Moringa oleifera Leaf Infusion as a Functional Beverage: Polyphenol Content, Antioxidant Capacity, and Its Potential Role in the Prevention of Metabolopathies
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Material and Preparation of MO Infusion
2.2. DPPH Scavenging Activity of Polyphenols from MO Infusion
2.3. Polyphenol Content Using the Folin-Ciocalteu Method
2.4. Anti-Browning Assay of Freshly-Cut Apple Slices
2.5. Reducing Sugar Content
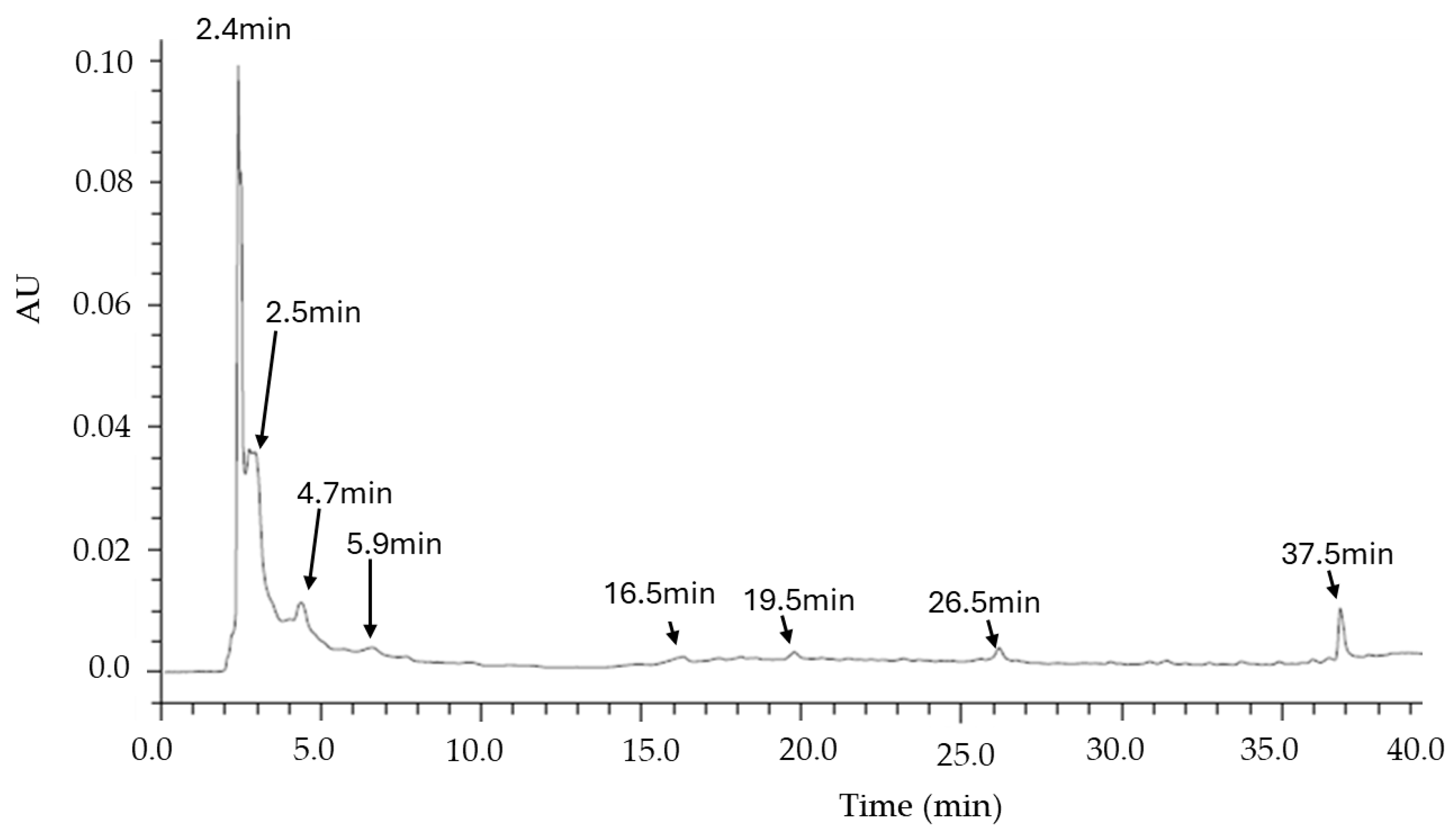
2.6. Chromatographic Analysis
2.7. Prophylactic Animal Model Design for MO Infusion
2.7.1. Diet, Grouping, and Dosing
2.7.2. Body Weight and Food Intake
2.7.3. Blood Analysis
2.7.4. Histopathological Liver Analysis
2.7.5. Psychomotor Evaluation
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Antioxidant Activity and Polyphenol Content
3.2. TLC and HPLC Analysis of the MO Infusion
3.3. Food Intake and Weight Gain
3.4. Biochemical and Hematic Parameters
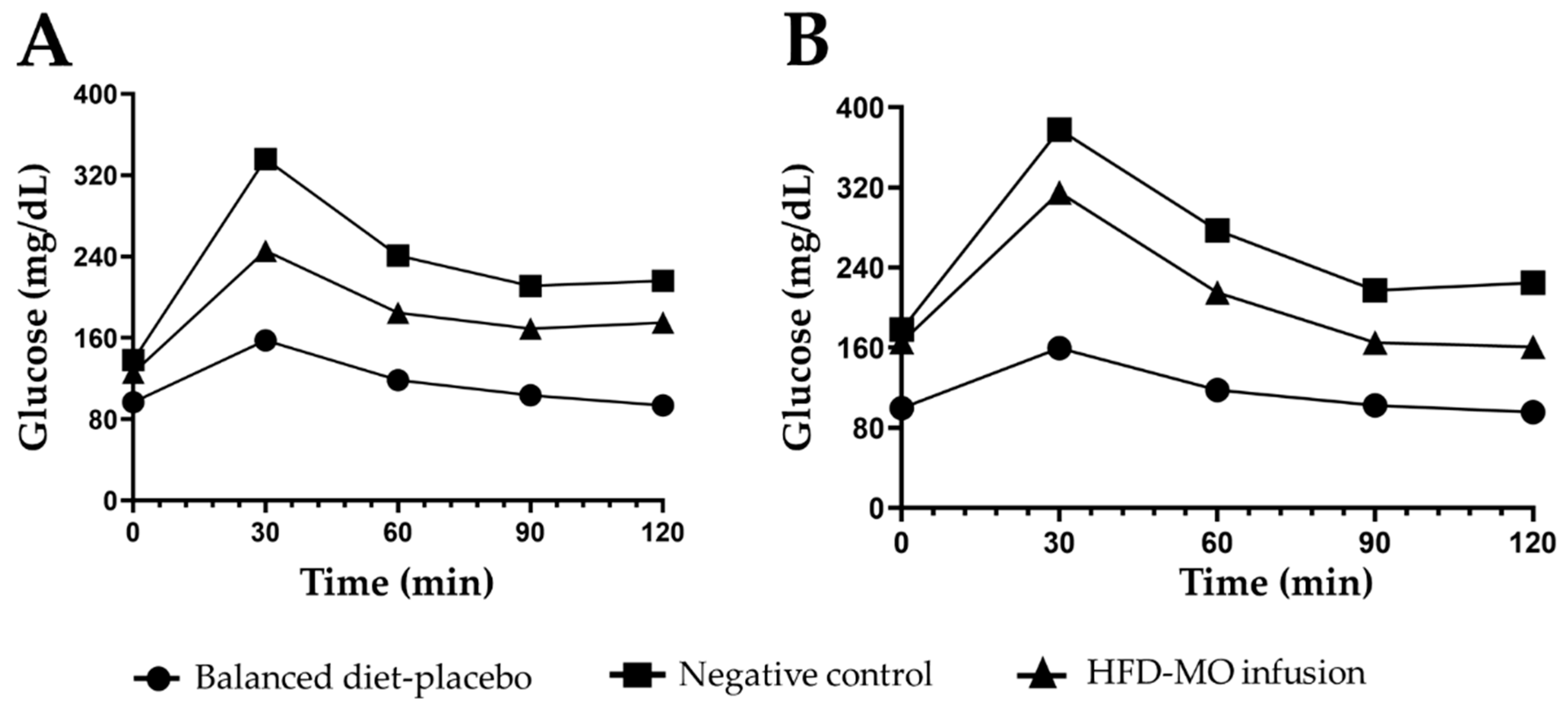
3.5. Glucose Metabolism
3.6. Histopathological Parameters Analysis
3.7. Locomotor Activity Evaluation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lopez Entrago, E.; Manso Agustín, V.; Pazos Gonzalez, A.; Sanchez Celadam, B. Metabolopathies. The Importance of a Good Performance Nurse. Rev. Enferm. 2011, 34, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- WHO. W.H.O. Global Health Observatory Data Repository. Available online: https://data.who.int/indicators/i/C6262EC/BEFA58B (accessed on 7 October 2024).
- Garus-Pakowska, A. Metabolic Diseases—A Challenge for Public Health in the 21st Century. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 6789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saklayen, M.G. The Global Epidemic of the Metabolic Syndrome. Curr. Hypertens. Rep. 2018, 20, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saudubray, J.-M.; Garcia-Cazorla, À. Inborn Errors of Metabolism Overview. Pediatr. Clin. N. Am. 2018, 65, 179–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahed, G.; Aoun, L.; Bou Zerdan, M.; Allam, S.; Bou Zerdan, M.; Bouferraa, Y.; Assi, H.I. Metabolic Syndrome: Updates on Pathophysiology and Management in 2021. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wachtel-Galor, S.; Benzie, I.F.F. Herbal Medicine: An Introduction to Its History, Usage, Regulation, Current Trends, and Research Needs. In Herbal Medicine: Biomolecular and Clinical Aspects, 2nd ed.; CRC Press/Taylor & Francis: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2011; ISBN 9781439807132. [Google Scholar]
- Ekor, M. The Growing Use of Herbal Medicines: Issues Relating to Adverse Reactions and Challenges in Monitoring Safety. Front. Pharmacol. 2014, 4, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Guo, W.; Zhang, C.; Chen, F.; Tan, H.Y.; Li, S.; Wang, N.; Feng, Y. Herbal Medicine in the Treatment of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Diseases-Efficacy, Action Mechanism, and Clinical Application. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharsallah, K.; Rezig, L.; Rajoka, M.S.R.; Mehwish, H.M.; Ali, M.A.; Chew, S.C. Moringa oleifera: Processing, Phytochemical Composition, and Industrial Applications. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2023, 160, 180–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, X.; Li, B.; Olayanju, J.; Drake, J.; Chen, N. Nutraceutical or Pharmacological Potential of Moringa oleifera Lam. Nutrients 2018, 10, 343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anwar, F.; Latif, S.; Ashraf, M.; Gilani, A.H. Moringa oleifera: A Food Plant with Multiple Medicinal Uses. Phytother. Res. 2007, 21, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olson, M.E.O.; Fahey, J.W. Moringa oleifera: Un Árbol Multiusos Para Las Zonas Tropicales Seca. Rev. Mex. Biodivers. 2011, 82, 1071–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leone, A.; Spada, A.; Battezzati, A.; Schiraldi, A.; Aristil, J.; Bertoli, S. Moringa oleifera Seeds and Oil: Characteristics and Uses for Human Health. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 2141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, J.; Peng, L.; Yang, M.; Jiang, W.; Mao, J.; Shi, C.; Tian, Y.; Sheng, J. Alkaloid Extract of Moringa oleifera Lam. Exerts Antitumor Activity in Human Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer via Modulation of the JAK2/STAT3 Signaling Pathway. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2021, 2021, 5591687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, N.; Sikder, K.; Ghosh, S.; Fromenty, B.; Dey, S. Moringa oleifera Lam. Leaf Extract Prevents Early Liver Injury and Restores Antioxidant Status in Mice Fed with High-Fat Diet. Indian J. Exp. Biol. 2012, 50, 404–412. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vongsak, B.; Sithisarn, P.; Mangmool, S.; Thongpraditchote, S.; Wongkrajang, Y.; Gritsanapan, W. Maximizing Total Phenolics, Total Flavonoids Contents and Antioxidant Activity of Moringa oleifera Leaf Extract by the Appropriate Extraction Method. Ind. Crops Prod. 2013, 44, 566–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusmiyati, K.; Rahmawati, E.; Waangsir, F.W.F.; Selasa, P. Alkaloids, Flavonoids, Tannins and Saponins Contents in Moringa oleifera Leaves. Indones. J. Glob. Health Res. 2022, 4, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhongade, H.K.J.; Paikra, B.K.; Gidwani, B. Phytochemistry and Pharmacology of Moringa oleifera Lam. J. Pharmacopunct. 2017, 20, 194–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Bao, Y.; Shen, X.; Zengin, G.; Lyu, Y.; Xiao, J.; Weng, Z. Niazirin from Moringa oleifera Lam. Attenuates High Glucose-Induced Oxidative Stress through PKCζ/Nox4 Pathway. Phytomedicine 2021, 86, 153066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manach, C.; Scalbert, A.; Morand, C.; Rémésy, C.; Jiménez, L. Polyphenols: Food Sources and Bioavailability. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2004, 79, 727–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, G.; Mei, X.; Hu, J. The Antioxidant Activities of Natural Polysaccharides. Curr. Drug Targets 2017, 18, 1296–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Yeap Foo, L. Polyphenolics of Salvia—A Review. Phytochemistry 2002, 59, 117–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moharram, F.A.; Marzouk, M.S.; El-Shenawy, S.M.; Gaara, A.H.; El Kady, W.M. Polyphenolic Profile and Biological Activity of Salvia splendens Leaves. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2012, 64, 1678–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gasmi, A.; Mujawdiya, P.K.; Noor, S.; Lysiuk, R.; Darmohray, R.; Piscopo, S.; Lenchyk, L.; Antonyak, H.; Dehtiarova, K.; Shanaida, M.; et al. Polyphenols in Metabolic Diseases. Molecules 2022, 27, 6280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Xu, M.; Zhang, W.; Liu, C.; Chen, S. Natural Polyphenols in Metabolic Syndrome: Protective Mechanisms and Clinical Applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makhtoomi, M.; Shateri, Z.; Mashoufi, A.; Nouri, M.; Honarvar, B.; Keshani, P. The Association between Dietary Polyphenol Intake and the Odds of Metabolic Syndrome. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 25559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, A.B.; Goud, V.V.; Das, C. Phenolic Compounds as Functional Ingredients in Beverages. In Value-Added Ingredients and Enrichments of Beverages; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 285–323. [Google Scholar]
- Dini, I. An Overview of Functional Beverages. In Functional and Medicinal Beverages; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 1–40. [Google Scholar]
- Sugajski, M.; Buszewska-Forajta, M.; Buszewski, B. Functional Beverages in the 21st Century. Beverages 2023, 9, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalska, A.; Leoniak, K.; Sołowiej, B.G. Consumers’ Attitudes and Intentions toward Functional Beverages: A Lesson for Producers and Retailers. Decision 2024, 51, 321–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olson, M.E.; Alvarado-Cárdenas, L.O. ¿Dónde Cultivar El Árbol Milagro, Moringa oleifera, En México? Un Análisis de Su Distribución Potencial. Rev. Mex. Biodivers. 2016, 87, 1089–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortes-Alvarez, S.I.; Delgado-Enciso, I.; Rodriguez-Hernandez, A.; Hernandez-Fuentes, G.A.; Aurelien-Cabezas, N.S.; Moy-Lopez, N.A.; Cortes-Alvarez, N.Y.; Guzman-Muñiz, J.; Guzman-Esquivel, J.; Rodriguez-Sanchez, I.P.; et al. Efficacy of Hot Tea Infusion vs. Ethanolic Extract of Moringa oleifera for the Simultaneous Treatment of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver, Hyperlipidemia, and Hyperglycemia in a Murine Model Fed with a High-Fat Diet. J. Nutr. Metab. 2024, 2024, 2209581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bitwell, C.; Indra, S.S.; Luke, C.; Kakoma, M.K. A Review of Modern and Conventional Extraction Techniques and Their Applications for Extracting Phytochemicals from Plants. Sci. Afr. 2023, 19, e01585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaikh, J.R.; Patil, M. Qualitative Tests for Preliminary Phytochemical Screening: An Overview. Int. J. Chem. Stud. 2020, 8, 603–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso-Castro, A.J.; Villarreal, M.L.; Salazar-Olivo, L.A.; Gomez-Sanchez, M.; Dominguez, F.; Garcia-Carranca, A. Mexican Medicinal Plants Used for Cancer Treatment: Pharmacological, Phytochemical and Ethnobotanical Studies. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2011, 133, 945–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baliyan, S.; Mukherjee, R.; Priyadarshini, A.; Vibhuti, A.; Gupta, A.; Pandey, R.P.; Chang, C.-M. Determination of Antioxidants by DPPH Radical Scavenging Activity and Quantitative Phytochemical Analysis of Ficus Religiosa. Molecules 2022, 27, 1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.J.; Oh, Y.C.; Cho, W.K.; Ma, J.Y. Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Activity Determination of One Hundred Kinds of Pure Chemical Compounds Using Offline and Online Screening HPLC Assay. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2015, 2015, 165457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beas-Guzmán, O.F.; Cabrera-Licona, A.; Hernández-Fuentes, G.A.; Ceballos-Magaña, S.G.; Guzmán-Esquivel, J.; De-León-Zaragoza, L.; Ramírez-Flores, M.; Diaz-Martinez, J.; Garza-Veloz, I.; Martínez-Fierro, M.L.; et al. Ethanolic Extract of Averrhoa carambola Leaf Has an Anticancer Activity on Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cells: An In Vitro Study. Pharmaceutics 2024, 17, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, J.; Ming, Y.; Cui, Q.; Zheng, N.; Yang, S.; Li, W.; Gao, H.; Zhang, R.; Cheng, X. Efficient Extraction and Antioxidant Activity of Polyphenols from Antrodia cinnamomea. BMC Biotechnol. 2022, 22, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, E.W.C.; Lim, Y.Y.; Chong, K.L.; Tan, J.B.L.; Wong, S.K. Antioxidant Properties of Tropical and Temperate Herbal Teas. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2010, 23, 185–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schorn, P.J. The European Pharmacopoeia. Med. Secoli 1993, 5, 103–114. [Google Scholar]
- Hudz, N.; Yezerska, O.; Shanajda, M.; Horčinová Sedláčková, V.; Wieczorek, P.P. Application of the Folin-Ciocalteu Method to the Evaluation of Salvia sclarea Extracts. Pharmacia 2019, 66, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafri, L.; Saleem, S.; Ihsan-ul-Haq; Ullah, N.; Mirza, B. In Vitro Assessment of Antioxidant Potential and Determination of Polyphenolic Compounds of Hedera nepalensis K. Koch. Arab. J. Chem. 2017, 10, S3699–S3706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Park, H.S.; Jung, H.J.; Park, Y.J.; Kang, M.K.; Kim, H.J.; Yoon, D.; Ullah, S.; Kang, D.; Park, Y.; et al. Anti-Browning Effect of 2-Mercaptobenzo Imidazole Analogs with Antioxidant Activity on Freshly-Cut Apple Slices and Their Highly Potent Tyrosinase Inhibitory Activity. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, Y.; Liang, Y.; Chai, W.; Wei, Q.; Yu, Z.; Wang, L. Effect of Ascorbic Acid on Tyrosinase and Its Anti-browning Activity in Fresh-cut Fuji Apple. J. Food Biochem. 2021, 45, e13995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, I.P.; Elliston, A.; Ryden, P.; Bancroft, I.; Roberts, I.N.; Waldron, K.W. Rapid Quantification of Reducing Sugars in Biomass Hydrolysates: Improving the Speed and Precision of the Dinitrosalicylic Acid Assay. Biomass Bioenergy 2012, 44, 117–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez-Fuentes, G.A.; Delgado-Enciso, O.G.; Larios-Cedeño, E.G.; Sánchez-Galindo, J.M.; Ceballos-Magaña, S.G.; Pineda-Urbina, K.; Alcalá-Pérez, M.A.; Magaña-Vergara, N.E.; Delgado-Enciso, J.; Díaz-Llerenas, U.; et al. Comparative Analysis of Infusions and Ethanolic Extracts of Annona muricata Leaves from Colima, Mexico: Phytochemical Profile and Antioxidant Activity. Life 2024, 14, 1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakakibara, H.; Honda, Y.; Nakagawa, S.; Ashida, H.; Kanazawa, K. Simultaneous Determination of All Polyphenols in Vegetables, Fruits, and Teas. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2003, 51, 571–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- George, V.C.; Kumar, D.R.N.; Suresh, P.K.; Kumar, R.A. Antioxidant, DNA Protective Efficacy and HPLC Analysis of Annona muricata (Soursop) Extracts. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 52, 2328–2335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Secretaría de Agricultura y Desarrollo Rural. Mexican Norm NOM 0062-ZOO-1999 Entitled Technical Specifications for the Production, Care and Use of Laboratory Animals; Gobierno de México: Mexico City, Mexico, 1999; pp. 1–59. [Google Scholar]
- Leary, S.R.A.; Underwood, W.; Raymond, A.; Samuel, C.; Greenacre, C.; Gwaltney-Brant, S.; Grandin, T.; McCrackin, M.A.; Meyer, R.; Miller, D.; et al. AVMA Guidelines for the Euthanasia of Animals: 2020 Edition; American Veterinary Medical Association: Schaumburg, IL, USA, 2020; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Madrigal-Perez, V.M.; García-Rivera, A.; Rodriguez-Hernandez, A.; Ceja-Espiritu, G.; Briseño-Gomez, X.G.; Galvan-Salazar, H.R.; Soriano-Hernandez, A.D.; Guzman-Esquivel, J.; Martinez-Fierro, M.L.; Newton-Sanchez, O.A.; et al. Preclinical Analysis of Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drug Usefulness for the Simultaneous Prevention of Steatohepatitis, Atherosclerosis and Hyperlipidemia. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2015, 8, 22477–22483. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, J.; Liu, S.; Li, M.; Guo, F.; Wu, X.; Hu, J.; Wen, L.; Wang, J.; Li, X. Optimal Fasting Duration for Mice as Assessed by Metabolic Status. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 21509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Rivera, A.; Madriga, V.M.; Rodriguez-Hernandez, A.; Martinez-Martinez, R.; Martine, M.L.; Soriano, A.D.; Galvan-Salazar, H.R.; Gonzalez-Alvarez, R.; L. Valdez-Velazquez, L.; Espinoza-Gómez, F.; et al. A Simple and Low-Cost Experimental Mouse Model for the Simultaneous Study of Steatohepatitis and Preclinical Atherosclerosis. Asian J. Anim. Vet. Adv. 2014, 9, 202–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddad, Y.; Vallerand, D.; Brault, A.; Spénard, J.; Haddad, P.S. NCX 1000 Alone or in Combination with Vitamin E Reverses Experimental Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis in the Rat Similarly to UDCA. Int. J. Hepatol. 2011, 2011, 136816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mostafavi, H.; Ghassemifard, L.; Rostami, A.; Alipour, M.; Nadri, S. Trabecular Meshwork Mesenchymal Stem Cell Transplantation Improve Motor Symptoms of Parkinsonian Rat Model. Biologicals 2019, 61, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walf, A.A.; Frye, C.A. The Use of the Elevated plus Maze as an Assay of Anxiety-Related Behavior in Rodents. Nat. Protoc. 2007, 2, 322–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, H.; Matar, M.A.; Joseph, Z. Animal Models of Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder. Curr. Protoc. Neurosci. 2013, 64, 9–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Estrada-Reyes, R.; López-Rubalcava, C.; Ferreyra-Cruz, O.A.; Dorantes-Barrón, A.M.; Heinze, G.; Moreno Aguilar, J.; Martínez-Vázquez, M. Central Nervous System Effects and Chemical Composition of Two Subspecies of Agastache mexicana; an Ethnomedicine of Mexico. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2014, 153, 98–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivadeneyra-Domínguez, E.; Rosas-Jarquín, C.J.; Vázquez-Luna, A.; Díaz-Sobac, R.; Rodríguez-Landa, J.F. Efecto de La Acetona Cianohidrina, Un Derivado de La Yuca, Sobre La Actividad Motora y La Función Renal y Hepática En Ratas Wistar. Neurología 2019, 34, 300–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dudley, W.N.; Benuzillo, J.G.; Carrico, M.S. SPSS and SAS Programming for the Testing of Mediation Models. Nurs. Res. 2004, 53, 59–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosner, B. Fundamentals of Biostatistics/Bernard Rosner, 7th ed.; Cengage Learning, c2011; Brooks/Cole: Boston, MA, USA, 2011; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Almatrafi, M.; Vergara-Jimenez, M.; Murillo, A.; Norris, G.; Blesso, C.; Fernandez, M. Moringa Leaves Prevent Hepatic Lipid Accumulation and Inflammation in Guinea Pigs by Reducing the Expression of Genes Involved in Lipid Metabolism. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbagallo, I.; Vanella, L.; Distefano, A.; Nicolosi, D.; Maravigna, A.; Lazzarino, G.; Di Rosa, M.; Tibullo, D.; Acquaviva, R.; Li Volti, G. Moringa oleifera Lam. Improves Lipid Metabolism during Adipogenic Differentiation of Human Stem Cells. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2016, 20, 5223–5232. [Google Scholar]
- Seriki, S. Effects of Moringa oleifera Leaves on Hematological Indices in Humans; Austin Publishing Group: Monroe Township, NJ, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Arabshahi-Delouee, S.; Aalami, M.; Urooj, A.; Krishnakantha, T.P. Moringa oleifera Leaves as an Inhibitor of Human Platelet Aggregation. Pharm. Biol. 2009, 47, 734–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamza, A.A. Ameliorative Effects of Moringa oleifera Lam Seed Extract on Liver Fibrosis in Rats. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2010, 48, 345–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bais, S.; Singh, G.S.; Sharma, R. Antiobesity and Hypolipidemic Activity of Moringa oleifera Leaves against High Fat Diet-Induced Obesity in Rats. Adv. Biol. 2014, 2014, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joung, H.; Kim, B.; Park, H.; Lee, K.; Kim, H.-H.; Sim, H.-C.; Do, H.-J.; Hyun, C.-K.; Do, M.-S. Fermented Moringa oleifera Decreases Hepatic Adiposity and Ameliorates Glucose Intolerance in High-Fat Diet-Induced Obese Mice. J. Med. Food 2017, 20, 439–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srivastava, G.; Ganjewala, D. An Update on the Emerging Neuroprotective Potential of Moringa oleifera and Its Prospects in Complimentary Neurotherapy. Phytomed. Plus 2024, 4, 100532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.T.; Martins, N.; Imran, M.; Hameed, A.; Ali, S.W.; Salehi, B.; Ahmad, I.; Hussain, A.; Sharifi-Rad, J. Anxiolytic-like Effects of Moringa oleifera in Swiss Mice. Cell. Mol. Biol. 2020, 66, 73–77. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rosdy, M.S.; Rofiee, M.S.; Samsulrizal, N.; Salleh, M.Z.; Teh, L.K. Understanding the Effects of Moringa oleifera in Chronic Unpredictable Stressed Zebrafish Using Metabolomics Analysis. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2021, 278, 114290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, N.; Mukhtar, H. Tea Polyphenols for Health Promotion. Life Sci. 2007, 81, 519–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wongsa, P.; Phatikulrungsun, P.; Prathumthong, S. FT-IR Characteristics, Phenolic Profiles and Inhibitory Potential against Digestive Enzymes of 25 Herbal Infusions. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 6631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

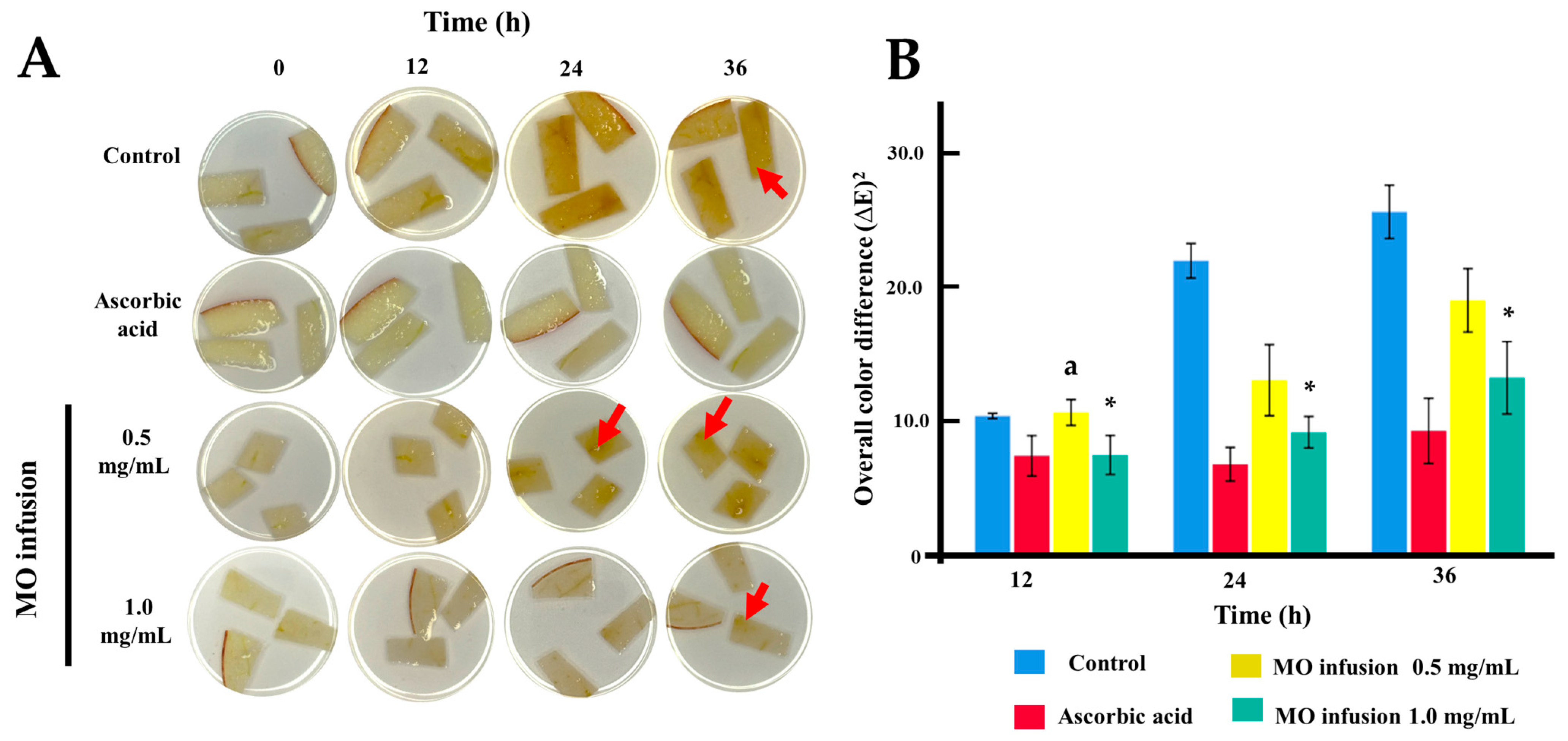


| Groups | Control | Ascorbic Acid | MO Infusion 0.5 mg/mL | MO Infusion 1.0 mg/mL | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hour 12 | Mean + SD | post Hoc p-values on hour 12 | |||
| Control | 10.39 ± 0.24 | <0.001 | 1.000 | <0.001 | |
| Ascorbic acid | 7.41± 1.84 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 1.000 | |
| MO infusion 0.5 mg/mL | 10.65 ± 1.19 | 1.000 | <0.001 | 0.004 | |
| MO infusion 1.0 mg/mL | 7.47 ± 1.78 | 0.009 | 1.000 | 0.004 | |
| p (ANOVA) | <0.001 | ||||
| Hour 24 | Mean + SD | post Hoc p-values on hour 24 | |||
| Control | 21.97 ± 1.58 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |
| Ascorbic acid | 6.78 ± 1.53 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.230 | |
| MO infusion 0.5 mg/mL | 13.05 ± 3.25 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.020 | |
| MO infusion 1.0 mg/mL | 9.16 ± 1.44 | <0.001 | 0.230 | 0.020 | |
| p (ANOVA) | <0.001 | ||||
| Hour 36 | Mean + SD | post Hoc p-values on hour 36 | |||
| Control | 25.63 ± 2.44 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |
| Ascorbic acid | 9.27 ± 2.98 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.119 | |
| MO infusion 0.5 mg/mL | 19.02 ± 2.90 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.013 | |
| MO infusion 1.0 mg/mL | 13.24 ± 3.32 | <0.001 | 0.119 | 0.013 | |
| p (ANOVA) | <0.001 | ||||
| Parameters | Balanced Diet | Negative Control | HFD-MO Infusion | p ANOVA |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cholesterol | 116.9 ± 12.0 | 181.2 ± 15.0 a | 90.4 ± 16.1 c | <0.001 |
| Triglycerides | 114.8 ± 15.5 | 185.5 ± 12.6 a | 87.0 ± 14.9 c | <0.001 |
| Total Lipids | 156.1 ± 9.6 | 299.8 ± 15.1 a | 166.6 ± 11.3 c | <0.001 |
| SGOT | 184.0 ± 14.2 | 403.0 ± 12.1 a | 159.2 ± 10.9 c | <0.001 |
| SGPT | 128.9 ± 11.9 | 241.6 ± 16.3 a | 111.2 ± 12.3 c | <0.001 |
| Blood glucose | 88.9 ± 13.8 | 141.1 ± 20.9 a | 94.2 ± 5.4 c | 0.002 |
| Urea | 11.9 ± 5.3 | 15.4 ± 5.8 | 11.4 ± 1.8 | 0.525 |
| Hemoglobin | 12.5 ± 1.1 | 14.3 ± 0.5 a | 14.6 ± 0.4 b | <0.001 |
| Hematocrit | 35.6 ± 4.1 | 39.7 ± 1.5 | 39.7 ± 1.3 | <0.001 |
| Platelets | 1207.2 ± 38.1 | 1210.8 ± 48.8 | 1085.8 ± 32.6 | 0.575 |
| Leukocytes | 6.4 ± 2.0 | 6.4 ± 2.1 | 6.5 ± 0.3 | 0.262 |
| Erythrocytes | 8.1 ± 1.0 | 7.7 ± 0.9 | 7.3 ± 0.6 | 0.675 |
| Glucose | Balanced Diet | Negative Control | HFD-MO Infusion | p ANOVA |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | 84.80 ± 0.8 | 88.60 ± 3.3 | 90.80 ± 3.7 | 0.153 |
| 3 months | 94.00 ± 0.7 | 99.02 ± 2.5 | 98.50 ± 1.6 | <0.001 |
| 6 months | 96.70 ± 2.4 | 138.00 ± 2.0 a | 125.62 ± 2.8 b,c | <0.001 |
| Minutes | Balanced Diet | Negative Control | HFD-MO Infusion | p ANOVA | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Time 1 | 0 | 96.70 ± 2.4 | 138.00 ± 2.0 a | 125.62 ± 2.8 b,c | <0.001 |
| 30 | 157.60 ± 2.9 | 336.00 ± 2.6 a | 245.62 ± 3.9 b,c | <0.001 | |
| 60 | 118.40 ± 3.2 | 241.00 ± 3.6 a | 184.62 ± 4.1 b,c | <0.001 | |
| 90 | 103.40 ± 3.2 | 211.00 ± 3.6 a | 169.00 ± 3.9 b,c | <0.001 | |
| 120 | 93.50 ± 3.3 | 216.00 ± 3.6 a | 175.00 ± 3.7 b,c | <0.001 | |
| Time 2 | 0 | 99.57 ± 3.1 | 178.09 ± 3.9 a | 165.75 ± 2.1 b,c | <0.001 |
| 30 | 159.57 ± 3.1 | 377.81 ± 3.9 a | 315.12 ± 2.9 b,c | <0.001 | |
| 60 | 117.71 ± 3.0 | 277.27 ± 3.9 a | 215.00 ± 2.9 b,c | <0.001 | |
| 90 | 102.57 ± 3.1 | 217.18 ± 3.9 a | 165.25 ± 2.5 b,c | <0.001 | |
| 120 | 95.57 ± 3.1 | 224.90 ± 3.3 a | 161.00 ± 2.6 b,c | <0.001 | |
| Parameters | Balanced Diet | Negative Control | HFD-MO Infusion | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steatosis (%) | 5.00 ± 3.3 | 68.18 ± 10.5 a | 8.12 ± 3.7 b | <0.001 * |
| Necroinflammatory activity *** | 0 (0–1) | 3 (2–3) a | 1 (0–1) b | <0.001 ** |
| Parameters | Balanced Diet | Negative Control | HFD-MO Infusion | p ANOVA |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of rotations | 8.85 ± 2.5 | 9.1 ± 3.0 | 17.50 ± 3.6 b,c | 0.003 |
| Number of falls | 17.07 ± 3.7 a | 21.91 ± 3.1 | 15.25 ± 5.0 c | <0.001 |
| Anxiety like | 0.86 ± 0.09 | 0.86 ± 0.11 | 0.61 ± 0.07 b,c | <0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hernández-Fuentes, G.A.; Sanchez-Ramirez, C.A.; Cortes-Alvarez, S.I.; Rodriguez-Hernández, A.; Cabrera-Medina, A.O.; Moy-López, N.A.; Guzman-Muñiz, J.; Garza-Veloz, I.; Rodriguez-Sanchez, I.P.; Martinez-Fierro, M.L.; et al. Moringa oleifera Leaf Infusion as a Functional Beverage: Polyphenol Content, Antioxidant Capacity, and Its Potential Role in the Prevention of Metabolopathies. Life 2025, 15, 636. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15040636
Hernández-Fuentes GA, Sanchez-Ramirez CA, Cortes-Alvarez SI, Rodriguez-Hernández A, Cabrera-Medina AO, Moy-López NA, Guzman-Muñiz J, Garza-Veloz I, Rodriguez-Sanchez IP, Martinez-Fierro ML, et al. Moringa oleifera Leaf Infusion as a Functional Beverage: Polyphenol Content, Antioxidant Capacity, and Its Potential Role in the Prevention of Metabolopathies. Life. 2025; 15(4):636. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15040636
Chicago/Turabian StyleHernández-Fuentes, Gustavo A., Carmen A. Sanchez-Ramirez, Salma I. Cortes-Alvarez, Alejandrina Rodriguez-Hernández, Ana O. Cabrera-Medina, Norma A. Moy-López, Jorge Guzman-Muñiz, Idalia Garza-Veloz, Iram P. Rodriguez-Sanchez, Margarita L. Martinez-Fierro, and et al. 2025. "Moringa oleifera Leaf Infusion as a Functional Beverage: Polyphenol Content, Antioxidant Capacity, and Its Potential Role in the Prevention of Metabolopathies" Life 15, no. 4: 636. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15040636
APA StyleHernández-Fuentes, G. A., Sanchez-Ramirez, C. A., Cortes-Alvarez, S. I., Rodriguez-Hernández, A., Cabrera-Medina, A. O., Moy-López, N. A., Guzman-Muñiz, J., Garza-Veloz, I., Rodriguez-Sanchez, I. P., Martinez-Fierro, M. L., Álvarez-Barajas, J. J., Cortes-Alvarez, N. Y., Ceballos-Magaña, S. G., Meza-Robles, C., & Delgado-Enciso, I. (2025). Moringa oleifera Leaf Infusion as a Functional Beverage: Polyphenol Content, Antioxidant Capacity, and Its Potential Role in the Prevention of Metabolopathies. Life, 15(4), 636. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15040636