Influence of Blade Type on the Flow Structure of a Vortex Pump for Solid-Liquid Two-Phase Flow
Abstract
1. Introduction
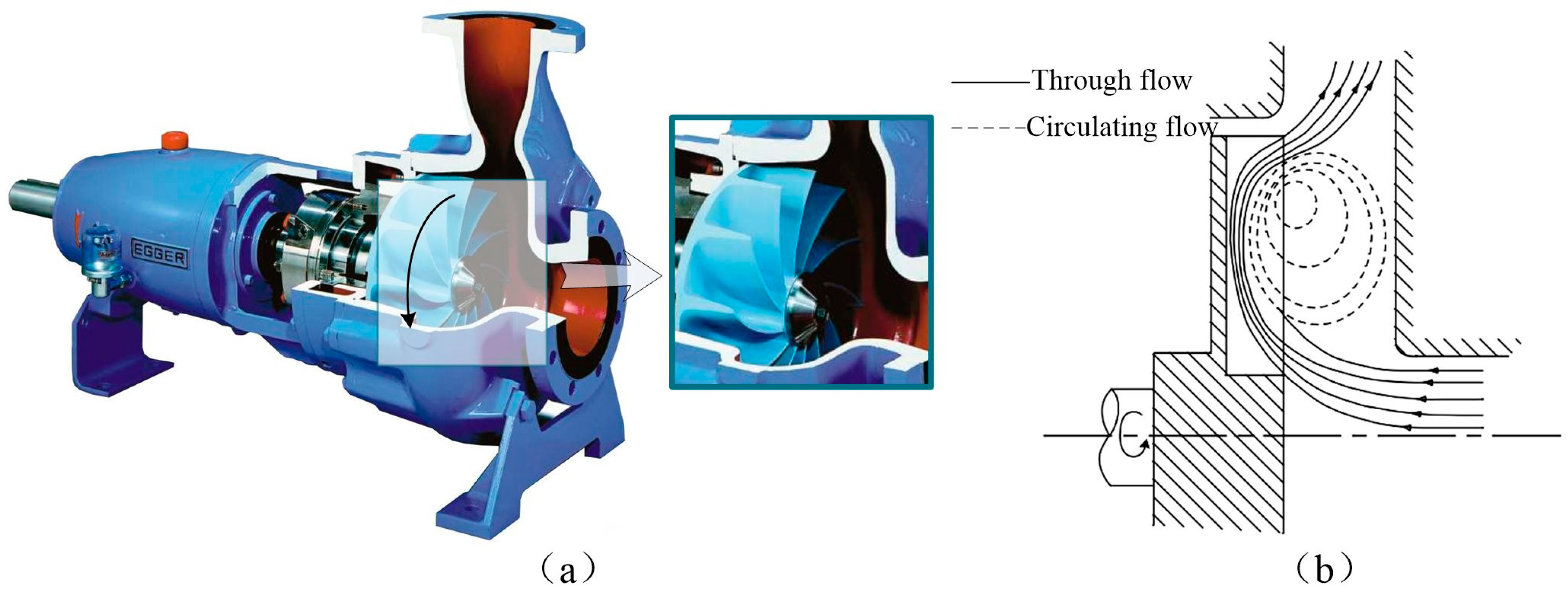
2. Vortex Pump Model and Numerical Method
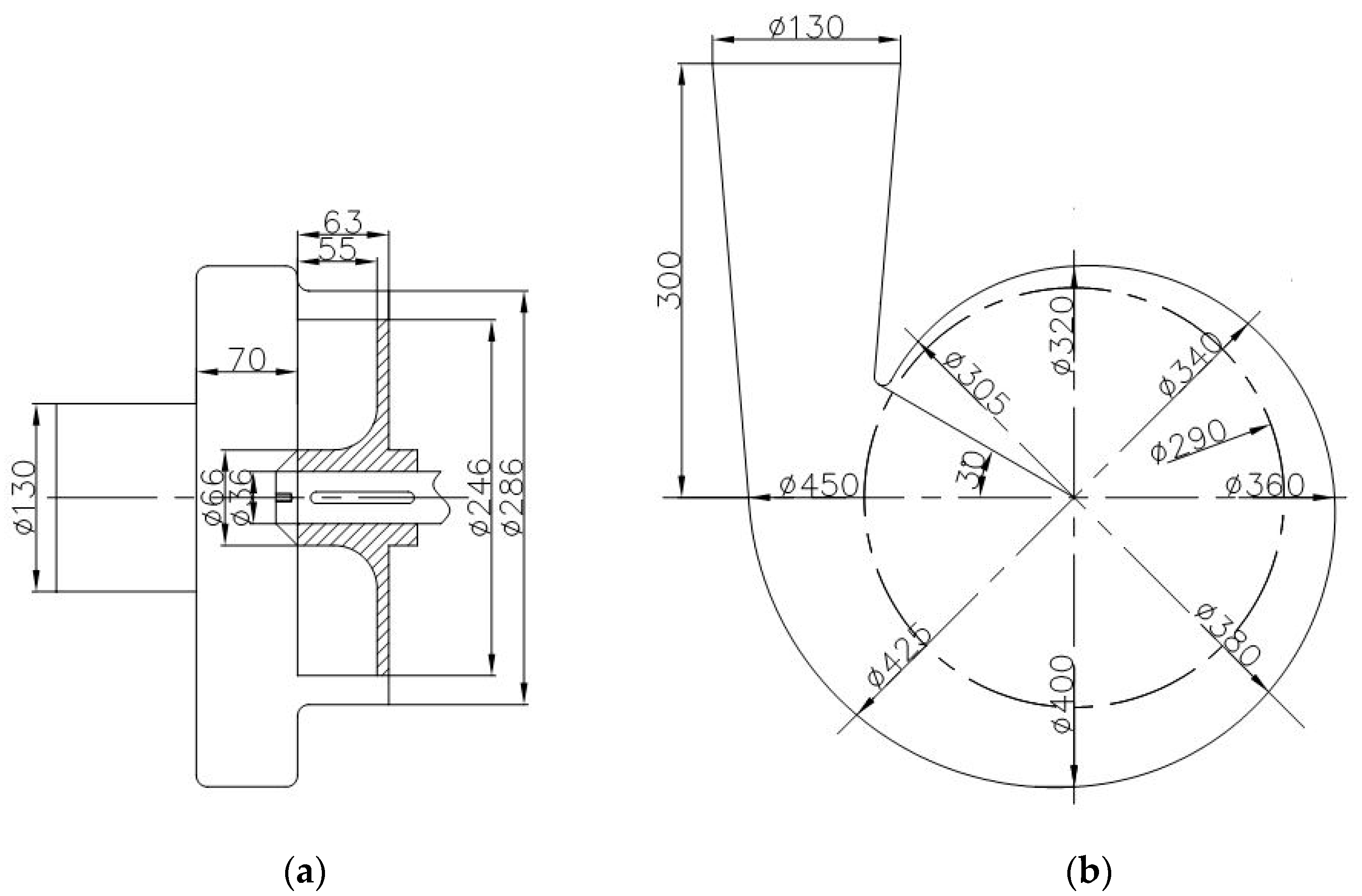
2.1. Design of the Model Pump and Geometric Parameters
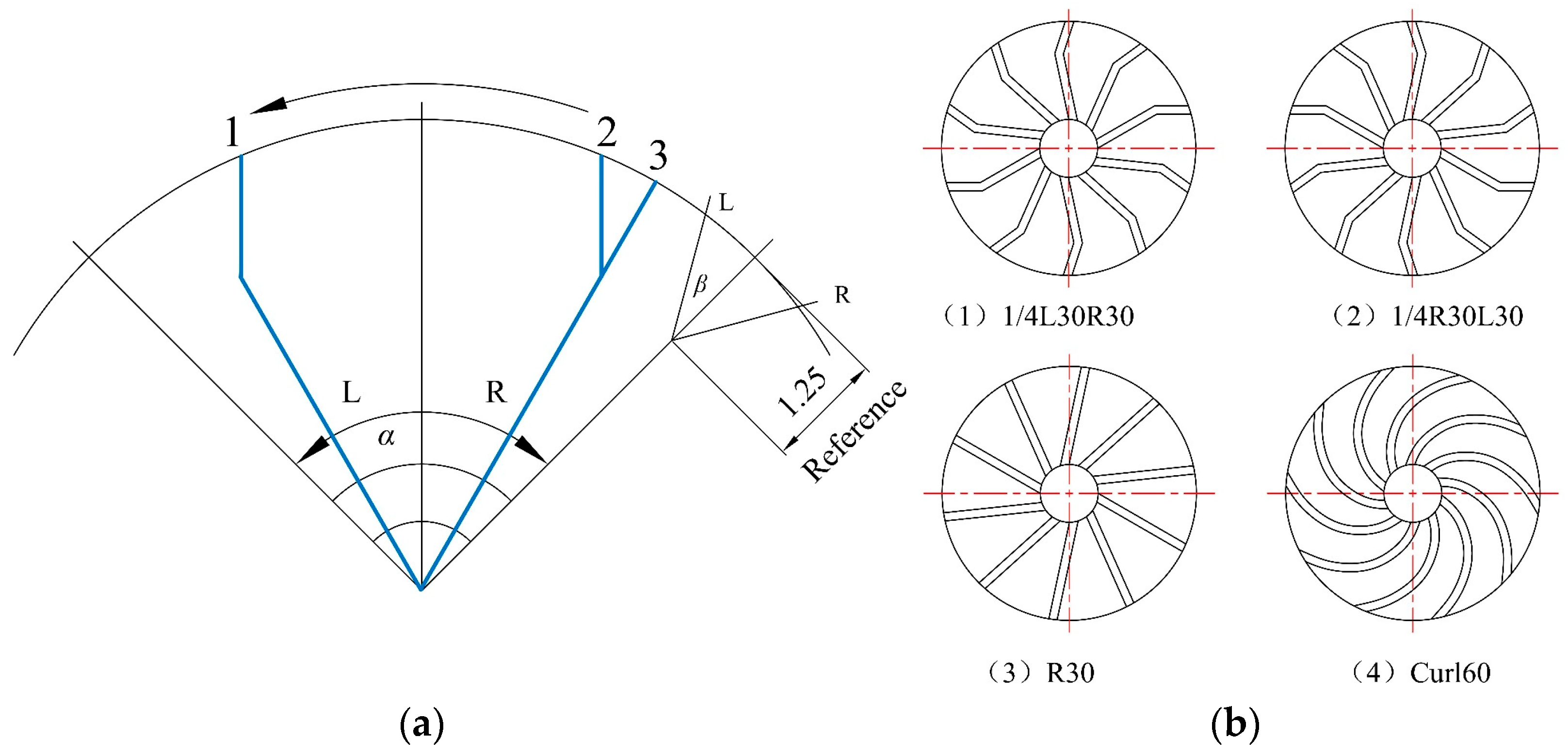
2.2. Blade Design
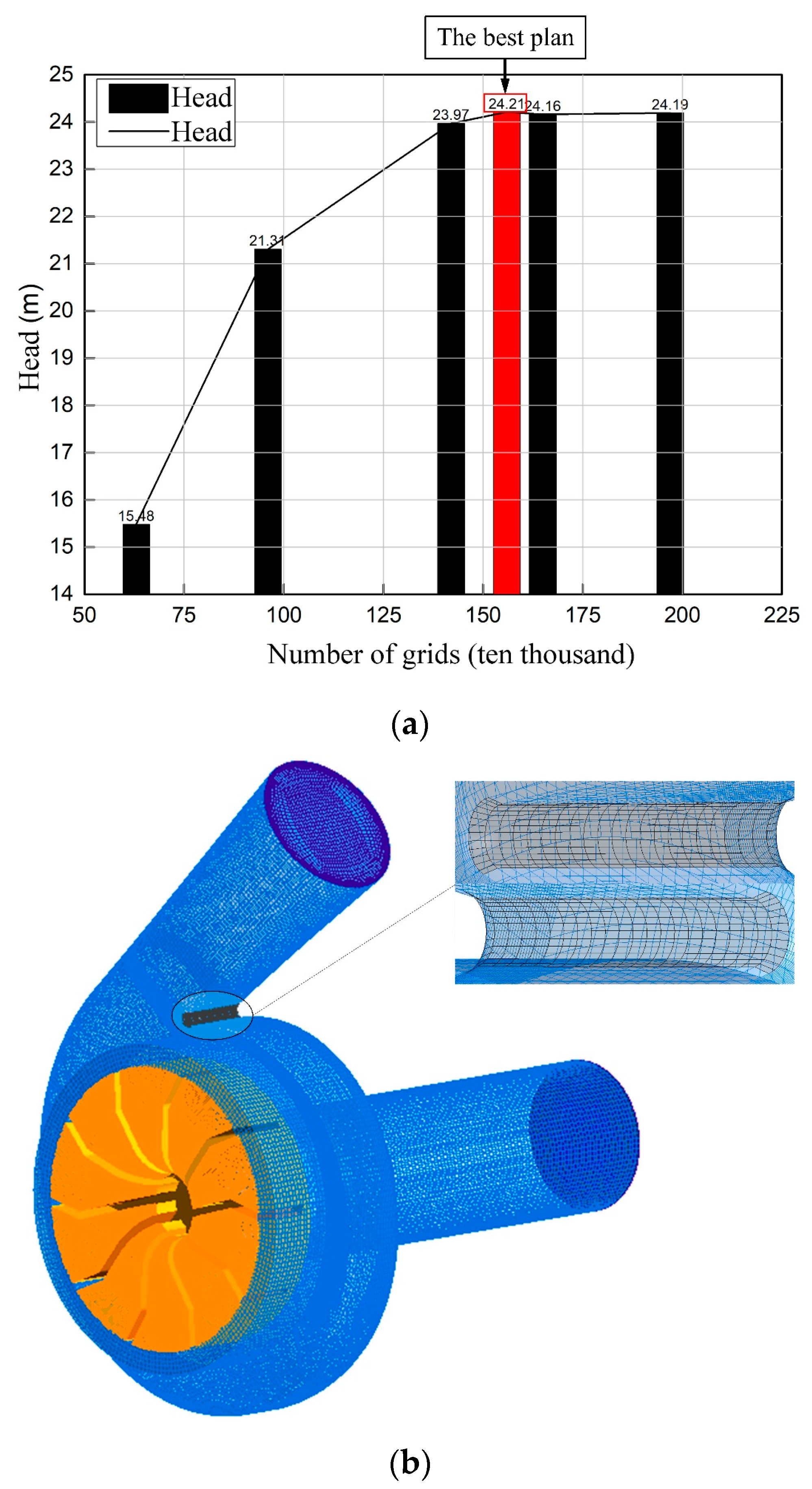
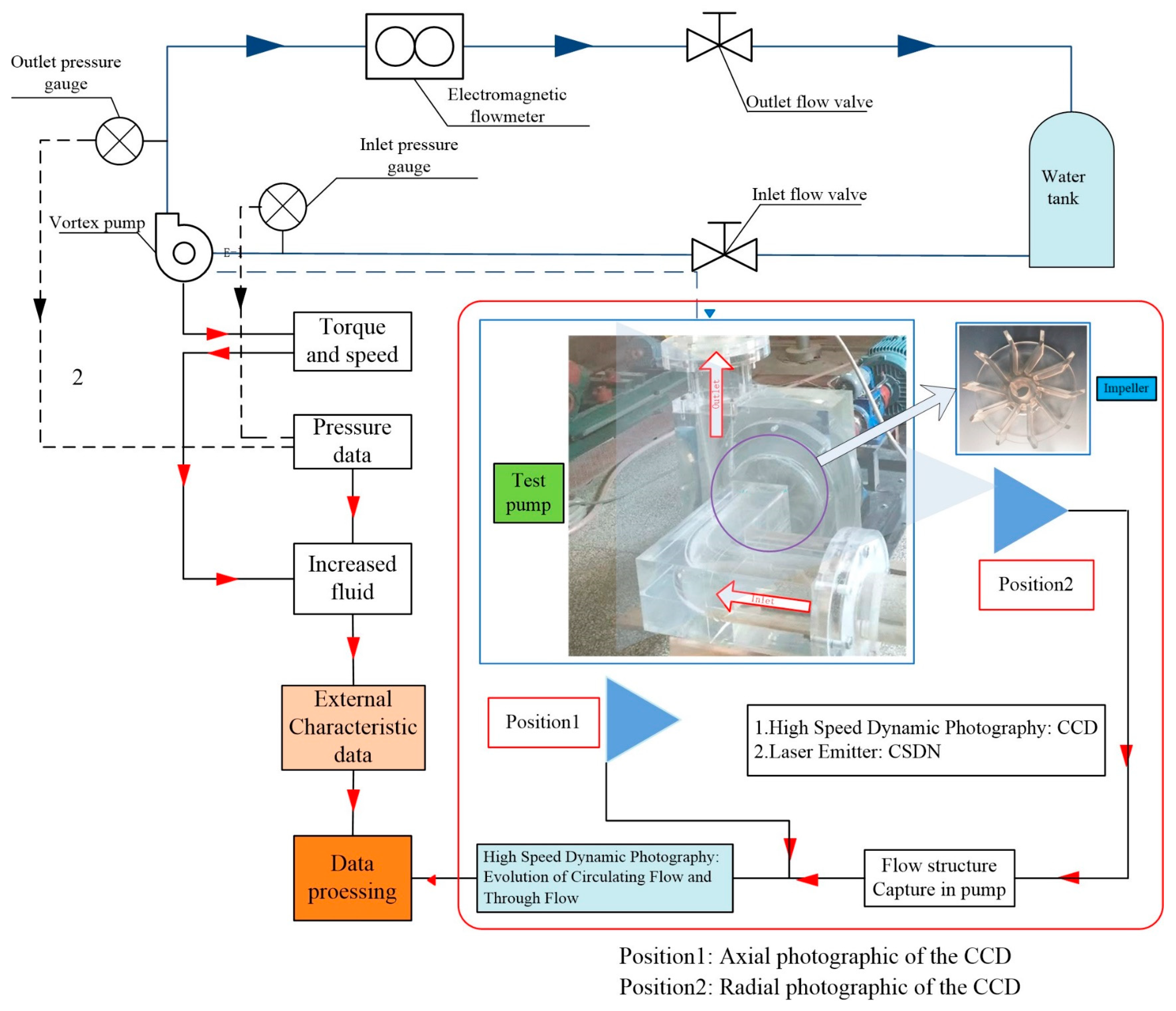
2.3. Model Construction and Meshing
3. Calculation Method
3.1. Determination of Characterization Parameters
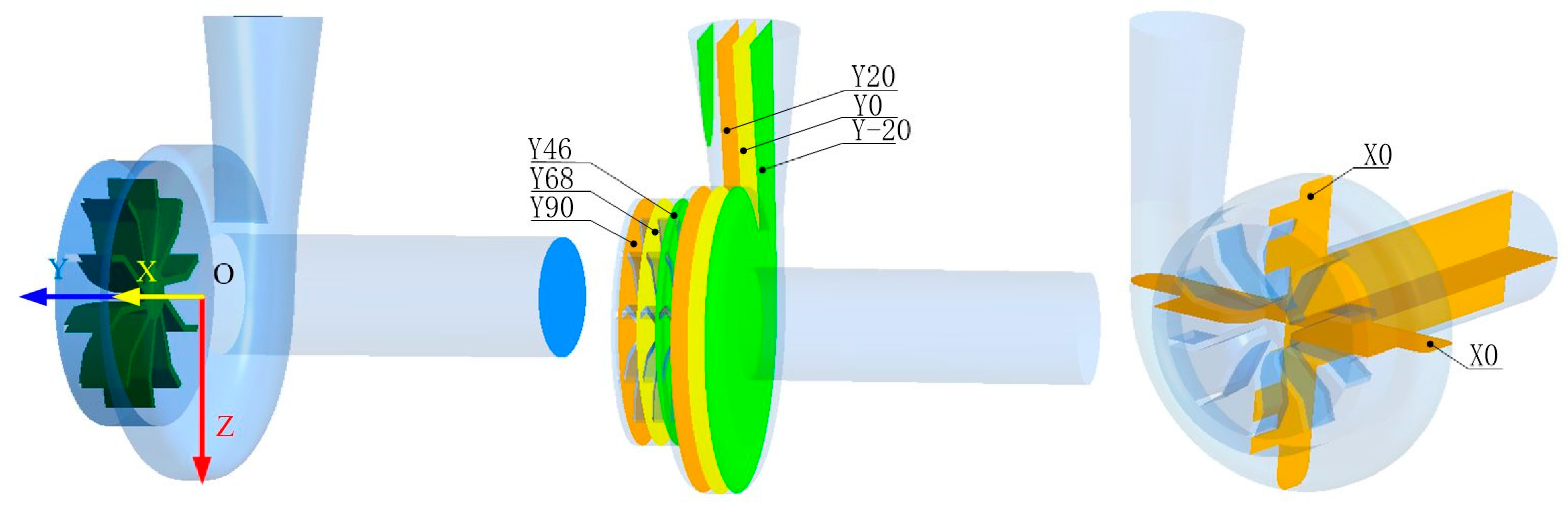
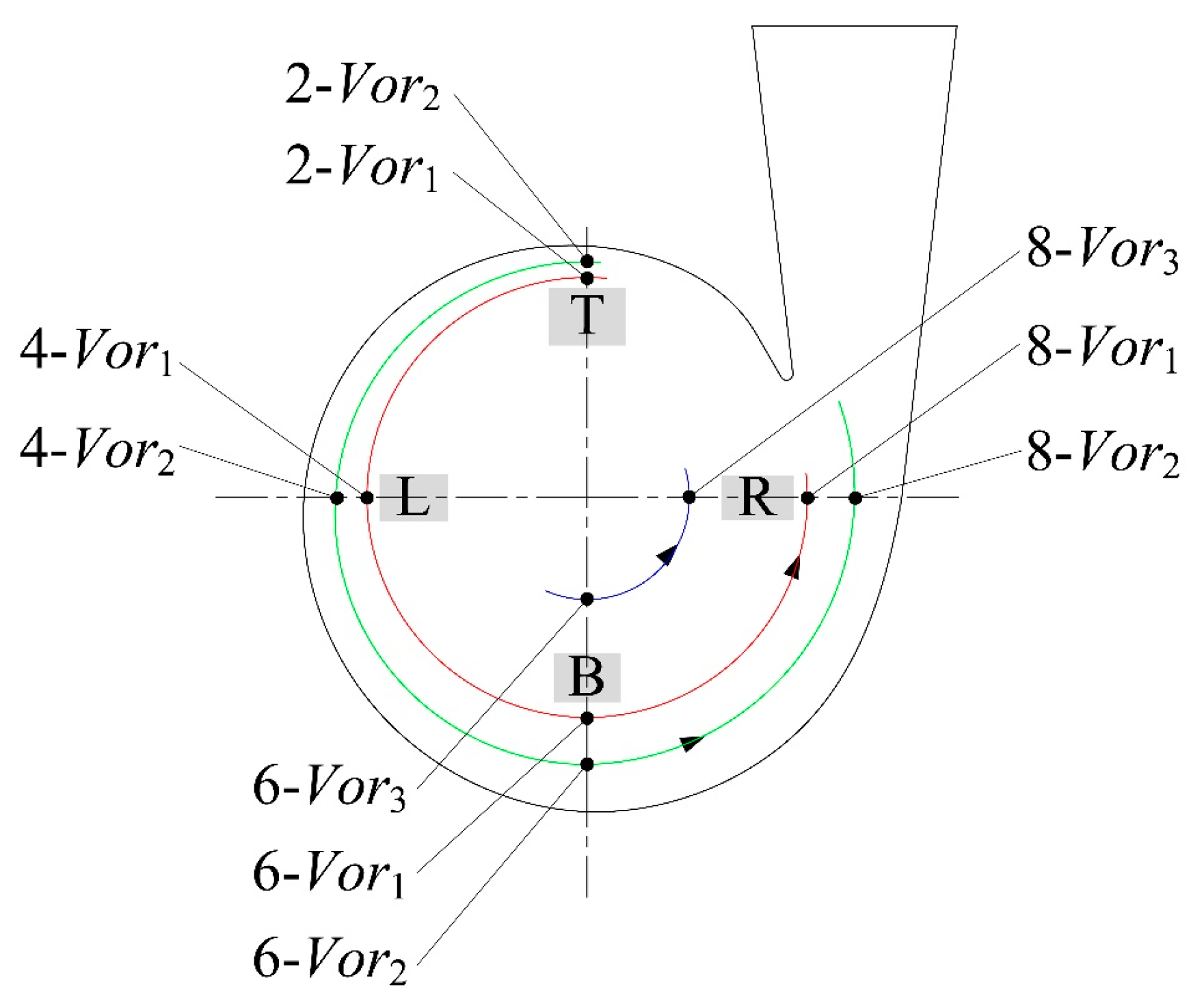
3.1.1. Section Selection
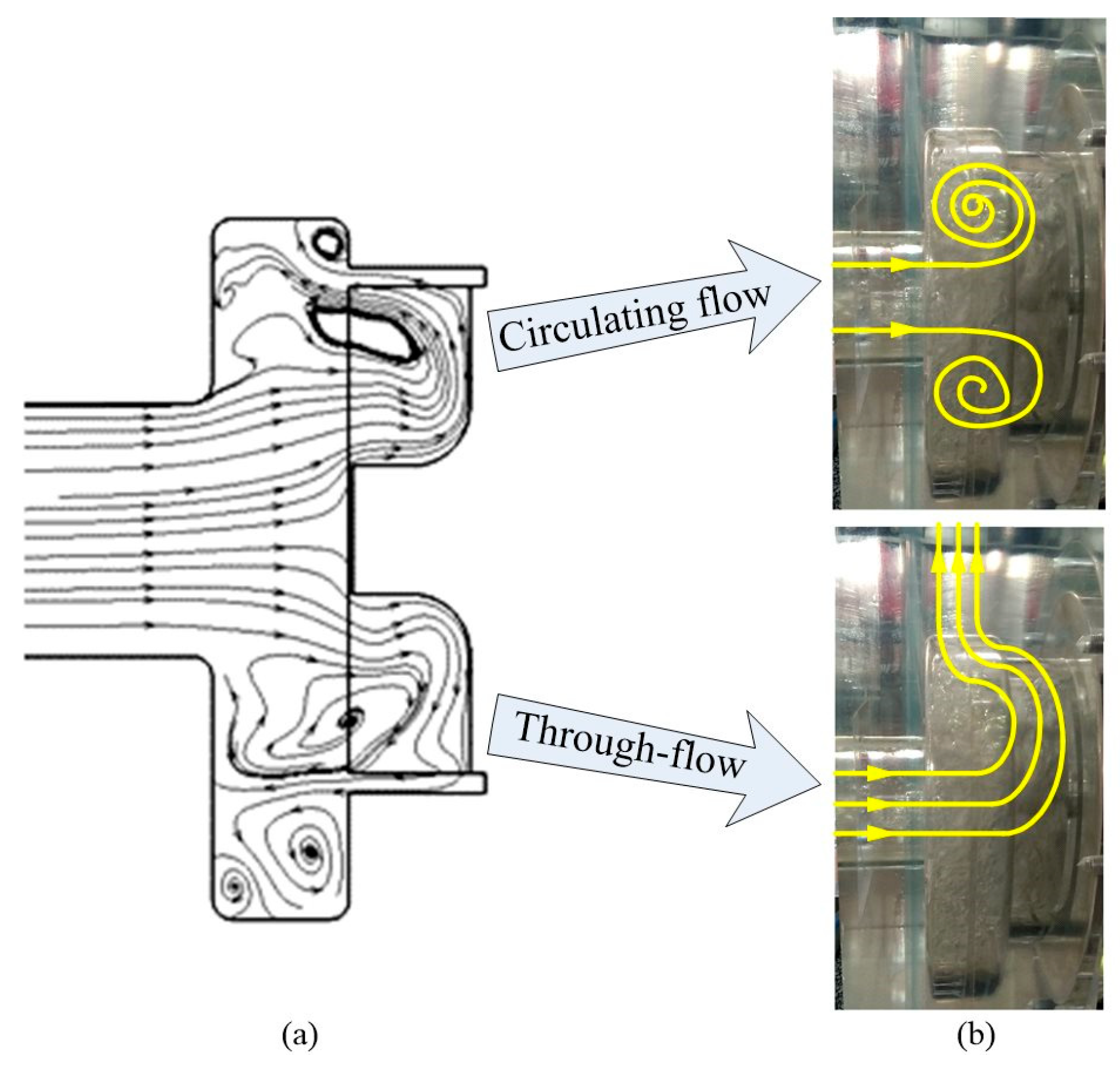
3.1.2. Geometric Characteristics of Circulating Flow
3.2. Description of Geometric and Physical Parameters of the Vortex Structure
4. Results and Analysis
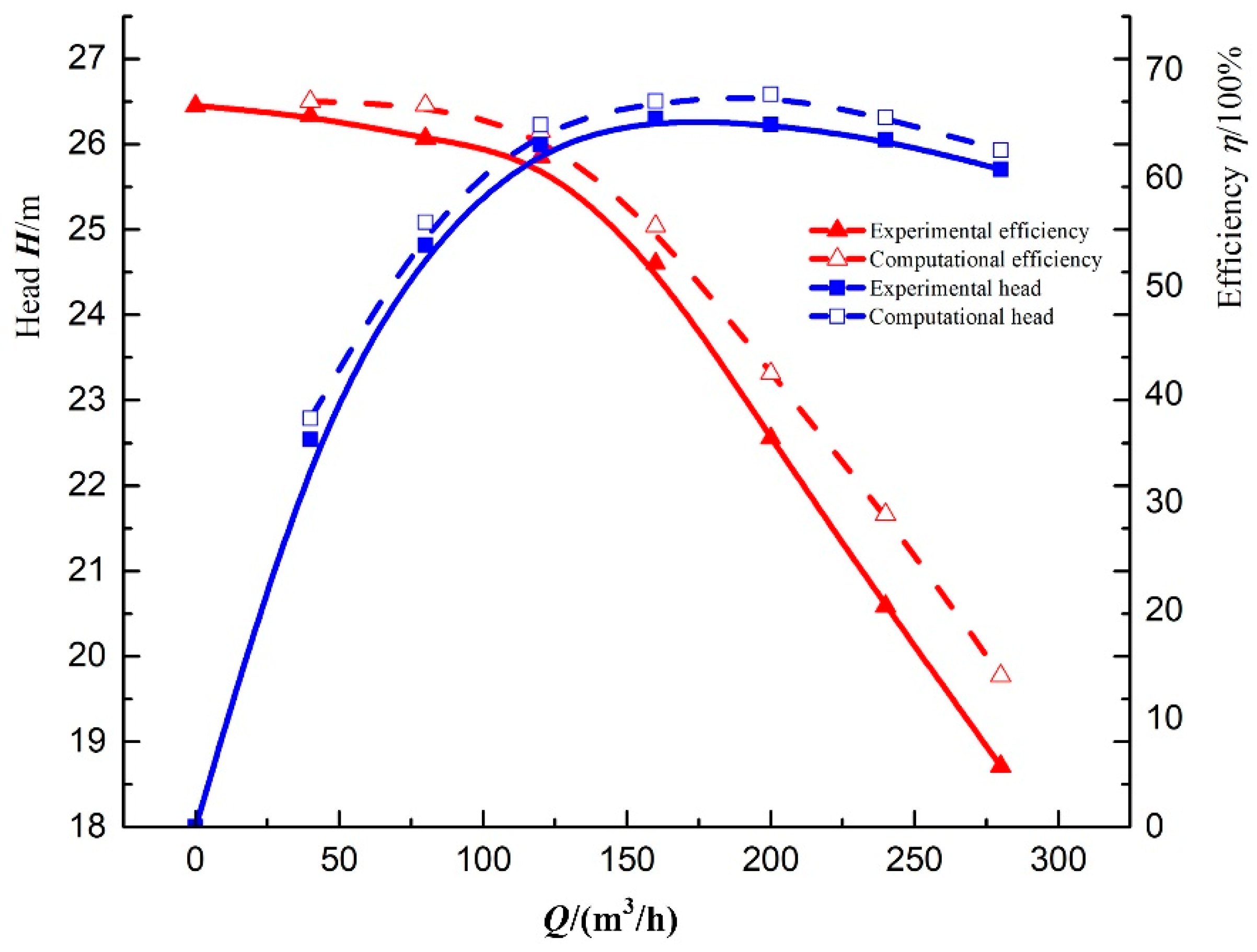
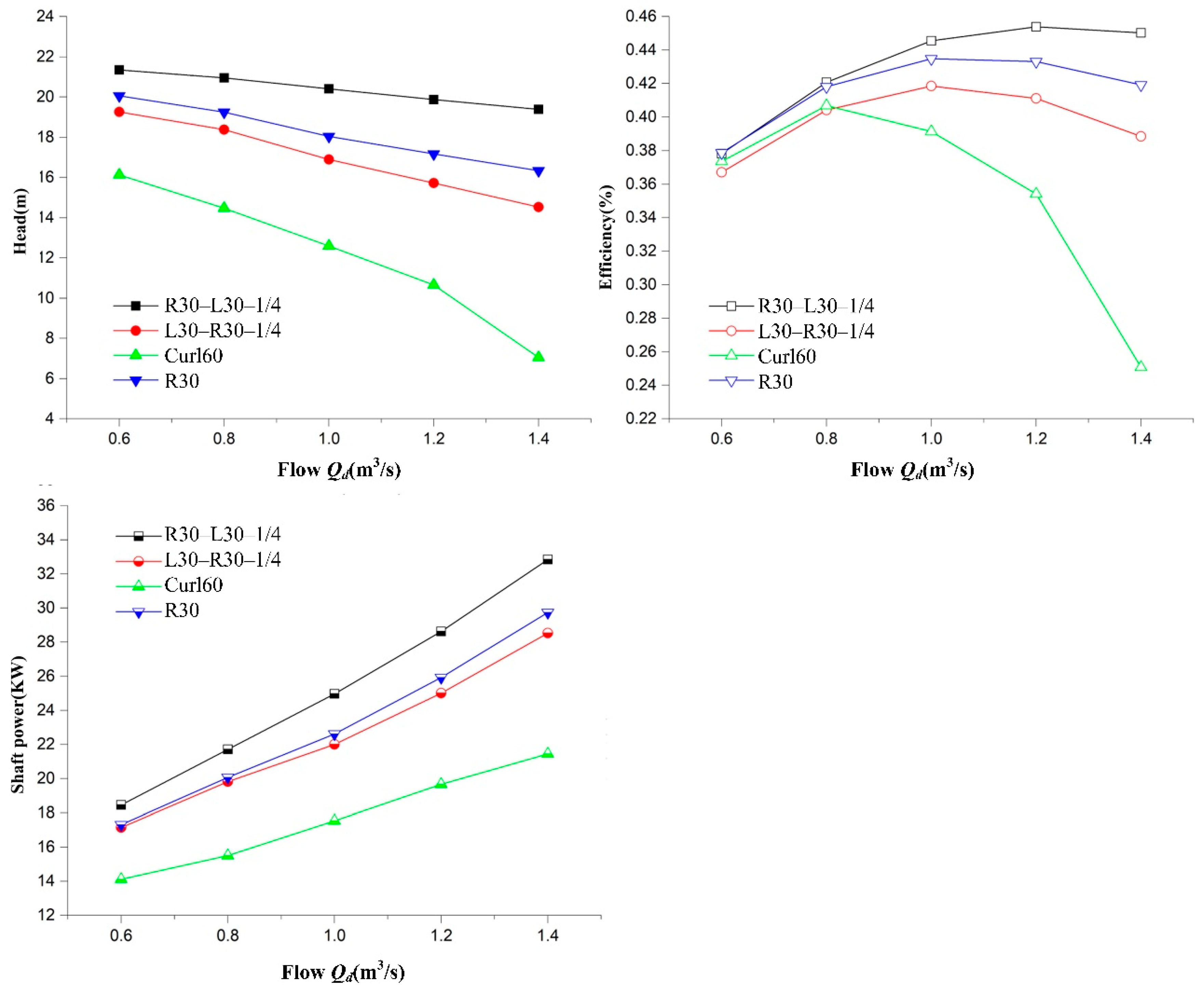
4.1. Influence of the Blade Shape on the External Characteristics Performance of the Pump
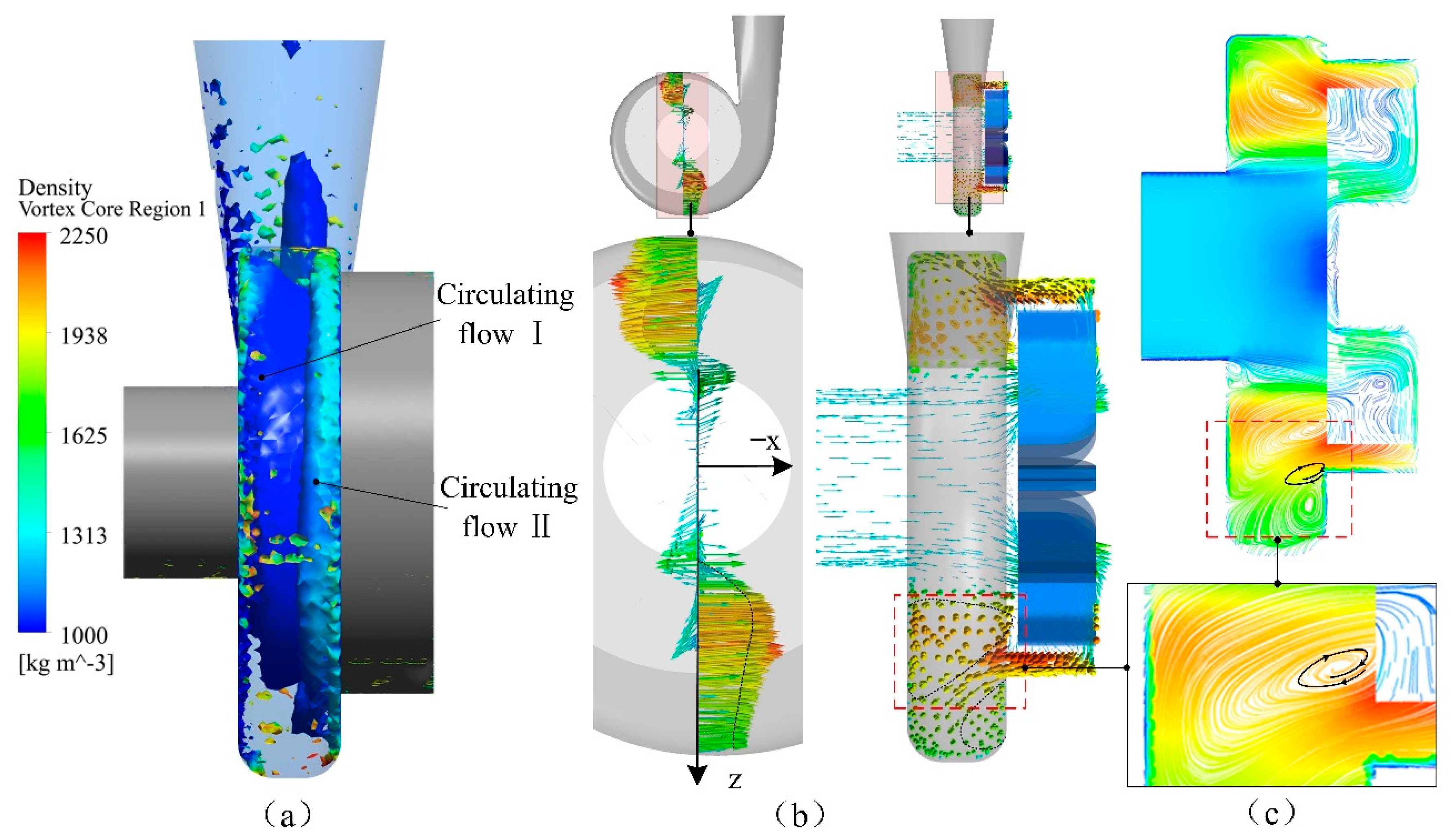
4.2. Effect of Blade Shape on Circulating Flow in the Bladeless Cavity
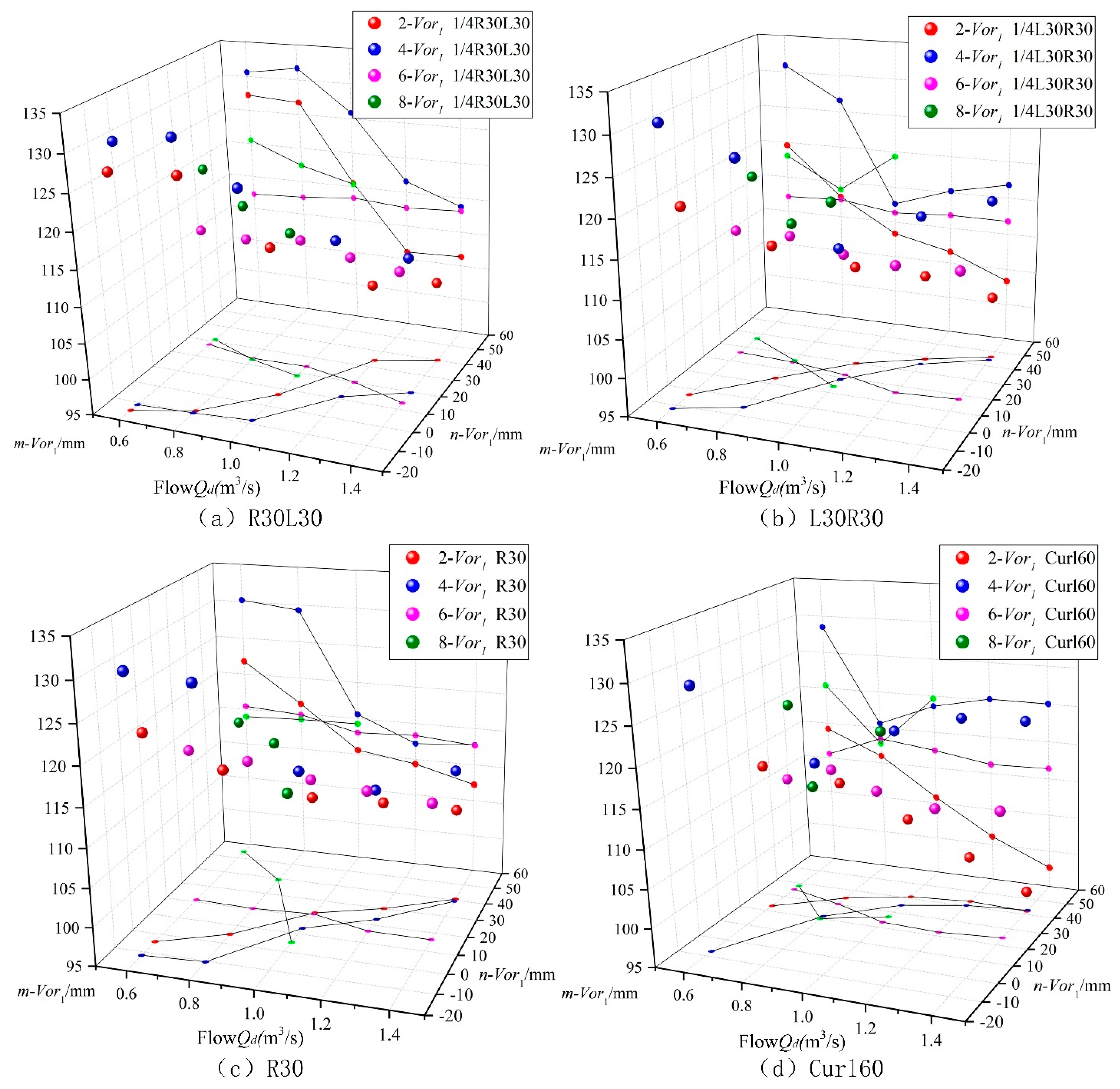
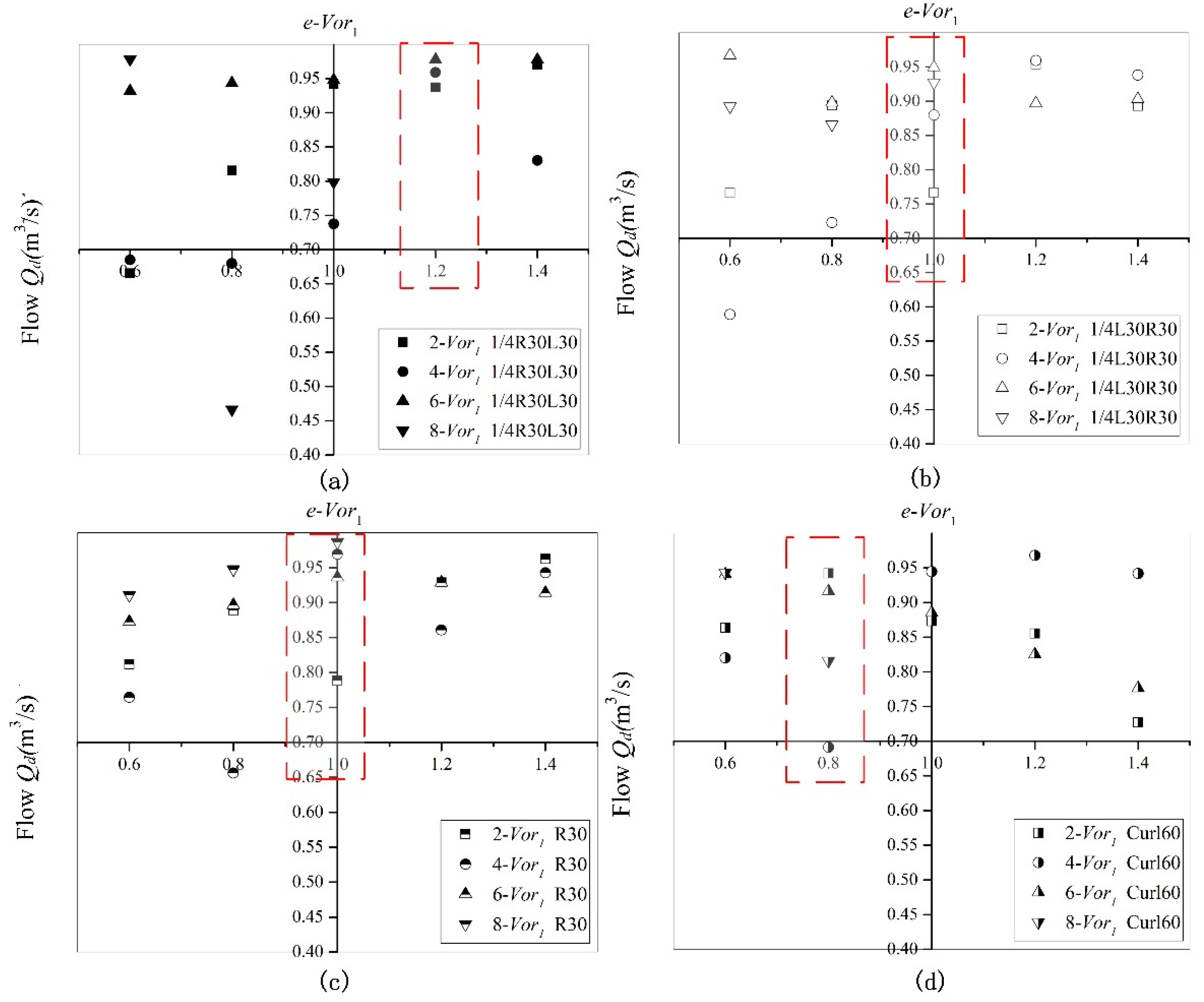
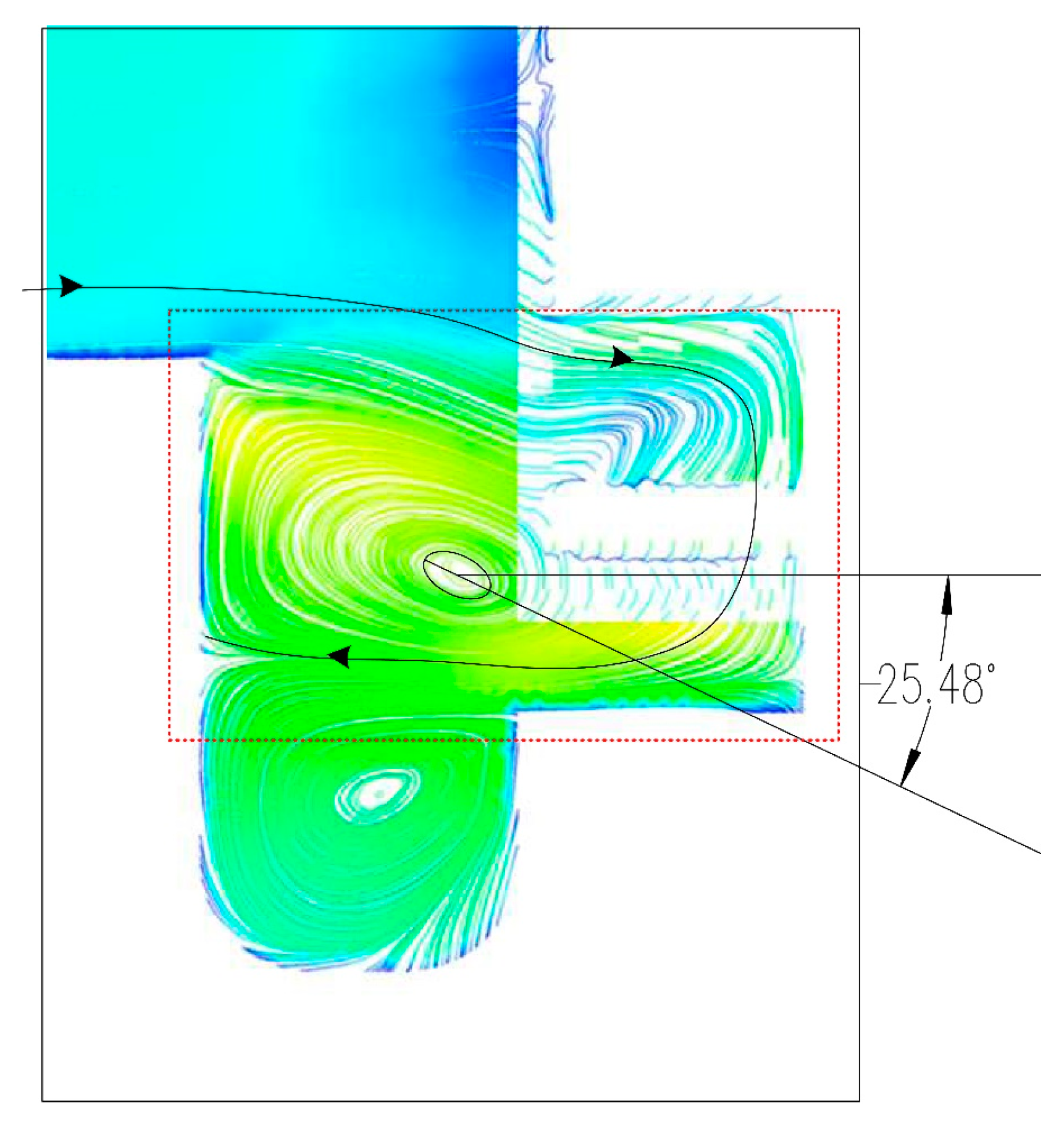
4.2.1. Effect of Blade Shape on Vortex Core Position
4.2.2. Influence of Blade Shape on Vortex Shape
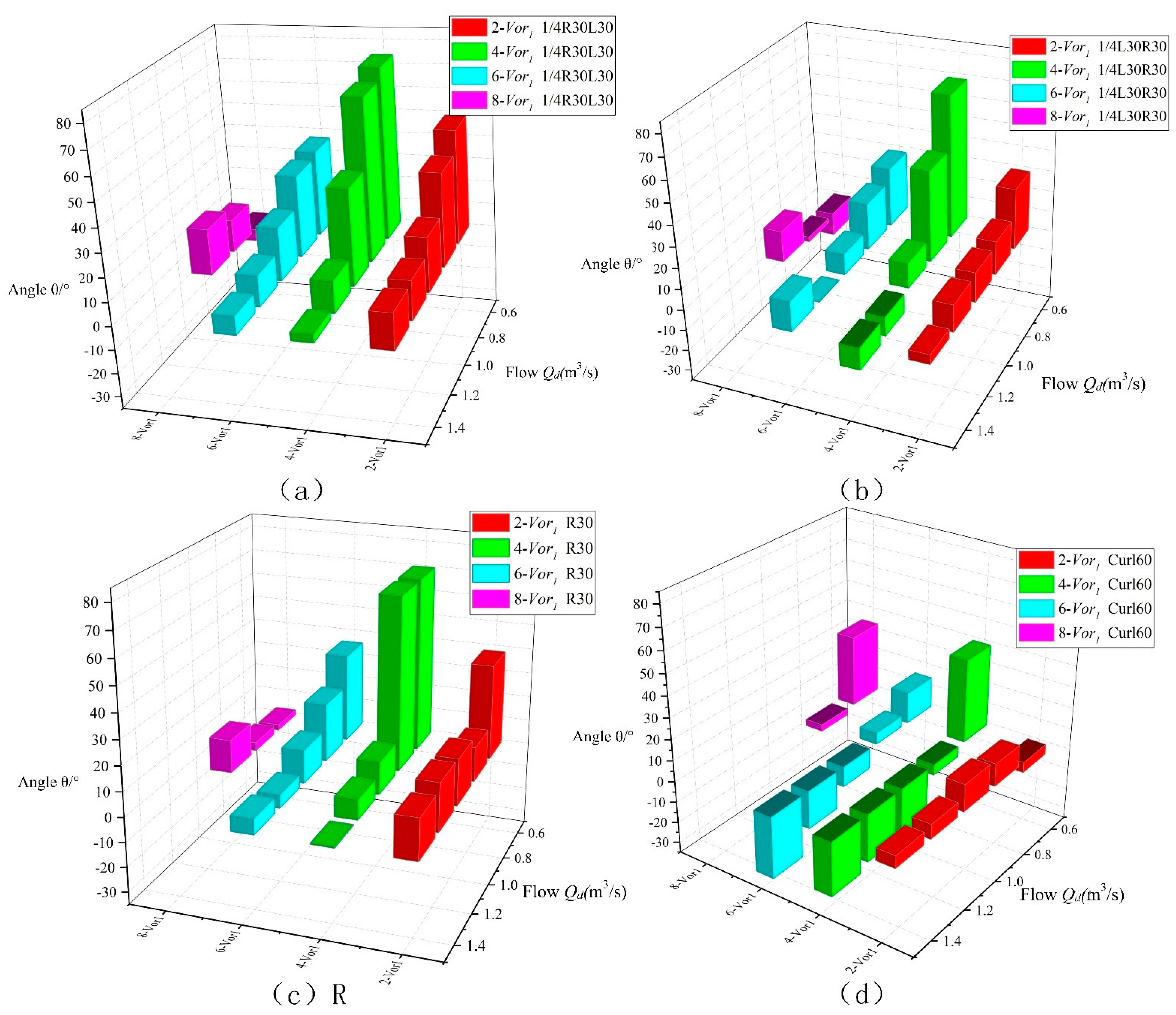
4.2.3. Influence of the Blade Shape on the Vortex Core Position Angle
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lu, Z.; Tao, R.; Jin, F.; Li, P.; Xiao, R.; Liu, W. The Temporal-Spatial Features of Pressure Pulsation in the Diffusers of a Large-Scale Vaned-Voluted Centrifugal Pump. Machines 2021, 9, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Long, B.; Wang, C.; Han, C.; Li, L. Effects of the impeller blade with a slot structure on the centrifugal pump performance. Energies 2020, 13, 1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Shi, W.; Zhao, R.; Zhao, T.; Wang, H.; Mucka, P. Optimization Design and Internal Flow Field Study of Open-Design Vortex Pump. Shock Vib. 2021, 2021, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, H.; Chai, Y.; Li, R.; Guo, J. Numerical simulation and experiment for study on internal flow pattern of vortex pump. Eng. Comput. 2019, 36, 1579–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerlach, A.; Thamsen, P.; Wulff, S.; Jacobsen, C. Design Parameters of Vortex Pumps: A Meta-Analysis of Experimental Studies. Energies 2017, 10, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, Y.-P.; Liu, S.; Zhang, C.-H. Effect of blade shape on hydraulic performance and vortex structure of vortex pumps. J. Hydrodyn. 2018, 30, 499–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Zhang, Y. The Vortex Pump under Highly Viscous Liquid Flow Conditions. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2018, 43, 4739–4761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Zhao, M.; Wang, C.; Gao, Z. Optimal design of diversion piers of lateral intake pumping station based on orthogonal test. Shock Vib. 2021, 6616456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W. Vortex Pump as Turbine—A Type Turbine for Energy Generation or Recovery Based on Computational Fluid Dynamics Prediction. J. Fluids Eng. 2019, 141, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Hu, Q.; Yang, Y.; Wang, C. Performance differences of electrical submersible pump under variable speed schemes. Int. J. Simul. Model. 2021, 20, 76–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinmann, A.; Wurm, H.; Otto, A. Numerical and experimental investigations of the unsteady cavitating flow in a vortex pump. J. Hydrodyn. Ser. B 2010, 22 (Suppl. 1), 324–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, D.; Li, H.; Ma, Q.; Han, Q.; Sun, X. Numerical Investigation of Performance Improvement and Erosion Characteristics of Vortex Pump Using Particle Model. Shock Vib. 2020, 2020, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihalić, T.; Guzović, Z.; Predin, A. CFD flow analysis in the centrifugal vortex pump. Int. J. Numer. Methods Heat Fluid Flow 2014, 24, 545–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Gerlach, A.; Preuss, E.; Thamsen, P.U.; Lykholt-Ustrup, F. Numerical simulations of the internal flow pattern of a vortex pump compared to the Hamel-Oseen vortex. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 2017, 31, 1711–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.-X. Research on turbulent flow within the vortex pump. J. Hydrodyn. 2004, 16, 701–707. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, X.; Shi, W.; Shi, Y.; Chang, H.; Zhao, T. DEM-CFD Simulation and Experiments on the Flow Characteristics of Particles in Vortex Pumps. Water 2020, 12, 2444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Xiang, W.; He, Z.; Shi, W. Numerical study of coupled flow in blocking pulsed jet impinging on a rotating wall. J. Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng. 2021, 43, 508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Zhu, J.; Tang, F.; Wang, C. Multi-Disciplinary optimization design of axial-flow pump impellers based on the approximation model. Energies 2020, 13, 779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucius, A.; Brenner, G. Numerical Simulation and Evaluation of Velocity Fluctuations During Rotating Stall of a Centrifugal Pump. J. Fluids Eng. 2011, 133, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, H.; Guo, Y.; Li, R.N.; Su, Q.M.; Chai, Y. Optimization design and experimental study of vortex pump based on orthogonal test [Review]. Sci. Prog. 2020, 103, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quan, H.; Cheng, J.; Guo, Y.; Kang, L.; Peng, G. Influence of Screw Centrifugal Inducer on Internal Flow Structure of Vortex Pump. J. Fluids Eng. 2020, 142, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Qian, Z.; Zhang, D.; Wang, T.; Wang, C. Numerical study of the normal impinging water jet at different impinging height, based on Wray–Agarwal turbulence model. Energies 2020, 13, 1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, J.; Hussain, F. On the identification of a vortex. J. Fluid Mech. 1995, 285, 69–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariotti, A.; Galletti, C.; Salvetti, M.V.; Brunazzi, E.J.I.; Research, E.C. Unsteady Flow Regimes in a T-Shaped Micromixer: Mixing and Characteristic Frequencies. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2019, 58, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Cai, X.-S.; Liu, C. Liutex (vortex) core definition and automatic identification for turbulence vortex structures. J. Hydrodyn. 2019, 31, 857–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Impeller Hydraulic Geometric Parameters | Volute Hydraulic Parameters | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Impeller outer diameter, D2/mm | 246 | Volute width, L/mm | 70 |
| Impeller width, b/mm | 60 | The bladeless cavity base circle, D3/mm | 290 |
| Number of blades, Z | 10 | Clearance between impeller outer diameter and shell, e/mm | 20 |
| Blade thickness, b2/mm | 8 | The bladeless cavity throat area, Fthr/cm2 | 110 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Quan, H.; Li, Y.; Kang, L.; Yu, X.; Song, K.; Wu, Y. Influence of Blade Type on the Flow Structure of a Vortex Pump for Solid-Liquid Two-Phase Flow. Machines 2021, 9, 353. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines9120353
Quan H, Li Y, Kang L, Yu X, Song K, Wu Y. Influence of Blade Type on the Flow Structure of a Vortex Pump for Solid-Liquid Two-Phase Flow. Machines. 2021; 9(12):353. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines9120353
Chicago/Turabian StyleQuan, Hui, Yanan Li, Lei Kang, Xinyang Yu, Kai Song, and Yongkang Wu. 2021. "Influence of Blade Type on the Flow Structure of a Vortex Pump for Solid-Liquid Two-Phase Flow" Machines 9, no. 12: 353. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines9120353
APA StyleQuan, H., Li, Y., Kang, L., Yu, X., Song, K., & Wu, Y. (2021). Influence of Blade Type on the Flow Structure of a Vortex Pump for Solid-Liquid Two-Phase Flow. Machines, 9(12), 353. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines9120353






