Unveiling the Effects of Natural Disasters and Nuclear Energy on the Secondary Sex Ratio: A Comprehensive Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Review Methodology
3. Natural Disasters
3.1. Earthquakes
3.1.1. The 1999 Gölcük Earthquake
3.1.2. The 2001 Gujarat Earthquake
3.1.3. The 2003 Bam Earthquake
3.1.4. Seismic Sequence on Zakynthos Island
3.1.5. The 2009 L’Aquila Earthquake
3.1.6. The 2011 Tohoku Earthquake
3.1.7. Great Hanshin Earthquake
3.1.8. The 2016 Kumamoto Earthquake
3.1.9. The 2005 Tarapaca Earthquake
3.1.10. The 2008 Sichuan Earthquake
3.2. Cyclones and Hurricanes
3.2.1. Cyclones Yasi and Marcia
3.2.2. Hurricane Katrina
3.3. Floods
3.3.1. The 1965 Brisbane Flood
3.3.2. The 2010 and 2011 Pakistan Floods
3.4. Volcanic Eruptions
3.4.1. The 2010 Eruptions of Eyjafjallajökull
3.4.2. The 1783 and 1784 Eruptions of Laki
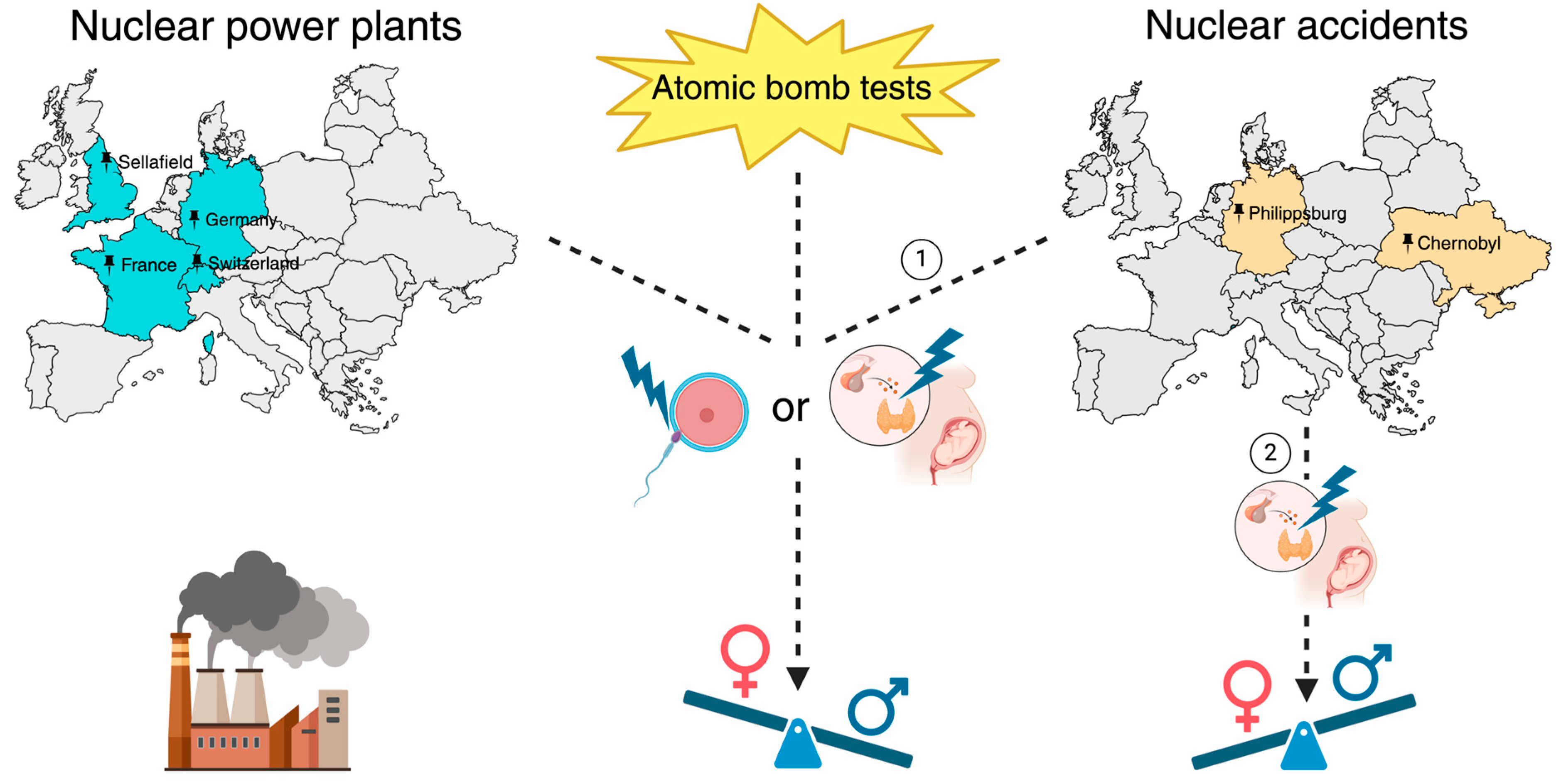
4. Nuclear Energy and Accidents
4.1. Chernobyl Disaster and Atomic Bomb Tests
4.2. Other Nuclear Power Plants and Incidents
5. Future Directions and Research Prospects
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Louis, G.M.B.; Platt, R.W. Reproductive and Perinatal Epidemiology; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2011; ISBN 978-0-19-987479-8. [Google Scholar]
- Chao, F.; Gerland, P.; Cook, A.R.; Alkema, L. Systematic Assessment of the Sex Ratio at Birth for All Countries and Estimation of National Imbalances and Regional Reference Levels. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 9303–9311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nieczuja-Dwojacka, J.; Marchewka-Długońska, J.; Budnik, A.; Wojtowicz, P.; Giemza, B.; Skrzypczyk, B.; Zvarik, A. Factors Influencing Sex Ratio at Birth in Krosno, Poland. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- James, W.H. Coital Rate, Sex Ration, and Parental Age. Lancet 1971, 1, 1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cagnacci, A. Influences of Maternal Weight on the Secondary Sex Ratio of Human Offspring. Hum. Reprod. 2004, 19, 442–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobsen, R.; Møller, H.; Engholm, G. Fertility Rates in Denmark in Relation to the Sexes of Preceding Children in the Family. Hum. Reprod. 1999, 14, 1127–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fakorede, S.T.; Ojo, S.D.; Shonde, K.M.; Adekoya, K.O.; Ogunkanmi, L.A.; Oboh, B. Trends and Seasonal Variations in Human Secondary Sex Ratio in Southwest Nigeria: A 10-Year Survey. Adv. Hum. Biol. 2022, 12, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dermitzakis, I.; Theotokis, P.; Axarloglou, E.; Delilampou, E.; Miliaras, D.; Meditskou, S.; Manthou, M.E. The Impact of Lifestyle on the Secondary Sex Ratio: A Review. Life 2024, 14, 662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catalano, R.; Bruckner, T.; Marks, A.R.; Eskenazi, B. Exogenous Shocks to the Human Sex Ratio: The Case of September 11, 2001 in New York City. Hum. Reprod. 2006, 21, 3127–3131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graffelman, J.; Hoekstra, R.F. A Statistical Analysis of the Effect of Warfare on the Human Secondary Sex Ratio. Hum. Biol. 2000, 72, 433–445. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Catalano, R.; Bruckner, T.; Hartig, T.; Ong, M. Population Stress and the Swedish Sex Ratio. Paediatr. Perinat. Epidemiol. 2005, 19, 413–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dermitzakis, I.; Theotokis, P.; Axarloglou, E.; Delilampou, E.; Manthou, M.E.; Meditskou, S. Effects of Hazardous Chemicals on Secondary Sex Ratio: A Comprehensive Review. Chemosphere 2024, 361, 142467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, D.; Kaminski, E.; Mckelvey, G.; Wang, H. Firstborn Offspring Sex Ratio Is Skewed towards Female Offspring in Anesthesia Care Providers: A Questionnaire-Based Nationwide Study from United States. J. Anaesthesiol. Clin. Pharmacol. 2013, 29, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dermitzakis, I.; Theotokis, P.; Delilampou, E.; Axarloglou, E.; Gouta, C.; Manthou, M.E.; Meditskou, S.; Miliaras, D. The Impact of Infections and Genetics on Secondary Sex Ratio. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2025, 132, 105770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukuda, M.; Fukuda, K.; Mason, S.; Shimizu, T.; Andersen, C.Y. Effects of Earthquakes and Other Natural Catastrophic Events on the Sex Ratio of Newborn Infants. Early Hum. Dev. 2020, 140, 104859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scherb, H.; Grech, V. The Secondary Sex Ratio in Italy over the Past Eighty Years (1940 to 2019) and Potential Impact of Radiological Contamination after Atmospheric Nuclear Testing and after Chernobyl: Temporal Change-Point Analysis Using Markov Chain Monte Carlo. Reprod. Toxicol. 2021, 100, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chahnazarian, A. Determinants of the Sex Ratio at Birth: Review of Recent Literature. Soc. Biol. 1988, 35, 214–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- James, W.H. “Over-Ripeness Ovopathy, Sex Ratio Increase and Sex Ratio Reversal a Challenging Hypothesis for Sex Ratio Modulation”: An Alternative Interpretation. Hum. Reprod. 2004, 19, 775–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jongbloet, P.H. Over-Ripeness Ovopathy: A Challenging Hypothesis for Sex Ratio Modulation. Hum. Reprod. 2004, 19, 769–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, M.S.; Pang, M.-G. New Biological Insights on X and Y Chromosome-Bearing Spermatozoa. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2019, 7, 388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orzack, S.H.; Stubblefield, J.W.; Akmaev, V.R.; Colls, P.; Munné, S.; Scholl, T.; Steinsaltz, D.; Zuckerman, J.E. The Human Sex Ratio from Conception to Birth. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, E2102–E2111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukuda, M.; Fukuda, K.; Shimizu, T.; Yomura, W.; Shimizu, S. Kobe Earthquake and Reduced Sperm Motility. Hum. Reprod. 1996, 11, 1244–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- James, W.H. Further Support for the Hypothesis That Parental Hormone Levels around the Time of Conception Are Associated with Human Sex Ratios at Birth. J. Biosoc. Sci. 2008, 40, 855–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- James, W.H. Proximate Causes of the Variation of the Human Sex Ratio at Birth. Early Hum. Dev. 2015, 91, 795–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dermitzakis, I.; Kyriakoudi, S.A.; Chatzianagnosti, S.; Chatzi, D.; Vakirlis, E.; Meditskou, S.; Manthou, M.E.; Theotokis, P. Epigenetics in Skin Homeostasis and Ageing. Epigenomes 2025, 9, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dermitzakis, I.; Chatzi, D.; Kyriakoudi, S.A.; Evangelidis, N.; Vakirlis, E.; Meditskou, S.; Theotokis, P.; Manthou, M.E. Skin Development and Disease: A Molecular Perspective. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2024, 46, 8239–8267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dermitzakis, I.; Manthou, M.E.; Meditskou, S.; Tremblay, M.-È.; Petratos, S.; Zoupi, L.; Boziki, M.; Kesidou, E.; Simeonidou, C.; Theotokis, P. Origin and Emergence of Microglia in the CNS—An Interesting (Hi)Story of an Eccentric Cell. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2023, 45, 2609–2628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dermitzakis, I.; Theotokis, P.; Evangelidis, P.; Delilampou, E.; Evangelidis, N.; Chatzisavvidou, A.; Avramidou, E.; Manthou, M.E. CNS Border-Associated Macrophages: Ontogeny and Potential Implication in Disease. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2023, 45, 4285–4300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dermitzakis, I.; Manthou, M.E.; Meditskou, S.; Miliaras, D.; Kesidou, E.; Boziki, M.; Petratos, S.; Grigoriadis, N.; Theotokis, P. Developmental Cues and Molecular Drivers in Myelinogenesis: Revisiting Early Life to Re-Evaluate the Integrity of CNS Myelin. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2022, 44, 3208–3237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- James, W.H. Hypothesis: High Levels of Maternal Adrenal Androgens Are a Major Cause of Miscarriage and Other Forms of Reproductive Suboptimality. J. Theor. Biol. 2015, 364, 316–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catalano, R.A.; Saxton, K.B.; Bruckner, T.A.; Pearl, M.; Anderson, E.; Goldman-Mellor, S.; Margerison-Zilko, C.; Subbaraman, M.; Currier, R.J.; Kharrazi, M. Hormonal Evidence Supports the Theory of Selection in Utero. Am. J. Hum. Biol. 2012, 24, 526–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catalano, R.; Bruckner, T. Secondary Sex Ratios and Male Lifespan: Damaged or Culled Cohorts. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 1639–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voegtline, K.M.; Costigan, K.A.; Kivlighan, K.T.; Henderson, J.L.; DiPietro, J.A. Sex-Specific Associations of Maternal Prenatal Testosterone Levels with Birth Weight and Weight Gain in Infancy. J. Dev. Orig. Health Dis. 2013, 4, 280–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DiPietro, J.A.; Voegtline, K.M. The Gestational Foundation of Sex Differences in Development and Vulnerability. Neuroscience 2017, 342, 4–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keller, M.C.; Nesse, R.M.; Hofferth, S. The Trivers–Willard Hypothesis of Parental Investment: No Effect in the Contemporary United States. Evol. Hum. Behav. 2001, 22, 343–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trivers, R.L.; Willard, D.E. Natural Selection of Parental Ability to Vary the Sex Ratio of Offspring. Science 1973, 179, 90–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bates, M. Natural Disasters and Public Health. IEEE Pulse 2019, 10, 24–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makwana, N. Disaster and Its Impact on Mental Health: A Narrative Review. J. Fam. Med. Prim. Care 2019, 8, 3090–3095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasegawa, A.; Tanigawa, K.; Ohtsuru, A.; Yabe, H.; Maeda, M.; Shigemura, J.; Ohira, T.; Tominaga, T.; Akashi, M.; Hirohashi, N.; et al. Health Effects of Radiation and Other Health Problems in the Aftermath of Nuclear Accidents, with an Emphasis on Fukushima. Lancet 2015, 386, 479–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scherb, H.; Voigt, K. The Human Sex Odds at Birth after the Atmospheric Atomic Bomb Tests, after Chernobyl, and in the Vicinity of Nuclear Facilities. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2011, 18, 697–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellidokuz, H.; Ucku, R.; Aydin, U.Y.; Ellidokuz, E. Risk Factors for Death and Injuries in Earthquake: Cross-Sectional Study from Afyon, Turkey. Croat. Med. J. 2005, 46, 613–618. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mavrouli, M.; Mavroulis, S.; Lekkas, E.; Tsakris, A. The Impact of Earthquakes on Public Health: A Narrative Review of Infectious Diseases in the Post-Disaster Period Aiming to Disaster Risk Reduction. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ripoll Gallardo, A.; Pacelli, B.; Alesina, M.; Serrone, D.; Iacutone, G.; Faggiano, F.; Della Corte, F.; Allara, E. Medium- and Long-Term Health Effects of Earthquakes in High-Income Countries: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2018, 47, 1317–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stroebe, K.; Kanis, B.; Richardson, J.; Oldersma, F.; Broer, J.; Greven, F.; Postmes, T. Chronic Disaster Impact: The Long-Term Psychological and Physical Health Consequences of Housing Damage Due to Induced Earthquakes. BMJ Open 2021, 11, e040710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruckner, T.A.; Catalano, R. Selection in Utero and Population Health: Theory and Typology of Research. SSM—Popul. Health 2018, 5, 101–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doğer, E.; Çakıroğlu, Y.; Köpük, Ş.Y.; Ceylan, Y.; Şimşek, H.U.; Çalışkan, E. Impact of Earthquakes on Sex Ratio at Birth: Eastern Marmara Earthquakes. J. Turk. Ger. Gynecol. Assoc. 2013, 14, 92–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasapoğlu, A.; Ecevit, M. Impact of the 1999 East Marmara Earthquake in Turkey. Popul. Environ. 2003, 24, 339–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, V.J.; Irwin, R.J. A Simple Model for Adaptive Variation in the Sex Ratios of Mammalian Offspring. J. Theor. Biol. 2009, 258, 38–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirchengast, S.; Hartmann, B. The Male Disadvantage Hypothesis Reconsidered: Is There Really a Weaker Sex? An Analysis of Gender Differences in Newborn Somatometrics and Vital Parameters. J. Life Sci. 2009, 1, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catalano, R.; Ahern, J.; Bruckner, T.; Anderson, E.; Saxton, K. Gender-Specific Selection in Utero among Contemporary Human Birth Cohorts. Paediatr. Perinat. Epidemiol. 2009, 23, 273–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phalkey, R.; Reinhardt, J.D.; Marx, M. Injury Epidemiology after the 2001 Gujarat Earthquake in India: A Retrospective Analysis of Injuries Treated at a Rural Hospital in the Kutch District Immediately after the Disaster. Glob. Health Action 2011, 4, 7196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatterjee, P. One Year after the Gujarat Earthquake. Lancet 2002, 359, 327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nandi, A.; Mazumdar, S.; Behrman, J.R. The Effect of Natural Disaster on Fertility, Birth Spacing, and Child Sex Ratio: Evidence from a Major Earthquake in India. J. Popul. Econ. 2018, 31, 267–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghi-Bazargani, H.; Azami-Aghdash, S.; Kazemi, A.; Ziapour, B. Crisis Management Aspects of Bam Catastrophic Earthquake: Review Article. Health Promot. Perspect. 2015, 5, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saadat, M. Decline in Sex Ratio at Birth after Bam (Kerman Province, Southern Iran) Earthquake. J. Biosoc. Sci. 2008, 40, 935–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- James, W.H. Evidence That Mammalian Sex Ratios at Birth Are Partially Controlled by Parental Hormone Levels at the Time of Conception. J. Theor. Biol. 1996, 180, 271–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baum, A.; Garofalo, J.P.; Yali, A.M. Socioeconomic Status and Chronic Stress. Does Stress Account for SES Effects on Health? Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1999, 896, 131–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tourikis, J.D.; Beratis, I.N. Community Psychological Stressor-Induced Secondary Sex Ratio Decline after a Seismic Sequence in the Greek Island of Zakynthos. J. Biosoc. Sci. 2013, 45, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mavroulis, S.; Lekkas, E. Revisiting the Most Destructive Earthquake Sequence in the Recent History of Greece: Environmental Effects Induced by the 9, 11 and 12 August 1953 Ionian Sea Earthquakes. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 8429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Alfonso, A.; Patacchiola, F.; Colagrande, I.; D’Alessandro, G.; Di Fonso, A.; Palermo, P.; Carta, G. A Decrease in Sex Ratio at Birth Nine Months after the Earthquake in L’Aquila. Sci. World J. 2012, 2012, 162017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satake, K. Geological and Historical Evidence of Irregular Recurrent Earthquakes in Japan. Philos. Transact. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2015, 373, 20140375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Great East Japan Earthquake and Tsunami and Impacts on Japanese Nuclear Plants. In Lessons Learned from the Fukushima Nuclear Accident for Improving Safety of U.S. Nuclear Plants; National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2014.
- Goodwin, R.; Sugiyama, K.; Sun, S.; Aida, J.; Ben-Ezra, M. Psychological Distress after the Great East Japan Earthquake: Two Multilevel 6-Year Prospective Analyses. Br. J. Psychiatry 2020, 216, 144–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamamatsu, Y.; Inoue, Y.; Watanabe, C.; Umezaki, M. Impact of the 2011 Earthquake on Marriages, Births and the Secondary Sex Ratio in Japan. J. Biosoc. Sci. 2014, 46, 830–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, K.; Yamagata, Z.; Kawado, M.; Hashimoto, S. Effects of the Great East Japan Earthquake on Secondary Sex Ratio and Perinatal Outcomes. J. Epidemiol. 2016, 26, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukuda, M.; Fukuda, K.; Mason, S.; Shimizu, T.; Yding Andersen, C. The Sex Ratio at Birth after Recent Major Earthquakes in Japan. Early Hum. Dev. 2018, 123, 30–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catalano, R.; Yorifuji, T.; Kawachi, I. Natural Selection In Utero: Evidence from the Great East Japan Earthquake. Am. J. Hum. Biol. 2013, 25, 555–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ukai, T. The Great Hanshin-Awaji Earthquake and the Problems with Emergency Medical Care. Ren. Fail. 1997, 19, 633–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inui, A.; Kitaoka, H.; Majima, M.; Takamiya, S.; Uemoto, M.; Yonenaga, C.; Honda, M.; Shirakawa, K.; Ueno, N.; Amano, K.; et al. Effect of the Kobe Earthquake on Stress and Glycemic Control in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus. Arch. Intern. Med. 1998, 158, 274–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- duPont, W.; Noy, I.; Okuyama, Y.; Sawada, Y. The Long-Run Socio-Economic Consequences of a Large Disaster: The 1995 Earthquake in Kobe. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0138714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukuda, M.; Fukuda, K.; Shimizu, T.; Møller, H. Decline in Sex Ratio at Birth after Kobe Earthquake. Hum. Reprod. 1998, 13, 2321–2322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeda, K.; Inaba, K. The Damage and Reconstruction of the Kumamoto Earthquake: An Analysis on the Impact of Changes in Expenditures with Multi-Regional Input–Output Table for Kumamoto Prefecture. J. Econ. Struct. 2022, 11, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popli, R.; Sahaf, B.; Nakasone, H.; Lee, J.Y.Y.; Miklos, D.B. Clinical Impact of H-Y Alloimmunity. Immunol. Res. 2014, 58, 249–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, H.S.; Wu, F.; Aghai, Z.; Steffensen, R.; van Halteren, A.G.; Spierings, E.; Christiansen, O.B.; Miklos, D.; Goulmy, E. H-Y Antibody Titers Are Increased in Unexplained Secondary Recurrent Miscarriage Patients and Associated with Low Male: Female Ratio in Subsequent Live Births. Hum. Reprod. 2010, 25, 2745–2752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, H.S. Secondary Recurrent Miscarriage and H-Y Immunity. Hum. Reprod. Update 2011, 17, 558–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torche, F.; Kleinhaus, K. Prenatal Stress, Gestational Age and Secondary Sex Ratio: The Sex-Specific Effects of Exposure to a Natural Disaster in Early Pregnancy. Hum. Reprod. 2012, 27, 558–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, F. Well-Being Effects of Natural Disasters: Evidence from China’s Wenchuan Earthquake. J. Happiness Stud. 2023, 24, 563–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harville, E.; Xiong, X.; Buekens, P. Disasters and Perinatal Health:A Systematic Review. Obstet. Gynecol. Surv. 2010, 65, 713–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carmichael, S.L.; Shaw, G.M.; Yang, W.; Abrams, B.; Lammer, E.J. Maternal Stressful Life Events and Risks of Birth Defects. Epidemiology 2007, 18, 356–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, C.E.; Li, H.J.; Zhang, X.G.; Zhang, H.; Han, P.Y.; An, Q.; Ding, W.J.; Wang, M.Q. The Impact of the Wenchuan Earthquake on Birth Outcomes. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e8200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeffers, N.K.; Glass, N. Integrative Review of Pregnancy and Birth Outcomes After Exposure to a Hurricane. J. Obstet. Gynecol. Neonatal Nurs. 2020, 49, 348–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parks, R.M.; Anderson, G.B.; Nethery, R.C.; Navas-Acien, A.; Dominici, F.; Kioumourtzoglou, M.-A. Tropical Cyclone Exposure Is Associated with Increased Hospitalization Rates in Older Adults. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, W.; Gao, Y.; Xu, R.; Yang, Z.; Yu, P.; Ye, T.; Ritchie, E.A.; Li, S.; Guo, Y. Health Effects of Cyclones: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Epidemiological Studies. Environ. Health Perspect. 2023, 131, 086001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parayiwa, C.; Harley, D.; Richardson, A.; Behie, A. Severe Cyclones and Sex-specific Birth Outcomes in Queensland, Australia: An Interrupted Time-series Analysis. Am. J. Hum. Biol. 2023, 35, e23846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zacher, M.; Raker, E.J.; Arcaya, M.C.; Lowe, S.R.; Rhodes, J.; Waters, M.C. Physical Health Symptoms and Hurricane Katrina: Individual Trajectories of Development and Recovery More Than a Decade After the Storm. Am. J. Public Health 2021, 111, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diaz, J.H.; Brisolara, K.F.; Harrington, D.J.; Hu, C.-Y.; Katner, A.L. The Environmental Health Impact of Hurricane Katrina on New Orleans. Am. J. Public Health 2020, 110, 1480–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meir, O.; Satu, K.; Xie, X.; Abdissa, N.; Lubna, P.; Sangita, J. The Impact of Hurricane Katrina, a Major Natural Disaster, on Assisted Reproductive Outcomes through an Analysis of 451,848 ART Cycles. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 17864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, Y.; Chen, Q.; Larsson, H.; Rzhetsky, A. Observable Variations in Human Sex Ratio at Birth. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2021, 17, e1009586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grech, V.; Scherb, H. Hurricane Katrina: Influence on the Male-to-Female Birth Ratio. Med. Princ. Pract. 2015, 24, 477–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyster, W.R. Altered Sex Ratio after the London Smog of 1952 and the Brisbane Flood of 1965. BJOG Int. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. 1974, 81, 626–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasir, M. Prenatal Exposure to Shocks and Early-Life Health: Impact of Terrorism and Flood on Birth Outcomes in Pakistan. Def. Peace Econ. 2021, 32, 572–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grech, V.; Borg, T. Seasonality of Sex Ratio at Births in Iceland and Effects of the 2010 Eyjafjallajökull Volcanic Eruption. Acta Paediatr. 2016, 105, 1369–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catalano, R.; Casey, J.A.; Bruckner, T.A. A Test of Oscillation in the Human Secondary Sex Ratio. Evol. Med. Public Health 2020, 2020, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alderman, K.; Turner, L.R.; Tong, S. Floods and Human Health: A Systematic Review. Environ. Int. 2012, 47, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michelozzi, P.; de’ Donato, F. Climate changes, floods, and health consequences. Recenti Prog. Med. 2014, 105, 48–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Twiddy, M.; Trump, B.; Ramsden, S. Understanding the Long-Term Impact of Flooding on the Wellbeing of Residents: A Mixed Methods Study. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0274890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bei, B.; Bryant, C.; Gilson, K.-M.; Koh, J.; Gibson, P.; Komiti, A.; Jackson, H.; Judd, F. A Prospective Study of the Impact of Floods on the Mental and Physical Health of Older Adults. Aging Ment. Health 2013, 17, 992–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyster, W.R.; Bishop, M.W. An Association Between Rainfall and Sex Ratio in Man. J. Reprod. Fertil. 1965, 10, 35–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirsch, T.D.; Wadhwani, C.; Sauer, L.; Doocy, S.; Catlett, C. Impact of the 2010 Pakistan Floods on Rural and Urban Populations at Six Months. PLoS Curr. 2012, 4, e4fdfb212d2432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gudmundsson, G. Respiratory Health Effects of Volcanic Ash with Special Reference to Iceland. A Review. Clin. Respir. J. 2011, 5, 2–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gudmundsson, G.; Larsen, G. Effects of volcanic eruptions on human health in Iceland. Review. Laeknabladid 2016, 102, 433–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gissurardóttir, Ó.S.; Hlodversdóttir, H.; Thordardóttir, E.B.; Pétursdóttir, G.; Hauksdóttir, A. Mental Health Effects Following the Eruption in Eyjafjallajökull Volcano in Iceland: A Population-Based Study. Scand. J. Public Health 2019, 47, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- James, W.H.; Grech, V. A Review of the Established and Suspected Causes of Variations in Human Sex Ratio at Birth. Early Hum. Dev. 2017, 109, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruckner, T.; Catalano, R. The Sex Ratio and Age-Specific Male Mortality: Evidence for Culling in Utero. Am. J. Hum. Biol. Off. J. Hum. Biol. Counc. 2007, 19, 763–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casey, J.A.; Gemmill, A.; Elser, H.; Karasek, D.; Catalano, R. Sun Smoke in Sweden: Perinatal Implications of the Laki Volcanic Eruptions, 1783–1784. Epidemiology 2019, 30, 330–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horvath, A.; Rachlew, E. Nuclear Power in the 21st Century: Challenges and Possibilities. Ambio 2016, 45 (Suppl. S1), S38–S49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukunaga, H.; Yokoya, A.; Taki, Y.; Prise, K.M. Radiobiological Implications of Fukushima Nuclear Accident for Personalized Medical Approach. Tohoku J. Exp. Med. 2017, 242, 77–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirichenko, V.A.; Kirichenko, A.V.; Werts, D.E. Consequences and Countermeasures in a Nuclear Power Accident: Chernobyl Experience. Biosecur. Bioterror. Biodef. Strategy Pract. Sci. 2012, 10, 314–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cwikel, J.; Sergienko, R.; Gutvirtz, G.; Abramovitz, R.; Slusky, D.; Quastel, M.; Sheiner, E. Reproductive Effects of Exposure to Low-Dose Ionizing Radiation: A Long-Term Follow-Up of Immigrant Women Exposed to the Chernobyl Accident. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scherb, H.; Voigt, K. Trends in the Human Sex Odds at Birth in Europe and the Chernobyl Nuclear Power Plant Accident. Reprod. Toxicol. 2007, 23, 593–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tronko, M.D.; Brenner, A.V.; Olijnyk, V.A.; Robbins, J.; Epstein, O.V.; McConnell, R.J.; Bogdanova, T.I.; Fink, D.J.; Likhtarev, I.A.; Lubin, J.H.; et al. Autoimmune Thyroiditis and Exposure to Iodine 131 in the Ukrainian Cohort Study of Thyroid Cancer and Other Thyroid Diseases after the Chornobyl Accident: Results from the First Screening Cycle (1998–2000). J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2006, 91, 4344–4351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubrova, Y.E.; Grant, G.; Chumak, A.A.; Stezhka, V.A.; Karakasian, A.N. Elevated Minisatellite Mutation Rate in the Post-Chernobyl Families from Ukraine. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2002, 71, 801–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peterka, M.; Peterková, R.; Likovský, Z. Chernobyl: Prenatal Loss of Four Hundred Male Fetuses in the Czech Republic. Reprod. Toxicol. 2004, 18, 75–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peterka, M.; Peterková, R.; Likovský, Z. Chernobyl: Relationship between the Number of Missing Newborn Boys and the Level of Radiation in the Czech Regions. Environ. Health Perspect. 2007, 115, 1801–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grossman, C.M.; Morton, W.E.; Nussbaum, R.H. Hypothyroidism and Spontaneous Abortions among Hanford, Washington, Downwinders. Arch. Environ. Health 1996, 51, 175–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogris, E. Exposure to radioactive iodine in pregnancy: Significance for mother and child. Acta Med. Austriaca 1997, 24, 150–153. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dickinson, H.O.; Parker, L.; Binks, K.; Wakeford, R.; Smith, J. The Sex Ratio of Children in Relation to Paternal Preconceptional Radiation Dose: A Study in Cumbria, Northern England. J. Epidemiol. Community Health 1996, 50, 645–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- James, W.H.; Rostron, J. Parental Age, Parity and Sex Ratio in Births in England and Wales, 1968–1977. J. Biosoc. Sci. 1985, 17, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scherb, H.; Kusmierz, R.; Voigt, K. Human Sex Ratio at Birth and Residential Proximity to Nuclear Facilities in France. Reprod. Toxicol. 2016, 60, 104–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gottlieb, S.F.; Tupper, C.; Kerndt, C.C.; Tegay, D.H. Genetics, Nondisjunction. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Petersen, M.B.; Mikkelsen, M. Nondisjunction in Trisomy 21: Origin and Mechanisms. Cytogenet. Cell Genet. 2000, 91, 199–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uchida, I.A. Radiation-Induced Nondisjunction. Environ. Health Perspect. 1979, 31, 13–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goulart, V.V.; Liao, A.W.; Carvalho, M.H.B.d.; Brizot, M.d.L.; Francisco, R.P.V.; Zugaib, M. Intrauterine Death in Singleton Pregnancies with Trisomy 21, 18, 13 and Monosomy X. Rev. Assoc. Medica Bras. 1992 2016, 62, 162–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scherb, H.; Kusmierz, R.; Voigt, K. Secondary Sex Ratio and Trends in the Associated Gender-Specific Births near Nuclear Facilities in France and Germany: Update of Birth Counts. Reprod. Toxicol. 2019, 89, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
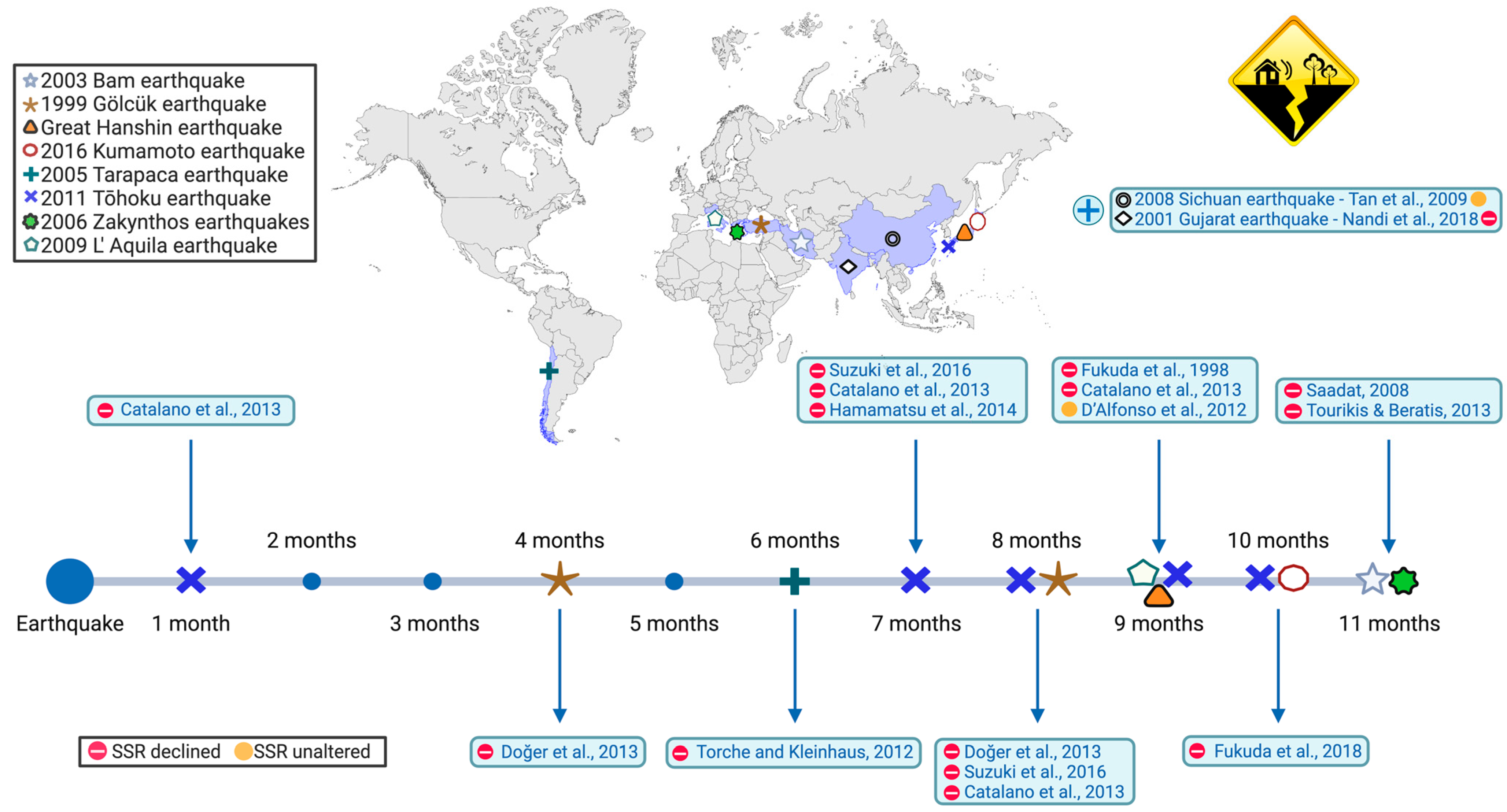
| Natural Disaster | Country | Date | SSR a | Time to Alteration b | Time of Effect c | Parental Effect c | Mechanism | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cyclone Marcia | Australia | Feb.–Mar. 2015 | Unaltered | - | - | - | - | [84] |
| Cyclone Yasi | Australia | Jan.–Feb. 2011 | Increase | 7–9 months | Gestation | Maternal | Increased female in utero mortality | [84] |
| Hurricane Katrina | USA | Aug. 2005 | Unaltered | - | - | - | - | [87] |
| Hurricane Katrina | USA | Aug. 2005 | Increase | 8–10 months | Conception | Paternal; maternal | Increased radiation;lethal mutations in X gametes | [89] |
| Hurricane Katrina | USA | Aug. 2005 | Unaltered | - | - | - | - | [88] |
| Brisbane flood | Australia | July 1965 | Decline | 10 months; 11 months | Conception | Paternal | Increased vulnerability of Y gametes | [90] |
| Pakistan floods | Pakistan | July–Sept. 2010; Aug.–Sept. 2011 | Unaltered | - | - | - | - | [91] |
| Eyjafjallajökull eruption | Iceland | Apr. 2010 | Decline | 5 months; 7 months | Gestation | Maternal | In utero exposure to maternal stress; selection in utero | [92] |
| Laki eruption | Iceland | June 1783– Jan. 1784 | Decline | Unspecified; in 1784 | Gestation | Maternal | In utero exposure to maternal stress; selection in utero | [93] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dermitzakis, I.; Theotokis, P.; Delilampou, E.; Axarloglou, E.; Gargani, S.; Miliaras, D.; Manthou, M.E.; Meditskou, S. Unveiling the Effects of Natural Disasters and Nuclear Energy on the Secondary Sex Ratio: A Comprehensive Review. Life 2025, 15, 1127. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15071127
Dermitzakis I, Theotokis P, Delilampou E, Axarloglou E, Gargani S, Miliaras D, Manthou ME, Meditskou S. Unveiling the Effects of Natural Disasters and Nuclear Energy on the Secondary Sex Ratio: A Comprehensive Review. Life. 2025; 15(7):1127. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15071127
Chicago/Turabian StyleDermitzakis, Iasonas, Paschalis Theotokis, Efthymia Delilampou, Evangelos Axarloglou, Sofia Gargani, Dimosthenis Miliaras, Maria Eleni Manthou, and Soultana Meditskou. 2025. "Unveiling the Effects of Natural Disasters and Nuclear Energy on the Secondary Sex Ratio: A Comprehensive Review" Life 15, no. 7: 1127. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15071127
APA StyleDermitzakis, I., Theotokis, P., Delilampou, E., Axarloglou, E., Gargani, S., Miliaras, D., Manthou, M. E., & Meditskou, S. (2025). Unveiling the Effects of Natural Disasters and Nuclear Energy on the Secondary Sex Ratio: A Comprehensive Review. Life, 15(7), 1127. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15071127











