Resveratrol as a Potential Platelet Inhibitor in Aspirin-Resistant Diabetic Patients—A Novel Therapeutic Strategy Targeting F0F1-ATP Synthase Inhibition
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Platelet Hyperactivation and Aspirin Resistance in T2DM
Endothelial Dysfunction in Type 2 Diabetes
3. Clinical Use of Resveratrol in Diabetes
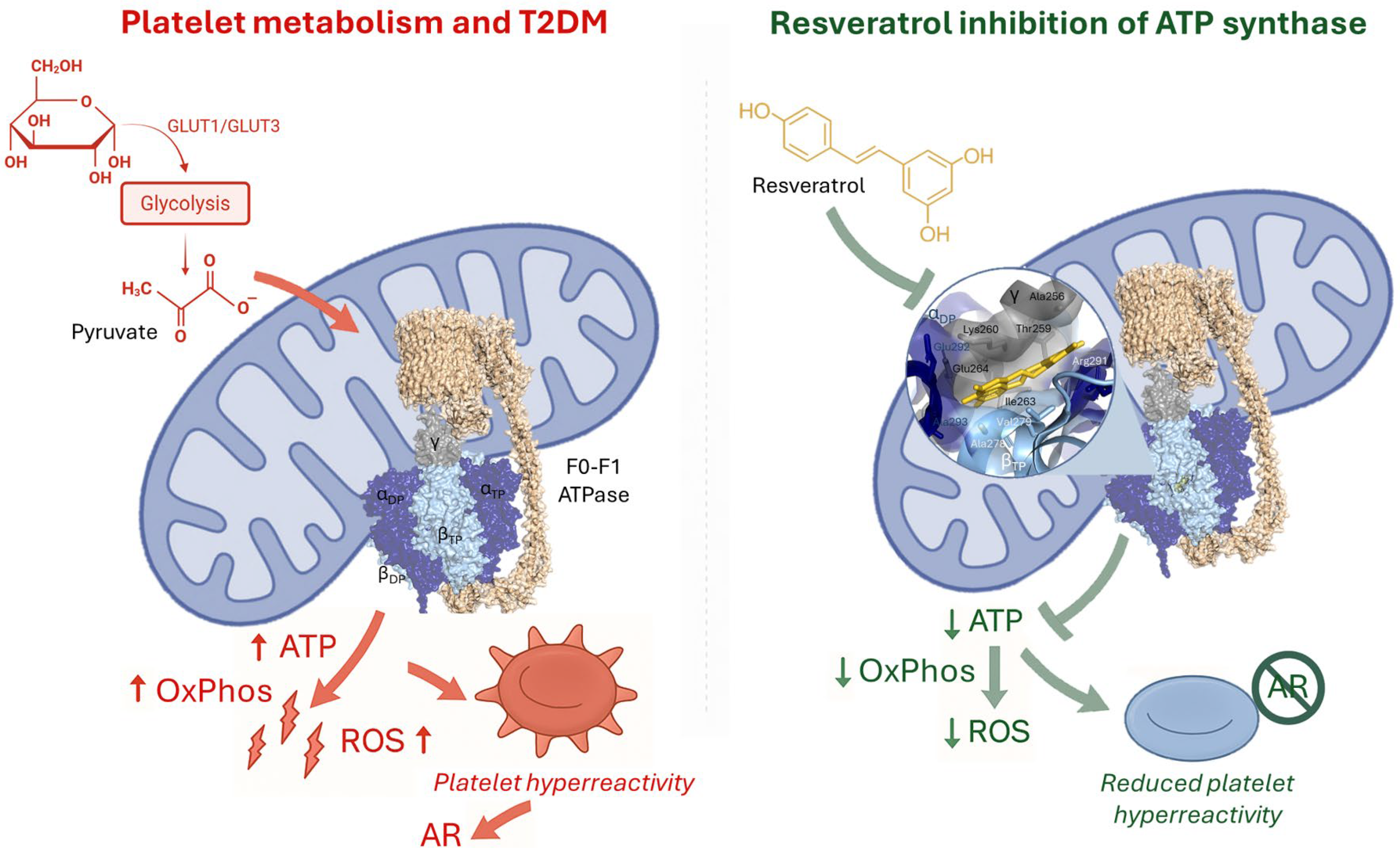
4. The F1Fo-ATP Synthase
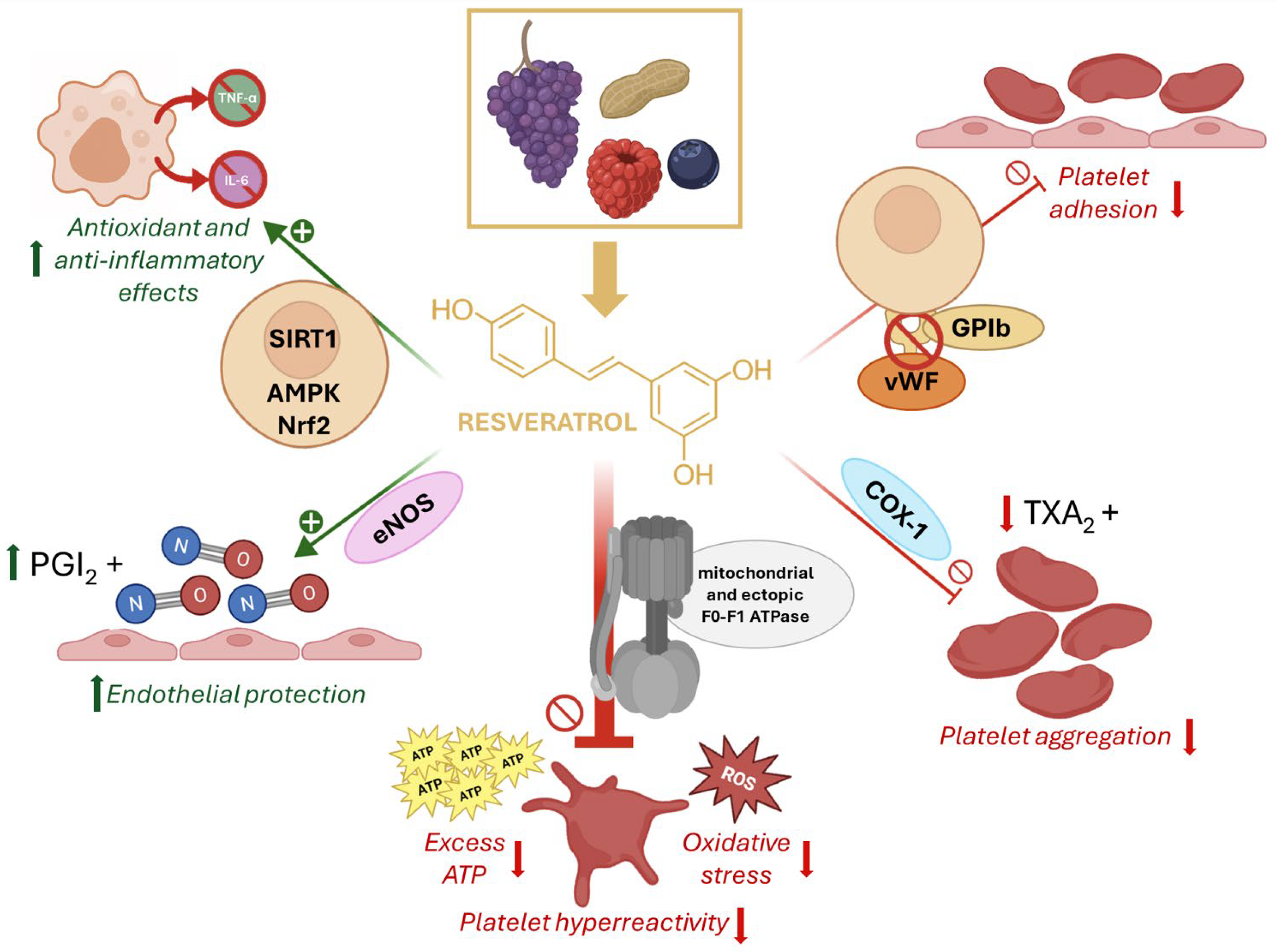
5. Resveratrol Inhibition of ATP Synthase and Its Relevance in AR
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CVD | Cardiovascular Disease |
| DM | Diabetes mellitus |
| ETC | Electron Trasport Chain |
| RSV | Resveratrol |
| AR | Aspirin Resistance |
| T2DM | Type 2 Diabetes mellitus |
| TXA2 | Thromboxane A2 |
References
- Atkinson, M.A.; Eisenbarth, G.S.; Michels, A.W. Type 1 Diabetes. Lancet 2014, 383, 69–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.A.B.; Hashim, M.J.; King, J.K.; Govender, R.D.; Mustafa, H.; Kaabi, J. Al Epidemiology of Type 2 Diabetes—Global Burden of Disease and Forecasted Trends. J. Epidemiol. Glob. Health 2020, 10, 107–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, K.L.; Stafford, L.K.; McLaughlin, S.A.; Boyko, E.J.; Vollset, S.E.; Smith, A.E.; Dalton, B.E.; Duprey, J.; Cruz, J.A.; Hagins, H.; et al. Global, Regional, and National Burden of Diabetes from 1990 to 2021, with Projections of Prevalence to 2050: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021. Lancet 2023, 402, 203–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Chang, G.Y.; Jiang, Y.H.; Xu, L.; Shen, L.; Gu, Z.C.; Lin, H.W.; Shi, F.H. System Dynamic Model Simulates the Growth Trend of Diabetes Mellitus in Chinese Population: Implications for Future Urban Public Health Governance. Int. J. Public. Health 2022, 67, 1605064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.; Ley, S.H.; Hu, F.B. Global Aetiology and Epidemiology of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Its Complications. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2018, 14, 88–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaribeygi, H.; Sathyapalan, T.; Atkin, S.L.; Sahebkar, A. Molecular Mechanisms Linking Oxidative Stress and Diabetes Mellitus. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2020, 2020, 609213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, M.C.; Shulman, G.I. Mechanisms of Insulin Action and Insulin Resistance. Physiol. Rev. 2018, 98, 2133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, R.; Colon-Negron, K.; Papa, F.R. Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress, Degeneration of Pancreatic Islet β-Cells, and Therapeutic Modulation of the Unfolded Protein Response in Diabetes. Mol. Metab. 2019, 27, S60–S68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Wang, W.; Liu, J.; Xie, M.; Liu, Q.; Li, S. Vascular Complications of Diabetes: A Narrative Review. Medicine 2023, 102, E35285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Souza, L.F.; Oliveira, M.F. Mitochondria: Biological Roles in Platelet Physiology and Pathology. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2014, 50, 156–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konieczyńska, M.; Bryk, A.H.; Malinowski, K.P.; Draga, K.; Undas, A. Interplay between Elevated Cellular Fibronectin and Plasma Fibrin Clot Properties in Type 2 Diabetes. Thromb. Haemost. 2017, 117, 1671–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pretorius, E. Platelets as Potent Signaling Entities in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2019, 30, 532–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.X.; Ma, X.N.; Guan, C.H.; Li, Y.D.; Mauricio, D.; Fu, S.B. Cardiovascular Disease in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Progress toward Personalized Management. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2022, 21, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capodanno, D.; Angiolillo, D.J. Aspirin for Primary Cardiovascular Risk Prevention and Beyond in Diabetes Mellitus. Circulation 2016, 134, 1579–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Zong, Y.; Pang, Y.; Zheng, Z.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, C.; Gao, J. Platelets and Diseases: Signal Transduction and Advances in Targeted Therapy. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2025, 10, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.X.; Li, C.X.; Kakar, M.U.; Khan, M.S.; Wu, P.F.; Amir, R.M.; Dai, D.F.; Naveed, M.; Li, Q.Y.; Saeed, M.; et al. Resveratrol (RV): A Pharmacological Review and Call for Further Research. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 143, 112164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camont, L.; Cottart, C.H.; Rhayem, Y.; Nivet-Antoine, V.; Djelidi, R.; Collin, F.; Beaudeux, J.L.; Bonnefont-Rousselot, D. Simple Spectrophotometric Assessment of the Trans-/Cis-Resveratrol Ratio in Aqueous Solutions. Anal. Chim. Acta 2009, 634, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maier-Salamon, A.; Böhmdorfer, M.; Riha, J.; Thalhammer, T.; Szekeres, T.; Jaeger, W. Interplay between Metabolism and Transport of Resveratrol. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2013, 1290, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitaglione, P.; Sforza, S.; Galaverna, G.; Ghidini, C.; Caporaso, N.; Vescovi, P.P.; Fogliano, V.; Marchelli, R. Bioavailability of Trans-Resveratrol from Red Wine in Humans. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2005, 49, 495–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szymkowiak, I.; Marcinkowska, J.; Kucinska, M.; Regulski, M.; Murias, M. Resveratrol Bioavailability After Oral Administration: A Meta-Analysis of Clinical Trial Data. Phytother. Res. 2025, 39, 453–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gambini, J.; Inglés, M.; Olaso, G.; Lopez-Grueso, R.; Bonet-Costa, V.; Gimeno-Mallench, L.; Mas-Bargues, C.; Abdelaziz, K.M.; Gomez-Cabrera, M.C.; Vina, J.; et al. Properties of Resveratrol: In Vitro and In Vivo Studies about Metabolism, Bioavailability, and Biological Effects in Animal Models and Humans. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2015, 2015, 837042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- La Porte, C.; Voduc, N.; Zhang, G.; Seguin, I.; Tardiff, D.; Singhal, N.; Cameron, D.W. Steady-State Pharmacokinetics and Tolerability of Trans-Resveratrol 2000 Mg Twice Daily with Food, Quercetin and Alcohol (Ethanol) in Healthy Human Subjects. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2010, 49, 449–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franco, A.T.; Corken, A.; Ware, J. Platelets at the Interface of Thrombosis, Inflammation, and Cancer. Blood 2015, 126, 582–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broos, K.; Feys, H.B.; De Meyer, S.F.; Vanhoorelbeke, K.; Deckmyn, H. Platelets at Work in Primary Hemostasis. Blood Rev. 2011, 25, 155–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lordan, R.; Tsoupras, A.; Zabetakis, I. Platelet Activation and Prothrombotic Mediators at the Nexus of Inflammation and Atherosclerosis: Potential Role of Antiplatelet Agents. Blood Rev. 2021, 45, 100694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jena, S.; Raizada, N.; Kalra, S.; Bhattacharya, S. Platelet Indices as Predictors of Glycaemic Status and Complications in Diabetes Mellitus. Apollo Med. 2025, 22, 214–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evangelista, V.; De Berardis, G.; Totani, L.; Avanzini, F.; Giorda, C.B.; Brero, L.; Levantesi, G.; Marelli, G.; Pupillo, M.; Iacuitti, G.; et al. Persistent Platelet Activation in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Treated with Low Doses of Aspirin. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2007, 5, 2197–2203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pretorius, L.; Thomson, G.J.A.; Adams, R.C.M.; Nell, T.A.; Laubscher, W.A.; Pretorius, E. Platelet Activity and Hypercoagulation in Type 2 Diabetes. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2018, 17, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Zheng, H. Clinical Predictors of Aspirin Resistance in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Rev. Cardiovasc. Med. 2025, 26, 26009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, R.; Kaur, M.; Singh, J. Endothelial Dysfunction and Platelet Hyperactivity in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Molecular Insights and Therapeutic Strategies. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2018, 17, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagar, R.C.; Yates, D.M.; Pearson, S.M.; Kietsiriroje, N.; Hindle, M.S.; Cheah, L.T.; Webb, B.A.; Ajjan, R.A.; Naseem, K.M. Insulin Resistance in Type 1 Diabetes Is a Key Modulator of Platelet Hyperreactivity. Diabetologia 2025, 68, 1544–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrucci, G.; Rizzi, A.; Bellavia, S.; Dentali, F.; Frisullo, G.; Pitocco, D.; Ranalli, P.; Rizzo, P.A.; Scala, I.; Silingardi, M.; et al. Stability of the Thromboxane B2 Biomarker of Low-Dose Aspirin Pharmacodynamics in Human Whole Blood and in Long-Term Stored Serum Samples. Res. Pr. Thromb. Haemost. 2024, 8, 102623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, H.L.; Kristensen, S.D.; Hvas, A.-M. Is the New Point-of-Care Test VerifyNow® Aspirin Able To Identify Aspirin Resistance Using the Recommended Cut-Off? Blood 2007, 110, 3896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reny, J.L.; De Moerloose, P.; Dauzat, M.; Fontana, P. Use of the PFA-100TM Closure Time to Predict Cardiovascular Events in Aspirin-Treated Cardiovascular Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2008, 6, 444–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renda, G.; Zurro, M.; Malatesta, G.; Ruggieri, B.; de Caterina, R. Inconsistency of Different Methods for Assessing Ex Vivo Platelet Function: Relevance for the Detection of Aspirin Resistance. Haematologica 2010, 95, 2095–2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakouros, N.; Rade, J.J.; Kourliouros, A.; Resar, J.R. Platelet Function in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus: From a Theoretical to a Practical Perspective. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2011, 2011, 742719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razmara, M.; Hjemdahl, P.; Östenson, C.G.; Li, N. Platelet Hyperprocoagulant Activity in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Attenuation by Glycoprotein IIb/IIIa Inhibition. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2008, 6, 2186–2192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Violi, F.; Pignatelli, P. Platelet Oxidative Stress and Thrombosis. Thromb. Res. 2012, 129, 378–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Chang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhai, L.; Zhang, S.; Qi, Z.; Yan, H.; Yan, Y.; Luo, X.; Zhang, S.; et al. Platelets Express Activated P2Y12 Receptor in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus. Circulation 2017, 136, 817–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Committee, A.D.A.P.P.; ElSayed, N.A.; Aleppo, G.; Bannuru, R.R.; Bruemmer, D.; Collins, B.S.; Das, S.R.; Ekhlaspour, L.; Hilliard, M.E.; Johnson, E.L.; et al. 10. Cardiovascular Disease and Risk Management: Standards of Care in Diabetes—2024. Diabetes Care 2024, 47, S179–S218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bethel, M.A.; Harrison, P.; Sourij, H.; Sun, Y.; Tucker, L.; Kennedy, I.; White, S.; Hill, L.; Oulhaj, A.; Coleman, R.L.; et al. Randomized Controlled Trial Comparing Impact on Platelet Reactivity of Twice-Daily with Once-Daily Aspirin in People with Type 2 Diabetes. Diabet. Med. 2016, 33, 224–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dillinger, J.-G.; Pezel, T.; Batias, L.; Angoulvant, D.; Goralski, M.; Ferrari, E.; Cayla, G.; Silvain, J.; Gilard, M.; Lemesle, G.; et al. Twice-a-Day Administration of Aspirin in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus or Aspirin Resistance after Acute Coronary Syndrome: Rationale and Design of the Randomized ANDAMAN Trial. Am. Heart J. 2025, 288, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narcisse, D.I.; Kim, H.; Wruck, L.M.; Stebbins, A.L.; Muñoz, D.; Kripalani, S.; Effron, M.B.; Gupta, K.; Anderson, R.D.; Jain, S.K.; et al. Comparative Effectiveness of Aspirin Dosing in Cardiovascular Disease and Diabetes Mellitus: A Subgroup Analysis of the ADAPTABLE Trial. Diabetes Care 2024, 47, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krüger-Genge, A.; Blocki, A.; Franke, R.P.; Jung, F. Vascular Endothelial Cell Biology: An Update. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaidya, A.R.; Wolska, N.; Vara, D.; Mailer, R.K.; Schröder, K.; Pula, G. Diabetes and Thrombosis: A Central Role for Vascular Oxidative Stress. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lum, H.; Roebuck, K.A. Oxidant Stress and Endothelial Cell Dysfunction. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2001, 280, C719–C741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Sofiani, M.E.; Yanek, L.R.; Faraday, N.; Kral, B.G.; Mathias, R.; Becker, L.C.; Becker, D.M.; Vaidya, D.; Kalyani, R.R. Diabetes and Platelet Response to Low-Dose Aspirin. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2018, 103, 4599–4608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duttaroy, A.K. Functional Foods in Preventing Human Blood Platelet Hyperactivity-Mediated Diseases-An Updated Review. Nutrients 2024, 16, 3717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, W.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Liu, F.; Duan, G.; Chen, S.; Long, J.; Jin, Y.; Yang, H. Recent Advances in the Use of Resveratrol against Staphylococcus Aureus Infections (Review). Med. Int. 2024, 4, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, M.; Zhao, W.; Xu, S.; Weng, J. Resveratrol in Treating Diabetes and Its Cardiovascular Complications: A Review of Its Mechanisms of Action. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koushki, M.; Farahani, M.; Yekta, R.F.; Frazizadeh, N.; Bahari, P.; Parsamanesh, N.; Chiti, H.; Chahkandi, S.; Fridoni, M.; Amiri-Dashatan, N. Potential Role of Resveratrol in Prevention and Therapy of Diabetic Complications: A Critical Review. Food Nutr. Res. 2024, 68, 9731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.H.; Kim, Y.S.; Roh, G.S.; Choi, W.S.; Cho, G.J. Resveratrol Blocks Diabetes-Induced Early Vascular Lesions and Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Induction in Mouse Retinas. Acta Ophthalmol. 2012, 90, e31–e37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaštelan, S.; Konjevoda, S.; Sarić, A.; Urlić, I.; Lovrić, I.; Čanović, S.; Matejić, T.; Šešelja Perišin, A. Resveratrol as a Novel Therapeutic Approach for Diabetic Retinopathy: Molecular Mechanisms, Clinical Potential, and Future Challenges. Molecules 2025, 30, 3262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lannan, K.L.; Refaai, M.A.; Ture, S.K.; Morrell, C.N.; Blumberg, N.; Phipps, R.P.; Spinelli, S.L. Resveratrol Preserves the Function of Human Platelets Stored for Transfusion. Br. J. Haematol. 2015, 172, 794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michno, A.; Grużewska, K.; Ronowska, A.; Gul-Hinc, S.; Zyśk, M.; Jankowska-Kulawy, A. Resveratrol Inhibits Metabolism and Affects Blood Platelet Function in Type 2 Diabetes. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubatka, P.; Mazurakova, A.; Koklesova, L.; Samec, M.; Sokol, J.; Samuel, S.M.; Kudela, E.; Biringer, K.; Bugos, O.; Pec, M.; et al. Antithrombotic and Antiplatelet Effects of Plant-Derived Compounds: A Great Utility Potential for Primary, Secondary, and Tertiary Care in the Framework of 3P Medicine. EPMA J. 2022, 13, 407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsamanesh, N.; Asghari, A.; Sardari, S.; Tasbandi, A.; Jamialahmadi, T.; Xu, S.; Sahebkar, A. Resveratrol and Endothelial Function: A Literature Review. Pharmacol. Res. 2021, 170, 105725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bo, S.; Ponzo, V.; Ciccone, G.; Evangelista, A.; Saba, F.; Goitre, I.; Procopio, M.; Pagano, G.F.; Cassader, M.; Gambino, R. Six Months of Resveratrol Supplementation Has No Measurable Effect in Type 2 Diabetic Patients. A Randomized, Double Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Pharmacol. Res. 2016, 111, 896–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahjabeen, W.; Khan, D.A.; Mirza, S.A. Role of Resveratrol Supplementation in Regulation of Glucose Hemostasis, Inflammation and Oxidative Stress in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus Type 2: A Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Complement. Ther. Med. 2022, 66, 102819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bo, S.; Ponzo, V.; Evangelista, A.; Ciccone, G.; Goitre, I.; Saba, F.; Procopio, M.; Cassader, M.; Gambino, R. Effects of 6 Months of Resveratrol versus Placebo on Pentraxin 3 in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Double-Blind Randomized Controlled Trial. Acta Diabetol. 2017, 54, 499–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timmers, S.; De Ligt, M.; Phielix, E.; Van De Weijer, T.; Hansen, J.; Moonen-Kornips, E.; Schaart, G.; Kunz, I.; Hesselink, M.K.C.; Schrauwen-Hinderling, V.B.; et al. Resveratrol as Add-on Therapy in Subjects with Well-Controlled Type 2 Diabetes: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Diabetes Care 2016, 39, 2211–2217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thazhath, S.S.; Wu, T.; Bound, M.J.; Checklin, H.L.; Standfield, S.; Jones, K.L.; Horowitz, M.; Rayner, C.K. Administration of Resveratrol for 5 Wk Has No Effect on Glucagon-like Peptide 1 Secretion, Gastric Emptying, or Glycemic Control in Type 2 Diabetes: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 103, 66–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdollahi, S.; Salehi-Abargouei, A.; Toupchian, O.; Sheikhha, M.H.; Fallahzadeh, H.; Rahmanian, M.; Tabatabaie, M.; Mozaffari-Khosravi, H. The Effect of Resveratrol Supplementation on Cardio-Metabolic Risk Factors in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Randomized, Double-Blind Controlled Trial. Phytother. Res. 2019, 33, 3153–3162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seyyedebrahimi, S.S.; Khodabandehloo, H.; Nasli Esfahani, E.; Meshkani, R. Correction to: The Effects of Resveratrol on Markers of Oxidative Stress in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trial. Acta Diabetol. 2018, 55, 1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoseini, A.; Namazi, G.; Farrokhian, A.; Reiner, Ž.; Aghadavod, E.; Bahmani, F.; Asemi, Z. The Effects of Resveratrol on Metabolic Status in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Coronary Heart Disease. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 6042–6051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Martínez, B.I.; Ruiz-Ramos, M.; Pedraza-Chaverri, J.; Santiago-Osorio, E.; Mendoza-Núñez, V.M. Effect of Resveratrol on Markers of Oxidative Stress and Sirtuin 1 in Elderly Adults with Type 2 Diabetes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 7422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Martínez, B.I.; Ruiz-Ramos, M.; Pedraza-Chaverri, J.; Santiago-Osorio, E.; Mendoza-Núñez, V.M. Influence of Age and Dose on the Effect of Resveratrol for Glycemic Control in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Molecules 2022, 27, 5232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, P.; Jin, Y.; Sun, J.; Zhou, X. The Efficacy of Resveratrol Supplementation on Inflammation and Oxidative Stress in Type-2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients: Randomized Double-Blind Placebo Meta-Analysis. Front. Endocrinol. 2025, 15, 1463027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, N.; Zhang, Y. Effects of Resveratrol Therapy on Glucose Metabolism, Insulin Resistance, Inflammation, and Renal Function in the Elderly Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial Protocol. Medicine 2022, 101, E30049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, J.E. The ATP Synthase: The Understood, the Uncertain and the Unknown. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2013, 41, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyer, P.D. The ATP Synthase—A Splendid Molecular Machine. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1997, 66, 717–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campanella, M.; Casswell, E.; Chong, S.; Farah, Z.; Wieckowski, M.R.; Abramov, A.Y.; Tinker, A.; Duchen, M.R. Regulation of Mitochondrial Structure and Function by the F1Fo-ATPase Inhibitor Protein, IF1. Cell Metab. 2008, 8, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardino Gomes, T.M.; Ng, Y.S.; Pickett, S.J.; Turnbull, D.M.; Vincent, A.E. Mitochondrial DNA Disorders: From Pathogenic Variants to Preventing Transmission. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2021, 30, R245–R253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panfoli, I.; Ravera, S.; Bruschi, M.; Candiano, G.; Morelli, A. Proteomics Unravels the Exportability of Mitochondrial Respiratory Chains. Expert. Rev. Proteomics 2011, 8, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez, L.O.; Jacquet, S.; Esteve, J.P.; Rolland, C.; Cabezon, E.; Champagne, E.; Pineau, T.; Georgeaud, V.; Walker, J.E.; Terce, F.; et al. Ectopic Beta-Chain of ATP Synthase Is an Apolipoprotein A-I Receptor in Hepatic HDL Endocytosis. Nature 2003, 421, 75–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, Y.W.; Hsu, C.L.; Tang, C.W.; Chen, X.J.; Huang, H.C.; Juan, H.F. Multiomics Reveals Ectopic ATP Synthase Blockade Induces Cancer Cell Death via a LncRNA-Mediated Phospho-Signaling Network. Mol. Cell Proteom. 2020, 19, 1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, K.-H.; Song, S.-H.; Paik, J.-Y.; Koh, B.-H.; Choe, Y.S.; Lee, E.J.; Kim, B.-T.; Lee, K.-H. Direct Targeting of Tumor Cell F(1)F(0) ATP-Synthase by Radioiodine Angiostatin In Vitro and In Vivo. Cancer Biother. Radiopharm. 2007, 22, 704–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stockwin, L.H.; Blonder, J.; Bumke, M.A.; Lucas, D.A.; Chan, K.C.; Conrads, T.P.; Issaq, H.J.; Veenstra, T.D.; Newton, D.L.; Rybak, S.M. Proteomic Analysis of Plasma Membrane from Hypoxia-Adapted Malignant Melanoma. J. Proteome Res. 2006, 5, 2996–3007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, K.; Shimizu, N.; Obi, S.; Kumagaya, S.; Taketani, Y.; Kamiya, A.; Ando, J. Involvement of Cell Surface ATP Synthase in Flow-Induced ATP Release by Vascular Endothelial Cells. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2007, 293, H1646–H1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arakaki, N.; Nagao, T.; Niki, R.; Toyofuku, A.; Tanaka, H.; Kuramoto, Y.; Emoto, Y.; Shibata, H.; Magota, K.; Higuti, T. Possible Role of Cell Surface H+ -ATP Synthase in the Extracellular ATP Synthesis and Proliferation of Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells. Mol. Cancer Res. 2003, 1, 931–939. [Google Scholar]
- Mangiullo, R.; Gnoni, A.; Leone, A.; Gnoni, G.V.; Papa, S.; Zanotti, F. Structural and Functional Characterization of FoF1-ATP Synthase on the Extracellular Surface of Rat Hepatocytes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Bioenerg. 2008, 1777, 1326–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, S.-L.; Yan, J.; Yu, Z.-H.; Zhu, C.-Q. Neuronal Cell Surface ATP Synthase Mediates Synthesis of Extracellular ATP and Regulation of Intracellular PH. Cell Biol. Int. 2011, 35, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravera, S.; Bartolucci, M.; Calzia, D.; Morelli, A.M.; Panfoli, I. Efficient Extra-Mitochondrial Aerobic ATP Synthesis in Neuronal Membrane Systems. J. Neurosci. Res. 2021, 99, 2250–2260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panfoli, I.; Ravera, S.; Podestà, M.; Cossu, C.; Santucci, L.; Bartolucci, M.; Bruschi, M.; Calzia, D.; Sabatini, F.; Bruschettini, M.; et al. Exosomes from Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells Conduct Aerobic Metabolism in Term and Preterm Newborn Infants. FASEB J. 2016, 30, 1416–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruschi, M.; Santucci, L.; Ravera, S.; Bartolucci, M.; Petretto, A.; Calzia, D.; Ghiggeri, G.M.; Ramenghi, L.A.; Candiano, G.; Panfoli, I. Metabolic Signature of Microvesicles from Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cells of Preterm and Term Infants. Proteom. Clin. Appl. 2018, 12, 1700082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravera, S.; Signorello, M.G.; Bartolucci, M.; Ferrando, S.; Manni, L.; Caicci, F.; Calzia, D.; Panfoli, I.; Morelli, A.; Leoncini, G. Extramitochondrial Energy Production in Platelets. Biol. Cell 2018, 110, 97–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravera, S.; Signorello, M.G.; Panfoli, I. Platelet Metabolic Flexibility: A Matter of Substrate and Location. Cells 2023, 12, 1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Li, D.; Zhou, L.; Li, Y.; Xi, Q.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, J. The Role of Mitochondria-Associated ER Membranes in Disease Pathology: Protein Complex and Therapeutic Targets. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2025, 13, 1629568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, P.P.; Tiwari, A.; Singh, N.; Gautam, D.; Sonkar, V.K.; Agarwal, V.; Dash, D. Aerobic Glycolysis Fuels Platelet Activation: Small-Molecule Modulators of Platelet Metabolism as Anti-Thrombotic Agents. Haematologica 2019, 104, 806–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, P.P.; Ekhlak, M.; Dash, D. Energy Metabolism in Platelets Fuels Thrombus Formation: Halting the Thrombosis Engine with Small-Molecule Modulators of Platelet Metabolism. Metabolism 2023, 145, 155596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aibibula, M.; Naseem, K.M.; Sturmey, R.G. Glucose Metabolism and Metabolic Flexibility in Blood Platelets. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2018, 16, 2300–2314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravera, S.; Bartolucci, M.; Cuccarolo, P.; Litamè, E.; Illarcio, M.; Calzia, D.; Degan, P.; Morelli, A.; Panfoli, I. Oxidative Stress in Myelin Sheath: The Other Face of the Extramitochondrial Oxidative Phosphorylation Ability. Free Radic. Res. 2015, 49, 1050962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamagishi, S.I.; Edelstein, D.; Du, X.L.; Brownlee, M. Hyperglycemia Potentiates Collagen-Induced Platelet Activation through Mitochondrial Superoxide Overproduction. Diabetes 2001, 50, 1491–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siewiera, K.; Kassassir, H.; Talar, M.; Wieteska, L.; Watala, C. Higher Mitochondrial Potential and Elevated Mitochondrial Respiration Are Associated with Excessive Activation of Blood Platelets in Diabetic Rats. Life Sci. 2016, 148, 293–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlini, L.; Tancreda, G.; Iobbi, V.; Caicci, F.; Bruno, S.; Esposito, A.; Calzia, D.; Benini, S.; Bisio, A.; Manni, L.; et al. The Flavone Cirsiliol from Salvia x Jamensis Binds the F1 Moiety of ATP Synthase, Modulating Free Radical Production. Cells 2022, 11, 3169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asmat, U.; Abad, K.; Ismail, K. Diabetes Mellitus and Oxidative Stress—A Concise Review. Saudi Pharm. J. 2016, 24, 547–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brand, M.D. Mitochondrial Generation of Superoxide and Hydrogen Peroxide as the Source of Mitochondrial Redox Signaling. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2016, 100, 14–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, Y.; Li, H.; Liao, P.; Chen, L.; Pan, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, C.; Liu, D.; Zheng, M.; Gao, J. Mitochondrial Dysfunction: Mechanisms and Advances in Therapy. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2024, 9, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Hu, L.; Li, H.; Lai, Y.T.; Wei, X.; Xu, X.; Cao, Z.; Cao, H.; Wan, Q.; Chang, Y.Y.; et al. Mitochondrial ATP Synthase as a Direct Molecular Target of Chromium(III) to Ameliorate Hyperglycaemia Stress. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, L.O.; Genoux, A.; Ferrières, J.; Duparc, T.; Perret, B. Serum Inhibitory Factor 1, High-Density Lipoprotein and Cardiovascular Diseases. Curr. Opin. Lipidol. 2017, 28, 337–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Citation | Design | Study Population | Dose & Duration | Primary Endpoints | Main Findings |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mahjabeen et al. [59] | Randomized, double-blind, placebocontrolled, parallel-group | n = 110 randomized; 94 completed; adults with T2D on OHDs | Resveratrol 200 mg/day, 24 weeks | Fasting glucose, insulin, HOMA-IR; hs-CRP, TNF-α, IL-6; MDA; circulating microRNAs | Significant reductions in glucose, insulin, HOMA-IR, hs-CRP, TNF-α, IL-6, and MDA vs. placebo; favorable miRNA changes; no major AEs |
| Bo et al. [58] | Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, 3-arm | n = 192; adults with T2D | Resveratrol 40 mg/day or 500 mg/day vs. placebo, 6 months | CRP; metabolic parameters incl. HbA1c, glucose, insulin, BP, lipids | No significant effects on CRP or metabolic profile vs. placebo (dose-dependent trend only for CRP); well tolerated |
| Bo et al. [60] | Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, 3-arm (secondary analysis) | n = 192; adults with T2D | Resveratrol 40 or 500 mg/day vs. placebo, 6 months | Pentraxin-3 (PTX3) and Total Antioxidant Status (TAS) | Dose-dependent increase in PTX3 and TAS vs. placebo; clinical significance uncertain |
| Timmers et al. [61] | Randomized, double-blind, crossover | n = 17; men with well-controlled T2D | Resveratrol 150 mg/day, 30 days per period | Hepatic & peripheral insulin sensitivity (clamp); secondary: muscle mitochondrial function | No improvement in insulin sensitivity; ex vivo muscle mitochondrial function increased; possible interaction with metformin |
| Thazhath et al. [62] | Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, crossover | n = 14; diet-controlled T2D | Resveratrol 500 mg twice daily, 5 weeks per period | GLP-1 secretion, gastric emptying; secondary: HbA1c, glucose, weight, energy intake | No effect on GLP-1, gastric emptying, or glycemic control vs. placebo |
| Abdollahi et al. [63] | Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled | n = 71; overweight adults with T2D (BMI 25–30) | Resveratrol 1000 mg/day, 8 weeks | Fasting glucose, insulin, HOMA-IR; lipids; body composition | Decreased fasting glucose, insulin, HOMA-IR; increased HDL; no changes in anthropometrics |
| Seyyedebrahimi et al. [64] | Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled | n = 48; adults with T2D | Resveratrol 800 mg/day, 8 weeks | Oxidative stress markers in blood PBMCs (MDA, antioxid. enzymes) | Significant antioxidant effects vs. placebo; |
| Hoseini et al. [65] | Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial | n = 56; T2D with coronary heart disease | Resveratrol 500 mg/day, 4 weeks | Metabolic status (glycemic indices, lipids), inflammatory markers | Short-term improvements in metabolic status vs. placebo |
| García-Martínez et al. [66] | Randomized, three-arm clinical trial | n = 97 (EG1000 n = 37; EG500 n = 32; placebo n = 28) | Resveratrol 500 or 1000 mg/day vs. placebo, 6 months | Oxidative stress panel; SIRT1 | Improved antioxidant indices and SIRT1 with 1000 mg/day; no significant changes in glucose/HbA1c |
| García-Martínez et al. [67] | Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial | n = 71 adults with T2D | Resveratrol 500 mg/day, 6 months | Oxidative stress and inflammatory biomarkers (MDA, SOD, CAT, GPx, IL-6, TNF-α) | Resveratrol significantly reduced MDA, IL-6, and TNF-α and increased SOD, CAT, and GPx vs. placebo; improved antioxidant and inflammatory profile; well tolerated. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Panfoli, I.; Carlini, L. Resveratrol as a Potential Platelet Inhibitor in Aspirin-Resistant Diabetic Patients—A Novel Therapeutic Strategy Targeting F0F1-ATP Synthase Inhibition. Life 2025, 15, 1718. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15111718
Panfoli I, Carlini L. Resveratrol as a Potential Platelet Inhibitor in Aspirin-Resistant Diabetic Patients—A Novel Therapeutic Strategy Targeting F0F1-ATP Synthase Inhibition. Life. 2025; 15(11):1718. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15111718
Chicago/Turabian StylePanfoli, Isabella, and Lavinia Carlini. 2025. "Resveratrol as a Potential Platelet Inhibitor in Aspirin-Resistant Diabetic Patients—A Novel Therapeutic Strategy Targeting F0F1-ATP Synthase Inhibition" Life 15, no. 11: 1718. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15111718
APA StylePanfoli, I., & Carlini, L. (2025). Resveratrol as a Potential Platelet Inhibitor in Aspirin-Resistant Diabetic Patients—A Novel Therapeutic Strategy Targeting F0F1-ATP Synthase Inhibition. Life, 15(11), 1718. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15111718








