Berberine—A Promising Therapeutic Approach to Polycystic Ovary Syndrome in Infertile/Pregnant Women
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
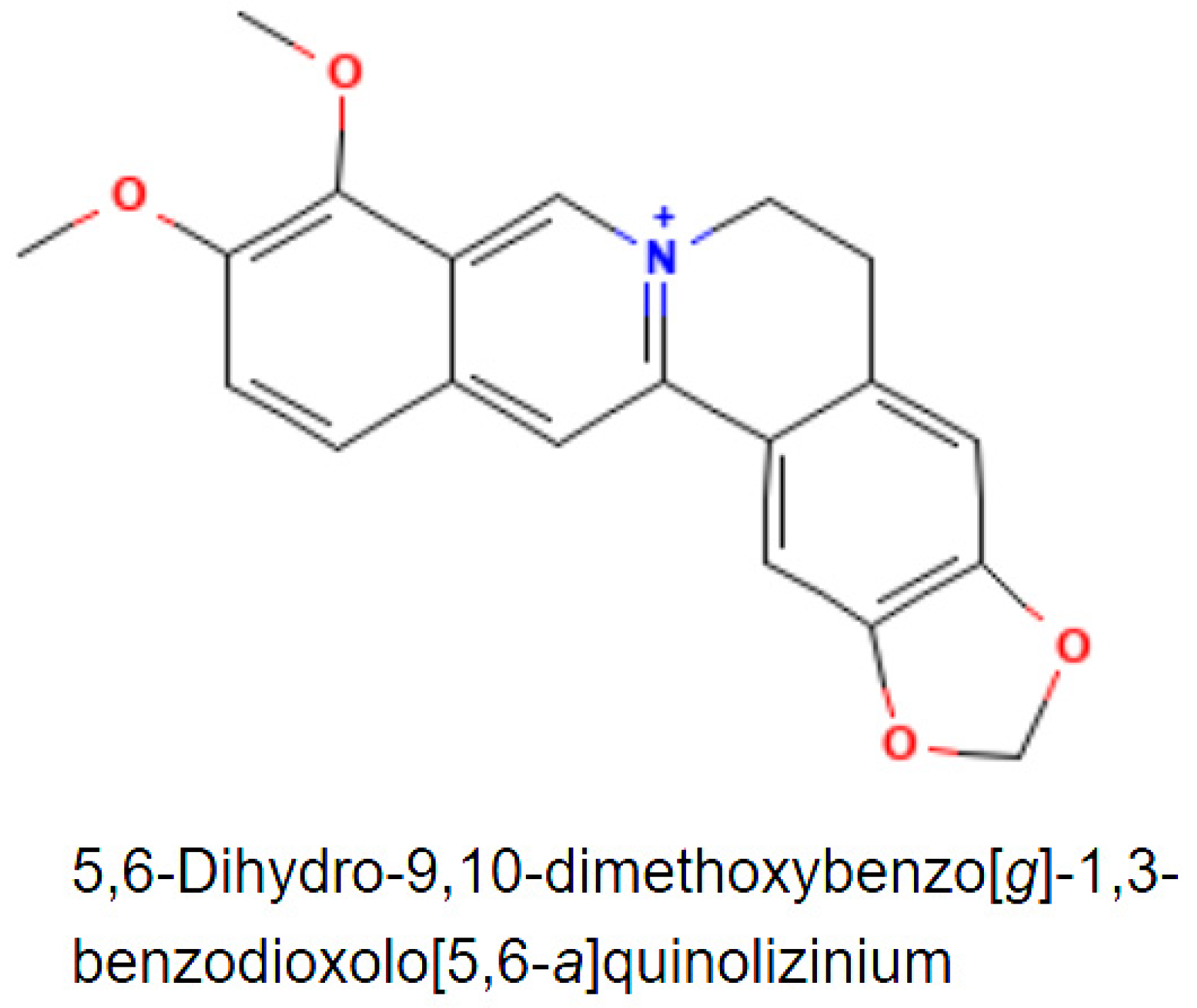
3.1. Natural Sources of Berberine and Its Uses
3.2. Berberine Pharmacokinetics
3.3. Berberine’s Hypoglycemic Effect
3.3.1. Berberine Alleviates Insulin Resistance
3.3.2. Berberine Promotes Insulin Secretion
3.3.3. Berberine Promotes Glucose Uptake
3.3.4. Berberine Reduces Glucose Intestinal Absorption
3.3.5. BBR Induces Glycolysis and Inhibits Gluconeogenesis in the Liver
3.4. Berberine Improves Fertility and Pregnancy Outcome in PCOS Women
3.5. Berberine Intake Side Effects
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Aversa, A.; La Vignera, S.; Rago, R.; Gambineri, A.; Nappi, R.E.; Calogero, A.E.; Ferlin, A. Fundamental Concepts and Novel Aspects of Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome: Expert Consensus Resolutions. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganie, M.A.; Vasudevan, V.; Wani, I.A.; Baba, M.S.; Arif, T.; Rashid, A. Epidemiology, pathogenesis, genetics & management of polycystic ovary syndrome in India. Indian J. Med. Res. 2019, 150, 333–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palioura, E.; Diamanti-Kandarakis, E. Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) and endocrine disrupting chemicals (EDCs). Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2015, 16, 365–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balen, A.H.; Morley, L.C.; Misso, M.; Franks, S.; Legro, R.S.; Wijeyaratne, C.N.; Stener-Victorin, E.; Fauser, B.C.; Norman, R.J.; Teede, H. The management of anovulatory infertility in women with polycystic ovary syndrome: An analysis of the evidence to support the development of global WHO guidance. Hum. Reprod. Update 2016, 22, 687–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lizneva, D.; Suturina, L.; Walker, W.; Brakta, S.; Gavrilova-Jordan, L.; Azziz, R. Criteria, prevalence, and phenotypes of polycystic ovary syndrome. Fertil. Steril. 2016, 106, 6–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palomba, S.; de Wilde, M.A.; Falbo, A.; Koster, M.P.; La Sala, G.B.; Fauser, B.C. Pregnancy complications in women with polycystic ovary syndrome. Hum. Reprod. Update 2015, 21, 575–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palomba, S.; Santagni, S.; Falbo, A.; La Sala, G.B. Complications and challenges associated with polycystic ovary syndrome: Current perspectives. Int. J. Womens Health 2015, 7, 745–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kollmann, M.; Klaritsch, P.; Martins, W.P.; Guenther, F.; Schneider, V.; Herzog, S.A.; Craciunas, L.; Lang, U.; Obermayer-Pietsch, B.; Lerchbaum, E.; et al. Maternal and neonatal outcomes in pregnant women with PCOS: Comparison of different diagnostic definitions. Hum. Reprod. 2015, 30, 2396–2403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joham, A.E.; Palomba, S.; Hart, R. Polycystic Ovary Syndrome, Obesity, and Pregnancy. Semin. Reprod. Med. 2016, 34, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macut, D.; Bjekić-Macut, J.; Rahelić, D.; Doknić, M. Insulin and the polycystic ovary syndrome. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pr. 2017, 130, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Leo, V.; Musacchio, M.C.; Cappelli, V.; Massaro, M.G.; Morgante, G.; Petraglia, F. Genetic, hormonal and metabolic aspects of PCOS: An update. Reprod. Biol. Endocrinol. 2016, 14, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, Y.; Sun, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, B.; Guan, Y.; Lu, M. The use of berberine for women with polycystic ovary syndrome undergoing IVF treatment. Clin. Endocrinol. 2014, 80, 425–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodarzi, M.O.; Dumesic, D.A.; Chazenbalk, G.; Azziz, R. Polycystic ovary syndrome: Etiology, pathogenesis and diagnosis. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2011, 7, 219–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ong, M.; Peng, J.; Jin, X.; Qu, X. Chinese Herbal Medicine for the Optimal Management of Polycystic Ovary Syndrome. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2017, 45, 405–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDonnell, R.; Hart, R.J. Pregnancy-related outcomes for women with polycystic ovary syndrome. Womens Health (Lond) 2017, 13, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hart, R. Generational Health Impact of PCOS on Women and their Children. Med. Sci. 2019, 7, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cicero, A.F.; Baggioni, A. Berberine and Its Role in Chronic Disease. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2016, 928, 27–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rad, S.Z.K.; Rameshrad, M.; Hosseinzadeh, H. Toxicology effects of Berberis vulgaris (barberry) and its active constituent, berberine: A review. Iran J. Basic Med. Sci. 2017, 20, 516–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzpatrick, L.R.; Woldemariam, T. Small-Molecule Drugs for the Treatment of Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Compr. Med. Chem. III 2017, 495–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berberine. Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/2353 (accessed on 31 December 2022).
- Cicero, A.F.; Tartagni, E. Antidiabetic properties of berberine: From cellular pharmacology to clinical effects. Hosp. Pr. (1995) 2012, 40, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Habtemariam, S. Berberine pharmacology and the gut microbiota: A hidden therapeutic link. Pharmacol. Res. 2020, 155, 104722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A.; Duggal, A.; Kaur Net Singh, J. Berberine: Alkaloid with wide spectrum of pharmacological activities. J. Nat. Prod. 2010, 3, 64–75. [Google Scholar]
- Neag, M.A.; Mocan, A.; Echeverría, J.; Pop, R.M.; Bocsan, C.I.; Crişan, G.; Buzoianu, A.D. Berberine: Botanical Occurrence, Traditional Uses, Extraction Methods, and Relevance in Cardiovascular, Metabolic, Hepatic, and Renal Disorders. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andola, H.C.; Rawal, R.S.; Rawat, M.S.M.; Bhatt, I.D.; Purohit, V.K. Analysis of berberine content using HPTLC fingerprinting of root and bark of three Himalayan Berberis species. Asian J. Biotechnol. 2010, 2, 239–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prajwala, B.; Raghu, N.; Gopenath, T.S.; Kaginelli, S.B.; Karthikeyan, M.; Ashok, G.; Ranjith, M.S.; Srinivasan, V.; Basalingappa, K.M. Berberine and its pharmacology potential: A review. EJBPS 2020, 7, 115–123. [Google Scholar]
- Gaba, S.; Saini, A.; Singh, G.; Monga, V. An insight into the medicinal attributes of berberine derivatives: A review. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2021, 38, 116143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imenshahidi, M.; Hosseinzadeh, H. Berberis Vulgaris and Berberine: An Update Review. Phytother. Res. 2016, 30, 1745–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Feng, X.; Chai, L.; Cao, S.; Qiu, F. The metabolism of berberine and its contribution to the pharmacological effects. Drug Metab. Rev. 2017, 49, 139–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, W.; Zhao, H.; Wang, A.; Sui, M.; Liang, K.; Deng, H.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Guan, Y. A clinical study on the short-term effect of berberine in comparison to metformin on the metabolic characteristics of women with polycystic ovary syndrome. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2012, 166, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, H.R.; Xu, X.; Li, X.L. Berberine exerts a protective effect on rats with polycystic ovary syndrome by inhibiting the inflammatory response and cell apoptosis. Reprod. Biol. Endocrinol. 2021, 19, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Khadka, D.B.; Cho, W.J. Pharmacological effects of berberine and its derivatives: A patent update. Expert Opin. Ther. Pat. 2016, 26, 229–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.; Ekavali Chopra, K.; Mukherjee, M.; Pottabathini, R.; Dhull, D.K. Current knowledge and pharmacological profile of berberine: An update. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 761, 288–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Och, A.; Podgórski, R.; Nowak, R. Biological Activity of Berberine-A Summary Update. Toxins 2020, 12, 713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, B.; Zhao, L.H.; Zhou, Q.; Zhao, T.Y.; Wang, H.; Gu, C.J.; Tong, X.L. Application of berberine on treating type 2 diabetes mellitus. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2015, 2015, 905749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugimoto, T.; Kato, Y.; Tsunoda, Y. The Effect of Berberine Treatment on the Reversibility of the Development of Mouse Zygotes and Gametes, and on the Fertilization and Subsequent Development. J. Mamm. Ova Res. 2012, 29, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, X.; Yu, P.; Peng, L.; Luo, L.; Liu, J.; Li, S.; Lai, X.; Luan, F.; Meng, X. Berberine: A Review of its Pharmacokinetics Properties and Therapeutic Potentials in Diverse Vascular Diseases. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 762654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Xiang, Y.; Shi, Y.; Tang, X.; Pan, L.; Gao, J.; Bi, R.; Lai, X. Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacological Activities of Berberine in Diabetes Mellitus Treatment. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2021, 2021, 9987097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Kong, H.; Jin, M.; Li, X.; Stoika, R.; Lin, H.; Liu, K. Synthesis of disaccharide modified berberine derivatives and their anti-diabetic investigation in zebrafish using a fluorescence-based technology. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2020, 18, 3563–3574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, X.; Wang, K.; Cao, S.; Ding, L.; Qiu, F. Pharmacokinetics and Excretion of Berberine and Its Nine Metabolites in Rats. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 11, 594852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Xue, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, J. Berberine is a potential therapeutic agent for metabolic syndrome via brown adipose tissue activation and metabolism regulation. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2018, 10, 3322–3329. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, A.; Kamble, S.; Deshkar, S.; Kothapalli, L.; Chitlange, S. Bioavailability of berberine: Challenges and solutions. Istanb. J. Pharm. 2021, 51, 141–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Sheng, W.; Li, X.; Sik, A.; Lin, H.; Liu, K.; Wang, L. Novel carbohydrate modified berberine derivatives: Synthesis and in vitro anti-diabetic investigation. Medchemcomm 2019, 10, 598–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, M.; Lim, D.Y.; Lee, C.H.; Jeon, J.H.; Choi, M.K.; Song, I.S. Enhanced Intestinal Absorption and Pharmacokinetic Modulation of Berberine and Its Metabolites through the Inhibition of P-Glycoprotein and Intestinal Metabolism in Rats Using a Berberine Mixed Micelle Formulation. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pirillo, A.; Catapano, A.L. Berberine, a plant alkaloid with lipid- and glucose-lowering properties: From in vitro evidence to clinical studies. Atherosclerosis 2015, 243, 449–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lan, J.; Zhao, Y.; Dong, F.; Yan, Z.; Zheng, W.; Fan, J.; Sun, G. Meta-analysis of the effect and safety of berberine in the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus, hyperlipemia and hypertension. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2015, 161, 69–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Wei, J.; Xue, R.; Wu, J.D.; Zhao, W.; Wang, Z.Z.; Wang, S.K.; Zhou, Z.X.; Song, D.Q.; Wang, Y.M.; et al. Berberine lowers blood glucose in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients through increasing insulin receptor expression. Metabolism 2010, 59, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, W.J.; Zhang, H.; Song, D.Q.; Xue, R.; Zhao, W.; Wei, J.; Wang, Y.M.; Shan, N.; Zhou, Z.X.; Yang, P.; et al. Berberine reduces insulin resistance through protein kinase C-dependent up-regulation of insulin receptor expression. Metabolism 2009, 58, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shan, Y.; Zhang, S.; Gao, B.; Liang, S.; Zhang, H.; Yu, X.; Zhao, J.; Ye, L.; Yang, Q.; Shang, W. Adipose Tissue SIRT1 Regulates Insulin Sensitizing and Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Berberine. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 591227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.S.; Kim, W.S.; Kim, K.H.; Yoon, M.J.; Cho, H.J.; Shen, Y.; Ye, J.M.; Lee, C.H.; Oh, W.K.; Kim, C.T.; et al. Berberine, a natural plant product, activates AMP-activated protein kinase with beneficial metabolic effects in diabetic and insulin-resistant states. Diabetes 2006, 55, 2256–2264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khvostov, M.V.; Gladkova, E.D.; Borisov, S.A.; Zhukova, N.A.; Marenina, M.K.; Meshkova, Y.V.; Luzina, O.A.; Tolstikova, T.G.; Salakhutdinov, N.F. Discovery of the First in Class 9-N-Berberine Derivative as Hypoglycemic Agent with Extra-Strong Action. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 2138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, B.S.; Choi, S.B.; Park, S.K.; Jang, J.S.; Kim, Y.E.; Park, S. Insulin sensitizing and insulinotropic action of berberine from Cortidis rhizoma. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2005, 28, 1431–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Hou, L.; Li, S.; Tian, H.; Zhao, T. Berberine Modulates Gut Microbiota and Reduces Insulin Resistance via the TLR4 Signaling Pathway. Exp. Clin. Endocrinol. Diabetes 2018, 126, 513–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, N.; Liu, X.; Zhuang, L.; Liu, X.; Zhao, H.; Shan, Y.; Liu, Z.; Li, F.; Wang, Y.; Fang, J. Berberine decreases insulin resistance in a PCOS rats by improving GLUT4: Dual regulation of the PI3K/AKT and MAPK pathways. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2020, 110, 104544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Yi, H.; Wu, J.; Kuang, T.; Zhang, J.; Li, Q.; Du, H.; Xu, T.; Jiang, G.; Fan, G. Therapeutic effect of berberine on metabolic diseases: Both pharmacological data and clinical evidence. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 133, 110984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, S.S.; Yu, Y.L.; Zhu, H.J.; Liu, X.D.; Liu, L.; Liu, Y.W.; Wang, P.; Xie, L.; Wang, G.J. Berberine promotes glucagon-like peptide-1 (7-36) amide secretion in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. J. Endocrinol. 2009, 200, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Xiao, X.; Feng, K.; Wang, T.; Li, W.; Yuan, T.; Sun, X.; Sun, Q.; Xiang, H.; Wang, H. Berberine Moderates Glucose and Lipid Metabolism through Multipathway Mechanism. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2011, 2011, 924851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, G.Y.; Huang, Z.J.; Wang, G.J.; Fawcett, J.P.; Liu, X.D.; Zhao, X.C.; Sun, J.G.; Xie, Y.Y. The antihyperglycaemic activity of berberine arises from a decrease of glucose absorption. Planta Med. 2003, 69, 632–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, J.; Gao, Z.; Liu, D.; Liu, Z.; Ye, J. Berberine improves glucose metabolism through induction of glycolysis. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2008, 294, E148–E156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Xiao, Y.; Yin, J.; Hou, W.; Yu, X.; Shen, L.; Liu, F.; Wei, L.; Jia, W. Berberine promotes glucose consumption independently of AMP-activated protein kinase activation. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e103702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Pan, Y.; Xu, L.; Tang, D.; Dorfman, R.G.; Zhou, Q.; Yin, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhou, L.; Zhao, S.; et al. Berberine promotes glucose uptake and inhibits gluconeogenesis by inhibiting deacetylase SIRT3. Endocrine 2018, 62, 576–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, L.; Zhang, D.; Ma, H.; He, H.; Xia, Q.; Shen, W.; Chang, H.; Deng, Y.; Wu, Q.; Cong, J.; et al. The Effect of Berberine on Reproduction and Metabolism in Women with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Control Trials. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2019, 2019, 7918631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dumesic, D.A.; Padmanabhan, V.; Abbott, D.H. Polycystic ovary syndrome and oocyte developmental competence. Obstet. Gynecol. Surv. 2008, 63, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.Y.; Song, Z.; Song, M.J.; Qin, J.W.; Zhao, M.L.; Yang, Z.M. Impaired receptivity and decidualization in DHEA-induced PCOS mice. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 38134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, N.X.; Li, X.L. The Disorders of Endometrial Receptivity in PCOS and Its Mechanisms. Reprod. Sci. 2021, 29, 2465–2476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Nie, K.; Su, H.; Tang, Y.; Wang, H.; Xu, X.; Dong, H. Berberine improves ovulation and endometrial receptivity in polycystic ovary syndrome. Phytomedicine 2021, 91, 153654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Li, C.; Pan, P.; Chen, X.; Wu, X.; Ng, E.H.; Yang, D. A Single Arm Pilot Study of Effects of Berberine on the Menstrual Pattern, Ovulation Rate, Hormonal and Metabolic Profiles in Anovulatory Chinese Women with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0144072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Li, Y.; Kuang, H.; Shen, W.; Ma, H.; Zhang, Y.; Stener-Victorin, E.; Hung, E.; Ng, Y.; Liu, J.; Kuang, H.; et al. Letrozole, berberine, or their combination for anovulatory infertility in women with polycystic ovary syndrome: Study design of a double-blind randomised controlled trial. BMJ Open 2013, 3, e003934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.L.; Gao, J.S.; Tian, F.; YNg, E.H.; Wu, X.K.; Liu, J.P. Effect of letrozole, berberine, or their combination for infertility in women with polycystic ovary syndrome: Statistical analysis plan for a multicenter randomized controlled trial. World J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2016, 2, 36–42. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, X.K.; Wang, Y.Y.; Liu, J.P.; Liang, R.N.; Xue, H.Y.; Ma, H.X.; Shao, X.G.; Ng, E.H. Reproductive and Developmental Network in Chinese Medicine. Randomized controlled trial of letrozole, berberine, or a combination for infertility in the polycystic ovary syndrome. Fertil. Steril. 2016, 106, 757–765.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Gong, W.; Lv, S.; Qu, H.; He, Y. Berberine improves insulin resistance in adipocyte models by regulating the methylation of hypoxia-inducible factor-3α. Biosci. Rep. 2019, 39, BSR20192059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belwal, T.; Bisht, A.; Devkota, H.P.; Ullah, H.; Khan, H.; Pandey, A.; Bhatt, I.D.; Echeverría, J. Phytopharmacology and Clinical Updates of Berberis Species Against Diabetes and Other Metabolic Diseases. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.F.; Zhou, X.M.; Li, X.L. The Effect of Berberine on Polycystic Ovary Syndrome Patients with Insulin Resistance (PCOS-IR): A Meta-Analysis and Systematic Review. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2018, 2018, 2532935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.H.; Wang, F.T.; Chan, W.H. Dose-dependent beneficial and harmful effects of berberine on mouse oocyte maturation and fertilization and fetal development. Toxicol. Res. (Camb) 2020, 9, 431–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.H.; Huang, Z.W.; Ho, F.M.; Chan, W.H. Berberine impairs embryonic development in vitro and in vivo through oxidative stress-mediated apoptotic processes. Environ. Toxicol. 2018, 33, 280–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Shi, Y.R.; Liu, X.R.; Cao, Y.C.; Zhen, D.; Jia, Z.Y.; Jiang, J.Q.; Tian, J.H.; Gao, J.M. The Anti-Apoptotic Role of Berberine in Preimplantation Embryo In Vitro Development through Regulation of miRNA-21. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0129527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
| Family | Scientific Name of the Plant | Common Name of the Plant | Plants Used in Gynecology Condition/Diabetes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Annonaceae | Annickia chlorantha | Diabetes; promote conception | |
| Annickia Pilosa | |||
| Annickia polycarpa | |||
| Rollinia mucosa | |||
| Xylopia polycarpa | |||
| Berberidaceae | Berberis actinacantha | ||
| Berberis aquifolium | Oregon grape | Sore womb following childbirth and/or menstruation | |
| Berberis aristata | Tree turmeric | Menorrhagia | |
| Berberis asiatica | Chutro | Diabetes | |
| Berberis buxifolia | |||
| Berberis chitria | |||
| Berberis congestiflora | Michay | ||
| Berberis croatica | Croatian barberry | ||
| Berberis darwinii | |||
| Berberis empetrifolia | |||
| Berberis floribunda | Nepal barberry | ||
| Berberis integerrima | Diabetes | ||
| Berberis jaeschkeana | |||
| Berberis koreana | |||
| Berberis leschenaultia | Treatment of complications during post-natal period | ||
| Berberis libanotica | |||
| Berberis lyceum | Boxthorn barberry | Diabetes | |
| Berberis microphylla | |||
| Berberis oblonga | |||
| Berberis petiolaris | Chochar | ||
| Berberis pseudumbellata | Oxytocic effect | ||
| Berberis thunbergia | |||
| Berberis tinctoria | Nilgiri barberry | ||
| Berberis umbellate | |||
| Berberis vulgaris | Berberry | ||
| Caulophyllum thalictroides | Inducer of menstruation | ||
| Jeffersonia diphylla | |||
| Mahonia fortune | |||
| Mahonia napaulensis | |||
| Nandina domestica | |||
| Sinopodophyllum hexandrum | Regulate menstruation, treat amenorrhea, difficult labor and retention of dead fetus or placenta | ||
| Menispermaceae | Tinospora sinensis | Heart leaves moonseed | Anti-diabetic effect |
| Papaveraceae | Argemone albiflora | ||
| Argemone Mexicana | Prickly poppy | ||
| Argemone platyceras | |||
| Bocconia frutescens | |||
| Chelidonium majus | |||
| Corydalis solida | |||
| Corydalis turtschaninovii | Dysmenorrhea | ||
| Eschscholzia californica | Californian poppy | Suppress the milk in lactating women | |
| Glaucium corniculatum | |||
| Macleaya cordata | |||
| Macleaya macrocarpa | |||
| Papaver dubium | Long head poppy | ||
| Papaver rhoeas | |||
| Papaver hybridum | Poppy | ||
| Ranunculaceae | Coptis chinensis | Chinese goldthread | Diabetes |
| Coptis japonica | Japanese goldthread | ||
| Coptis teeta | |||
| Hydrastis canadensis | Goldenseal | Vaginal disorders | |
| Xanthorhiza simplicissima | Yellow root | ||
| Rutaceae | Phellodendron amurense | Amur cork tree | Vaginal infections (with Trichomonas vaginalis) |
| Zanthoxylum monophylum |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ionescu, O.-M.; Frincu, F.; Mehedintu, A.; Plotogea, M.; Cirstoiu, M.; Petca, A.; Varlas, V.; Mehedintu, C. Berberine—A Promising Therapeutic Approach to Polycystic Ovary Syndrome in Infertile/Pregnant Women. Life 2023, 13, 125. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13010125
Ionescu O-M, Frincu F, Mehedintu A, Plotogea M, Cirstoiu M, Petca A, Varlas V, Mehedintu C. Berberine—A Promising Therapeutic Approach to Polycystic Ovary Syndrome in Infertile/Pregnant Women. Life. 2023; 13(1):125. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13010125
Chicago/Turabian StyleIonescu, Oana-Maria, Francesca Frincu, Andra Mehedintu, Mihaela Plotogea, Monica Cirstoiu, Aida Petca, Valentin Varlas, and Claudia Mehedintu. 2023. "Berberine—A Promising Therapeutic Approach to Polycystic Ovary Syndrome in Infertile/Pregnant Women" Life 13, no. 1: 125. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13010125
APA StyleIonescu, O.-M., Frincu, F., Mehedintu, A., Plotogea, M., Cirstoiu, M., Petca, A., Varlas, V., & Mehedintu, C. (2023). Berberine—A Promising Therapeutic Approach to Polycystic Ovary Syndrome in Infertile/Pregnant Women. Life, 13(1), 125. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13010125