Serological Distribution of Salmonella enterica subsp. Isolated from Feces of Domesticated Crested Gecko (Correlophus ciliates) in Busan Province, South Korea
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection and Study Design
2.2. Identification of Bacteria
2.3. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing (AST)
2.4. Serogrouping and Serotyping of Salmonella Species
2.5. Detection of Antimicrobial Resistance Genes
3. Results
3.1. The Prevalence of Gram-Negative Bacteria
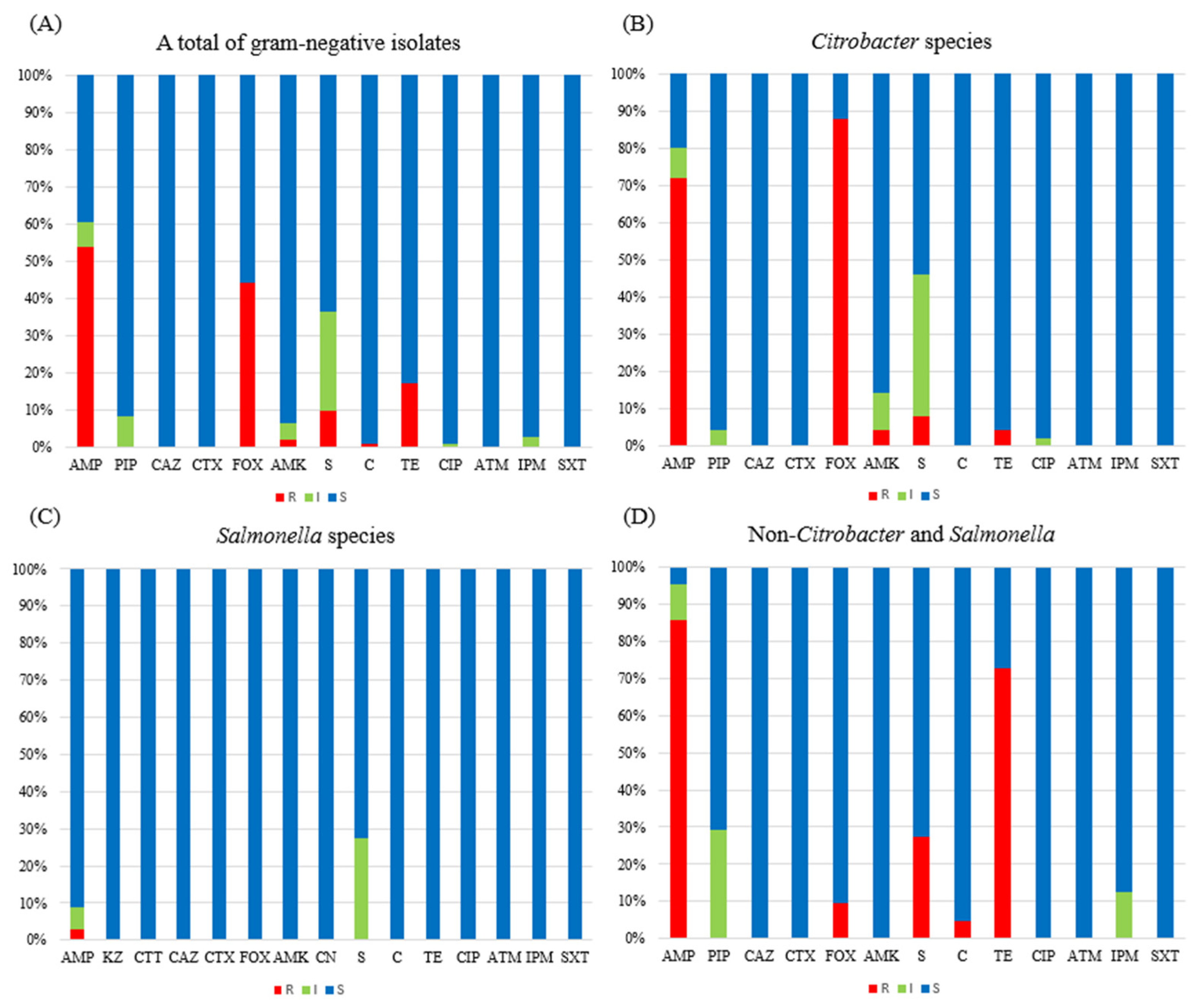
3.2. Antimicrobial Resistance
3.3. AMR Determinants
3.4. Serological Prevalence of the Salmonella enterica subsp.
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pees, M.; Brockmann, M.; Steiner, N.; Marschang, R.E. Salmonella in reptiles: A review of occurrence, interactions, shedding and risk factors for human infections. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2023, 11, 1251036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, X.R.; Dai, Y.Y.; Wang, Y.R.; Guo, K.; Du, Y.; Gao, J.F.; Lin, L.H.; Li, P.; Li, H.; Ji, X.; et al. Dietary and Sexual Correlates of Gut Microbiota in the Japanese Gecko, Gekko japonicus (Schlegel, 1836). Animals 2023, 13, 1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szabo, B.; Ringler, E. Fear of the new? Geckos hesitate to attack novel prey, feed near objects and enter a novel space. Anim. Cogn. 2023, 26, 537–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valdez, J.W. Using Google Trends to Determine Current, Past, and Future Trends in the Reptile Pet Trade. Animals 2021, 11, 676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merkevičienė, L.; Butrimaitė-Ambrozevičienė, Č.; Paškevičius, G.; Pikūnienė, A.; Virgailis, M.; Dailidavičienė, J.; Daukšienė, A.; Šiugždinienė, R.; Ruzauskas, M. Serological Variety and Antimicrobial Resistance in Salmonella Isolated from Reptiles. Biology 2022, 11, 836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, B.R.; Singh, V.; Ebibeni, N.; Singh, R.K. Antimicrobial and Herbal Drug Resistance in Enteric Bacteria Isolated from Faecal Droppings of Common House Lizard/Gecko (Hemidactylus frenatus). Int. J. Microbiol. 2013, 2013, 340848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gugnani, H.C.; Oguike, J.U.; Sakazaki, R. Salmonellae and other enteropathogenic bacteria in the intestines of wall geckos in Nigeria. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 1986, 52, 117–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, S.; Li, Y.; Huang, C.; Yan, S.; Li, Y.; Chen, Z.; Wu, Z. Comparison of Gut Microbiota Diversity Between Captive and Wild Tokay Gecko (Gekko gecko). Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 897923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.T.; Sobur, M.A.; Islam, M.S.; Ievy, S.; Hossain, M.J.; El Zowalaty, M.E.; Rahman, A.T.; Ashour, H.M. Zoonotic Diseases: Etiology, Impact, and Control. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marin, C.; Lorenzo-Rebenaque, L.; Laso, O.; Villora-Gonzalez, J.; Vega, S. Pet Reptiles: A Potential Source of Transmission of Multidrug-Resistant Salmonella. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 7, 613718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rees, E.M.; Minter, A.; Edmunds, W.J.; Lau, C.L.; Kucharski, A.J.; Lowe, R. Transmission modelling of environmentally persistent zoonotic diseases: A systematic review. Lancet Planet. Health 2021, 5, e466–e478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoelzer, K.; Moreno Switt, A.I.; Wiedmann, M. Animal contact as a source of human non-typhoidal salmonellosis. Vet. Res. 2011, 42, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.Y.; Kim, J.A.; Jeong, H.S.; Shin, J.H.; Chang, C.L.; Jeong, J.; Cho, J.H.; Kim, M.N.; Kim, S.; Kim, Y.R.; et al. Serotyping and antimicrobial susceptibility of Salmonella spp.: Nationwide multicenter study in Korea. Jpn. J. Infect. Dis. 2013, 66, 284–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popoff, M.Y. Antigenic Formulas of the Salmonella serovars, 8th ed.; WHO Collaborating Centre for Reference and Research on Salmonella: Paris, France, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, S.; Zhang, W.; Li, C.; Liu, X.; Zhu, L.; Chen, L.; Yang, B. Serotyping, MLST, and Core Genome MLST Analysis of Salmonella enterica from Different Sources in China During 2004–2019. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 688614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McQuiston, J.R.; Waters, R.J.; Dinsmore, B.A.; Mikoleit, M.L.; Fields, P.I. Molecular determination of H antigens of Salmonella by use of a microsphere-based liquid array. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2011, 49, 565–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Lan, R.; Liu, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Xu, J. Antimicrobial Resistance and Cytotoxicity of Citrobacter spp. in Maanshan Anhui Province, China. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Hou, H.; Huang, J. Citrobacter arsenatis sp. nov., an arsenate-reducing bacterium isolated from freshwater sediment. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2021, 114, 1285–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Tang, M.; Zhang, X.; Lu, J.; Tang, X.; Gao, Y. Detection of AmpC β-lactamases in gram-negative bacteria. Heliyon 2022, 8, e12245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decré, D.; Verdet, C.; Raskine, L.; Blanchard, H.; Burghoffer, B.; Philippon, A.; Sanson-Le-Pors, M.J.; Petit, J.C.; Arlet, G. Characterization of CMY-type beta-lactamases in clinical strains of Proteus mirabilis and Klebsiella pneumoniae isolated in four hospitals in the Paris area. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2002, 50, 681–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mammeri, H.; Guillon, H.; Eb, F.; Nordmann, P. Phenotypic and biochemical comparison of the carbapenem-hydrolyzing activities of five plasmid-borne AmpC β-lactamases. Antimicrob. Agents. Chemother. 2010, 54, 4556–4560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grimont, P.A.D.; Weill, F.-X. Antigenic Formulae of the Salmonella serovars, 9th ed.; WHO Collaborating Centre for Reference and Research on Salmonella: Paris, France, 2007; p. 166. [Google Scholar]
- Perez-Perez, F.J.; Hanson, N.D. Detection of plasmid-mediated AmpC β-lactamase genes in clinical isolates by using multiplex PCR. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2002, 40, 2153–2162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fratire, M.A.; Deckers, M.; Papazova, N.; Roosens, N.H.C. Detection strategy targeting a chloramphenicol resistance gene from genetically modified bacteria in food and feed products. Food Control 2020, 108, 106873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caugant, D.A.; Levin, B.R.; Selander, R.K. Distribution of multilocus genotypes of Escherichia coli within and between host families. J. Hyg. 1984, 92, 377–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, A.M. Geckos in traditional medicine: Forensic implications. Appl. Herpetol. 2009, 6, 81–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamal, W.; Khodakhast, F.B.; Albert, M.J.; Rotimi, V. Epidemiology, Serogroups and Resistance of Salmonella During a 15-Year Period (2006–2020) in Kuwait. Infect. Drug Resist. 2021, 14, 4957–4966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.H.; Sung, G.H.; Park, E.H.; Hwang, I.Y.; Kim, G.R.; Song, S.A.; Lee, H.K.; Uh, Y.; Kim, Y.A.; Jeong, S.H.; et al. Serotype Distribution and Antimicrobial Resistance of Salmonella Isolates in Korea between 2016 and 2017. Ann. Lab. Med. 2022, 42, 268–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.H.; Yu, Y.A.; Song, M.O.; Kwon, E.Y.; Kim, J.K.; Suh, H.S.; Baek, S.Y.; Kim, E.S.; Hwang, Y.O.; Lee, J.H. Serotype Distribution and Antimicrobial Resistance of Salmonella Isolates in Seoul, 2020–2022. J. Bacteriol. Virol. 2023, 53, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palma, E.; Tilocca, B.; Roncada, P. Antimicrobial Resistance in Veterinary Medicine: An Overview. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, J.H.; Shin, D.; Kwon, K.T.; Ko, W.S. Colistin heteroresistance in Citrobacter freundii clinical isolates from Republic of Korea. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2024, 108, 116187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Yoon, E.J.; Kim, D.; Shin, J.H.; Shin, J.H.; Shin, K.S.; Kim, Y.A.; Uh, Y.; Kim, H.S.; Kim, Y.R.; et al. Antimicrobial resistance in South Korea: A report from the Korean global antimicrobial resistance surveillance system (Kor-GLASS) for 2017. J. Infect. Chemother. 2019, 25, 845–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahyot, S.; Mammeri, H. Hydrolysis spectrum extension of CMY-2-like β-lactamases resulting from structural alteration in the Y-X-N loop. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2012, 56, 1151–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stock, I.; Wiedemann, B. Identification and natural antibiotic susceptibility of Morganella morganii. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 1998, 30, 153–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Zhu, J.; Hu, Q.; Rao, X. Morganella morganii, a non-negligent opportunistic pathogen. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2016, 50, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Primer Name | Target Gene | Nucleotide Sequences (5′ to 3′) | Amplicon Size | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MOXM-F | MOX, CMY-1-type | GCTGCTCAAGGAGCACAGGAT | 520 bp | [23] |
| MOXM-R | CACATTGACATAGGTGTGGTGC | |||
| CITM-F | LAT, CMY-2-type, BIL | TGGCCAGAACTGACAGGCAAA | 462 bp | |
| CITM-R | TTTCTCCTGAACGTGGCTGGC | |||
| DHAM-F | DHA | AACTTTCACAGGTGTGCTGGGT | 405 bp | |
| DHAM-R | CCGTACGCATACTGGCTTTGC | |||
| ACCM-F | ACC | AACAGCCTCAGCAGCCGGTTA | 346 bp | |
| ACCM-R | TTCGCCGCAATCATCCCTAGC | |||
| EBCM-F | MIR, ACT, AZECL | TCGGTAAAGCCGATGTTGCGG | 302 bp | |
| EBCM-R | CTTCCACTGCGGCTGCCAGTT | |||
| FOXM-F | FOX | AACATGGGGTATCAGGGAGATG | 190 bp | |
| FOXM-R | CAAAGCGCGTAACCGGATTGG | |||
| cat-F1 | CAT | TTTGAACCAACAAACGACTTT | 573 bp | [24] |
| cat-R1 | GGCCTATCTGACAATTCCTGA | |||
| cat-F2 | CCAACAAAACGACTTTTAGTATAACC | 529 bp | ||
| cat-R2 | TCCTGCATGATAACCATCAC |
| No. of the Crested Gecko | Diet Type | Identification | Phenotypic Non-Susceptible | O-Group | Serotype |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 13 | Superworm | S. enterica | Amp | C1 | II 6,7:g,[m],s,t:[z42] |
| 21 | Cricket | S. enterica | - | C1 | II 6,7:g,[m],s,t:[z42] |
| 23 | S. enterica | - | D1 | Durban | |
| 24 | S. enterica | Amp, S | C1 | Mbandaka | |
| 25 | S. enterica | - | C1 | II 6,7:g,[m],s,t:[z42] | |
| 26 | S. enterica | S | C1 | II 6,7:g,[m],s,t:[z42] | |
| 27 | S. enterica | - | C2 | Virginia | |
| 28 | S. enterica | - | D1 | Durban | |
| 31 | S. enterica | S | C1 | II 6,7:g,[m],s,t:[z42] | |
| 32 | S. enterica | - | C1 | II 6,7:g,[m],s,t:[z42] | |
| 33 | S. enterica | - | C2 | Virginia | |
| 34 | S. enterica | - | V | Christiansborg | |
| 35 | S. enterica | - | C1 | II 6,7:g,[m],s,t:[z42] | |
| 36 | S. enterica | - | V | Christiansborg | |
| 40 | S. enterica | - | C1 | II 6,7:g,[m],s,t:[z42] | |
| 41 | S. enterica | - | C2 | Virginia | |
| 42 | S. enterica | - | C2 | Lindenburg | |
| 44 | S. enterica | - | C2 | Virginia | |
| 45 | S. enterica | - | C2 | Virginia | |
| 46 | S. enterica | S | D1 | Ouakam | |
| 47 | S. enterica | - | C2 | Virginia | |
| 48 | S. enterica | - | C2 | Lindenburg | |
| 52 | S. enterica | - | C2 | Lindenburg | |
| 53 | S. enterica | S | D1 | Durban | |
| 54 | S. enterica | - | M | Pomona | |
| 55 | S. enterica | S | D1 | Ouakam | |
| 57 | S. enterica | S | D1 | Durban | |
| 60 | S. enterica | Amp | C2 | Lindenburg | |
| 64 | S. enterica | - | C2 | Virginia | |
| 65 | S. enterica | - | C2 | Virginia | |
| 68 | S. enterica | - | C2 | Virginia | |
| 71 | S. enterica | S | D1 | Ouakam | |
| 76 | S. enterica | S | C1 | II 6,7:g,[m],s,t:[z42] |
| Serogroup | Group C | Group D | Group M | Group V | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Serotype (H Antigen) | No. (%) | Serotype (H Antigen) | No. (%) | Serotype (H Antigen) | No. (%) | Serotype (H Antigen) | No. (%) | |
| Serotype | II 6,7:g,[m],s,t:[z42] (g,m,s,t) | 9 (27.3) | Durban (a,e,n,z15) | 4 (12.1) | Pomona (y,1,7) | 1 (3.0) | Christiansborg (z4,z24) | 2 (6.1) |
| Virginia (d,1,2) | 9 (27.3) | Ouakam (g,m) | 3 (9.1) | |||||
| Lindenburg (i,1,2) | 4 (12.1) | |||||||
| Mbandaka (z10,e,n,z15) | 1 (3.0) | |||||||
| Total (n = 33) | 23 (69.7) | 7 (21.2) | 1 (3.0) | 2 (6.1) | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bae, I.K.; Park, Y.-k.; Park, S.H.; Hong, J.S. Serological Distribution of Salmonella enterica subsp. Isolated from Feces of Domesticated Crested Gecko (Correlophus ciliates) in Busan Province, South Korea. Life 2025, 15, 405. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15030405
Bae IK, Park Y-k, Park SH, Hong JS. Serological Distribution of Salmonella enterica subsp. Isolated from Feces of Domesticated Crested Gecko (Correlophus ciliates) in Busan Province, South Korea. Life. 2025; 15(3):405. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15030405
Chicago/Turabian StyleBae, Il Kwon, Yon-koung Park, So Hyun Park, and Jun Sung Hong. 2025. "Serological Distribution of Salmonella enterica subsp. Isolated from Feces of Domesticated Crested Gecko (Correlophus ciliates) in Busan Province, South Korea" Life 15, no. 3: 405. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15030405
APA StyleBae, I. K., Park, Y.-k., Park, S. H., & Hong, J. S. (2025). Serological Distribution of Salmonella enterica subsp. Isolated from Feces of Domesticated Crested Gecko (Correlophus ciliates) in Busan Province, South Korea. Life, 15(3), 405. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15030405






