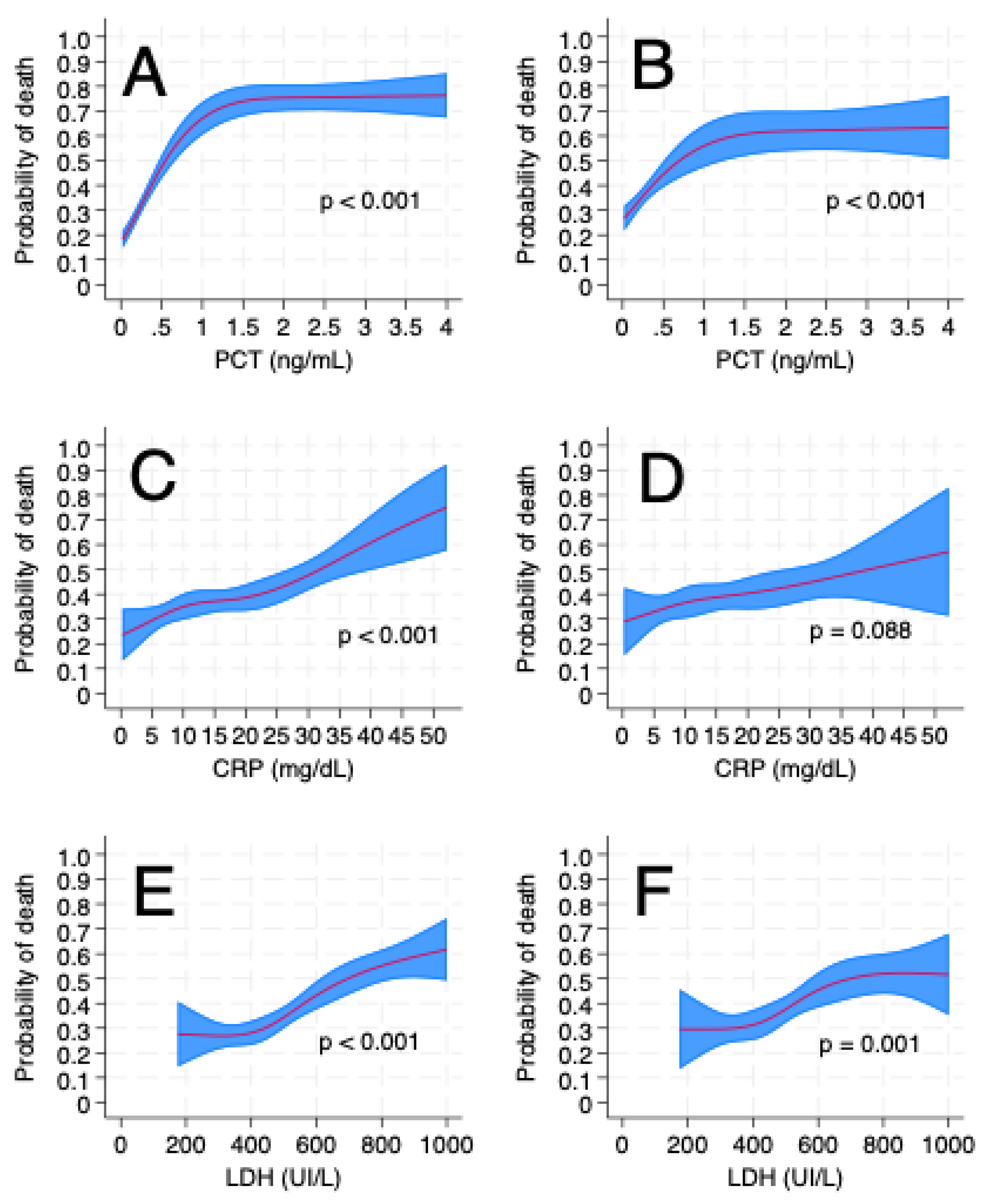
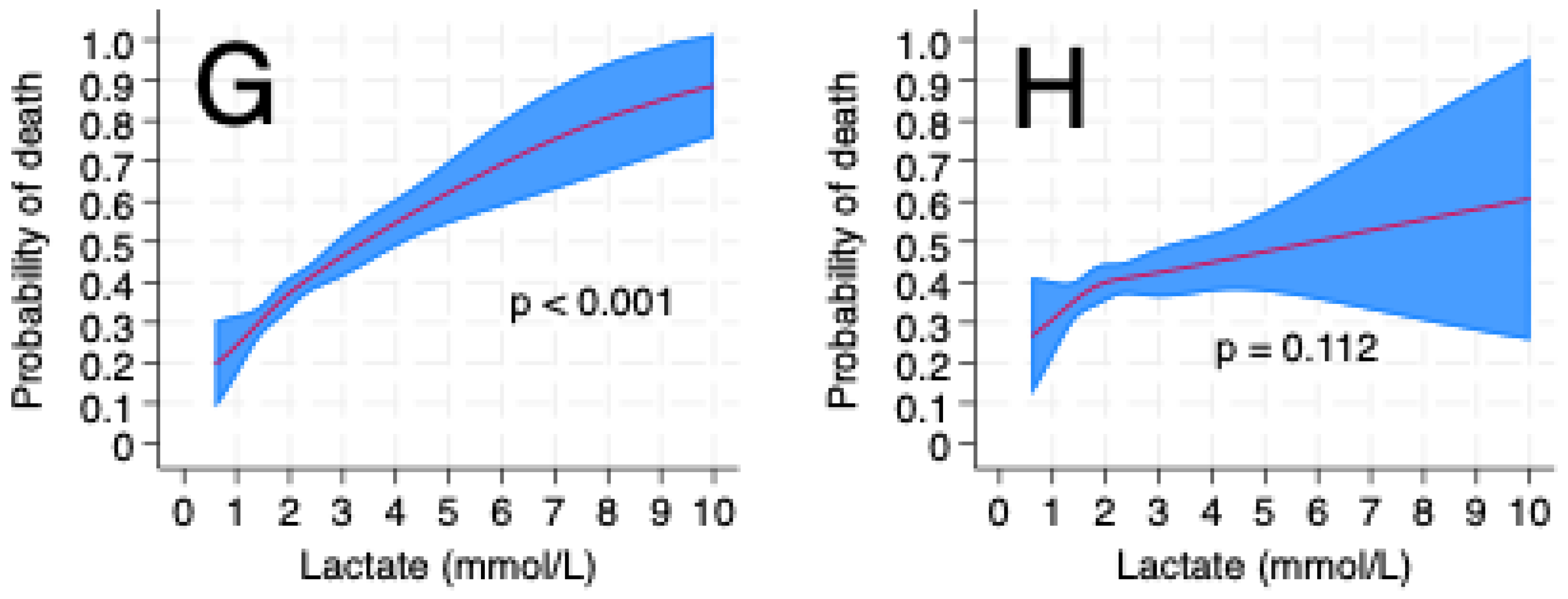
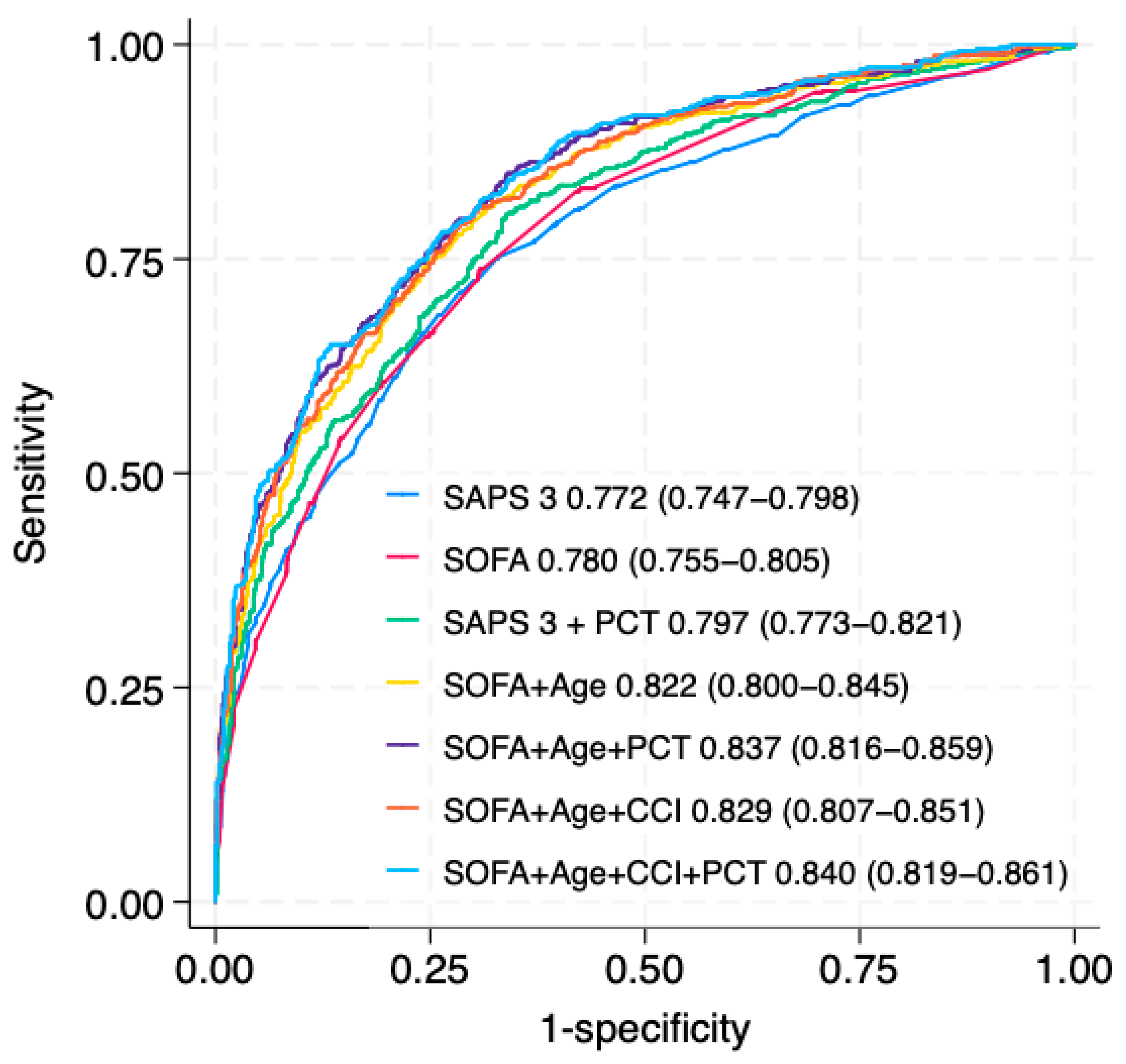
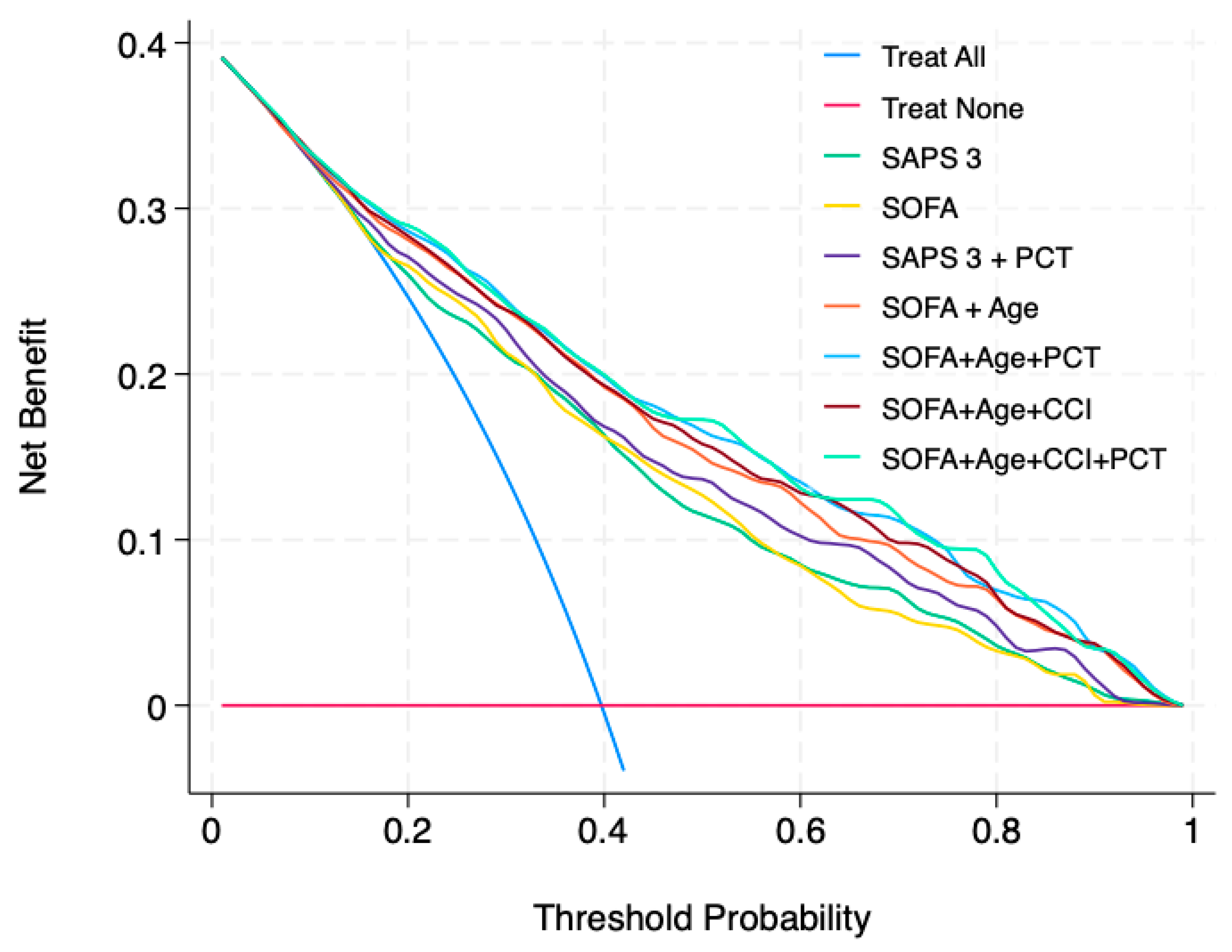
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Main Findings
4.2. Relationship with the Literature
4.3. Implications
4.4. Strengths and Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Moreno, R.P.; Metnitz, P.G.; Almeida, E.; Jordan, B.; Bauer, P.; Campos, R.A.; Iapichino, G.; Edbrooke, D.; Capuzzo, M.; Le Gall, J.R. SAPS 3—From evaluation of the patient to evaluation of the intensive care unit. Part 1: Development of a prognostic model for hospital mortality at ICU admission. Intensive Care Med. 2005, 31, 1345–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vincent, J.L.; Moreno, R.; Takala, J.; Willatts, S.; De Mendonça, A.; Bruining, H.; Reinhart, C.K.; Suter, P.M.; Thijs, L.G. The SOFA (Sepsis-related Organ Failure Assessment) score to describe organ dysfunction/failure. On behalf of the Working Group on Sepsis-Related Problems of the European Society of Intensive Care Medicine. Intensive Care Med. 1996, 22, 707–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pölkki, A.; Pekkarinen, P.T.; Takala, J.; Selander, T.; Reinikainen, M. Association of Sequential Organ Failure Assessment (SOFA) components with mortality. Acta Anaesthesiol. Scand. 2022, 66, 731–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quintairos, A.; Rezende, E.A.D.C.; Soares, M.; Lobo, S.M.A.; Salluh, J.I.F. Leveraging a national cloud-based intensive care registry for COVID-19 surveillance, research and case-mix evaluation in Brazil. Rev. Bras. Ter. Intensiv. 2022, 34, 205–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roepke, R.M.L.; Besen, B.A.M.P.; Daltro-Oliveira, R.; Guazzelli, R.M.; Bassi, E.; Salluh, J.I.F.; Damous, S.H.B.; Utiyama, E.M.; Malbouisson, L.M.S. Predictive Performance for Hospital Mortality of SAPS 3, SOFA, ISS, and New ISS in Critically Ill Trauma Patients: A Validation Cohort Study. J. Intensive Care Med. 2023, 39, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.J.; Ko, B.S.; Ryoo, S.M.; Han, E.; Suh, G.J.; Choi, S.H.; Chung, S.P.; Lim, T.H.; Kim, W.Y.; Kwon, W.Y.; et al. Modified cardiovascular SOFA score in sepsis: Development and internal and external validation. BMC Med. 2022, 20, 163. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.H.; Ali, M.A.; Salim, B. Prediction of Mortality Using the Sequential Organ Failure Assessment Score in Critically Ill COVID-19 Patients. J. Coll. Physicians Surg. Pak. 2024, 34, 874–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gruyters, I.; De Ridder, T.; Bruckers, L.; Geebelen, L.; Gharmaoui, S.; Callebaut, I.; Vandenbrande, J.; Berends, N.; Dubois, J.; Stessel, B. Predictive value of serial evaluation of the Sequential Organ Failure Assessment (SOFA) score for intensive care unit mortality in critically ill patients with COVID-19: A retrospective cohort study. Anaesthesiol. Intensive Ther. 2022, 54, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Póvoa, P.; Coelho, L.; Cidade, J.P.; Ceccato, A.; Morris, A.C.; Salluh, J.; Nobre, V.; Nseir, S.; Martin-Loeches, I.; Lisboa, T.; et al. Biomarkers in pulmonary infections: A clinical approach. Ann. Intensive Care 2024, 14, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreno, M.S.; Nietmann, H.; Matias, C.M.; Lobo, S.M. C-reactive protein: A tool in the follow-up of nosocomial pneumonia. J. Infect. 2010, 61, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maves, R.C.; Enwezor, C.H. Uses of Procalcitonin as a Biomarker in Critical Care Medicine. Infect. Dis. Clin. 2022, 36, 897–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, J.C.; Ho, Y.-L.; Besen, B.A.M.P.; Malbouisson, L.M.S.; Taniguchi, L.U.; Mendes, P.V.; Costa, E.L.V.; Park, M.; Daltro-Oliveira, R.; Roepke, R.M.L.; et al. Protective ventilation and outcomes of critically ill patients with COVID-19: A cohort study. Ann. Intensive Care 2021, 11, 92. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Michels, E.H.; Appelman, B.; de Brabander, J.; van Amstel, R.B.; Chouchane, O.; van Linge, C.C.; Schuurman, A.R.; Reijnders, T.D.; Sulzer, T.A.; Klarenbeek, A.M.; et al. Age-related changes in plasma biomarkers and their association with mortality in COVID-19. Eur. Respir. J. 2023, 62, 1300011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moons, K.G.; Altman, D.G.; Reitsma, J.B.; Collins, G.S. Transparent Reporting of a Multivariate Prediction Model for Individual Prognosis or Development Initiative. New Guideline for the Reporting of Studies Developing, Validating, or Updating a Multivariable Clinical Prediction Model: The TRIPOD Statement. Adv. Anat. Pathol. 2015, 22, 303–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alhazzani, W.; Møller, M.H.; Arabi, Y.M.; Loeb, M.; Gong, M.N.; Fan, E.; Oczkowski, S.; Levy, M.M.; Derde, L.; Dzierba, A.; et al. Surviving Sepsis Campaign: Guidelines on the Management of Critically Ill Adults with Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19). Crit. Care Med. 2020, 48, e440–e469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeLong, E.R.; DeLong, D.M.; Clarke-Pearson, D.L. Comparing the areas under two or more correlated receiver operating characteristic curves: A nonparametric approach. Biometrics 1988, 44, 837–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Calster, B.; McLernon, D.J.; Van Smeden, M.; Wynants, L.; Steyerberg, E.W. Topic Group ‘Evaluating diagnostic tests and prediction models’ of the STRATOS initiative. Calibration: The Achilles heel of predictive analytics. BMC Med. 2019, 17, 130. [Google Scholar]
- Vickers, A.J.; Elkin, E.B. Decision curve analysis: A novel method for evaluating prediction models. Med. Decis. Mak. 2006, 16, 565–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vesin, A.; Azoulay, E.; Ruckly, S.; Vignoud, L.; Rusinovà, K.; Benoit, D.; Soares, M.; Azeivedo-Maia, P.; Abroug, F.; Benbenishty, J.; et al. Reporting and handling missing values in clinical studies in intensive care units. Intensive Care Med. 2013, 39, 1396–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavrentieva, A.; Kaimakamis, E.; Voutsas, V.; Bitzani, M. An observational study on factors associated with ICU mortality in Covid-19 patients and critical review of the literature. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 7804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gómez-Romero, F.J.; Muñoz-Rodríguez, J.R.; Serrano-Oviedo, L.; García-Jabalera, I.; López-Juárez, P.; Pérez-Ortiz, J.M.; Redondo-Calvo, F.J. COVID-19 SESCAM Network. Clinical features and mortality of COVID-19 patients admitted to ICU according to SOFA score. Medicine 2022, 101, e19106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luan, Y.Y.; Yin, C.H.; Yao, Y.M. Update Advances on C-Reactive Protein in COVID-19 and Other Viral Infections. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 720363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vedovati, M.C.; Barbieri, G.; Urbini, C.; D’AGostini, E.; Vanni, S.; Papalini, C.; Pucci, G.; Cimini, L.A.; Valentino, A.; Ghiadoni, L.; et al. Clinical prediction models in hospitalized patients with COVID-19: A multicenter cohort study. Respir. Med. 2022, 202, 106954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knight, S.R.; Ho, A.; Pius, R.; Buchan, I.; Carson, G.; Drake, T.M.; Dunning, J.; Fairfield, C.J.; Gamble, C.; Green, C.A.; et al. Risk stratification of patients admitted to hospital with covid-19 using the ISARIC WHO Clinical Characterisation Protocol: Development and validation of the 4C Mortality Score. BMJ 2020, 370, m3339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galli, F.; Bindo, F.; Motos, A.; Fernández-Barat, L.; Barbeta, E.; Gabarrús, A.; Ceccato, A.; Bermejo-Martin, J.F.; Ferrer, R.; Riera, J.; et al. Procalcitonin and C-reactive protein to rule out early bacterial coinfection in COVID-19 critically ill patients. Intensive Care Med. 2023, 49, 934–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DE Backer, D.; Creteur, J.; Zhang, H.; Norrenberg, M.; Vincent, J.-L. Lactate production by the lungs in acute lung injury. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1997, 156 Pt 1, 1099–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gershengorn, H.B.; Patel, S.; Shukla, B.; Warde, P.R.; Soorus, S.M.; Holt, G.E.; Kett, D.H.; Parekh, D.J.; Ferreira, T. Predictive Value of Sequential Organ Failure Assessment Score across Patients with and without COVID-19 Infection. Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2021, 19, 790–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huber, M.; Bello, C.; Schober, P.; Filipovic, M.G.; Luedi, M.M. Decision Curve Analysis of In-Hospital Mortality Prediction Models: The Relative Value of Pre- and Intraoperative Data for Decision-Making. Anesth. Analg. 2024, 139, 617–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riley, R.D.; Hayden, J.A.; Steyerberg, E.W.; Moons, K.G.M.; Abrams, K.; Kyzas, P.A.; Malats, N.; Briggs, A.; Schroter, S.; Altman, D.G.; et al. Prognosis Research Strategy (PROGRESS) 2: Prognostic factor research. PLoS Med. 2013, 10, e1001380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steyerberg, E.W.; Moons, K.G.; van der Windt, D.A.; Hayden, J.A.; Perel, P.; Schroter, S.; Riley, R.D.; Hemingway, H.; Altman, D.G.; PROGRESS Group. Prognosis Research Strategy (PROGRESS) 3: Prognostic model research. PLoS Med. 2013, 10, e1001381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hingorani, A.D.; Windt, D.A.V.D.; Riley, R.D.; Abrams, K.; Moons, K.G.M.; Steyerberg, E.W.; Schroter, S.; Sauerbrei, W.; Altman, D.G.; Hemingway, H.; et al. Prognosis research strategy (PROGRESS) 4: Stratified medicine research. BMJ 2013, 346, e5793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Variables | All Cohort (N = 1395) | Survivors (n = 841) | Non Survivors (n = 554) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age, years | 54.8 ± 16.1 | 50.1 ± 14.5 | 61.1 ± 15.9 | <0.001 |
| Sex, male | 808 (57.9%) | 479 (57%) | 319 (59.4%) | 0.38 |
| Hypertension (%) | 670 (61.2%)301 | 339 (55.2%)227 | 331 (69.0%)74 | <0.001 |
| Diabetes (%) | 396 (36.2%)301 | 187 (30.5%)227 | 209 (43.5%)74 | <0.001 |
| Obesity (%) | 220 (20.2%)305 | 136 (22.3%)230 | 84 (17.5%)75 | 0.057 |
| Coronary heart disease (%) | 78 (7.1%)302 | 31 (5.0%)227 | 47 (9.8%)75 | 0.003 |
| Asthma (%) | 40 (3.7%)302 | 20 (3.3%)228 | 20 (4.2%)74 | 0.52 |
| COPD (%) | 77 (7.0%)301 | 28 (4.6%)227 | 49 (10.2%)74 | <0.001 |
| Heart failure (%) | 38 (3.5%)301 | 15 (2.4%)227 | 23 (4.8%)74 | 0.045 |
| Chronic kidney disease (%) | 34 (5.4%)768 | 7 (1.9%)481 | 27 (10.1%)287 | <0.001 |
| Cirrhosis (%) | 15 (1.4%)302 | 6 (1.0%)228 | 9 (1.9%)74 | 0.29 |
| Immunossupression (%) | 42 (3.8%)304 | 13 (2.1%)230 | 29 (6.0%)74 | 0.001 |
| CCI | 1.0 (0.0–1.0)191 | 0 (0.0–1.0)101 | 1.0 (0.0–1.0)91 | <0.001 |
| SAPS 3 | 57.7 (16.4) 133 | 51.5 (11.3)91 | 66.8 (17.4)41 | <0.001 |
| SOFA | 5.6 (3.0–9.0)154 | 3.0 (2.0–5.0)91 | 8.0 (4.0–11.0)63 | <0.001 |
| Lactate, mEq/L | 1.1 (1.6–1.7)91 | 1.0 (1.6–1.5)51 | 1.3 (1.7–1.9)41 | <0.001 |
| CRP, mg/dL | 14.1 (8.1–11.9)489 | 13.4 (7.5–10.9)181 | 16.1 (9.7–16.1)108 | <0.001 |
| PCT, ng/mL | 0.11 (0.1–0.6)313 | 0.1 (0.1–0.3)174 | 0.5 (0.1–1.5)139 | <0.001 |
| LDH, U/L | 494 (380–632)638 | 459 (366–579)306 | 559.5 (415–691)151 | <0.001 |
| RRT (%) | 135 (17.1) | 39 (4.6) | 196 (35.4) | <0.001 |
| MV (%) | 910 (65.9) | 395 (47) | 515 (94.8) | <0.001 |
| MV, days | 5 (0.0–13.0) | 0.0 (0.0–10.0) | 9.0 (4.0–17.0) | <0.001 |
| Vasoactive drug (%) | 831 (59.7) | 344 (40.9) | 488 (88.1) | <0.001 |
| ICU LOS, days | 11.0 (5.0–19.0) | 11.0 (6.0–19.0) | 11.0 (5.0–10.0) | 0.11 |
| Hospital LOS, days | 15.0 (9.0–16.0) | 16.0 (11.0–17.0) | 13.0 (6.0–14.0) | <0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Roepke, R.M.L.; Janzantti, H.B.L.; Cantamessa, M.B.; Machado, L.F.; Luckemeyer, G.D.; Gandolfi, J.V.; Besen, B.A.M.P.; Lobo, S.M. Predictive Performance of SAPS-3, SOFA Score, and Procalcitonin for Hospital Mortality in COVID-19 Viral Sepsis: A Cohort Study. Life 2025, 15, 1161. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15081161
Roepke RML, Janzantti HBL, Cantamessa MB, Machado LF, Luckemeyer GD, Gandolfi JV, Besen BAMP, Lobo SM. Predictive Performance of SAPS-3, SOFA Score, and Procalcitonin for Hospital Mortality in COVID-19 Viral Sepsis: A Cohort Study. Life. 2025; 15(8):1161. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15081161
Chicago/Turabian StyleRoepke, Roberta Muriel Longo, Helena Baracat Lapenta Janzantti, Marina Betschart Cantamessa, Luana Fernandes Machado, Graziela Denardin Luckemeyer, Joelma Villafanha Gandolfi, Bruno Adler Maccagnan Pinheiro Besen, and Suzana Margareth Lobo. 2025. "Predictive Performance of SAPS-3, SOFA Score, and Procalcitonin for Hospital Mortality in COVID-19 Viral Sepsis: A Cohort Study" Life 15, no. 8: 1161. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15081161
APA StyleRoepke, R. M. L., Janzantti, H. B. L., Cantamessa, M. B., Machado, L. F., Luckemeyer, G. D., Gandolfi, J. V., Besen, B. A. M. P., & Lobo, S. M. (2025). Predictive Performance of SAPS-3, SOFA Score, and Procalcitonin for Hospital Mortality in COVID-19 Viral Sepsis: A Cohort Study. Life, 15(8), 1161. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15081161






