Toxoplasma gondii Seroprevalence and Associated Risk Factors in Psychiatric Patients Diagnosed with Moderate and Major Depression from Western Romania: A Case—Control Retrospective Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
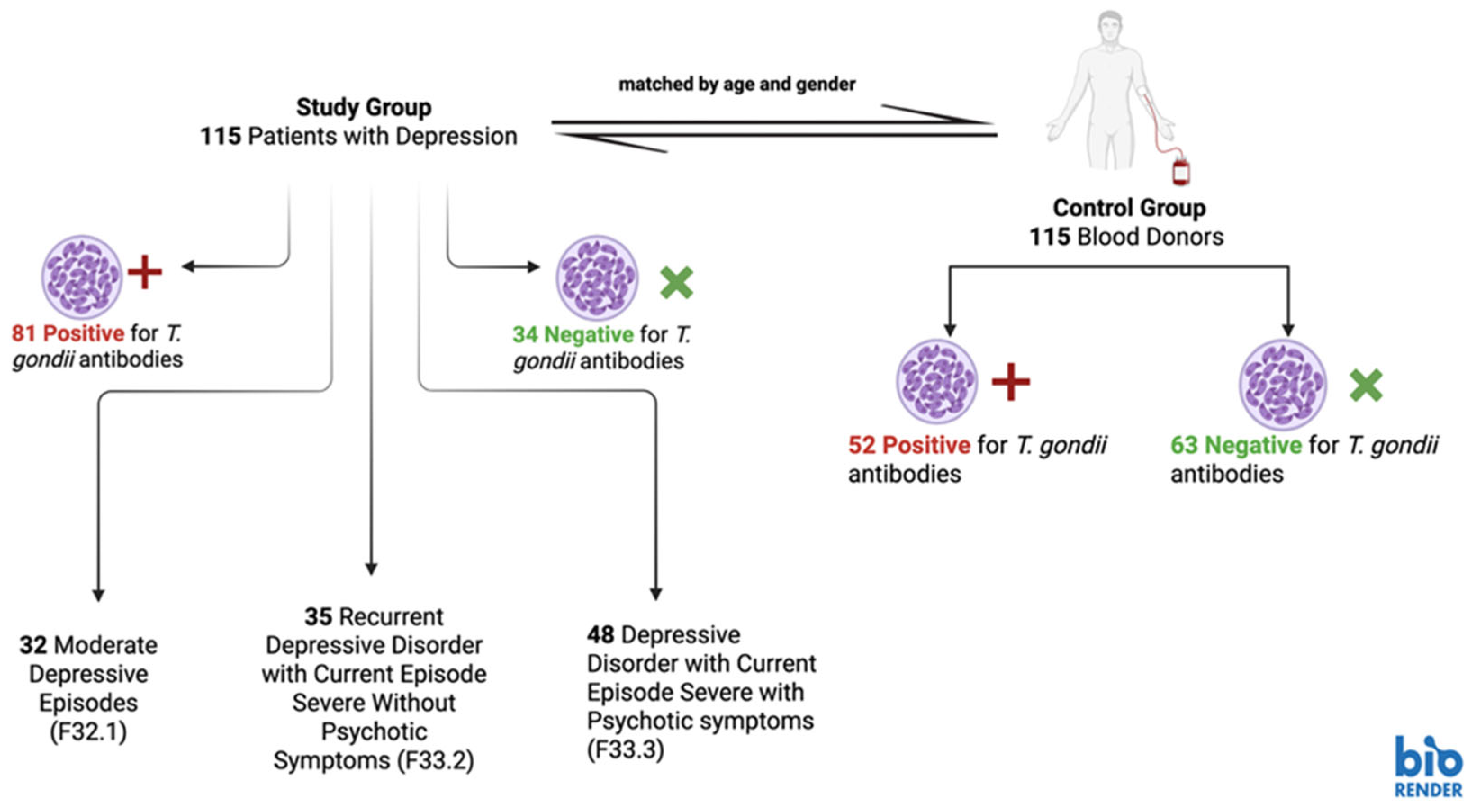
2.1. Study Design, Study Group and Control Group
2.2. Blood Collection and Laboratory Tests
2.3. Data Collection and Questionnaire
2.4. Statistical Analysis
2.5. Ethics and Informed Consent
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| T. gondi | Toxoplasma gondi |
| 4EPS | 4-ethylphenyl sulfate |
| 5-HT | Serotonin |
| aOR | Adjusted odds ratio |
| CI | Confidence interval |
| DSM | Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders |
| GABA | Gamma-aminobutyric acid |
| ICD | International Classification of Diseases |
| IDO | Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase |
| IFN-γ | Interferon gamma |
| IL-17A | Interleukin-17A |
| IL-1β | Interleukin-1β |
| IL-2 | Interleukin-2 |
| IL-33 | Interleukin-33 |
| IL-6 | Interleukin-6 |
| OR | Odds ratio |
| TDO | Tryptophan-2,3-dioxygenase |
| TNF-α | Tumor necrosis factor α |
References
- Dupont, D.; Robert, M.G.; Brenier-Pinchart, M.P.; Lefevre, A.; Wallon, M.; Pelloux, H. Toxoplasma gondii, a Plea for a Thorough Investigation of Its Oncogenic Potential. Heliyon 2023, 9, e22147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Attias, M.; Teixeira, D.E.; Benchimol, M.; Vommaro, R.C.; Crepaldi, P.H.; De Souza, W. The Life-Cycle of Toxoplasma gondii Reviewed Using Animations. Parasites Vectors 2020, 13, 588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saadatnia, G.; Golkar, M. A Review on Human Toxoplasmosis. Scand. J. Infect. Dis. 2012, 44, 805–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiss, W.L.; Kim, K. Toxoplasma gondii: The Model Apicomplexan: Perspectives and Methods; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2007; pp. 367–386. [Google Scholar]
- Peyron, F.; Wallon, M.; Kieffer, F.; Garweg, J. Toxoplasmosis. In Infectious Diseases of the Fetus and Newborn Infant, 8th ed.; Wilson, C.B., Nizet, V.M., Maldonado, Y.A., Remington, J.S., Klein, J.O., Eds.; Saunders: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2016; pp. 949–1042. [Google Scholar]
- Maisarah, A.; Mohamad, S.; Husain, M.; Abdullah, S.; Noordin, R. Association between Infection with Toxoplasma gondii and Psychiatric Disorders. Folia Parasitol. 2022, 69, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mares, A.M.; Varlam, C.I.; Iliuta, F.P.; Lacau, R.M.; Manea, M.C. A Comprehensive Assessment of Toxoplasmosis and Its Dormant Impact on Psychotic Disorders (Review). Biomed. Rep. 2024, 20, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bisetegn, H.; Debash, H.; Ebrahim, H.; Mahmood, N.; Gedefie, A.; Tilahun, M.; Alemayehu, E.; Mohammed, O.; Feleke, D.G. Global Seroprevalence of Toxoplasma gondii Infection among Patients with Mental and Neurological Disorders: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Health Sci. Rep. 2023, 6, e1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petersen, E. Toxoplasmosis. Semin. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2007, 12, 214–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tyebji, S.; Seizova, S.; Hannan, A.J.; Tonkin, C.J. Toxoplasmosis: A Pathway to Neuropsychiatric Disorders. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2019, 96, 72–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasirpour, S.; Kheirandish, F.; Fallahi, S. Depression and Toxoplasma gondii Infection: Assess the Possible Relationship through a Seromolecular Case-Control Study. Arch. Microbiol. 2020, 202, 2689–2695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nayeri Chegeni, T.; Sharif, M.; Sarvi, S.; Moosazadeh, M.; Montazeri, M.; Aghayan, S.A.; Balalami, N.J.; Gholami, S.; Hosseininejad, Z.; Saberi, R.; et al. Is There Any Association between Toxoplasma gondii Infection and Depression? A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0218524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martynowicz, J.; Augusto, L.; Wek, R.C.; Boehm, S.L.; Sullivan, W.J. Guanabenz Reverses a Key Behavioral Change Caused by Latent Toxoplasmosis in Mice by Reducing Neuroinflammation. mBio 2019, 10, e00381-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McConkey, G.A.; Martin, H.L.; Bristow, G.C.; Webster, J.P. Toxoplasma gondii Infection and Behaviour—Location, Location, Location? J. Exp. Biol. 2013, 216, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortiz-Guerrero, G.; Gonzalez-Reyes, R.E.; de-la-Torre, A.; Medina-Rincón, G.; Nava-Mesa, M.O. Pathophysiological Mechanisms of Cognitive Impairment and Neurodegeneration by Toxoplasma gondii Infection. Brain Sci. 2020, 10, 369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villares, M.; Berthelet, J.; Weitzman, J.B. The Clever Strategies Used by Intracellular Parasites to Hijack Host Gene Expression. Semin. Immunopathol. 2020, 42, 215–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, K.; Xu, C.; Zhao, G.; Xie, H. Epigenetic Manipulation of Psychiatric Behavioral Disorders Induced by Toxoplasma gondii. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 803502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuijpers, P.; Smit, F. Excess Mortality in Depression: A Meta-Analysis of Community Studies. J. Affect. Disord. 2002, 72, 227–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvarado-Esquivel, C.; Sánchez-Anguiano, L.F.; Hernández-Tinoco, J.; Berumen-Segovia, L.O.; Torres-Prieto, Y.E.; Estrada-Martínez, S.; Pérez-Álamos, A.R.; Ortiz-Jurado, M.N.; Molotla-de-León, G.; Beristain-García, I.; et al. Toxoplasma gondii Infection and Depression: A Case-Control Seroprevalence Study. Eur. J. Microbiol. Immunol. 2016, 6, 85–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamal, A.M.; Kamal, A.M.; Abd El-Fatah, A.S.; Rizk, M.M.; Hassan, E.E. Latent Toxoplasmosis Is Associated with Depression and Suicidal Behavior. Arch. Suicide Res. 2022, 26, 819–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abd El-Aal, N.F.; Saber, M.; Fawzy, N.; Ashour, W.R. Sero-Prevalence of Anti-Toxoplasma gondii Antibodies among Patients with Neuropsychiatric Disorders: Epilepsy and Depression. J. Egypt. Soc. Parasitol. 2016, 46, 729–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hlaváčová, J.; Flegr, J.; Fiurašková, K.; Kaňková, Š. Relationship between Latent Toxoplasmosis and Depression in Clients of a Center for Assisted Reproduction. Pathogens 2021, 10, 1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, P.-C.; Groer, M.; Beckie, T. New Findings: Depression, Suicide, and Toxoplasma gondii Infection. J. Am. Assoc. Nurse Pract. 2014, 26, 629–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Hussainy, N.H.; Al-Saedi, A.M.; Al-Lehaibi, J.H.; Al-Lehaibi, Y.A.; Al-Sehli, Y.M.; Afifi, M.A. Serological Evidences Link Toxoplasmosis with Schizophrenia and Major Depression Disorder. J. Microsc. Ultrastruct. 2015, 3, 148–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalimi, A.; Abdoli, A. Latent Toxoplasmosis and Human. Iran. J. Parasitol. 2012, 7, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Grada, S.; Mihu, A.G.; Oatis, D.A.; Susan, M.; Lupu, M.A.; Olariu, T.R. Prevalence of Toxoplasma gondii IgG Antibodies and Associated Risk Factors in Psychiatric Patients from Western Romania: A Cross-Sectional Study. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grada, S.; Mihu, A.G.; Oatis, D.A.; Marc, C.C.; Chicea, L.M.; Petrescu, C.; Lupu, A.M.; Olariu, T.R. Seroprevalence and Associated Risk Factors of Toxoplasma gondii in Patients Diagnosed with Schizophrenia: A Case-Control Cross Sectional Study. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 5th ed.; American Psychiatric Association: Arlington, TX, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems; 10th Revision (ICD-10); World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2016; Available online: https://iris.who.int/handle/10665/246208 (accessed on 15 April 2025).
- Romanian Ministry of Public Health. ORDER Nr. 1193 of July 7, 2007 for the Approval of the Rules on the Information to Be Provided to Donors of Blood and Blood Components of Human Origin, as Well as the Information to Be Communicated by Donors at Each Donation and the Admissibility of Donors of Human Blood and Blood Components. Available online: http://Legislatie.Just.Ro/Public/DetaliiDocumentAfis/117980 (accessed on 20 March 2025). (In Romanian).
- Centonze, A.R.; Tonolli, E.; Fontana, R. Performance Characteristics of Current-Generation Immulite 2000 TORCH Assays. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2013, 20, 122–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.; Gao, P.; Bu, D.; Liu, D. Association between Toxoplasma gondii Infection and Psychiatric Disorders: A Cross-Sectional Study in China. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 15092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, Z.M.; Toledo, D.N.M.; Pio, S.; Machado, B.A.A.; Dos Santos, P.V.; Hó, F.G.; Medina, Y.N.; de Miranda Cordeiro, P.; Perucci, L.O.; Pinto, K.M.d.C.; et al. Neuroserpin, IL-33 and IL-17A as Potential Markers of Mild Symptoms of Depressive Syndrome in Toxoplasma gondii-Infected Pregnant Women. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1394456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvarado-Esquivel, C.; Mendoza-Larios, L.A.; García-Dolores, F.; Sánchez-Anguiano, L.F.; Antuna-Salcido, E.I.; Hernández-Tinoco, J.; Rocha-Salais, A.; Segoviano-Mendoza, M.A.; Sifuentes-Álvarez, A. Association between Toxoplasma gondii Infection in Brain and a History of Depression in Suicide Decedents: A Cross-Sectional Study. Pathogens 2021, 10, 1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yalın Sapmaz, Ş.; Şen, S.; Özkan, Y.; Kandemir, H. Relationship between Toxoplasma gondii Seropositivity and Depression in Children and Adolescents. Psychiatry Res. 2019, 278, 263–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Zhong, Y.; Chen, N.; Chen, J. From the Immune System to Mood Disorders Especially Induced by Toxoplasma gondii: CD4+ T Cell as a Bridge. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2023, 13, 1078984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Zhao, J.; Guo, W. Emotional Roles of Mono-Aminergic Neurotransmitters in Major Depressive Disorder and Anxiety Disorders. Front. Psychol. 2018, 9, 2201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delgado, P.L. Depression: The Case for a Monoamine Deficiency. J. Clin. Psychiatry 2000, 61 (Suppl. S6), 7–11. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Belmaker, R.H.; Agam, G. Major Depressive Disorder. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 358, 55–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daher, D.; Shaghlil, A.; Sobh, E.; Hamie, M.; Hassan, M.E.; Moumneh, M.B.; Itani, S.; El Hajj, R.; Tawk, L.; El Sabban, M.; et al. Comprehensive Overview of Toxoplasma gondii-Induced and Associated Diseases. Pathogens 2021, 10, 1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, W.-Q.; Bai, S.-Y.; Pan, M.; Jin, Q.-W.; Liu, Z.; Bo, X.; Huang, S.-Y. Chronic Toxoplasmosis Induces Depression-like Behaviors and Neuroinflammatory Responses in Mice. Acta Trop. 2025, 264, 107568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moradi, F.; Dashti, N.; Farahvash, A.; Baghaei Naeini, F.; Zarebavani, M. Curcumin Ameliorates Chronic Toxoplasma gondii Infection-Induced Affective Disorders through Modulation of Proinflammatory Cytokines and Oxidative Stress. Iran. J. Basic. Med. Sci. 2023, 26, 461–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, X.; Yang, X.; Tan, S.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Tian, X.; Huang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; He, C.; Yin, K.; et al. Gut Microbiota Mediates Anxiety-like Behaviors Induced by Chronic Infection of Toxoplasma gondii in Mice. Gut Microbes 2024, 16, 2391535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Zhang, C.; Yang, Z.; Wu, W.; Zou, W.; Xin, Z.; Zheng, S.; Liu, R.; Yang, L.; Peng, H. Intestinal Microbiota Imbalance Resulted by Anti-Toxoplasma gondii Immune Responses Aggravate Gut and Brain Injury. Parasites Vectors 2024, 17, 284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, J.-X.; Wei, X.-Y.; Guo, H.; Chen, Y.; Wang, W.; Geng, H.-L.; Yang, X.; Jiang, J.; Zhang, X.-X. Metagenomic Insights into the Composition and Function of the Gut Microbiota of Mice Infected with Toxoplasma gondii. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1156397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olariu, T.R.; Ursoniu, S.; Hotea, I.; Dumitrascu, V.; Anastasiu, D.; Lupu, M.A. Seroprevalence and Risk Factors of Toxoplasma gondii Infection in Pregnant Women from Western Romania. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2020, 20, 763–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, J.L.; Dargelas, V.; Roberts, J.; Press, C.; Remington, J.S.; Montoya, J.G. Risk Factors for Toxoplasma gondii Infection in the United States. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2009, 49, 878–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, J.L.; Ogunmodede, F.; Scheftel, J.; Kirkland, E.; Lopez, A.; Schulkin, J.; Lynfield, R. Toxoplasmosis-Related Knowledge and Practices among Pregnant Women in the United States. Infect. Dis. Obstet. Gynecol. 2003, 11, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martini, A.; Pietrafesa, E.; Rondinone, B.M.; Iavicoli, S.; D’amelio, S.; Cavallero, S.; Bonafede, M. Toxoplasmosis and Knowledge: What Do the Italian Women Know About? Epidemiol. Infect. 2020, 148, e256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mörkl, S.; Varnagy, A.; Wagner-Skacel, J.; Lahousen, T.; Brodtrager, D.; Sallmutter, K.; Bengesser, S.A.; Painold, A.; Narrath, M.; Pieter, L.; et al. Culinary Medicine Cooking Workshops as Add-On Therapy for Inpatients with Depression and Eating Disorders. Nutrients 2024, 16, 3973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Şirin, M.C.; Kılıç, F.; Demirdaş, A.; Arıdoğan, B.; Sesli Çetin, E. An Investigation into the Association Between Toxoplasma gondii Infection and Bipolar Disorder. Turk. J. Parasitol. 2021, 45, 241–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lupu, M.A.; Lighezan, R.; Paduraru, A.A.; Dragomir, A.; Pavel, R.; Grada, S.; Mihu, A.G.; Ursoniu, S.; Olariu, T.R. Seroepidemiology of Toxoplasma gondii Infection in Blood Donors from Western Romania. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Oliveira, P.R.F.; de Melo, R.P.B.; Sierra, T.A.O.; da Silva, R.A.; da Silva de Oliveira, J.E.; de Almeida, B.G.; Mota, R.A. Investigation of Soil Contaminated with Toxoplasma gondii Oocyst in Urban Public Environment, in Brazil. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2021, 79, 101715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gotteland, C.; Gilot-Fromont, E.; Aubert, D.; Poulle, M.-L.; Dupuis, E.; Dardé, M.-L.; Forin-Wiart, M.-A.; Rabilloud, M.; Riche, B.; Villena, I. Spatial Distribution of Toxoplasma gondii Oocysts in Soil in a Rural Area: Influence of Cats and Land Use. Vet. Parasitol. 2014, 205, 629–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kakakhel, M.A.; Wu, F.; Anwar, Z.; Saif, I.; Akbar, N.U.; Gul, N.; Ali, I.; Feng, H.; Wang, W. The Presence of Toxoplasma gondii in Soil, Their Transmission, and Their Influence on the Small Ruminants and Human Population: A Review. Microb. Pathog. 2021, 158, 104850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marković-Denić, L.; Stopić, M.; Bobić, B.; Nikolić, V.; Djilas, I.; Srzentić, S.J.; Štajner, T. Factors Associated with Toxoplasma gondii Seroprevalence in Pregnant Women: A Cross-Sectional Study in Belgrade, Serbia. Pathogens 2023, 12, 1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dragomir, A.; Lupu, M.A.; Maciuceanu, C.G.; Chicea, L.M.; Olariu, T.R. Risk Factors Associated with Toxoplasma gondii in Patients with Cardiovascular Diseases from Western Romania. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krittanawong, C.; Maitra, N.S.; Qadeer, Y.K.; Wang, Z.; Fogg, S.; Storch, E.A.; Celano, C.M.; Huffman, J.C.; Jha, M.; Charney, D.S.; et al. Association of Depression and Cardiovascular Disease. Am. J. Med. 2023, 136, 881–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Zhou, J.; Wang, M.; Yang, C.; Sun, G. Cardiovascular Disease and Depression: A Narrative Review. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2023, 10, 1274595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elsaid, M.; Azbedah, A.; El-Alem, D.; Alkout, A. The Prevalence of Toxoplasma gondii Infection in Psychiatric Patients in Tripoli, Libya. J. Am. Sci. 2014, 10, 135–140. [Google Scholar]
- Elmore, S.A.; Jones, J.L.; Conrad, P.A.; Patton, S.; Lindsay, D.S.; Dubey, J.P. Toxoplasma gondii: Epidemiology, Feline Clinical Aspects, and Prevention. Trends Parasitol. 2010, 26, 190–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lilly, E.L.; Wortham, C.D. High Prevalence of Toxoplasma gondii Oocyst Shedding in Stray and Pet Cats (Felis Catus) in Virginia, United States. Parasites Vectors 2013, 6, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, M.; Dubey, J.P.; Hill, D.; Buchanan, R.L.; Gamble, H.R.; Jones, J.L.; Pradhan, A.K. Prevalence and Risk Factors for Toxoplasma gondii Infection in Meat Animals and Meat Products Destined for Human Consumption. J. Food Prot. 2015, 78, 457–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demirel, Ö.F.; Akgül, Ö.; Bulu, E.; Tanrıöver Aydın, E.; Uysal Cesur, N.; Aksoy Poyraz, C.; Öner, Y.A. Are Bipolar Disorder, Major Depression, and Suicidality Linked with Toxoplasma gondii? A Seromolecular Case-Control Study. Postgrad. Med. 2023, 135, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gulshan, J.E.; Lira, S.S.; Qusar, M.M.A.S.; Hosen, M.I.; Rahman, A.; Islam, M.R.; Rahman, T. Association Between Toxoplasma gondii Infection and Serum Neurotransmitter Levels in Major Depressive Disorder Patients: A Case-Control Study in Bangladesh. J. Parasitol. Res. 2024, 2024, 7054920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Cheng, Z. Cross-Sectional Studies: Strengths, Weaknesses, and Recommendations. Chest 2020, 158, S65–S71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenman, R.; Tennekoon, V.; Hill, L.G. Measuring Bias in Self-Reported Data. Int. J. Behav. Healthc. Res. 2011, 2, 320–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Variable | Positive T. gondii Antibodies/Total (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (Years) | Patients with Depression | Blood Donors | OR | 95% CI | p Value |
| 19–29 | 1/2 (50) | 1/2 (50) | N/A | ||
| 30–39 | 5/10 (50) | 5/10 (50) | N/A | ||
| 40–49 | 14/22 (63.64) | 9/23 (39.13) | 2.72 | 0.82–9.1 | 0.14 |
| 50–59 | 37/52 (71.15) | 30/66 (45.45) | 2.96 | 1.37–6.4 | 0.009 |
| 60+ | 24/29 (82.76) | 7/14 (50) | 4.8 | 1.16–1.19 | 0.04 |
| Gender | |||||
| Male | 28/43 (65.12) | 24/43 (55.81) | 1.48 | 0.62–3.53 | 0.4 |
| Female | 53/72 (73.61) | 28/72 (38.89) | 4.38 | 2.16–8.89 | <0.001 |
| Total | 81/115 (70.43) | 52/115 (45.22) | 2.89 | 1.68–4.97 | <0.001 |
| Detectable T. gondii Antibodies/Total Investigated (%) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Risk Factor | Patients with Depression | Blood Donors | OR | 95% CI | p Value |
| Educational level (High) | 21/32 (65.63) | 17/36 (47.22) | 2.13 | 0.8–5.69 | 0.15 |
| Educational level (Low) | 60/83 (72.29) | 35/79 (44.30) | 3.28 | 1.71–6.31 | <0.001 |
| Contact with the soil | 57/75 (76) | 24/40 (60) | 2.11 | 0.93–4.82 | 0.09 |
| Consumption of undercooked meat | 19/29 (65.52) | 16/37 (43.24) | 2.49 | 0.91–6.81 | 0.09 |
| Contact with cat feces | 69/96 (71.88) | 14/21 (66.67) | 1.28 | 0.47–3.51 | 0.61 |
| Total | 81/115 (70.43) | 52/115 (45.22) | 2.89 | 1.68–4.97 | <0.001 |
| Diagnosys (ICD Code) | Detectable T. gondii Antibodies/Total Investigated (%) | OR | 95% CI | p Value * |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Moderate depression (F32.1) | 33 (68.75)/48 | 2.67 | 1.31–5.44 | 0.01 |
| Recurrent severe depressive disorder (no psychosis) (F33.2) | 26 (81.25)/32 | 3.5 | 1.51–8.13 | 0.004 |
| Recurrent severe depressive disorder (with psychosis) (F33.3) | 22 (62.86)/35 | 2.67 | 1.15–6.13 | 0.03 |
| Total | 81(70.43)/115 | 2.89 | 1.68–4.97 | <0.001 |
| Variable | aOR | 95% CI | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age group (years) (ref: 30–39) | |||
| 40–49 | 1.21 | 0.57–2.56 | 0.619 |
| 50–59 | 1.8 | 0.68–4.75 | 0.233 |
| Sex (ref: Female) | 1.24 | 0.64–2.37 | 0.524 |
| High education (ref: Low) | 0.95 | 0.49–1.86 | 0.886 |
| Depression diagnosis (ref: blood donors) | |||
| Moderate depression (F32.1) | 2.91 | 1.32–6.41 | 0.008 |
| Recurrent severe depressive disorder (no psychosis) (F33.2) | 4.76 | 1.76–12.86 | 0.002 |
| Recurrent severe depressive disorder (with psychosis) (F33.3) | 2.53 | 1.07–5.99 | 0.035 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mihu, A.G.; Olariu, A.T.; Piros, L.E.; Grada, S.; Ardelean, A.A.; Sprintar, S.A.; Oatis, D.A.; Lighezan, R.; Olariu, T.R. Toxoplasma gondii Seroprevalence and Associated Risk Factors in Psychiatric Patients Diagnosed with Moderate and Major Depression from Western Romania: A Case—Control Retrospective Study. Life 2025, 15, 1157. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15081157
Mihu AG, Olariu AT, Piros LE, Grada S, Ardelean AA, Sprintar SA, Oatis DA, Lighezan R, Olariu TR. Toxoplasma gondii Seroprevalence and Associated Risk Factors in Psychiatric Patients Diagnosed with Moderate and Major Depression from Western Romania: A Case—Control Retrospective Study. Life. 2025; 15(8):1157. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15081157
Chicago/Turabian StyleMihu, Alin Gabriel, Alexander Tudor Olariu, Ligia Elisaveta Piros, Sebastian Grada, Ana Alexandra Ardelean, Sergiu Adrian Sprintar, Daniela Adriana Oatis, Rodica Lighezan, and Tudor Rares Olariu. 2025. "Toxoplasma gondii Seroprevalence and Associated Risk Factors in Psychiatric Patients Diagnosed with Moderate and Major Depression from Western Romania: A Case—Control Retrospective Study" Life 15, no. 8: 1157. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15081157
APA StyleMihu, A. G., Olariu, A. T., Piros, L. E., Grada, S., Ardelean, A. A., Sprintar, S. A., Oatis, D. A., Lighezan, R., & Olariu, T. R. (2025). Toxoplasma gondii Seroprevalence and Associated Risk Factors in Psychiatric Patients Diagnosed with Moderate and Major Depression from Western Romania: A Case—Control Retrospective Study. Life, 15(8), 1157. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15081157








