Overcoming Mohs Limitations in Treating DFSP: Retrospective Analysis of a Novel Excision Technique
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Ethics
2.3. Study Cohort
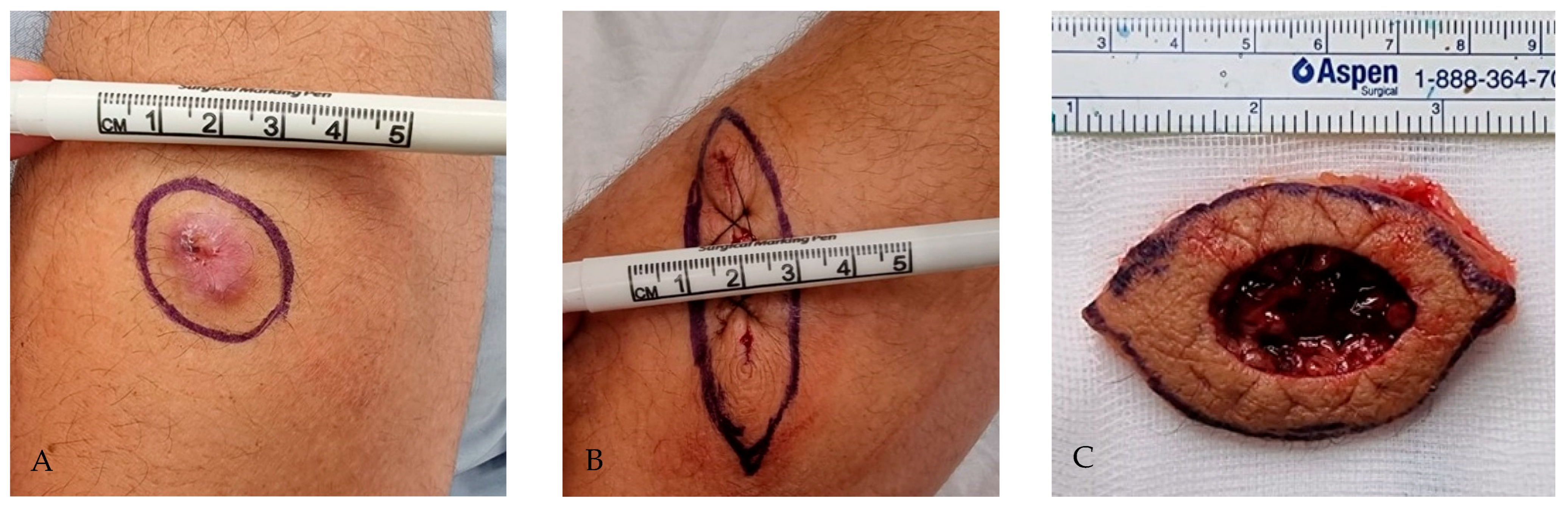
2.4. Surgical Technique
2.5. Patient Follow-Up
2.6. Data Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. DFSP Tumor-Related Factors
4.2. Procedural Factors
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DFSP | Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans |
References
- Hao, X.; Billings, S.D.; Wu, F.; Stultz, T.W.; Procop, G.W.; Mirkin, G.; Vidimos, A.T. Dermatofibrosarcoma Protuberans: Update on the Diagnosis and Treatment. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 1752. Available online: https://pubmed-ncbi-nlm-nih-gov.meir.idm.oclc.org/32516921/ (accessed on 12 August 2023). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thway, K.; Noujaim, J.; Jones, R.L.; Fisher, C. Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans: Pathology, genetics, and potential therapeutic strategies. Ann. Diagn. Pathol. 2016, 25, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bogucki, B.; Neuhaus, I.; Hurst, E.A. Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans: A review of the literature. Dermatol. Surg. 2012, 38, 537–551. Available online: https://pubmed-ncbi-nlm-nih-gov.meir.idm.oclc.org/22288484/ (accessed on 22 December 2023). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koh, C.K.; Ko, C.B.; Bury, H.P.R.; Wyatt, E.H. Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans. Int. J. Dermatol. 1995, 34, 256–260. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/7790140/ (accessed on 17 December 2022). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badhey, A.K.; Tikhtman, R.; Tang, A.L. Management of dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans. Curr. Opin. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2021, 29, 278–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llombart, B.; Serra-Guillén, C.; Rubio, L.; Nagore, E.; Requena, C.; Traves, V.; Calomarde, L.; Bancalari, B.; López-Guerrero, J.A.; Guillen-Barona, C.; et al. Subcutaneous dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans, a rare subtype with predilection for the head: A retrospective series of 18 cases. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2017, 77, 503–511.e1. Available online: https://pubmed-ncbi-nlm-nih-gov.meir.idm.oclc.org/28420485/ (accessed on 12 August 2023). [CrossRef]
- Lowe, G.C.; Onajin, O.; Baum, C.L.; Otley, C.C.; Arpey, C.J.; Roenigk, R.K.; Brewer, J.D. A Comparison of Mohs Micrographic Surgery and Wide Local Excision for Treatment of Dermatofibrosarcoma Protuberans with Long-Term Follow-up: The Mayo Clinic Experience. Dermatol. Surg. 2017, 43, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acosta, A.E.; Vélez, C.S. Dermatofibrosarcoma Protuberans. Curr. Treat. Options Oncol. 2017, 18, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farma, J.M.; Ammori, J.B.; Zager, J.S.; Marzban, S.S.; Bui, M.M.; Bichakjian, C.K.; Johnson, T.M.; Lowe, L.; Sabel, M.S.; Wong, S.L.; et al. Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans: How wide should we resect? Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2010, 17, 2112–2118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monnier, D.; Vidal, C.; Martin, L.; Danzon, A.; Pelletier, F.; Puzenat, E.; Algros, M.; Blanc, D.; Laurent, R.; Humbert, P.; et al. Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans: A population-based cancer registry descriptive study of 66 consecutive cases diagnosed between 1982 and 2002. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2006, 20, 1237–1242. Available online: https://pubmed-ncbi-nlm-nih-gov.meir.idm.oclc.org/17062038/ (accessed on 10 March 2023). [CrossRef]
- Snow, H.; Davies, E.; Strauss, D.C.; Smith, M.; Hayes, A.J. Conservative Re-excision is a Safe and Simple Alternative to Radical Resection in Revision Surgery for Dermatofibrosarcoma Protuberans. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2020, 27, 919–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, C.K.; Jacobs, I.A.; Salti, G.I. Outcomes of surgery for dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 2004, 30, 341–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiore, M.; Miceli, R.; Mussi, C.; Vullo, S.L.; Mariani, L.; Lozza, L.; Collini, P.; Olmi, P.; Casali, P.G.; Gronchi, A. Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans treated at a single institution: A surgical disease with a high cure rate. J. Clin. Oncol. 2005, 23, 7669–7675. Available online: https://pubmed-ncbi-nlm-nih-gov.meir.idm.oclc.org/16234529/ (accessed on 10 March 2023). [CrossRef]
- Paradisi, A.; Abeni, D.; Rusciani, A.; Cigna, E.; Wolter, M.; Scuderi, N.; Rusciani, L.; Kaufmann, R.; Podda, M. Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans: Wide local excision vs. Mohs micrographic surgery. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2008, 34, 728–736. Available online: https://pubmed-ncbi-nlm-nih-gov.meir.idm.oclc.org/18684568/ (accessed on 14 August 2023). [CrossRef]
- Khatri, V.P.; Galante, J.M.; Bold, R.J.; Schneider, P.D.; Ramsamooj, R.; Goodnight, J.E. Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans: Reappraisal of wide local excision and impact of inadequate initial treatment. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2003, 10, 1118–1122. Available online: https://pubmed-ncbi-nlm-nih-gov.meir.idm.oclc.org/14597453/ (accessed on 1 March 2024). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malan, M.; Xuejingzi, W.; Quan, S.J. The efficacy of Mohs micrographic surgery over the traditional wide local excision surgery in the cure of dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans. Pan Afr. Med. J. 2019, 33, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, D.K.; Goldberg, D.J. Mohs Micrographic Surgery: Past, Present, and Future. Dermatol. Surg. 2019, 45, 329–339. Available online: https://pubmed-ncbi-nlm-nih-gov.meir.idm.oclc.org/30608296/ (accessed on 22 December 2023). [CrossRef]
- Hancox, J.G.; Kelley, B.; Greenway, H.T. Treatment of dermatofibroma sarcoma protuberans using modified Mohs micrographic surgery: No recurrences and smaller defects. Dermatol. Surg. 2008, 34, 780–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pallure, V.; Dupin, N.; Guillot, B. Surgical treatment of Darier-Ferrand dermatofibrosarcoma: A systematic review. Dermatol. Surg. 2013, 39, 1417–1433. Available online: https://pubmed-ncbi-nlm-nih-gov.meir.idm.oclc.org/24090253/ (accessed on 17 August 2023).
- Lemm, D.; Mügge, L.O.; Mentzel, T.; Höffken, K. Current treatment options in dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 135, 653–665. Available online: https://pubmed-ncbi-nlm-nih-gov.meir.idm.oclc.org/19205737/ (accessed on 16 March 2023). [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Oh, Y.; Nam, K.A.; Oh, B.; Roh, M.R.; Chung, K.Y. Mohs micrographic surgery for dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans: Comparison of frozen and paraffin techniques. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2018, 32, 2171–2177. Available online: https://pubmed-ncbi-nlm-nih-gov.meir.idm.oclc.org/30067886/ (accessed on 12 August 2023). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, E.C.S.; Vyas, K.S.; Batbold, S.; Erwin, P.J.; Brewer, J.D. Dermatofibrosarcoma Protuberans Recurrence After Wide Local Excision Versus Mohs Micrographic Surgery: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Dermatol. Surg. 2022, 48, 479–485. Available online: https://pubmed-ncbi-nlm-nih-gov.meir.idm.oclc.org/35353755/ (accessed on 12 August 2023). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foroozan, M.; Sei, J.F.; Amini, M.; Beauchet, A.; Saiag, P. Efficacy of Mohs micrographic surgery for the treatment of dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans: Systematic review. Arch. Dermatol. 2012, 148, 1055–1064. Available online: https://pubmed-ncbi-nlm-nih-gov.meir.idm.oclc.org/22986859/ (accessed on 22 December 2023). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowne, W.B.; Antonescu, C.R.; Leung, D.H.Y.; Katz, S.C.; Hawkins, W.G.; Woodruff, J.M.; Brennan, M.F.; Lewis, J.J. Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans: A clinicopathologic analysis of patients treated and followed at a single institution. Cancer 2000, 88, 2711–2720. Available online: https://pubmed-ncbi-nlm-nih-gov.meir.idm.oclc.org/10870053/ (accessed on 11 March 2023). [CrossRef]
- Harati, K.; Lange, K.; Goertz, O.; Lahmer, A.; Kapalschinski, N.; Stricker, I.; Lehnhardt, M.; Daigeler, A. A single-institutional review of 68 patients with dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans: Wide re-excision after inadequate previous surgery results in a high rate of local control. World J. Surg. Oncol. 2017, 15, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DuBay, D.; Cimmino, V.; Lowe, L.; Johnson, T.M.; Sondak, V.K. Low Recurrence Rate after Surgery for Dermatofibrosarcoma Protuberans: A Multidisciplinary Approach from a Single Institution. Cancer 2004, 100, 1008–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.Y.; Silapunt, S.; Migden, M.R.; McGinness, J.L.; Nguyen, T.H. Mohs Mapping Fidelity: Optimizing Orientation, Accuracy, and Tissue Identification in Mohs Surgery. Dermatol. Surg. 2018, 44, 1–9. Available online: https://pubmed-ncbi-nlm-nih-gov.meir.idm.oclc.org/28654580/ (accessed on 17 August 2023). [CrossRef]
- Smith-Zagone, M.J.; Schwartz, M.R. Frozen section of skin specimens. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2005, 129, 1536–1543. Available online: https://pubmed-ncbi-nlm-nih-gov.meir.idm.oclc.org/16329726/ (accessed on 22 December 2023). [CrossRef]
- Nelson, T.G.; Gonda, P.; Sheppard, P.; Keohane, S. Dermatofibrosarcoma Protuberans of the Scalp: A Challenging Tumor With a Proposed Modification to the Slow Mohs Technique. Dermatol. Surg. 2020, 46, 1742–1745. Available online: https://pubmed-ncbi-nlm-nih-gov.meir.idm.oclc.org/31517659/ (accessed on 17 August 2023). [CrossRef]
- Serra-Guillén, C.; Llombart, B.; Nagore, E.; Requena, C.; Traves, V.; Llorca, D.; Kindem, S.; Alcalá, R.; Guillén, C.; Sanmartín, O. Positive margins in excised dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans: A study of 58 cases treated with slow-Mohs surgery. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2014, 28, 1012–1015. Available online: https://pubmed-ncbi-nlm-nih-gov.meir.idm.oclc.org/23931335/ (accessed on 12 August 2023). [CrossRef]
- Asilian, A.; Honarjou, N.; Faghihi, G.; Saber, M.; Mozafarpoor, S.; Hafezi, H. An experience of slow-Mohs micrographic surgery for the treatment of Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans: A long-term cohort study. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2020, 19, 2701–2705. Available online: https://pubmed-ncbi-nlm-nih-gov.meir.idm.oclc.org/32039548/ (accessed on 12 August 2023). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Massey, R.A.; Tok, J.; Strippoli, B.A.; Szabolcs, M.J.; Silvers, D.N.; Eliezri, Y.D. A comparison of frozen and paraffin sections in dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans. Dermatol. Surg. 1998, 24, 995–998. Available online: https://pubmed-ncbi-nlm-nih-gov.meir.idm.oclc.org/9754088/ (accessed on 12 August 2023). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaput, B.; Filleron, T.; Le Guellec, S.; Meresse, T.; Courtade-Saïdi, M.; Grolleau, J.-L.; Chevreau, C.; Garrido, I.; Gangloff, D. Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans: Margins reduction using slow-Mohs micrographic surgery. Experience with 35 patients. Ann. Chir. Plast. Esthet. 2014, 59, 219–225. Available online: https://pubmed-ncbi-nlm-nih-gov.meir.idm.oclc.org/24411817/ (accessed on 24 June 2025). [CrossRef]
- Charles, T.W.D.; Barry, H.P.; Rasgon, M. Dermatofibrosarcoma Protuberans of the Head and Neck: Treatment With Mohs Surgery Using Inverted Horizontal Paraffin Sections. Laryngoscope 2003, 113, 1289–1293. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, W.P.; Barlow, R.J.; Robson, A.; Kurwa, H.A.; McKenna, J.; Mallipeddi, R. Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans: 35 patients treated with Mohs micrographic surgery using paraffin sections. Br. J. Dermatol. 2011, 164, 363–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loss, L.; Zeitouni, N.C. Management of Scalp Dermatofibrosarcoma Protuberans. Dermatol. Surg. 2005, 31, 1428–1433. [Google Scholar]
- Nouri, K.; Lodha, R.; Jimenez, G.; Robins, P. Mohs Micrographic Surgery for Dermatofibrosarcoma Protuberans: University of Miami and NYU Experience. Dermatol. Surg. 2002, 28, 1060–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Variable | N (%) |
|---|---|
| Total patients | 22 |
| Male to female ratio | 16 (73%):6 (27%) |
| Median age, y, (range) | 42.5 (28–72) |
| Smoking | 0 |
| Location of Lesion | |
| Head and neck | 6 (27%) |
| Chest | 3 (14%) |
| Abdomen | 3 (14%) |
| Back | 3 (14%) |
| Extremities | 7 (31%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shoufani, R.; Berl, A.; Shir-az, O.; Kidron, D.; Mann, D.; Castel, N.; Shalom, A. Overcoming Mohs Limitations in Treating DFSP: Retrospective Analysis of a Novel Excision Technique. Life 2025, 15, 1025. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15071025
Shoufani R, Berl A, Shir-az O, Kidron D, Mann D, Castel N, Shalom A. Overcoming Mohs Limitations in Treating DFSP: Retrospective Analysis of a Novel Excision Technique. Life. 2025; 15(7):1025. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15071025
Chicago/Turabian StyleShoufani, Rami, Ariel Berl, Ofir Shir-az, Deborah Kidron, Din Mann, Noam Castel, and Avshalom Shalom. 2025. "Overcoming Mohs Limitations in Treating DFSP: Retrospective Analysis of a Novel Excision Technique" Life 15, no. 7: 1025. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15071025
APA StyleShoufani, R., Berl, A., Shir-az, O., Kidron, D., Mann, D., Castel, N., & Shalom, A. (2025). Overcoming Mohs Limitations in Treating DFSP: Retrospective Analysis of a Novel Excision Technique. Life, 15(7), 1025. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15071025






