Abstract
Specific gut microorganisms and their metabolic by-products have been identified as key regulators of host physiology, contributing to the modulation of the immune system, inflammatory processes, brain function, and behavior, which highlights the gut microbiome as a potential modulator of the neurobiological mechanisms involved in substance use disorders. This narrative review provides an updated overview of how drugs of abuse influence the composition and dynamics of the human gut microbiome and how bacterial dysbiosis may be a contributing factor to substance use disorders by modulating the communication between the gut and the brain. Thus, by examining commonly abused substances such as alcohol, psychostimulants, opioids, cannabinoids, and nicotine, this review aimed to deepen the understanding of the bidirectional relationship between the gut microbiome and substance use. There is evidence indicating that gut microbiome alterations may influence addiction through changes in gut-brain signaling. Furthermore, changes in the gut microbiome and its metabolites may not only result from substance use disorders, but could also modulate behavioral responses to drugs of abuse. Although the exact mechanisms by which the gut microbiome modulates behavioral responses to drugs of abuse are not fully understood, microbial products such as short-chain fatty acids, tryptophan metabolites, bile acids, and neurotransmitters have been suggested to play a role in this process by influencing the blood–brain barrier permeability, host immune activation, neural signaling, and gene expression. Therefore, manipulating the gut microbiome or its by-products may represent a promising approach for enhancing substance use disorder treatments, identifying individuals at increased risk of pathological drug use, and elucidating its role in substance-related behaviors.
1. Introduction
Initial experimentation with drugs of abuse is typically prompted by curiosity and expansion motives, but through repeated reinforcement, this behavior can transform into a habitual pattern, ultimately culminating in a substance use disorder (SUD) [1]. SUDs are psychiatric conditions with a high morbidity worldwide, characterized by the abusive and/or hazardous consumption of one or multiple drugs [2]. Although SUDs can include several substances with different molecular mechanisms of action, in most cases, they share common patterns such as craving, seeking, dependence, abstinence, and relapse [2]. SUDs result in functional and health-related adverse outcomes, constituting a significant threat to individual and community well-being [3]. Evidence-based treatments can support recovery, but evolving substance use patterns challenge their long-term effectiveness, highlighting the need for new approaches to address factors such as drug potency, overdose risk, and the emergence of new substances and methods of use [3]. In addition, an increase in consumption intensity and more severe SUDs among young populations further underscores the need to understand the underlying mechanisms involved in substance use [4].
Substance use exerts a direct neurobiological effect and triggers different behavioral responses that can be directly or indirectly modulated by various host systems such as the endocrine system [5,6], the immune system [7], and the gut microbiome (GM) [8,9]. A multitude of mechanisms and pathways have been postulated through which SUDs can influence the diversity and composition of the GM including dietary habits, xenobiotic effects of the drugs, and alteration of the neural regulation of gut motility [10,11,12,13].
The human GM harbors a highly diverse and dense microbial community, estimated to contain between 1011 and 1012 microbial cells per milliliter [14]. This community encompasses representatives from multiple microbial domains, including bacteria, archaea, protozoa, viruses, and fungi, with bacteria constituting the most predominant taxon [15,16]. The bacteria domain comprises more than 3000 species belonging to the following eight phyla: Actinomycetota, Bacillota, Bacteroidota, Campylobacterota, Fusobacteriota, Pseudomonadota, Thermodesulfobacteriota, and Verrucomicrobiota [14,17,18]. Although the taxonomic and functional composition of the GM is shaped by several host-related and environmental factors (e.g., genetics, age, dietary habits, drug consumption, psychological stressors) [19,20,21,22,23,24], certain bacterial genera consistently dominate in healthy individuals including Lactobacillus, Bacillus, Clostridium, Enterococcus, Ruminococcus, Faecalibacterium, Roseburia, Blautia, Dorea, and Eubacterium (phylum Bacillota); Bacteroides and Prevotella (phylum Bacteroidota); Bifidobacterium (phylum Actinomycetota); and Escherichia (phylum Pseudomonadota) [14,16,25]. However, disruption of the ecological balance of the GM leads to a state known as bacterial dysbiosis, which affects microbial diversity, alters metabolic and immune-related functions, and compromises intestinal barrier integrity [26].
A substantial body of evidence has revealed the existence of a connection between the brain and the gut via the vagus nerve and chemical molecules including microbial metabolites, hormones, and neurotransmitters [12,27,28]. In particular, specific gut microorganisms and their metabolic by-products have been identified as key regulators of host physiology, contributing to the modulation of the immune system [29,30], inflammatory processes [31,32], and brain function and behavior [33,34]. These findings have progressively highlighted the GM as a potential modulator of the neurobiological mechanisms involved in SUDs. However, despite the considerable number of studies investigating the link between the GM and SUDs in animal models, research in humans remains scarce and has primarily focused on the effects of individual substances [12,35,36]. In response, this narrative review provides an updated overview of how drugs of abuse influence the composition and dynamics of the human GM and how bacterial dysbiosis may be a contributing factor to SUDs by modulating the communication between the gut and the brain. Thus, by examining commonly abused substances such as alcohol, psychostimulants, opioids, cannabinoids, and nicotine, this review aims to deepen the understanding of the bidirectional relationship between the GM and substance use.
2. Method
The present review adopted a narrative approach, synthesizing the existing literature in a qualitative and interpretative manner to provide an overview of the topic and present an informed analysis [37]. Both authors independently conducted an extensive literature search aligned with the subject under investigation. For this purpose, the PubMed, Scopus, and Web of Science databases were examined from January to February 2025 using various combinations of terms related to the research topic. The search strategy also involved reviewing reference lists from previous studies and research articles. All relevant records were independently evaluated by both authors, considering studies conducted on humans and focusing on the impact of substances of abuse on the GM or vice versa. In the initial stage, the title and abstract of each article were reviewed for relevance. Duplicate entries were removed as well as studies unlikely to meet the inclusion criteria due to their subject matter. The remaining articles were thoroughly assessed, and pertinent data were extracted for further analysis. Studies lacking substantial information on the relationship between the human GM and substance use or SUDs as well as those based on meta-analyses of endocrine disorders or related to physiological, autoimmune, or viral diseases were excluded from the review.
3. Substances of Abuse and Human GM Composition
Recent interest has focused on the potential role of GM dysbiosis in the pathogenesis of SUDs, with some evidence suggesting that GM alterations may influence addiction via changes in gut-brain signaling. Furthermore, changes in the GM and its metabolites may not only result from SUDs, but could also modulate behavioral responses to substances of abuse. The following section examines the impact of various substances on GM composition.
3.1. Alcohol
Alcohol is one of the most ancient and widely consumed psychoactive substances, primarily acting as a central nervous system depressant by enhancing γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) activity, the brain’s main inhibitory neurotransmitter, thereby exerting sedative and anxiolytic effects [38]. It also targets N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptors, which are key components of the glutamatergic system involved in synaptic plasticity, learning, and memory, further contributing to its neurodepressive action [39]. Chronic alcohol misuse leads to alcohol use disorder (AUD), a complex condition that encompasses a broad spectrum of neurological, metabolic, and psychological symptoms, with significant implications for individual, social, and public health [40]. Notably, severe withdrawal syndrome related to AUD (i.e., delirium tremens) is associated with high mortality rates [41]. In terms of immune function and disease, alcohol displays a dose-dependent relationship: high levels of consumption are consistently associated with increased risk for both infectious and non-communicable diseases, whereas low-to-moderate intake may confer protective effects in specific contexts including certain autoimmune diseases [42,43]. Nevertheless, the classification of drinking patterns remains inconsistent across the literature, with substantial variability in the definitions of low, moderate, and heavy alcohol consumption [44]. In addition, large interindividual and interethnic differences in alcohol-induced toxicity have been attributed to genetic and environmental variability in ethanol metabolism [45]. Moreover, recent studies have identified a direct link between alterations in GM composition and both acute and chronic alcohol consumption, highlighting a potential pathway through which this substance exerts systemic effects [46,47].
Various studies have indicated that alcohol consumption produces an increase in the abundance of the bacterial families Erysipelotrichaceae, Enterobacteriaceae, and Lachnospiraceae, in the genera Bacteroides, Sutterella, Streptococcus, Holdemania, and Clostridium as well as a decrease in the genera Akkermansia and Faecalibacterium [48,49,50,51]. More recently, Du et al. [52] reported alterations in GM diversity and composition among patients with AUD, characterized by reduced α-diversity and elevated β-diversity indices. These dysregulated indices included a lower abundance of members from the genera Bacteroides, Faecalibacterium, Dialister, Clostridium cluster XIVa, Lachnospiraceae incertae sedis, and Gemmiger, alongside the increased representation of genera including Prevotella, Megamonas, Escherichia, Coprobacillus, Clostridium, Gemella, Rothia, and Fusobacterium. In patients with alcoholic cirrhosis, Baltazar-Díaz et al. [53] found an increase in Escherichia/Shigella and Prevotella and a decrease in the Blautia and Faecalibacterium genera.
Dysbiosis associated with alcohol consumption has been shown to provoke a series of biochemical, physiological, and immunological alterations including oxidative stress and the downregulation of antibacterial peptides such as α-defensins [54,55]. Furthermore, microbial dysbiosis has been demonstrated to compromise the integrity of the intestinal mucous barrier by increasing circulating pro-inflammatory cytokines like tumor necrosis factor (TNF-α) and interleukin IL-1β [56,57]. This phenomenon may, in turn, contribute to the development of liver diseases including alcoholic hepatitis and chronic alcohol-related cirrhosis [55,56,58].
The augmented prevalence of Bacteroidota and Fusobacteriota in AUD patients suggests a potential implication of alcohol consumption in colorectal cancer pathogenesis, given the established correlation between alcohol metabolism and the subsequent tumorigenesis driven by Fusobacterium [59]. Conversely, the heightened prevalence of Pseudomonadota members, including Escherichia and Shigella genera, in individuals with AUD [48] could be associated with gut inflammation [60]. This inflammation has been shown to trigger IL-1β and corticosterone production, which has been related to depression and cognitive impairment [61,62]. Moreover, the levels of Faecalibacterium were reduced in AUD individuals, indicating that alcohol intake results in negative outcomes for beneficial gut bacteria, which plays a pivotal role on anticancer immunosurveillance and liver pathologies [63,64].
The variation in the abundance of Faecalibacterium, Gemmiger, Escherichia, and Fusobacterium in the GM of AUD individuals has been suggested as an indicator to predict cognitive impairment in domains such as emotional processing, memory, and executive functions [65,66]. Indeed, numerous authors have underscored the pivotal role of the GM in emotional and social cognition including drug addiction [15,67,68]. In this sense, Ling et al. [69] reported that the abundance of Faecalibacterium and Gemmiger, both butyrate-producing genera, was reduced in AUD patients, which positively correlated with cognitive functions [70], while showed a negative correlation with inflammatory cytokines like TNF-α and chemokines [69].
Binge Drinking and Alcohol Craving
The term “binge drinking” defines the rapid consumption of a substantial quantity of alcohol within a short timeframe, leading to a sudden increase in blood alcohol concentration [71]. This practice is particularly prevalent during adolescence, a period when social and emotional traits are undergoing significant development [67,72,73,74,75]. Consequently, binge drinking may imply a significant impact on future alcohol consumption patterns [76]. Carbia et al. [77] examined the relationship between binge drinking and GM dysbiosis, along with the concomitant social cognition. Their findings revealed that among adolescents engaging in binge drinking, there was no difference in α-diversity index. On the other hand, β-diversity exhibited a relationship with alcohol consumption, with changes in diversity contingent on the amount of alcohol consumed. The GM composition showed significant alterations in the genera Alistipes (decreases) and Veillonella (increases), although binge drinking was also linked to changes in the abundance of Bacteroides spp., Blautia wexlerae, Ruminococcus lactaris, and Coprococcus eutactus. Concerning this issue, β-diversity differences associated with young people and the relationship between decreases in Alistipes or increases in Veillonella with several liver diseases have been reported by different authors [78,79,80,81].
Alcohol craving, a critical mechanism implicated in AUD, is characterized by an intense urge or irrepressible desire to consume alcohol. Impulsivity has been noted as a pivotal factor in the development of craving [82]. Nevertheless, associations with inhibition and thought suppression continue to be insufficiently clarified in the current body of research [83]. Alcohol craving has been associated with a decrease in Ruthenibacterium lactatiformans (family Ruminococcaceae), and a reduced abundance of members of this taxon has also been related to high levels of craving in AUD patients [68]. In the context of social cognition, Carbia et al. [77] observed that a decline in the levels of Clostridium spp., Flavonifractor plautii, and Eggerthella lenta, accompanied by an increase in Coprococcus spp., was linked to a diminished recognition of sadness. Conversely, heightened impulsivity was related to a decrease in Collinsella spp. and to an increase in Roseburia and Parabacteroides spp.
3.2. Psychostimulants
Psychostimulants are substances that indirectly activate the sympathetic nervous system, sharing characteristics with sympathomimetic agents and possessing a significant risk for abuse and dependency. They primarily act by increasing synaptic dopamine release and enhancing the availability of monoamines like dopamine, norepinephrine, and serotonin [84]. Psychostimulants are well-known for their energizing effects and widespread use, encompassing both prescribed and non-prescribed applications, which is why they are commonly consumed to enhance performance and for recreational purposes [85]. Psychostimulants exhibit diverse chemical structures and mechanisms of action, contributing to their varying effects on neurotransmitter systems, which result in differences in mood, alertness, and cognitive performance [86]. Prolonged use may lead to SUDs, manifesting as clinically significant impairments and distress [87]. Psychostimulants can be classified into two major groups: those that act as passive monoamine reuptake inhibitors (e.g., cocaine) and those that stimulate monoamine release by serving as substrates for monoamine transporters (e.g., amphetamines). Despite differences in their chemical structures, both classes produce similar discriminative stimulus effects, primarily mediated by dopaminergic mechanisms, although these effects can also be modulated by changes in the noradrenergic and serotonergic systems [86]. The abuse of psychostimulants induces various neurochemical changes, including alterations in dopaminergic, glutamatergic, serotonergic, and GABAergic signaling, and is associated with oxidative stress and epigenetic modifications, such as altered DNA methylation and gene expression, contributing to neurological impairments [88,89]. Although clinical studies on the influence of psychostimulants on the GM are limited, emerging evidence points to a bidirectional relationship between psychostimulant use and GM composition, with the GM modulating the behavioral response of the brain and vice versa [84].
Clinical studies on the influence of psychostimulants (e.g., cocaine, amphetamines, methamphetamine, MDMA) on the human GM are sparse. However, research has revealed a reciprocal relationship between the GM and psychostimulant drugs, with the latter modulating the brain’s behavioral response [84]. In a study on cocaine users, Volpe et al. [90] reported that drug use was linked to an increased and decreased abundance in the Bacteroidota and Bacillota phyla members, respectively. However, a study on methamphetamine use revealed no significant alterations in GM diversity [91], although the drug administration was associated with increases in Murdochiella and Eubacterium, along with a decrease in Butyricicoccus and Faecalibacterium. Concurrently, other clinical studies have demonstrated that methamphetamines compromise the intestinal barrier and trigger inflammatory responses, thereby disrupting the gut ecosystem [92,93].
Yang et al. [94] reported significant reductions in Deltaproteobacteria and Bacteroidaceae levels, alongside an increased abundance of Xanthomonadales, Sphingomonadales, Lachnospiraceae, and Romboutsia in the GM of methamphetamine users. Moreover, the abundance of Fusobacteriota phylum was found to be correlated with the duration of drug use. In a recent study performed by He et al. [95], it was established that participants with methamphetamine use disorder (MUD) and methamphetamine causal use (MCU) exhibited significant changes in their GM composition compared with the control group. The most prevalent phyla in the MCU and MUD groups were Bacillota (70%), Bacteriodota (20%), Pseudomonadota (5%) and Actinomycetota (>2%). At the genera level, the GM showed a preponderance of Faecalibacterium, Bacteroides, Roseburia, Ruminococcus, Megamonas, Prevotella, Lachnospira, Blautia, Coprococcus, and Dialister among both groups. These authors also reported higher abundance of the Clostridiaceae, Halomonadaceae, Hyphomicrobiaceae, and Xanthomonadaceae families, and the Halomonas, Clostridium, Devosia, and Dorea genera in the GM of the MUD group compared with the MCU group. In the context of cocaine, Gerace et al. [96] observed that the predominant genera in stool samples of consumers were Bacteroides, Bifidobacterium, Blautia, Collinsella, and Faecalibacterium. A subsequent comparison of the GM of cocaine users with that of non-users revealed a significant reduction in the α-diversity among the former group. In addition, they identified higher fecal abundances of Dorea, Erysipelotrichaceae, Eubacterium, Blautia, Collinsella, Holdemanella, Escherichia/Shigella, Megamonas, Romboutsia, Peptococcus, Senegalimassilia, Rothia, Turicibacter, and Streptococcus. Conversely, a decrease in Christensenellaceae, Desulfovibrionaceae, Lachnospiraceae, Alistipes, Bacteroides, Coprobacter, Odoribacter, Oscillospira, Paraprevotella, Parasutterella, Sutterella, and Barnesiella was found in the cohort of drug users.
GM dysbiosis triggered by psychostimulant use has been linked to a number of physiological diseases including inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract, Crohn’s disease, and colorectal cancer [97,98,99]. Furthermore, the depletion of GM in psychostimulant users has been demonstrated to alter the genes related to synaptic plasticity, resulting in an increased inclination toward drug seeking and use following prolonged abstinence [100,101]. Recent studies have indicated a potential association between genetics and/or neuroimmunology and methamphetamine addiction [93,102,103]. Moreover, methamphetamine-dependent individuals have been observed to exhibit a heightened prevalence of psychotic symptoms and psychiatric disorders [94,95,104]. Anxiety, depression, violent behavior, insomnia, psychosis, and schizophrenia have also been reported in chronic methamphetamine users [98,105,106].
3.3. Opioids
Opioids are a group of powerful drugs derived from the opium poppy plant (Papaver somniferum), widely used for their potent analgesic and sedative effects [107,108,109]. Several opioids are commonly employed in clinical practice including fentanyl, methadone, morphine, levorphanol, hydromorphone, meperidine, oxymorphone, and oxycodone [110]. Despite their extraordinary clinical utility, opioids carry a high risk of dependency and abuse [111], raising significant concerns regarding their impact on public health including the dramatic recent increase in overdose deaths [112]. Opioids produce their effects by binding to G-protein-coupled opioid receptors (μ, κ, δ, and NOP), which are found in the brain, periphery, and gut [113,114]. These receptors are activated by both endogenous neurotransmitters, hormones, and peptides (e.g., enkephalins, endorphins) as well as exogenous opioids (e.g., heroin, morphine, fentanyl), modulating pain and other physiological processes [114]. However, prolonged opioid use can result in opioid use disorder (OUD), a persistent condition characterized by clinically significant impairment, intense withdrawal symptoms, and recurrent relapse [115]. Moreover, the economic burden of OUD has been reported, affecting insurers, healthcare payers, and individuals or families, contributing to significant financial strain on both personal and public healthcare systems [112]. Opioids also affect the gut by causing peristaltic slowing and constipation, which can lead to changes in gut barrier permeability and promote bacterial translocation [35,115,116,117]. These disruptions contribute to dysbiosis of the GM, which in turn plays a significant role in opioid tolerance. The alterations in GM composition exacerbate the effects of opioids, creating a detrimental positive feedback loop that further impacts gut health and opioid response [118].
The relationship between gut dysbiosis and OUD in humans has received scant attention from the research community [24,112]. The GM of OUD patients has been observed to exhibit an increase in α-diversity, a phenomenon attributed to the time-delay in colon transit induced by the opioids, which has been demonstrated to enhance bacterial proliferation within the gastrointestinal tract [119]. Clinical studies on chronic opioid users have shown a reduction in members of the phylum Bacteroidota, family Bacteroidaceae, and genus Bacteroides [24,120]. Contradictory results have also been reported regarding the abundance of the genera Prevotella, Bifidobacterium, and Ruminococcus as well as of the family Ruminococcaceae in the GM of individuals with OUD [24,120,121]. In turn, opioid use also induces other GM changes, exerting a deleterious effect on members of the family Bacteroidaceae and the genera Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium [112]. Concurrently, it has been demonstrated to stimulate an increase in the prevalence of several pathogenic genera such as Enterococcus, Flavobacterium, Fusobacterium, Sutterella, Ruminococcus, and Clostridium [122,123]. Interestingly, Bacteroidaceae members have been shown to prevent the overgrowth of these nosocomial pathogenic bacteria, which are a cause of serious microbial infections that necessitate hospitalization [124]. The association of opioid use with an elevated risk of sepsis has been posited by several authors [115,125,126].
Numerous studies have documented the implications of OUD on diverse immune system functions, such as the upregulation of pro-inflammatory cytokines following short- or prolonged-exposure to opioids, the enhanced activation of microglia, the attenuation of the immune response to microbial pathogens [84,127,128], and the disruption of intestinal permeability, resulting in systemic bacterial propagation [125,129]. The neuroinflammation that results from prolonged opioid use may play a role in the development of drug-related symptoms including tolerance, dependence, reward processing, anxiety, and depression [84,122,130].
3.4. Cannabinoids
Cannabinoids are bioactive compounds found in the cannabis plant (Cannabis sativa) that interact with the endocannabinoid system (ECS), including psychoactive Δ-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (Δ9-THC) and non-psychoactive compounds such as cannabigerol (CBG), cannabichromene (CBC), and cannabidiol (CBD), among over 560 other identified constituents, all of which are related to natural endocannabinoids (eCBs) [131,132]. Cannabinoids are consumed worldwide for cultural, medicinal, and recreational purposes, exhibiting low dependence potential, mild side effects, and a broad range of therapeutic benefits including anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, and immunosuppressive effects as well as positive outcomes in several physiological, physical, neurological, neurodegenerative, and mental health conditions [133,134,135,136,137,138]. In contrast, cannabis use has also been associated with greater levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines like IL-1β, IL-6, IL-8, and TNF-α [139]. While persistent cannabis use can lead individuals to seek treatment, its impact on health is generally less severe than that of other SUDs [140]. Furthermore, cannabinoids may influence the GM by modulating pain responses and related biological processes through their interaction with the ECS, with THC potentially preventing alterations in microbial composition and CBD supporting gut health and motility, offering a beneficial effect in contrast to the detrimental impact of antibiotics on the microbiota [141,142].
The ECS serves as a crucial link between the brain and the GM, regulating intestinal homeostasis and modulating stress responses [132,143,144,145,146]. The ECS is comprised of two cannabinoid receptors (CB1 and CB2), their respective endogenous ligands, and the biosynthetic mechanisms and enzymes that regulate the availability of these ligands [147,148]. The psychoactive and gut effects of cannabis are mediated via the CB1 and CB2 receptors [149]. CB1 is expressed in the intestinal epithelium and in the brain. Its activation has been shown to reduce gastrointestinal motility and gastric acid secretion while increasing feeding and binge-like behaviors [150]. CB2, in turn, is predominantly expressed in plasmatic cells such as macrophages, with minimal expression in the brain [151]. CB2 activation has been implicated in the modulation of intestinal inflammation, the regulation of aberrant gut motility, and the limitation of visceral sensitivity and pain [152].
Considering that the most common method of human consumption of cannabis is via smoking, a paucity of studies has been performed on the effects of this substance on the GM. Cani et al. [143] established that exogenic cannabinoids and the ECS regulate the GM. In a related study, Mehrpouya-Bahrami et al. [153] reported that antagonizing CB1 attenuated cytokine release, lowered intestinal permeability, and modified the GM including an increase in Akkermansia muciniphila and a decrease in Lachnospiraceae and Erysipelotrichaceae abundances. In a cohort study involving cannabis users and non-users, Panee et al. [154] noted that the abundance of Prevotella and Bacteroides exhibited an inverse correlation among participants, with the ratio of Prevotella to Bacteroides being 13-fold higher in non-users. Human dietary interventions involving specific fatty acids have been shown to elevate the levels of eCBs, which can be attributed to changes in diverse GM such as Peptostreptococcaceae, Veillonellaceae, and Akkermansiaceae [155]. Vijay et al. [156] revealed a positive relationship of ECS with bacterial α-diversity and with short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs)-producers Bifidobacterium, Coprococcus, and Faecalibacterium, but presented a negative relationship with Collinsella and Escherichia/Shigella.
3.5. Nicotine
Nicotine is a compound derived from the tobacco plant (Nicotiana tabacum L.), predominantly consumed through cigarette smoking, consistently used for non-medical purposes, and associated with serious health consequences [157,158,159,160]. It is highly addictive, with dependence developing rapidly, making it difficult to quit [161,162,163]. Nicotine primarily acts as an agonist at most nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (nAChRs), except for the nAChRα9 and nAChRα10 subunits, where it functions as an antagonist [164]. Prolonged exposure to nicotine leads to neuroadaptations, including upregulation and desensitization of nAChRs, while withdrawal symptoms, triggered by the absence of nicotine, are primarily influenced by nAChRs containing α2, α3, α5, and β4 subunits in the epithalamic habenular complex [164]. Nicotine use, whether through smoking or vaping, affects the oral, gut, and respiratory microbiomes [165,166,167]. Smoking is a well-known risk factor for gastrointestinal cancers, Crohn’s disease, and liver disease [168,169,170]. In addition, nicotine negatively impacts specific innate immune cells such as dendritic cells, neutrophils, natural killer cells, and macrophages/monocytes [171]. Nicotine also affects the central nervous system influencing the gut–brain axis and GM composition, with nicotine exposure leading to alterations in bacterial metabolic pathways, neurotransmitter levels, and neuroactive metabolites, which contribute to physiological responses and behavioral outcomes [172].
There is a notable lack of clinical research exploring the impact of tobacco use on the GM. However, smoking withdrawal has been associated with substantial shifts in the GM, including increased microbial diversity and a higher relative abundance of the phyla Bacillota and Actinomycetota, along with a concurrent reduction in members of the Bacteroidota and Pseudomonadota phyla [173]. Subsequent research by Vogtmann et al. [174] examined the impact of smoking on the upper gastrointestinal microbiome. Their findings indicated that smoking was related to increased α- and β-diversities, with the species Dialister invisus and Megasphaera micronuciformis being the most prevalent in smokers. Conversely, decreases in microbial population diversity as well as in the genera Faecalibacterium, Collinsella, Enterorhabdus, and Gordonibacter were observed in smoking Crohn’s disease patients [175]. A parallel observation was made in another study, which reported a decline in Faecalibacterium and an increase in Proteus levels in smoking hemicolectomy patients when compared with subjects who underwent no surgical resection [176].
Lee et al. [177] reported no differences in α-diversity between three participant groups (never, former, and current smokers). However, the bacterial β-diversity showed a significant difference. Current smokers exhibited an increase in the abundance of the phylum Bacteroidota, and a decrease in Bacillota and Pseudomonadota compared with never smokers, whereas there were no differences observed between former and never smokers. In another study, Savin et al. [167] noted increases in the abundance of the Pseudomonadota and Bacteroidota phyla as well as in the genera Prevotella, Bacteroides, and Clostridium. Furthermore, a decline in the abundance of Actinomycetota and Bacillota phyla, along with the genera Bifidobacterium and Lactococcus, was also reported by these authors.
Shanahan et al. [178] demonstrated that tobacco smokers exhibited a lower bacterial diversity in the upper small intestinal mucosa in comparison with non-smokers. The GM in smokers presented a higher relative abundance of Bacillota (genera Streptococcus and Veillonella) and Actinomycetota (genus Rothia) and lower levels of Bacteroidota (genus Prevotella) and Pseudomonadota (genus Neisseria). These findings contrast with those reported by Stewart et al. [179], who observed an increase in Pseudomonadota and Bacteroidota abundance, with the predominant genera being Clostridium and Prevotella, and a decrease in the genus Bacteroides. Moreover, Nolan-Kenney et al. [180] observed a relative increase in the abundance of Catenibacterium genus, representatives of the family Erysipelotrichaceae, and of the Alphaproteobacteria taxon in current smokers. On the contrary, Lin et al. [181] revealed that cigarette and alcohol use were associated with shifts in the relative abundances of the phyla Bacteroidota and Bacillota, along with changes in over 40 bacterial genera. The most pronounced reduction in relative abundance was detected among members of the Ruminococcaceae family. More recently, Antinozzi et al. [182] examined the impact of conventional and electronic (e-) cigarette smoking on the human intestinal microbiota. The analysis showed a substantial increase in the prevalence of the Prevotella genus in cigarette smokers, but this increase was not observed in e-cigarette users. Additionally, the study identified a progressive increase in the Desulfovibrio genus, depending on the specific type of cigarette consumer, and an augmentation in the Alphaproteobacteria among current-smokers in comparison with non-smokers.
The contradictory results obtained in the aforementioned studies may be explained by the presence of different bacterial species contained in tobacco products [174,183]. In this respect, some of these bacteria are opportunistic potential pathogenic bacteria such as Campylobacter, Acinetobacter, Clostridium, Bacillus, Burkholderia, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Klebsiella, Proteus, Serratia, Staphylococcus, and Enterococcus [184]. Another potential explanation relates to the immunosuppressive nature of tobacco, which has been demonstrated to decrease the activity of natural killer cells, thereby increasing the susceptibility to microbial infection [174]. Table 1 presents the primary alterations in GM composition associated with the use of various substances.

Table 1.
Influence of various substances on the human GM composition.
4. Signal Pathways Between the GM and SUDs
The potential for substances of abuse to influence the GM may have implications for the development of addiction disorders. Although the exact mechanisms by which the GM modulates behavioral responses to drugs of abuse are not fully understood, microbial products such as SCFAs, tryptophan metabolites, bile acids, and neurotransmitters have been suggested to play a role in this process by influencing BBB permeability, host immune activation, neural signaling, and gene expression. The following section examines how these microbial products and their interactions with neural pathways may contribute to the modulation of SUDs.
4.1. Intermediate Bacterial Metabolites
SCFAs, such as butyric acid, propionic acid, and acetic acid, are bacterial metabolites that have been linked to a variety of metabolic, immunological, and neural host functions [185,186,187]. SCFAs, along with tyrptophol, an indole derivative, have been shown to regulate host cytokine production. These circulating cytokines have the potential to cross the blood–brain barrier (BBB) and exert their influence on the brain, thereby modulating behavioral response to SUDs [186,188]. In addition, SCFAs have been shown to promote beneficial effects on the host based on their anti-inflammatory properties and on their epigenetic regulation of gene expression [185,189]. Inflammation has been demonstrated to impact glutamatergic signaling, a key neurotransmitter system in drug addiction and relapse [190]. Alterations in peripheral inflammatory processes have the potential to influence drug taking and seeking behaviors in SUDs [84,191,192]. Moreover, SCFAs may act as histone deacetylase inhibitors, stimulate histone acetyltransferases, and serve as molecular substrates for histone post-translational modifications [193,194,195,196]. These modifications are critical for the proper functioning of microglia [197]. While the established role of microglia in immune surveillance is well-defined, emerging evidence suggests a potential complementary role for microglia in regulating behavioral aspects related to SUDs [198]. Furthermore, Walker and Nestler [196] proposed that the mechanisms regulating SUD-associated behaviors could involve changes in gene expression within the mesolimbic dopamine system, which is part of the brain’s reward circuitry.
The GM has been identified as a potential alternative route for the production of kynurenic acid (KYNA), an endogenous tryptophan metabolite [199]. Decreased levels of KYNA, which modulate glutamatergic neurotransmission, have been correlated with alcohol craving in AUD patients [200]. In a similar way, Morales-Puerto et al. [201] reported that the modulation of KYNA metabolism could reduce drug seeking behaviors involving various substances such as alcohol, nicotine, cannabis, amphetamines, cocaine, and opioids.
4.2. Signaling Molecules: Bile Acids and Neurotransmitters
Bile acids (BAs) are key signaling molecules that regulate immune homeostasis, inflammation induction, and even cell death. The GM is responsible for the balance of primary and secondary BAs involved in lipid intestinal absorption and in the acquisition of energy [202]. Dysbiosis, which is marked by an imbalance in the composition of the GM, has been observed to reduce the production of secondary BAs, resulting in an over-abundance of primary BAs. This, in turn, has the potential to enhance the bioavailability of drugs to the host or modify drug metabolism [203,204].
The GM produces acetylcholine, serotonin, dopamine, epinephrine, norepinephrine, and GABA, which fulfill crucial functions as neurotransmitters within the CNS [12,205]. Bacterial dysbiosis affects the synthesis and regulation of gut neurotransmitters including serotonin [206]. In a classical study, Ciccocioppo [207] reported that serotonergic 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) plays a role in the regulation of drug intake, and consequently in the maintenance of addictive behaviors. A subsequent study by Müller and Homberg [208] expanded upon this research by conducting a review of the role of 5-HT in behaviors associated with the establishment, transition, and maintenance of addiction to various drugs of abuse including amphetamines, cocaine, methamphetamine, morphine, heroin, MDMA (ecstasy), cannabis, nicotine, and alcohol. These authors identified various drug-specific mechanisms in the 5-HT system including serotonergic adaptations within this system. They also identified genetic risk factors for the establishment of controlled behaviors associated with substance use and for the transition to compulsive substance use behaviors.
The role of dopamine signaling within the nucleus accumbens in relation to the reinforcing effects of drugs is well-established. Moreover, chronic exposure to drugs, a major cause of addiction, has been shown to trigger glutamatergic-mediated neuroadaptations in dopamine striato-thalamo-cortical and limbic pathways including the amygdala and hippocampus [209]. The GM plays an important role in regulating dopamine concentrations within the brain, facilitating its synthesis and modulating its catabolism [210]. Interestingly, GM can metabolize drugs, modifying their effectiveness and pharmacokinetics [211], thereby altering the magnitude of reward and withdrawal symptoms [212].
4.3. Neural Pathways
The vagus nerve, which is a part of the parasympathetic nervous system, facilitates indirect bidirectional communication within the brain–gut axis [213]. It receives and responds to signals from gut bacterial metabolites like SCFAs [27,214]. In addition, enteroendocrine cells of the gut epithelium transmit signals to the vagus nerve via the release of serotonin, cholecystokinin, peptide YY, and glucagon-like peptide-1 [27,215]. These interactions between the gut-enteric and the nervous system may potentially influence interoceptive signals that may play a pivotal role in the development of SUDs and other psychiatric conditions [216,217]. While the role of the vagus nerve in SUD behavioral responses is well-documented, the influence of the human GM via the vagal route to modulate these responses remains to be fully elucidated [122].
Microglia constitute resident immune cells in the brain and spinal cord that are mobilized in response to CNS infection or injury and exert protection against many neurodegenerative diseases [19,218]. The activation of microglia has been shown to promote tissue repair and homeostasis through the release of cytokines and the phagocytosis of cellular debris [219]. However, the mechanisms that regulate these functions are not fully understood, especially with regard to the impact of extrinsic factors such as the human GM [220]. The GM, through the secretion of bacterial metabolites and neurotransmitters, modulates the inflammatory response of microglia in the CNS [221]. During SUDs, the resident macrophages of the CNS are activated, and the subsequent TNF-α and IL-1β released by the microglia contribute to the pathophysiology of SUDs [222]. Therefore, the communication between the microglia and GM may be regarded as an important factor in the mechanism of microglial activation during SUDs. This is due to the fact that microglial cells are dependent on a healthy and balanced GM for proper development, maturation, and function. Translocated gut bacteria can release pro-inflammatory cytokines, including TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6, which can further cause disruption in the epithelium, affecting the functionality of microglia [223].
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) has emerged as a promising candidate for elucidating the role of the GM in drug addiction. BDNF is synthesized by both neuronal and glial cells as well as by peripheral immune cells and the vascular endothelium [224]. Epigenetic modifications, specifically alterations in histone acetylation, have been identified in the context of cocaine use, and BDNF has been demonstrated to mediate the behavioral effects of opioids [225].
The hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal (HPA) axis, a neuroendocrine system linked to stress-related processes, is responsible for cortisol production in humans. Appropriate levels of this glucocorticoid are essential for normal neurodevelopment and neural function, and it also participates in several cognitive processes such as learning and memory [226]. Evidence suggests an intricate interconnection between the GM, the HPA axis, and cognitive processes through various substances (e.g., neurotransmitters, hormones, bacterial metabolites) and pathways (e.g., vagus nerve, immune system, and BBB regulation) [227]. Gut dysbiosis, resulting from drug use and other factors, can impact the stress response of the host, HPA axis activity, and even cognitive health [227]. The impact of stress on drug craving and consumption has been a subject of considerable research, with findings indicating that stress hormones may play a role in regulating these behaviors [228]. However, the specific mechanisms through which stress hormones influence addiction memory remain to be fully elucidated. Figure 1 shows various potential signal pathways between GM metabolites and SUDs.
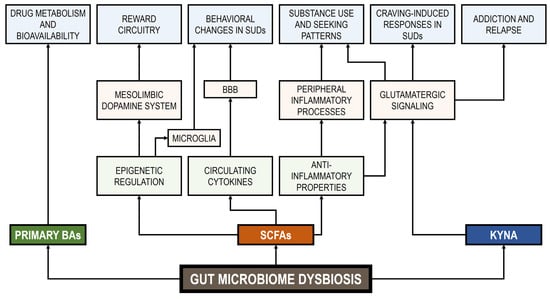
Figure 1.
Signal pathways between GM metabolites and SUDs. BBB: blood–brain barrier. BAs: bile acids. SCFAs: short-chain fatty acids. KYNA: kynurenic acid.
5. SUD Treatments
The treatment of SUDs presents significant challenges due to their complex and multifactorial etiology as well as the wide variety of effects associated with different substances of abuse [1]. For instance, treatments for alcohol, tobacco, and opioid use disorders frequently prove ineffective or unsuitable [229,230,231], while treatments for other substances such as cannabis or psychostimulant use disorders are not yet approved [232,233,234].
Current therapeutic interventions for SUDs are multimodal, encompassing and including psychotherapy, behavior modification, and pharmacotherapy [235]. However, the variability in the efficacy of these treatments has led to the proposal of alternative approaches including support group treatment, neuromodulation, and GM interventions [236,237,238,239]. A substantial body of evidence from animal models supports the notion that the GM could be a viable therapeutic target for various SUDs, with probiotics, prebiotics, and fecal microbiota transplantation (FMT) being the main approaches [192,213]. In clinical studies, the microbial treatment of alcohol detoxification patients using Bifidobacterium bifidum and Lactiplantibacillus (formerly Lactobacillus) plantarum has shown beneficial outcomes by lowering liver enzymes [240]. Conversely, patients diagnosed with AUD who exhibited GM dysbiosis presented an augmentation in the proportion of Faecalibacterium prausnitzii and Bifidobacterium spp. following the administration of prebiotics derived from galactooligosaccharide or inulin-type fructans [241]. In a study by Bajaj et al. [242], an FMT procedure to enrich Lachnospiraceae and Ruminococcaceae was performed on subjects diagnosed with AUD and suffering cirrhosis. The subjects who underwent the intervention exhibited a reduction in alcohol cravings. In a more recent study, Letchumanan et al. [238] reported that probiotics, specifically Lactobacillus spp. and Bifidobacterium spp., provided promising results in reducing endotoxemia and systemic inflammation, thereby protecting against alcohol-induced neuroinflammation. Interestingly, prebiotic treatment based on inulin supplemented with dietary fiber during alcohol withdrawal has been shown to modulate the intestinal microbiota, increase the serum levels of BDNF, and improve social behavior in patients with AUD [243].
In an alternative approach, Lee et al. [244] employed an opioid antagonist (naltrexone), which impedes the binding of opioid agonists to the μ-opioid receptor, to prevent opioid relapse. This opioid antagonist has also been used to manage cravings associated with both AUD and OUD [245], alleviate opioid-induced constipation [246], and reduce gut mucosal injury associated with Crohn’s disease [247]. Treatment with the opioid agonist buprenorphine-naloxone was found to reverse the respiratory depression that occurs during an opioid overdose [244]. While these findings were not conclusive, both treatments (antagonist and agonist) were equally safe and effective in controlling the overall opioid relapse. A separate study has indicated that the utilization of opioid agonists is linked to a reduction in GM diversity, as evidenced by a decrease in the relative abundances of butyrate-producing Roseburia and of BA-metabolizing Bilophila genera [248].
6. Discussion
In this review, we summarize the current evidence on the bidirectional interaction between substance of abuse consumption and GM homeostasis, underscoring its role in the development of SUDs. Indeed, this complex interplay appears to profoundly affect both gut and brain health [249]. In this regard, evidence suggests that substance abuse induces gut dysbiosis, characterized by changes in bacterial diversity, disrupted GM composition, and reduced SCFA levels [35]. In addition, the examination of the pathogenetic mechanisms revealed that drug-induced dysbiosis could be linked to compromised gut permeability and heightened local and systemic inflammatory response. These shifts trigger a cascade of physiological and behavioral responses that exacerbate SUDs and reinforce drug dependence. Figure 2 presents the bidirectional interplay between substances of abuse and the GM.
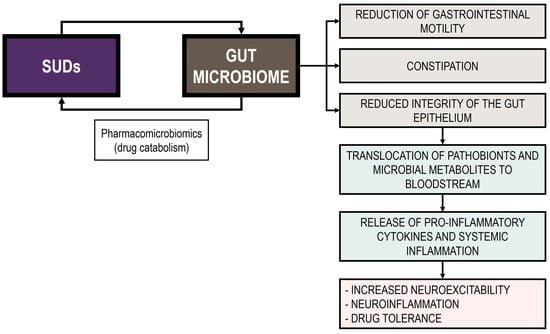
Figure 2.
Bidirectional interplay between substances of abuse and the GM.
Experimental research has demonstrated the substantial impact of the GM on SUDs, acting via mechanisms such as altered gene expression in the nucleus accumbens [250], the modulation of reward and addiction circuits [251], and changes in pain perception [252,253]. These results reinforce the direct involvement of the GM in both reward-related responses to substances of abuse [254] and withdrawal states [209], highlighting its relevance across multiple phases of addiction. Within this compelling physiological framework, targeting the GM has emerged as a promising strategy to counteract the detrimental effects of SUDs and enhance compliance with treatment interventions.
Despite the established relationship between the GM and substances of abuse, several potential limitations must be considered in studies examining this association. These include: (i) confounding variables, as many studies have failed to account for pre-existing mental health conditions; (ii) limited sample diversity, with some studies restricted in terms of age or cultural background, making it difficult to generalize findings across different demographic groups; (iii) the cross-sectional design of many studies, which limits their ability to establish causal relationships; (iv) self-reporting bias; (v) the influence of genetic and environmental factors; (vi) lack of long-term follow-up; (vii) the varying effects of SUDs across developmental stages; and (viii) substance use co-occurrence, which may lead to inconsistencies in the findings.
Emerging evidence highlights the significance of the GM in the pathogenesis of SUDs in animal models. However, further research is necessary to substantiate this association in human populations. In the future, it will be desirable to design studies aimed at identifying the different factors involved in this relationship such as the impact of drug exposure duration on the human host microbiome and how changes in GM composition influence SUD symptoms. While recent inquiries have explored whether the GM constitutes a potential environmental risk factor or a potential indicator of SUDs, current clinical studies have yet to provide definitive answers. Research on the GM and SUDs should also prioritize more diverse, representative populations and long-term, longitudinal designs. Incorporating objective biomarkers and self-reports as well as accounting for genetic and environmental variables would help mitigate biases and improve the reliability of the findings. Moreover, exploring the impact of substance use across different developmental stages could lead to more precise and customized interventions. In addition to methodological issues, it is pivotal to reassess the dominant narrative surrounding substances of abuse. In this sense, the consumption of these substances is often stigmatized, lacking a comprehensive understanding, which in turn tends to obscure open discussion and hinder the development of accurate knowledge, particularly among adolescents. In fact, this may inadvertently fuel curiosity and increase the likelihood of experimentation within young populations [1], potentially resulting in reckless patterns of consumption that exceed reasonable limits [255]. Thus, viewing substance use through a lens of condemnation fails to acknowledge the complexity of the issue and may contribute to negative outcomes such as risky behaviors and the reinforcement of stigma toward users. A more balanced, scientifically informed perspective would not only reduce stigma, but also provide a clearer understanding of the physiological and psychological impacts of substance use, individual susceptibility, and how these insights can inform more effective prevention and treatment strategies as well as the creation of optimal environments.
It is essential to recognize that many psychoactive substances, when used in non-abusive settings, confer therapeutic benefits. For instance, opioids are indispensable tools in clinical practice for anesthesia and pain management [112], moderate alcohol consumption has been linked to improved cardiovascular health and antioxidant effects [256], cannabis has demonstrated effectiveness across a wide range of pathological conditions including its key role as an antiemetic [257], and ecstasy has shown potential applications in the treatment of various psychiatric disorders [258]. Nevertheless, these substances can also impact the GM, even with short-term use. Therefore, a promising direction for future research would be to investigate the effects of such substances on the GM under non-abusive conditions. To date, a paucity of research has examined GM alterations following low-dose or short-term exposure. In the case of alcohol, Lee et al. [259] reported that short-term, low-dose alcohol consumption in mice resulted in a decreased abundance of members of the phylum Bacteroidota and an increased abundance of Bacillota. Specifically, Muribaculum intestinale was identified as the predominant species and a key contributor to the phylum-level shifts induced by alcohol. The prevalence of M. intestinale accounted for over 60% of the total in the control group, but its abundance was significantly reduced after just one week of alcohol intake. Similarly, a growing body of evidence supports the effectiveness of psychostimulants in alleviating symptoms of inattention and hyperactivity/impulsivity in individuals with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). Boonchooduang et al. [260] investigated the effects of psychostimulant medication on GM composition and SCFA levels. They found that medicated children with ADHD exhibited significantly reduced microbial diversity and lower abundances of several bacterial taxa, including Ruminococcaceae, Haemophilus, Enhydrobacter, Kytococcus, Micrococcus, Staphylococcus, Corynebacterium, Brevundimonas, and Odoribacter, compared with their untreated counterparts. In contrast, Anaerostipes was more abundant in the medicated group, and Parvimonas was significantly more prevalent in medicated children compared with healthy controls. In the context of therapeutic cannabis use, various clinical and preclinical studies have investigated its effects on GM composition. In clinical research, Vijay et al. [156] reported a positive correlation between eCBs and bacterial α-diversity as well as with SCFA-producing genera such as Bifidobacterium, Coprococcus, and Faecalibacterium. In a study examining the impact of drug use on GM during HIV infection, Fulcher et al. [261] found that cannabis consumption was associated with an increased abundance of the genera Clostridium, Fusobacterium, Ruminococcus, and Solobacterium and a decreased abundance of Acidaminococcus, Anaerostipes, Dialister, Dorea, and Prevotella. Similarly, in a cohort comparing cannabis users and non-users, Panee et al. [154] observed a positive correlation between cannabis use and Prevotella abundance and an inverse correlation with Bacteroides. Notably, the Prevotella/Bacteroides ratio was found to be 13 times higher in non-users. Preclinical studies also revealed substantial alterations in GM associated with cannabis exposure. Mehrpouya-Bahrami et al. [153] observed that cannabis administration in mice led to increased levels of A. muciniphila and a decreased abundance of Lachnospiraceae and Erysipelotrichaceae. Furthermore, THC administration was shown to enhance the abundance of the beneficial species Ruminococcus gnavus while reducing the levels of the potentially pathogenic A. muciniphila in both the lung and gut [262]. The therapeutic use of opioids has long raised concerns, particularly regarding their impact on the GM. However, only a limited number of studies have explored this effect under medically supervised conditions. Wang et al. [123] demonstrated that morphine administration promoted the growth of pathogenic bacterial communities and that Enterococcus faecalis contributed to morphine-induced analgesic tolerance in mice. Supporting these findings, Zhang et al. [263] provided direct evidence of morphine-induced alterations in the rat GM. The authors suggested that a baseline reduction in Olsenella and Rothia, alongside an increase in Helicobacter, may serve as a potential biomarker for heightened vulnerability to addictive behaviors following morphine exposure.
In the context of this discussion, it is worth mentioning the utilization of probiotics as a promising adjunct therapy for SUDs, either as a standalone intervention or as a pharmacotherapy supplement. Preclinical studies have reported the potential benefits of probiotic supplementation in relation to drug abuse. For instance, administration of the commercial probiotic mixture VSL#3, which contains the bacterial species Lactobacillus acidophilus, Lactobacillus delbrueckii subsp. bulgaricus, Lactiplantibacillus plantarum, Lacticaseibacillus casei, Bifidobacterium breve, B. longum, B. longum subsp. infantis, and Streptococcus salivarius subsp. thermophilus, mitigated the development of analgesic tolerance to morphine in mice. This effect was associated with a partial restoration of GM components and a reduction in proinflammatory cytokines [264]. In addition, Ezquer et al. [265] noted that combined administration of the probiotic strain GG of Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus with N-acetylcysteine and acetylsalicylic acid modulated dopaminergic activity and reduced relapse to ethanol consumption, highlighting its potential as a probiotic adjuvant in AUD treatment. However, further research is needed to optimize probiotic interventions (e.g., combination of probiotic strains and dosage) in clinical studies targeting SUDs. Within this framework, Sarkar et al. [213] proposed the category of psychobiotics including probiotics, prebiotics, or both in combination (synbiotics), which impact microbial-neural signaling. Psychobiotics have demonstrated significant benefits in addressing various psychological adverse states, including stress, anxiety, and depression [266], which could contribute to the alleviation of some of the aversive symptoms associated with drug use such as cravings or withdrawal. Therefore, a promise area for future investigation will involve clinical trials evaluating the effects of psychobiotics on drug addiction. Moreover, the emerging field of nutritional psychiatry could play a pivotal role, emphasizing the importance of diet and gut health in modulating psychological well-being and supporting addiction treatment strategies [267].
Finally, concerted efforts to conceptualize and operationalize randomized controlled trials in human subjects are imperative to ascertain the microbial features associated with SUDs. In addition, therapies that target novel pathways implicated in microbial signaling within the brain–gut axis will enhance our understanding of the role of the GM in drug addiction.
7. Conclusions
A substantial body of research, including both preclinical and human studies, has demonstrated a bidirectional relationship between the GM and SUDs. This relationship encompasses the impact of SUDs on GM composition and dynamics as well as the role of GM dysbiosis in mediating behavioral responses to substances of abuse. As a result, manipulating the GM or its by-products may represent a promising approach for SUD treatments. Another important aspect that merits consideration is the potential use of human microbiomes (e.g., oral, gut, upper respiratory tract) or their bacterial metabolites in identifying individuals at increased risk of pathological drug use. Furthermore, novel insights into the interactions between host genetics and the GM may be pivotal for elucidating the role of the microbiome in SUDs and addiction behaviors.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.B.-R. and J.J.B.; Investigation, A.B.-R. and J.J.B.; Writing—original draft preparation, A.B.-R. and J.J.B.; Writing—review and editing, A.B.-R.; Supervision, J.J.B. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
No new data were created or analyzed in this study. Data sharing is not applicable to this article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| AUD | Alcohol use disorder |
| BAs | Bile acids |
| BBB | Blood–brain barrier |
| BIN | Binge-drinking |
| BDNF | Brain-derived neurotrophic factor |
| CAN | Cannabinoid use |
| CRA | Alcohol craving |
| CUD | Cocaine use disorder |
| ECS | Endocannabinoid system |
| FMT | Fecal microbiota transplantation |
| GABA | γ-Aminobutyric acid |
| GM | Gut microbiome |
| HPA | Hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal |
| 5-HT | 5-Hydroxytryptamine |
| KYNA | Kynurenic acid |
| MUD | Methamphetamine use disorder |
| NIC | Nicotine use |
| OUD | Opioid use disorder |
| SCFAs | Short-chain fatty acids |
| SUDs | Substance use disorders |
| TNF-α | Tumor necrosis factor-alpha |
References
- Borrego-Ruiz, A. Motivación intrínseca y consumo de drogas: Una revisión de estudios sobre los motivos de curiosidad y de expansión. Health Addict. 2024, 24, 47–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hofford, R.S.; Kiraly, D.D. Clinical and preclinical evidence for gut microbiome mechanisms in substance use disorder. Biol. Psychiatry 2024, 95, 329–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodwin, S.; Kirby, K.C.; Raiff, B.R. Evolution of the substance use landscape: Implications for contingency management. J. Appl. Behav. Anal. 2025, 58, 36–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, N.A.; Weitzman, E.R. Intensifying substance use trends among youth: A narrative review of recent trends and implications. Curr. Psychiatry Rep. 2024, 26, 822–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peart, D.R.; Andrade, A.K.; Logan, C.N.; Knackstedt, L.A.; Murray, J.E. Regulation of cocaine-related behaviours by estrogen and progesterone. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2022, 135, 104584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wemm, S.E.; Sinha, R. Drug-induced stress responses and addiction risk and relapse. Neurobiol. Stress 2019, 10, 100148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucerne, K.E.; Kiraly, D.D. The role of gut-immune-brain signaling in substance use disorders. Int. Rev. Neurobiol. 2021, 157, 311–370. [Google Scholar]
- Meckel, K.R.; Kiraly, D.D. A potential role for the gut microbiome in substance use disorders. Psychopharmacology 2019, 236, 1513–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, J.T.; Zhou, Y.; Weinstock, G.M.; Bubier, J.A. The gut microbiome and substance use disorder. Front. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 725500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galligan, J.J.; Sternini, C. Insights into the role of opioid receptors in the GI tract: Experimental evidence and therapeutic relevance. Handb. Exp. Pharmacol. 2017, 239, 363–378. [Google Scholar]
- Maier, L.; Pruteanu, M.; Kuhn, M.; Zeller, G.; Telzerow, A.; Anderson, E.; Brochado, A.R.; Fernandez, K.C.; Dose, H.; Mori, H.; et al. Extensive impact of non-antibiotic drugs on human gut bacteria. Nature 2018, 555, 623–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simpson, S.; Mclellan, R.; Wellmeyer, E.; Matalon, F.; George, O. Drugs and bugs: The gut-brain axis and substance use disorders. J. Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2022, 17, 33–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, A.S.; Koller, K.R.; Ramaboli, M.C.; Nesengani, L.T.; Ocvirk, S.; Chen, C.; Flanagan, C.A.; Sapp, F.R.; Merritt, Z.T.; Bhatti, F.; et al. Diet and the human gut microbiome: An international review. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2020, 65, 723–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinninella, E.; Raoul, P.; Cintoni, M.; Franceschi, F.; Miggiano, G.A.D.; Gasbarrini, A.; Mele, M.C. What is the healthy gut microbiota composition? A changing ecosystem across age, environment, diet, and diseases. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borrego-Ruiz, A.; Borrego, J.J. An updated overview on the relationship between human gut microbiome dysbiosis and psychiatric and psychological disorders. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2024, 128, 110861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lloyd-Price, J.; Abu-Ali, G.; Huttenhower, C. The healthy human microbiome. Genome Med. 2016, 8, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jandhyala, S.M.; Talukdar, R.; Subramanyam, C.; Vuyyuru, H.; Sasikala, M.; Nageshwar Reddy, D. Role of the normal gut microbiota. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 8787–8803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberg, E. Diversity of bacteria within the human gut and its contribution to the functional unity of holobionts. NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes 2024, 10, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borrego-Ruiz, A.; Borrego, J.J. Influence of human gut microbiome on the healthy and the neurodegenerative aging. Exp. Gerontol. 2024, 194, 112497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borrego-Ruiz, A.; Borrego, J.J. Human gut microbiome, diet, and mental disorders. Int. Microbiol. 2025, 28, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, T.S.; Shanahan, F.; O’Toole, P.W. The gut microbiome as a modulator of healthy ageing. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 19, 565–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madison, A.; Kiecolt-Glaser, J.K. Stress, depression, diet, and the gut microbiota: Human-bacteria interactions at the core of psychoneuroimmunology and nutrition. Curr. Opin. Behav. Sci. 2019, 28, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothschild, D.; Weissbrod, O.; Barkan, E.; Kurilshikov, A.; Korem, T.; Zeevi, D.; Costea, P.I.; Godneva, A.; Kalka, I.N.; Bar, N.; et al. Environment dominates over host genetics in shaping human gut microbiota. Nature 2018, 555, 210–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Xie, Z.; Wang, H.; Shen, Z.; Guo, Y.; Gao, Y.; Chen, X.; Wu, Q.; Li, X.; Wang, K. Bacterial diversity of intestinal microbiota in patients with substance use disorders revealed by 16S rRNA gene deep sequencing. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 3628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, B.; Nair, G.B. Homeostasis and dysbiosis of the gut microbiome in health and disease. J. Biosci. 2019, 44, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hrncir, T. Gut microbiota dysbiosis: Triggers, consequences, diagnostic and therapeutic options. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonaz, B.; Bazin, T.; Pellissier, S. The vagus nerve at the interface of the microbiota-gut-brain axis. Front. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fülling, C.; Dinan, T.G.; Cryan, J.F. Gut microbe to brain signaling: What happens in vagus... Neuron 2019, 101, 998–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gensollen, T.; Iyer, S.S.; Kasper, D.L.; Blumberg, R.S. How colonization by microbiota in early life shapes the immune system. Science 2016, 352, 539–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, D.; Liwinski, T.; Elinav, E. Interaction between microbiota and immunity in health and disease. Cell Res. 2020, 30, 492–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blander, J.M.; Longman, R.S.; Iliev, I.D.; Sonnenberg, G.F.; Artis, D. Regulation of inflammation by microbiota interactions with the host. Nat. Immunol. 2017, 18, 851–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clemente, J.C.; Manasson, J.; Scher, J.U. The role of the gut microbiome in systemic inflammatory disease. BMJ 2018, 360, j5145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinan, T.G.; Stilling, R.M.; Stanton, C.; Cryan, J.F. Collective unconscious: How gut microbes shape human behavior. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2015, 63, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.T.; Lai, J.B.; Du, Y.L.; Xu, Y.; Ruan, L.M.; Hu, S.H. Current understanding of gut microbiota in mood disorders: An update of human studies. Front. Genet. 2019, 10, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-Lebrón, A.; Johnson, R.; Mazahery, C.; Troyer, Z.; Joussef-Piña, S.; Quiñones-Mateu, M.E.; Strauch, C.M.; Hazen, S.L.; Levine, A.D. Chronic opioid use modulates human enteric microbiota and intestinal barrier integrity. Gut Microbes 2021, 13, 1946368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, J.E.; Kahana, D.D.; Ghuman, S.; Wilson, H.P.; Wilson, J.; Kim, S.C.J.; Lagishetty, V.; Jacobs, J.P.; Sinha-Hikim, A.P.; Friedman, T.C. Unhealthy lifestyle and gut dysbiosis: A better understanding of the effects of poor diet and nicotine on the intestinal microbiome. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 667066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parums, D.V. Review articles, systematic reviews, meta-analysis, and the updated preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses (PRISMA) 2020 guidelines. Med. Sci. Monit. 2021, 27, e934475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krystal, J.H.; Staley, J.; Mason, G.; Petrakis, I.L.; Kaufman, J.; Harris, R.A.; Gelernter, J.; Lappalainen, J. Gamma-aminobutyric acid type A receptors and alcoholism: Intoxication, dependence, vulnerability, and treatment. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 2006, 63, 957–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naassila, M.; Pierrefiche, O. GluN2B subunit of the NMDA receptor: The keystone of the effects of alcohol during neurodevelopment. Neurochem. Res. 2019, 44, 78–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuckit, M.A. Alcohol-use disorders. Lancet 2009, 373, 492–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grover, S.; Ghosh, A. Delirium tremens: Assessment and management. J. Clin. Exp. Hepatol. 2018, 8, 460–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levesque, C.; Sanger, N.; Edalati, H.; Sohi, I.; Shield, K.D.; Sherk, A.; Stockwell, T.; Butt, P.R.; Paradis, C. A systematic review of relative risks for the relationship between chronic alcohol use and the occurrence of disease. Alcohol Clin. Exp. Res. 2023, 47, 1238–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caslin, B.; Mohler, K.; Thiagarajan, S.; Melamed, E. Alcohol as friend or foe in autoimmune diseases: A role for gut microbiome? Gut Microbes 2021, 13, 1916278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roerecke, M. Alcohol’s impact on the cardiovascular system. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gemma, S.; Vichi, S.; Testai, E. Individual susceptibility and alcohol effects: Biochemical and genetic aspects. Ann. Ist. Super. Sanita 2006, 42, 8–16. [Google Scholar]
- Day, A.W.; Kumamoto, C.A. Gut microbiome dysbiosis in alcoholism: Consequences for health and recovery. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 840164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dedon, L.R.; Yuan, H.; Chi, J.; Gu, H.; Arias, A.J.; Covault, J.M.; Zhou, Y. Baseline gut microbiome and metabolites are correlated with changes in alcohol consumption in participants in a randomized Zonisamide clinical trial. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 10486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addolorato, G.; Ponziani, F.R.; Dionisi, T.; Mosoni, C.; Vassallo, G.A.; Sestito, L.; Petito, V.; Picca, A.; Marzetti, E.; Tarli, C.; et al. Gut microbiota compositional and functional fingerprint in patients with alcohol use disorder and alcohol-associated liver disease. Liver Int. 2020, 40, 878–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ames, N.J.; Barb, J.J.; Schuebel, K.; Mudra, S.; Meeks, B.K.; Tuason, R.T.S.; Brooks, A.T.; Kazmi, N.; Yang, S.; Ratteree, K.; et al. Longitudinal gut microbiome changes in alcohol use disorder are influenced by abstinence and drinking quantity. Gut Microbes 2020, 11, 1608–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjørkhaug, S.T.; Aanes, H.; Neupane, S.P.; Bramness, J.G.; Malvik, S.; Henriksen, C.; Skar, V.; Medhus, A.W.; Valeur, J. Characterization of gut microbiota composition and functions in patients with chronic alcohol overconsumption. Gut Microbes 2019, 10, 663–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litwinowicz, K.; Choroszy, M.; Waszczuk, E. Changes in the composition of the human intestinal microbiome in alcohol use disorder: A systematic review. Am. J. Drug Alcohol Abus. 2020, 46, 4–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Li, L.; Gong, C.; Li, T.; Xia, Y. The diversity of the intestinal microbiota in patients with alcohol use disorder and its relationship to alcohol consumption and cognition. Front. Psychiatry 2022, 13, 1054685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baltazar-Díaz, T.A.; González-Hernández, L.A.; Aldana-Ledesma, J.M.; Peña-Rodríguez, M.; Vega-Magaña, A.N.; Zepeda-Morales, A.S.M.; López-Roa, R.I.; Del Toro-Arreola, S.; Martínez-López, E.; Salazar-Montes, A.M.; et al. Escherichia/Shigella, SCFAs, and metabolic pathways—The triad that orchestrates intestinal dysbiosis in patients with decompensated alcoholic cirrhosis from Western Mexico. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Shi, F.; Yin, W.; Guo, Y.; Liu, A.; Shuai, J.; Sun, J. Gut microbiota dysbiosis: The potential mechanisms by which alcohol disrupts gut and brain functions. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 916765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pohl, K.; Moodley, P.; Dhanda, A.D. Alcohol’s impact on the gut and liver. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhanda, A.D.; Collins, P.L. Immune dysfunction in acute alcoholic hepatitis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 11904–11913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leclercq, S.; De Saeger, C.; Delzenne, N.; de Timary, P.; Stärkel, P. Role of inflammatory pathways, blood mononuclear cells, and gut-derived bacterial products in alcohol dependence. Biol. Psychiatry 2014, 76, 725–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Routy, B.; Gopalakrishnan, V.; Daillère, R.; Zitvogel, L.; Wargo, J.A.; Kroemer, G. The gut microbiota influences anticancer immunosurveillance and general health. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 15, 382–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Lee, S.T.; Choi, S.; Lee, H.; Kwon, S.S.; Byun, J.H.; Kim, Y.A.; Rhee, K.J.; Choi, J.R.; Kim, T.I.; et al. Fusobacterium nucleatum in biopsied tissues from colorectal cancer patients and alcohol consumption in Korea. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 19915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bleibtreu, A.; Kapel, N.; Galperine, T. Drug-resistant bacteremia after fecal microbiota transplant. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 1960–1962. [Google Scholar]
- Flores-Medina, Y.; Rodríguez-Agudelo, Y.; Bernal-Hernández, J.; Cruz-Fuentes, C.S. Cognitive impairment in the co-occurrence of alcohol dependence and major depression: Neuropsychological assessment and event-related potentials analyses. Heliyon 2022, 8, e09899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pich, E.M.; Tarnanas, I.; Brigidi, P.; Collo, G. Gut microbiome-liver-brain axis in alcohol use disorder. The role of gut dysbiosis and stress in alcohol-related cognitive impairment progression: Possible therapeutic approaches. Neurobiol. Stress 2025, 35, 100713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Bai, C.; Zhao, L.; Ge, Y.; Li, X. Characterization of the fecal microbiota in gastrointestinal cancer patients and healthy people. Clin. Transl. Oncol. 2022, 24, 1134–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stärkel, P.; Leclercq, S.; de Timary, P.; Schnabl, B. Intestinal dysbiosis and permeability: The yin and yang in alcohol dependence and alcoholic liver disease. Clin. Sci. 2018, 132, 199–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, A.L.; Xia, K.; Azcarate-Peril, M.A.; Goldman, B.D.; Ahn, M.; Styner, M.A.; Thompson, A.L.; Geng, X.; Gilmore, J.H.; Knickmeyer, R.C. Infant gut microbiome associated with cognitive development. Biol. Psychiatry 2018, 83, 148–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Berre, A.P.; Fama, R.; Sullivan, E.V. Executive functions, memory, and social cognitive deficits and recovery in chronic alcoholism: A critical review to inform future research. Alcohol Clin. Exp. Res. 2017, 41, 1432–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbia, C.; Lannoy, S.; Maurage, P.; López-Caneda, E.; O’Riordan, K.J.; Dinan, T.G.; Cryan, J.F. A biological framework for emotional dysregulation in alcohol misuse: From gut to brain. Mol. Psychiatry 2021, 26, 1098–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leclercq, S.; Matamoros, S.; Cani, P.D.; Neyrinck, A.M.; Jamar, F.; Stärkel, P.; Windey, K.; Tremaroli, V.; Bäckhed, F.; Verbeke, K.; et al. Intestinal permeability, gut-bacterial dysbiosis, and behavioral markers of alcohol-dependence severity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, E4485–E4493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, Z.; Zhu, M.; Yan, X.; Cheng, Y.; Shao, L.; Liu, X.; Jiang, R.; Wu, S. Structural and functional dysbiosis of fecal microbiota in Chinese patients with Alzheimer’s disease. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 8, 634069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valles-Colomer, M.; Falony, G.; Darzi, Y.; Tigchelaar, E.F.; Wang, J.; Tito, R.Y.; Schiweck, C.; Kurilshikov, A.; Joossens, M.; Wijmenga, C.; et al. The neuroactive potential of the human gut microbiota in quality of life and depression. Nat. Microbiol. 2019, 4, 623–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortés-Tomás, M.T.; Giménez-Costa, J.A.; Martín-Del-Río, B.; Gómez-Íñiguez, C.; Solanes-Puchol, Á. Binge drinking: The top 100 cited papers. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 9203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carbia, C.; Corral, M.; Caamaño-Isorna, F.; Cadaveira, F. Emotional memory bias in binge drinking women. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2020, 209, 107888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lannoy, S.; Benzerouk, F.; Maurage, P.; Barrière, S.; Billieux, J.; Naassila, M.; Kaladjian, A.; Gierski, F. Disrupted fear and sadness recognition in binge drinking: A combined group and Individual analysis. Alcohol Clin. Exp. Res. 2019, 43, 1978–1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lannoy, S.; Gilles, F.; Benzerouk, F.; Henry, A.; Oker, A.; Raucher-Chéné, D.; Besche-Richard, C.; Gierski, F. Disentangling the role of social cognition processes at early steps of alcohol abuse: The influence of affective theory of mind. Addict. Behav. 2020, 102, 106187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lannoy, S.; Duka, T.; Carbia, C.; Billieux, J.; Fontesse, S.; Dormal, V.; Gierski, F.; López-Caneda, E.; Sullivan, E.V.; Maurage, P. Emotional processes in binge drinking: A systematic review and perspective. Clin. Psychol. Rev. 2021, 84, 101971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zyoud, S.H. Global scientific research landscape on binge drinking: A comprehensive bibliometric and visualization analysis of trends, collaborations, and future directions. Subst. Abus. Treat. Prev. Policy 2025, 20, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbia, C.; Bastiaanssen, T.F.S.; Iannone, L.F.; García-Cabrerizo, R.; Boscaini, S.; Berding, K.; Strain, C.R.; Clarke, G.; Stanton, C.; Dinan, T.G.; et al. The microbiome-gut-brain axis regulates social cognition and craving in young binge drinkers. EBioMedicine 2023, 89, 104442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajaj, J.S.; Shamsaddini, A.; Fagan, A.; McGeorge, S.; Gavis, E.; Sikaroodi, M.; Brenner, L.A.; Wade, J.B.; Gillevet, P.M. Distinct gut microbial compositional and functional changes associated with impaired inhibitory control in patients with cirrhosis. Gut Microbes 2021, 13, 1953247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, B.J.; Wearsch, P.A.; Veloo, A.C.M.; Rodriguez-Palacios, A. The genus Alistipes: Gut bacteria with emerging implications to inflammation, cancer, and mental health. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segovia-Rodríguez, L.; Echeverry-Alzate, V.; Rincón-Pérez, I.; Calleja-Conde, J.; Bühler, K.M.; Giné, E.; Albert, J.; Hinojosa, J.A.; Huertas, E.; Gómez-Gallego, F.; et al. Gut microbiota and voluntary alcohol consumption. Transl. Psychiatry 2022, 12, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, L.; Ling, Z.; Chen, D.; Liu, Y.; Yang, F.; Li, L. Disorganized gut microbiome contributed to liver cirrhosis progression: A meta-omics-based study. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 3166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flaudias, V.; Teisseidre, F.; De Chazeron, I.; Chalmeton, M.; Bertin, C.; Izaute, M.; Chakroun-Baggioni, N.; Pereira, B.; Brousse, G.; Maurage, P. A multi-dimensional evaluation of craving and impulsivity among people admitted for alcohol-related problems in emergency department. Psychiatry Res. 2019, 272, 569–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernard, L.; Cyr, L.; Bonnet-Suard, A.; Cutarella, C.; Bréjard, V. Drawing alcohol craving process: A systematic review of its association with thought suppression, inhibition and impulsivity. Heliyon 2021, 7, e05868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashok, A.H.; Mizuno, Y.; Volkow, N.D.; Howes, O.D. Association of stimulant use with dopaminergic alterations in users of cocaine, amphetamine, or methamphetamine: A systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Psychiatry 2017, 74, 511–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morelli, M.; Tognotti, E. Brief history of the medical and non-medical use of amphetamine-like psychostimulants. Exp. Neurol. 2021, 342, 113754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berquist, M.D.; Fantegrossi, W.E. Discriminative stimulus effects of psychostimulants. Curr. Top. Behav. Neurosci. 2018, 39, 29–49. [Google Scholar]
- Lappin, J.M.; Sara, G.E. Psychostimulant use and the brain. Addiction 2019, 114, 2065–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCreary, A.C.; Müller, C.P.; Filip, M. Psychostimulants: Basic and clinical pharmacology. Int. Rev. Neurobiol. 2015, 120, 41–83. [Google Scholar]
- Sundar, V.; Ramasamy, T.; Doke, M.; Samikkannu, T. Psychostimulants influence oxidative stress and redox signatures: The role of DNA methylation. Redox Rep. 2022, 27, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volpe, G.E.; Ward, H.; Mwamburi, M.; Dinh, D.; Bhalchandra, S.; Wanke, C.; Kane, A.V. Associations of cocaine use and HIV infection with the intestinal microbiota, microbial translocation, and inflammation. J. Stud. Alcohol Drugs 2014, 75, 347–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, R.R.; Fulcher, J.A.; Tobin, N.H.; Li, F.; Lee, D.J.; Woodward, C.; Javanbakht, M.; Brookmeyer, R.; Shoptaw, S.; Bolan, R.; et al. Alterations to the gastrointestinal microbiome associated with methamphetamine use among young men who have sex with men. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 14840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, D.; Su, H.; Song, Y.; Chen, T.; Sun, Q.; Jiang, H.; Zhao, M. Altered fecal microbiota correlated with systemic inflammation in male subjects with methamphetamine use disorder. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 783917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, S.; Chen, T.; Zhao, M. The crosstalk between neurons and glia in methamphetamine-induced neuroinflammation. Neurochem. Res. 2022, 47, 872–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Yu, X.; Liu, X.; Liu, G.; Zeng, K.; Wang, G. Altered fecal microbiota composition in individuals who abuse methamphetamine. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 18178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Yang, B.Z.; Ma, Y.J.; Wen, L.; Liu, F.; Zhang, X.J.; Liu, T.Q. Differences in clinical features and gut microbiota between individuals with methamphetamine casual use and methamphetamine use disorder. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2023, 13, 1103919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerace, E.; Baldi, S.; Salimova, M.; Di Gloria, L.; Curini, L.; Cimino, V.; Nannini, G.; Russo, E.; Pallecchi, M.; Ramazzotti, M.; et al. Oral and fecal microbiota perturbance in cocaine users: Can rTMS-induced cocaine abstinence support eubiosis restoration? iScience 2023, 26, 106627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allali, I.; Boukhatem, N.; Bouguenouch, L.; Hardi, H.; Boudouaya, H.A.; Cadena, M.B.; Ouldim, K.; Amzazi, S.; Azcarate-Peril, M.A.; Ghazal, H. Gut microbiome of Moroccan colorectal cancer patients. Med. Microbiol. Immunol. 2018, 207, 211–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, J.E.; Brown, I.E.; Olson, K.A.; Iverson, K.; Cocanour, C.S.; Galante, J.M. Nonocclusive mesenteric ischemia in patients with methamphetamine use. J. Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2018, 84, 885–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magro, D.O.; Santos, A.; Guadagnini, D.; Moreira de Godoy, F.; Monteiro-Silva, S.H.; Fernandes-Lemos, W.J.; Vitulo, N.; Torriani, S.; Pinheiro, L.V.; Martinez, C.A.R.; et al. Remission in Crohn’s disease is accompanied by alterations in the gut microbiota and mucins production. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 13263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiraly, D.D.; Walker, D.M.; Calipari, E.S.; Labonte, B.; Issler, O.; Pena, C.J.; Ribeiro, E.A.; Russo, S.J.; Nestler, E.J. Alterations of the host microbiome affect behavioral responses to cocaine. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 35455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meckel, K.R.; Simpson, S.S.; Godino, A.; Peck, E.G.; Sens, J.P.; Leonard, M.Z.; George, O.; Calipari, E.S.; Hofford, R.S.; Kiraly, D.D. Microbial short-chain fatty acids regulate drug seeking and transcriptional control in a model of cocaine seeking. Neuropsychopharmacology 2023, 49, 386–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayo, L.M.; Paul, E.; DeArcangelis, J.; Van Hedger, K.; de Wit, H. Gender differences in the behavioral and subjective effects of methamphetamine in healthy humans. Psychopharmacology 2019, 236, 2413–2423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Yu, Z.; Sun, Y.; Chang, X.; Lu, L.; Chang, S.; Shi, J. Risk factors and an early prediction model for persistent methamphetamine-related psychiatric symptoms. Addict. Biol. 2020, 25, e12709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKetin, R. Methamphetamine psychosis: Insights from the past. Addiction 2018, 113, 1522–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moszczynska, A.; Callan, S.P. Molecular, behavioral, and physiological consequences of methamphetamine neurotoxicity: Implications for treatment. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2017, 362, 474–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wearne, T.A.; Cornish, J.L. A comparison of methamphetamine-induced psychosis and schizophrenia: A review of positive, negative, and cognitive symptomatology. Front. Psychiatry 2018, 9, 491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fincham, J.E. Global use and misuse of opioids. Int. J. Pharm. Pract. 2018, 26, 91–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzeo, F.; Meccariello, R.; Guatteo, E. Molecular and epigenetic aspects of opioid receptors in drug addiction and pain management in sport. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 7831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, C. New concepts in opioid analgesia. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2018, 27, 765–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inturrisi, C.E. Clinical pharmacology of opioids for pain. Clin. J. Pain 2002, 18, S3–S13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benyamin, R.; Trescot, A.M.; Datta, S.; Buenaventura, R.; Adlaka, R.; Sehgal, N.; Glaser, S.E.; Vallejo, R. Opioid complications and side effects. Pain Physician 2008, 11, S105–S120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borrego-Ruiz, A. A holistic review of fentanyl use and its impact on public health. Curr. Addict. Res. 2024, 8, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faouzi, A.; Varga, B.R.; Majumdar, S. Biased opioid ligands. Molecules 2020, 25, 4257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, M.; Lotfipour, S. The role of the gut microbiome in opioid use. Behav. Pharmacol. 2020, 31, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalodia, R.; Abu, Y.F.; Oppenheimer, M.R.; Herlihy, B.; Meng, J.; Chupikova, I.; Tao, J.; Ghosh, N.; Dutta, R.K.; Kolli, U.; et al. Opioid use, gut dysbiosis, inflammation, and the nervous system. J. Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2022, 17, 76–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, R.; Wang, L.; Xu, X.; Chen, Y.; Wang, H.; Wang, G.; Zhao, J.; Chen, W. Crosstalk between the gut microbiome and colonic motility in chronic constipation: Potential mechanisms and microbiota modulation. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rueda-Ruzafa, L.; Cruz, F.; Cardona, D.; Hone, A.J.; Molina-Torres, G.; Sánchez-Labraca, N.; Roman, P. Opioid system influences gut-brain axis: Dysbiosis and related alterations. Pharmacol. Res. 2020, 159, 104928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taboun, Z.S.; Sadeghi, J. The bidirectional relationship between opioids and the gut microbiome: Implications for opioid tolerance and clinical interventions. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2023, 125, 111142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vincent, C.; Miller, M.A.; Edens, T.; Mehrotra, S.; Dewar, K.; Manges, A.R. Bloom and bust: Intestinal microbiota dynamics in response to hospital exposures and Clostridium difficile colonization or infection. Microbiome 2016, 4, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acharya, C.; Betrapally, N.S.; Gillevet, P.M.; Sterling, R.K.; Akbarali, H.; Ganapathy, D.; Fagan, A.; Sikaroodi, M.; Bajaj, J.S. Chronic opioid use is associated with altered gut microbiota and predicts readmissions in patients with cirrhosis. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2017, 45, 319–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barengolts, E.; Green, S.J.; Eisenberg, Y.; Akbar, A.; Reddivari, B.; Layden, B.T.; Dugas, L.; Chlipala, G. Gut microbiota varies by opioid use, circulating leptin and oxytocin in African American men with diabetes and high burden of chronic disease. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0194171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herlihy, B.; Roy, S. Gut-microbiome implications in opioid use disorder and related behaviors. Adv. Drug Alcohol Res. 2022, 2, 10311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Meng, J.; Zhang, L.; Johnson, T.; Chen, C.; Roy, S. Morphine induces changes in the gut microbiome and metabolome in a morphine dependence model. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 3596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajaj, J.S.; Betrapally, N.S.; Hylemon, P.B.; Thacker, L.R.; Daita, K.; Kang, D.J.; White, M.B.; Unser, A.B.; Fagan, A.; Gavis, E.A.; et al. Gut microbiota alterations can predict hospitalizations in cirrhosis independent of diabetes mellitus. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 20447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, J.; Banerjee, S.; Li, D.; Sindberg, G.M.; Wang, F.; Ma, J.; Roy, S. Opioid exacerbation of Gram-positive sepsis, induced by gut microbial modulation, is rescued by IL-17A neutralization. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 10918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Meng, J.; Lian, Q.; Chen, X.; Bauman, B.; Chu, H.; Segura, B.; Roy, S. Prescription opioids are associated with higher mortality in patients diagnosed with sepsis: A retrospective cohort study using electronic health records. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0190362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franchi, S.; Moschetti, G.; Amodeo, G.; Sacerdote, P. Do all opioid drugs share the same immunomodulatory properties? A review from animal and human studies. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meijerink, H.; Indrati, A.; Utami, F.; Soedarmo, S.; Alisjahbana, B.; Netea, M.G.; van Crevel, R.; Wisaksana, R.; van der Ven, A.J. Heroin use is associated with suppressed pro-inflammatory cytokine response after LPS exposure in HIV-infected individuals. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0122822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Roy, S. Gut homeostasis, microbial dysbiosis, and opioids. Toxicol. Pathol. 2017, 45, 150–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salter, M.W.; Stevens, B. Microglia emerge as central players in brain disease. Nat. Med. 2017, 23, 1018–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ElSohly, M.A.; Radwan, M.M.; Gul, W.; Chandra, S.; Galal, A. Phytochemistry of Cannabis sativa L. In Phytocannabinoids: Unraveling the Complex Chemistry and Pharmacology of Cannabis sativa; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; Volume 103, pp. 1–36. [Google Scholar]
- Srivastava, R.K.; Lutz, B.; Ruiz de Azua, I. The microbiome and gut endocannabinoid system in the regulation of stress responses and metabolism. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 867267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andre, C.M.; Hausman, J.F.; Guerriero, G. Cannabis sativa: The plant of the thousand and one molecules. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraguas-Sánchez, A.I.; Torres-Suárez, A.I. Medical use of cannabinoids. Drugs 2018, 78, 1665–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legare, C.A.; Raup-Konsavage, W.M.; Vrana, K.E. Therapeutic potential of cannabis, cannabidiol, and cannabinoid-based pharmaceuticals. Pharmacology 2022, 107, 131–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nichols, J.M.; Kaplan, B.L.F. Immune responses regulated by cannabidiol. Cannabis Cannabinoid Res. 2020, 5, 12–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adejumo, A.C.; Flanagan, R.; Kuo, B.; Staller, K. Relationship between recreational marijuana use and bowel function in a nationwide cohort study. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 114, 1894–1903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tartakover-Matalon, S.; Azar, S.; Meiri, D.; Hadar, R.; Nemirovski, A.; Abu Jabal, N.; Konikoff, F.M.; Drucker, L.; Tam, J.; Naftali, T. Endocannabinoid levels in ulcerative colitis patients correlate with clinical parameters and are affected by cannabis consumption. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 685289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayazit, H.; Selek, S.; Karababa, I.F.; Cicek, E.; Aksoy, N. Evaluation of oxidant/antioxidant status and cytokine levels in patients with cannabis use disorder. Clin. Psychopharmacol. Neurosci. 2017, 15, 237–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connor, J.P.; Stjepanović, D.; Le Foll, B.; Hoch, E.; Budney, A.J.; Hall, W.D. Cannabis use and cannabis use disorder. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2021, 7, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rea, K.; O’ Mahony, S.M.; Cryan, J.F. High and mighty? Cannabinoids and the microbiome in pain. Neurobiol. Pain 2021, 9, 100061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, I.; Syamala, S.; Ayariga, J.A.; Xu, J.; Robertson, B.K.; Meenakshisundaram, S.; Ajayi, O.S. Modulatory effect of gut microbiota on the gut-brain, gut-bone axes, and the impact of cannabinoids. Metabolites 2022, 12, 1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cani, P.D.; Plovier, H.; Van Hul, M.; Geurts, L.; Delzenne, N.M.; Druart, C.; Everard, A. Endocannabinoids—At the crossroads between the gut microbiota and host metabolism. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2016, 12, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuddihey, H.; MacNaughton, W.K.; Sharkey, K.A. Role of the endocannabinoid system in the regulation of intestinal homeostasis. Cell. Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 14, 947–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iannotti, F.A.; Di Marzo, V. The gut microbiome, endocannabinoids and metabolic disorders. J. Endocrinol. 2021, 248, R83–R97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharkey, K.A.; Wiley, J.W. The role of the endocannabinoid system in the brain-gut axis. Gastroenterology 2016, 151, 252–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristino, L.; Bisogno, T.; Di Marzo, V. Cannabinoids and the expanded endocannabinoid system in neurological disorders. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2020, 16, 9–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.C.; Mackie, K. Review of the endocannabinoid system. Biol. Psychiatry Cogn. Neurosci. Neuroimaging 2021, 6, 607–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gyires, K.; Zádori, Z.S. Role of cannabinoids in gastrointestinal mucosal defense and inflammation. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2016, 14, 935–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crowley, K.; Kiraga, Ł.; Miszczuk, E.; Skiba, S.; Banach, J.; Latek, U.; Mendel, M.; Chłopecka, M. Effects of cannabinoids on intestinal motility, barrier permeability, and therapeutic potential in gastrointestinal diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 6682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komorowska-Müller, J.A.; Schmöle, A.C. CB2 receptor in microglia: The guardian of self-control. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 22, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, K.L.; Duncan, M.; Sharkey, K.A. Cannabinoid CB2 receptors in the gastrointestinal tract: A regulatory system in states of inflammation. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 153, 263–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehrpouya-Bahrami, P.; Chitrala, K.N.; Ganewatta, M.S.; Tang, C.; Murphy, E.A.; Enos, R.T.; Velazquez, K.T.; McCellan, J.; Nagarkatti, M.; Nagarkatti, P. Blockade of CB1 cannabinoid receptor alters gut microbiota and attenuates inflammation and diet-induced obesity. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 15645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panee, J.; Gerschenson, M.; Chang, L. Associations between microbiota, mitochondrial function, and cognition in chronic marijuana users. J. Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2018, 13, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castonguay-Paradis, S.; Lacroix, S.; Rochefort, G.; Parent, L.; Perron, J.; Martin, C.; Lamarche, B.; Raymond, F.; Flamand, N.; Di Marzo, V.; et al. Dietary fatty acid intake and gut microbiota determine circulating endocannabinoidome signaling beyond the effect of body fat. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 15975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijay, A.; Kouraki, A.; Gohir, S.; Turnbull, J.; Kelly, A.; Chapman, V.; Barrett, D.A.; Bulsiewicz, W.J.; Valdes, A.M. The anti-inflammatory effect of bacterial short chain fatty acids is partially mediated by endocannabinoids. Gut Microbes 2021, 13, 1997559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benowitz, N.L.; Liakoni, E. Tobacco use disorder and cardiovascular health. Addiction 2022, 117, 1128–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorotheo, E.U.; Arora, M.; Banerjee, A.; Bianco, E.; Cheah, N.P.; Dalmau, R.; Eissenberg, T.; Hasegawa, K.; Naidoo, P.; Nazir, N.T.; et al. Nicotine and cardiovascular health: When poison is addictive—A WHF policy brief. Glob. Heart 2024, 19, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grief, S.N. Nicotine dependence: Health consequences, smoking cessation therapies, and pharmacotherapy. Prim. Care 2011, 38, 23–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondo, T.; Nakano, Y.; Adachi, S.; Murohara, T. Effects of tobacco smoking on cardiovascular disease. Circ. J. 2019, 83, 1980–1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benowitz, N.L. Pharmacology of nicotine: Addiction, smoking-induced disease, and therapeutics. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2009, 49, 57–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, L.M.; Sayette, M.A. A review of the effects of nicotine on social functioning. Exp. Clin. Psychopharmacol. 2018, 26, 425–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valentine, G.; Sofuoglu, M. Cognitive effects of nicotine: Recent progress. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2018, 16, 403–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wittenberg, R.E.; Wolfman, S.L.; De Biasi, M.; Dani, J.A. Nicotinic acetylcholine receptors and nicotine addiction: A brief introduction. Neuropharmacology 2020, 177, 108256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacCallum, C.A.; Lo, L.A.; Pistawka, C.A.; Christiansen, A.; Boivin, M. Cannabis vaporisation: Understanding products, devices and risks. Drug Alcohol Rev. 2024, 43, 732–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prochaska, J.J.; Benowitz, N.L. Current advances in research in treatment and recovery: Nicotine addiction. Sci. Adv. 2019, 5, eaay9763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savin, Z.; Kivity, S.; Yonath, H.; Yehuda, S. Smoking and the intestinal microbiome. Arch. Microbiol. 2018, 200, 677–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berkowitz, L.; Schultz, B.M.; Salazar, G.A.; Pardo-Roa, C.; Sebastián, V.P.; Álvarez-Lobos, M.M.; Bueno, S.M. Impact of cigarette smoking on the gastrointestinal tract inflammation: Opposing effects in Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutledge, S.M.; Asgharpour, A. Smoking and liver disease. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 16, 617–625. [Google Scholar]
- Scherübl, H. Tobacco smoking and gastrointestinal cancer risk. Visc. Med. 2022, 38, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaspers, I. Cigarette smoke effects on innate immune mechanisms in the nasal mucosa. Potential effects on the microbiome. Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2014, 11, S38–S42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, L.; Mahbub, R.; Gao, B.; Bian, X.; Tu, P.; Ru, H.; Lu, K. Nicotine alters the gut microbiome and metabolites of gut-brain interactions in a sex-specific manner. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2017, 30, 2110–2119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biedermann, L.; Zeitz, J.; Mwinyi, J.; Sutter-Minder, E.; Rehman, A.; Ott, S.J.; Steurer-Stey, C.; Frei, A.; Frei, P.; Scharl, M.; et al. Smoking cessation induces profound changes in the composition of the intestinal microbiota in humans. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e59260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogtmann, E.; Flores, R.; Yu, G.; Freedman, N.D.; Shi, J.; Gail, M.H.; Dye, B.A.; Wang, G.Q.; Klepac-Ceraj, V.; Paster, B.J.; et al. Association between tobacco use and the upper gastrointestinal microbiome among Chinese men. Cancer Causes Control 2015, 26, 581–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opstelten, J.L.; Plassais, J.; van Mil, S.W.; Achouri, E.; Pichaud, M.; Siersema, P.D.; Oldenburg, B.; Cervino, A.C. Gut microbial diversity is reduced in smokers with Crohn’s disease. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2016, 22, 2070–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, E.K.; Kamm, M.A.; Wagner, J.; Teo, S.M.; Cruz, P.; Hamilton, A.L.; Ritchie, K.J.; Inouye, M.; Kirkwood, C.D. Microbial factors associated with postoperative Crohn’s disease recurrence. J. Crohns Colitis 2017, 11, 191–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Yun, Y.; Kim, S.J.; Lee, E.J.; Chang, Y.; Ryu, S.; Shin, H.; Kim, H.L.; Kim, H.N.; Lee, J.H. Association between cigarette smoking status and composition of gut microbiota: Population-based cross-sectional study. J. Clin. Med. 2018, 7, 282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanahan, E.R.; Shah, A.; Koloski, N.; Walker, M.M.; Talley, N.J.; Morrison, M.; Holtmann, G.J. Influence of cigarette smoking on the human duodenal mucosa-associated microbiota. Microbiome 2018, 6, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, C.J.; Auchtung, T.A.; Ajami, N.J.; Velasquez, K.; Smith, D.P.; De La Garza, R.; Salas, R.; Petrosino, J.F. Effects of tobacco smoke and electronic cigarette vapor exposure on the oral and gut microbiota in humans: A pilot study. PeerJ 2018, 6, e4693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nolan-Kenney, R.; Wu, F.; Hu, J.; Yang, L.; Kelly, D.; Li, H.; Jasmine, F.; Kibriya, M.G.; Parvez, F.; Shaheen, I.; et al. The association between smoking and gut microbiome in Bangladesh. Nicotine Tob. Res. 2020, 22, 1339–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, R.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, L.; Qi, Y.; He, J.; Hu, M.; Zhang, Y.; Fan, L.; Yang, T.; Wang, L.; et al. The effects of cigarettes and alcohol on intestinal microbiota in healthy men. J. Microbiol. 2020, 58, 926–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antinozzi, M.; Giffi, M.; Sini, N.; Gallè, F.; Valeriani, F.; De Vito, C.; Liguori, G.; Romano Spica, V.; Cattaruzza, M.S. Cigarette smoking and human gut microbiota in healthy adults: A systematic review. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smyth, E.M.; Kulkarni, P.; Claye, E.; Stanfill, S.; Tyx, R.; Maddox, C.; Mongodin, E.F.; Sapkota, A.R. Smokeless tobacco products harbor diverse bacterial microbiota that differ across products and brands. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 101, 5391–5403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapkota, A.R.; Berger, S.; Vogel, T.M. Human pathogens abundant in the bacterial metagenome of cigarettes. Environ. Health Perspect. 2010, 118, 351–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalile, B.; Van Oudenhove, L.; Vervliet, B.; Verbeke, K. The role of short-chain fatty acids in microbiota-gut-brain communication. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 16, 461–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schirmer, M.; Smeekens, S.P.; Vlamakis, H.; Jaeger, M.; Oostin, M.; Franzosa, E.A.; Ter Horst, R.; Jansen, T.; Jacobs, L.; Bonder, M.J.; et al. Linking the human gut microbiome to inflammatory cytokine production capacity. Cell 2016, 167, 1125–1136.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, Y.P.; Bernardi, A.; Frozza, R.L. The role of short-chain fatty acids from gut microbiota in gut-brain communication. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahearn, O.C.; Watson, M.N.; Rawls, S.M. Chemokines, cytokines and substance use disorders. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2021, 220, 108511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.H.; Park, J.; Kim, M. Gut microbiota-derived short-chain fatty acids, T cells, and inflammation. Immune Netw. 2014, 14, 277–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Taylor, J.R.; Wolf, M.E.; Shaham, Y. Circuit and synaptic plasticity mechanisms of drug relapse. J. Neurosci. 2017, 37, 10867–10876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calipari, E.S.; Godino, A.; Peck, E.G.; Salery, M.; Mervosh, N.L.; Landry, J.A.; Russo, S.J.; Hurd, Y.L.; Nestler, E.J.; Kiraly, D.D. Granulocyte-colony stimulating factor controls neural and behavioral plasticity in response to cocaine. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Timary, P.; Stärkel, P.; Delzenne, N.M.; Leclercq, S. A role for the peripheral immune system in the development of alcohol use disorders? Neuropharmacology 2017, 122, 148–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borrego-Ruiz, A.; Borrego, J.J. Epigenetic mechanisms in aging: Extrinsic factors and gut microbiome. Genes 2024, 15, 1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mews, P.; Egervari, G.; Nativio, R.; Sidoli, S.; Donahue, G.; Lombroso, S.I.; Alexander, D.C.; Riesche, S.L.; Heller, E.A.; Nestler, E.J.; et al. Alcohol metabolism contributes to brain histone acetylation. Nature 2019, 574, 717–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, S.P.; Denu, J.M. Short-chain fatty acids activate acetyltransferase p300. eLife 2021, 10, e72171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, D.M.; Nestler, E.J. Neuroepigenetics and addiction. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2018, 148, 747–765. [Google Scholar]
- Colonna, M.; Butovsky, O. Microglia function in the central nervous system during health and neurodegeneration. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2017, 35, 441–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilca, S.J.; Margetts, A.V.; Pollock, T.A.; Tuest, L.M. Transcriptional and epigenetic regulation of microglia in substance use disorders. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 2023, 125, 103838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehhaghi, M.; Kazemi-Shariat-Panahi, H.; Guillemin, G.J. Microorganisms, tryptophan metabolism, and kynurenine pathway: A complex interconnected loop influencing human health status. Int. J. Tryptophan Res. 2019, 12, 1178646919852996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leclercq, S.; Schwarz, M.; Delzenne, N.M.; Stärkel, P.; de Timary, P. Alterations of kynurenine pathway in alcohol use disorder and abstinence: A link with gut microbiota, peripheral inflammation and psychological symptoms. Transl. Psychiatry 2021, 11, 503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales-Puerto, N.; Giménez-Gómez, P.; Pérez-Hernández, M.; Abuin-Martínez, C.; Gil de Biedma-Elduayen, L.; Vidal, R.; Gutiérrez-López, M.D.; O’Shea, E.; Colado, M.I. Addiction and the kynurenine pathway: A new dancing couple? Pharmacol. Ther. 2021, 223, 107807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez-Pérez, O.; Cruz-Ramón, V.; Chinchilla-López, P.; Méndez-Sánchez, N. The role of the gut microbiota in bile acid metabolism. Ann. Hepatol. 2017, 16, s15–s20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavlović, N.; Goločorbin-Kon, S.; Ðanić, M.; Stanimirov, B.; Al-Salami, H.; Stankov, K.; Mikov, M. Bile acids and their derivatives as potential modifiers of drug release and pharmacokinetic profiles. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ridlon, J.M.; Kang, D.J.; Hylemon, P.B.; Bajaj, J.S. Bile acids and the gut microbiome. Curr. Opin. Gastroenterol. 2014, 30, 332–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, R.; Debs, L.H.; Patel, A.P.; Nguyen, D.; Patel, K.; O’Connor, G.; Grati, M.; Mittal, J.; Yan, D.; Eshraghi, A.; et al. Neurotransmitters: The critical modulators regulating gut-brain axis. J. Cell. Physiol. 2017, 232, 2359–2372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinan, T.G.; Cryan, J.F. The microbiome-gut-brain axis in health and disease. Gastroenterol. Clin. N. Am. 2017, 46, 77–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciccocioppo, R. The role of serotonin in craving: From basic research to human studies. Alcohol Alcohol. 1999, 34, 244–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Müller, C.P.; Homberg, J.R. The role of serotonin in drug use and addiction. Behav. Brain Res. 2015, 277, 146–192. [Google Scholar]
- Volkow, N.D.; Michaelides, M.; Baler, R. The neuroscience of drug reward and addiction. Physiol. Rev. 2019, 99, 2115–2140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamamah, S.; Aghazarian, A.; Nazaryan, A.; Hajnal, A.; Covasa, M. Role of microbiota-gut-brain axis in regulating dopaminergic signaling. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borrego-Ruiz, A.; Borrego, J.J. Pharmacogenomic and pharmacomicrobiomic aspects of drugs of abuse. Genes 2025, 16, 403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmermann, M.; Zimmermann-Kogadeeva, M.; Wegmann, R.; Goodman, A.L. Mapping human microbiome drug metabolism by gut bacteria and their genes. Nature 2019, 570, 462–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarkar, A.; Lehto, S.M.; Harty, S.; Dinan, T.G.; Cryan, J.F.; Burnet, P.W.J. Psychobiotics and the manipulation of bacteria-gut-brain signals. Trends Neurosci. 2016, 39, 763–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mansuy-Aubert, V.; Ravussin, Y. Short chain fatty acids: The messengers from down below. Front. Neurosci. 2023, 17, 1197759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharkey, K.A.; Mawe, G.M. The enteric nervous system. Physiol. Rev. 2023, 103, 1487–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dowling, L.R.; Strazzari, M.R.; Keely, S.; Kaiko, G.E. Enteric nervous system and intestinal epithelial regulation of the gut-brain axis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2022, 150, 513–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margolis, K.G.; Cryan, J.F.; Mayer, E.A. The microbiota-gut-brain axis: From motility to mood. Gastroenterology 2021, 160, 1486–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, M.; Pearse, D.D. The Yin and Yang of microglia-derived extracellular vesicles in CNS injury and diseases. Cells 2024, 13, 1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casali, B.T.; Reed-Geaghan, E.G. Microglial function and regulation during development, homeostasis and Alzheimer’s disease. Cells 2021, 10, 957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Li, F.; Jia, J.; Song, X.; Qin, S.; Wang, R.; Jin, F.; Kitazato, K.; et al. The gut-microglia connection: Implications for central nervous system diseases. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, R.; Qian, S.; Cho, W.C.S.; Zhou, J.; Jin, C.; Zhong, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhang, X.; Xu, Z.; Tian, M.; et al. Microbiota-microglia connections in age-related cognition decline. Aging Cell 2022, 21, e13599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antoine, D.; Venigalla, G.; Truitt, B.; Roy, S. Linking the gut microbiome to microglial activation in opioid use disorder. Front. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 1050661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasarello, K.; Cudnoch-Jedrzejewska, A.; Czarzasta, K. Communication of gut microbiota and brain via immune and neuroendocrine signaling. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1118529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subedi, L.; Huang, H.; Pant, A.; Westgate, P.M.; Bada, H.S.; Bauer, J.A.; Giannone, P.J.; Sithisarn, T. Plasma brain-derived neurotrophic factor levels in newborn infants with neonatal abstinence syndrome. Front. Pediatr. 2017, 5, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palma-Álvarez, R.F.; Ros-Cucurull, E.; Amaro-Hosey, K.; Rodriguez-Cintas, L.; Grau-López, L.; Corominas-Roso, M.; Sánchez-Mora, C.; Roncero, C. Peripheral levels of BDNF and opiate-use disorder: Literature review and update. Rev. Neurosci. 2017, 28, 499–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinds, J.A.; Sanchez, E.R. The role of the hypothalamus-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis in test-induced anxiety: Assessments, physiological responses, and molecular details. Stresses 2022, 2, 146–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusch, J.A.; Layden, B.T.; Dugas, L.R. Signalling cognition: The gut microbiota and hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1130689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soravia, L.M.; Moggi, F.; de Quervain, D.J. Effects of cortisol administration on craving during in vivo exposure in patients with alcohol use disorder. Transl. Psychiatry 2021, 11, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, J.; Strang, J. Medication treatment of opioid use disorder. Biol. Psychiatry 2020, 87, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soyka, M.; Müller, C.A. Pharmacotherapy of alcoholism—An update on approved and off-label medications. Expert. Opin. Pharmacother. 2017, 18, 1187–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witkiewitz, K.; Litten, R.Z.; Leggio, L. Advances in the science and treatment of alcohol use disorder. Sci. Adv. 2019, 5, eaax4043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brezing, C.A.; Levin, F.R. The current state of pharmacological treatments for cannabis use disorder and withdrawal. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2018, 43, 173–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kampman, K.M. The treatment of cocaine use disorder. Sci. Adv. 2019, 5, eaax1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shorter, D.; Domingo, C.B.; Kosten, T.R. Emerging drugs for the treatment of cocaine use disorder: A review of neurobiological targets and pharmacotherapy. Expert. Opin. Emerg. Drugs 2015, 20, 15–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaulieu, M.; Tremblay, J.; Baudry, C.; Pearson, J.; Bertrand, K. A systematic review and meta-analysis of the efficacy of the long-term treatment and support of substance use disorders. Soc. Sci. Med. 2021, 285, 114289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bari, A.; DiCesare, J.; Babayan, D.; Runcie, M.; Sparks, H.; Wilson, B. Neuromodulation for substance addiction in human subjects: A review. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2018, 95, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koob, G.F.; Volkow, N.D. Neurobiology of addiction: A neurocircuitry analysis. Lancet Psychiatry 2016, 3, 760–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letchumanan, V.; Low, S.; Tan, L.T.; Law, J.W.F.; Ratnasingam, V.; Thurairajasingam, S.; Lee, L.H. Exploring the potential role of probiotics in substance use disorders. Gut 2022, 71, A58–A59. [Google Scholar]
- López, G.; Orchowski, L.M.; Reddy, M.K.; Nargiso, J.; Johnson, J.E. A review of research-supported group treatments for drug use disorders. Subst. Abus. Treat. Prev. Policy 2021, 16, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.C.; Chen, Y.C.; Chen, S.J.; Lee, C.H.; Cheng, C.M. Alcohol addiction, gut microbiota, and alcoholism treatment: A review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewulf, E.M.; Cani, P.D.; Claus, S.P.; Fuentes, S.; Puylaert, P.G.; Neyrinck, A.M.; Bindels, L.B.; de Vos, W.M.; Gibson, G.R.; Thissen, J.P.; et al. Insight into the prebiotic concept: Lessons from an exploratory, double blind intervention study with inulin-type fructans in obese women. Gut 2013, 62, 1112–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajaj, J.S.; Gavis, E.A.; Fagan, A.; Wade, J.B.; Thacker, L.R.; Fuchs, M.; Patel, S.; Davis, B.; Meador, J.; Puri, P.; et al. A randomized clinical trial of fecal microbiota transplant for alcohol use disorder. Hepatology 2021, 73, 1688–1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amadieu, C.; Coste, V.; Neyrinck, A.M.; Thijssen, V.; Leyrolle, Q.; Bindels, L.B.; Piessevaux, H.; Stärkel, P.; de Timary, P.; Delzenne, N.M.; et al. Restoring an adequate dietary fiber intake by inulin supplementation: A pilot study showing an impact on gut microbiota and sociability in alcohol use disorder patients. Gut Microbes 2022, 14, 2007042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.D.; Nunes, E.V., Jr.; Novo, P.; Bachrach, K.; Bailey, G.L.; Bhatt, S.; Farkas, S.; Fishman, M.; Gauthier, P.; Hodgkins, C.C.; et al. Comparative effectiveness of extended-release naltrexone versus buprenorphine-naloxone for opioid relapse prevention (X:BOT): A multicentre, open-label, randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2018, 391, 309–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helstrom, A.W.; Blow, F.C.; Slaymaker, V.; Kranzler, H.R.; Leong, S.; Oslin, D. Reductions in alcohol craving following naltrexone treatment for heavy drinking. Alcohol Alcohol. 2016, 51, 562–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenwood-Van Meerveld, B.; Standifer, K.M. Methylnaltrexone in the treatment of opioid-induced constipation. Clin. Exp. Gastroenterol. 2008, 1, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klenske, E.; Bojarski, C.; Waldner, M.; Rath, T.; Neurath, M.F.; Atreya, R. Targeting mucosal healing in Crohn’s disease: What the clinician needs to know. Ther. Adv. Gastroenterol. 2019, 12, 1756284819856865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gicquelais, R.E.; Bohnert, A.S.B.; Thomas, L.; Foxman, B. Opioid agonist and antagonist use and the gut microbiota: Associations among people in addiction treatment. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 19471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barkus, A.; Baltrūnienė, V.; Baušienė, J.; Baltrūnas, T.; Barkienė, L.; Kazlauskaitė, P.; Baušys, A. The gut-brain axis in opioid use disorder: Exploring the bidirectional influence of opioids and the gut microbiome—A comprehensive review. Life 2024, 14, 1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofford, R.S.; Meckel, K.R.; Wiser, E.J.; Wang, W.; Sens, J.P.; Kim, M.; Godino, A.; Lam, T.T.; Kiraly, D.D. Microbiome depletion increases fentanyl self-administration and alters the striatal proteome through short-chain fatty acids. eNeuro 2024, 11, EENEURO.0388-23.2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volkow, N.D.; Blanco, C. Substance use disorders: A comprehensive update of classification, epidemiology, neurobiology, clinical aspects, treatment and prevention. World Psychiatry 2023, 22, 203–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Z.; Xue, Q.; Luo, Y.; Yu, B.; Hua, B.; Liu, Z. The interplay between the microbiota and opioid in the treatment of neuropathic pain. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1390046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vadivelu, N.; Lumermann, L.; Zhu, R.; Kodumudi, G.; Elhassan, A.O.; Kaye, A.D. Pain control in the presence of drug addiction. Curr. Pain Headache Rep. 2016, 20, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, S.; Robison, A.J.; Mazei-Robison, M.S. Reward circuitry in addiction. Neurotherapeutics 2017, 14, 687–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borrego-Ruiz, A. A current overview on adolescent alcohol misuse and its potential negative impacts. Alcohol. Drug Addict./Alkohol. Narkom. 2024, 37, 213–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arranz, S.; Chiva-Blanch, G.; Valderas-Martínez, P.; Medina-Remón, A.; Lamuela-Raventós, R.M.; Estruch, R. Wine, Beer, Alcohol and Polyphenols on Cardiovascular Disease and Cancer. Nutrients 2012, 4, 759–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagano, C.; Navarra, G.; Coppola, L.; Avilia, G.; Bifulco, M.; Laezza, C. Cannabinoids: Therapeutic Use in Clinical Practice. Int J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldo, B.A. The entactogen 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA; ecstasy) as a treatment aid in psychotherapy and its safety concerns. Arch Toxicol. 2024, 98, 2409–2427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.E.; Ha, J.S.; Park, H.Y.; Lee, E. Alteration of gut microbiota composition by short-term low-dose alcohol intake is restored by fermented rice liquor in mice. Food Res. Int. 2020, 128, 108800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boonchooduang, N.; Louthrenoo, O.; Likhitweerawong, N.; Kunasol, C.; Thonusin, C.; Sriwichaiin, S.; Nawara, W.; Chattipakorn, N.; Chattipakorn, S.C. Impact of psychostimulants on microbiota and short-chain fatty acids alterations in children with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 3034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fulcher, J.A.; Hussain, S.K.; Cook, R.; Li, F.; Tobin, N.H.; Ragsdale, A.; Shoptaw, S.; Gorbach, P.M.; Aldrovandi, G.M. Effects of substance use and sex practices on the intestinal microbiome during HIV-1 infection. J. Infect. Dis. 2018, 218, 1560–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, A.; Alghetaa, H.K.; Zhou, J.; Chatterjee, S.; Nagarkatti, P.; Nagarkatti, M. Protective effects of Δ(9)-tetrahydrocannabinol against enterotoxin-induced acute respiratory distress syndrome are mediated by modulation of microbiota. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2020, 177, 5078–5095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Yang, J.; Yang, C.; Chen, T.; Wang, Z.; Li, J.; Qin, F.; Deng, Q.; Zhang, X. Sensitivity to morphine reward associates with gut dysbiosis in rats with morphine-induced conditioned place preference. Front. Psychiatry 2020, 11, 631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Meng, J.; Ban, Y.; Jalodia, R.; Chupikova, I.; Fernandez, I.; Brito, N.; Sharma, U.; Abreu, M.T.; Ramakrishnan, S.; et al. Morphine tolerance is attenuated in germfree mice and reversed by probiotics, implicating the role of gut microbiome. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 13523–13532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezquer, F.; Quintanilla, M.E.; Morales, P.; Santapau, D.; Munita, J.M.; Moya-Flores, F.; Ezquer, M.; Herrera-Marschitz, M.; Israel, Y. A dual treatment blocks alcohol binge-drinking relapse: Microbiota as a new player. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2022, 236, 109466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borrego-Ruiz, A.; Borrego, J.J. Psychobiotics: A new perspective on the treatment of stress, anxiety, and depression. Anxiety Stress 2024, 30, 79–93. [Google Scholar]
- Borrego-Ruiz, A.; Borrego, J.J. Nutritional psychiatry: A novel approach to the treatment of mental health disorders. Actas Esp. Psiquiatr. 2025, 53, 443–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).