Abstract
Rhizoctonia solani is a basidiomycete phytopathogenic fungus that causes rapid necrosis in a wide range of crop species, leading to substantial agricultural losses worldwide. The species complex is divided into 13 anastomosis groups (AGs) based on hyphal fusion compatibility and further subdivided by culture morphology. While R. solani classifications were shown to be independent of host specificity, it remains unclear whether different R. solani isolates share similar virulence mechanisms. Here, we investigated the infectivity of Japanese R. solani isolates on Brachypodium distachyon and barley. Two isolates, AG-1 IA (from rice) and AG-4 HG-I+II (from cauliflower), infected leaves of both plants, but only AG-4 HG-I+II infected roots. B. distachyon accessions Bd3-1 and Gaz-4 and barley cultivar ‘Morex’ exhibited enhanced resistance to both isolates compared to B. distachyon Bd21 and barley cultivars ‘Haruna Nijo’ and ‘Golden Promise’. During AG-1 IA infection, but not AG-4 HG-I+II infection, resistant Bd3-1 and Morex induced genes for salicylic acid (SA) and N-hydroxypipecolic acid (NHP) biosynthesis. Pretreatment with SA or NHP conferred resistance to AG-1 IA, but not AG-4 HG-I+II, in susceptible B. distachyon Bd21 and barley Haruna Nijo. On the leaves of susceptible Bd21 and Haruna Nijo, AG-1 IA developed extensive mycelial networks with numerous infection cushions, which are specialized infection structures well-characterized in rice sheath blight. In contrast, AG-4 HG-I+II formed dispersed mycelial masses associated with underlying necrosis. We propose that the R. solani species complex encompasses at least two distinct infection strategies: AG-1 IA exhibits a hemibiotrophic lifestyle, while AG-4 HG-I+II follows a predominantly necrotrophic strategy.
1. Introduction
Rhizoctonia solani Khün, a soilborne necrotrophic basidiomycete fungus, is one of the most destructive plant pathogens due to its wide host range and geographical distribution [1]. The pathogen infects over 200 plant species worldwide, including economically important crops and ornamental plants [2], with 188 host species from 32 families reported in Japan alone [3]. On rice leaves, R. solani forms specialized structures, called infection cushions, when mycelia or sclerotia contact the host surface. These structures facilitate host colonization by degrading plant cell walls, ultimately leading to tissue death. In addition to infection cushions, lobate appressoria and direct mycelial penetration through stomata have also been observed [4]. During the infection, R. solani isolates release various types of carbohydrate-active enzymes (CAZymes) to degrade plant tissue, as well as small secreted proteins called effectors, which possess necrosis-inducing or immunity-suppressing activities [5,6,7,8]. Following infection, the fungus produces resilient sclerotia, which can persist in soil for years, ensuring long-term survival [9,10]. Symptoms of R. solani infection include foliar and sheath blights, damping-off, crown rot, stem rot, root rot, and seed decay [11].
R. solani isolates are classified into 13 anastomosis groups (AG-1 through AG-13) based on hyphal fusion reactions [12]. These AGs are further subdivided according to DNA sequence features, colony morphology, host range, pathogenicity, and nutritional requirements, establishing R. solani as a species complex [13]. In Japan, eight AGs (AG-1 through AG-7 and AG-11) are naturally present in agroecosystems [14]. However, AG classification does not strictly correlate with host or tissue specificity. For example, three AG-1 IA isolates from different hosts (two from rice and one from sudangrass) all infected the leaves of the monocot model plant Brachypodium distachyon [15]. Yet, when tested on the dicot model Arabidopsis thaliana, only one isolate infected both roots and leaves, while the other two were non-virulent [16]. Similarly, among three AG-2-2 IIIB isolates from rice, broccoli, and Welch onion, all infected Arabidopsis roots, but only one infected its leaves [16]. These findings indicate that virulence and host specificity in R. solani likely evolved independently of AG classification, although the conservation of infection mechanisms among isolates remains poorly understood.
Plant defense mechanisms against fungal pathogens consist of preformed and induced responses. Preformed defenses include physical barriers, such as the cuticle and cell walls, as well as chemical barriers, including phytoanticipins and inhibitory proteins. To successfully invade and obtain nutrients, pathogens must overcome these initial defenses. During invasion, host enzymes degrade a pathogen’s cell walls, releasing microbe-associated molecular patterns (MAMPs). The recognition of MAMPs triggers pattern-triggered immunity (PTI), which is characterized by the formation of papillae and the synthesis of phytoalexins. To establish biotrophic interactions, some pathogens suppress PTI by deploying effector proteins. Plants counteract this suppression through nucleotide-binding leucine-rich repeat (NLR) receptors, which recognize these effectors and activate effector-triggered immunity (ETI), a more robust and specific form of PTI [17]. This recognition also induces systemic acquired resistance (SAR), which primes uninfected tissues for enhanced defense against future infections. In contrast, necrotrophic pathogens kill host cells using CAZymes and toxins. Application of hydraulic force, ice nucleation, induction of reactive oxygen species production, creation of an acidic environment, manipulation of the regulated cell death machinery, etc., also function as virulence mechanisms [18,19,20,21]. However, pathogen infection strategies are not strictly dichotomous [22]. Some necrotrophic pathogens including R. solani employ effectors to enhance virulence, like biotrophic and hemibiotrophic pathogens, as described above.
Phytohormones are critical regulators of plant immunity. Salicylic acid (SA) activates defenses against biotrophic and hemibiotrophic pathogens, while jasmonic acid (JA) and/or ethylene (ET) mediate responses to necrotrophic pathogens [23,24,25,26]. Among them, SA is biosynthesized in plants through two major pathways: the isochorismate synthase (ICS) pathway and the phenylalanine ammonia-lyase (PAL) pathway. In the ICS pathway of Arabidopsis, chorismate is converted to isochorismate by ICS. Isochorismate is then transported to the cytoplasm by Enhanced Disease Susceptibility 5 (EDS5). AvrPphB susceptible 3 (PBS3) conjugates isochorismate to glutamate (Glu) to produce IC-9-Glu. Enhanced Pseudomonas Susceptibility 1 (EPS1) cleaves IC-9-Glu to SA [27]. Recently, N-hydroxy pipecolic acid (NHP) has been identified as a key signaling molecule in SAR [28,29,30]. NHP biosynthesis at infection sites follows a three-step pathway: AGD2-LIKE DEFENSE RESPONSE PROTEIN 1 (ALD1) converts L-lysine to dehydropipecolic acid, SAR DEFICIENT 4 (SARD4) reduces it to pipecolic acid (Pip), and FLAVIN-DEPENDENT MONOOXYGENASE 1 (FMO1) converts Pip to NHP [30,31]. Both NHP and Pip confer resistance in dicots and monocots, showing strong efficacy against biotrophic and hemibiotrophic pathogens, but limited activity against necrotrophic pathogens [29,31,32].
Phytohormone-mediated defense responses against R. solani vary depending on the infection site, pathogen isolate, and host species. For instance, in A. thaliana, single mutations in SA, ET, JA, ABA, camalexin, or auxin biosynthesis or signaling pathways did not affect root infection by R. solani AG-2-1 and AG-8 [33]. However, combined mutations in ET (ein2), JA (coi1), and PENETRATION2 (pen2) pathways compromised the defense against AG-8 in both the leaves and roots [34]. In Medicago truncatula, ET signaling was essential for flavonoid-mediated resistance to AG-8 root infection [35]. Our previous studies demonstrated that exogenous SA application induced resistance to AG-1 IA in B. distachyon and rice, but not in A. thaliana [15,16]. Furthermore, rice plants expressing the bacterial SA hydrolase gene (NahG) showed increased susceptibility to R. solani [15]. In tomato, SA priming provided protection against AG-1 IA compared to JA priming [36]. Conversely, JA application induced resistance to AG-1 IA in rice [37], while in Tartary buckwheat, JA was the primary mediator of resistance against AG-4 HGI3 [38]. These findings suggest that different R. solani isolates employ distinct infection strategies that are countered by either SA- or JA-mediated defenses independently of their AGs classification. Notably, the potential effects of exogenous NHP application on plant resistance to R. solani remain unexplored.
In this study, we compared the virulence of two Japanese R. solani isolates, AG-1 IA and AG-4 HG-I+II, using B. distachyon and barley (Hordeum vulgare) as host plants. Despite belonging to a single species complex, these isolates exhibited different infection mechanisms. Our results challenge the long-held assumption of uniform pathogenicity strategies within R. solani. Our findings provide new insights into the biology and ecology of this fungal species, advancing its taxonomic classification and our understanding of its pathogenic behavior. This knowledge may inform the development of more effective, pathotype-specific strategies for managing R. solani and reducing its impact on global agriculture.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Fungal and Plant Materials
Eight R. solani isolates representing six anastomosis groups were obtained from the Genebank of the National Agricultural Research Organization (NARO), Tsukuba, Japan. The isolates were maintained on potato dextrose agar (PDA) medium (24 g/L Difco™ potato dextrose broth, 20 g/L Bacto™ agar) at 23 °C for 3–5 days before inoculation experiments. Stock cultures were preserved on PDA slants at 4 °C.
Seeds of B. distachyon and barley were obtained from the National Plant Germplasm System of the United States Department of Agriculture–Agriculture Research Service (USDA-ARS) and the National Bioresource Project (NBRP) in charge at the Institute of Plant Sciences and Resources (IPSR), Kurashiki, Okayama University, Japan, respectively. The seeds were stored in a Dry keeper™ cabinet at 25 °C and 60% relative humidity. Surface sterilization was performed using 1% sodium hypochlorite for 3 min, followed by three rinses in sterile distilled water. The seeds were imbibed on wet filter paper in Petri dishes at 4 °C in darkness for 3 days. Seed germination was induced in an LED growth chamber (Nippon Medical & Chemical Instruments, Osaka, Japan) under a 16 h light/8 h dark cycle at 23 °C. After 2–3 days, the seedlings were transplanted into plastic pots filled with 300 cm3 of soil (Sakata super mix A, Yokohama, Japan).
2.2. Aboveground Infection Assays
Three to four-week-old B. distachyon plants and 10-day-old barley plants were used to assess R. solani Japanese isolates’ virulence on aboveground tissues. A cylindrical mycelial plug (3 or 6 mm in diameter) was taken from the growing edge of a 3–5-day-old fungal culture and placed on individual leaves. Control plants received sterile PDA plugs of identical dimensions. Both inoculated and control plants were maintained in moisture chambers at 100% relative humidity and 23 °C, with a 16 h light/8 h dark photoperiod for 3 days.
2.3. Belowground Infection Assays
For belowground inoculation, the inoculum was prepared using a mixture of vermiculite (Uganda No 3, AICHI-mederu, Nishio, Japan) and wheat bran (Nisshin Seifun Welna, Tokyo, Japan) at a 2:1 (w/w) ratio. The mixture was placed in an autoclavable container, moistened with 300 mL of water, and autoclaved. Fifteen actively growing mycelial agar plugs (6–10 mm in diameter) from the edge of a 3–5-day-old culture were placed within the sterilized vermiculite–wheat bran mixture. The container was incubated at 23 °C under 100% relative humidity. After 7 days of fungal colonization, the inoculum was mixed with autoclaved soil (Sakata prime mix TKS-1, Yokohama, Japan) at a 1:4 ratio and transferred to plastic pots (~300 cm3). Each pot was watered with 30 mL of tap water, and the growth substrate was allowed to undergo fungal colonization for 2 additional days under the same conditions. Control pots were prepared using the same mixture without fungal inoculum. Seedlings (2–5-day-old, 2–3 cm roots for barley, and 5–6 cm roots for B. disatchyon) were carefully transplanted into the soil medium with or without fungal inoculum and incubated at 23 °C. A relative humidity of 100% was maintained for 2 days.
2.4. Phenotypic Measurements
For assessing infectivity on aboveground tissues, photographs were taken at 1, 2, and 3 days post-infection (dpi). The lesion area at 3 dpi was quantified using Leaf Doctor software (version 1.1; a quantitative assessment tool for plant diseases developed by Dr. Scot Nelson, University of Hawaii at Manoa) [39], and the measured lesion areas obtained for different genotypes were compared. To evaluate belowground virulence, three parameters were measured: number of dead seedlings, plant height, and fresh biomass. Plant height was measured from the base to the tip of the primary leaf. The fresh biomass of the shoots was determined by cutting plants at the base and immediately weighing them using a digital balance [40,41]. For each inoculated plant, the height and fresh biomass were compared to the mean values of non-inoculated control plants. Growth performance ratios were calculated by dividing each parameter value of inoculated plants by the mean value of the corresponding parameter in non-inoculated control plants [42]. The growth performance ratios were then analyzed alongside the mortality rates.
2.5. Phytohormone and NHP Treatment
The defense-inducing chemicals used in this study included sodium salicylate (Wako, Osaka, Japan), NHP (TargetMol, Boston, MA, USA), ethephon (an ethylene generator; Sigma-Aldrich, St Louis, MO, USA), and methyl jasmonate (Wako, Japan). The phytohormones were dissolved in dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) and diluted with distilled water to a final DMSO concentration of 0.1%. NHP was dissolved in water. Prior to pathogen inoculation, detached leaves or seedlings were either sprayed (~4 mL for every three plants, ensuring even coverage of the entire leaf surface) with the chemical solutions (100, 500, or 1000 µM) or subjected to soil drenching (30 mL per pot, with each pot containing three plants), followed by a 24 h incubation at 23 °C.
2.6. Fungal Biomass Quantification
Disease severity was assessed by quantifying fungal biomass using qPCR, following our previously reported protocol [15]. Genomic DNA was extracted from inoculated tissues using the Nucleospin Plant II Kit (Takara Bio, Shiga, Japan). qPCR was performed using Luna Universal qPCR Master Mix (NEB, Ipswich, MA, USA) on a LightCycler® 96 system (Roche, IN, USA). PCR conditions consisted of a pre-incubation step at 95 °C for 60 s, followed by denaturation at 95 °C for 15 s and annealing and extension at 60 °C for 30 s, with 40 cycles. Melting was performed at 95 °C for 10 s, 65 °C for 60 s, and 97 °C for 1 s, and the data were analyzed using the equipped software. The primer sets specifically detecting R. solani AG-1 IA and AG-4 HG-I+II were used for each isolate, and BdFIM was used for normalization [14,43,44,45]. All primers used in this study are listed in Table S1.
2.7. Gene Expression Analysis
Total RNA was extracted from inoculated leaves using the ISOPIN Plant RNA Extraction Kit (NIPPON GENE, Tokyo, Japan). cDNA synthesis was performed with the PrimeScript™ RT Reagent Kit with gDNA Eraser (TaKaRa Bio, Kusatsu, Japan). Gene expression was quantified by quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) using Luna Universal qPCR Master Mix (NEB, Ipswich, MA, USA) on a LightCycler 96 system (Roche, IN, USA). Expression levels were calculated using the 2−ΔΔCt method, where ΔΔCt represents the difference in the ΔCt values between the inoculated samples and the non-inoculated controls at each time point. ΔCt was determined by subtracting the Ct value of the reference gene (to normalize the data) from the Ct value of the target gene for each sample. The reference genes used were BdUbi4 (ubiquitin gene) for B. distachyon and HvEF2 (elongation factor) for barley [46,47]. The primers and marker genes used in this study are listed in Tables S1 and S2.
2.8. Microscopy
The leaves of B. distachyon and barley were separately inoculated with R. solani AG-1 IA and AG-4 HG-I+II. Leaf samples (2–3 cm) containing the inoculation site, were collected in 2 mL tubes and fixed overnight in absolute ethanol until complete chlorophyll removal. Fungal mycelia were stained with Trypan Blue (Wako, Japan) in a mixture of equal parts by volume (v/v) of lactic acid, glycerol, phenol, and distilled water, and samples were stored in 30% glycerol. Samples were observed under a ZEISS Stemi 305 stereomicroscope, and photomicrographs were captured using an attached Axiocam 208 color camera (ZEISS, Oberkochen, Germany).
3. Results
3.1. Above- and Belowground Infectivity of R. solani Japanese Isolates on B. distachyon and Barley
We previously assessed the virulence of the Japanese field isolates of R. solani on the leaves of B. distachyon standard accession Bd21 [15]. Among the isolates tested, AG-1 IA (MAFF305230), AG-4 HG-I+II (MAFF305225), and AG-5 (MAFF305256) showed strong virulence, whereas AG-1 IA (MAFF305219) and AG-6 (MAFF305262) caused only mild symptoms (Table 1; see the note regarding the designation of the AG-4 isolate in Figure S1). In this study, we evaluated the infectivity of these isolates on the underground tissues of B. distachyon to investigate tissue-specific virulence. AG-4 HG-I+II and AG-6 caused strong and weak growth retardation of B. distachyon seedlings, respectively, while the other isolates were non-virulent on the roots (Table 1, Figure S1). Notably, AG-1 IA infected only the leaves, while AG-4 HG-I+II demonstrated strong virulence in both the leaves and roots of B. distachyon.

Table 1.
The infectivity of Japanese field isolates of R. solani on the above- and belowground tissues of B. distachyon and barley.
To assess host specificity, we further evaluated the infectivity of these R. solani isolates on the leaves and roots of the barley cultivar (cv.) ‘Golden Promise’, another monocot species. The isolates displayed similar pathogenicity patterns on barley leaves, with the exception that AG-2-1 II (MAFF305203) and AG-2-2 IIIB (MAFF305244) caused lower disease severity. Isolate AG-1 IA (MAFF305230), a known causal agent of rice sheath blight, and AG-4 HG-I+II caused the most severe symptoms with rapid disease progression. In the soil inoculation assays, the isolates showed pathogenicity patterns on barley roots similar to those observed for B. distachyon. Specifically, AG-4 HG-I+II caused strong growth retardation, while AG-6 caused weak growth retardation (Table 1, Figure S1).
In summary, the AG-1 IA isolate was highly virulent on the leaves of both plant species but did not infect root tissues. In contrast, the isolate AG-4 HG-I+II exhibited high virulence on both the leaves and roots of B. distachyon and barley.
3.2. Resistance Genotypes of B. distachyon and Barley Against R. solani
Previous studies have shown that B. distachyon accessions Bd3-1, Gaz-4, and Tek-3 exhibit relative resistance to leaf infection by the R. solani AG-1 IA isolate (MAFF305230) [15,48]. In this study, we investigated whether B. distachyon and barley possess genetic variation for resistance to AG-4 HG-I+II infection in both above- and belowground tissues.
To evaluate resistance, we first compared lesion formation following AG-4 HG-I+II leaf inoculation among three B. distachyon accessions: Bd21, Bd3-1, and Gaz-4. Bd3-1 and Gaz-4 displayed milder symptoms compared to the susceptible accession Bd21 (Figure 1A,B). Similarly, we assessed AG-4 HG-I+II infectivity on the leaves of three barley cvs. ‘Haruna Nijo’, ‘Golden Promise’, and ‘Morex’. Barley cv. Morex showed relatively milder symptoms than Haruna Nijo and Golden Promise (Figure 1C,D). Additionally, we tested the susceptibility of these barley cultivars to AG-1 IA leaf infection. Once again, Morex displayed less severe symptoms compared to Haruna Nijo and Golden Promise (Figure 1E,F).
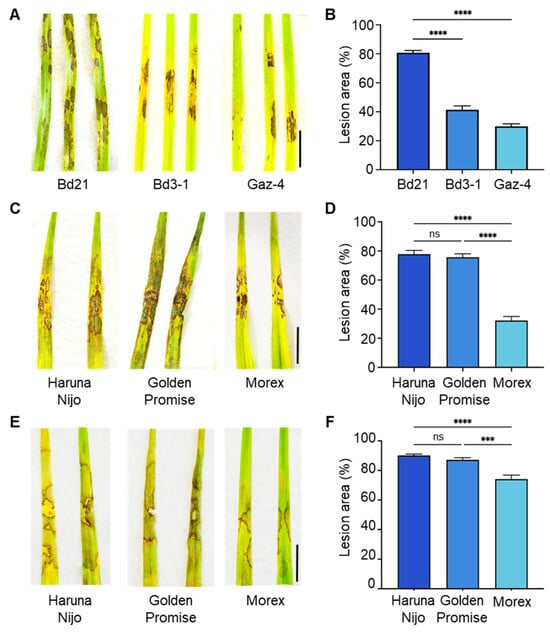
Figure 1.
Differential leaf susceptibility to R. solani isolates among B. distachyon accessions and barley cultivars. (A,B) Disease symptoms (A) and quantified lesion areas (B) on detached leaves of B. distachyon accessions Bd21, Bd3-1, and Gaz-4 inoculated with R. solani AG-4 HG-I+II. (C,D) Disease symptoms (C) and quantified lesion areas (D) on detached leaves of barley cvs. Haruna Nijo, Golden Promise, and Morex inoculated with R. solani AG-4 HG-I+II. (E,F) Disease symptoms (E) and quantified lesion areas (F) on detached leaves of barley cultivars inoculated with R. solani AG-1 IA. Lesion areas are presented as mean percentages, i.e., the ratio of lesion area to total leaf area, ±SE (n = 6). Statistical significance was analyzed using one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s test (***, p < 0.001; ****, p < 0.0001; ns, not significant). Scale bars: 1 cm.
We next evaluated root infection by AG-4 HG-I+II in three B. distachyon accessions and three barley cultivars. Among the B. distachyon accessions, Bd3-1 and Gaz-4 exhibited moderate resistance compared to the susceptible Bd21, showing better growth and lower mortality rates in the presence of the pathogen (Figure 2A, Table 2). Similarly, among barley cultivars, Morex displayed the lowest mortality rate and superior growth performance compared to Haruna Nijo and Golden Promise (Figure 2B,C, Table 2).
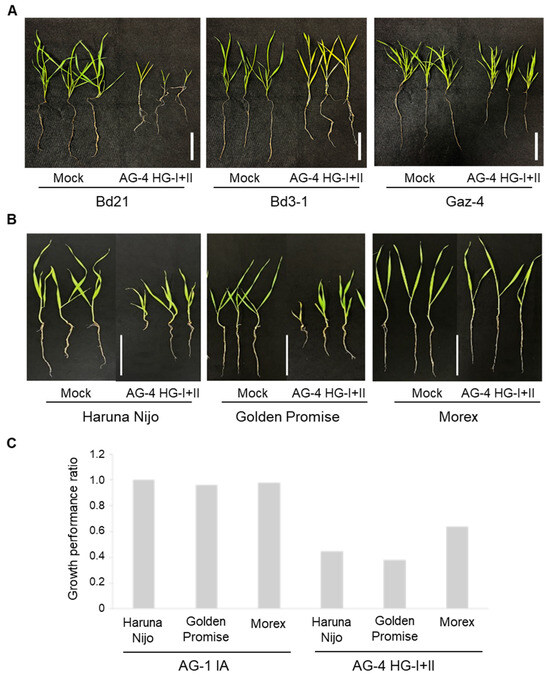
Figure 2.
Root and shoot symptoms in B. distachyon accessions and barley cultivars grown in R. solani AG-4 HG-I+II-infested soil. (A) Representative images of B. distachyon accessions Bd21, Bd3-1, and Gaz-4 after 22 days of growth in soil infested with R. solani AG-4 HG-I+II. (B) Representative images of barley cvs. Haruna Nijo, Golden Promise, and Morex after 10 days of growth in soil infested with R. solani AG-4 HG-I+II. (C) Growth performance ratios (calculated by dividing each parameter value of inoculated plants by the mean value of the corresponding parameter in non-inoculated control plants) of three barley cultivars grown in soil infested with either R. solani AG-1 IA (left) or AG-4 HG-I+II (right). Scale bars: 5 cm.

Table 2.
Phenotypic responses of different genotypes of B. distachyon (22 dpi) and barley (10 dpi) to belowground infection of R. solani AG-4 HG-I+II.
Additionally, we tested AG-1 IA root infection using the soil inoculation method on barley cvs. Haruna Nijo and Morex. The results confirmed that AG-1 IA is not virulent to these cultivars, consistent with its lack of virulence to Golden Promise under root inoculation conditions (Figure 2C, Table 1).
3.3. Comparison of Defense Responses in Leaves of Resistant B. distachyon and Barley Lines During Infection by R. solani AG-1 IA and AG-4 HG-I+II
Our study demonstrated that both R. solani AG-1 IA and AG-4 HG-I+II can infect the leaves of B. distachyon and barley. B. distachyon accession Bd21 and barley cvs. Haruna Nijo and Golden Promise were susceptible, whereas B. distachyon accessions Bd3-1 and Gaz-4 and barley cv. Morex were resistant to both AG-1 IA and AG-4 HG-I+II. Previous research showed that Bd3-1 and Gaz-4 activate SA-dependent immune responses immediately after infection with AG-1 IA [15].
To determine whether similar responses occur against AG-4 HG-I+II, we used Bd3-1 and Morex as representative resistance lines for B. distachyon and barley, respectively. In B. distachyon Bd3-1, rapid and strong induction of BdWRKY38 and BdICS (Bradi4g28670) was detected at 12 hpi with AG-1 IA, in agreement with our previous findings (Figure 3A,B). Additionally, potential NHP biosynthesis genes, BdALD1 (Bradi1g71530) and BdFMO1 (Bradi1g72500), which show sequence similarity to A. thaliana AtADL1 and AtFMO1, whose functions have been characterized, were strongly upregulated at 36 and 24 hpi, respectively, during AG-1 IA infection (Figure 3C,D; a summary of the marker genes is given in Table S2). These results confirmed the induction of an SA-dependent response in Bd3-1 to AG-1 IA. In contrast, during infection by AG-4 HG-I+II, Bd3-1 exhibited only weak induction of these marker genes. Furthermore, the expression patterns of these genes differed distinctly from those observed during AG-1 IA infection.
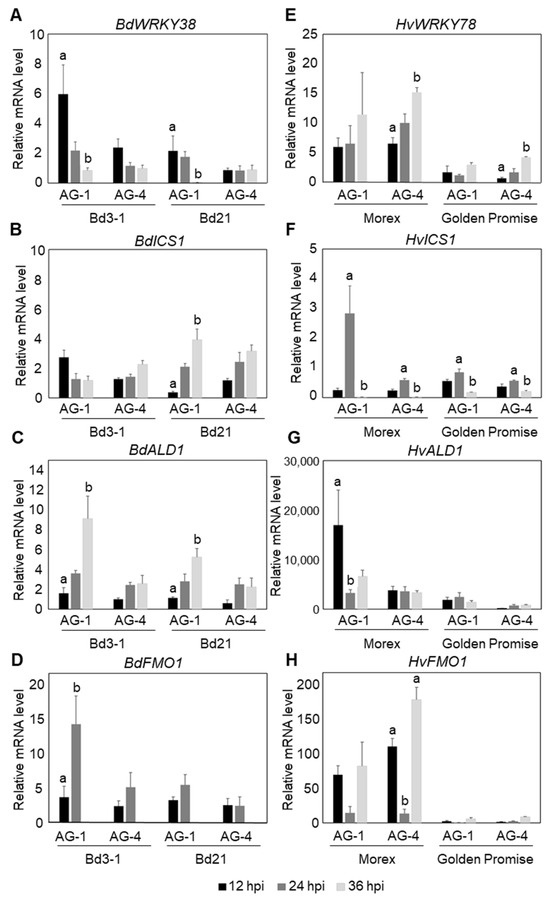
Figure 3.
Temporal expression patterns of SA- and NHP-related defense genes in B. distachyon and barley leaves following R. solani AG-1 IA and AG-4 HG-I+II infection. (A–D) Expression analysis in resistant B. distachyon Bd3-1 and susceptible Bd21: (A) SA-responsive gene BdWRKY38, (B) putative SA biosynthesis gene BdICS, and putative NHP biosynthesis genes (C) BdALD1 and (D) BdFMO1. (E–H) Expression analysis in resistant barley cv. Morex and susceptible cv. Golden Promise: (E) HvWRKY78 (barley homolog of BdWRKY38), (F) putative SA biosynthesis gene HvICS, and putative NHP biosynthesis genes (G) HvALD1 and (H) HvFMO1. Gene expression was quantified by qRT-PCR at 12, 24, and 36 hpi. Data are presented as means ± SEs from three independent biological replicates. Significant differences among time points for each isolate were determined using ANOVA followed by Tukey’s HSD. The letters above the bars indicate significant differences (p < 0.05). Comparisons are independent across isolates; therefore, the same letters in different isolates do not indicate comparability.
In barley cv. Morex, a clear induction of HvICS (HORVU5Hr1G057050) was detected at 24 hpi during AG-1 IA infection (Figure 3F). Although this response was delayed by 12 h compared to the rapid induction observed in B. distachyon Bd3-1, the result suggests that a similar SA-dependent response may occur in the resistant barley cv. Morex. We selected HvWRKY78 (HORVU7Hr1G083270) as the closest homolog to BdWRKY38 based on amino acid sequence similarity. However, its expression patterns were similar during infection with both AG-1 IA and AG-4 HG-I+II (Figure 3E), suggesting that it may not specifically respond to SA. In contrast, HvALD1 (HORVU4Hr1G071300), the closest homolog of AtALD1, was rapidly induced to AG-1 IA infection but showed no response to AG-4 HG-I+II in Morex (Figure 3G). Similarly, we identified HvFMO1 (HORVU4Hr1G077170) as a homolog of AtFMO1, but its expression patterns were comparable during infection with AG-1 IA and AG-4 HG-I+II (Figure 3H).
These results suggest that although both Bd3-1 and Morex are resistant to AG-1 IA and AG-4 HG-I+II leaf inoculations, the underlying resistance mechanisms differ between these two plant species.
3.4. Effects of Exogenous SA and NHP Applications on Leaf Infection by R. solani AG-1 IA and AG-4 HG-I+II
To further confirm which defense responses are effective against R. solani AG-1 IA and AG-4 HG-I+II, we evaluated the effects of exogenously applied SA and NHP on the fungal infection. Intact B. distachyon plantlets were sprayed with SA or NHP at the indicated concentrations, and agar plugs of R. solani were inoculated onto leaves prepared from the treated plants. This approach yielded clearer effects of phytohormone pretreatments compared to treatments on detached leaves. Consistent with our previous findings, SA pretreatment reduced the symptoms caused by AG-1 IA in the susceptible B. distachyon accession Bd21 (Figure 4A,B). Similarly, NHP treatments suppressed AG-1 IA infection, with higher concentrations demonstrating greater efficacy (Figure 4A,B). The suppressive effects of SA and NHP on R. solani AG-1 IA were also observed when these compounds were applied by soil drenching (Figure S2). In the resistant accession Bd3-1, NHP pretreatment induced hyper-resistance to AG-1 IA (Figure 4C,D). In contrast, neither SA nor NHP pretreatment induced resistance to AG-4 HG-I+II in Bd21 (Figure 4E,F).
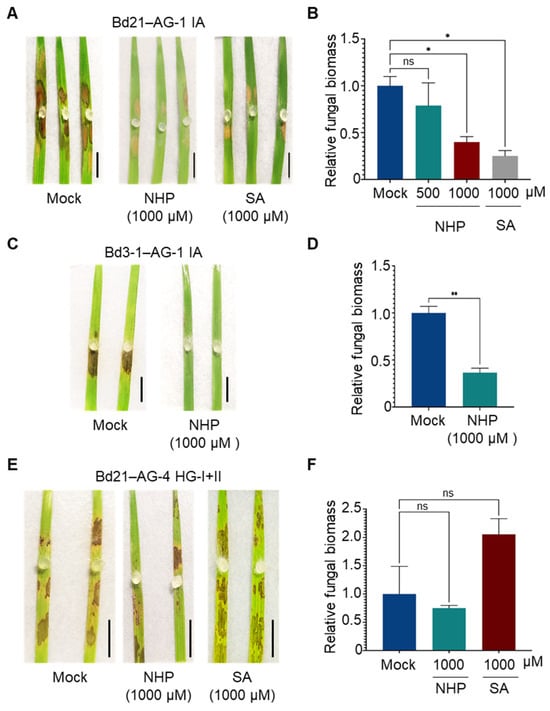
Figure 4.
Differential effects of NHP and SA pretreatments on R. solani AG-1 IA and AG-4 HG-I+II infection in B. distachyon leaves. (A,B) Disease symptoms (A) and relative fungal biomass (B) in leaves of susceptible accession Bd21 pretreated with the indicated concentrations of NHP or SA before inoculation with R. solani AG-1 IA. (C,D) Disease symptoms (C) and relative fungal biomass (D) in leaves of resistant accession Bd3-1 pretreated with NHP before inoculation with R. solani AG-1 IA. (E,F) Disease symptoms (E) and relative fungal biomass (F) in leaves of susceptible accession Bd21 pretreated with NHP or SA before inoculation with R. solani AG-4 HG-I+II. Plants were pretreated with NHP, SA, or Mock (0.1% DMSO dissolved in water). Photographs were taken, and samples were collected for qPCR analysis at 48 hpi. Data are presented as means ± SEs (n = 3; a sampling unit is a randomly selected leaf representing an individual plant). Statistical significance was analyzed by one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s test (*, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.001; ns, not significant). Scale bars: 1 cm.
Next, we evaluated the effects of these phytohormones in barley. Foliar pretreatment with SA or NHP reduced the symptoms caused by AG-1 IA in the susceptible barley cv. Haruna Nijo (Figure 5A), and resistance induction was further confirmed by a reduction in fungal biomass in the treated leaves (Figure 5B). Similar results were observed in the relatively resistant cv. Morex (Figure 5C,D). However, neither SA nor NHP induced resistance to AG-4 HG-I+II in either Haruna Nijo or Morex (Figure 5E–H). Instead, SA appeared to increase susceptibility to AG-4 HG-I+II in both cultivars, although this effect was not statistically significant. Additional experiments with varying SA concentrations (100, 500, and 1000 μM) revealed that higher concentrations of SA exacerbated disease severity caused by AG-4 HG-I+II (Figure S3).
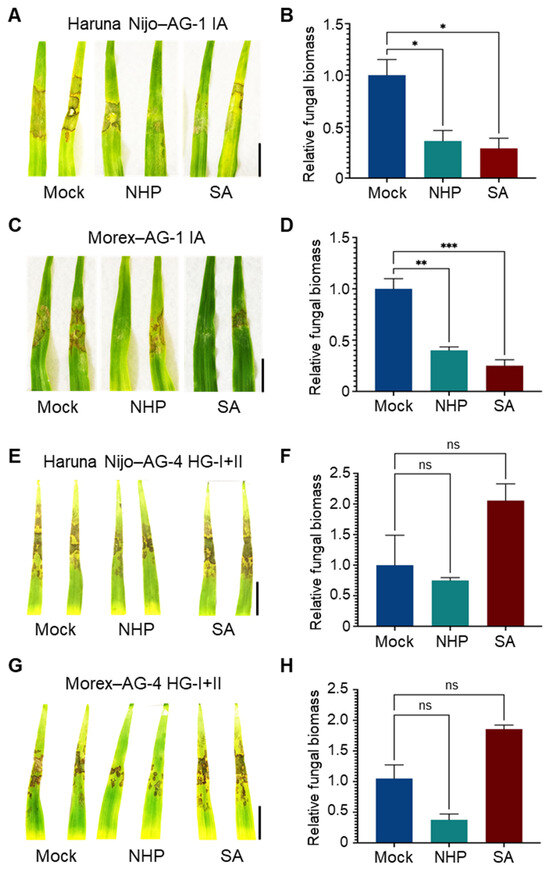
Figure 5.
Differential effects of NHP and SA pretreatments on R. solani AG-1 IA and AG-4 HG-I+II infection in barley leaves. (A,B) Disease symptoms (A) and relative fungal biomass (B) in leaves of susceptible cv. Haruna Nijo pretreated with NHP or SA before inoculation of R. solani AG-1. (C,D) Disease symptoms (C) and relative fungal biomass (D) in leaves of resistant cv. Morex pretreated with NHP or SA before inoculation with R. solani AG-1 IA. (E,F) Disease symptoms (E) and relative fungal biomass (F) in leaves of susceptible cv. Haruna Nijo pretreated with NHP or SA before inoculation with R. solani AG-4 HG-I+II. (G,H) Disease symptoms (G) and relative fungal biomass (H) in leaves of resistant cv. Morex pretreated with NHP or SA before inoculation with R. solani AG-4 HG-I+II. Plants were pretreated with 1000 µM NHP or SA by foliar spray, with 0.1% DMSO dissolved in water as a mock control. Photographs were taken, and samples were collected for qPCR analysis at 48 hpi. Data are presented as means ± SEs (n = 3; a sampling unit is a randomly selected leaf representing an individual plant). Statistical significance was analyzed by one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s test (*, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001; ns, not significant). Scale bars: 3 cm.
Finally, we examined the effects of JA and ET on AG-4 HG-I+II infection in the leaves of B. distachyon and barley. However, neither phytohormone had any significant impact on infection outcomes, at least at the concentrations used (Figure S4).
3.5. Differences in Infection Behavior Between R. solani AG-1 IA and AG-4 HG-I+II
The differences in induced defense responses against R. solani AG-1 IA and AG-4 HG-I+II in both B. distachyon and barley suggest that the infection mechanisms of these isolates may differ, despite these isolates belonging to the same genus and species. To explore this further, we conducted microscopic observations of mycelial growth and infection cushion formation on both plant species. Infected leaves were observed at 20 hpi in B. distachyon and 32 hpi in barley.
In B. distachyon Bd21 infected with AG-1 IA, fungal hyphae spread evenly across the leaves, and massive infection cushions were detected throughout the infected area, consistent with previous reports (Figure 6A) [15,48]. Similarly, in barley cv. Haruna Nijo, AG-1 IA formed a widely dispersed mycelial network with abundant infection cushions covering the entire leaf surface at this time point (Figure 6B).
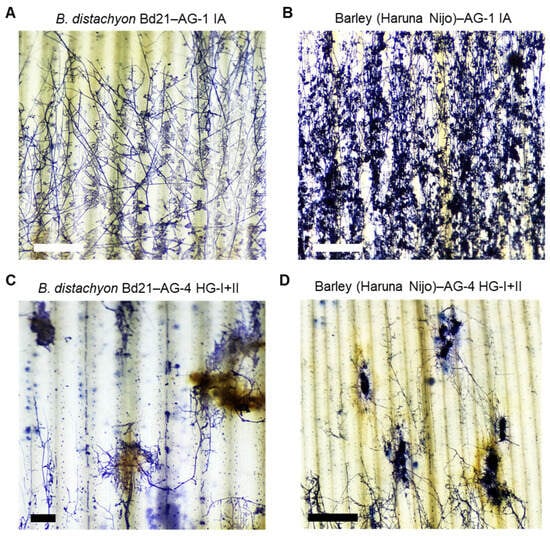
Figure 6.
Hyphal growth of R. solani AG-1 IA and AG-4 HG-I+II on infected B. distachyon and barley leaves. (A,B) Hyphae of R. solani AG-1 IA on the leaf surface of susceptible B. distachyon accession Bd21 (A) and susceptible barley cv. Haruna Nijo (B). (C,D) Hyphae of R. solani AG-4 HG-I+II on the leaf surface of susceptible B. distachyon accession Bd21 (C) and susceptible barley cv. Haruna Nijo (D). Leaves were sampled at 20 hpi for B. distachyon and 36 hpi for barley and then stained with trypan blue. Scale bars: 1 cm.
In contrast, AG-4 HG-I+II displayed a distinct infection pattern in both B distachyon and barley. Fungal mycelia grew in aggregated clusters, forming thick, encircling masses around specific infection sites (Figure 6C,D). Connections between these mycelial aggregates were sparse, resulting in a dotted hyphal distribution compared to the extensive mycelial networks and infection cushion connections observed in AG1-IA infections. The leaf tissue surrounding these hyphal aggregates of AG-4 HG-I+II exhibited necrosis with pronounced brownish pigmentation in both plant species (Figure 6C,D and Figure S4).
4. Discussion
In this study, we evaluated the infectivity of selected Japanese field isolates of R. solani on two cereal plants, B. distachyon and barley. Among the tested isolates, AG-1 IA (MAFF305230) and AG-4 HG-I+II (MAFF305225) were highly virulent on the aboveground tissues of both plant species, but only AG-4 HG-I+II exhibited virulence on the belowground tissues.
R. solani AG-1 IA (MAFF305230), originally isolated from rice sheath blight in Fukuoka, Japan, is representative of isolates frequently associated with this disease globally [49]. Historically, R. solani AG-1 and AG-2 have been recognized for their broad host ranges [50]. Previous studies showed that AG-1 IA is highly virulent on the aboveground tissues of B. distachyon [15] and on both the above- and belowground tissues of A. thaliana [16]. When grown in identical soil (growth substrate) conditions, AG-1 IA infected the roots of A. thaliana but not B. distachyon, suggesting tissue-specific virulence patterns.
R. solani AG-4 HG-I+II (MAFF305225), isolated from cauliflower plants in Fukushima, is a recently classified isolate [14]. While R. solani AG-8 has historically been the primary AG associated with Rhizoctonia root disease in cereals in the USA and Australia, AG-4 and AG-6 have been identified as pathogens in regions including the USA, Turkey, Azerbaijan, South Africa, and Tanzania. AG-4 is known to cause seedling blight in rice [51] and foliar blights in barley [52,53,54]. Additionally, AG-4 affects a wide range of dicot crops [54]. A Japanese AG-4 isolate from peanuts was shown to infect wheat under controlled conditions [55], and AG-4 HGI3, isolated from buckwheat, exhibited a broad host range [38].
Understanding the molecular mechanisms of R. solani virulence is essential for developing effective crop protection strategies. However, progress has been limited by the challenges associated with genetic engineering in this pathogen. To overcome this limitation, we focused on exploring host resistance mechanisms. Kidd et al. (2021) demonstrated the role of defense barriers in Arabidopsis nonhost resistance against leaf and root infections by AG-8 [34]. Building on this approach, our first strategy involved leveraging genetic variation in host resistance. Previously, we identified B. distachyon accessions Bd3-1 and Gaz-4 as resistant to AG-1 IA leaf inoculation [15]. In this study, we observed AG-1 IA virulence on barley leaves, with cv. Morex showing moderate resistance compared to the more susceptible cvs. Haruna Nijo and Golden Promise. Similarly, B. distachyon accessions Bd3-1 and Gaz-4 demonstrated resistance to AG-4 HG-I+II leaf infection, similar to their resistance to AG-1 IA. Barley cv. Morex also exhibited resistance to AG-4 HG-I+II leaf infection. When evaluating root infection by AG-4 HG-I+II, B. distachyon Bd3-1 and Gaz-4, along with barley cv. Morex, displayed enhanced resistance compared to other accessions and cultivars. Previous studies have also highlighted genetic variation in B. distachyon resistance to AG-8 root infection, with accessions Bd3-1, Koz-3, and Bd30-1 showing relatively higher resistance than Bd21 [40]. These findings suggest that plants employ diverse strategies to combat R. solani. The identification and pyramiding of such resistance traits could pave the way for effective, durable strategies to control this pathogen and protect valuable crops.
The second strategy focused on defense responses and phytohormone-induced resistance. Among the plants tested against R. solani isolates AG-1 IA and AG-4 HG-I+II, B. distachyon accessions Bd3-1 and Gaz-4, and barley cv. Morex consistently showed resistance. Initially, we hypothesized that these plants might use similar resistance mechanisms against both isolates. However, the expression patterns of defense-related marker genes during infection revealed distinct responses to each pathogen isolate. In Bd3-1 and Morex, genes associated with SA and NHP biosynthesis were induced earlier in response to AG-1 IA than to AG-4 HG-I+II. This suggests that SA- and NHP-related immunity specifically targets AG-1 IA. Chemical pretreatment experiments supported this hypothesis: pretreatment with either SA or NHP effectively suppressed AG-1 IA infection in both resistant and susceptible B. distachyon accessions and barley cultivars but had no impact on AG-4 HG-I+II. While previous studies demonstrated that SA pretreatment induced resistance to AG-1 IA in B. distachyon and rice, we now show that NHP similarly induces defense against this isolate in both B. distachyon and barley. NHP, a recently identified mobile signal for SAR, functions in concert with SA to defend against biotrophic pathogens. SA accumulates in locally infected tissues, triggering NHP synthesis, which then travels to systemic tissues and amplifies SA production and defense responses [56]. Enhanced NHP biosynthesis has been linked to resistance against biotrophic and hemibiotrophic pathogens in monocots, including B. distachyon and barley [57]. Similarly, Pip pretreatment reduced infections by hemibiotrophic pathogens such as Xanthomonas translucens pv. cerealis and Blumeria graminis f. sp. hordei in barley [32]. Although Pip pretreatment did not significantly enhance resistance to the necrotrophic pathogen Pyrenophora teres, it modestly reduced lesion size without negative effects [32]. We previously demonstrated that SA-related immunity plays a significant role in Bd3-1′s resistance to AG-1 IA through BdWRKY38, a key regulator of SA signaling [48]. The effectiveness of NHP pretreatment against AG-1 IA further supports the existence of a biotrophic interaction phase during its infection of B. distachyon and barley leaves. Such biotrophic infection and host recognition of pathogens could be mediated by the effector proteins released by R. solani.
In contrast, neither SA nor NHP pretreatment was effective against AG-4 HG-I+II leaf infections in B. distachyon or barley, suggesting different infection mechanisms between the two isolates. These results imply that AG-4 HG-I+II operates as a purely necrotrophic pathogen or has a very brief biotrophic phase compared to AG-1 IA, which exhibits a hemibiotrophic lifestyle. Consistently, neither B. distachyon Bd3-1 nor barley cv. Morex induced SA- or NHP-biosynthesis genes during AG-4 HG-I+II infection. Although both Bd3-1 and Morex are resistant to AG-1 IA, their resistance mechanisms against AG-1 IA and AG-4 HG-I+II appear to differ. This is further supported by the observation that Bd3-1′s resistance to AG-1 IA was compromised by the expression of the bacterial NahG gene, which encodes SA hydroxylase and degrades SA [15,48]. This result suggests that SA is necessary for resistance in Bd3-1 to R. solani AG-1 IA. Understanding these diverse defense mechanisms provides valuable insights into nonhost resistance and may inform the development of resistant crop varieties.
Consistent with these findings, R. solani AG-1 IA and AG-4 HG-I+II exhibited distinct infection behaviors. AG-1 IA infected leaves by forming an extensive mycelial network with abundant infection cushions, whereas AG-4 HG-I+II produced localized, compact mycelial masses in dispersed areas. Our results suggest that the R. solani species complex contains at least two types of pathogens with different styles of infection. Infection cushion formation, a hallmark of the penetration stage, has been well-documented in sheath blight disease [58,59,60,61]. Studies have reported a correlation between disease resistance and the number and distribution of infection cushions [36,60]. We previously demonstrated that SA pretreatment prevented AG-1 IA progression to the infection cushion-forming stage on B. distachyon, and resistant B. distachyon accessions blocked infection cushion formation entirely [15,48]. This suggests that R. solani isolates utilizing infection cushions may adopt a biotrophic phase before transitioning to necrotrophy, marked by extensive tissue penetration through these specialized structures. In contrast, no phytohormone pretreatments tested were effective against AG-4 HG-I+II in B. distachyon or barley. This is notable because JA and ET pretreatments typically induce resistance against some necrotrophic pathogens [62]. Consistent with this, previous studies have shown that SA application can increase susceptibility to necrotrophic pathogens, such as Alternaria brassicicola, by suppressing JA-related defense mechanisms [63]. Similarly, SA pretreatment enhanced tomato susceptibility to Botrytis cinerea [64], although in A. thaliana, both SA and JA are required for resistance against B. cinerea [65]. We previously reported that no defense-related phytohormone pretreatments conferred resistance to either AG-1 IA or AG-4 HG-I+II in A. thaliana [16]. These findings suggest that the necrotrophic lifestyle of AG-4 HG-I+II in B. distachyon and barley, as well as that of both AG-1 IA and AG-4 HG-I+II in Arabidopsis, may parallel the behavior of well-studied necrotrophic pathogens like B. cinerea and A. brassicicola.
We hypothesize that AG-4 HG-I+II employs secreted CAZymes and/or toxins to kill host cells prior to invasion. This strategy, which may limit direct contact with host defenses, renders chemically or physically induced barriers by phytohormones ineffective. Observations showed that AG-4 HG-I+II induced necrosis beneath hyphal masses more rapidly than AG-1 IA. The resulting dead host tissue, characterized by brownish pigment accumulation, further supports its necrotrophic lifestyle. A recent genomic comparison between AG-1 IA and AG-4 HGI3 (isolated from buckwheat) revealed that AG-4 HGI3 possesses significantly more CAZymes, including cellulases, ligninases, hemicellulases, and pectinases [38]. These CAZymes likely enable its necrotrophic lifestyle. He et al. (2023) also demonstrated that JA-mediated resistance contributes to the AG-4 HGI 3 isolate in Tartary buckwheat, suggesting another different type of virulence mechanism in the R. solani species complex [38]. In conclusion, the differential responses to SA pretreatment between AG-1 IA and AG-4 HG-I+II in B. distachyon and barley leaves reflect AG-1 IA’s hemibiotrophic nature versus AG-4 HG-I+II’s necrotrophic strategy. Further studies focusing on host responses and microscopic analysis of hyphal infection behavior may uncover additional lifestyle adaptations within the R. solani species complex, which have evolved to target diverse hosts.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/life15020235/s1: Figure S1. Criteria for the disease severity assay caused by R. solani isolates in the leaf and root inoculation in Table 1 and Table 2; Figure S2: Root-applied salicylic acid and N-hydroxypipecolic acid affect R. solani AG-1 IA infection on B. distachyon leaves; Figure S3: Salicylic acid pretreatment increases susceptibility to R. solani AG-4 HGI+II in resistant B. distachyon and barley leaves; Figure S4: Jasmonic acid and ethylene pretreatments do not affect R. solani AG-4 HG-I+II infection in susceptible B. distachyon and barley leaves; Figure S5: Necrotrophic lesions under R. solani AG-4 HG-I+II mycelial masses on leaves of susceptible barley cv. Haruna Nijo; Table S1: Primers used in this study; Table S2: Marker genes analyzed in this study.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, N.M. and Y.N.; validation, N.M., R.F., Y.K., N.K., R.N., K.T.N., M.W., and Y.N.; investigation, N.M., R.F., N.K., R.N., K.T.N., M.W., and Y.N.; resources, K.M. and H.H.; writing—original draft preparation, N.M.; writing—review and editing, Y.N.; visualization, N.M. and Y.N.; supervision, N.S., H.M., K.T., Y.I., and Y.N.; project administration, Y.N.; funding acquisition, Y.K. and Y.N. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was financially supported by the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS), KAKENHI Grant No. JP21H02197 and JP24K01759 to Y.N., and JP21K05610 to Y.K.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data are contained within this article or Supplementary Materials.
Acknowledgments
We thank the National Bio-Resource Project (NBRP) of the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology (MEXT) for the distribution of barley seeds. We also thank the NARO Genebank, Japan for maintaining and distributing the R. solani isolates. N.M. was supported by a Ph.D. scholarship from the MEXT.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
References
- Li, D.; Li, S.; Wei, S.; Sun, W. Strategies to manage rice sheath blight: Lessons from interactions between rice and Rhizoctonia solani. Rice 2021, 14, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Q.; Yang, L.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Hu, K.; Yang, W.; Zuo, S.; Xu, J.; Kang, Z.; Xiao, X.; et al. A high-quality genome of Rhizoctonia solani, a devastating fungal pathogen with a wide host range. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 2022, 35, 954–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozaka, T. Ecological studies on sheath blight of rice caused by Pellicualria sasakii and its chemical control. Chugoku Agric. Res. 1961, 20, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Matsuura, K. Scanning electron microscopy of the infection process of Rhizoctonia solani in leaf sheaths of rice plants. Phytopathology 1986, 76, 811–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, A.; Lin, R.; Zhang, D.; Qin, P.; Xu, L.; Ai, P.; Ding, L.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Y.; et al. The evolution and pathogenic mechanisms of the rice sheath blight pathogen. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelsalam, S.S.H.; Kouzai, Y.; Watanabe, M.; Inoue, K.; Matsui, H.; Yamamoto, M.; Ichinose, Y.; Toyoda, K.; Tsuge, S.; Mochida, K.; et al. Identification of effector candidate genes of Rhizoctonia solani AG-1 IA expressed during infection in Brachypodium distachyon. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 14889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Wang, Z.; Yamamoto, N.; Wang, M.; Yi, X.; Li, P.; Lin, R.; Nasimi, Z.; Okada, K.; Mochida, K.; et al. Secreted glycosyltransferase RsIA_GT of Rhizoctonia solani AG-1 IA inhibits defense responses in Nicotiana benthamiana. Pathogens 2022, 11, 1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Lin, R.; Yamamoto, N.; Wang, Z.; Lin, H.; Okada, K.; Liu, Y.; Xiang, X.; Zheng, T.; Zheng, H.; et al. Mitochondrial-targeting effector RsIA_CtaG/Cox11 in Rhizoctonia solani AG-1 IA has two functions: Plant immunity suppression and cell death induction mediated by a rice cytochrome c oxidase subunit. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2024, 25, e13397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdoulaye, A.H.; Foda, M.F.; Kotta-Loizou, I. Viruses infecting the plant pathogenic fungus Rhizoctonia solani. Viruses 2019, 11, 1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Xia, X.; Du, Q.; Xia, L.; Ma, X.; Li, Q.; Liu, W. Genome sequence of Rhizoctonia solani anastomosis group 4 strain Rhs4ca, a widespread pathomycete in field crops. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 2021, 34, 826–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajayi-Oyetunde, O.O.; Bradley, C.A. Rhizoctonia solani: Taxonomy, population biology and management of rhizoctonia seedling disease of soybean. Plant Pathol. 2018, 67, 3–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carling, D.E.; Kuninaga, S.; Brainard, K.A. Hyphal anastomosis reactions, rDNA-internal transcribed spacer sequences, and virulence levels among subsets of Rhizoctonia solani anastomosis group-2 (AG-2) and AG-BI. Phytopathology 2002, 92, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senapati, M.; Tiwari, A.; Sharma, N.; Chandra, P.; Bashyal, B.M.; Ellur, R.K.; Bhowmick, P.K.; Bollinedi, H.; Vinod, K.K.; Singh, A.K.; et al. Rhizoctonia solani Kühn pathophysiology: Status and prospects of sheath blight disease management in rice. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 881116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Misawa, T.; Kurose, D. Anastomosis group and subgroup identification of Rhizoctonia solani strains deposited in NARO Genebank, Japan. J. Gen. Plant Pathol. 2019, 85, 282–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouzai, Y.; Kimura, M.; Watanabe, M.; Kusunoki, K.; Osaka, D.; Suzuki, T.; Matsui, H.; Yamamoto, M.; Ichinose, Y.; Toyoda, K.; et al. Salicylic acid-dependent immunity contributes to resistance against Rhizoctonia solani, a necrotrophic fungal agent of sheath blight, in rice and Brachypodium distachyon. New Phytol. 2018, 217, 771–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelghany, M.M.A.; Kurikawa, M.; Watanabe, M.; Matsui, H.; Yamamoto, M.; Ichinose, Y.; Toyoda, K.; Kouzai, Y.; Noutoshi, Y. Surveillance of pathogenicity of Rhizoctonia solani Japanese isolates with varied anastomosis groups and subgroups on Arabidopsis thaliana. Life 2022, 12, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, J.D.G.; Staskawicz, B.J.; Dangl, J.L. The plant immune system: From discovery to deployment. Cell 2024, 187, 2095–2116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laluk, K.; Mengiste, T. Necrotroph attacks on plants: Wanton destruction or covert extortion? Arab. Book 2010, 2010, e0136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, T.; Bronkhorst, J.; Müller, J.; Safari, N.; Hahn, M.; Sprakel, J.; Scheuring, D. Plant infection by the necrotrophic fungus Botrytis requires actin-dependent generation of high invasive turgor pressure. New Phytol. 2024, 244, 192–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, W.; Qian, C.; Ren, D.; Cai, Y.; Deng, Z.; Zhang, N.; Wang, C.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, P.; Xu, L. The GATA transcription factor BcWCL2 regulates citric acid secretion to maintain redox homeostasis and full virulence in Botrytis cinerea. mBio 2024, 15, e00133-24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.U.; Liu, X.; Wang, X.; Fan, B. Grapevine gray mold disease: Infection, defense and management. Horticulture Res. 2024, 11, uhae182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glazebrook, J. Contrasting mechanisms of defense against biotrophic and necrotrophic pathogens. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2005, 43, 205–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vlot, A.C.; Dempsey, D.A.; Klessig, D.F. Salicylic acid, a multifaced hormone to combat disease. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2009, 47, 177–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilroy, E.; Breen, S. Interplay between phytohormone signalling pathways in plant defence—other than salicylic acid and jasmonic acid. Essays Biochem. 2022, 66, 657–671. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, X.; Chen, Y.; Li, B.; Zhang, Z.; Qin, G.; Chen, T.; Tian, S. Molecular mechanisms underlying multi-level defense responses of horticultural crops to fungal pathogens. Hortic. Res. 2022, 9, uhac066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monte, I. Jasmonates and salicylic acid: Evolution of defense hormones in land plants. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2023, 76, 102470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Yang, J.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y. Salicylic acid: Biosynthesis and signaling. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2021, 72, 761–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.C.; Holmes, E.C.; Rajniak, J.; Kim, J.G.; Tang, S.; Fischer, C.R.; Mudgett, M.B.; Sattely, E.S. N-hydroxy-pipecolic acid is a mobile metabolite that induces systemic disease resistance in Arabidopsis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E4920–E4929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartmann, M.; Zeier, J. L-lysine metabolism to N-hydroxypipecolic acid: An integral immune-activating pathway in plants. Plant J. 2018, 96, 5–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shields, A.; Shivnauth, V.; Castroverde, C.D.M. Salicylic acid and N-hydroxypipecolic acid at the fulcrum of the plant immunity-growth equilibrium. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 841688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartmann, M.; Zeier, T.; Bernsdorff, F.; Reichel-Deland, V.; Kim, D.; Hohmann, M.; Scholten, N.; Schuck, S.; Bräutigam, A.; Hölzel, T.; et al. Flavin monooxygenase-generated N-hydroxypipecolic acid is a critical element of plant systemic immunity. Cell 2018, 173, 456–469.e16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lenk, M.; Wenig, M.; Bauer, K.; Hug, F.; Knappe, C.; Lange, B.; Timsy; Häußler, F.; Mengel, F.; Dey, S.; et al. Pipecolic acid is induced in barley upon infection and triggers immune responses associated with elevated nitric oxide accumulation. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 2019, 32, 1303–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foley, R.C.; Gleason, C.A.; Anderson, J.P.; Hamann, T.; Singh, K.B. Genetic and genomic analysis of Rhizoctonia solani interactions with Arabidopsis; evidence of resistance mediated through NADPH oxidases. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e56814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kidd, B.N.; Foley, R.; Singh, K.B.; Anderson, J.P. Foliar resistance to Rhizoctonia solani in Arabidopsis is compromised by simultaneous loss of ethylene, jasmonate and PEN2 mediated defense pathways. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 2546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Hassan, S.; Kidd, B.N.; Garg, G.; Mathesius, U.; Singh, K.B.; Anderson, P. Ethylene signaling is important for isoflavonoid-mediated resistance to Rhizoctonia solani in roots of Medicago truncatula. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 2017, 30, 691–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koley, P.; Brahmachari, S.; Saha, A.; Deb, C.; Mondal, M.; Das, N.; Das, A.; Lahiri, S.; Das, M.; Thakur, M.; et al. Phytohormone priming of tomato plants evoke differential behavior in Rhizoctonia solani during infection, with salicylate priming imparting greater tolerance than jasmonate. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 12, 766095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taheri, P.; Tarighi, S. Riboflavin induces resistance in rice against Rhizoctonia solani via jasmonate-mediated priming of phenylpropanoid pathway. J. Plant Physiol. 2010, 167, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Zhang, K.; Li, S.; Lu, X.; Zhao, H.; Guan, C.; Huang, X.; Shi, Y.; Kang, Z.; Fan, Y.; et al. Multiomics analysis reveals the molecular mechanisms underlying virulence in Rhizoctonia and jasmonic acid-mediated resistance in Tartary buckwheat (Fagopyrum tataricum). Plant Cell 2023, 35, 2773–2798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pethybridge, S.J.; Nelson, S.C. Leaf doctor: A new portable application for quantifying plant disease severity. Plant Dis. 2015, 99, 1310–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneebeli, K.; Mathesius, U.; Zwart, A.B.; Bragg, J.N.; Vogel, J.P.; Watt, M. Brachypodium distachyon genotypes vary in resistance to Rhizoctonia solani AG8. Funct. Plant Biol. 2016, 43, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foley, R.C.; Kidd, B.N.; Hane, J.K.; Anderson, J.P.; Singh, K.B. Reactive oxygen species play a role in the infection of the necrotrophic fungi, Rhizoctonia solani in wheat. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0152548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okubara, P.A.; Leston, N.; Micknass, U.; Kogel, K.H.; Imani, J. Rapid quantitative assessment of Rhizoctonia resistance in roots of selected wheat and barley genotypes. Plant Dis. 2016, 100, 640–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sayler, R.J.; Yang, Y. Detection and quantification of Rhizoctonia solani AG-1 IA, the rice sheath blight pathogen, in rice using real-time PCR. Plant Dis. 2007, 91, 1663–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Budge, G.E.; Shaw, M.W.; Colyer, A.; Pietravalle, S.; Boonham, N. Molecular tools to investigate Rhizoctonia solani distirution in soil. Plant Pathol. 2009, 58, 1071–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Wen, F.; Li, P.; Liu, X.; Cao, J.; Jiang, M.; Ming, F.; Chu, Z. Validation of a reference gene (BdFIM) for quantifying transgene copy numbers in Brachypodium distachyon by real-time PCR. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2014, 172, 3163–3175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chambers, J.P.; Behpour, A.; Bird, A.; Ng, C.K.-Y. Evaluation of the use of the polyubiquitin genes, Ubi4 and Ubi10 as reference genes for expression studies in Brachypodium distachyon. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e49372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Gines, M.; Baldwin, T.; Rashid, A.; Bregitzer, P.; Maughan, P.J.; Jillen, E.N.; Klos, K.E. Selection of expression reference genes with demonstrated stability in barley among a diverse set of tissues and cultivars. Crop Sci. 2018, 58, 332–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouzai, Y.; Shimizu, M.; Inoue, K.; Uehara-Yamaguchi, Y.; Takahagi, K.; Nakayama, R.; Matsuura, T.; Mori, I.C.; Hirayama, T.; Abdelsalam, S.S.H.; et al. BdWRKY38 is required for the incompatible interaction of Brachypodium distachyon with the necrotrophic fungus Rhizoctonia solani. Plant J. 2020, 104, 995–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Xuan, Y.; Yi, J.; Xiao, G.; Yuan, D.P.; Li, D. Progress in rice sheath blight resistance research. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1141697. [Google Scholar]
- Wibberg, D.; Jelonek, L.; Rupp, O.; Hennig, M.; Eikmeyer, F.; Goesmann, A.; Hartmann, A.; Borriss, R.; Grosch, R.; Pühler, A.; et al. Establishment and interpretation of the genome sequence of the phytopathogenic fungus Rhizoctonia solani AG1-IB isolate 7/3/14. J. Biotechnol. 2013, 167, 142–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaire, S.P.; Zhou, X.G.; Zhou, Y.; Shi, J.; Jo, Y.K. Identification and distribution of fungal pathogens associated with seedling blight of rice in the southern United States. Plant Pathol. 2023, 72, 76–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacharis, C.; Gouziotis, A.; Kalogeropoulou, P.; Koutita, O.; Tzavella-Klonari, K.; Karaoglanidis, G.S. Characterization of Rhizoctonia spp. isolates associated with damping-off disease in cotton and tobacco seedlings in Greece. Plant Dis. 2010, 94, 1314–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choupannejad, R.; Sharifnabi, B.; Fadaei Tehrani, A.A.; Gholami, J. Rhizoctonia solani AG4 associated with foliar blight symptoms on barley in Iran. Australas. Plant Dis. Notes 2017, 12, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pizolotto, C.A.; Brown, L.; Harrington, S.; Murdock, M.R.; Harrington, M.; Woodhall, J.W.; Moll, M.; Marshall, J.M. First report of Rhizoctonia solani AG4 HG-II infecting barley stems in Idaho. Plant Dis. 2020, 104, 3058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucharska, K.; Katulski, B.; Goriewa, K.; Duba, A.; Wachowska, U. Pathogenicity and fungicide sensitivity of Rhizoctonia solani and R. cerealis isoates. Gesunde Pflanzen 2018, 70, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spoel, S.H.; Dong, X. Salicylic acid in plant immunity and beyond. Plant Cell 2024, 36, 1451–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnake, A.; Hartmann, M.; Schreiber, S.; Malik, J.; Brahmann, L.; Yildiz, I.; von Dahlen, J.; Rose, L.E.; Schaffrath, U.; Zeier, J. Inducible biosynthesis and immune function of the systemic acquired resistance inducer N-hydroxypipecolic acid in monocotyledonous and dicotyledonous plants. J. Exp. Bot. 2020, 71, 6444–6459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofman, T.W.; Jongebloed, P.H.J. Infection process of Rhizoctonia solani on Solarium tuberosum and effects of granular nematicides. Neth. J. Plant Pathol. 1988, 94, 243–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Rohila, R.; Savary, S.; Willocquet, L.; Singh, U.S. Infection process in sheath blight of rice caused by Rhizoctonia solani. Indian Phytopathol. 2003, 56, 434–438. [Google Scholar]
- Basu, A.; Chowdhury, S.; Chaudhuri, T.R.; Kundu, S. Differential behaviour of sheath blight pathogen Rhizoctonia solani in tolerant and susceptible rice varieties before and during infection. Plant Pathol. 2016, 65, 1333–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Wang, T.; Meng, G.; Liu, J.; Lu, D.; Liu, X.; Zeng, Y. Cytological observation and transcriptome analysis reveal dynamic changes of Rhizoctonia solani colonization on leaf sheath and different genes recruited between the resistant and susceptible genotypes in rice. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 1055277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hönig, M.; Roeber, V.M.; Schmülling, T.; Cortleven, A. Chemical priming of plant defense responses to pathogen attacks. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1146577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spoel, S.H.; Johnson, J.S.; Dong, X. Regulation of tradeoffs between plant defenses against pathogens with different lifestyles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 18842–18847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abd El Rahman, T.; El Oirdi, M.; Gonzalez-Lamothe, R.; Bouarab, K. Necrotrophic pathogens use the salicylic acid signaling pathway to promote disease development in tomato. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 2012, 25, 1584–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrari, S.; Plotnikova, J.M.; De Lorenzo, G.; Ausubel, F.M. Arabidopsis local resistance to Botrytis cinerea involves salicylic acid and camalexin and requires EDS4 and PAD2, but not SID2, EDS5 or PAD4. Plant J. 2003, 35, 193–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).