Open-Label Uncontrolled, Monocentric Study to Evaluate the Efficacy and Safety of the Electromagnetic Field and Negative Pressure in the Treatment of Cellulite
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Efficacy Evaluation
2.2. Safety Evaluation
2.2.1. Adverse Events (AEs)
2.2.2. Adverse Device Effects
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gabriel, A.; Chan, V.; Caldarella, M.; Wayne, T.; O’Rorke, E. Cellulite: Current Understanding and Treatment. Aesthet. Surg. J. Open Forum 2023, 5, ojad050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scarano, A.; Petrini, M.; Sbarbati, A.; Amore, R.; Iorio, E.L.; Marchetti, M.; Amuso, D. Pilot Study of Histology Aspect of Cellulite in Seventy Patients Who Differ in BMI and Cellulite Grading. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2021, 20, 4024–4031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Update in Cosmetic Dermatology. Available online: https://link.springer.com/book/10.1007/978-3-642-34029-1 (accessed on 13 July 2025).
- Nürnberger, F.; Müller, G. So-Called Cellulite: An Invented Disease. J. Dermatol. Surg. Oncol. 1978, 4, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rudolph, C.; Hladik, C.; Hamade, H.; Frank, K.; Kaminer, M.S.; Hexsel, D.; Gotkin, R.H.; Sadick, N.S.; Green, J.B.; Cotofana, S. Structural Gender Dimorphism and the Biomechanics of the Gluteal Subcutaneous Tissue: Implications for the Pathophysiology of Cellulite. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2019, 143, 1077–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tokarska, K.; Tokarski, S.; Woźniacka, A.; Sysa-Jędrzejowska, A.; Bogaczewicz, J. Cellulite: A Cosmetic or Systemic Issue? Contemporary Views on the Etiopathogenesis of Cellulite. Postepy Dermatol. Alergol. 2018, 35, 442–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryan, T.J.; Curri, S.B. The Development of Adipose Tissue and Its Relationship to the Vascular System. Clin. Dermatol. 1989, 7, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossi, A.B.; Vergnanini, A.L. Cellulite: A Review. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2000, 14, 251–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Undavia, S.S.; Berger, V.; Kaley, G.; Messina, E.J. Myogenic Responses of Isolated Adipose Tissue Arterioles. Microvasc. Res. 2003, 66, 140–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Godoy, J.M.P.; de Godoy, M. de F.G. Physiopathological Hypothesis of Cellulite. Open Cardiovasc. Med. J. 2009, 3, 96–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tajima, R.; Kawaguchi, N.; Horino, Y.; Takahashi, Y.; Toriyama, K.; Inou, K.; Torii, S.; Kitagawa, Y. Hypoxic Enhancement of Type IV Collagen Secretion Accelerates Adipose Conversion of 3T3-L1 Fibroblasts. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2001, 1540, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lotti, T.; Ghersetich, I.; Grappone, C.; Dini, G. Proteoglycans in So-Called Cellulite. Int. J. Dermatol. 1990, 29, 272–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de la Casa Almeida, M.; Suarez Serrano, C.; Rebollo Roldán, J.; Jiménez Rejano, J.J. Cellulite’s Aetiology: A Review. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2013, 27, 273–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hexsel, D.M.; Abreu, M.; Rodrigues, T.C.; Soirefmann, M.; Do Prado, D.Z.; Gamboa, M.M.L. Side-By-Side Comparison of Areas with and without Cellulite Depressions Using Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Dermatol. Surg. 2009, 35, 1471–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.H.; Victor, F.; Rao, B.; Sadick, N.S. Treatment of Cellulite. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2010, 62, 361–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Querleux, B.; Cornillon, C.; Jolivet, O.; Bittoun, J. Anatomy and Physiology of Subcutaneous Adipose Tissue by in Vivo Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Spectroscopy: Relationships with Sex and Presence of Cellulite. Skin Res. Technol. 2002, 8, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirrashed, F.; Sharp, J.C.; Krause, V.; Morgan, J.; Tomanek, B. Pilot Study of Dermal and Subcutaneous Fat Structures by MRI in Individuals Who Differ in Gender, BMI, and Cellulite Grading. Skin Res. Technol. 2004, 10, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bielfeldt, S.; Buttgereit, P.; Brandt, M.; Springmann, G.; Wilhelm, K.-P. Non-Invasive Evaluation Techniques to Quantify the Efficacy of Cosmetic Anti-Cellulite Products. Skin Res. Technol. 2008, 14, 336–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christman, M.P.; Belkin, D.; Geronemus, R.G.; Brauer, J.A. An Anatomical Approach to Evaluating and Treating Cellulite. J. Drugs Dermatol. 2017, 16, 58–61. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hexsel, D.M.; Dal’forno, T.; Hexsel, C.L. A Validated Photonumeric Cellulite Severity Scale. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2009, 23, 523–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avram, M.M. Cellulite: A Review of Its Physiology and Treatment. J. Cosmet. Laser Ther. 2004, 6, 181–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emanuele, E. Cellulite: Advances in Treatment: Facts and Controversies. Clin. Dermatol. 2013, 31, 725–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franchi, J.; Pellicier, F.; André, P.; Schnebert, S. The adipocyte in the history of slimming agents. Pathol. Biol. 2003, 51, 244–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veronese, S.; Brunetti, B.; Minichino, A.M.; Sbarbati, A. Vacuum and Electromagnetic Fields Treatment to Regenerate a Diffuse Mature Facial Scar Caused by Sulfuric Acid Assault. Bioengineering 2022, 9, 799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Athanasiou, A.; Karkambounas, S.; Batistatou, A.; Lykoudis, E.; Katsaraki, A.; Kartsiouni, T.; Papalois, A.; Evangelou, A. The Effect of Pulsed Electromagnetic Fields on Secondary Skin Wound Healing: An Experimental Study. Bioelectromagnetics 2007, 28, 362–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Medical Association General Assembly. World Medical Association Declaration of Helsinki: Ethical Principles for Medical Research Involving Human Subjects. J. Int. Bioethique 2004, 15, 124–129. [Google Scholar]
- Giroud, D. A revised guideline for medical device clinical investigations: ISO 14155 Part 1 and 2: 2003. Qual. Assur. J. 2004, 8, 37–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schunck, M.; Zague, V.; Oesser, S.; Proksch, E. Dietary Supplementation with Specific Collagen Peptides Has a Body Mass Index-Dependent Beneficial Effect on Cellulite Morphology. J. Med. Food 2015, 18, 1340–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soares, J.L.M.; Miot, H.A.; Sanudo, A.; Bagatin, E. Cellulite: Poor Correlation between Instrumental Methods and Photograph Evaluation for Severity Classification. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2015, 37, 134–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mlosek, R.K.; Malinowska, S.P. High-Frequency Ultrasound in the Assessment of Cellulite-Correlation between Ultrasound-Derived Measurements, Clinical Assessment, and Nürnberger-Müller Scale Scores. Diagnostics 2024, 14, 1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valentim da Silva, R.M.; Barichello, P.A.; Medeiros, M.L.; de Mendonça, W.C.M.; Dantas, J.S.C.; Ronzio, O.A.; Froes, P.M.; Galadari, H. Effect of Capacitive Radiofrequency on the Fibrosis of Patients with Cellulite. Dermatol. Res. Pract. 2013, 2013, 715829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bravo, B.S.F.; Issa, M.C.A.; Muniz, R.L.S.; Torrado, C.M. Treatment of Gynoid Lipodystrophy with Unipolar Radiofrequency: Clinical, Laboratory, and Ultrasonographic Evaluation. Surg. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2013, 5, 138–144. [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg, D.J.; Fazeli, A.; Berlin, A.L. Clinical, Laboratory, and MRI Analysis of Cellulite Treatment with a Unipolar Radiofrequency Device. Dermatol. Surg. 2007, 34, 204–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duscher, D.; Maan, Z.N.; Wong, V.W.; Rennert, R.C.; Januszyk, M.; Rodrigues, M.; Hu, M.; Whitmore, A.J.; Whittam, A.J.; Longaker, M.T.; et al. Mechanotransduction and Fibrosis. J. Biomech. 2014, 47, 1997–2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martino, F.; Perestrelo, A.R.; Vinarský, V.; Pagliari, S.; Forte, G. Cellular Mechanotransduction: From Tension to Function. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicoletti, G.; Perugini, P.; Bellino, S.; Capra, P.; Malovini, A.; Jaber, O.; Tresoldi, M.; Faga, A. Scar Remodeling with the Association of Monopolar Capacitive Radiofrequency, Electric Stimulation, and Negative Pressure. Photomed. Laser Surg. 2017, 35, 246–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farage, M.A.; Miller, K.W.; Maibach, H.I. (Eds.) Skin Aging and Cellulite in Women. In Textbook of Aging Skin; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 1–9. ISBN 978-3-642-27814-3. [Google Scholar]
- Uitto, J.; Fazio, M.J.; Olsen, D.R. Molecular Mechanisms of Cutaneous Aging. Age-Associated Connective Tissue Alterations in the Dermis. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 1989, 21, 614–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uitto, J.; Bernstein, E.F. Molecular Mechanisms of Cutaneous Aging: Connective Tissue Alterations in the Dermis. J. Investig. Dermatol. Symp. Proc. 1998, 3, 41–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uitto, J. The Role of Elastin and Collagen in Cutaneous Aging: Intrinsic Aging versus Photoexposure. J. Drugs Dermatol. 2008, 7, s12–s16. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Scarano, A.; Sbarbati, A.; Amore, R.; Iorio, E.L.; Ferraro, G.; Amuso, D. A New Treatment for Local Adiposity with Ascorbic Acid and Ascorbyl-Palmitate Solution: Clinical and Histological Study. Aesthetic Plast. Surg. 2020, 44, 1604–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumaran, B.; Watson, T. Thermal Build-up, Decay and Retention Responses to Local Therapeutic Application of 448 kHz Capacitive Resistive Monopolar Radiofrequency: A Prospective Randomised Crossover Study in Healthy Adults. Int. J. Hyperth. 2015, 31, 883–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tashiro, Y.; Hasegawa, S.; Yokota, Y.; Nishiguchi, S.; Fukutani, N.; Shirooka, H.; Tasaka, S.; Matsushita, T.; Matsubara, K.; Nakayama, Y.; et al. Effect of Capacitive and Resistive Electric Transfer on Haemoglobin Saturation and Tissue Temperature. Int. J. Hyperth. 2017, 33, 696–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clijsen, R.; Leoni, D.; Schneebeli, A.; Cescon, C.; Soldini, E.; Li, L.; Barbero, M. Does the Application of Tecar Therapy Affect Temperature and Perfusion of Skin and Muscle Microcirculation? A Pilot Feasibility Study on Healthy Subjects. J. Altern. Complement. Med. 2020, 26, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marmotti, A.; Peretti, G.M.; Mattia, S.; Mangiavini, L.; de Girolamo, L.; Viganò, M.; Setti, S.; Bonasia, D.E.; Blonna, D.; Bellato, E.; et al. Pulsed Electromagnetic Fields Improve Tenogenic Commitment of Umbilical Cord-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells: A Potential Strategy for Tendon Repair-An In Vitro Study. Stem Cells Int. 2018, 2018, 9048237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marques, M.-A.; Combes, M.; Roussel, B.; Vidal-Dupont, L.; Thalamas, C.; Lafontan, M.; Viguerie, N. Impact of a Mechanical Massage on Gene Expression Profile and Lipid Mobilization in Female Gluteofemoral Adipose Tissue. Obes. Facts 2011, 4, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veronese, S.; Beatini, A.; Urbani, C.; Lanza, E.; Paz, O.M.; Saussaye, Y.; Lomuto, M.; Sbarbati, A. V-EMF Treatment of Facial Scar: First Results. J. Tissue Viability 2022, 31, 614–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laura, S.; Veronese, S.; Alberti, G.; Bacci, P.A.; Beatini, A.; Fulgione, E.; Urbani, C.; Sbarbati, A. Vacuum and Electromagnetic Field in Synergy for Skin Rejuvenation: A Retrospective Study on 217 Patients. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2023, 22, 2989–2995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vergallo, C.; Dini, L.; Szamosvölgyi, Z.; Tenuzzo, B.A.; Carata, E.; Panzarini, E.; László, J.F. In Vitro Analysis of the Anti-Inflammatory Effect of Inhomogeneous Static Magnetic Field-Exposure on Human Macrophages and Lymphocytes. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e72374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Longano, C.; de Faria Coelho, C.; Buslik, S.A.; Foguel, C.; Katsuragi, C.; Leonardo, P.S.; Lopes-Martins, R.Á.B. Does Electrophysical Agents Work for Cellulite Treatment? A Systematic Review of Clinical Trials. Lasers Med. Sci. 2024, 39, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

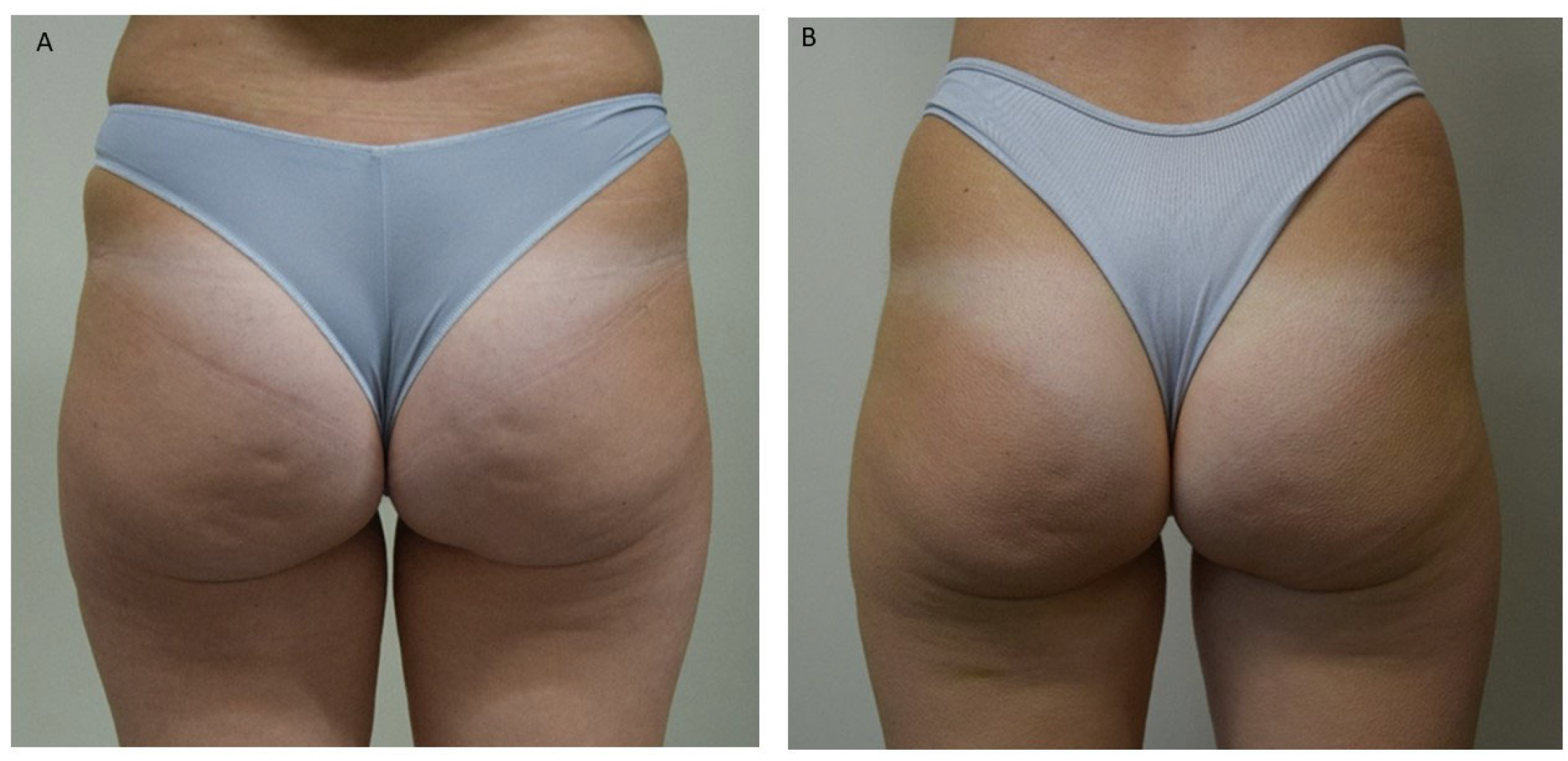
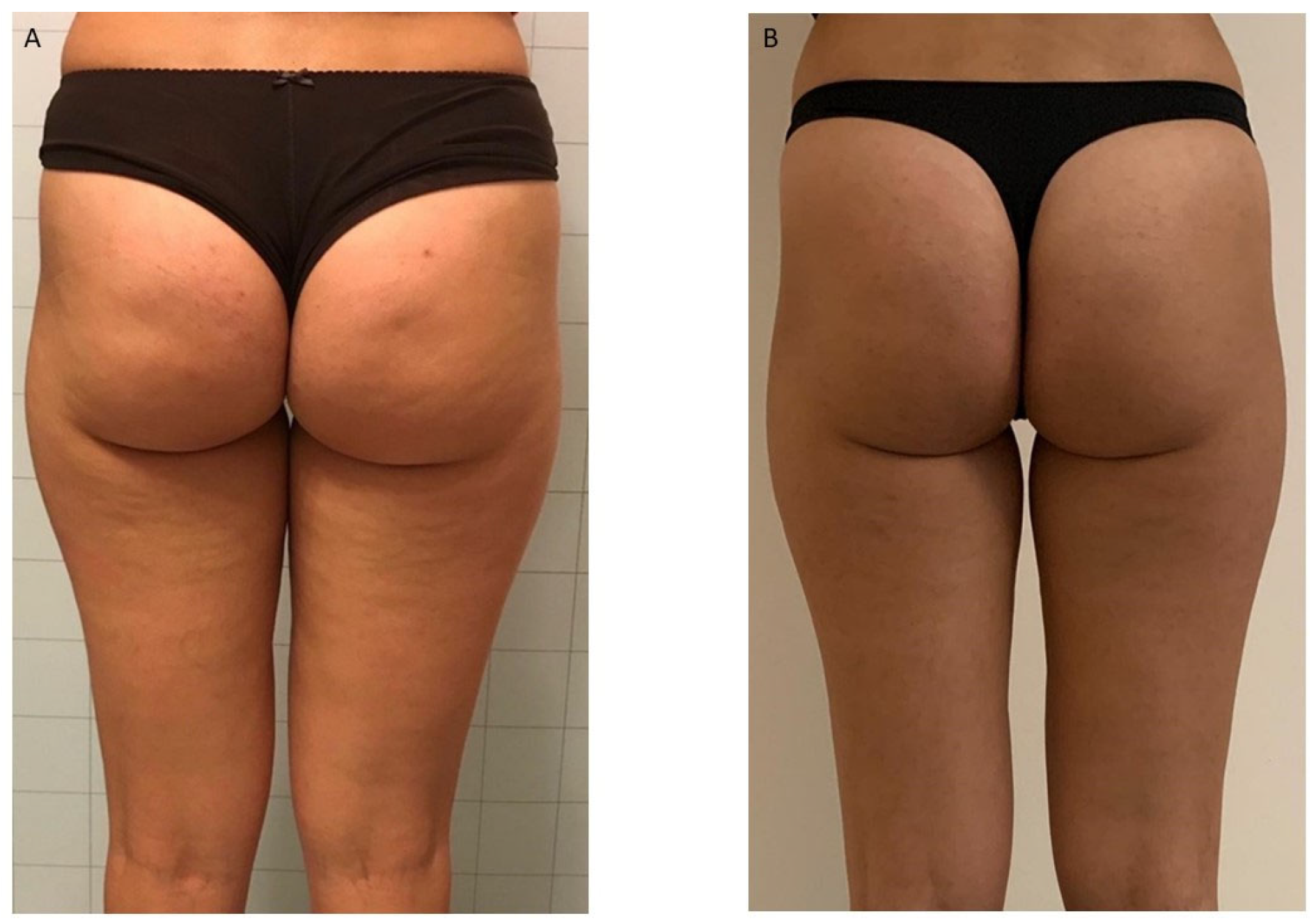
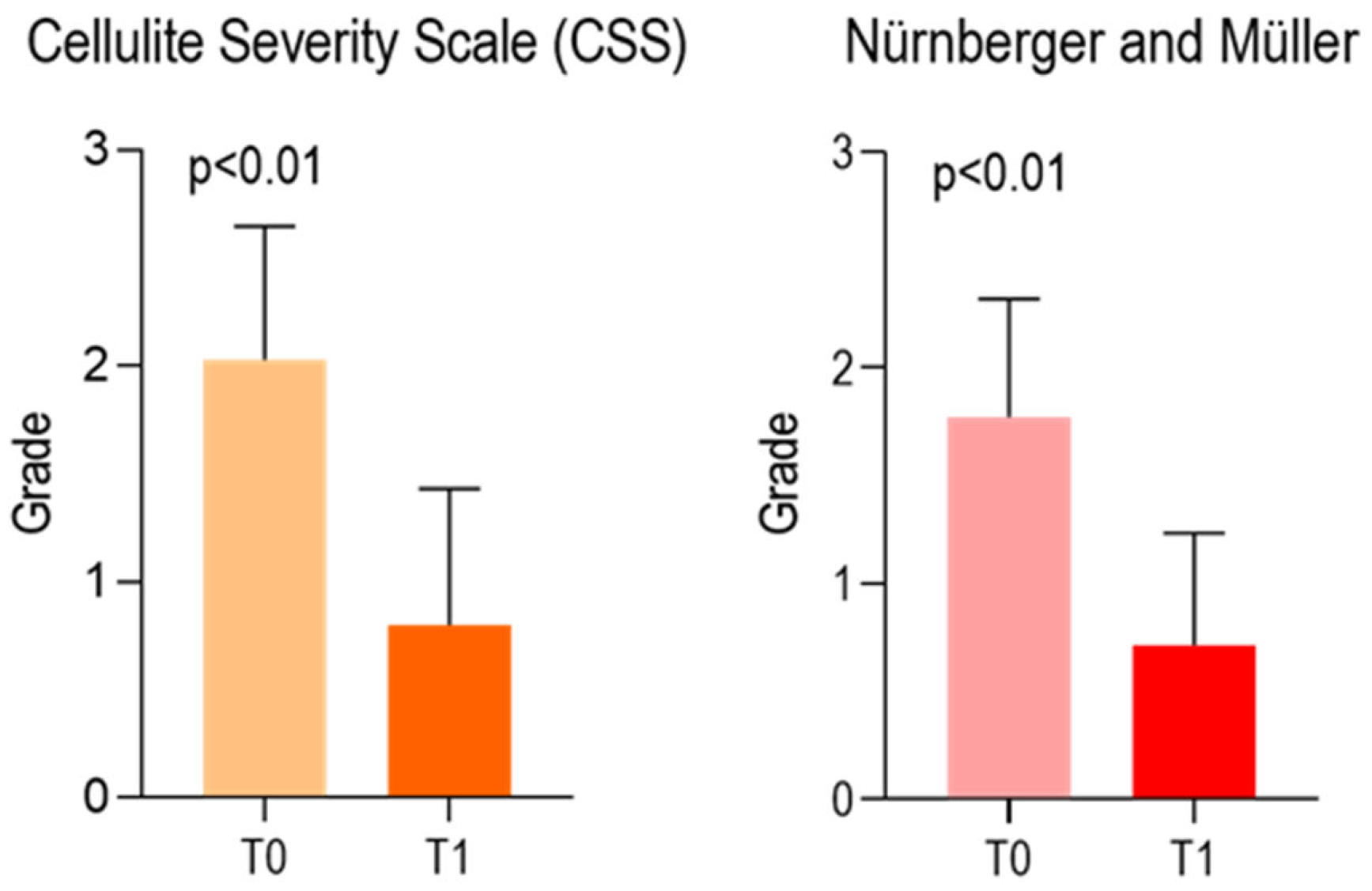
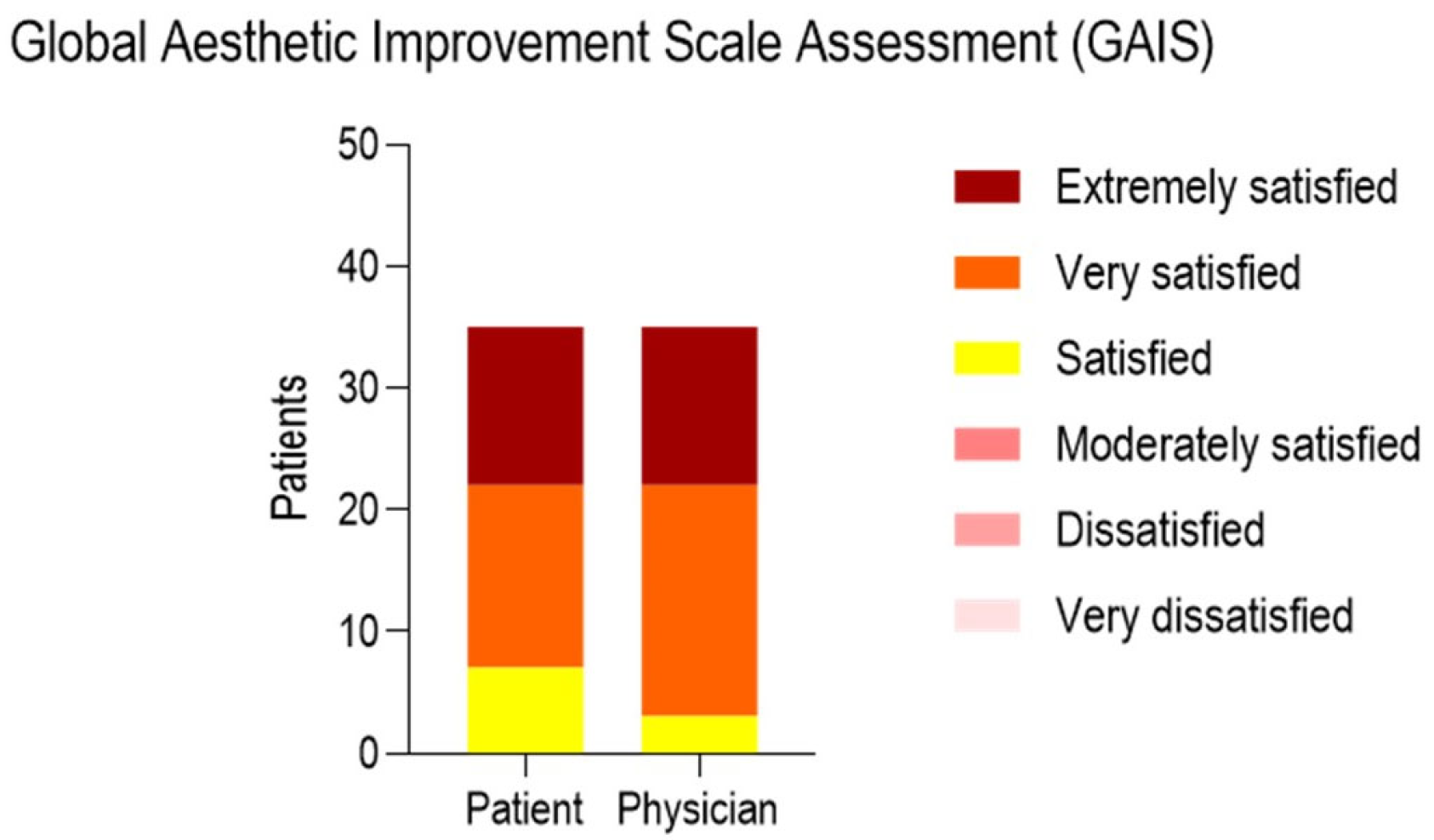
| Cellulite Severity Scale (CSS) | ||
| T0 | T1 | |
| Median | 2.000 | 1.000 |
| Mean | 2.029 | 0.8000 |
| Std. Deviation | 0.6177 | 0.6325 |
| 95% CI of mean | (1.816–2.241) | (0.5827–1.017) |
| 25% Percentile | 2.0 | 0.0 |
| 75% Percentile | 2.0 | 1.0 |
| Δ mean (T0–T1) | 1.2286 ± 0.5983 | |
| Nürnberger and Müller Scale | ||
| T0 | T1 | |
| Median | 2.000 | 1.000 |
| Mean | 1.771 | 0.7143 |
| Std. Deviation | 0.5470 | 0.5186 |
| 95% CI of mean | (1.584–1.959) | (0.5362–0.8924) |
| 25% Percentile | 1.0 | 0.0 |
| 75% Percentile | 2.0 | 1.0 |
| Δ mean (T0–T1) | 1.0571 ± 0.4815 | |
| Cellulite Severity Scale | BMI | Age |
| F | 0.4032 | 2.003 |
| DFn, DFd | 1, 33 | 1, 33 |
| p-value | 0.5298 | 0.1664 |
| Pearson’s r | −0.1099 | 0.239 |
| Nürnberger and Müller | BMI | Age |
| F | 0.9702 | 1.465 |
| DFn, DFd | 1, 33 | 1, 33 |
| p-value | 0.3318 | 0.2347 |
| Pearson’s r | −0.1690 | 0.239 |
| CSS Cellulite Severity Scale | Nürnberger and Müller | ||||
| T0 | T1 | T0 | T1 | ||
| None (0) | 0 | 6 (29%) | None (0) | 0 | 6 (29%) |
| Mild (1) | 4 (19%) | 12 (57%) | Mild (1) | 6 (29%) | 14 (66%) |
| Moderate (2) | 12 (57%) | 3 (14%) | Moderate (2) | 13 (62%) | 1 (5%) |
| Severe (3) | 5 (24%) | 0 | Severe (3) | 2 (9%) | 0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Scarano, A.; Calopresti, A.; Marafioti, S.; Nicolai, G.; Qorri, E. Open-Label Uncontrolled, Monocentric Study to Evaluate the Efficacy and Safety of the Electromagnetic Field and Negative Pressure in the Treatment of Cellulite. Life 2025, 15, 1148. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15071148
Scarano A, Calopresti A, Marafioti S, Nicolai G, Qorri E. Open-Label Uncontrolled, Monocentric Study to Evaluate the Efficacy and Safety of the Electromagnetic Field and Negative Pressure in the Treatment of Cellulite. Life. 2025; 15(7):1148. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15071148
Chicago/Turabian StyleScarano, Antonio, Antonio Calopresti, Salvatore Marafioti, Gianluca Nicolai, and Erda Qorri. 2025. "Open-Label Uncontrolled, Monocentric Study to Evaluate the Efficacy and Safety of the Electromagnetic Field and Negative Pressure in the Treatment of Cellulite" Life 15, no. 7: 1148. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15071148
APA StyleScarano, A., Calopresti, A., Marafioti, S., Nicolai, G., & Qorri, E. (2025). Open-Label Uncontrolled, Monocentric Study to Evaluate the Efficacy and Safety of the Electromagnetic Field and Negative Pressure in the Treatment of Cellulite. Life, 15(7), 1148. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15071148








