Placental Pathology and Placental Growth Factor (PlGF)/Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Receptor-1 (VEGFR-1) Pathway Expression Evaluation in Fetal Congenital Heart Defects
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Maternal and Fetal Data Collection
2.3. Placental Gross and Microscopic Evaluation
2.4. Placental Immunohistochemical Evaluation
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of the Study Groups
3.2. Morphological Characteristics of the Placenta and the Umbilical Cord
3.3. Immunohistochemical Study
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AVSD | Atrioventricular septal defect |
| CHD | Congenital heart defect |
| CHL | Crown–heel length |
| CRL | Crown–rump length |
| HC | Head circumference |
| HLHS | Hypoplastic left heart syndrome |
| IHC | Immunohistochemistry |
| PLGF | Placental growth factor |
| UC | Umbilical cord |
| VEGFR-1 | Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-1 |
| VSD | Ventricular septal defect |
References
- Liu, Y.; Chen, S.; Zühlke, L.; Black, G.C.; Choy, M.K.; Li, N.; Keavney, B.D. Global Birth Prevalence of Congenital Heart Defects 1970–2017: Updated Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of 260 Studies. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2019, 48, 455–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, T.B.; Foo, S.Y.R.; Chen, C.K. The Role of Epigenetics in Congenital Heart Disease. Genes 2021, 12, 390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buijtendijk, M.F.J.; Barnett, P.; van den Hoff, M.J.B. Development of the Human Heart. Am. J. Med. Genet. Part C Semin. Med. Genet. 2020, 184, 7–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diab, N.S.; Barish, S.; Dong, W.; Zhao, S.; Allington, G.; Yu, X.; Kahle, K.T.; Brueckner, M.; Jin, S.C. Molecular Genetics and Complex Inheritance of Congenital Heart Disease. Genes 2021, 12, 1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burton, G.J.; Jauniaux, E. Development of the Human Placenta and Fetal Heart: Synergic or Independent? Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andescavage, N.N.; Limperopoulos, C. Placental Abnormalities in Congenital Heart Disease. Transl. Pediatr. 2021, 10, 2148–2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Courtney, J.A.; Cnota, J.F.; Jones, H.N. The Role of Abnormal Placentation in Congenital Heart Disease; Cause, Correlate, or Consequence? Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahadevan, A.; Tipler, A.; Jones, H. Shared Developmental Pathways of the Placenta and Fetal Heart. Placenta 2023, 141, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maslen, C.L. Recent Advances in Placenta-Heart Interactions. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huhta, J.; Linask, K.K. Environmental Origins of Congenital Heart Disease: The Heart-Placenta Connection. Semin. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2013, 18, 245–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linask, K.K. The Heart-Placenta Axis in the First Month of Pregnancy: Induction and Prevention of Cardiovascular Birth Defects. J. Pregnancy 2013, 2013, 320413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, J.A.; Rychik, J.; Savlab, J.J. The Placenta as the Window to Congenital Heart Disease. Curr. Opin. Cardiol. 2021, 36, 56–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, R.L.; Yuan, V.; Courtney, J.A.; Tipler, A.; Cnota, J.F.; Jones, H.N. Analysis of Commonly Expressed Genes between First Trimester Fetal Heart and Placenta Cell Types in the Context of Congenital Heart Disease. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 10756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camm, E.J.; Botting, K.J.; Sferruzzi-Perri, A.N. Near to One’s Heart: The Intimate Relationship between the Placenta and Fetal Heart. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Falco, S. The Discovery of Placenta Growth Factor and Its Biological Activity. Exp. Mol. Med. 2012, 44, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melincovici, C.S.; Boşca, A.B.; Şuşman, S.; Mărginean, M.; Mihu, C.; Istrate, M.; Moldovan, I.M.; Roman, A.L.; Mihu, C.M. Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF)—Key Factor in Normal and Pathological Angiogenesis. Rom. J. Morphol. Embryol. 2018, 59, 455–467. [Google Scholar]
- Shibuya, M. Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor and Its Receptor System: Physiological Functions in Angiogenesis and Pathological Roles in Various Diseases. J. Biochem. 2013, 153, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, D.B.; Zheng, J. Regulation of Placental Angiogenesis. Microcirculation 2014, 21, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witman, N.; Zhou, C.; Häneke, T.; Xiao, Y.; Huang, X.; Rohner, E.; Sohlmér, J.; Grote Beverborg, N.; Chien, K.R.; Sahara, M. Placental Growth Factor Exerts a Dual Function for Cardiomyogenesis and Vasculogenesis during Heart Development. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 5435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Archie, J.G.; Collins, J.S.; Lebel, R.R. Quantitative Standards for Fetal and Neonatal Autopsy. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2006, 126, 255–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Hare, C.B.; Mangin-Heimos, K.S.; Gu, H.; Edmunds, M.; Bebbington, M.; Lee, C.K.; He, M.; Ortinau, C.M. Placental Delayed Villous Maturation Is Associated with Fetal Congenital Heart Disease. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2023, 228, e1–e231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matthiesen, N.B.; Henriksen, T.B.; Gaynor, J.W.; Agergaard, P.; Bach, C.C.; Hjortdal, V.E.; Østergaard, J.R. Congenital Heart Defects and Indices of Fetal Cerebral Growth in a Nationwide Cohort of 924 422 Liveborn Infants. Circulation 2016, 133, 566–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, H.N.; Olbrych, S.K.; Smith, K.L.; Cnota, J.F.; Habli, M.; Ramos-Gonzales, O.; Owens, K.J.; Hinton, A.C.; Polzin, W.J.; Muglia, L.J.; et al. Hypoplastic Left Heart Syndrome Is Associated with Structural and Vascular Placental Abnormalities and Leptin Dysregulation. Placenta 2015, 36, 1078–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leon, R.L.; Sharma, K.; Mir, I.N.; Herrera, C.L.; Brown, S.L.; Spong, C.Y.; Chalak, L.F. Placental Vascular Malperfusion Lesions in Fetal Congenital Heart Disease. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2022, 227, e1–e620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rychik, J.; Goff, D.; McKay, E.; Mott, A.; Tian, Z.; Licht, D.J.; Gaynor, J.W. Characterization of the Placenta in the Newborn with Congenital Heart Disease: Distinctions Based on Type of Cardiac Malformation. Pediatr. Cardiol. 2018, 39, 1165–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snoep, M.C.; Aliasi, M.; van der Meeren, L.E.; Jongbloed, M.R.M.; DeRuiter, M.C.; Haak, M.C. Placenta Morphology and Biomarkers in Pregnancies with Congenital Heart Disease—A Systematic Review. Placenta 2021, 112, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andescavage, N.; Yarish, A.; Donofrio, M.; Bulas, D.; Evangelou, I.; Vezina, G.; McCarter, R.; Duplessis, A.; Limperopoulos, C. 3-D Volumetric MRI Evaluation of the Placenta in Fetuses with Complex Congenital Heart Disease. Placenta 2015, 36, 1024–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, M.E.; Ford, S.P. Comparative Aspects of Placental Efficiency. Reprod. Suppl. 2001, 58, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Courtney, J.; Troja, W.; Owens, K.J.; Brockway, H.M.; Hinton, A.C.; Hinton, R.B.; Cnota, J.F.; Jones, H.N. Abnormalities of Placental Development and Function Are Associated with the Different Fetal Growth Patterns of Hypoplastic Left Heart Syndrome and Transposition of the Great Arteries. Placenta 2020, 101, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misra, D.P.; Salafia, C.M.; Miller, R.K.; Charles, A.K. Non-Linear and Gender-Specific Relationships among Placental Growth Measures and the Fetoplacental Weight Ratio. Placenta 2009, 30, 1052–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albalawi, A.; Brancusi, F.; Askin, F.; Ehsanipoor, R.; Wang, J.; Burd, I.; Sekar, P. Placental Characteristics of Fetuses with Congenital Heart Disease. J. Ultrasound Med. 2017, 36, 965–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takemoto, R.; Anami, A.; Koga, H. Relationship between Birth Weight to Placental Weight Ratio and Major Congenital Anomalies in Japan. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0206002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fowden, A.L.; Sferruzzi-Perri, A.N.; Coan, P.M.; Constancia, M.; Burton, G.J. Placental Efficiency and Adaptation: Endocrine Regulation. J. Physiol. 2009, 587, 3459–3472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montaña-Jimenez, L.; Lasalvia, P.; Diaz Puentes, M.; Olaya-C, M. Congenital Heart Defects and Umbilical Cord Abnormalities, an Unknown Association? J. Neonatal Perinat. Med. 2022, 15, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khong, T.Y.; Mooney, E.E.; Ariel, I.; Balmus, N.C.M.; Boyd, T.K.; Brundler, M.A.; Derricott, H.; Evans, M.J.; Faye-Petersen, O.M.; Gillan, J.E.; et al. Sampling and Definitions of Placental Lesions Amsterdam Placental Workshop Group Consensus Statement. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2016, 140, 698–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakha, S.; Mohamed, A.A.; Yussif, S.M. Placental Histopathologic Findings in the Setting of Prenatally Diagnosed Major Congenital Heart Disease. Fetal Pediatr. Pathol. 2023, 42, 922–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharjee, J.; Mohammad, S.; Goudreau, A.D.; Adamo, K.B. Physical Activity Differentially Regulates VEGF, PlGF, and Their Receptors in the Human Placenta. Physiol. Rep. 2021, 9, e14710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrlich, L.; Hoeller, A.; Golic, M.; Herse, F.; Perschel, F.H.; Henrich, W.; Dechend, R.; Huppertz, B.; Verlohren, S. Increased Placental SFlt-1 but Unchanged PlGF Expression in Late-Onset Preeclampsia. Hypertens. Pregnancy 2017, 36, 175–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alahakoon, T.I.; Zhang, W.; Arbuckle, S.; Zhang, K.; Lee, V. Reduced Angiogenic Factor Expression in Intrauterine Fetal Growth Restriction Using Semiquantitative Immunohistochemistry and Digital Image Analysis. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. Res. 2018, 44, 861–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapustin, R.V.; Kopteeva, E.V.; Alekseenkova, E.N.; Tral, T.G.; Tolibova, G.K.; Arzhanova, O.N. Placental Expression of Endoglin, Placental Growth Factor, Leptin, and Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-1 in Diabetic Pregnancy and Pre-Eclampsia. Gynecol. Endocrinol. 2021, 37, 35–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.-B.; Xu, Y.-Y.; Cheng, W.-W.; Yuan, B.; Zhao, J.-R.; Wang, Y.-L.; Zhang, H.-J. Decreased PGF May Contribute to Trophoblast Dysfunction in Fetal Growth Restriction. Reproduction 2017, 154, 319–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agrawal, S.; Parks, W.T.; Zeng, H.D.; Ravichandran, A.; Ashwal, E.; Windrim, R.C.; Hobson, S.R.; Melamed, N.; Kingdom, J.C. Diagnostic Utility of Serial Circulating Placental Growth Factor Levels and Uterine Artery Doppler Waveforms in Diagnosing Underlying Placental Diseases in Pregnancies at High Risk of Placental Dysfunction. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2022, 227, e1–e618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fantasia, I.; Kasapoglu, D.; Kasapoglu, T.; Syngelaki, A.; Akolekar, R.; Nicolaides, K.H. Fetal Major Cardiac Defects and Placental Dysfunction at 11–13 Weeks’ Gestation. Ultrasound Obstet. Gynecol. 2018, 51, 194–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugimoto, M.; Oka, H.; Kajihama, A.; Nakau, K.; Kuwata, S.; Kurishima, C.; Azuma, H. Ratio between Fms-like Tyrosine Kinase 1 and Placental Growth Factor in Children with Congenital Heart Disease. Pediatr. Cardiol. 2015, 36, 591–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
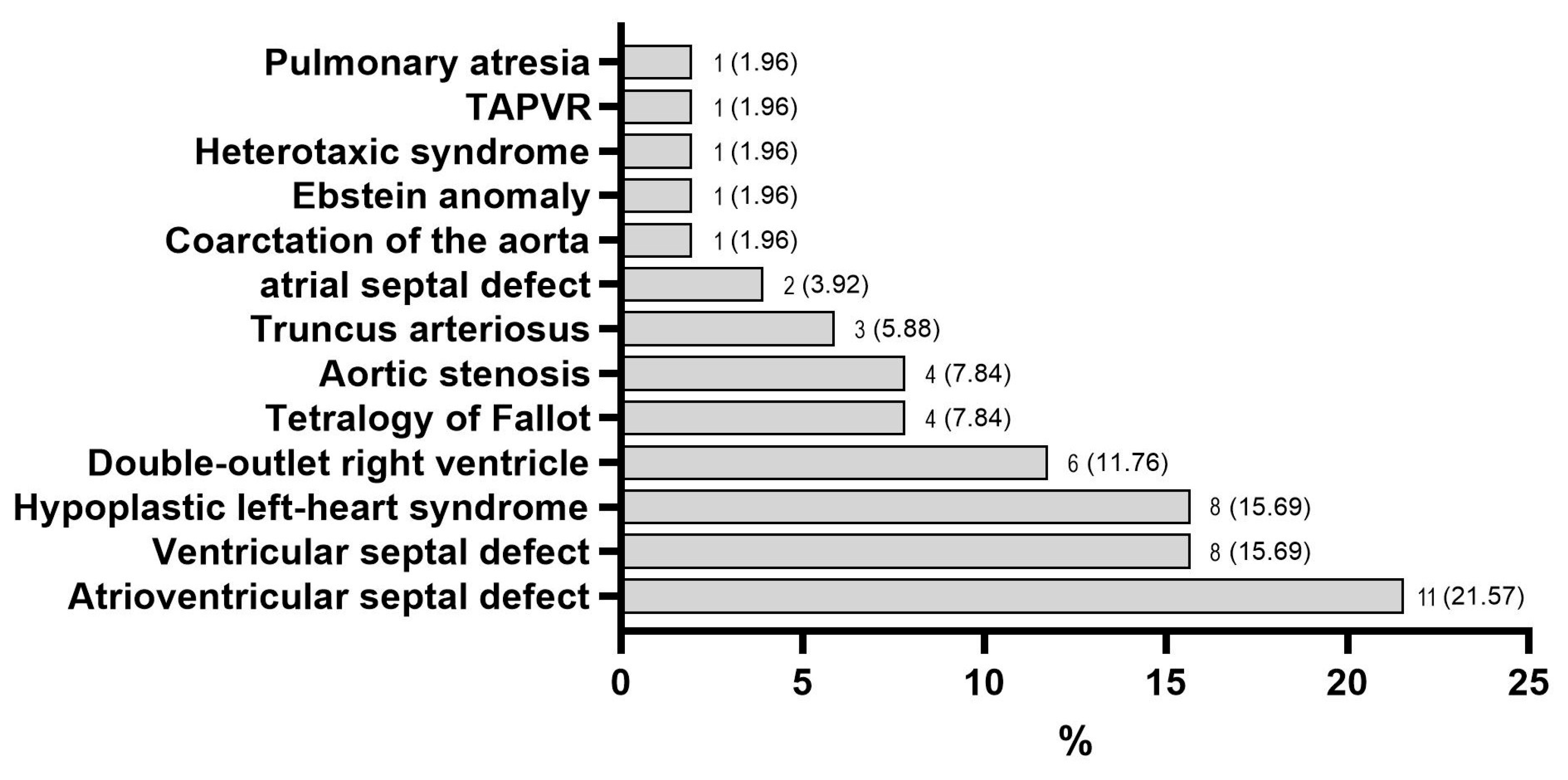

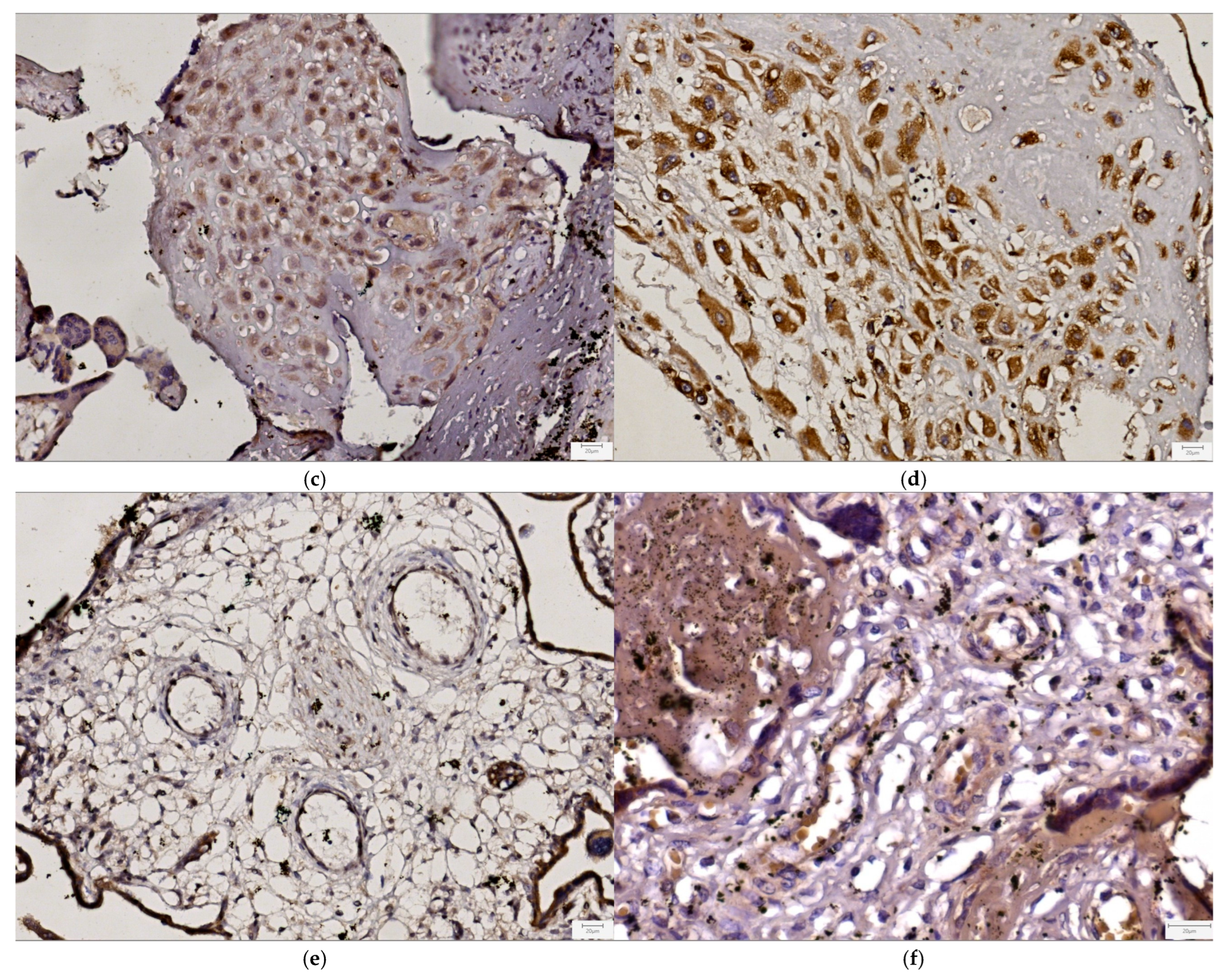
| Characteristic | CHD (51 Subjects) | Control (51 Subjects) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Female sex, n (%) | 23 (45.1) | 33 (64.7) | 0.0727 |
| Other congenital defects, n (%) | 38 (74.5) | 25 (49.0) | 0.0139 |
| Fetal weight (g), median [Q1–Q3] | 303 [75.8–599] | 321 [123–694] | 0.0885 ‡ |
| Fetal weight Z-score, median [Q1–Q3] | −0.21 [−1.75–1.57] | 0.95 [−0.07–1.9] | 0.0283 |
| Fetal CRL (cm), median [Q1–Q3] | 16 [10.75–21] | 17.5 [12–21.5] | 0.0006 ‡ |
| Fetal CRL Z-score, median [Q1–Q3] | −0.72 [−2.06–0.4] | 0.18 [−0.55–1.06] | 0.0017 |
| Fetal CHL (cm), median [Q1–Q3] | 23 [15.75–31.63] | 25 [18–32.5] | 0.0027 ‡ |
| Fetal CHL Z-score, median [Q1–Q3] | −0.195 [−1.79–1.2] | 0.81 [−0.27–1.94] | 0.0098 |
| Fetal HC (cm), median [Q1–Q3] | 17.75 [11.88–22.63] | 19 [12.5–22.5] | 0.1625 ‡ |
| Fetal HC Z-score, median [Q1–Q3] | 0.21 [−1.11–1.47] | 0.42 [−0.08–1.57] | 0.2092 |
| Characteristic | CHD (51 Subjects) | Control (51 Subjects) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Central UC insertion, n (%) | 6 (11.8) | 25 (49.0) | <0.0001 |
| Eccentric UC insertion, n (%) | 9 (17.7) | 9 (17.7) | >0.9999 |
| Marginal or velamentous UC insertion, n (%) | 32 (62.8) | 14 (27.5) | 0.0006 |
| UC length (cm), median [Q1–Q3] | 17.25 [11.88–25.88] | 25 [18–33.5] | <0.0001 ‡ |
| UC diameter (cm), median [Q1–Q3] | 0.8 [0.5–1] | 1 [0.6–1.2] | 0.1616 ‡ |
| Hypercoiled * UC, n (%) | 23 (45.1) | 23 (45.1) | >0.9999 |
| Single umbilical artery, n (%) | 12 (23.5) | 3 (5.9) | 0.0228 |
| Characteristic | CHD (51 Subjects) | Control (51 Subjects) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Placental weight (g), median [Q1–Q3] | 130 [84–187] | 137 [90–190] | 0.6878 ‡ |
| Placental length (cm), median [Q1–Q3] | 11 [9.5–13] | 12 [10–14] | 0.2212 ‡ |
| Placental width (cm), median [Q1–Q3] | 9.5 [7.25–12] | 10 [8–12.5] | 0.6874 ‡ |
| Placental thickness (cm), median [Q1–Q3] | 3 [2–3] | 3 [2.5–3] | 0.7455 ‡ |
| Fetal-to-placental weight ratio, median [Q1–Q3] | 2.23 [1.38–3.51] | 2.49 [1.66–3.83] | 0.0223 ‡ |
| Placental-to-fetal weight ratio, median [Q1–Q3] | 0.45 [0.28–0.73] | 0.4 [0.26–0.6] | 0.0141 ‡ |
| Villous vascular congestion, n (%) | 22 (43.1) | 26 (51.0) | 0.5520 |
| Maternal vascular malperfusion, n (%) | 27 (52.9) | 29 (56.9) | 0.8424 |
| Infarction, n (%) | 8 (15.7) | 9 (17.7) | >0.9999 |
| Subchorionic hemorrhage, n (%) | 24 (47.1) | 23 (45.1) | 0.8429 |
| Decidual arteriopathy, n (%) | 6 (11.8) | 12 (23.5) | 0.1932 |
| Fetal vascular malperfusion, n (%) | 35 (68.6) | 39 (76.5) | 0.5061 |
| Thrombosis, n (%) | 10 (19.6) | 23 (45.1) | 0.0105 |
| Fibrin deposits, n (%) | 24 (47.1) | 31 (60.8) | 0.2332 |
| Chorangiosis, n (%) | 3 (5.9) | 1 (1.96) | 0.6175 |
| Calcifications, n (%) | 11 (21.6) | 3 (5.9) | 0.0410 |
| Chorioamnionitis, n (%) | 10 (19.6) | 16 (31.4) | 0.2558 |
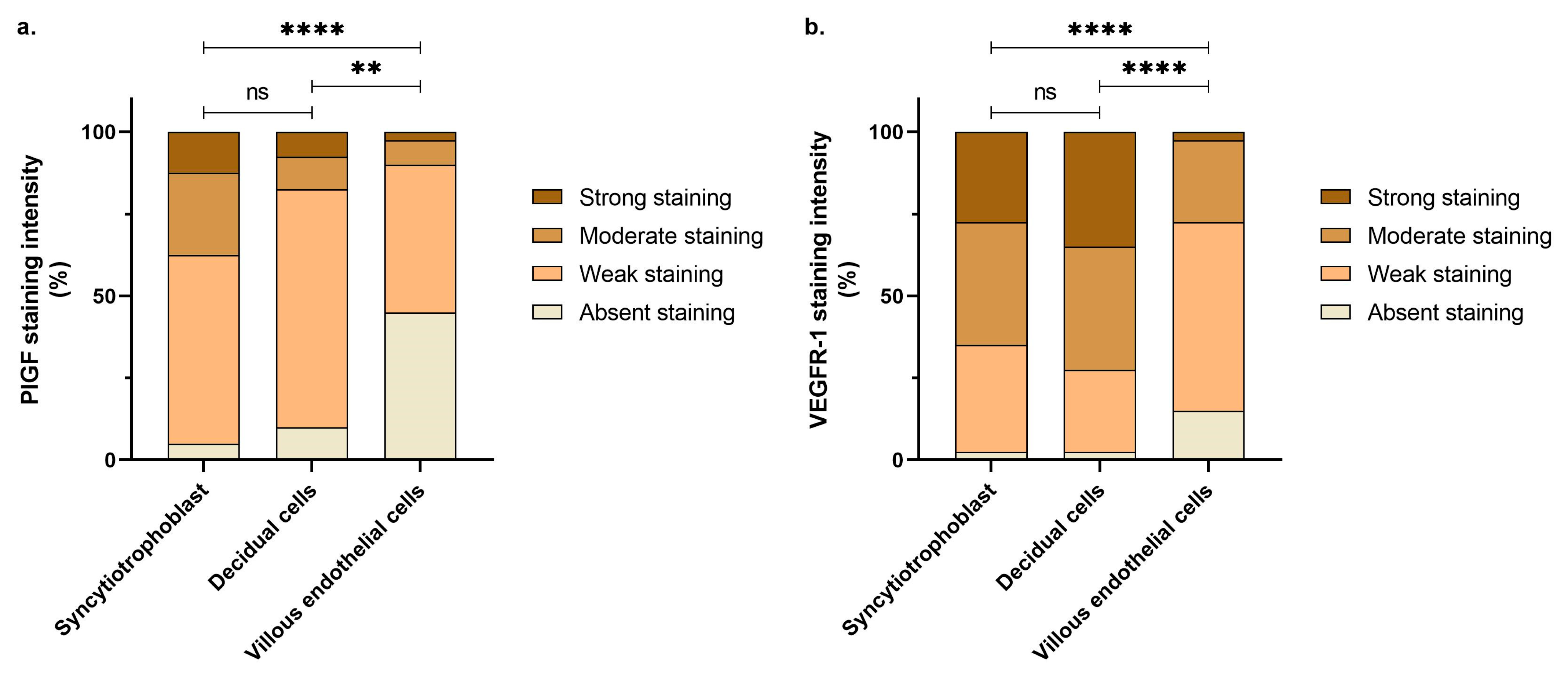
| Localization | Staining Intensity | VEGFR-1 | PlGF | p-Value * |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Syncytiotrophoblast | Absent staining, n | 1/40 | 2/40 | 0.0164 |
| Weak staining, n | 13/40 | 23/40 | ||
| Moderate staining, n | 15/40 | 10/40 | ||
| Strong staining, n | 11/40 | 5/40 | ||
| Decidual cells | Absent staining, n | 1/40 | 4/40 | <0.0001 |
| Weak staining, n | 10/40 | 29/40 | ||
| Moderate staining, n | 15/40 | 4/40 | ||
| Strong staining, n | 14/40 | 3/40 | ||
| Villous endothelial cells | Absent staining, n | 6/40 | 18/40 | 0.0046 |
| Weak staining, n | 23/40 | 18/40 | ||
| Moderate staining, n | 10/40 | 3/40 | ||
| Strong staining, n | 1/40 | 1/40 |
| Localization | Staining Intensity | CHD | Control | p-Value * |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| a. Placental growth factor (PlGF) | ||||
| Syncytiotrophoblast | Absent staining, n | 2/20 | 0/20 | 0.0046 |
| Weak staining, n | 15/20 | 8/20 | ||
| Moderate staining, n | 2/20 | 8/20 | ||
| Strong staining, n | 1/20 | 4/20 | ||
| Decidual cells | Absent staining, n | 4/20 | 0/20 | 0.0067 |
| Weak staining, n | 15/20 | 14/20 | ||
| Moderate staining, n | 1/20 | 3/20 | ||
| Strong staining, n | 0/20 | 3/20 | ||
| Villous endothelial cells | Absent staining, n | 10/20 | 8/20 | 0.8284 |
| Weak staining, n | 8/20 | 10/20 | ||
| Moderate staining, n | 1/20 | 2/20 | ||
| Strong staining, n | 1/20 | 0/20 | ||
| b. Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-1 (VEGFR-1) | ||||
| Syncytiotrophoblast | Absent staining, n | 0/20 | 1/20 | 0.7069 |
| Weak staining, n | 8/20 | 5/20 | ||
| Moderate staining, n | 5/20 | 10/20 | ||
| Strong staining, n | 7/20 | 4/20 | ||
| Decidual cells | Absent staining, n | 1/20 | 0/20 | 0.2620 |
| Weak staining, n | 7/20 | 3/20 | ||
| Moderate staining, n | 5/20 | 10/20 | ||
| Strong staining, n | 7/20 | 7/20 | ||
| Villus endothelial cells | Absent staining, n | 3/20 | 3/20 | >0.9999 |
| Weak staining, n | 11/20 | 12/20 | ||
| Moderate staining, n | 6/20 | 4/20 | ||
| Strong staining, n | 0/20 | 1/20 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bolunduț, A.C.; Mureșan, X.M.; Suflețel, R.T.; Mocan, L.P.; Pîrv, S.; Șușman, S.; Mihu, C.M. Placental Pathology and Placental Growth Factor (PlGF)/Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Receptor-1 (VEGFR-1) Pathway Expression Evaluation in Fetal Congenital Heart Defects. Life 2025, 15, 837. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15060837
Bolunduț AC, Mureșan XM, Suflețel RT, Mocan LP, Pîrv S, Șușman S, Mihu CM. Placental Pathology and Placental Growth Factor (PlGF)/Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Receptor-1 (VEGFR-1) Pathway Expression Evaluation in Fetal Congenital Heart Defects. Life. 2025; 15(6):837. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15060837
Chicago/Turabian StyleBolunduț, Alexandru Cristian, Ximena Maria Mureșan, Rada Teodora Suflețel, Lavinia Patricia Mocan, Simina Pîrv, Sergiu Șușman, and Carmen Mihaela Mihu. 2025. "Placental Pathology and Placental Growth Factor (PlGF)/Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Receptor-1 (VEGFR-1) Pathway Expression Evaluation in Fetal Congenital Heart Defects" Life 15, no. 6: 837. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15060837
APA StyleBolunduț, A. C., Mureșan, X. M., Suflețel, R. T., Mocan, L. P., Pîrv, S., Șușman, S., & Mihu, C. M. (2025). Placental Pathology and Placental Growth Factor (PlGF)/Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Receptor-1 (VEGFR-1) Pathway Expression Evaluation in Fetal Congenital Heart Defects. Life, 15(6), 837. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15060837









