Characterization of Malectin/Malectin-like Receptor-like Kinase Family Members in Foxtail Millet (Setaria italica L.)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Identification of MRLK Family Members in Foxtail Millet
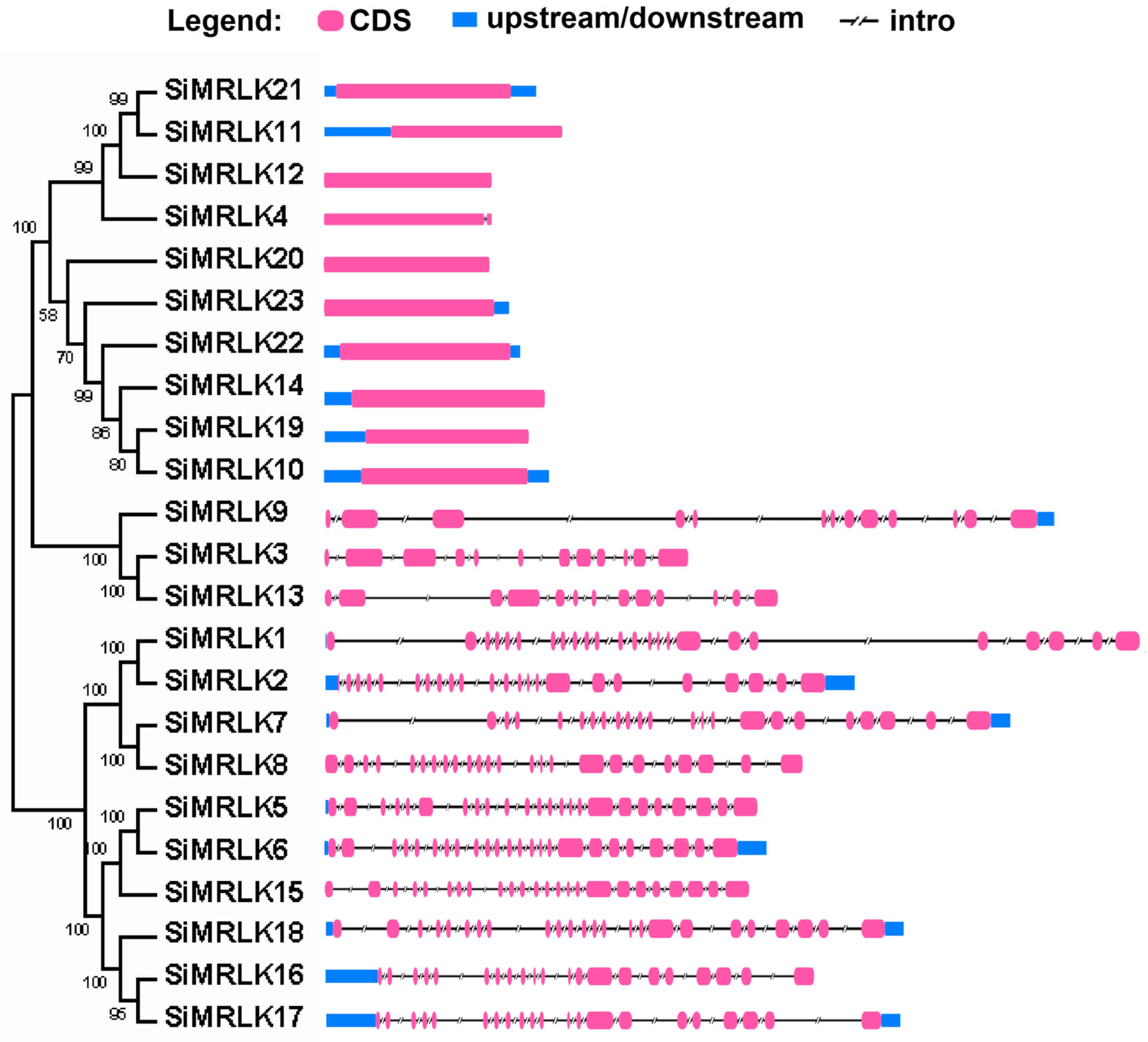
2.2. Distribution of Genes on Chromosomes, Organization of Exons and Introns, and Conserved Amino Acid Motifs Arrangement
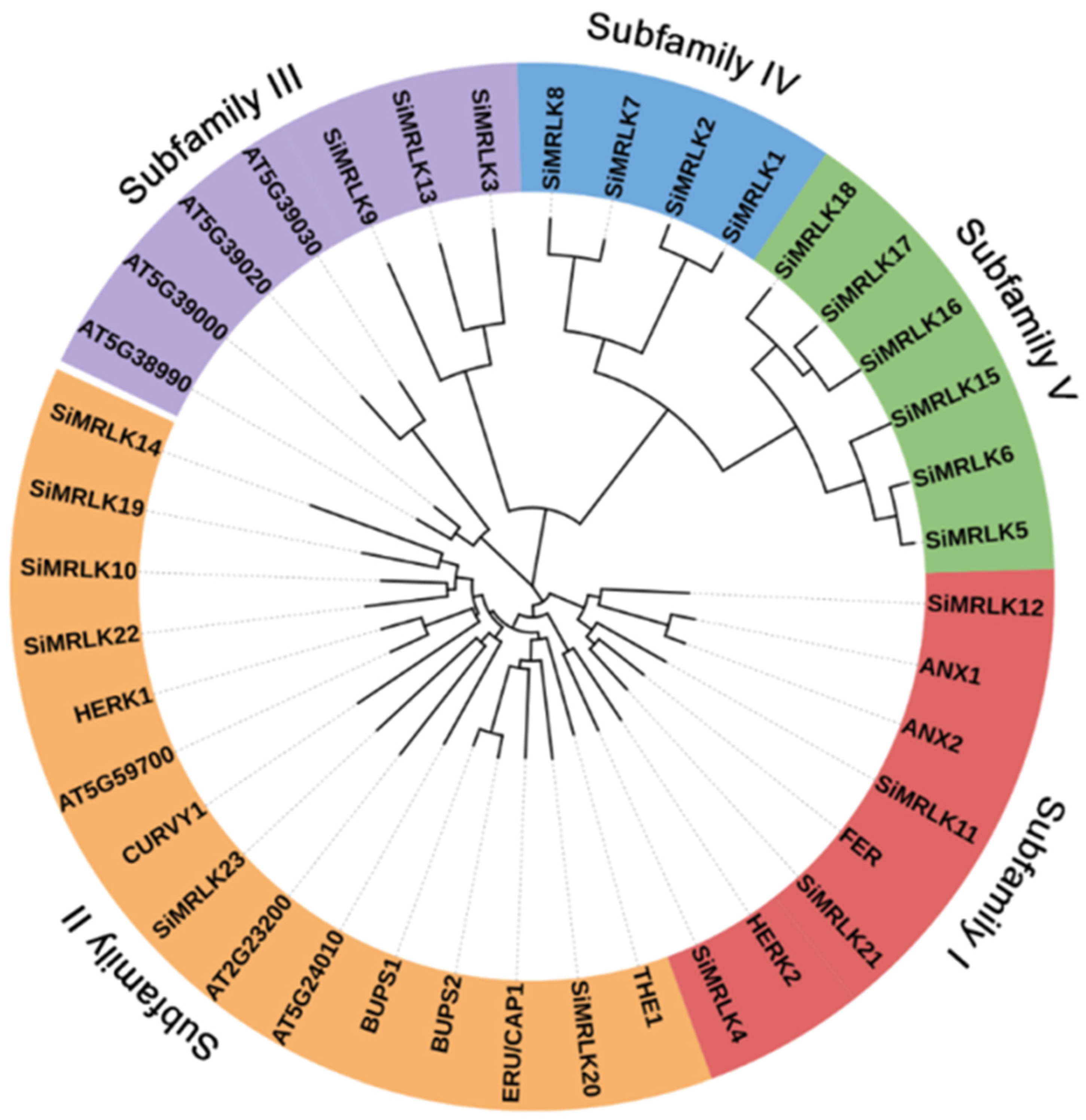
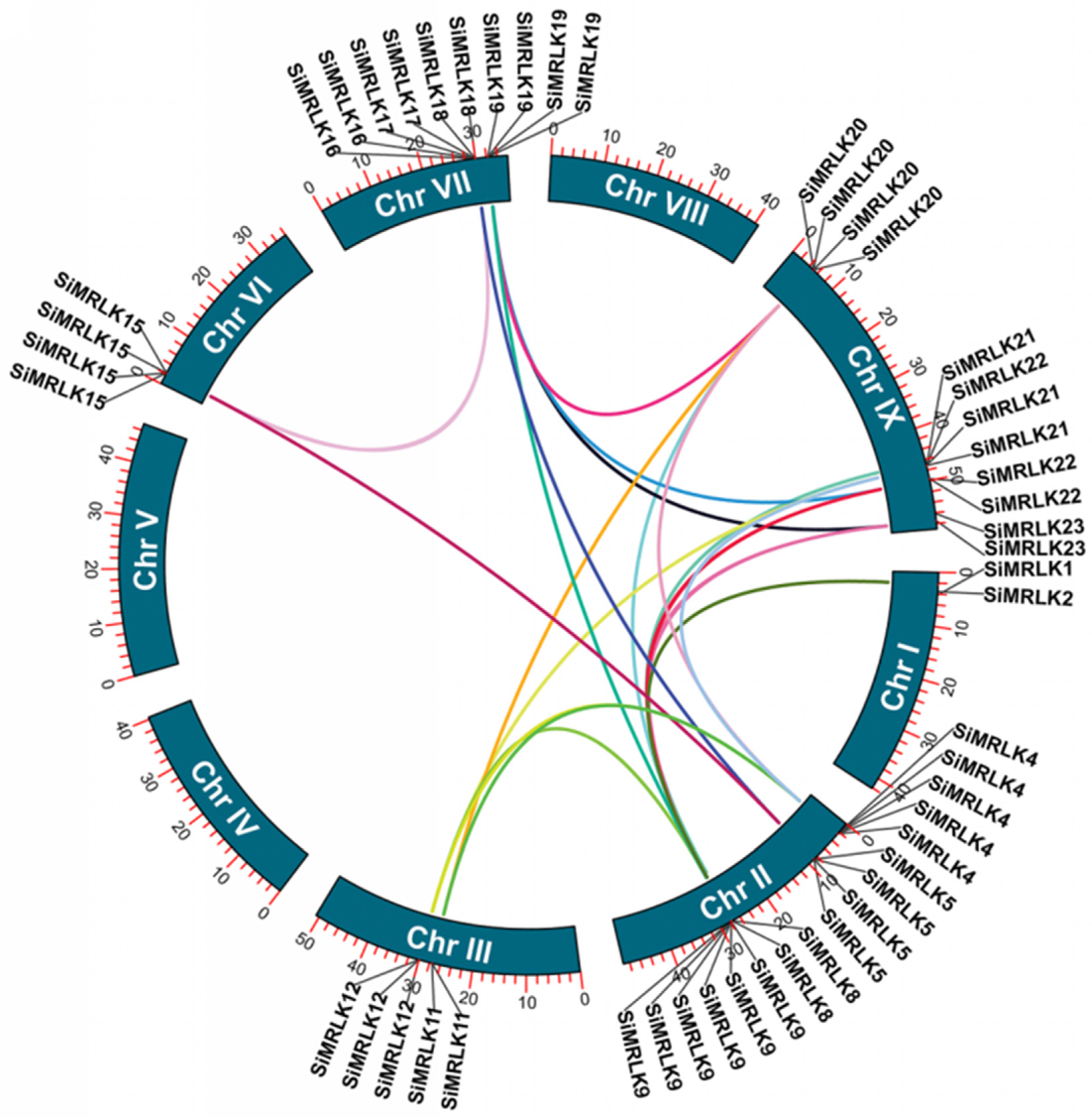
2.3. Phylogenetic Relationship and Syntenic Regions Analysis
2.4. Plant Material, Growth Conditions, Abiotic Stresses and Hormonal Applications in Foxtail Millet
2.5. Total RNA Extraction, cDNA Reverse Transcription, and qRT-PCR Analysis
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Identification of SiMRLK Family Members in the Foxtail Millet Genome
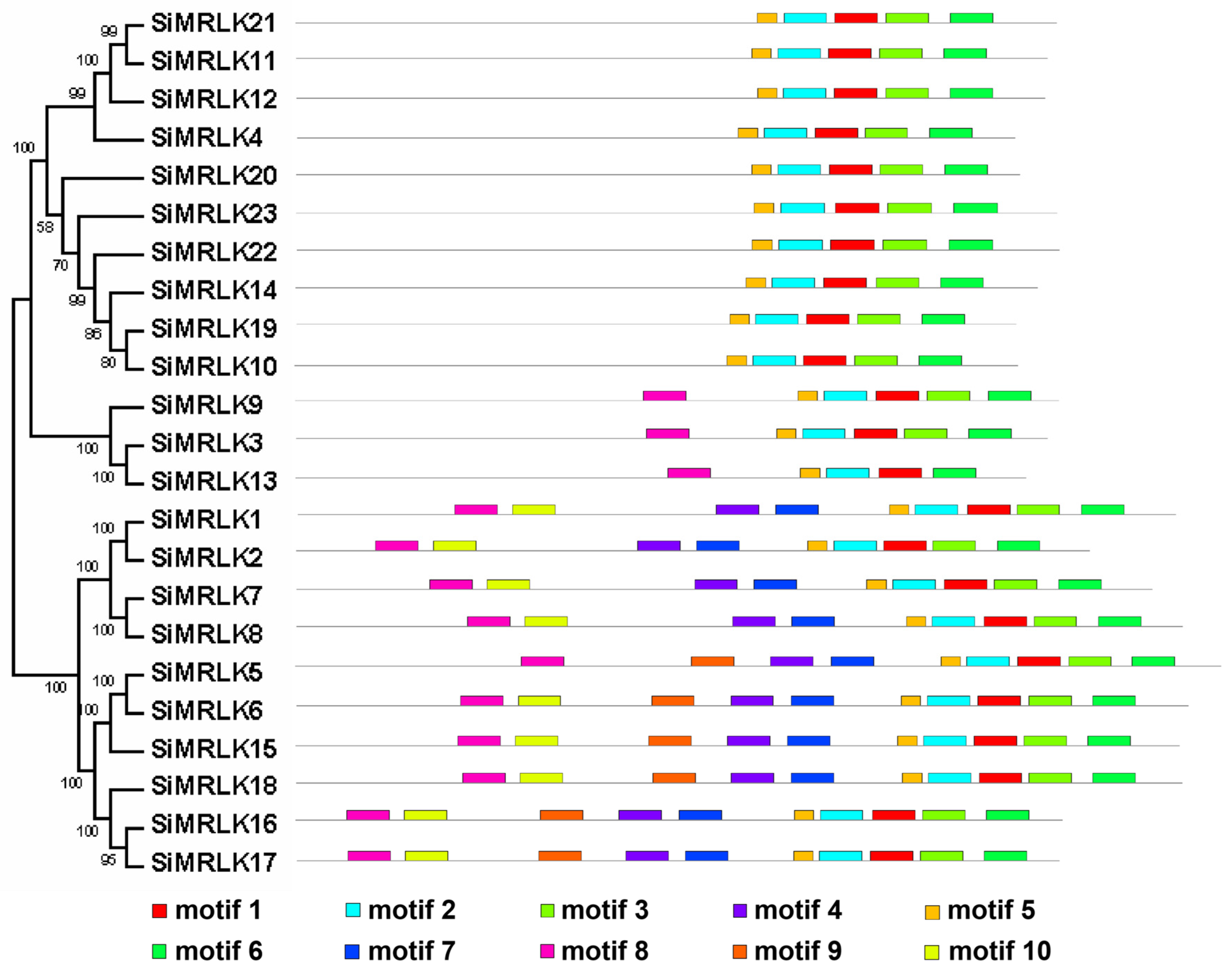
3.2. Phylogenetic Analysis and Conserved Motif Analysis of the SiMRLKs in Foxtail Millet
3.3. Structural Diversity and Duplication Analysis of SiMRLK Genes in Foxtail Millet
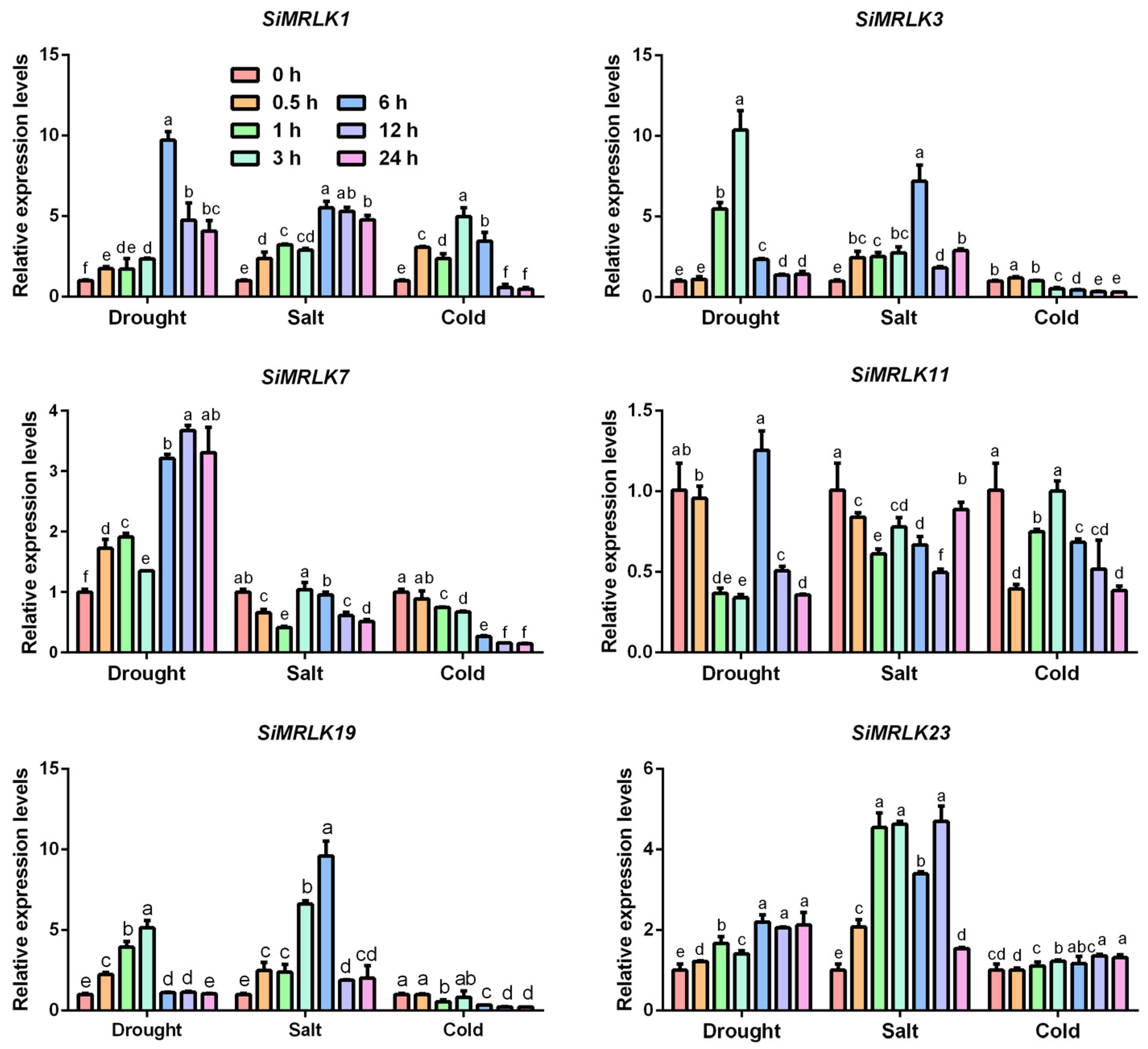
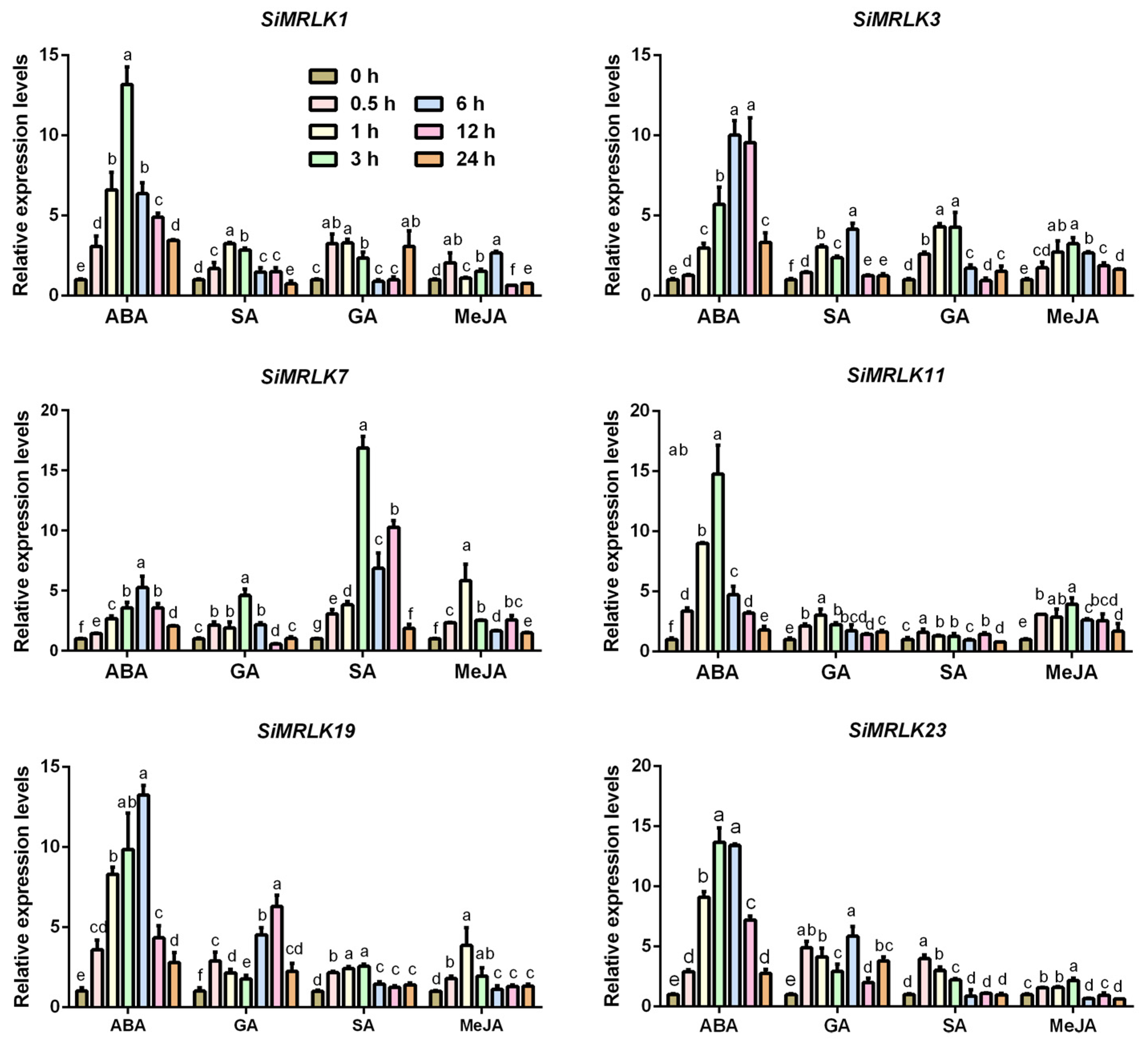
3.4. Transcriptional Profiles of SiMRLK Family Genes under Abiotic Stresses and Phytohormone
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lata, C.; Gupta, S.; Prasad, M. Foxtail millet: A model crop for genetic and genomic studies in bioenergy grasses. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2013, 33, 328–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bennetzen, J.L.; Schmutz, J.; Wang, H.; Percifield, R.; Hawkins, J.; Pontaroli, C.A.; Estep, M.; Liang, F.; Vaughn, J.N.; Grimwood, J. Reference genome sequence of the model plant Setaria. Nat. Biotechnol. 2012, 30, 555–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sachdev, N.; Sangeeta, G.; Rajenderkumar, S.L. Foxtail millet: A potential crop to meet future demand scenario for alternative sustainable protein. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2021, 101, 831–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Chen, J.; Zhi, H.; Yang, L.; Li, W.; Wang, Y.; Li, H.; Zhao, B.; Chen, M.; Diao, X. Population genetics of foxtail millet and its wild ancestor. BMC Genet. 2010, 11, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.; Liu, X.; Quan, Z.; Cheng, S.; Xu, X.; Pan, S.; Xie, M.; Zeng, P.; Yue, Z.; Wang, W. Genome sequence of foxtail millet (Setaria italica) provides insights into grass evolution and biofuel potential. Nat. Biotechnol. 2012, 30, 549–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Smet, I.; Ute, V.; Gerd, J.; Tom, B. Receptor-like kinases shape the plant. Nat. Cell Biol. 2009, 11, 1166–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antolin-Llovera, M.; Ried, M.K.; Binder, A.; Parniske, M. Receptor kinase signaling pathways in plant-microbe interactions. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2012, 50, 451–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niederhuth, C.E.; Cho, S.K.; Seitz, K.; Walker, J.C. Letting go is never easy: Abscission and receptor-like protein kinases. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2013, 55, 1251–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boisson-Dernier, A.; Roy, S.; Kritsas, K.; Grobei, M.A.; Jaciubek, M.; Schroeder, J.I. Disruption of the pollen-expressed FERONIA homologs ANXUR1 and ANXUR2 triggers pollen tube discharge. Development 2009, 136, 3279–3288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyazaki, S.; Murata, T.; Sakurai-Ozato, N.; Kubo, M.; Demura, T.; Fukuda, H.; Hasebe, M. ANXUR1 and 2, sister genes to FERONIA/SIRENE, are male factors for coordinated fertilization. Curr. Biol. 2009, 19, 1327–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boisson-Dernier, A.; Kessler, S.A.; Grossniklaus, U. The walls have ears: The role of plant CrRLK1Ls in sensing and transducing extracellular signals. J. Exp. Bot. 2011, 62, 1581–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boisson-Dernier, A.; Lituiev, D.S.; Nestorova, A.; Franck, C.; Thirugnanarajah, S.; Grossniklaus, U. ANXUR receptor-like kinases coordinate cell wall integrity with growth at the pollen tube tip via NADPH oxidases. PLoS Biol. 2013, 11, e1001719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kessler, S.A.; Lindner, H.; Jones, D.S.; Grossniklaus, U. Functional analysis of related CrRLK1L receptor-like kinases in pollen tube reception. EMBO Rep. 2015, 16, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeh, Y.H.; Panzeri, D.; Kadota, Y.; Huang, Y.; Huang, P.; Chia-Nan, T.; Roux, M.; Hsiao-Chiao, C.; Tzu-Chuan, C.; Po-Wei, C.; et al. The Arabidopsis Malectin-Like/LRR-RLK IOS1 Is Critical for BAK1-Dependent and BAK1-Independent Pattern-Triggered Immunity. Plant Cell 2016, 28, 1701–1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, W.; Daniel, K.; Alexis, P.; Heather, N.C.; Vinh, D.; Duan, Q.; Liu, M.; Jacob, M.; Leonie, S.; Schmitz-Thom, I.; et al. The FERONIA Receptor Kinase Maintains Cell-Wall Integrity during Salt Stress through Ca2+ Signaling. Curr. Biol. 2018, 28, 666–675.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franck, C.M.; Westermann, J.; Boisson-Dernier, A. Plant Malectin-Like Receptor Kinases: From Cell Wall Integrity to Immunity and Beyond. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2018, 69, 301–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.; Lin, W.; Zhou, X.; Guo, J.; Dang, X.; Li, B.; Lin, D.; Yang, Z. Mechano-transduction via the pectin-FERONIA complex activates ROP6 GTPase signaling in Arabidopsis pavement cell morphogenesis. Curr. Biol. 2022, 32, 508–517.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, Q.N.; Lee, Y.S.; Cho, L.H.; Jeong, H.J.; An, G.; Jung, K.H. Genome-wide identification and analysis of Catharanthus roseus RLK1-like kinases in rice. Planta 2015, 241, 603–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, X.-Q.; Abdullah, S.; Zhou, M.-R.; Shi, P.-T.; Izhar, M.; Shi, Y.; Rahat, S.; Li, W.-Q.; Liu, W.-T.; Chen, K.-M. Genome-Wide Identification of Malectin/Malectin-Like Domain Containing Protein Family Genes in Rice and Their Expression Regulation Under Various Hormones, Abiotic Stresses, and Heavy Metal Treatments. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2019, 39, 492–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Guo, C.; Wang, Q.; Li, Z.; Cai, J.; Wu, D.; Li, Y.; Yang, A.; Guo, Y.; Gao, J.; et al. Systematic Analysis of Tobacco CrRLK1L Family Genes and Functional Identification of NtCrRLK1L47 in Environmental Stresses. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 838857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, S.; Wu, X.; Zheng, H.; Lu, Y.; Peng, J.; Wu, G.; Chen, J.; Yan, F. Genome-wide identification and analysis of Catharanthus roseus RLK1-like kinases in Nicotiana benthamiana. BMC Plant Biol. 2021, 21, 425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, W.; Liu, X.; Chen, K.; Yu, X.; Ji, D. Genome-Wide Re-Identification and Analysis of CrRLK1Ls in Tomato. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 3142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Meiru, J.; Xing, Y.; Qin, L.; Li, B.; Wensuo, J. Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of MRLK family genes associated with strawberry (Fragaria vesca) fruit ripening and abiotic stress responses. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0163647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nissen, K.S.; Willats, W.G.T.; Malinovsky, F.G. Understanding CrRLK1L Function: Cell Walls and Growth Control. Trends Plant Sci. 2016, 21, 516–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udomchalothorn, T.; Plaimas, K.; Comai, L.; Buaboocha, T.; Chadchawan, S. Molecular Karyotyping and Exome Analysis of Salt-Tolerant Rice Mutant from Somaclonal Variation. Plant Genome 2014, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.J.; Kim, M.H.; Hong, W.J.; Moon, S.; Tae, K.S.; Ki, P.S.; Jung, K.H. OsMTD2-mediated reactive oxygen species (ROS) balance is essential for intact pollen-tube elongation in rice. Plant J. 2021, 107, 1131–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, X.; Sun, J.; Wang, P.; Wang, D.; Cao, P.; Lin, J.; Chang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Wu, J. PbrRALF2-elicited reactive oxygen species signaling is mediated by the PbrCrRLK1L13-PbrMPK18 module in pear pollen tubes. Hortic. Res. 2021, 8, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, X.; Cao, P.; He, Q.; Wang, P.; Zhang, S.; Wu, J. PbrROP1/2-elicited imbalance of cellulose deposition is mediated by a CrRLK1L-ROPGEF module in the pollen tube of Pyrus. Hortic. Res. 2022, 9, uhab034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shalmani, A.; Jing, X.-Q.; Shi, Y.; Muhammad, L.; Zhou, M.-R.; Wei, X.-Y.; Chen, Q.-Q.; Li, W.-Q.; Liu, W.-T.; Chen, K.-M. Characterization of B-BOX gene family and their expression profiles under hormonal, abiotic and metal stresses in Poaceae plants. BMC Genom. 2019, 20, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altschul, S.F.; Madden, T.L.; Schäffer, A.A.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Miller, W.; Lipman, D.J. Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: A new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997, 25, 3389–3402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finn, R.D.; Clements, J.; Eddy, S.R. HMMER web server: Interactive sequence similarity searching. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, W29–W37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, S.; Wang, J.; Chitsaz, F.; Derbyshire, M.K.; Geer, R.C.; Gonzales, N.R.; Gwadz, M.; Hurwitz, D.I.; Marchler, G.H.; Song, J.S. CDD/SPARCLE: The conserved domain database in 2020. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, D265–D268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duvaud, S.; Gabella, C.; Lisacek, F.; Stockinger, H.; Ioannidis, V.; Durinx, C. Expasy, the Swiss Bioinformatics Resource Portal, as designed by its users. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, W216–W227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rigden, D.J.; Fernandez, X.M. The 2022 Nucleic Acids Research database issue and the online molecular biology database collection. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, D1–D10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voorrips, R. MapChart: Software for the graphical presentation of linkage maps and QTLs. J. Hered. 2002, 93, 77–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; Jin, J.; Guo, A.-Y.; Zhang, H.; Luo, J.; Gao, G. GSDS 2.0: An upgraded gene feature visualization server. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 1296–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, T.L.; Williams, N.; Misleh, C.; Li, W.W. MEME: Discovering and analyzing DNA and protein sequence motifs. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006, 34 (Suppl. S2), W369–W373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuckerkandl, E.; Pauling, L. Evolutionary Divergence and Convergence in Proteins. Evol. Genes Proteins 1965, 97, 97–166. [Google Scholar]
- Felsenstein, J. Confidence Limits on Phylogenies: An Approach Using the Bootstrap. Evolution 1985, 39, 783–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Tamura, K. MEGA7: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darzentas, N. Circoletto: Visualizing sequence similarity with Circos. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 2620–2621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, H.; Landherr, L.L.; Frohlich, M.W.; Jim, L.-M.; Ma, H.; DePamphilis, C.W. Patterns of gene duplication in the plant SKP1 gene family in angiosperms: Evidence for multiple mechanisms of rapid gene birth. Plant J. 2007, 50, 873–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellande, K.; Bono, J.-J.; Savelli, B.; Jamet, E.; Canut, H.; Damme, E.V. Plant lectins and lectin receptor-like kinases: How do they sense the outside? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schallus, T.; Jaeckh, C.; Fehér, K.; Palma, A.S.; Liu, Y.; Simpson, J.C.; Mackeen, M.; Stier, G.; Gibson, T.J.; Ten, F.; et al. Malectin: A novel carbohydrate-binding protein of the endoplasmic reticulum and a candidate player in the early steps of protein N-glycosylation. Mol. Biol. Cell 2008, 19, 3404–3414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortiz-Morea, F.A.; Liu, J.; Shan, L.; He, P. Malectin-like receptor kinases as protector deities in plant immunity. Nat. Plants 2022, 8, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, D.; Chen, T.; Zhang, Z.; Li, B.; Tian, S. Versatile Roles of the Receptor-Like Kinase Feronia in Plant Growth, Development and Host-Pathogen Interaction. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hématy, K.; Höfte, H. Novel receptor kinases involved in growth regulation. Curr. Opin. Plant. Biol. 2008, 11, 321–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galindo-Trigo, S.; Blanco-Touriñán, N.; DeFalco, T.A.; Wells, E.S.; Gray, J.E.; Zipfel, C.; Smith, L.M. CrRLK1L receptor-like kinases HERK1 and ANJEA are female determinants of pollen tube reception. EMBO Rep. 2020, 21, e48466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Fu, Q.; Xu, F.; Zheng, H.; Yu, F. New paradigms in cell adaptation: Decades of discoveries on the CrRLK1L receptor kinase signalling network. New. Phytol. 2021, 232, 1168–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, E.; Cai, C.; Zheng, Y.; Shang, X.; Fang, L.; Guo, W. Genome-wide analysis of CrRLK1L gene family in Gossypium and identification of candidate CrRLK1L genes related to fiber development. Mol. Genet. Genom. 2016, 291, 1137–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.Q.; Yu, T.F.; Sun, G.Z.; Zheng, J.C.; Chen, J.; Zhou, Y.B.; Chen, M.; Ma, Y.Z.; Wei, W.L.; Xu, Z.S. Genome-Wide Analysis of the Catharanthus roseus RLK1-Like in Soybean and GmCrRLK1L20 Responds to Drought and Salt Stresses. Front. Plant. Sci. 2021, 12, 614909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kou, X.; Qi, k.; Qiao, X.; Yin, H.; Liu, X.; Zhang, S.; Wu, J. Evolution, expression analysis, and functional verification of Catharanthus roseus RLK1-like kinase (CrRLK1L) family proteins in pear (Pyrus bretchneideri). Genomics 2017, 109, 290–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuo, C.; Zhang, W.; Ma, Z.; Chu, M.; Mao, J.; An, Z.; Chen, B. Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Analysis of the CrRLK1L Gene Family in Apple (Malus domestica). Plant Mol. Biol. Report. 2018, 36, 844–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, H.; Tang, R.; Zhang, X.; Luan, S.; Yu, F. FERONIA Receptor Kinase at the Crossroads of Hormone Signaling and Stress Responses. Plant Cell. Physiol. 2017, 58, 1143–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deslauriers, S.D.; Larsen, P.B. FERONIA is a key modulator of brassinosteroid and ethylene responsiveness in Arabidopsis hypocotyls. Mol. Plant 2010, 3, 626–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergonci, T.; Ribeiro, B.; Ceciliato, P.H.; Guerrero-Abad, J.C.; Silva-Filho, M.C.; Moura, D.S. Arabidopsis thaliana RALF1 opposes brassinosteroid effects on root cell elongation and lateral root formation. J. Exp. Bot. 2014, 65, 2219–2230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, E.; De Smet, I. Understanding the RALF family: A tale of many species. Trends Plant Sci. 2014, 19, 664–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Sun, P.; Li, Z.; Zhang, F.; You, C.; Zhang, Z. FERONIA Receptor Kinase Integrates with Hormone Signaling to Regulate Plant Growth, Development, and Responses to Environmental Stimuli. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.Q.; Li, E.; Ge, F.R.; Li, S.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, C.Q.; Zhang, Y. Arabidopsis RopGEF4 and RopGEF10 are important for FERONIA-mediated developmental but not environmental regulation of root hair growth. New. Phytol. 2013, 200, 1089–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buti, M.; Pasquariello, M.; Ronga, D.; Milc, J.A.; Pecchioni, N.; Ho, V.T.; Pucciariello, C.; Perata, P.; Francia, E. Transcriptome profiling of short-term response to chilling stress in tolerant and sensitive Oryza sativa ssp. Japonica seedlings. Funct. Integr. Genom. 2018, 18, 627–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldoni, E.; Bagnaresi, P.; Locatelli, F.; Mattana, M.; Genga, A. Comparative Leaf and Root Transcriptomic Analysis of two Rice Japonica Cultivars Reveals Major Differences in the Root Early Response to Osmotic Stress. Rice 2016, 9, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Formentin, E.; Sudiro, C.; Perin, G.; Riccadonna, S.; Barizza, E.; Baldoni, E.; Lavezzo, E.; Stevanato, P.; Sacchi, G.A.; Fontana, P.; et al. Transcriptome and Cell Physiological Analyses in Different Rice Cultivars Provide New Insights Into Adaptive and Salinity Stress Responses. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
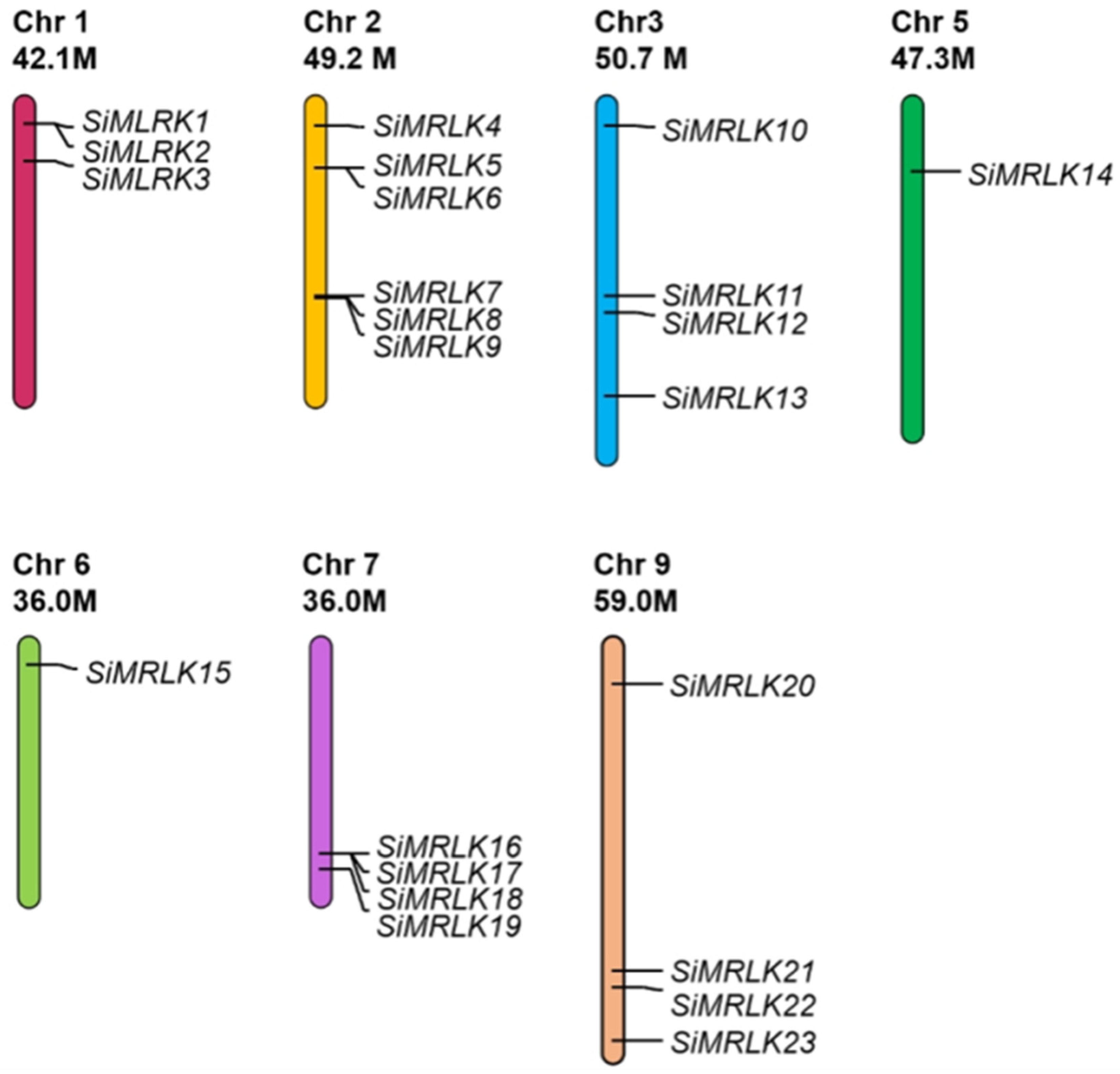

| Name | Gene | Genomic Location | Orientation | DNA | mRNA | PROTEIN | Exons |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SiMRLK1 | SETIT_016192mg | Chr I: 2,269,336-2,281,707 | Reverse | 12372 | 3075 | 1020 | 24 |
| SiMRLK2 | SETIT_016251mg | Chr I: 2,286,255-2,294,201 | Reverse | 7947 | 3395 | 922 | 23 |
| SiMRLK3 | SETIT_016287mg | Chr I: 7,753,767-7,759,223 | Forward | 5457 | 2622 | 873 | 12 |
| SiMRLK4 | SETIT_028931mg | Chr II: 2,466,757-2,469,304 | Reverse | 2548 | 2505 | 834 | 2 |
| SiMRLK5 | SETIT_028769mg | Chr II: 8,797,129-8,803,723 | Reverse | 6595 | 3290 | 1082 | 24 |
| SiMRLK6 | SETIT_028790mg | Chr II: 8,808,248-8,814,896 | Reverse | 6649 | 3602 | 1036 | 24 |
| SiMRLK7 | SETIT_028810mg | Chr II: 27,658,950-27,669,289 | Forward | 10340 | 3325 | 994 | 23 |
| SiMRLK8 | SETIT_028799mg | Chr II: 27,683,557-27,690,810 | Forward | 7254 | 3090 | 1029 | 24 |
| SiMRLK9 | SETIT_028878mg | Chr II: 27,824,611-27,835,635 | Forward | 11049 | 2916 | 887 | 13 |
| SiMRLK10 | SETIT_021217mg | Chr III: 2,531,201-2,534,600 | Forward | 3400 | 3400 | 840 | 1 |
| SiMRLK11 | SETIT_021180mg | Chr III: 27,523,701-27,527,334 | Forward | 3634 | 3634 | 873 | 1 |
| SiMRLK12 | SETIT_024804mg | Chr III: 29,987,665-29,990,274 | Reverse | 2610 | 2610 | 869 | 1 |
| SiMRLK13 | SETIT_024630mg | Chr III: 42,311,418-42,318,343 | Forward | 6926 | 2547 | 848 | 13 |
| SiMRLK14 | SETIT_000277mg | Chr V: 9,293,577-9,296,524 | Forward | 2948 | 2948 | 862 | 1 |
| SiMRLK15 | SETIT_013178mg | Chr VI: 2,184,449-2,190,852 | Reverse | 6404 | 3084 | 1027 | 24 |
| SiMRLK16 | SETIT_009322mg | Chr VII: 29,953,522-29,960,949 | Reverse | 7428 | 3471 | 891 | 21 |
| SiMRLK17 | SETIT_009325mg | Chr VII: 29,970,651-29,979,365 | Reverse | 8715 | 3703 | 886 | 21 |
| SiMRLK18 | SETIT_009240mg | Chr VII: 30,011,401-30,020,155 | Reverse | 8755 | 3481 | 1029 | 24 |
| SiMRLK19 | SETIT_009354mg | Chr VII: 32,306,664-32,309,798 | Forward | 3135 | 3135 | 836 | 1 |
| SiMRLK20 | SETIT_039238mg | Chr IX: 5,036,546-5,039,071 | Forward | 2526 | 2526 | 841 | 1 |
| SiMRLK21 | SETIT_034180mg | Chr IX: 47,183,943-47,187,152 | Reverse | 3210 | 3210 | 884 | 1 |
| SiMRLK22 | SETIT_034215mg | Chr IX: 49,665,610-49,668,585 | Reverse | 2976 | 2976 | 863 | 1 |
| SiMRLK23 | SETIT_034221mg | Chr IX: 57,483,937-57,486,745 | Reverse | 2809 | 2809 | 861 | 1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jing, X.; Deng, N.; Shalmani, A. Characterization of Malectin/Malectin-like Receptor-like Kinase Family Members in Foxtail Millet (Setaria italica L.). Life 2023, 13, 1302. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13061302
Jing X, Deng N, Shalmani A. Characterization of Malectin/Malectin-like Receptor-like Kinase Family Members in Foxtail Millet (Setaria italica L.). Life. 2023; 13(6):1302. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13061302
Chicago/Turabian StyleJing, Xiuqing, Ning Deng, and Abdullah Shalmani. 2023. "Characterization of Malectin/Malectin-like Receptor-like Kinase Family Members in Foxtail Millet (Setaria italica L.)" Life 13, no. 6: 1302. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13061302
APA StyleJing, X., Deng, N., & Shalmani, A. (2023). Characterization of Malectin/Malectin-like Receptor-like Kinase Family Members in Foxtail Millet (Setaria italica L.). Life, 13(6), 1302. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13061302




