Remediation of Cadmium Stress in Strawberry Plants Using Humic Acid and Silicon Applications
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Material and Treatments
2.2. Plant Fresh and Dry Weight Measurements
2.3. Leaf Area, Total Number of Leaves and Relative Leaf Water Content Determinations
2.4. Stomatal Conductance, Chlorophyll Content and the Temperature and Membrane Permeability of Leaves
2.5. Proline and Malondialdehyde Determinations
2.6. Mineral Analysis of Leaves and Roots
2.7. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Strawberry Morphological, Physical and Physiological Analysis
3.2. Strawberry Biochemical Parameters
3.3. Mineral Contents in Roots and Leaves
3.4. Hierarchical Clustering Analysis (HCA)
3.5. Principal Component Analysis (PCA)
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Navarro-González, A.; Gutiérrez-Gamboa, G.; Cañón, P.; del Real, I. Efecto de Distintas Dosis de Extracto de Ajos Sobre La Mortalidad de Quistes de Margarodes Vitis. RIVAR 2022, 9, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahajan, S.; Tuteja, N. Cold, Salinity and Drought Stresses: An Overview. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2005, 444, 139–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Wu, Y.; Lan, X.; Yang, Y.; Wu, X.; Du, L. Comprehensive Assessment of Harmful Heavy Metals in Contaminated Soil in Order to Score Pollution Level. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 3552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butnariu, M.; Negrea, P.; Lupa, L.; Ciopec, M.; Negrea, A.; Pentea, M.; Sarac, I.; Samfira, I. Remediation of rare earth element pollutants by sorption process using organic natural sorbents. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2015, 12, 11278–11287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butnariu, M.; Goian, M.; Ianculov, I.; Gergen, I.; Negrea, P. Studies about CO2+ ion influence on soy plants development and acumulation of other chemical elements (Iron, magnesium, calcium, potassium and phosphorus). Rev. Chim. 2005, 56, 837–841. [Google Scholar]
- Tiecher, T.L.; Tiecher, T.; Ceretta, C.A.; Ferreira, P.A.A.; Nicoloso, F.T.; Soriani, H.H.; de Conti, L.; Kulmann, M.S.S.; Schneider, R.O.; Brunetto, G. Tolerance and Translocation of Heavy Metals in Young Grapevine (Vitis vinifera) Grown in Sandy Acidic Soil with Interaction of High Doses of Copper and Zinc. Sci. Hortic. 2017, 222, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, R.; Liu, X.; Luo, L.; Zhou, Y.; Wei, J.; Chen, A.; Tang, L.; Wu, H.; Deng, Y.; Zhang, F.; et al. Remediation of Cu, Pb, Zn and Cd-Contaminated Agricultural Soil Using a Combined Red Mud and Compost Amendment. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2017, 118, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caunii, A.; Negrea, A.; Pentea, M.; Samfira, I.; Motoc, M.; Butnariu, M. Mobility of heavy metals from soil in the two species of the aromatic plants. Rev. Chim. 2015, 66, 382–386. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. Chapter 6.3 Cadmium General Description. In Air Quality Guidelines for Europe; The World Health Organization, Ed.; European Seriesl WHO: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2000; pp. 136–138. [Google Scholar]
- Verkleij, J.A.C.; Golan-Goldhirsh, A.; Antosiewisz, D.M.; Schwitzguébel, J.P.; Schröder, P. Dualities in Plant Tolerance to Pollutants and Their Uptake and Translocation to the Upper Plant Parts. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2009, 67, 10–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krantev, A.; Yordanova, R.; Janda, T.; Szalai, G.; Popova, L. Treatment with Salicylic Acid Decreases the Effect of Cadmium on Photosynthesis in Maize Plants. J. Plant. Physiol. 2008, 165, 920–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radotić, K.; Dučić, T.; Mutavdžić, D. Changes in Peroxidase Activity and Isoenzymes in Spruce Needles after Exposure to Different Concentrations of Cadmium. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2000, 44, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moustakas, N.K.; Akoumianakis, K.A.; Passam, H.C. Cadmium Accumulation and Its Effect on Yield of Lettuce, Radish, and Cucumber. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2006, 32, 1793–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferencz, Á.; Juhász, R.; Butnariu, M.; Deér, A.; Varga, I.; Nemcsók, J. Expression analysis of heat shock genes in the skin, spleen and blood of common carp (Cyprinus carpio) after cadmium exposure and hypothermia. Acta Biol. Hung. 2012, 63, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trejo, N.; Matus, I.; del Pozo, A.; Walter, I.; Hirzel, J. Cadmium Phytoextraction Capacity of White Lupine (Lupinus albus L.) and Narrow-Leafed Lupine (Lupinus angustifolius L.) in Three Contrasting Agroclimatic Conditions of Chile. Chil. J. Agric. Res. 2016, 76, 228–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaffei, C.; Pageau, K.; Suzuki, A.; Gouia, H.; Ghorbel, M.H.; Masclaux-Daubresse, C. Cadmium Toxicity Induced Changes in Nitrogen Management in Lycopersicon Esculentum Leading to a Metabolic Safeguard Through an Amino Acid Storage Strategy. Plant Cell Physiol. 2004, 45, 1681–1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiraz, C.; Houda, G.; Habib, G.M. Nitrogen Metabolism in Tomato Plants Under Cadmium Stress. J. Plant. Nutr. 2006, 26, 1617–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olaniran, A.O.; Balgobind, A.; Pillay, B. Bioavailability of Heavy Metals in Soil: Impact on Microbial Biodegradation of Organic Compounds and Possible Improvement Strategies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 10197–10228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, J.; Jho, E.H.; Nam, K. Effect of Dissolved Humic Acid on the Pb Bioavailability in Soil Solution and Its Consequence on Ecological Risk. J. Hazard Mater. 2015, 286, 236–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Fang, F.; Wei, J.; Wu, X.; Cui, R.; Li, G.; Zheng, F.; Tan, D. Humic Acid Fertilizer Improved Soil Properties and Soil Microbial Diversity of Continuous Cropping Peanut: A Three-Year Experiment. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 12014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, J.; Zhang, S.; Yuan, L.; Li, Y.; Lin, Z.; Xiong, Q.; Zhao, B. Combining Humic Acid with Phosphate Fertilizer Affects Humic Acid Structure and Its Stimulating Efficacy on the Growth and Nutrient Uptake of Maize Seedlings. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 17502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canellas, L.P.; Olivares, F.L.; Aguiar, N.O.; Jones, D.L.; Nebbioso, A.; Mazzei, P.; Piccolo, A. Humic and Fulvic Acids as Biostimulants in Horticulture. Sci. Hortic. 2015, 196, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emamverdian, A.; Ding, Y.; Xie, Y.; Sangari, S. Silicon Mechanisms to Ameliorate Heavy Metal Stress in Plants. Biomed. Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 8492898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giampieri, F.; Alvarez-Suarez, J.M.; Mazzoni, L.; Romandini, S.; Bompadre, S.; Diamanti, J.; Capocasa, F.; Mezzetti, B.; Quiles, J.L.; Ferreiro, M.S.; et al. The Potential Impact of Strawberry on Human Health. Nat. Prod. Res. 2013, 27, 448–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farouk, S.; Mosa, A.A.; Taha, A.A.; El-Gahmery, A.M. Protective effect of humic acid and chitosan on radish (Raphanus sativus, L. var. sativus) plants subjected to cadmium stress. J. Stress Physiol. Biochem. 2011, 7, 99–116. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Gao, S.; Shan, C. Effects of sodium selenite on the antioxidant capacity and the fruit yield and quality of strawberry under cadmium stress. Sci. Hortic. 2020, 260, 108876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, A.; Li, Z.; Zhang, J.; Xue, G.; Fan, F.; Liang, Y. Silicon-enhanced resistance to cadmium toxicity in Brassica chinensis L. is attributed to Si-suppressed cadmium uptake and transport and Si-enhanced antioxidant defense capacity. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 172, 74–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, G.R.; Cai, Q.S.; Liu, C.F.; Wu, L. Silicon alleviates cadmium toxicity in peanut plants in relation to cadmium distribution and stimulation of antioxidative enzymes. Plant Growth Regul. 2010, 61, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yildiztugay, E.; Ozfidan-Konakci, C.; Elbasan, F.; Yildiztugay, A.; Kucukoduk, M. Humic acid protects against oxidative damage induced by cadmium toxicity in wheat (Triticum aestivum) roots through water management and the antioxidant defence system. Bot. Serbica 2019, 43, 161–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.; Liu, Y.; Gong, X.; Zeng, J.; Zheng, B.; Wang, D.; Sun, Z.; Zhou, L.; Zeng, X. Effects of selenium and silicon on enhancing antioxidative capacity in ramie (Boehmeria nivea (L.) Gaud.) under cadmium stress. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 9999–10008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Cong, Y.; Wang, H.; Chang, Y.; Sheng, B.; Lin, J.; Wang, Z. Effects of cadmium stress on oxygen enzyme system and genome DNA polymorphism in the root tips of strawberry plant. Acta Hortic. Sin. 2010, 37, 721–730. [Google Scholar]
- Farooq, M.A.; Ali, S.; Hameed, A.; Ishaque, W.; Mahmood, K.; Iqbal, Z. Alleviation of cadmium toxicity by silicon is related to elevated photosynthesis, antioxidant enzymes; suppressed cadmium uptake and oxidative stress in cotton. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2013, 96, 242–249. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rady, M.M.; Hemida, K.A. Modulation of cadmium toxicity and enhancing cadmium-tolerance in wheat seedlings by exogenous application of polyamines. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2015, 119, 178–185. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bolat, I.; Bakır, A.G.; Korkmaz, K.; Gutiérrez-Gamboa, G.; Kaya, O. Silicon and Nitric Oxide Applications Allow Mitigation of Water Stress in Myrobalan 29C Rootstocks (Prunus cerasifera Ehrh.). Agriculture 2022, 12, 1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehghanipoodeh, S.; Ghobadi, C.; Baninasab, B.; Gheysari, M.; Shiranibidabadi, S. Effect of silicon on growth and development of strawberry under water deficit conditions. Hortic. Plant J. 2018, 4, 226–232. [Google Scholar]
- Muradoglu, F.; Gundogdu, M.; Ercisli, S.; Encu, T.; Balta, F.; Ze Jaafar, H.; Zia-Ul-Haq, M. Cadmium Toxicity Affects Chlorophyll a and b Content, Antioxidant Enzyme Activities and Mineral Nutrient Accumulation in Strawberry. Biol. Res. 2015, 48, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klamkowski, K.; Treder, W. Response to Drought Stress of Three Strawberry Cultivars Grown under Greenhouse Condition. J. Fruit Ornam. Plant Res. 2008, 16, 179–188. [Google Scholar]
- Faúndez-López, P.; Delorenzo-Arancibia, J.; Gutiérrez-Gamboa, G.; Moreno-Simunovic, Y. Pruning Cuts Affect Wood Necrosis but Not the Percentage of Budburst or Shoot Development on Spur Pruned Vines for Different Grapevine Varieties. VITIS 2021, 60, 137–141. [Google Scholar]
- Gutiérrez-Gamboa, G.; Pardo, C.; Moreno-Simunovic, Y. Effects on Berry Shrinkage in Vitis vinifera L. Cv. ‘Merlot’ From Changes in Canopy/Root Ratio: A Preliminary Approach. S. Afr. J. Enol. Vitic. 2019, 40, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lutts, S.; Kinet, J.M.; Bouharmont, J. NaCl-Induced Senescence in Leaves of Rice (Oryza sativa L.) Cultivars Differing in Salinity Resistance. Ann. Bot. 1996, 78, 389–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bates, L.S.; Waldren, R.P.; Teare, I.D. Rapid Determination of Free Proline for Water-Stress Studies. Plant Soil 1973, 39, 205–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdul Jaleel, C.; Manivannan, P.; Sankar, B.; Kishorekumar, A.; Panneerselvam, R. Calcium Chloride Effects on Salinity-Induced Oxidative Stress, Proline Metabolism and Indole Alkaloid Accumulation in Catharanthus Roseus. C. R. Biol. 2007, 330, 674–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaya, O. Defoliation alleviates cold-induced oxidative damage in dormant buds of grapevine by up-regulating soluble carbohydrates and decreasing ROS. Acta Physiol. Plant. 2020, 42, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trader, W. Cadmium Uptake and Distribution in Strawberry Plants as Affected by Its Concentration in Soil. J. Fruit Ornam. Plant Res. 2000, 8, 127–135. [Google Scholar]
- Rady, M.M. Effect of 24-Epibrassinolide on Growth, Yield, Antioxidant System and Cadmium Content of Bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) Plants under Salinity and Cadmium Stress. Sci. Hortic. 2011, 129, 232–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Lin, L.; Cheng, W.; Zhang, G.; Wu, F. Genotypic Dependent Effect of Exogenous Glutathione on Cd-Induced Changes in Cadmium and Mineral Uptake and Accumulation in Rice Seedlings (Oryza sativa). Plant Soil Environ. 2010, 56, 516–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emamverdian, A.; Ding, Y.; Mokhberdoran, F.; Xie, Y. Heavy Metal Stress and Some Mechanisms of Plant Defense Response. Sci. World J. 2015, 2015, 756120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hédiji, H.; Djebali, W.; Belkadhi, A.; Cabasson, C.; Moing, A.; Rolin, D.; Brouquisse, R.; Gallusci, P.; Chaïbi, W. Impact of Long-Term Cadmium Exposure on Mineral Content of Solanum Lycopersicum Plants: Consequences on Fruit Production. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2015, 97, 176–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Przedpelska-Wasowicz, E.; Polatajko, A.; Wierzbicka, M. The Influence of Cadmium Stress on the Content of Mineral Nutrients and Metal-Binding Proteins in Arabidopsis Halleri. Water Air Soil. Pollut. 2012, 223, 5458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heyno, E.; Klose, C.; Krieger-Liszkay, A. Origin of Cadmium-Induced Reactive Oxygen Species Production: Mitochondrial Electron Transfer versus Plasma Membrane NADPH Oxidase. New Phytol. 2008, 179, 687–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akram, N.A.; Iqbal, M.; Muhammad, A.; Ashraf, M.; Al-Qurainy, F.; Shafiq, S. Aminolevulinic Acid and Nitric Oxide Regulate Oxidative Defense and Secondary Metabolisms in Canola (Brassica napus L.) under Drought Stress. Protoplasma 2018, 255, 163–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.; Prasad, S.M. Growth, Photosynthesis and Oxidative Responses of Solanum melongena L. Seedlings to Cadmium Stress: Mechanism of Toxicity Amelioration by Kinetin. Sci. Hortic. 2014, 176, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaya, C.; Akram, N.A.; Sürücü, A.; Ashraf, M. Alleviating Effect of Nitric Oxide on Oxidative Stress and Antioxidant Defence System in Pepper (Capsicum annuum L.) Plants Exposed to Cadmium and Lead Toxicity Applied Separately or in Combination. Sci. Hortic. 2019, 255, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Żabka, A.; Winnicki, K.; Polit, J.T.; Wróblewski, M.; Maszewski, J. Cadmium (II)-Induced Oxidative Stress Results in Replication Stress and Epigenetic Modifications in Root Meristem Cell Nuclei of Vicia Faba. Cells 2021, 10, 640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rostami, M.; Mohammadi, H.; Müller, T.; Mirzaeitalarposhti, R. Silicon Application Affects Cadmium Translocation and Physiological Traits of Lallemantia Royleana under Cadmium Stress. J. Plant Nutr. 2019, 43, 753–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Okkiah, S.A.F.; El-Tahan, A.M.; Ibrahim, O.M.; Taha, M.A.; Korany, S.M.; Alsherif, E.A.; AbdElgawad, H.; Abo Sen, E.Z.F.; Sharaf-Eldin, M.A. Under Cadmium Stress, Silicon Has a Defensive Effect on the Morphology, Physiology, and Anatomy of Pea (Pisum sativum L.) Plants. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 3605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.H.; Khan, A.L.; Kim, D.H.; Lee, S.Y.; Kim, K.M.; Waqas, M.; Jung, H.Y.; Shin, J.H.; Kim, J.G.; Lee, I.J. Silicon Mitigates Heavy Metal Stress by Regulating P-Type Heavy Metal ATPases, Oryza Sativa Low Silicon Genes, and Endogenous Phytohormones. BMC Plant Biol. 2014, 14, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, Z.F.; Ming, D.F.; Liu, D.; Wan, G.L.; Geng, X.X.; Gong, H.J.; Zhou, W.J. Silicon Improves the Tolerance to Water-Deficit Stress Induced by Polyethylene Glycol in Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) Seedlings. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2010, 29, 106–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treder, W.; Cieslinski, G. Effect of Silicon Application on Cadmium Uptake and Distribution in Strawberry Plants Grown on Contaminated Soils. J. Plant Nutr. 2006, 28, 917–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, Q.; Zhong, K.; Huang, H.; Li, C.; Zhang, C.; Nong, X. Humic Acid Reduces the Available Cadmium, Copper, Lead, and Zinc in Soil and Their Uptake by Tobacco. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhang, X.; Chen, H.; Xu, X. Physiology and Proteomics Reveal Fulvic Acid Mitigates Cadmium Adverse Effects on Growth and Photosynthetic Properties of Lettuce. Plant Sci. 2022, 323, 111418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozfidan-Konakci, C.; Yildiztugay, E.; Bahtiyar, M.; Kucukoduk, M. The Humic Acid-Induced Changes in the Water Status, Chlorophyll Fluorescence and Antioxidant Defense Systems of Wheat Leaves with Cadmium Stress. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 155, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakır, A.G.; Bolat, I.; Korkmaz, K.; Hasan, M.M.; Kaya, O. Exogenous Nitric Oxide and Silicon Applications Alleviate Water Stress in Apricots. Life 2022, 12, 1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korkmaz, K.; Bolat, I.; Karakas, S.; Dikilitas, M. Responses to Single and Combined Application of Humic Acid and Silicon Under Water Stress on Strawberry. Erwerbs-Obstbau 2022, 64, 523–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nwugo, C.C.; Huerta, A.J. Silicon-induced cadmium resistance in rice (Oryza sativa). J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2008, 171, 841–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
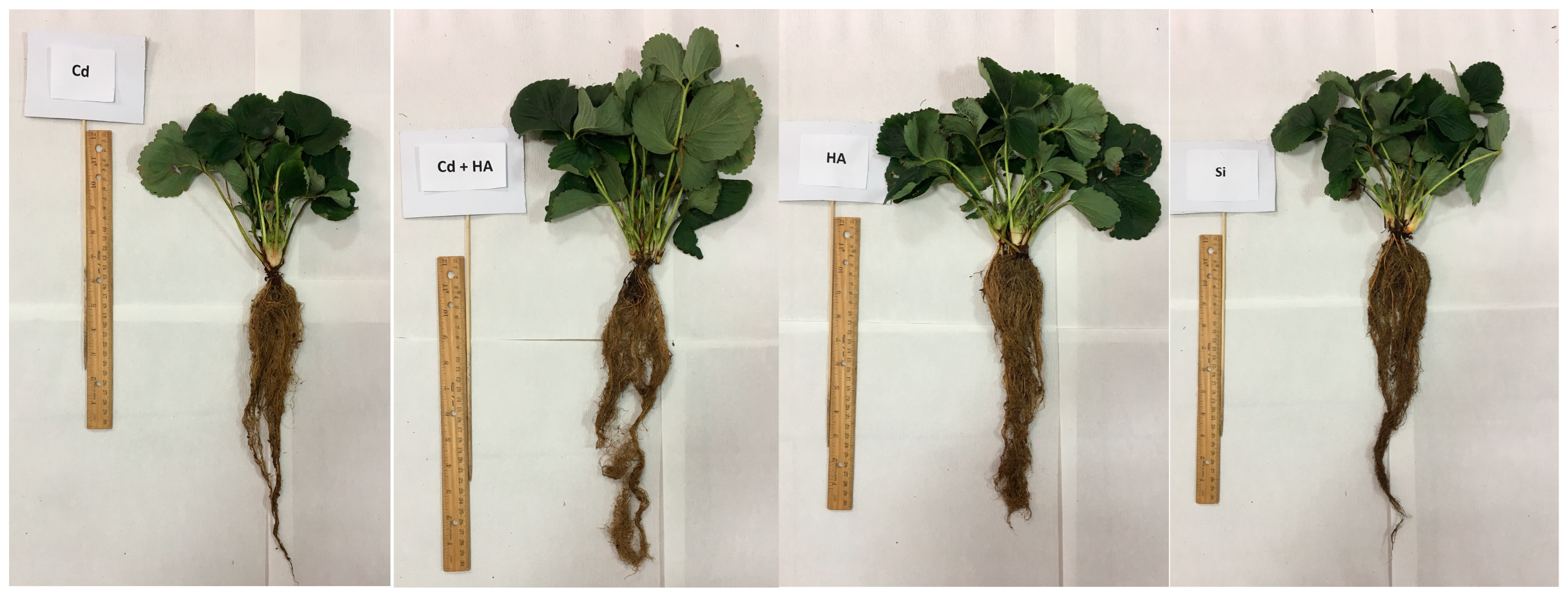


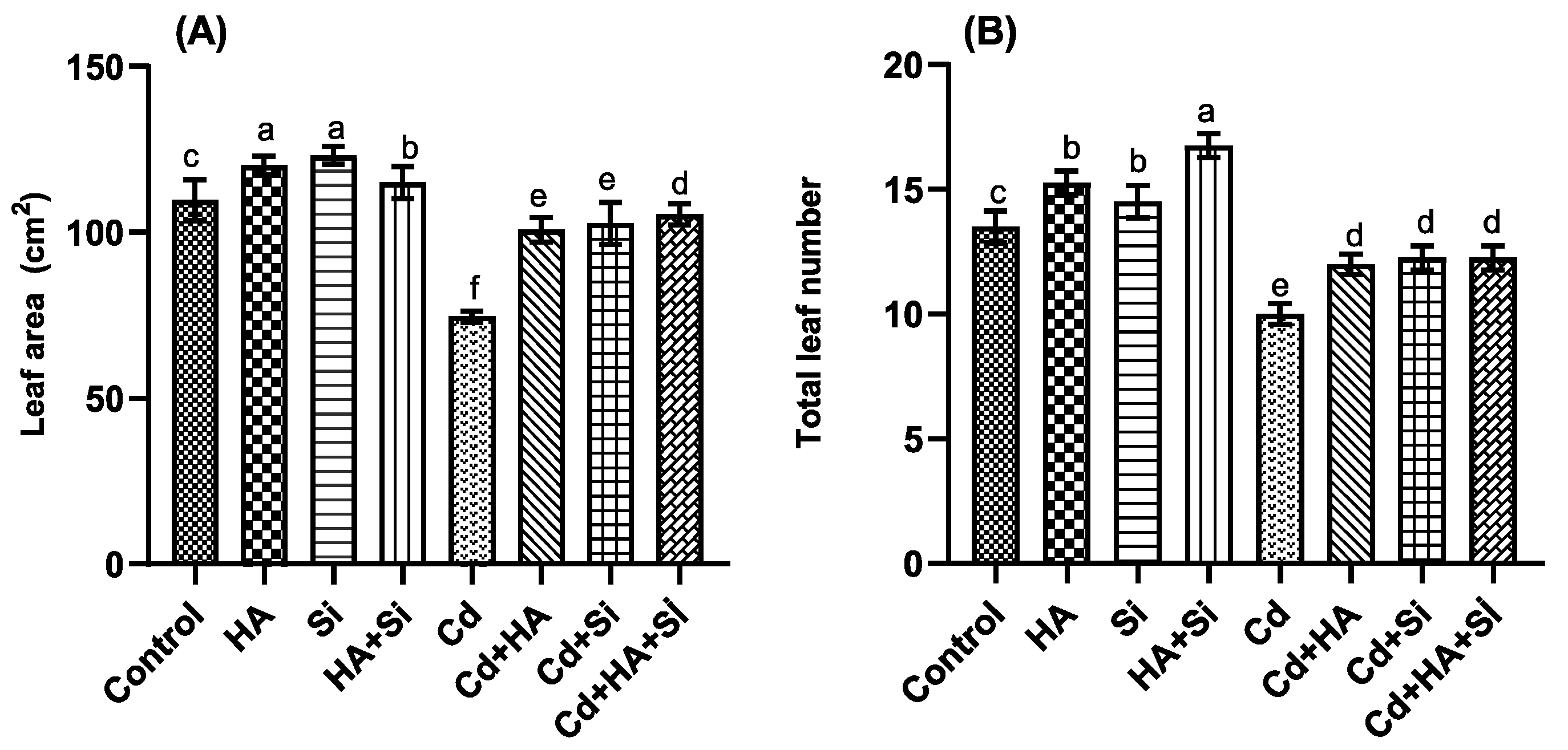

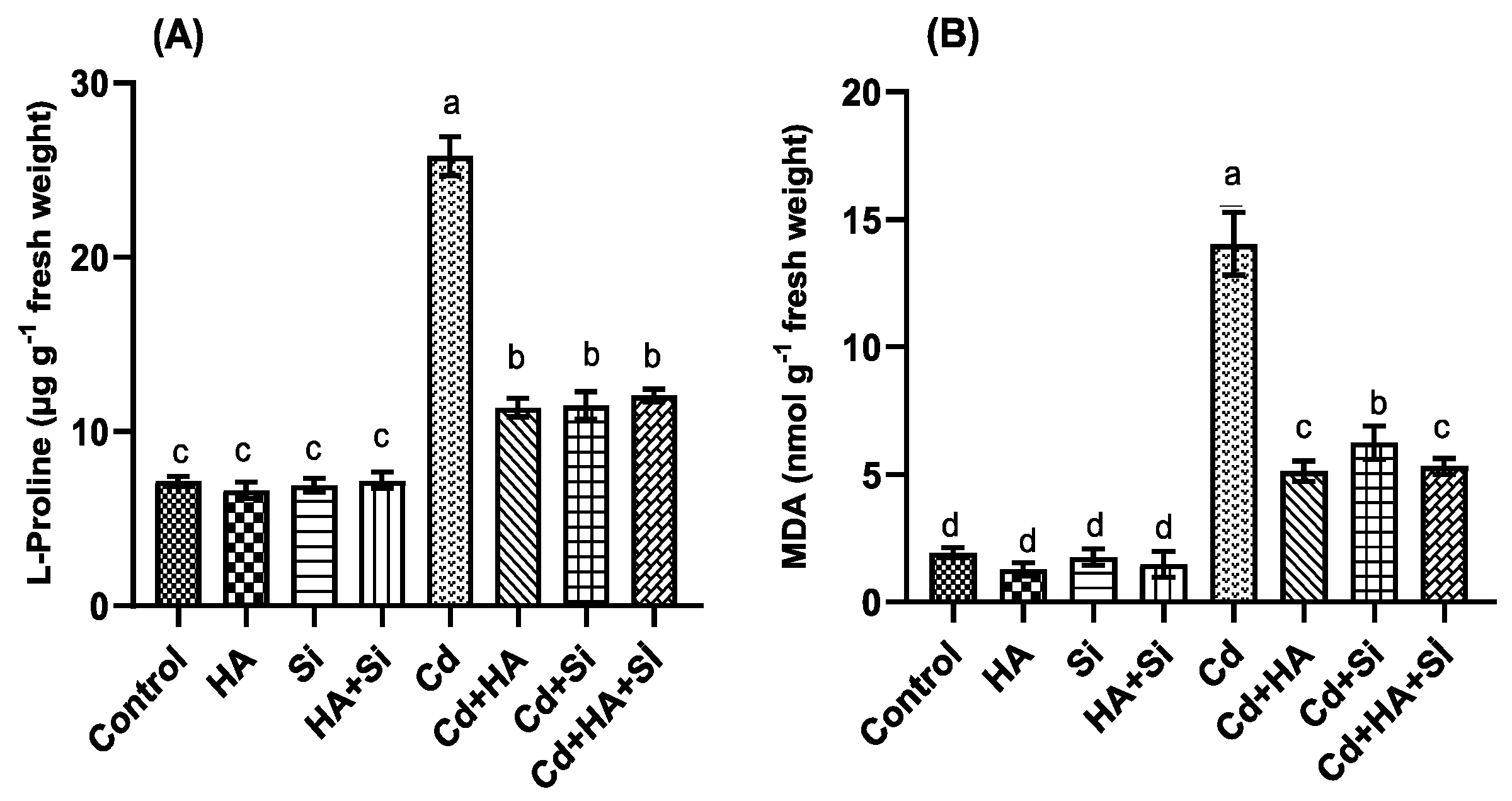
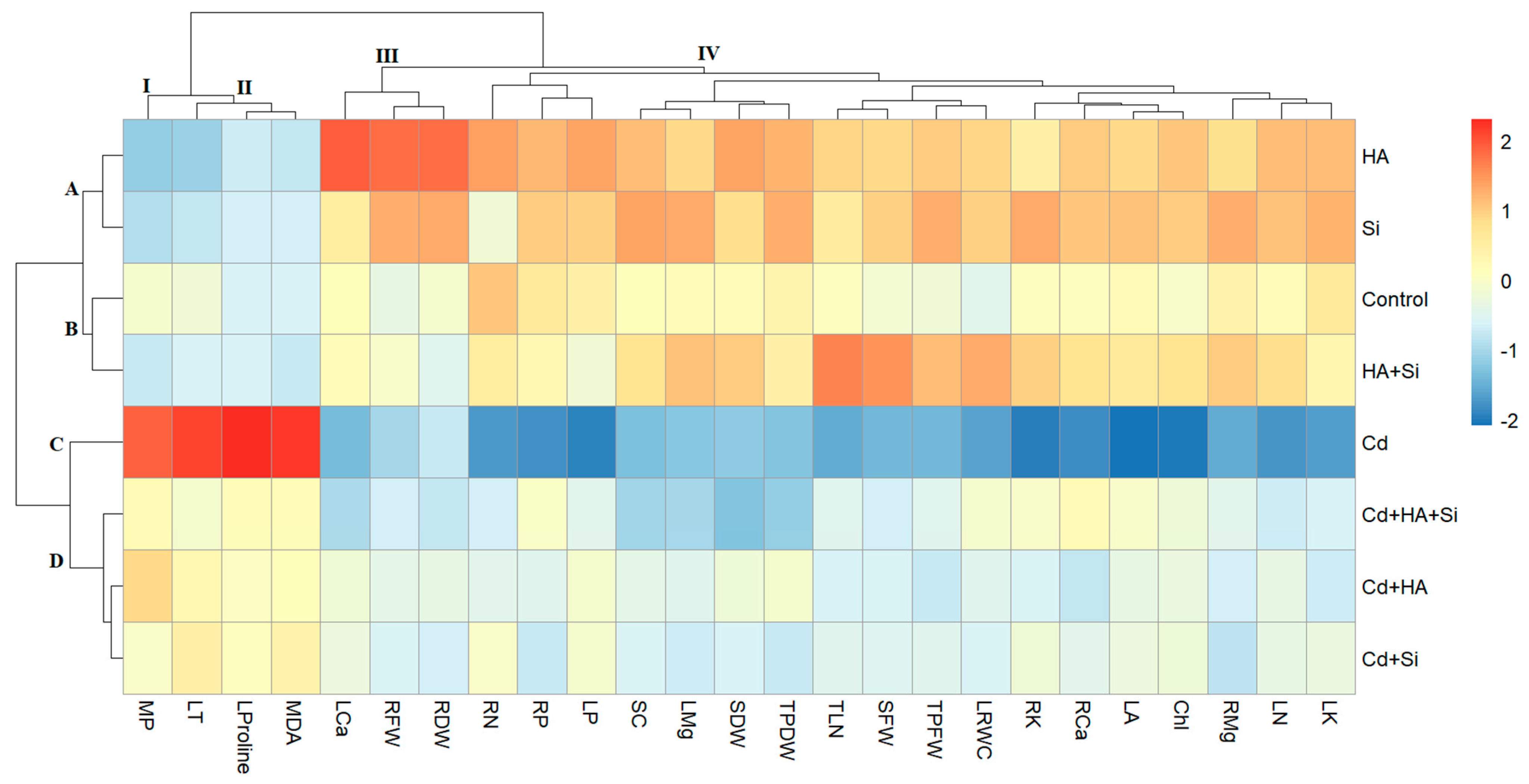

| Shoot Fresh Weight | Root Fresh Weight | Total Plant Fresh Weight | Shoot Dry Weight | Root Dry Weight | Total Plant Dry Weight | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 31.06 ± 0.31 b | 5.90 ± 0.08 b | 36.67 ± 0.38 b | 11.04 ± 0.42 a | 2.37 ± 0.14 b | 13.93 ± 0.42 b |
| Humic acid (HA) | 33.99 ± 0.95 a | 9.42 ± 0.52 a | 41.13 ± 1.18 a | 11.79 ± 0.15 a | 3.37 ± 0.21 a | 15.30 ± 0.28 a |
| Silicon (Si) | 34.20 ± 1.28 a | 8.52 ± 0.27 a | 42.12 ± 1.51 a | 11.45 ± 0.17 a | 3.11 ± 0.14 a | 15.31± 0.30 a |
| Humic acid + silicon (HA + Si) | 35.73 ± 0.99 a | 6.43 ± 0.40 b | 41.70 ± 0.68 a | 11.56 ± 0.19 a | 2.16 ± 0.04 b | 14.11± 0.15 b |
| Cadmium | 27.35 ± 0.44 c | 4.86 ± 0.84 c | 32.00 ± 0.40 c | 10.17 ± 0.15 d | 2.03 ± 0.06 b | 11.50± 0.12 d |
| Cadmium + humic acid (Cd + HA) | 29.74 ± 0.16 b | 5.83 ± 0.24 b | 34.54 ± 0.39 b | 10.79 ± 0.27 b | 2.22 ± 0.12 b | 13.32± 0.26 b |
| Cadmium + silicon (Cd + Si) | 29.94 ± 0.96 b | 5.59 ± 0.94 b | 35.51 ± 1.01 b | 10.54 ± 0.20 c | 2.07 ± 0.05 b | 12.32 ± 0.18 c |
| Cadmium + humic acid + silicon (Cd + HA + Si) | 29.58 ± 0.39 b | 5.46 ± 0.18 b | 35.49 ± 0.54 b | 10.10 ± 0.24 d | 2.01 ± 0.06 c | 11.69 ± 0.20 e |
| Leaf Mineral Content | Root Mineral Content | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | P | K | Mg | Ca | N | P | K | Mg | Ca | |
| Control | 2.71 ± 0.05 a | 1.34 ± 0.04 a | 2.78 ± 0.03 a | 0.40 ± 0.03 a | 2.13 ± 0.04 c | 2.07 ± 0.02 a | 0.97 ± 0.02 a | 2.27 ± 0.09 a | 0.97 ± 0.02 a | 0.79 ± 0.05 ab |
| HA | 2.82 ± 0.03 a | 1.42 ± 0.04 a | 2.86 ± 0.02 a | 0.43 ± 0.02 a | 2.56 ± 0.02 a | 2.10 ± 0.03 a | 1.01 ± 0.01 a | 2.33 ± 0.04 a | 1.00 ± 0.05 a | 0.88 ± 0.07 a |
| Si | 2.81 ± 0.05 a | 1.39 ± 0.03 ab | 2.87 ± 0.04 a | 0.45 ± 0.01 a | 2.22 ± 0.01 b | 1.97 ± 0.02 b | 0.99 ± 0.02 ab | 2.49 ± 0.14 a | 1.03 ± 0.03 a | 0.88 ± 0.05 a |
| HA + Si | 2.78 ± 0.03 a | 1.29 ± 0.03 b | 2.73 ± 0.03 bc | 0.44 ± 0.02 a | 2.13 ± 0.02 c | 2.03 ± 0.01 b | 0.94 ± 0.03 b | 2.42 ± 0.03 b | 1.01 ± 0.01 b | 0.85 ± 0.03 b |
| Cd | 2.48 ± 0.08 c | 1.14 ± 0.03 c | 2.43 ± 0.04 e | 0.34 ± 0.03 b | 1.77 ± 0.02 d | 1.85 ± 0.02 d | 0.80 ± 0.01 d | 1.91 ± 0.03 c | 0.86 ± 0.03 d | 0.61 ± 0.02 d |
| Cd + HA | 2.65 ± 0.06 b | 1.30 ± 0.02 b | 2.58 ± 0.03 d | 0.37 ± 0.01 b | 2.05 ± 0.01 c | 1.95 ± 0.02 c | 0.89 ± 0.03 c | 2.16 ± 0.08 b | 0.91 ± 0.02 b | 0.71 ± 0.04 c |
| Cd + Si | 2.64 ± 0.05 ab | 1.30 ± 0.03 b | 2.64 ± 0.03 cd | 0.36 ± 0.01 b | 2.03 ± 0.02 c | 1.99 ± 0.01 bc | 0.87 ± 0.02 c | 2.23 ± 0.07 b | 0.90 ± 0.03 c | 0.74 ± 0.05 a |
| Cd + Ha + Si | 2.60 ± 0.04 b | 1.27 ± 0.04 b | 2.59 ± 0.04 d | 0.35 ± 0.01 b | 1.86 ± 0.02 d | 1.94 ± 0.01 c | 0.92 ± 0.01 c | 2.25 ± 0.07 b | 0.92 ± 0.01 b | 0.80 ± 0.03 a |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dogan, M.; Bolat, I.; Karakas, S.; Dikilitas, M.; Gutiérrez-Gamboa, G.; Kaya, O. Remediation of Cadmium Stress in Strawberry Plants Using Humic Acid and Silicon Applications. Life 2022, 12, 1962. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12121962
Dogan M, Bolat I, Karakas S, Dikilitas M, Gutiérrez-Gamboa G, Kaya O. Remediation of Cadmium Stress in Strawberry Plants Using Humic Acid and Silicon Applications. Life. 2022; 12(12):1962. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12121962
Chicago/Turabian StyleDogan, Meral, Ibrahim Bolat, Sema Karakas, Murat Dikilitas, Gastón Gutiérrez-Gamboa, and Ozkan Kaya. 2022. "Remediation of Cadmium Stress in Strawberry Plants Using Humic Acid and Silicon Applications" Life 12, no. 12: 1962. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12121962
APA StyleDogan, M., Bolat, I., Karakas, S., Dikilitas, M., Gutiérrez-Gamboa, G., & Kaya, O. (2022). Remediation of Cadmium Stress in Strawberry Plants Using Humic Acid and Silicon Applications. Life, 12(12), 1962. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12121962








