Sex-Specific Differences in Extracellular Vesicle Protein Cargo in Synovial Fluid of Patients with Osteoarthritis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Samples
2.2. Preparation of Exosome-Enriched Fractions
2.3. Exosome Protein Extraction, Digestion, and LC-MS/MS Analysis
2.4. Normalization, Statistical Analysis, and Pathway Analysis of Female-Specific Protein
3. Results
3.1. EV Protein Cargo Differs Significantly between Male and Female Patients with OA
3.2. DAVID and QuickGO Analysis of Differentially Expressed Proteins
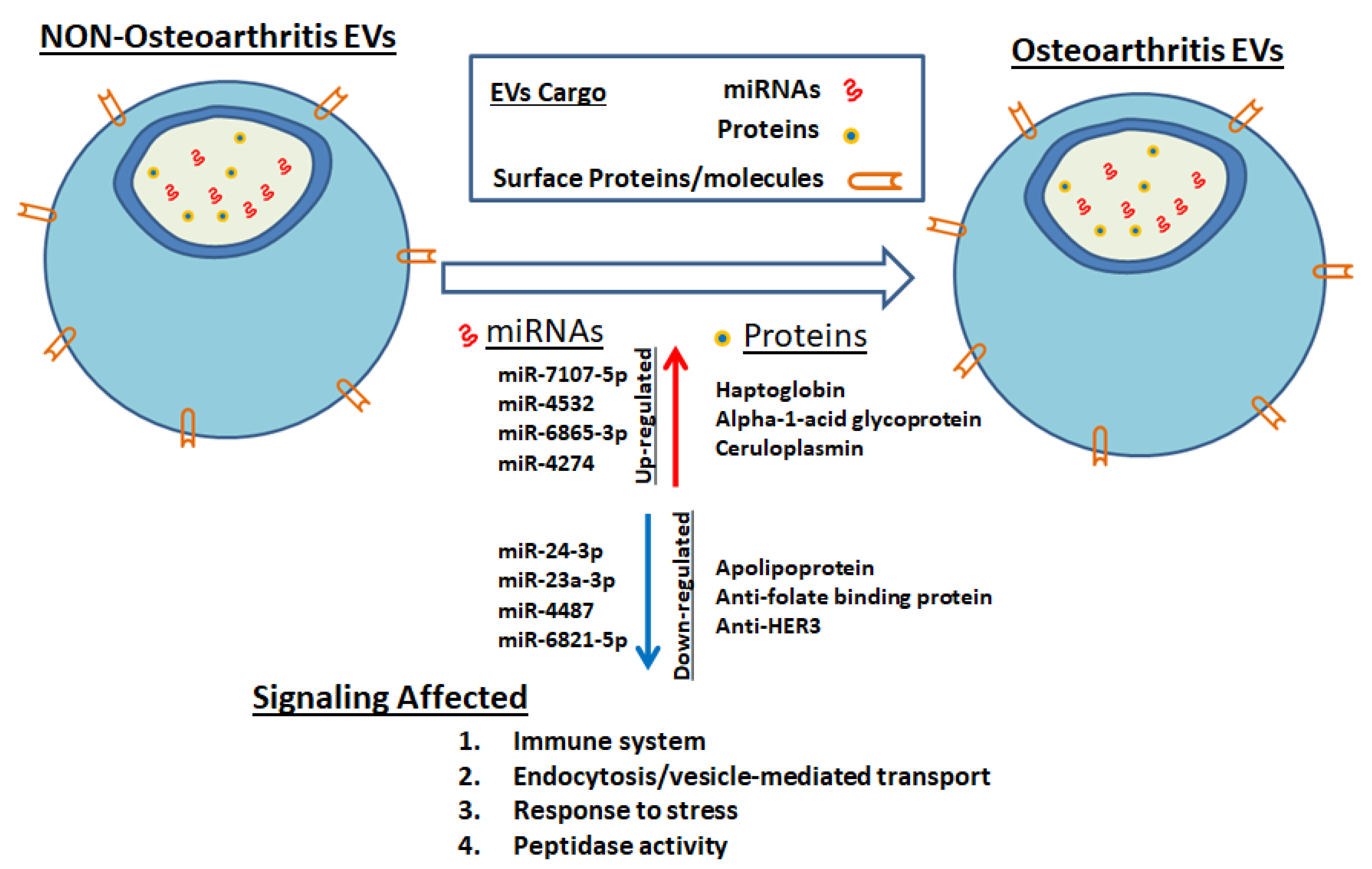
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Murphy, L.; Helmick, C.G. The impact of osteoarthritis in the United States: A population-health perspective. Am. J. Nurs. 2012, 112, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawrence, R.C.; Felson, D.T.; Helmick, C.G.; Arnold, L.M.; Choi, H.; Deyo, R.A.; Gabriel, S.; Hirsch, R.; Hochberg, M.C.; Hunder, G.G.; et al. Estimates of the prevalence of arthritis and other rheumatic conditions in the United States: Part II. Arthritis Rheum. 2008, 58, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hame, S.L.; Alexander, R.A. Knee osteoarthritis in women. Curr. Rev. Musculoskelet. Med. 2013, 6, 182–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’connor, M.I. Sex Differences in Osteoarthritis of the Hip and Knee. J. Am. Acad. Orthop. Surg. 2007, 15, S22–S25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piva, S.R.; Susko, A.M.; Khoja, S.S.; Josbeno, D.A.; Fitzgerald, G.K.; Toledo, F.G.S. Links between osteoarthritis and diabetes: Implications for management from a physical activity perspective. Clin. Geriatr. Med. 2015, 31, 67–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menashe, L.; Hirko, K.; Losina, E.; Kloppenburg, M.; Zhang, W.; Li, L.; Hunter, D.J. The diagnostic performance of MRI in osteoarthritis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2012, 20, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iolascon, G.; Gimigliano, F.; Moretti, A.; De Sire, A.; Migliore, A.; Brandi, M.; Piscitelli, P. Early osteoarthritis: How to define, diagnose, and manage. A systematic review. Eur. Geriatr. Med. 2017, 8, 383–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Sire, A.; De Sire, R.; Petito, V.; Masi, L.; Cisari, C.; Gasbarrini, A.; Scaldaferri, F.; Invernizzi, M. Gut–Joint Axis: The Role of Physical Exercise on Gut Microbiota Modulation in Older People with Osteoarthritis. Nutrients 2020, 12, 574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damiani, C.; Mangone, M.; Paoloni, M.; Goffredo, M.; Franceschini, M.; Servidio, M.; Pournajaf, S.; Santilli, V.; Agostini, F.; Bernetti, A. Trade-Offs with rehabilitation Effectiveness (REs) and Efficiency (REy) in a sample of Italian disabled persons in a in post-acuity rehabilitation unit. Ann. Ig. 2020, 32, 327–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Sire, A.; Stagno, D.; Minetto, M.A.; Cisari, C.; Baricich, A.; Invernizzi, M. Long-term effects of intra-articular oxygen-ozone therapy versus hyaluronic acid in older people affected by knee osteoarthritis: A randomized single-blind extension study. J. Back Musculoskelet Rehabil. 2020, 33, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santilli, V.; Mangone, M.; Paoloni, M.; Agostini, F.; Alviti, F.; Bernetti, A. Comment on Early Efficacy of Intra-Articular HYADD® 4 (Hymovis®) Injections for Symptomatic Knee Osteoarthritis. Joints 2018, 6, 131–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabini, A.; De Sire, A.; Marzetti, E.; Gimigliano, R.; Ferriero, G.; Piazzini, D.B.; Iolascon, G.; Gimigliano, F. Effects of focal muscle vibration on physical functioning in patients with knee osteoarthritis: A randomized controlled trial. Eur. J. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 2015, 51. [Google Scholar]
- Liao, W.; Li, Z.; Zhang, H.; Li, J.; Wang, K.; Yang, Y. Proteomic analysis of synovial fluid as an analytical tool to detect candidate biomarkers for knee osteoarthritis. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2015, 8, 9975–9989. [Google Scholar]
- Mabey, T.; Honsawek, S.; Tanavalee, A.; Yuktanandana, P.; Wilairatana, V.; Poovorawan, Y. Plasma and synovial fluid inflammatory cytokine profiles in primary knee osteoarthritis. Biomarkers 2016, 21, 639–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolhe, R.; Hunter, M.; Liu, S.; Jadeja, R.N.; Pundkar, C.; Mondal, A.K.; Mendhe, B.; Drewry, M.; Rojiani, M.V.; Liu, Y.; et al. Gender-specific differential expression of exosomal miRNA in synovial fluid of patients with osteoarthritis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rashed, M.H.; Bayraktar, E.; Helal, G.K.; Abd-Ellah, M.F.; Amero, P.; Chavez-Reyes, A.; Rodriguez-Aguayo, C. Exosomes: From Garbage Bins to Promising Therapeutic Targets. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Withrow, J.; Murphy, C.; Liu, Y.; Hunter, M.; Fulzele, S.; Hamrick, M.W. Extracellular vesicles in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis. Arthritis Res. 2016, 18, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domenis, R.; Zanutel, R.; Caponnetto, F.; Toffoletto, B.; Cifù, A.; Pistis, C.; Di Benedetto, P.; Causero, A.; Pozzi, M.; Bassini, F. Characterization of the pro-inflammatory profile of synovial fluid-derived exosomes of patients with osteoarthritis. Mediat. Inflamm. 2017, 2017, 4814987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berckmans, R.J.; Nieuwland, R.; Kraan, M.C.; Schaap, M.C.L.; Pots, D.; Smeets, T.J.M.; Sturk, A.; Tak, P.P. Synovial microparticles from arthritic patients modulate chemokine and cytokine release by synoviocytes. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2005, 7, R536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yu, D.; Liu, Z.; Zhou, F.; Dai, J.; Wu, B.; Zhou, J.; Heng, B.C.; Zou, X.H.; Ouyang, H.; et al. Exosomes from embryonic mesenchymal stem cells alleviate osteoarthritis through balancing synthesis and degradation of cartilage extracellular matrix. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2017, 8, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tofiño-Vian, M.; Guillén, M.I.; Del Caz, M.D.P.; Silvestre, A.; Alcaraz, M.J. Microvesicles from Human Adipose Tissue-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells as a New Protective Strategy in Osteoarthritic Chondrocytes. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 47, 11–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helwa, I.; Cai, J.; Drewry, M.D.; Zimmerman, A.; Dinkins, M.B.; Khaled, M.L.; Seremwe, M.; Dismuke, W.M.; Bieberich, E.; Stamer, W.D.; et al. A Comparative Study of Serum Exosome Isolation Using Differential Ultracentrifugation and Three Commercial Reagents. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0170628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rider, M.A.; Hurwitz, S.N.; Meckes, D.G., Jr. ExtraPEG: A Polyethylene Glycol-Based Method for Enrichment of Extracellular Vesicles. Sci. Rep. 2016, 12, 23978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, S.; Bollinger, K.E.; Kodeboyina, S.K.; Zhi, W.; Patton, J.; Bai, S.; Edwards, B.; Ulrich, L.; Bogorad, D.; Sharma, A. Proteomic Alterations in Aqueous Humor From Patients With Primary Open Angle Glaucoma. Investig. Opthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2018, 59, 2635–2643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dasari, R.; Zhi, W.; Bonsack, F.; Sukumari-Ramesh, S. A Combined Proteomics and Bioinformatics Approach Reveals Novel Signaling Pathways and Molecular Targets After Intracerebral Hemorrhage. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2020, 70, 1186–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, D.W.; Sherman, B.T.; Lempicki, R.A. Systematic and integrative analysis of large gene lists using DAVID bioinformatics resources. Nat. Protoc. 2009, 4, 44–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.W.; Sherman, B.T.; Lempicki, R.A. Bioinformatics enrichment tools: Paths toward the comprehensive functional analysis of large gene lists. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binns, D.; Dimmer, E.; Huntley, R.; Barrell, D.; O’Donovan, C.; Apweiler, R. QuickGO: A web-based tool for Gene Ontology searching. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 3045–3046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munjal, A.; Bapat, S.; Hubbard, D.; Hunter, M.; Kolhe, R.; Fulzele, S. Advances in Molecular biomarker for early diagnosis of Osteoarthritis. Biomol. Concepts 2019, 10, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruger, S.; Elmageed, Z.Y.A.; Hawke, D.H.; Wörner, P.M.; Jansen, D.A.; Abdel-Mageed, A.B.; Alt, E.; Izadpanah, R. Molecular characterization of exosome-like vesicles from breast cancer cells. BMC Cancer 2014, 14, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eitan, E.; Green, J.; Bodogai, M.; Mode, N.A.; Bæk, R.; Jørgensen, M.M.; Freeman, D.W.; Witwer, K.W.; Zonderman, A.B.; Biragyn, A.; et al. Age-Related Changes in Plasma Extracellular Vesicle Characteristics and Internalization by Leukocytes. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fulzele, S.; Mendhe, B.; Khayrullin, A.; Johnson, M.; Kaiser, H.; Liu, Y.; Isales, C.M.; Hamrick, M.W. Muscle-derived miR-34a increases with age in circulating extracellular vesicles and induces senescence of bone marrow stem cells. Aging 2019, 11, 1791–1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saha, B.; Momen-Heravi, F.; Furi, I.; Kodys, K.; Catalano, D.; Gangopadhyay, A.; Haraszti, R.; Satishchandran, A.; Iracheta-Vellve, A.; Adejumo, A.; et al. Extracellular vesicles from mice with alcoholic liver disease carry a distinct protein cargo and induce macrophage activation through heat shock protein 90. Hepatology 2018, 67, 1986–2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sammour, R.N.; Nakhoul, F.; Levy, A.P.; Miller-Lotan, R.; Nakhoul, N.; Awad, H.R.; Gonen, R.; Ohel, G. Haptoglobin phenotype in women with preeclampsia. Endocrine 2010, 38, 303–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez-Blasco, F.; Martínez-García, M.Á.; Luque-Ramírez, M.; Parraza, N.; Millán, J.L.S.; Escobar-Morreale, H.F. Role of Haptoglobin in Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS), Obesity and Disorders of Glucose Tolerance in Premenopausal Women. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e5606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berkova, N.; Lemay, A.; Dresser, D.W.; Fontaine, J.-Y.; Kerizit, J.; Goupil, S. Haptoglobin is present in human endometrium and shows elevated levels in the decidua during pregnancy. Mol. Hum. Reprod. 2001, 7, 747–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, K.Y.; Huang, S.-Y.; Cheng, T.-M.; Bai, C.-H.; Chang, J.-S. Haptoglobin phenotype influences the effectiveness of diet-induced weight loss in middle-age abdominally obese women with metabolic abnormalities. Clin. Nutr. 2020, 39, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huntoon, K.M.; Wang, Y.; Eppolito, C.A.; Barbour, K.W.; Berger, F.G.; Shrikant, P.A.; Kawasaki, T. The acute phase protein haptoglobin regulates host immunity. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2008, 84, 170–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smeets, M.B.; Fontijn, J.; Kavelaars, A.; Pasterkamp, G.; De Kleijn, D.P. The acute phase protein haptoglobin is locally expressed in arthritic and oncological tissues. Int. J. Exp. Pathol. 2003, 84, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghafouri, B.; Carlsson, A.; Holmberg, S.; Thelin, A.; Tagesson, C. Biomarkers of systemic inflammation in farmers with musculoskeletal disorders; a plasma proteomic study. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2016, 17, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Puente, P.; Calamia, V.; González-Rodríguez, L.; Lourido, L.; Camacho-Encina, M.; Oreiro, N.; Ruiz-Romero, C.; Blanco, F.J. Multiplexed mass spectrometry monitoring of biomarker candidates for osteoarthritis. J. Proteom. 2017, 152, 216–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, H.J.; Oh, M.-K.; Kim, N.-H.; Cho, M.-L.; Kim, I.-S. Identification of a specific haptoglobin C-terminal fragment in arthritic synovial fluid and its effect on interleukin-6 expression. Immunology 2013, 140, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magid, E.; Guldager, H.; Hesse, D.; Christiansen, M.S. Monitoring Urinary Orosomucoid in Acute Inflammation: Observations on Urinary Excretion of Orosomucoid, Albumin, α1-Microglobulin, and IgG. Clin. Chem. 2005, 51, 2052–2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ligresti, G.; Aplin, A.C.; Dunn, B.E.; Morishita, A.; Nicosia, R.F. The Acute Phase Reactant Orosomucoid-1 Is a Bimodal Regulator of Angiogenesis with Time- and Context-Dependent Inhibitory and Stimulatory Properties. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e41387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.; Lei, H.; Sun, Y.; Liu, X.; Su, D.-F. Orosomucoid, an acute response protein with multiple modulating activities. J. Physiol. Biochem. 2015, 71, 329–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rangé, H.; Poitou, C.; Boillot, A.; Ciangura, C.; Katsahian, S.; Lacorte, J.-M.; Czernichow, S.; Meilhac, O.; Bouchard, P.; Chaussain, C. Orosomucoid, a New Biomarker in the Association between Obesity and Periodontitis. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e57645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komori, H.; Watanabe, H.; Shuto, T.; Kodama, A.; Maeda, H.; Watanabe, K.; Kai, H.; Otagiri, M.; Maruyama, T. α1-Acid Glycoprotein Up-regulates CD163 via TLR4/CD14 Protein Pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 30688–30700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Qin, Z.; Wan, J.-J.; Wang, P.-Y.; Yang, Y.-L.; Yu, J.-G.; Hu, B.-H.; Su, D.-F.; Luo, Z.-M.; Liu, X. Estrogen weakens muscle endurance via estrogen receptor-p38 MAPK-mediated orosomucoid (ORM) suppression. Exp. Mol. Med. 2018, 50, e463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roman-Blas, J.; Castañeda, S.; Largo, R.; Herrero-Beaumont, G. Osteoarthritis associated with estrogen deficiency. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2009, 11, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, J.H.; Bang, C.H.; Song, G.G.; Kim, C.; Kim, J.-H.; Choi, S.J. Knee osteoarthritis and menopausal hormone therapy in postmenopausal women. Menopause 2019, 26, 598–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watt, F.M. Musculoskeletal pain and menopause. Post Reprod. Health 2018, 24, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khadilkar, S.S. Musculoskeletal Disorders and Menopause. J. Obstet. Gynecol. India 2019, 69, 99–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Xu, J. Synovial fluid-derived exosomal lncRNA PCGEM1 as biomarker for the different stages of osteoarthritis. Int. Orthop. 2018, 42, 2865–2872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, T.; Miyaki, S.; Ishitobi, H.; Nakamura, Y.; Nakasa, T.; Lotz, M.K.; Ochi, M. Exosomes from IL-1β stimulated synovial fibroblasts induce osteoarthritic changes in articular chondrocytes. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2014, 16, R163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
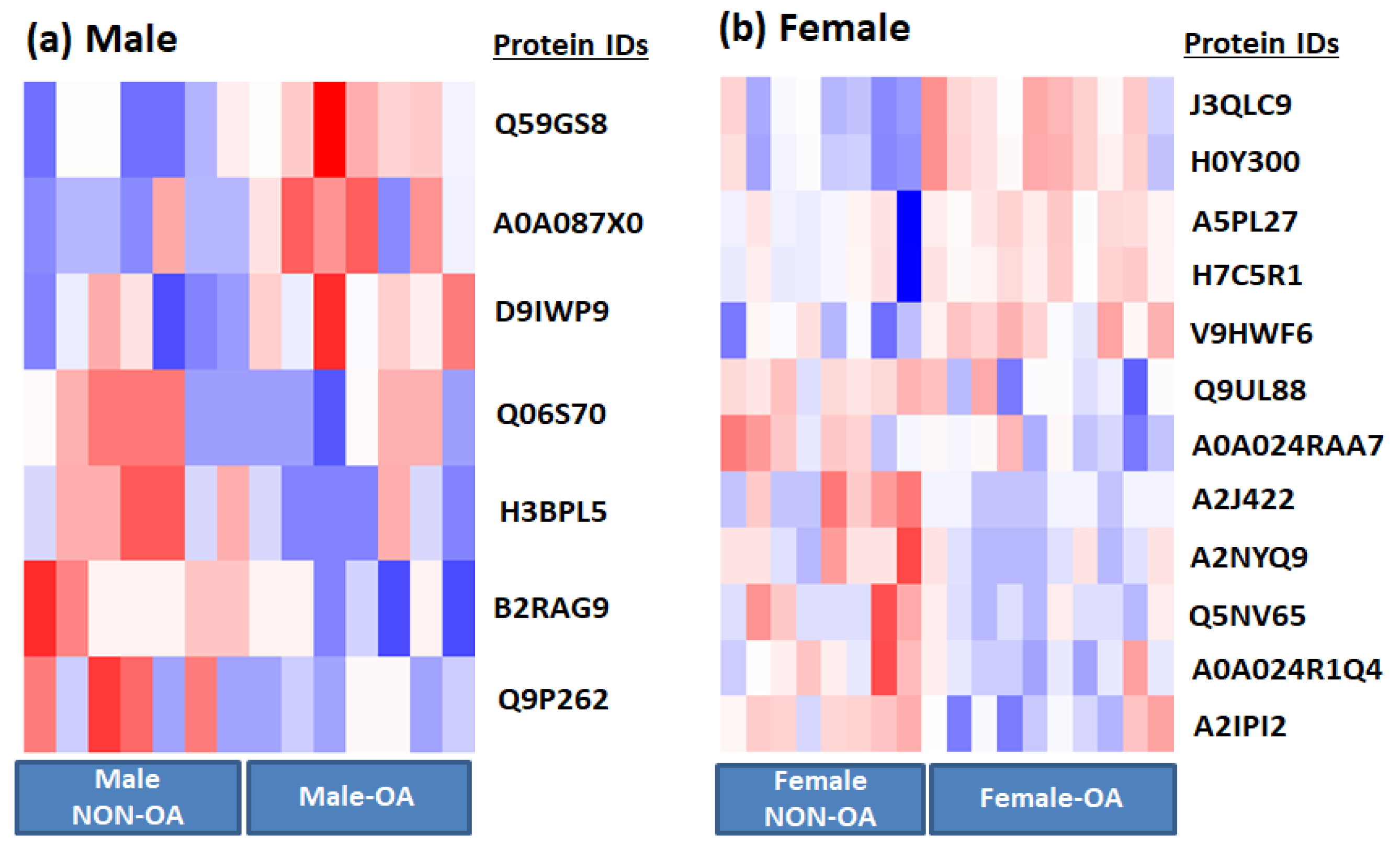
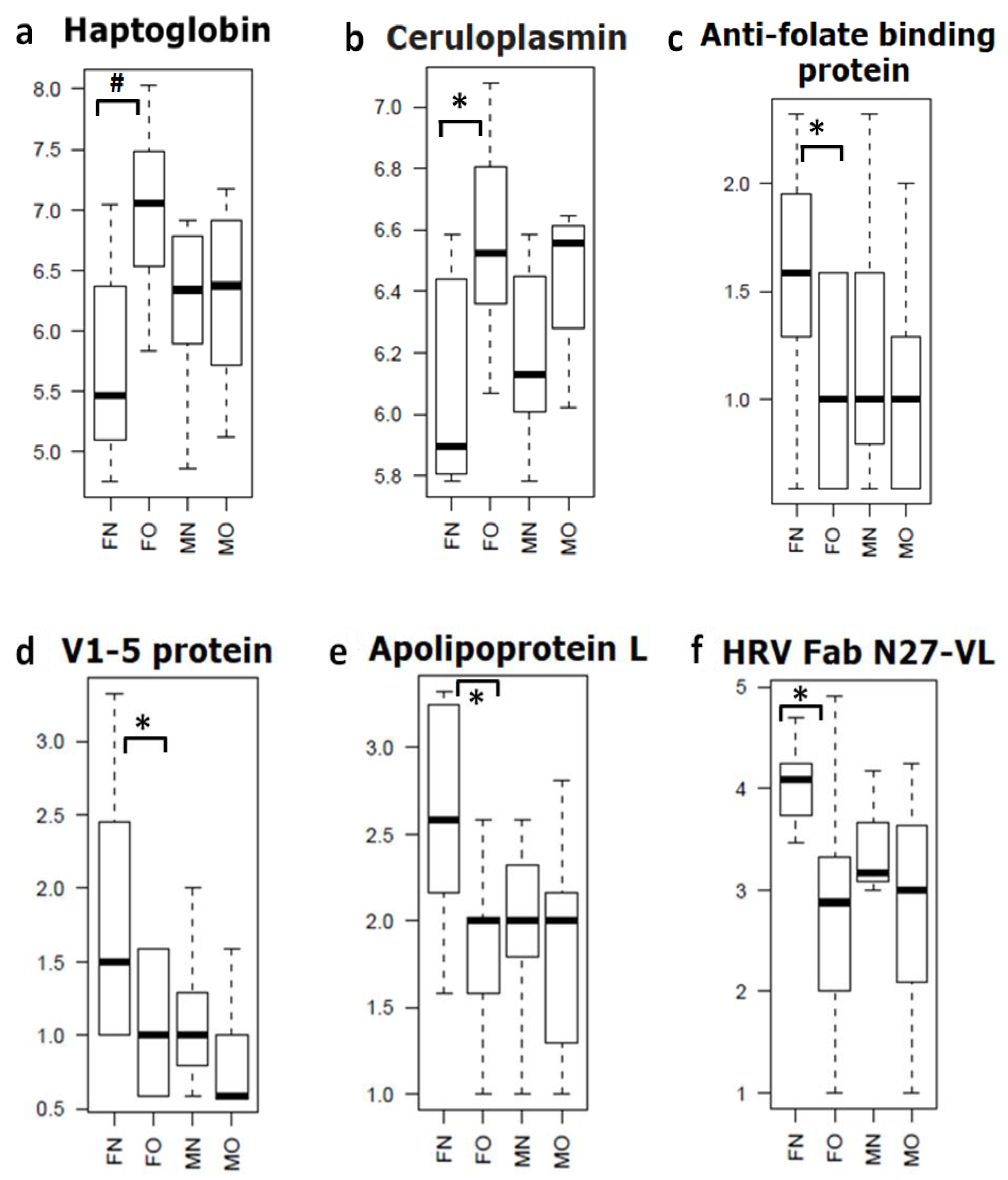

| Serial.No | Gene Name/Description | Fold Change | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| (a) | |||
| 1 | Haptoglobin (Fragment) GN = HP | 2.46 | 0.001 |
| 2 | Haptoglobin GN = HP | 2.32 | 0.001 |
| 3 | V1-5 protein (Fragment) GN = V1-5 | 0.60 | 0.014 |
| 4 | Alpha-1-acid glycoprotein GN = HEL-S-153w | 1.47 | 0.022 |
| 5 | Anti-HER3 scFv (Fragment) | 0.65 | 0.024 |
| 6 | Apolipoprotein L, 1, isoform CRA_c GN = APOL1 | 0.55 | 0.024 |
| 7 | Anti-folate binding protein (Fragment) GN = HuVH8B | 0.63 | 0.027 |
| 8 | Complement component 1, q subcomponent, C chain, isoform CRA_a GN = C1QC | 0.69 | 0.028 |
| 9 | HRV Fab N27-VL (Fragment) | 0.45 | 0.032 |
| 10 | Ceruloplasmin (Fragment) GN = CP | 1.93 | 0.032 |
| 11 | CP protein GN = CP | 2.01 | 0.034 |
| 12 | Myosin-reactive immunoglobulin heavy chain variable region (Fragment) | 0.80 | 0.038 |
| (b) | |||
| 1 | SAGA-associated factor 29 homolog GN = CCDC101 | 0.62 | 0.0002 |
| 2 | Collagen alpha-1(VI) chain GN = COL6A1 | 2.36 | 0.0060 |
| 3 | Complement component 5 variant (Fragment) | 2.77 | 0.0072 |
| 4 | KIAA1466 protein (Fragment) GN = KIAA1466 | 0.48 | 0.0085 |
| 5 | Beta-2-glycoprotein I (Fragment) | 1.94 | 0.0215 |
| 6 | cDNA, FLJ94908, highly similar to Homo sapiens PPAR binding protein (PPARBP), mRNA | 0.49 | 0.0283 |
| 7 | 3’-5’ exonuclease TREX2 long form | 0.72 | 0.0320 |
| GO Term | p Value |
|---|---|
| GO:0006898~receptor-mediated endocytosis | 0.00072 |
| GO:0004252~serine-type endopeptidase activity | 0.00134 |
| GO:0008236~serine-type peptidase activity | 0.00163 |
| GO:0017171~serine hydrolase activity | 0.00167 |
| GO:0006898~receptor-mediated endocytosis | 0.00232 |
| GO:0005576~extracellular region | 0.00257 |
| GO:0004175~endopeptidase activity | 0.00495 |
| GO:0006897~endocytosis | 0.00891 |
| GO:0070011~peptidase activity, acting on L-amino acid peptides | 0.00996 |
| GO:0008233~peptidase activity | 0.01066 |
| GO:0002376~immune system process | 0.01125 |
| GO:0016787~hydrolase activity | 0.01296 |
| GO:0016192~vesicle-mediated transport | 0.04203 |
| GO:0006955~immune response | 0.04508 |
| GO:0005576~extracellular region | 0.05286 |
| GO:0072562~blood microparticle | 0.00041 |
| GO:0005576~extracellular region | 0.00257 |
| GO:0002376~immune system process | 0.01125 |
| GO:0005615~extracellular space | 0.02962 |
| GO:0006950~response to stress | 0.03508 |
| GO:0006952~defense response | 0.04330 |
| Biological Function Involved | Signaling Involved |
|---|---|
| biological_process | lipid transport |
| biological_process | regulation of immune system process |
| biological_process | lipoprotein metabolic process |
| biological_process | receptor-mediated endocytosis |
| biological_process | Fc-epsilon receptor signaling pathway |
| biological_process | Fc-gamma receptor signaling pathway involved in phagocytosis |
| biological_process | complement activation |
| biological_process | complement activation, classical pathway |
| biological_process | proteolysis |
| biological_process | leukocyte migration |
| biological_process | regulation of immune response |
| biological_process | DNA recombination |
| biological_process | regulation of complement activation |
| molecular_function | hydrolase activity |
| molecular_function | ATP-dependent helicase activity |
| molecular_function | nucleic acid binding |
| molecular_function | serine-type endopeptidase activity |
| molecular_function | helicase activity |
| molecular_function | nucleotide binding |
| molecular_function | lipid binding |
| molecular_function | ATP binding |
| molecular_function | hemoglobin binding |
| cellular_component | extracellular region |
| cellular_component | nucleus |
| cellular_component | nucleoplasm |
| cellular_component | collagen trimer |
| cellular_component | extracellular space |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kolhe, R.; Owens, V.; Sharma, A.; Lee, T.J.; Zhi, W.; Ghilzai, U.; Mondal, A.K.; Liu, Y.; Isales, C.M.; Hamrick, M.W.; et al. Sex-Specific Differences in Extracellular Vesicle Protein Cargo in Synovial Fluid of Patients with Osteoarthritis. Life 2020, 10, 337. https://doi.org/10.3390/life10120337
Kolhe R, Owens V, Sharma A, Lee TJ, Zhi W, Ghilzai U, Mondal AK, Liu Y, Isales CM, Hamrick MW, et al. Sex-Specific Differences in Extracellular Vesicle Protein Cargo in Synovial Fluid of Patients with Osteoarthritis. Life. 2020; 10(12):337. https://doi.org/10.3390/life10120337
Chicago/Turabian StyleKolhe, Ravindra, Virgenal Owens, Ashok Sharma, Tae Jin Lee, Wenbo Zhi, Umar Ghilzai, Ashis K. Mondal, Yutao Liu, Carlos M. Isales, Mark W. Hamrick, and et al. 2020. "Sex-Specific Differences in Extracellular Vesicle Protein Cargo in Synovial Fluid of Patients with Osteoarthritis" Life 10, no. 12: 337. https://doi.org/10.3390/life10120337
APA StyleKolhe, R., Owens, V., Sharma, A., Lee, T. J., Zhi, W., Ghilzai, U., Mondal, A. K., Liu, Y., Isales, C. M., Hamrick, M. W., Hunter, M., & Fulzele, S. (2020). Sex-Specific Differences in Extracellular Vesicle Protein Cargo in Synovial Fluid of Patients with Osteoarthritis. Life, 10(12), 337. https://doi.org/10.3390/life10120337





