Urinary Glyphosate Concentrations and Serum Sex Hormones in a Nationally Representative U.S. Sample: NHANES 2017–2018
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
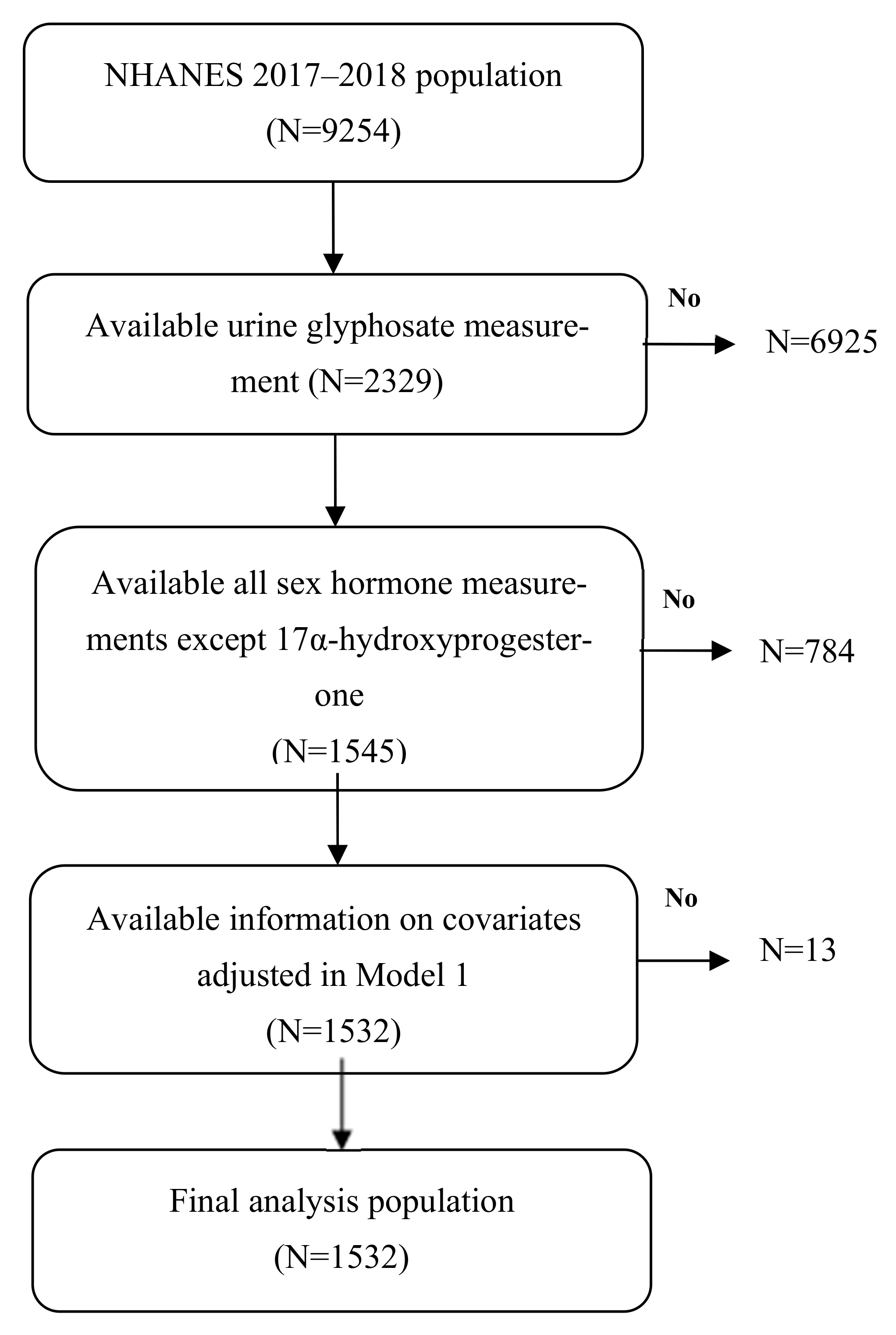
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Measurement of Urinary Glyphosate Levels
2.3. Measurement of Serum Sex Hormone Levels
2.4. Covariates
2.5. Statistics
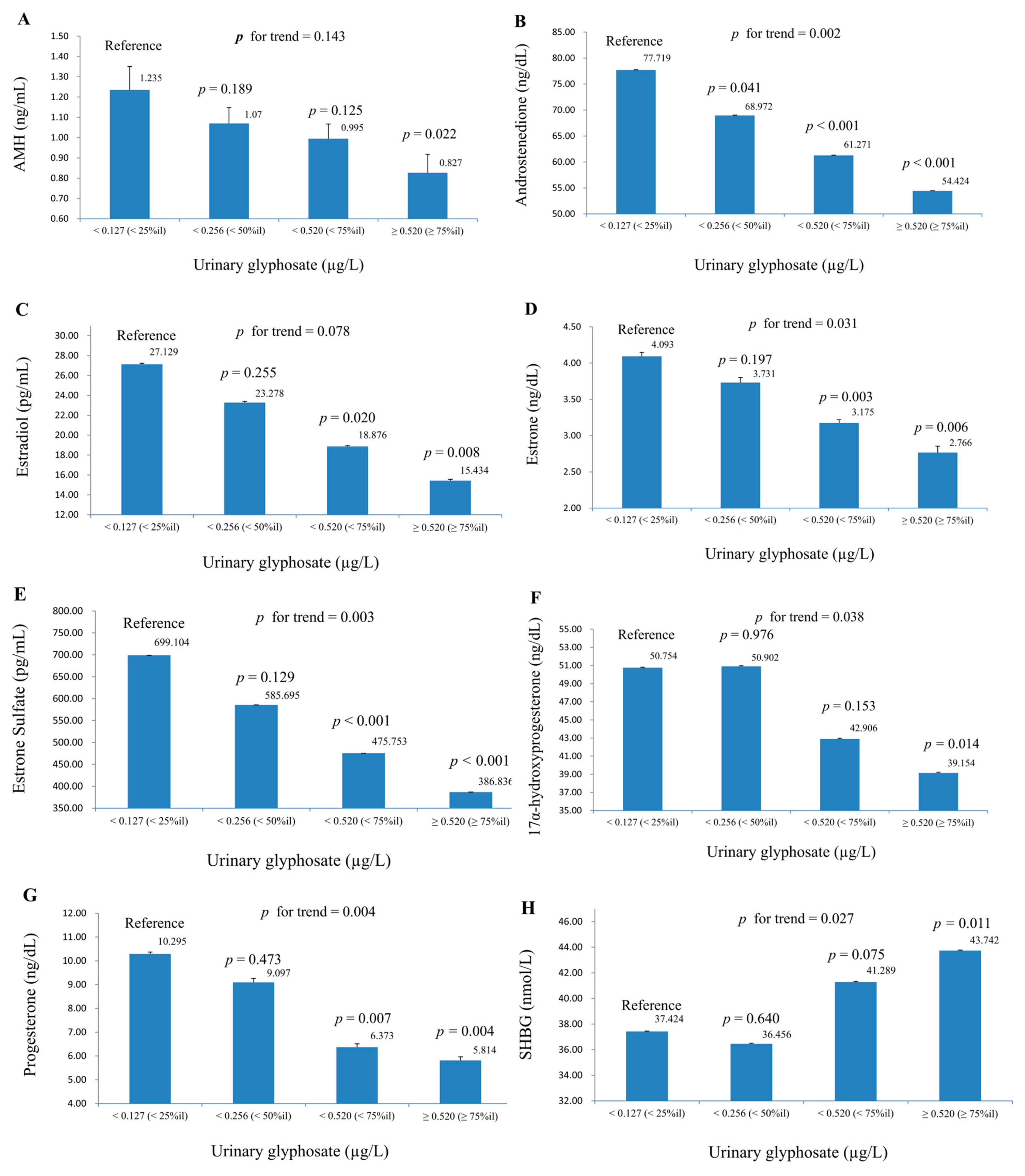
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AMH | Anti-Müllerian hormone |
| BMI | Body mass index |
| eGFR | Estimated glomerular filtration rate |
| ETS | Environmental tobacco smoke |
| FSH | Follicle-stimulating hormone |
| GBH | Glyphosate-based herbicide |
| HPG | Hypothalamic–pituitary–gonadal |
| hs-CRP | High-sensitivity C-reactive protein |
| IC-MS/MS | Ion chromatography paired with tandem mass spectrometry |
| LH | Luteinizing hormone |
| LOD | Limit of detection |
| Ln | Natural logarithm |
| NHANES | National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey |
| SHBG | Sex hormone-binding globulin |
References
- Lacroix, R.; Kurrasch, D.M. Glyphosate toxicity: In vivo, in vitro, and epidemiological evidence. Toxicol. Sci. 2023, 192, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baghel, R. Glyphosate Market Size, Demand, Trends & Growth (2023–2037). Available online: https://www.researchnester.com/reports/glyphosate-market/4333 (accessed on 4 June 2025).
- Mills, P.J.; Kania-Korwel, I.; Fagan, J.; McEvoy, L.K.; Laughlin, G.A.; Barrett-Connor, E. Excretion of the Herbicide Glyphosate in Older Adults Between 1993 and 2016. JAMA 2017, 318, 1610–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsiao, C.C.; Yang, A.M.; Wang, C.; Lin, C.Y. Association between glyphosate exposure and cognitive function, depression, and neurological diseases in a representative sample of US adults: NHANES 2013–2014 Analysis. Environ. Res. 2023, 237, 116860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnor, K.; Caton, J.; Miljkovic, D. The role of funding on research and science: The impact of glyphosate herbicides on health and the environment. J. Policy Model. 2023, 45, 103–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EPA. Interim Registration Review Decision and Responses to Public Comments for Glyphosate. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/ingredients-used-pesticide-products/interim-registration-review-decision-and-responses-public (accessed on 4 June 2025).
- EFSA. Glyphosate. Available online: https://www.efsa.europa.eu/en/topics/topic/glyphosate (accessed on 5 June 2025).
- BRC. Glyphosate Global Market Report. 2024. Available online: https://www.thebusinessresearchcompany.com/report/glyphosate-global-market-report (accessed on 31 March 2025).
- Benbrook, C. Shining a Light on Glyphosate-Based Herbicide Hazard, Exposures and Risk: Role of Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma Litigation in the USA. Eur. J. Risk Regul. 2020, 11, 498–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thongprakaisang, S.; Thiantanawat, A.; Rangkadilok, N.; Suriyo, T.; Satayavivad, J. Glyphosate induces human breast cancer cells growth via estrogen receptors. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2013, 59, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasnier, C.; Dumont, C.; Benachour, N.; Clair, E.; Chagnon, M.C.; Séralini, G.E. Glyphosate-based herbicides are toxic and endocrine disruptors in human cell lines. Toxicology 2009, 262, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romano, R.M.; Romano, M.A.; Bernardi, M.M.; Furtado, P.V.; Oliveira, C.A. Prepubertal exposure to commercial formulation of the herbicide glyphosate alters testosterone levels and testicular morphology. Arch. Toxicol. 2010, 84, 309–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romano, M.A.; Romano, R.M.; Santos, L.D.; Wisniewski, P.; Campos, D.A.; de Souza, P.B.; Viau, P.; Bernardi, M.M.; Nunes, M.T.; de Oliveira, C.A. Glyphosate impairs male offspring reproductive development by disrupting gonadotropin expression. Arch. Toxicol. 2012, 86, 663–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingaramo, P.; Alarcón, R.; Muñoz-de-Toro, M.; Luque, E.H. Are glyphosate and glyphosate-based herbicides endocrine disruptors that alter female fertility? Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2020, 518, 110934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Zhang, H.; Huang, X.; Yang, D.; Wu, C.; Liu, H.; Zhang, L. Associations of glyphosate exposure and serum sex steroid hormones among 6–19-year-old children and adolescents. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2024, 275, 116266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geier, D.A.; Geier, M.R. Urine glyphosate exposure and serum sex hormone disruption within the 2013–2014 National Health and Nutrition Examination survey (NHANES). Chemosphere 2023, 316, 137796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- CDC. NHANES 2017–2018. Available online: https://wwwn.cdc.gov/nchs/nhanes/continuousnhanes/default.aspx?BeginYear=2017 (accessed on 4 June 2025).
- CDC. 2017–2018 Data Documentation, Codebook, and Frequencies: Glyphosate (GLYP). Available online: https://wwwn.cdc.gov/Nchs/Data/Nhanes/Public/2017/DataFiles/SSGLYP_J.htm (accessed on 4 June 2025).
- CDC. Sex Steroid Hormone Panel—Serum (Surplus). Available online: https://wwwn.cdc.gov/Nchs/Data/Nhanes/Public/2017/DataFiles/SSTST_J.htm#Eligible_Sample (accessed on 4 June 2025).
- Howard, S.R. Interpretation of reproductive hormones before, during and after the pubertal transition-identifying health and disordered puberty. Clin. Endocrinol. 2021, 95, 702–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geyer, J.; Bakhaus, K.; Bernhardt, R.; Blaschka, C.; Dezhkam, Y.; Fietz, D.; Grosser, G.; Hartmann, K.; Hartmann, M.F.; Neunzig, J.; et al. The role of sulfated steroid hormones in reproductive processes. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2017, 172, 207–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezvanpour, A.; Don-Wauchope, A.C. Clinical implications of estrone sulfate measurement in laboratory medicine. Crit. Rev. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2017, 54, 73–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillerová, M.; Borbélyová, V.; Hodosy, J.; Riljak, V.; Renczés, E.; Frick, K.M.; Tóthová, Ľ. On the role of sex steroids in biological functions by classical and non-classical pathways. An update. Front. Neuroendocrinol. 2021, 62, 100926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herman-Giddens, M.E.; Steffes, J.; Harris, D.; Slora, E.; Hussey, M.; Dowshen, S.A.; Wasserman, R.; Serwint, J.R.; Smitherman, L.; Reiter, E.O. Secondary sexual characteristics in boys: Data from the Pediatric Research in Office Settings Network. Pediatrics 2012, 130, e1058–e1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.S.; Schubert, C.M.; Chumlea, W.C.; Roche, A.F.; Kulin, H.E.; Lee, P.A.; Himes, J.H.; Ryan, A.S. National estimates of the timing of sexual maturation and racial differences among US children. Pediatrics 2002, 110, 911–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.S.; Ettinger, B.; Stanczyk, F.Z.; Vittinghoff, E.; Hanes, V.; Cauley, J.A.; Chandler, W.; Settlage, J.; Beattie, M.S.; Folkerd, E.; et al. Comparison of methods to measure low serum estradiol levels in postmenopausal women. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2006, 91, 3791–3797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CDC. CDC Growth Charts Data Files. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/growthcharts/cdc-data-files.htm (accessed on 4 June 2025).
- CDC. National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES): Smoking-Cigarette Use. Available online: https://wwwn.cdc.gov/Nchs/Data/Nhanes/Public/2017/DataFiles/SMQ_J.htm (accessed on 4 June 2025).
- CDC. 2017–2018 Data Documentation, Codebook, and Frequencies: Physical Activity. Available online: https://wwwn.cdc.gov/Nchs/Data/Nhanes/Public/2017/DataFiles/PAQ_J.htm#Appendix_1.__Suggested_MET_Scores (accessed on 4 June 2025).
- NKF. CKD-EPI Creatinine-Cystatin Equation. 2021. Available online: https://www.kidney.org/ckd-epi-creatinine-cystatin-equation-2021 (accessed on 4 June 2025).
- CDC. NHANES Analytic Guidance and Brief Overview for the 2017-March 2020 Pre-Pandemic Data Files. Available online: https://wwwn.cdc.gov/nchs/nhanes/continuousnhanes/overviewbrief.aspx?cycle=2017-2020 (accessed on 4 June 2025).
- Ashley-Martin, J.; Huang, R.; MacPherson, S.; Brion, O.; Owen, J.; Gaudreau, E.; Bienvenu, J.-F.; Fisher, M.; Borghese, M.M.; Bouchard, M.F.; et al. Urinary concentrations and determinants of glyphosate and glufosinate in Pregnant Canadian participants in the MIREC study. Environ. Res. 2023, 217, 114842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Liu, J.-B.; Wang, J.-Q.; Lian, C.-Y.; Wang, Z.-Y.; Wang, L. Glyphosate-induced mitochondrial reactive oxygen species overproduction activates parkin-dependent mitophagy to inhibit testosterone synthesis in mouse leydig cells. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 314, 120314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anifandis, G.; Amiridis, G.; Dafopoulos, K.; Daponte, A.; Dovolou, E.; Gavriil, E.; Gorgogietas, V.; Kachpani, E.; Mamuris, Z.; Messini, C.I.; et al. The In Vitro Impact of the Herbicide Roundup on Human Sperm Motility and Sperm Mitochondria. Toxics 2017, 6, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sidthilaw, S.; Sapbamrer, R.; Pothirat, C.; Wunnapuk, K.; Khacha-ananda, S. Effects of exposure to glyphosate on oxidative stress, inflammation, and lung function in maize farmers, Northern Thailand. BMC Public Health 2022, 22, 1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, V.C.; Andreotti, G.; Ospina, M.; Parks, C.G.; Liu, D.; Shearer, J.J.; Rothman, N.; Silverman, D.T.; Sandler, D.P.; Calafat, A.M.; et al. Glyphosate exposure and urinary oxidative stress biomarkers in the Agricultural Health Study. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2023, 115, 394–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eaton, J.L.; Cathey, A.L.; Fernandez, J.A.; Watkins, D.J.; Silver, M.K.; Milne, G.L.; Velez-Vega, C.; Rosario, Z.; Cordero, J.; Alshawabkeh, A.; et al. The association between urinary glyphosate and aminomethyl phosphonic acid with biomarkers of oxidative stress among pregnant women in the PROTECT birth cohort study. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 233, 113300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasseur, C.; Serra, L.; El Balkhi, S.; Lefort, G.; Ramé, C.; Froment, P.; Dupont, J. Glyphosate presence in human sperm: First report and positive correlation with oxidative stress in an infertile French population. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2024, 278, 116410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Zhang, J.; Yang, L.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, D.; Jiang, H.; Li, Y.; Dong, H.; Ma, T.; et al. Glyphosate exposure attenuates testosterone synthesis via NR1D1 inhibition of StAR expression in mouse Leydig cells. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 785, 147323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, W.L.; Auchus, R.J. The molecular biology, biochemistry, and physiology of human steroidogenesis and its disorders. Endocr. Rev. 2011, 32, 81–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, W.L. Steroidogenesis: Unanswered Questions. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2017, 28, 771–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammond, G.L. Diverse roles for sex hormone-binding globulin in reproduction. Biol. Reprod. 2011, 85, 431–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connolly, A.; Jones, K.; Basinas, I.; Galea, K.S.; Kenny, L.; McGowan, P.; Coggins, M.A. Exploring the half-life of glyphosate in human urine samples. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2019, 222, 205–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarwal, A.; Aponte-Mellado, A.; Premkumar, B.J.; Shaman, A.; Gupta, S. The effects of oxidative stress on female reproduction: A review. Reprod. Biol. Endocrinol. 2012, 10, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herbison, A.E. Control of puberty onset and fertility by gonadotropin-releasing hormone neurons. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2016, 12, 452–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pugeat, M.; Crave, J.C.; Tourniaire, J.; Forest, M.G. Clinical utility of sex hormone-binding globulin measurement. Horm. Res. 1996, 45, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Number | Glyphosate (µg/g Creatinine) | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Total | 1532 | 0.38 (0.46) | |
| Sex | <0.001 | ||
| Male | 751 | 0.34 (0.36) | |
| Female | 781 | 0.43 (0.54) | |
| Age (years) | <0.001 | ||
| 6–17 | 223 | 0.41 (0.38) | |
| 18–59 | 842 | 0.31 (0.35) | |
| ≥60 | 467 | 0.50 (0.62) | |
| Ethnicity | <0.01 | ||
| Mexican-American | 241 | 0.38 (0.55) | |
| Other Hispanic | 140 | 0.38 (0.42) | |
| Non-Hispanic white | 553 | 0.43 (0.49) | |
| Non-Hispanic black | 324 | 0.30 (0.30) | |
| Non-Hispanic Asian | 191 | 0.39 (0.47) | |
| Other ethnicity | 83 | 0.42 (0.47) | |
| BMI z-score | <0.001 | ||
| <−0.39 | 517 | 0.45 (0.60) | |
| 0.5 | 505 | 0.37 (0.41) | |
| ≥0.5 | 510 | 0.33 (0.32) | |
| Smoking status * | <0.05 | ||
| Non-smoker | 795 | 0.40 (0.50) | |
| ETS | 223 | 0.34 (0.41) | |
| Current smoker | 291 | 0.34 (0.43) | |
| Alcohol consumption (drink/year) * | <0.001 | ||
| <12 | 540 | 0.33 (0.37) | |
| ≥12 | 769 | 0.41 (0.52) | |
| eGFR (mL/min/1.73 m2) * | 0.185 | ||
| <60 | 70 | 0.45 (0.45) | |
| ≥60 | 1239 | 0.37 (0.47) |
| Female | Male | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Children | Adolescents | Pre-Menopause | Menopause | Children | Adolescents | Adults | |
| Number | 28 | 99 | 259 | 395 | 11 | 85 | 655 |
| Glyphosate (ug/L) | 0.60 (0.21–1.04) | 0.26 (0.12–0.54) | 0.22 (0.11–0.44) | 0.23 (0.10–0.46) | 0.38 (0.23–0.63) | 0.38 (0.21–0.72) | 0.28 (0.14–0.53) |
| Glyphosate (μg/g creatinine) | 0.71 (0.52–1.45) | 0.24 (0.17–0.45) | 0.22 (0.13–0.36) | 0.29 (0.17–0.55) | 0.45 (0.29–0.62) | 0.25 (0.14–0.37) | 0.23 (0.13–0.38) |
| FSH (mIU/mL) | 2.07 (1.19–3.31) | 5.08 (3.87–6.63) | 5.27 (3.55–7.20) | 50.70 (31.31–73.45) | 1.84 (0.44–2.36) | 3.38 (2.24–5.11) | 4.70 (3.11–7.93) |
| LH (mIU/mL) | 0.10 (0.07–0.23) | 5.39 (3.19–8.35) | 7.48 (5.07–11.51) | 26.78 (15.77–37.55) | 0.60 (0.07–2.44) | 4.08 (2.72–5.64) | 5.77 (4.07–8.01) |
| AMH (ng/mL) | 1.99 (1.58–2.66) | 2.69 (1.92–4.41) | 2.12 (0.77–4.07) | 0.02 (0.02–0.02) | 15.97 (11.28–37.28) | 6.11 (4.42–8.48) | 4.26 (2.67–6.78) |
| Androstenedione (ng/dL) | 15.00 (8.13–22.03) | 103.00 (72.50–147.00) | 119.00 (83.50–151.00) | 46.50 (32.40–67.10) | 27.10 (12.80–32.90) | 56.70 (40.55–76.00) | 65.00 (49.70–85.60) |
| Estradiol (pg/mL) | 1.91 (1.22–9.57) | 49.70 (22.90–86.60) | 101.00 (50.60–168.00) | 6.78 (3.54–13.70) | 1.85 (1.22–5.04) | 18.40 (11.50–26.10) | 24.10 (18.50–31.40) |
| Estrone (ng/dL) | 0.42 (0.17–0.57) | 3.94 (2.64–6.52) | 7.59 (5.20–11.30) | 2.53 (1.68–3.78) | 0.57 (0.36–1.06) | 2.09 (1.70–2.96) | 3.42 (2.67–4.50) |
| Estrone Sulfate (pg/mL) | 48.70 (25.43–77.45) | 844.00 (376.00–1660.00) | 1400.00 (744.00–2440.00) | 262.00 (136.00–481.00) | 61.20 (24.60–116.00) | 452.00 (238.50–713.50) | 615.00 (371.00–954.00) |
| 17α-hydroxyprogesterone (ng/dL) * | 35.95 (25.28–75.38) | 69.30 (33.40–140.00) | 17.30 (11.00–26.30) | 70.90 (42.90–115.50) | 65.60 (44.50–94.30) | ||
| Progesterone (ng/dL) | 3.16 (1.97–3.86) | 8.01 (5.01–84.80) | 32.50 (7.28–743.00) | 3.18 (2.01–5.50) | 2.82 (1.93–5.03) | 4.42 (2.97–9.09) | 4.97 (3.21–7.89) |
| SHBG (nmol/L) | 84.84 (61.54–118.80) | 41.82 (27.69–57.74) | 52.44 (34.62–78.63 | 50.54 (33.72–78.19) | 89.39 (57.46–97.65) | 26.26 (18.26–36.28) | 34.68 (24.03–47.85) |
| Glyphosate (µg/L) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| β Coeff (S.E.) | p Value | p for Interaction (Age) | p for Interaction (Sex) | p for Interaction (Ethnicity) | p for Interaction (BMI z-Score) | |
| FSH (mIU/mL) | 0.083 (0.054) | 0.144 | 0.138 | 0.843 | 0.505 | 0.715 |
| LH (mIU/mL) | −0.024 (0.066) | 0.721 | 0.896 | 0.217 | 0.070 | 0.168 |
| AMH (ng/mL) | −0.140 (0.061) | <0.05 | <0.05 | 0.958 | 0.305 | 0.338 |
| Androstenedione (ng/dL) | −0.134 (0.027) | <0.001 | 0.879 | 0.686 | 0.813 | 0.661 |
| Estradiol (pg/mL) | −0.185 (0.079) | <0.05 | 0.066 | 0.369 | 0.783 | 0.888 |
| Estrone (ng/dL) | −0.132 (0.052) | <0.05 | <0.05 | 0.110 | 0.932 | 0.874 |
| Estrone Sulfate (pg/mL) | −0.196 (0.045) | <0.001 | 0.076 | 0.094 | 0.587 | 0.763 |
| 17α-hydroxyprogesterone (ng/dL) * | −0.097 (0.45) | <0.05 | 0.064 | 0.093 | 0.907 | 0.751 |
| Progesterone (ng/dL) | −0.212 (0.085) | <0.05 | 0.835 | 0.744 | 0.519 | 0.378 |
| SHBG (nmol/L) | 0.080 (0.022) | <0.01 | 0.110 | 0.443 | 0.686 | 0.378 |
| Glyphosate (µg/L) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | Male | Female | ||||
| Number | 223 | 96 | 127 | |||
| β Coefficient (S.E.) | p Value | β Coefficient (S.E.) | p Value | β Coefficient (S.E.) | p Value | |
| FSH (mIU/mL) | −0.037 (0.048) | 0.450 | −0.135 (0.078) | 0.105 | 0.008 (0.096) | 0.937 |
| LH (mIU/mL) | −0.134 (0.107) | 0.227 | −0.131 (0.089) | 0.163 | −0.196 (0.138) | 0.177 |
| AMH (ng/mL) | −0.022 (0.071) | 0.763 | 0.097 (0.118) | 0.425 | −0.092 (0.058) | 0.134 |
| Androstenedione (ng/dL) | −0.075 (0.050) | 0.154 | −0.081 (0.068) | 0.252 | −0.096 (0.074) | 0.215 |
| Estradiol (pg/mL) | −0.103 (0.130) | 0.440 | −0.262 (0.095) | <0.05 | −0.002 (0.198) | 0.993 |
| Estrone (ng/dL) | −0.056 (0.073) | 0.454 | −0.040 (0.057) | 0.498 | −0.094 (0.110) | 0.408 |
| Estrone sulfate (pg/mL) | −0.156 (0.096) | 0.125 | −0.374 (0.105) | <0.01 | −0.075 (0.138) | 0.593 |
| 17α-hydroxyprogesterone (ng/dL) | −0.030 (0.124) | 0.815 | −0.195 (0.199) | 0.345 | 0.331 (0.180) | 0.088 |
| Progesterone (ng/dL) | 0.149 (0.161) | 0.371 | −0.002 (0.158) | 0.990 | 0.484 (0.270) | 0.095 |
| SHBG (nmol/L) | 0.072 (0.085) | 0.410 | 0.160 (0.074) | <0.05 | −0.004 (0.066) | 0.950 |
| Glyphosate (µg/L) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | Male | Female | ||||
| Number | 1309 | 655 | 654 | |||
| β Coefficient (S.E.) | p Value | β Coefficient (S.E.) | p Value | β Coefficient (S.E.) | p Value | |
| FSH (mIU/mL) | ||||||
| Model 1 | 0.078 (0.056) | 0.182 | 0.110 (0.055) | 0.066 | 0.006 (0.078) | 0.936 |
| Model 2 | 0.074 (0.059) | 0.228 | 0.104 (0.057) | 0.090 | 0.023 (0.080) | 0.779 |
| LH (mIU/mL) | ||||||
| Model 1 | 0.068 (0.056) | 0.246 | 0.131 (0.068) | 0.075 | −0.018 (0.067) | 0.789 |
| Model 2 | 0.062 (0.062) | 0.332 | 0.121 (0.071) | 0.110 | −0.011 (0.073) | 0.883 |
| AMH (ng/mL) | ||||||
| Model 1 | −0.115 (0.065) | 0.098 | −0.044 (0.055) | 0.428 | −0.048 (0.084) | 0.573 |
| Model 2 | −0.103 (0.066) | 0.140 | −0.033 (0.049) | 0.503 | −0.066 (0.089) | 0.469 |
| Androstenedione (ng/dL) | ||||||
| Model 1 | −0.064 (0.028) | <0.05 | −0.062 (0.032) | 0.073 | −0.045 (0.042) | 0.294 |
| Model 2 | −0.069 (0.029) | <0.05 | −0.081 (0.031) | <0.05 | −0.052 (0.042) | 0.235 |
| Estradiol (pg/mL) | ||||||
| Model 1 | −0.064 (0.082) | 0.446 | −0.068 (0.025) | <0.05 | 0.008 (0.115) | 0.943 |
| Model 2 | −0.058 (0.082) | 0.489 | −0.067 (0.024) | <0.05 | 0.007 (0.113) | 0.952 |
| Estrone (ng/dL) | ||||||
| Model 1 | −0.035 (0.047) | 0.476 | −0.084 (0.029) | <0.05 | 0.036 (0.067) | 0.593 |
| Model 2 | −0.032 (0.047) | 0.507 | −0.088 (0.028) | <0.01 | 0.038 (0.065) | 0.570 |
| Estrone sulfate (pg/mL) | ||||||
| Model 1 | −0.075 (0.042) | 0.092 | −0.115 (0.032) | <0.01 | −0.001 (0.069) | 0.993 |
| Model 2 | −0.059 (0.043) | 0.187 | −0.094 (0.033) | <0.05 | 0.005 (0.069) | 0.943 |
| 17α-hydroxyprogesterone (ng/dL) | ||||||
| Model 1 | −0.088 (0.041) | <0.05 | −0.126 (0.035) | <0.01 | −0.033 (0.064) | 0.617 |
| Model 2 | −0.088 (0.040) | <0.05 | −0.131 (0.036) | <0.01 | −0.046 (0.063) | 0.476 |
| Progesterone (ng/dL) | ||||||
| Model 1 | −0.146 (0.082) | 0.097 | −0.087 (0.051) | 0.109 | −0.126 (0.136) | 0.367 |
| Model 2 | −0.145 (0.084) | 0.104 | −0.100 (0.052) | 0.071 | −0.140 (0.133) | 0.311 |
| SHBG (nmol/L) | ||||||
| Model 1 | 0.056 (0.021) | <0.05 | 0.046 (0.033) | 0.182 | 0.072 (0.031) | <0.05 |
| Model 2 | 0.056 (0.020) | <0.05 | 0.028 (0.029) | 0.352 | 0.073 (0.032) | <0.05 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, W.-Y.; Wang, D.-S.; Lin, H.-C.; Wang, C.; Lin, C.-Y. Urinary Glyphosate Concentrations and Serum Sex Hormones in a Nationally Representative U.S. Sample: NHANES 2017–2018. Life 2025, 15, 1024. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15071024
Wu W-Y, Wang D-S, Lin H-C, Wang C, Lin C-Y. Urinary Glyphosate Concentrations and Serum Sex Hormones in a Nationally Representative U.S. Sample: NHANES 2017–2018. Life. 2025; 15(7):1024. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15071024
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Wen-Yang, Du-Sheng Wang, Hsuan-Cheng Lin, Chikang Wang, and Chien-Yu Lin. 2025. "Urinary Glyphosate Concentrations and Serum Sex Hormones in a Nationally Representative U.S. Sample: NHANES 2017–2018" Life 15, no. 7: 1024. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15071024
APA StyleWu, W.-Y., Wang, D.-S., Lin, H.-C., Wang, C., & Lin, C.-Y. (2025). Urinary Glyphosate Concentrations and Serum Sex Hormones in a Nationally Representative U.S. Sample: NHANES 2017–2018. Life, 15(7), 1024. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15071024







