Contrasting Effects of Larval Escitalopram and Serotonin-Synthesis Inhibitor on Adult Phototaxis in Drosophila w1118
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Fly Stock and Rearing
2.2. Experimental Groups and Developmental Drug Exposure
2.3. Phototaxis Assay (FlyVac)
2.4. Robustness Checks
2.5. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
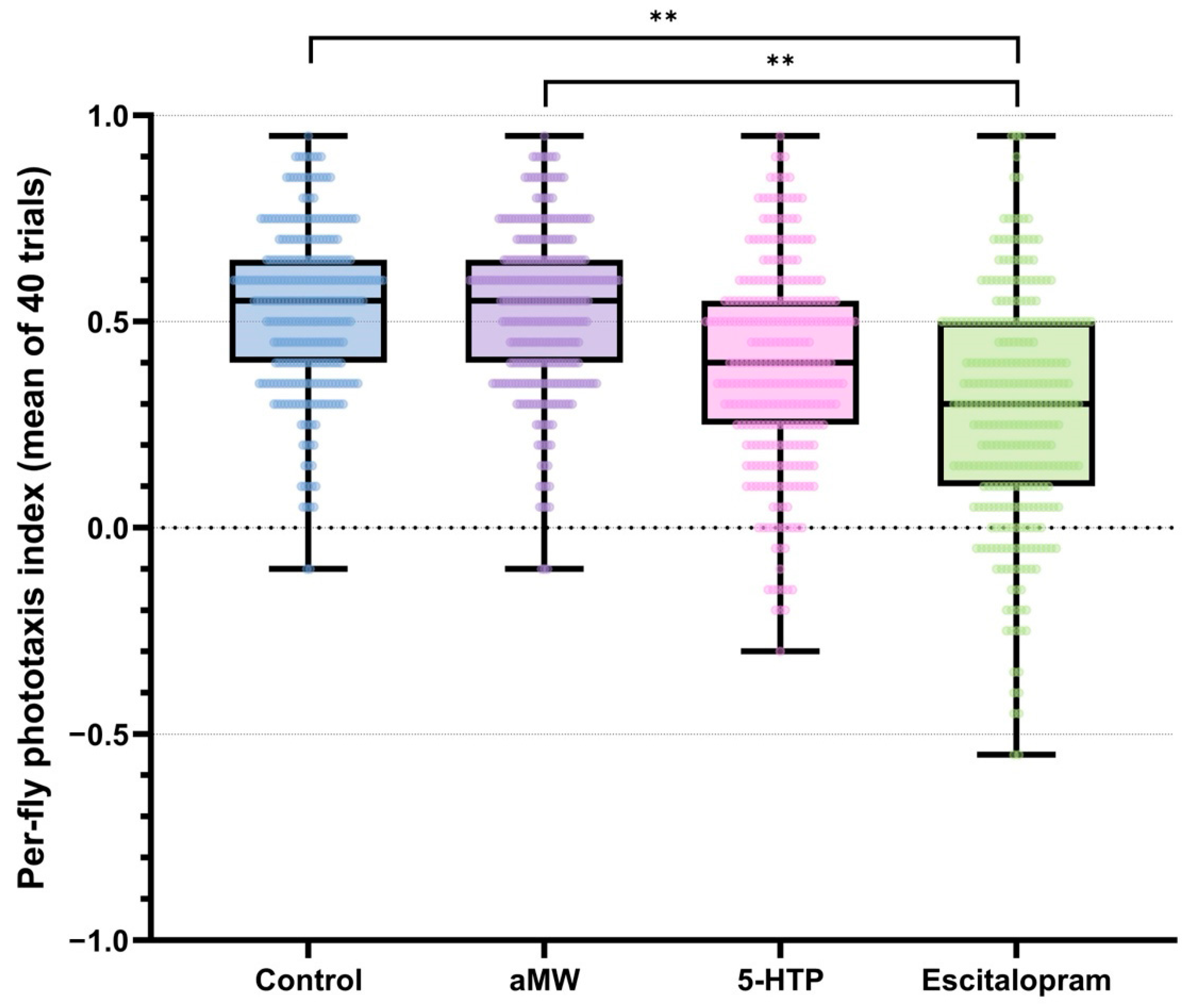
3.1. Light-Choice Probability (LCP)
3.2. Phototactic Variability
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Research Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Buchanan, S.M.; Kain, J.S.; De Bivort, B.L. Neuronal control of locomotor handedness in Drosophila. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 6700–6705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olofsson, H.; Ripa, J.; Jonzén, N. Bet-hedging as an evolutionary game: The trade-off between egg size and number. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2009, 276, 2963–2969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kain, J.S.; Zhang, S.; Akhund-Zade, J.; Samuel, A.D.; Klein, M.; de Bivort, B.L. Variability in thermal and phototactic preferences in Drosophila may reflect an adaptive bet-hedging strategy. Evolution 2015, 69, 3171–3185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krams, I.A.; Krama, T.; Krams, R.; Trakimas, G.; Popovs, S.; Jõers, P.; Munkevics, M.; Elferts, D.; Rantala, M.J.; Makņa, J.; et al. Serotoninergic modulation of phototactic variability underpins a bet-hedging strategy in Drosophila melanogaster. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 659331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popovs, S.; Munkevics, M.; Krama, T.; Krams, R.; Sledevskis, E.; Trakimas, G.; Zants, K.; Grigorjeva, T.; Mizers, V.; Kolbjonoks, V.; et al. Explaining the survival of the sickest: Altered walking patterns are linked with improved adult survival in Drosophila melanogaster grown with predators during larval development. Behaviour 2024, 161, 133–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kain, J.S.; Stokes, C.; de Bivort, B.L. Phototactic personality in fruit flies and its suppression by serotonin and white. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 19834–19839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayroles, J.F.; Buchanan, S.M.; O’Leary, C.; Skutt-Kakaria, K.; Grenier, J.K.; Clark, A.G.; Hartl, D.L.; De Bivort, B.L. Behavioral idiosyncrasy reveals genetic control of phenotypic variability. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 6706–6711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Honegger, K.; de Bivort, B. Stochasticity, individuality and behavior. Curr. Biol. 2018, 28, R8–R12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maloney, R.T. Neuromodulation and individuality. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 777873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Bivort, B.L. The Developmental Origins of Behavioral Individuality. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2025, 41, 331–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesch, K.P.; Waider, J. Serotonin in the modulation of neural plasticity and networks: Implications for neurodevelopmental disorders. Neuron 2012, 76, 175–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alekseyenko, O.V.; Chan, Y.B.; de la Paz Fernandez, M.; Bülow, T.; Pankratz, M.J.; Kravitz, E.A. Single serotonergic neurons that modulate aggression in Drosophila. Curr. Biol. 2014, 24, 2700–2707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.P.; Chiang, M.H.; Chang, L.Y.; Shyu, W.H.; Chiu, T.H.; Fu, T.F.; Wu, T.; Wu, C.L. Serotonin signals modulate mushroom body output neurons for sustaining water-reward long-term memory in Drosophila. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 755574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krama, T.; Munkevics, M.; Krams, R.; Grigorjeva, T.; Trakimas, G.; Jõers, P.; Popovs, S.; Zants, K.; Elferts, D.; Rantala, M.J.; et al. Development under predation risk increases serotonin-signaling, variability of turning behavior and survival in adult fruit flies Drosophila melanogaster. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2023, 17, 1189301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borycz, J.; Borycz, J.A.; Kubow, A.; Lloyd, V.; Meinertzhagen, I.A. Drosophila ABC transporter mutants white, brown and scarlet have altered contents and distribution of biogenic amines in the brain. J. Exp. Biol. 2008, 211, 3454–3466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krams, I.A.; Krams, R.; Jõers, P.; Munkevics, M.; Trakimas, G.; Luoto, S.; Eichler, S.; Butler, D.M.; Merivee, E.; Must, A.; et al. Developmental speed affects ecological stoichiometry and adult fat reserves in Drosophila melanogaster. Anim. Biol. 2020, 71, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tawa, E.; Notterman, D. Drosophila melanogaster as a neurobehavioral model for sex differences in stress response. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2025, 19, 1581763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, S.W.; Yang, Y.T.; Sun, Y.; Zhan, Y.P.; Zhu, Y. Serotonin signals overcome loser mentality in Drosophila. Iscience 2020, 23, 101651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ries, A.S.; Hermanns, T.; Poeck, B.; Strauss, R. Serotonin modulates a depression-like state in Drosophila responsive to lithium treatment. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Q.; Joiner, W.J.; Sehgal, A. A sleep-promoting role for the Drosophila serotonin receptor 1A. Curr. Biol. 2006, 16, 1051–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunham, K.E.; Venton, B.J. SSRI antidepressants differentially modulate serotonin reuptake and release in Drosophila. J. Neurochem. 2022, 162, 404–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, O.; Becnel, J.; Nichols, C.D. Serotonin 5-HT2 and 5-HT1A-like receptors differentially modulate aggressive behaviors in Drosophila melanogaster. Neuroscience 2009, 158, 1292–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palavicino-Maggio, C.B.; Sengupta, S. The neuromodulatory basis of aggression: Lessons from the humble fruit fly. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 836666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sitaraman, D.; Kramer, E.F.; Kahsai, L.; Ostrowski, D.; Zars, T. Discrete serotonin systems mediate memory enhancement and escape latencies after unpredicted aversive experience in Drosophila place memory. Front. Syst. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kesić, M.; Mokrović, G.; Tvrdeić, A.; Miše, B.; Štefulj, J.; Čičin-Šain, L. Constitutive serotonin tone modulates molecular and behavioral response to chronic fluoxetine treatment: A study on genetic rat model. Front. Psychiatry 2021, 12, 741222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bucher, D.; Prinz, A.A.; Marder, E. Animal-to-animal variability in motor pattern production in adults and during growth. J. Neurosci. 2005, 25, 1611–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, Y.H.; Spletter, M.L.; Yaksi, E.; Leong, J.C.; Wilson, R.I.; Luo, L. Diversity and wiring variability of olfactory local interneurons in the Drosophila antennal lobe. Nat. Neurosci. 2010, 13, 439–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krams, I.; Trakimas, G.; Kecko, S.; Elferts, D.; Krams, R.; Luoto, S.; Rantala, M.J.; Mänd, M.; Kuusik, A.; Kekäläinen, J.; et al. Linking organismal growth, coping styles, stress reactivity, and metabolism via responses against a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor in an insect. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 8599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neckameyer, W.S.; Nieto-Romero, A.R. Response to stress in Drosophila is mediated by gender, age and stress paradigm. Stress 2015, 18, 254–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neckameyer, W.S.; Bhatt, P. Protocols to study behavior in Drosophila. In Drosophila Methods and Protocols; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 303–320. [Google Scholar]
- Araujo, S.M.; Poetini, M.R.; Bortolotto, V.C.; de Freitas Couto, S.; Pinheiro, F.C.; Meichtry, L.B.; de Almeida, F.P.; Musachio, E.A.S.; de Paula, M.T.; Prigol, M. Chronic unpredictable mild stress-induced depressive-like behavior and dysregulation of brain levels of biogenic amines in Drosophila melanogaster. Behav. Brain Res. 2018, 351, 104–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hibicke, M.; Nichols, C.D. Validation of the forced swim test in Drosophila, and its use to demonstrate psilocybin has long-lasting antidepressant-like effects in flies. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 10019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cools, R.; Nakamura, K.; Daw, N.D. Serotonin and dopamine: Unifying affective, activational, and decision functions. Neuropsychopharmacology 2011, 36, 98–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enkhtaivan, E.; Nishimura, J.; Ly, C.; Cochran, A.L. A competition of critics in human decision-making. Comput. Psychiatry 2021, 5, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owens, M.J.; Knight, D.L.; Nemeroff, C.B. Second-generation SSRIs: Human monoamine transporter binding profile of escitalopram and R-fluoxetine. Biol. Psychiatry 2001, 50, 345–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salcedo, E.; Huber, A.; Henrich, S.; Chadwell, L.V.; Chou, W.H.; Paulsen, R.; Britt, S.G. Blue-and green-absorbing visual pigments ofDrosophila: Ectopic expression and physiological characterization of the R8 photoreceptor cell-specific Rh5 and Rh6 rhodopsins. J. Neurosci. 1999, 19, 10716–10726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharkey, C.R.; Blanco, J.; Leibowitz, M.M.; Pinto-Benito, D.; Wardill, T.J. The spectral sensitivity of Drosophila photoreceptors. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 18242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnaitmann, C.; Haikala, V.; Abraham, E.; Oberhauser, V.; Thestrup, T.; Griesbeck, O.; Reiff, D.F. Color processing in the early visual system of Drosophila. Cell 2018, 172, 318–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rantala, M.J.; Luoto, S.; Krams, I.; Karlsson, H. Depression subtyping based on evolutionary psychiatry: Proximate mechanisms and ultimate functions. Brain Behav. Immun. 2018, 69, 603–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Krams, I.; Kolbjonoks, V.; Popovs, S.; Munkevics, M.; Krams, R.; Trakimas, G.; Rantala, M.J.; Contreras-Garduño, J.; Jõers, P.; Adams, C.B.; et al. Contrasting Effects of Larval Escitalopram and Serotonin-Synthesis Inhibitor on Adult Phototaxis in Drosophila w1118. Life 2025, 15, 1782. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15111782
Krams I, Kolbjonoks V, Popovs S, Munkevics M, Krams R, Trakimas G, Rantala MJ, Contreras-Garduño J, Jõers P, Adams CB, et al. Contrasting Effects of Larval Escitalopram and Serotonin-Synthesis Inhibitor on Adult Phototaxis in Drosophila w1118. Life. 2025; 15(11):1782. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15111782
Chicago/Turabian StyleKrams, Indrikis, Vadims Kolbjonoks, Sergejs Popovs, Māris Munkevics, Ronalds Krams, Giedrius Trakimas, Markus J. Rantala, Jorge Contreras-Garduño, Priit Jõers, Colton B. Adams, and et al. 2025. "Contrasting Effects of Larval Escitalopram and Serotonin-Synthesis Inhibitor on Adult Phototaxis in Drosophila w1118" Life 15, no. 11: 1782. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15111782
APA StyleKrams, I., Kolbjonoks, V., Popovs, S., Munkevics, M., Krams, R., Trakimas, G., Rantala, M. J., Contreras-Garduño, J., Jõers, P., Adams, C. B., & Krama, T. (2025). Contrasting Effects of Larval Escitalopram and Serotonin-Synthesis Inhibitor on Adult Phototaxis in Drosophila w1118. Life, 15(11), 1782. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15111782







