Abstract
In-wheel motors (IWMs) have become a promising solution for electric vehicles due to their compact design, high integration, and flexible torque control. However, their exposure to harsh operating conditions increases the risk of mechanical, electrical, and magnetic faults, making reliable fault diagnosis essential for ensuring driving safety and system reliability. Although considerable progress has been made in fault diagnosis techniques related to IWMs, a systematic review in this area is still lacking. To address this gap, this paper provides a comprehensive review of fault diagnosis techniques for IWMs. First, typical faults in IWMs are analyzed with a focus on their unique structural and failure characteristics. Then, the applications and recent research progress of three major categories of fault diagnosis approaches—model-based, signal-based, and knowledge-based methods—in the context of IWMs are critically reviewed. Finally, key challenges and pain points in IWM diagnosis are discussed, along with promising future research directions.
1. Introduction
With the rapid development of the electric vehicle (EV) industry, the in-wheel motor (IWM) has emerged as a promising solution due to its compact structure, high efficiency, fast response, and independent control capabilities [1,2,3,4,5,6]. Unlike conventional centralized drive motors, IWMs are directly integrated into the wheel hub, eliminating traditional components such as the drive shaft and differential. This simplification leads to reduced vehicle weight, improved transmission efficiency, and enhanced system responsiveness. Additionally, independently driven wheels offer greater flexibility for vehicle dynamic control. Each wheel can be controlled separately in terms of torque output, allowing precise implementation of traction control, stability control, and regenerative braking—particularly beneficial under complex or variable road conditions. Furthermore, the modularity of IWMs contributes to lower manufacturing and maintenance costs, while also enabling innovative vehicle architectures.
However, these benefits come with new engineering challenges. Under frequently changing operating conditions and complex road environments, the unique installation position and high integration of IWMs lead to two major issues. First, road excitations cause continuous and intense impacts on the motor [7,8,9,10]. Second, it is difficult to balance heat dissipation and sealing performance [11,12]. These factors lead to a higher likelihood of faults in IWMs. Any fault in the motor can directly affect the driving force of individual wheels, potentially compromising overall vehicle stability and safety [13,14,15]. Thus, the development of robust fault diagnosis is essential for ensuring the safety and stability of IWMs.
At present, existing reviews on IWM technologies primarily focus on motor design [4,16], vertical dynamics [17], energy management [18], thermal management [4,5], and torque distribution strategies [17,19]. Summaries of safety-related research are largely limited to fault-tolerant control. However, in the absence of reliable fault diagnosis, control decisions may lack sufficient basis. On the other hand, existing reviews on fault diagnosis of conventional EV motors [20,21] offer limited guidance for fault diagnosis in IWMs. This is mainly due to the harsher operating environment of IWMs, where fault features are more likely to be obscured by persistent strong noise and intermittent high-intensity interference. Moreover, IWMs experience more frequent changes in operating conditions, making fault diagnosis particularly challenging. Therefore, a targeted review of IWM fault diagnosis is urgently needed to summarize current research, identify key challenges and explore future directions, thereby supporting the development of robust and reliable IWM drive technologies.
To this end, this paper provides a comprehensive and structured review of fault diagnosis for IWMs. The main contributions are summarized as follows: (1) The paper systematically differentiates the unique fault characteristics and mechanisms of IWMs from those of conventional motors. (2) A critical review is conducted on the application and recent advances of three major categories of fault diagnosis methods in the context of IWMs. (3) The key challenges and pain points in IWM fault diagnosis are identified and potential research directions are provided for future work.
The rest of the review is organized as follows. Section 2 introduces the motor types commonly used in IWMs, and typical faults. Section 3 presents a systematic review of mainstream IWM fault diagnosis approaches, with emphasis on their underlying principles, applications, and performance trade-offs. Section 4 discusses the key challenges in practical deployment and outlines promising future research directions. Finally, conclusions are presented in Section 5.
2. IWMs and Fault Types
To develop effective and reliable fault diagnosis methods, it is essential to understand the types of motors commonly used in IWMs, as well as the fault mechanisms associated with their structural and operational characteristics. This section provides an overview of the motor types employed in IWM systems, with a focus on radial flux and axial flux permanent magnet synchronous motors (PMSMs), and further classifies the major fault types into mechanical, electrical, and magnetic categories. By examining the origins, characteristics, and consequences of these faults, the section lays the foundation for subsequent analysis of fault diagnosis strategies.
2.1. Types of IWMs
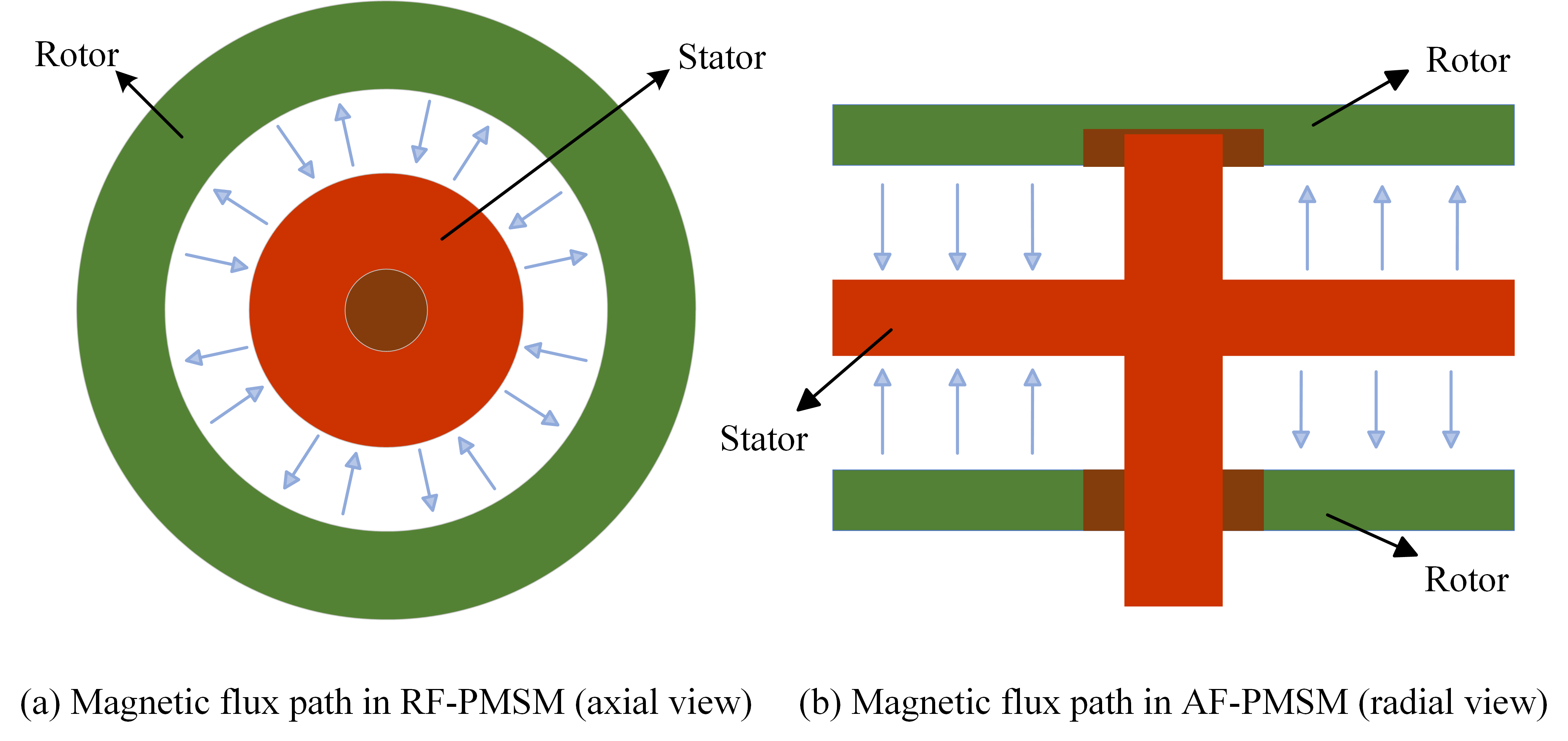
In current IWM-driven EV applications, PMSMs represent the most common motor type used in IWM systems, owing to their high power density, excellent efficiency, fast dynamic response, and precise torque control [22]. Depending on the orientation of magnetic flux, PMSMs can be broadly classified into radial flux PMSMs (RF-PMSMs) and axial flux PMSMs (AF-PMSMs), as shown in Figure 1. RF-PMSMs are currently the most widely adopted configuration in IWMs [23], benefiting from their stable performance and proven reliability in the automotive industry. In contrast, AF-PMSMs, with their flat and compact geometry, offer higher torque density and better integration potential for space-constrained applications such as wheel hubs [24,25,26], and are therefore receiving increasing attention as a promising alternative for next-generation designs [27].
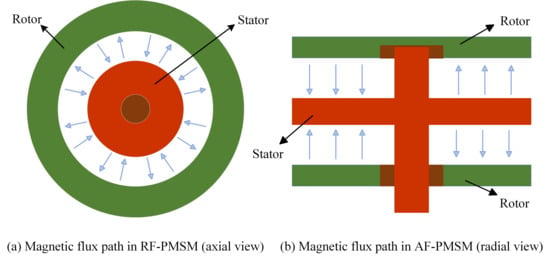
Figure 1.
Illustration of different flux orientations in (a) RF-PMSM (axial view), and (b) AF-PMSM (radial view).
In addition, several studies have investigated the possibility of alternative motor types for IWM-driven EVs, including brushless DC motors (BLDCs), switched reluctance motors (SRMs), and induction motors (IMs) [10,28]. Although BLDCs share structural similarities with PMSMs, they generally lack field-oriented control and are limited in high-performance applications [29,30]. SRMs are robust and economical but suffer from severe torque ripple, acoustic noise, and non-linear control complexity [30,31,32], which restrict their application in passenger vehicles. IMs, while reliable and cost-effective, exhibit lower efficiency, larger size, and higher thermal losses [32,33], making them less suitable for integration into wheel hubs. In comparison, PMSMs provide a superior balance of efficiency, controllability, NVH characteristics, and compactness. Given the advantages, PMSMs—particularly RF-PMSMs—remain the mainstream solution, while AF-PMSMs are emerging as a viable option for future lightweight and high-density IWM systems.
2.2. Common Fault Types
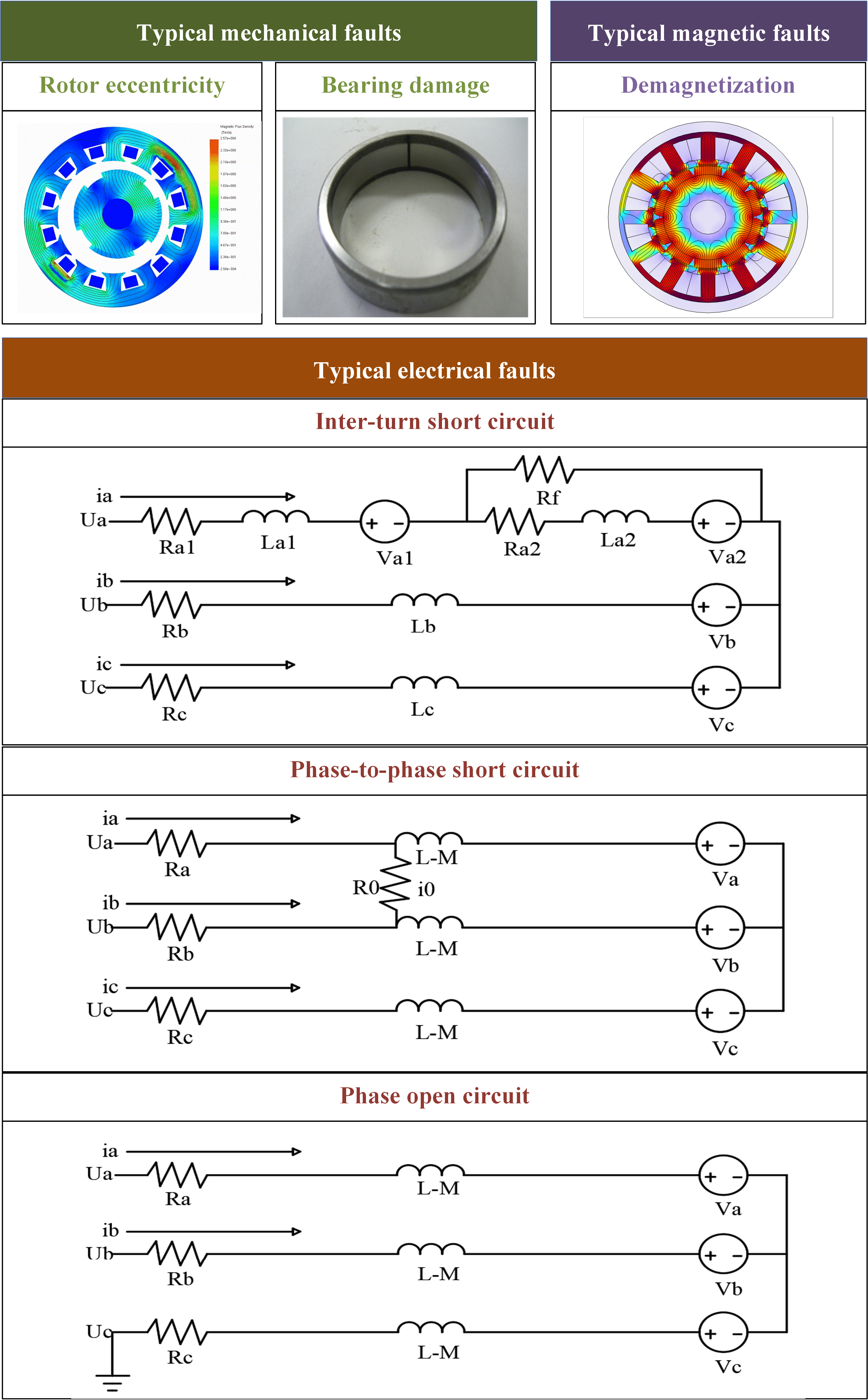
The RF-PMSM utilized in IWMs differs from its conventional counterpart primarily in adopting an outer-rotor, inner-stator structure and fractional slot-concentrated winding [34,35]. Nevertheless, the types of faults it exhibits remain largely consistent with those observed in traditional designs, and can be broadly categorized into mechanical, electrical, and magnetic faults based on their physical origins [36]. Typical faults are shown in Figure 2.
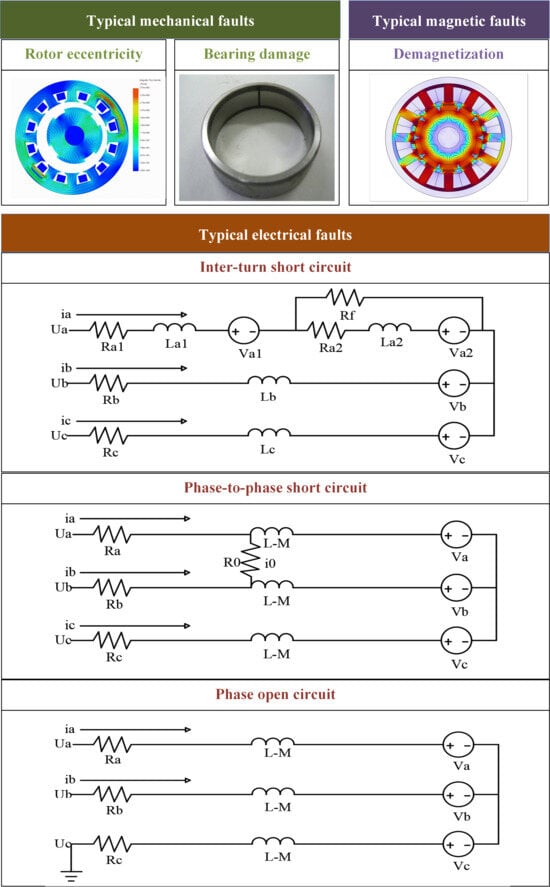
Figure 2.
Typical faults of IWMs.
2.2.1. Mechanical Faults
The primary mechanical fault types include bearing failure, rotor eccentricity, and mechanical deformation [37], which are interrelated and have a reciprocal impact on each other.
Bearings, as the critical component supporting the rotor’s motion in IWMs, are subjected to uneven radial force, heavy loads, and frequent shock impacts [38]. Prolonged operation under these conditions leads to wear, fatigue pitting, and lubrication failure [39,40]. Bearing wear leads to rotor imbalance and uneven air gaps, which in turn cause local contact between the stator and rotor, exacerbating vibrations and noise. In severe cases, bearing faults may lead to rotor seizure or fracture, resulting in instantaneous motor failure and posing a direct threat to vehicle safety.
Rotor eccentricity primarily arises from manufacturing or assembly errors, bearing faults, or mechanical deformation from long-term operation [41,42]. Moreover, external shock loads from road conditions, such as impact with potholes, can induce magnetic force oscillation [43] and slight bending of the shaft, further exacerbating the eccentricity. Eccentricity leads to uneven magnetic flux density distribution in the stator, producing unbalanced magnetic pull (UMP) [44]. In severe cases, mechanical rubbing between the stator and rotor may happen. This induces additional vibration and noise, reduces the uniformity of the torque output, and degrades vehicle performance and ride smoothness [45]. Prolonged eccentricity can also cause localized overheating of the windings and potentially lead to electrical faults.
2.2.2. Electrical Faults
Electrical faults common in IWMs are mainly winding faults, including inter-turn short circuits, phase-to-phase short circuits, and open-circuit faults [46].
Inter-turn short circuits occur when insulation between adjacent turns of a coil deteriorates or breaks down. This degradation is primarily caused by thermal aging, manufacturing defects, mechanical vibration, and exposure to moisture or chemical contaminants [47]. In addition, the compact structure of IWMs restricts effective heat dissipation, leading to localized overheating, which further accelerates insulation aging [48]. When an inter-turn short circuit occurs, it generates circulating fault currents within the affected coil, resulting in significant local heating [49]. This can lead to further insulation breakdown, the propagation of the short circuit to adjacent turns or phases, and severe thermal damage to the stator core [49,50].
Phase-to-phase short circuits typically arise from progressive insulation degradation between different phase windings [49]. Degradation factors include persistent high thermal stress, electrical transients from inverter malfunctions, and mechanical abrasion due to rotor eccentricity [51]. In IWM applications, road-induced vibrations and shock loads further increase the risk. A phase-to-phase short circuit leads to large fault currents flowing directly between phases [52], producing intense thermal stress and magnetic imbalances. It severely disrupts the electromagnetic torque production, causes pronounced torque ripple, and significantly accelerates the deterioration of the winding system.
Open-circuit faults are generally induced by broken winding conductors, failure of terminal connections, or malfunctioning power switches [53,54,55]. Mechanical fatigue from continuous vibration, thermal cycling, and sudden impact loads commonly encountered in in-wheel systems contributes significantly to the occurrence of open-circuit states. An open-circuit fault interrupts the current flow in one or more phases, leading to an immediate reduction in the motor’s torque production capability. Depending on the severity and control strategy, the IWM may continue operating at reduced performance or, in the worst case, lose propulsion capability entirely [56,57]. Furthermore, asymmetrical currents caused by open-circuit faults can generate additional vibrations and thermal stress, further threatening motor reliability [58].
Electrical faults have a significant impact on motor performance and tend to deteriorate continuously. If not detected promptly, this may escalate to severe faults such as stator burnout, catastrophic motor failure, and loss of driving capability [59].
2.2.3. Magnetic Faults
Permanent magnet demagnetization is a common magnetic fault in PMSMs [37], which is primarily triggered by excessive thermal stress, large short-circuit currents, or severe mechanical impacts [60]. In IWMs, the integration of the motor into the wheel hub exposes the magnets to high-temperature environments and frequent thermal cycling [61,62]. Moreover, short-circuit states can induce local overheating, surpassing the critical temperature of the permanent magnets [63], leading to irreversible magnetization loss [61,64,65]. External factors such as vibration-induced mechanical stress or improper assembly can also contribute to partial demagnetization.
When demagnetization occurs, the magnetic flux density in the air gap decreases, leading to a significant drop in torque production and overall motor efficiency. Furthermore, asymmetric demagnetization can cause unbalanced magnetic forces, increasing torque ripple and inducing mechanical vibrations [60]. Over time, this not only reduces the operational performance of the motor but also accelerates bearing wear and mechanical fatigue in the drivetrain.
2.2.4. Fault Comparison Between Axial-Flux and Radial-Flux IWMS
The flat structure and high power density of AF-PMSMs make them an ideal choice for IWM applications. Compared to RF-PMSMs, the primary distinctive features of AF-PMSMs lie in their electromagnetic topology and disk-shaped structural design. These structural differences also introduce unique fault mechanisms and failure modes. For mechanical faults, the rotor eccentricity of AF-PMSMs also includes axial deflection [66,67,68,69], which is attributed to their disk-shaped rotor and stator being more susceptible to axial vibration and end-face deformation [70]. This may result in significant axial displacement and uneven air gaps. In terms of electrical faults, AF-PMSMs typically adopt a planar winding arrangement [71]. During operation, end windings are subjected to electromagnetic forces as well as structural and magnetic field-induced stresses. Their compact and curved geometry increases susceptibility to fatigue damage and insulation degradation over time. Regarding magnetic faults, the end-face temperature distribution of AF-PMSMs is often uneven [72], and insufficient heat dissipation may lead to localized demagnetization. The fault similarities and differences between AF-PMSMs and RF-PMSMs are summarized in Table 1.

Table 1.
Comparison between faults of RF-PMSMs and AF-PMSMs.
2.3. Section Summary of IWMs and Fault Types
In summary, this section reviewed the motor types commonly used in IWM systems, with a particular focus on RF-PMSMs and AF-PMSMs, and categorized the major fault types into mechanical, electrical, and magnetic faults. Mechanical faults, such as bearing faults and rotor eccentricity, are mainly induced by road-induced vibrations and structural limitations. Electrical faults often result from insulation degradation and thermal stress, while magnetic faults are typically associated with demagnetization of permanent magnets due to overheating or mechanical impact. Furthermore, differences in electromagnetic topology and physical layout between AF-PMSMs and RF-PMSMs lead to distinct fault mechanisms and sensitivities.
3. Fault Diagnosis for IWMs
The reliability and safety of IWMs are critically dependent on effective fault diagnosis techniques. Although many fault types in IWMs are similar to those in conventional EV motors, the unique structural and environmental characteristics of IWMs introduce additional diagnostic challenges. These factors not only accelerate fault progression but also mask fault features under strong noise and interference, making early detection more difficult. Consequently, this underscores the need for targeted diagnostic approaches for IWMs. Fault diagnosis methods that have been developed or adapted for IWMs can be broadly classified into three main categories: model-based methods, signal-based diagnostic methods, and knowledge-based diagnostic methods. Each method leverages different principles and analytical techniques to identify faults. This section provides a comprehensive overview of these methods, highlighting their principles, applications, and specific advantages in IWM fault detection. A brief preview is shown in Table 2.

Table 2.
Summary of fault diagnosis methods for IWMs.
3.1. Model-Based Diagnosis
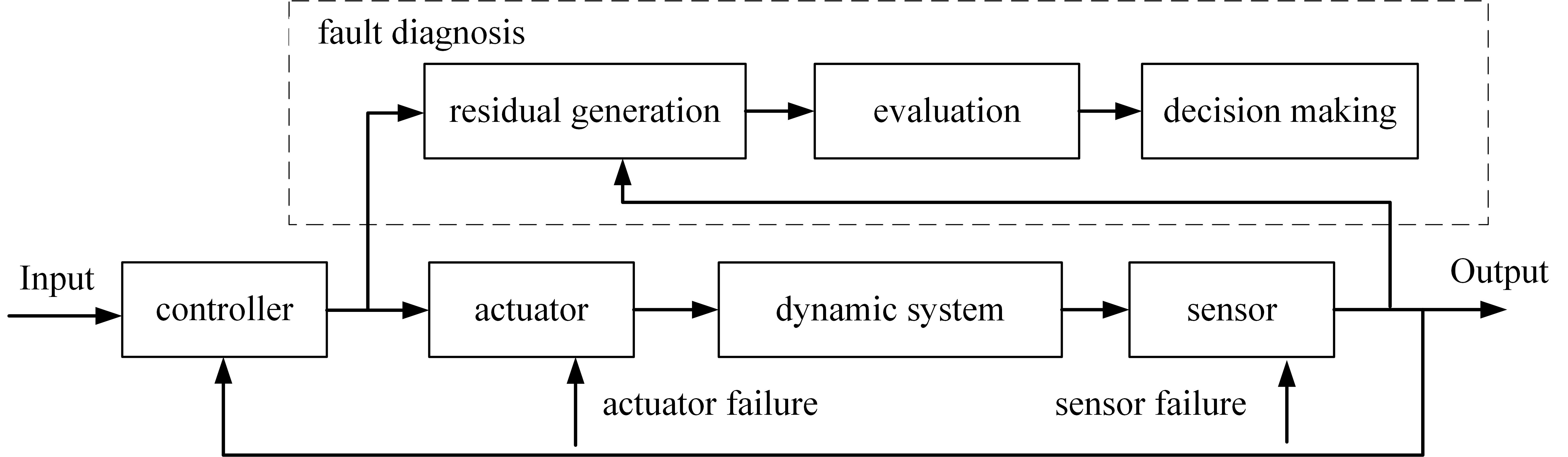
The model-based method utilizes mathematical representations of the physical behavior of IWMs to detect anomalies by comparing the expected behavior of the system with its actual measured outputs, as shown in Figure 3. It is grounded in physics-based modeling, parameter estimation, and residual generation. The difference between the observed and estimated outputs reflects the presence and potentially the type or severity of a fault. Given the deep integration of IWMs with vehicle dynamics and power electronics, model-based diagnosis provides an interpretable framework to detect actuator, sensor, and inverter faults.
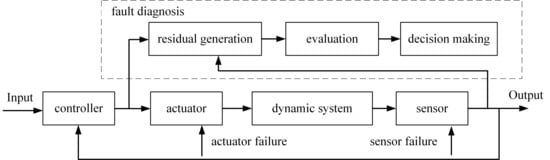
Figure 3.
Basic principle of model-based diagnosis methods.
The challenges posed by model uncertainties, disturbances, and noise have driven the development of parameter estimations and state observers.
3.1.1. Parameter Estimation-Based Methods
The core idea of parameter estimation–based methods is that faults within the motor or its associated components often manifest as variations in measurable key physical parameters, such as resistance, inductance, and back-electromotive force (EMF) constants [73,74,75]. For IWMs, certain common faults, such as bearing faults, are difficult to diagnose using only current and voltage signals [73,76]. As a result, control gain has also been widely employed to assess fault states [77,78]. By continuously estimating physical or control-related parameters and comparing them to their nominal or expected values, it becomes possible to detect, locate, and in some cases, quantify the severity of a fault.
Physical modeling forms the foundation of parameter estimation-based diagnostics. These models define the mathematical relationships between system inputs, outputs, and internal parameters under nominal conditions. Thus, it enables the computation of certain parameters that cannot be directly measured. The common fundamental models are summarized in Table 3 [77,79,80,81,82,83,84,85,86,87].

Table 3.
Common models.
Parameter estimation methods utilize algorithms such as recursive least squares (RLS) [77,81,82] to fit input–output data and solve for the parameter values that minimize estimation error. However, these methods rely heavily on accurate mathematical models, which are difficult to obtain for complex and nonlinear systems like IWMs. The performance is also affected by model uncertainties and measurement noise. In addition, parameter estimation methods typically require solving optimization problems online, imposing high demands on algorithmic efficiency and convergence.
3.1.2. State Estimation-Based Methods
The primary objective of state estimation–based methods is to reconstruct the system’s state variables (such as position, speed, and temperature) from input–output data when these variables are not directly measurable or are corrupted by significant noise. The estimated states are then compared with actual measurements or model-based predictions to generate residuals, which serve as the basis for fault diagnosis. Methods based on Kalman filtering and observers are most commonly used [73,88].
- a.
- Kalman Filtering
Kalman filtering provides an optimal recursive solution for estimating the internal states of a linear dynamic system in the presence of Gaussian noise [89]. It consists of two steps: a prediction step that propagates the previous state estimate forward in time using the system model, and an update step that corrects this estimate using the latest measurements. For instance, the standard Kalman filter has been used to estimate the bearing damping coefficient of IWMs based on rotational wheel dynamics and proved to converge faster than estimation methods based on RLS [90]. It has also been employed to estimate three-phase motor currents. The obtained averaged normalized residual signals can be used to detect open-switch faults [91]. However, it is only applicable to linear systems, while nonlinear systems in IWMs require extensions such as the extended Kalman filter [92,93] and unscented Kalman filter [94,95]. Even though Kalman filtering methods, in principle, offer a way to handle uncertainty arising from sensor noise and modeling errors, their performance depends heavily on the accuracy of the system model and noise statistics. Variations in motor parameters can cause model mismatch, potentially resulting in filter divergence. Moreover, in real-world applications, the noise could be non-Gaussian and may vary over time.
- b.
- Observers
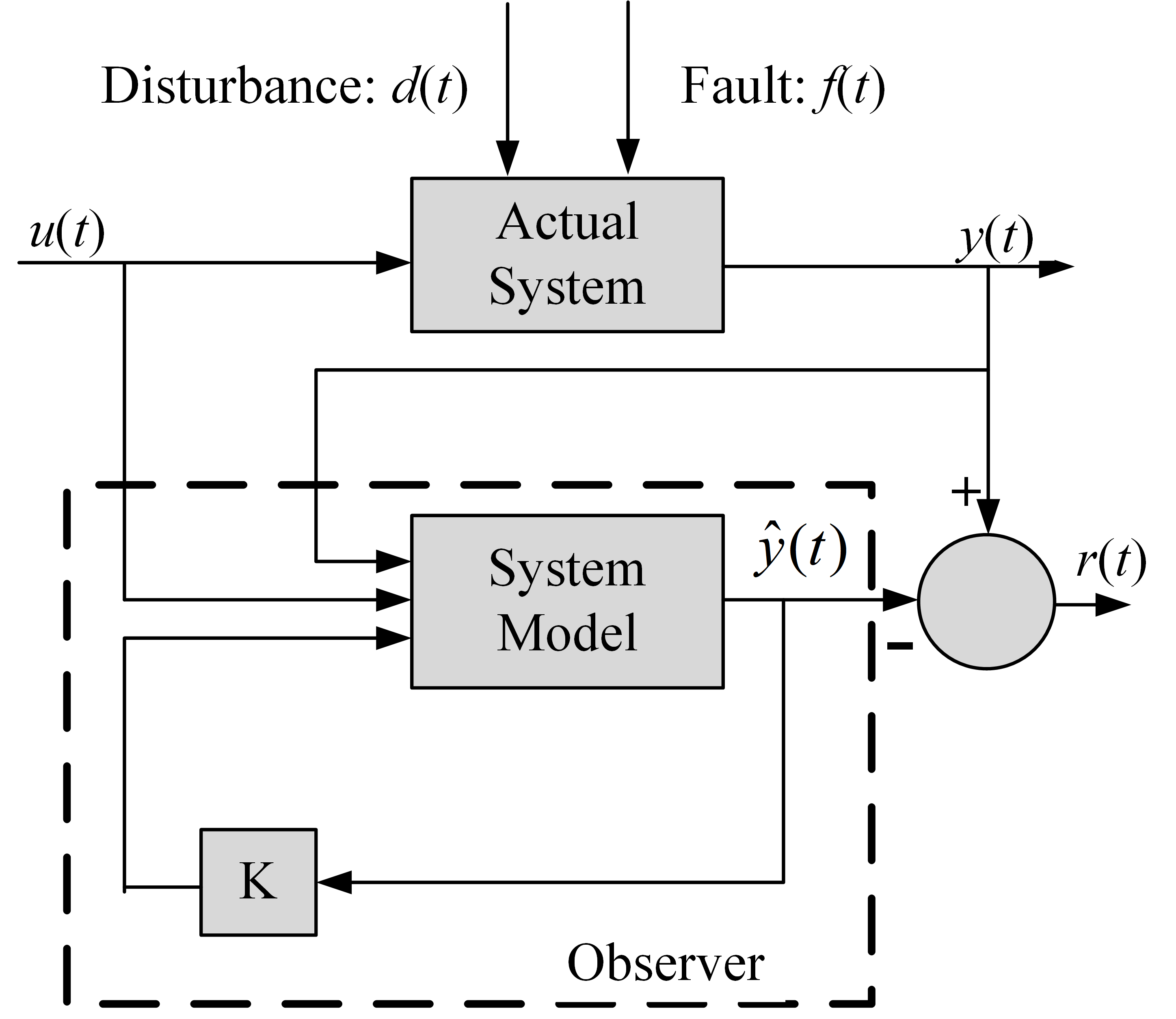
Observers estimate unmeasurable system states based on the system’s mathematical model and measured inputs and outputs [96]. Compared to Kalman filters, observers generally operate in a deterministic framework and are computationally lighter, making them attractive for embedded implementations in resource-constrained environments [97]. Figure 4 illustrates the residual generation process based on an observer. The Luenberger observer is one of the earliest and most widely used for additive faults (abrupt, intermittent) of PMSMs [73,98,99,100]. For a linear time-invariant system, the following applies:
where is the state vector (e.g., rotor speed, flux linkage), is the input vector (e.g., stator voltage), is the measured output (e.g., stator current), and A, B, C are system matrices of appropriate dimensions.
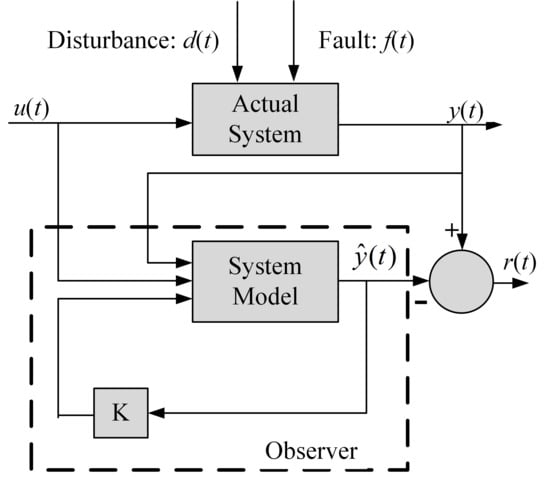
Figure 4.
Residual generation based on observer.
The Luenberger observer estimates the system states as follows:
where is the estimated state vector, is the estimated output, and is the observer gain matrix, which can be determined via pole placement, so that the error system meets the desired dynamic performance (convergence speed, overshoot, etc.).
The estimation error evolves as follows:
If the matrix A-LC is Hurwitz (i.e., all eigenvalues have negative real parts), the estimation error converges to zero asymptotically, ensuring reliable state reconstruction.
In IWM fault diagnosis, faults are typically detected by analyzing the residual signal:
The Luenberger observer introduces a correction term proportional to the difference between the measured and estimated outputs to drive the estimation error to zero. While simple and effective for noise-free environments, its performance may degrade in the presence of model uncertainty or disturbances.
To enhance robustness, many other observers have also been proposed for or applied to IWM fault diagnosis. Wang et al. [101] designed an observer for the tire–road friction coefficient, and eliminated erroneous estimations from the faulty IWM by fusing the estimates from all wheels. Li et al. [102] proposed a novel extended state observer to estimate both the system states and unknown disturbances for IWM-driven EVs experiencing actuator faults under varying road conditions. Salehifar et al. [103] employed the sliding mode observer (SMO) to estimate phase currents and calculated residuals based on cross-correlation factor for detecting open-switch or open-phase faults in IWMs. To eliminate SMO chattering and effectively decouple the influence of motor speed, the super-twisting algorithm-based SMO has also been applied for the detection of switch faults and demagnetization faults [104,105].
3.1.3. Limitations and Challenges
Model-based fault diagnosis methods offer a physically interpretable and structured framework for detecting faults in IWMs, leveraging the understanding of system dynamics through parameter and state estimation. These approaches are particularly useful for localizing faults and quantifying fault severity, and they are relatively well-suited for embedded implementation when simplified models and efficient algorithms are used.
Despite their theoretical rigor and effectiveness, model-based methods are sensitive to model accuracy, parameter uncertainties, nonlinearities and noise, which may lead to unreliable residuals and false alarms. The computational complexity of advanced observers also poses challenges for real-time implementation. Additionally, most methods require accurate and complete knowledge of system inputs and outputs, which is not always guaranteed in practical applications.
3.2. Signal-Based Diagnostic Methods
Signal-based fault diagnosis methods have significant advantages, including independence from precise system modeling, strong real-time capabilities, and broad applicability. They rely directly on measurable signals, which, in the case of IWMs, can include vibration, current, voltage, acoustic noise, and temperature signals [106]. The core of such methods lies in identifying features within these signals that are indicative of specific faults.
3.2.1. Time-Domain and Frequency-Domain Analysis
Ideally, fault-related information can be extracted through analysis in both the time and frequency domains [107]. In time-domain analysis, signal waveforms are examined to observe amplitude variations over time, capturing abrupt changes, periodic abnormalities, or the destruction of waveform symmetry [108]. Statistical parameters such as mean, variance, and kurtosis can be calculated to quantify signal fluctuations [37,109]. For instance, a significant increase in kurtosis often indicates the presence of periodic impulse in mechanical faults [110], such as bearing raceway spalling or rotor eccentricity.
Frequency-domain analysis, on the other hand, leverages tools like the Fourier transform to convert time-domain signals into representations in the frequency domain, thereby revealing the energy distribution across various frequency components [111,112]. For IWMs, signals such as vibration and current exhibit specific frequency patterns and energy distributions under normal operating conditions. When a fault occurs, changes in these spectral characteristics can be observed. The characteristic frequencies corresponding to some faults mentioned in Section 2.2 are shown in Table 4 [112,113,114,115,116], where f0 is the supply frequency, k is a positive integer, p is the number of pole pairs, n is the number of rollers, d is the roller diameter, D is the pitch diameter, β is the contact angle, and fr is the rotational frequency.

Table 4.
Characteristic frequencies of common faults.
However, in practical applications, the signals acquired from IWMs are often non-stationary, particularly under time-varying loads, speed fluctuations, or road irregularities. Traditional time-domain and frequency-domain methods, which assume signal stationarity, are often insufficient to capture the transient characteristics or evolving spectral content associated with incipient or intermittent faults. This has led to the increasing adoption of time–frequency analysis techniques and advanced signal decomposition methods to improve diagnostic capability.
3.2.2. Time–Frequency Analysis
Time–frequency analysis (TFA) enables the representation of a signal’s spectral characteristics as they evolve over time, providing a two-dimensional view that is particularly useful for transient or modulated signals. Short-time Fourier transform (STFT) is one of the most widely used techniques, which applies a sliding window to segment the signal and perform Fourier analysis within each window. In practical IWM applications, due to the sampling nature, continuous-time signals are often unavailable [117]. As a result, related processing is typically carried out in discrete form [118]:
where ω[n] is a window function of length L, H is the hop size, m is the frame index, N is the number of FFT points, and k is the frequency bin index. The resolution is fixed and determined by the choice of the window, which limits its ability to resolve both low and high-frequency components simultaneously.
Wavelet transform overcomes this limitation through its multi-resolution analysis capability and has been used to extract fault signatures based on the three-phase stator currents of IWMs [119]. The scalable and translatable basis functions known as wavelets, enable adaptive time–frequency resolution: fine time resolution with coarse frequency resolution at high frequencies, and fine frequency resolution with coarse time resolution at low frequencies [120].
In practical TFA, the energy distribution often suffers from limited resolution, noise interference, and multi-component signal overlap. These challenges are especially pronounced in IWMs operating under non-stationary conditions and multiple excitation sources. Synchrosqueezing transform and ridge extraction techniques are used [121,122,123,124] to concentrate energy and identify key trajectories, thereby highlighting fault-related features more effectively.
In recent studies, TFA has also been increasingly used as a preprocessing step for deep learning-based fault diagnosis of IWMs [121,125,126]. By converting raw one-dimensional signals into two-dimensional time–frequency images, convolutional neural networks (CNN) and other architectures are enabled to simultaneously exploit both temporal and spectral features, thereby enhancing the model’s ability to learn discriminative fault patterns.
3.2.3. Fault Component Extraction Techniques
Targeting complex mixed signals from IWMs, the core objective of the fault component extraction is to separate fault-related feature components from background noise or normal operating interference, thereby providing cleaner features for fault diagnosis [127].
For PMSMs like IWMs, signal decomposition methods such as empirical mode decomposition, variational mode decomposition, and their variants are commonly employed. Empirical mode decomposition (EMD) is designed to decompose signals into a set of intrinsic mode functions (IMFs), each representing a simple oscillatory mode [128,129]. Unlike TFA methods that rely on predefined basis functions, EMD adaptively identifies signal components based on local time-scale characteristics. The decomposition process involves identifying local extrema, constructing upper and lower envelopes via interpolation, and iteratively sifting to extract each IMF. The signal x(t) is decomposed as follows [130]:
where IMFi(t) denotes the i-th IMF, and rn(t) is the residual. Fault features can be extracted from selected IMFs based on energy or entropy criteria.
Despite its adaptability, EMD suffers from mode mixing (where different frequency components coexist in a single IMF or the same component appears in multiple IMFs) and sensitivity to noise. To address these problems, ensemble EMD (EEMD) adds white noise to the signal and performs multiple decompositions to average out noise effects, thus reducing mode mixing [131,132,133]. More recent methods, such as complete EEMD with adaptive noise (CEEMDAN) [134,135,136], further enhance decomposition completeness and reduce reconstruction error. These methods have been shown to be effective in handling non-stationary and high-noise signals in PMSM applications [131,132,134,135].
Variational mode decomposition (VMD) is a more robust alternative to EMD in separating fault features from noise [137]. It simultaneously decomposes signals into predefined modes with constrained bandwidths. The objective is to decompose the signal x(t) into K modal components {uk(t)} [138,139]:
where ωk is the center frequency. To transform the constrained optimization problem into an unconstrained one, a quadratic penalty term and a Lagrange multiplier λ(t) are commonly used to construct the augmented Lagrangian function [138,139]:
where α is the bandwidth constraint parameter, which controls the strength of the bandwidth limitation on each mode. It can be seen from the equation that improper selection of α and K may lead to mode mixing or information loss. Therefore, parameter optimization of VMD is one of the main research directions. VMD optimized by algorithms such as Bayesian optimization, PSO, whale optimization, and sparrow search has been applied to fault feature extraction in cases like inter-turn short circuits [139,140].
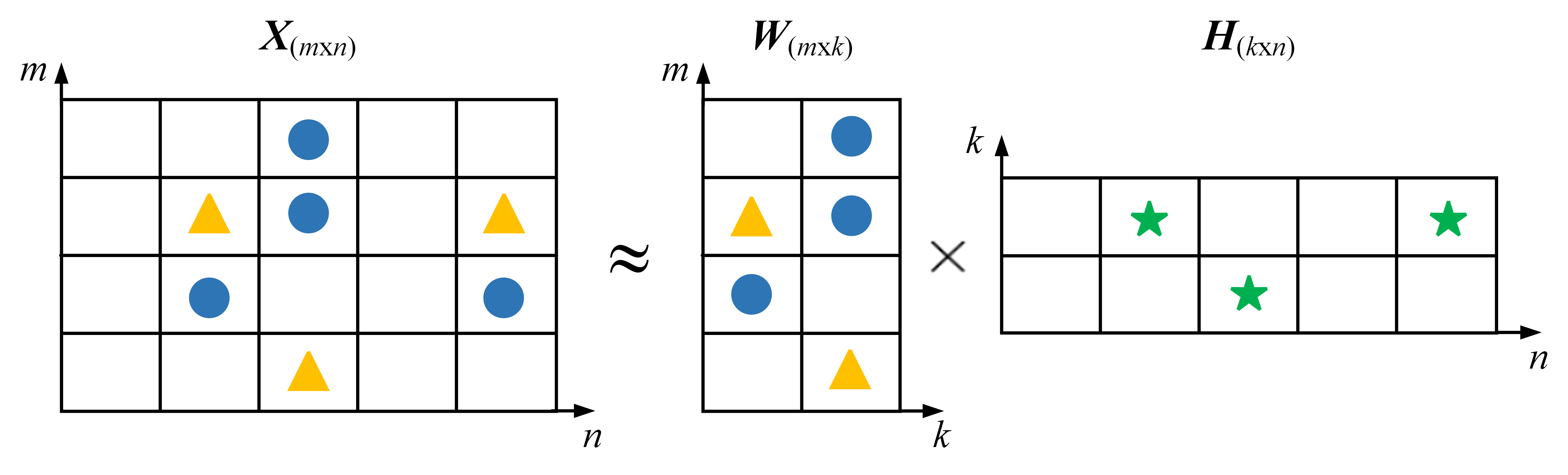
In the case of IWMs, signals tend to exhibit multi-source coupling characteristics due to the influence of various external excitations and potential compound faults. Algorithms with strong source separation capabilities, such as non-negative matrix factorization (NMF), have therefore attracted increasing attention. NMF factorizes a non-negative matrix X into the product of two non-negative matrices W and H, such that [141]
where W contains the basis components and H holds the corresponding activation coefficients. Figure 5 illustrates this process, in which colored symbols represent non-zero elements. In the context of IWM fault diagnosis, X is often constructed from the time–frequency representation [39]. Xue et al. [142] improved the NMF objective function by imposing sparsity constraints on the coefficient matrix and using Itakura–Saito divergence, which has strong feature discrimination capability, to extract compound fault features of IWMs. Tao et al. [39] combined signal decomposition techniques for pre-denoising and employed NMF for fault component separation, enabling the capture of weak fault signatures under strong background noise and intermittent disturbances.
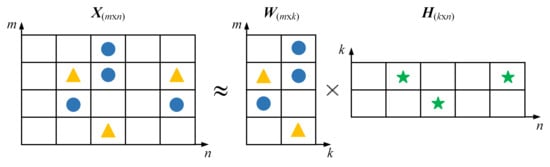
Figure 5.
Illustration of NMF.
3.2.4. Limitations and Challenges
Signal-based methods are widely used due to their simplicity, low computational cost, and ease of implementation. They are particularly effective in scenarios where fault-related features are prominent and noise levels are moderate.
However, their performance can degrade significantly in the presence of strong noise or low signal-to-noise ratios, which are common in the harsh operating environment of IWMs. These methods often depend on handcrafted features derived from expert knowledge, limiting their generalizability and making it difficult to adapt to new fault types or changing system dynamics. Additionally, signal characteristics can vary with speed, load, and other external factors, leading to nonstationary conditions that challenge the consistency and reliability of these techniques.
3.3. Knowledge-Based Diagnostic Methods
Model-based and signal-based fault diagnosis methods typically depend on prior knowledge and often require manual rule setting or expert judgment for fault identification. However, modern industrial applications increasingly demand efficient, one-stop automatic solutions [143]. With the rapid advancement of machine learning, knowledge-based diagnosis methods are quickly becoming mainstream. At present, such methods for IWMs can be broadly classified into traditional machine learning and deep learning.
3.3.1. Traditional Machine Learning Methods
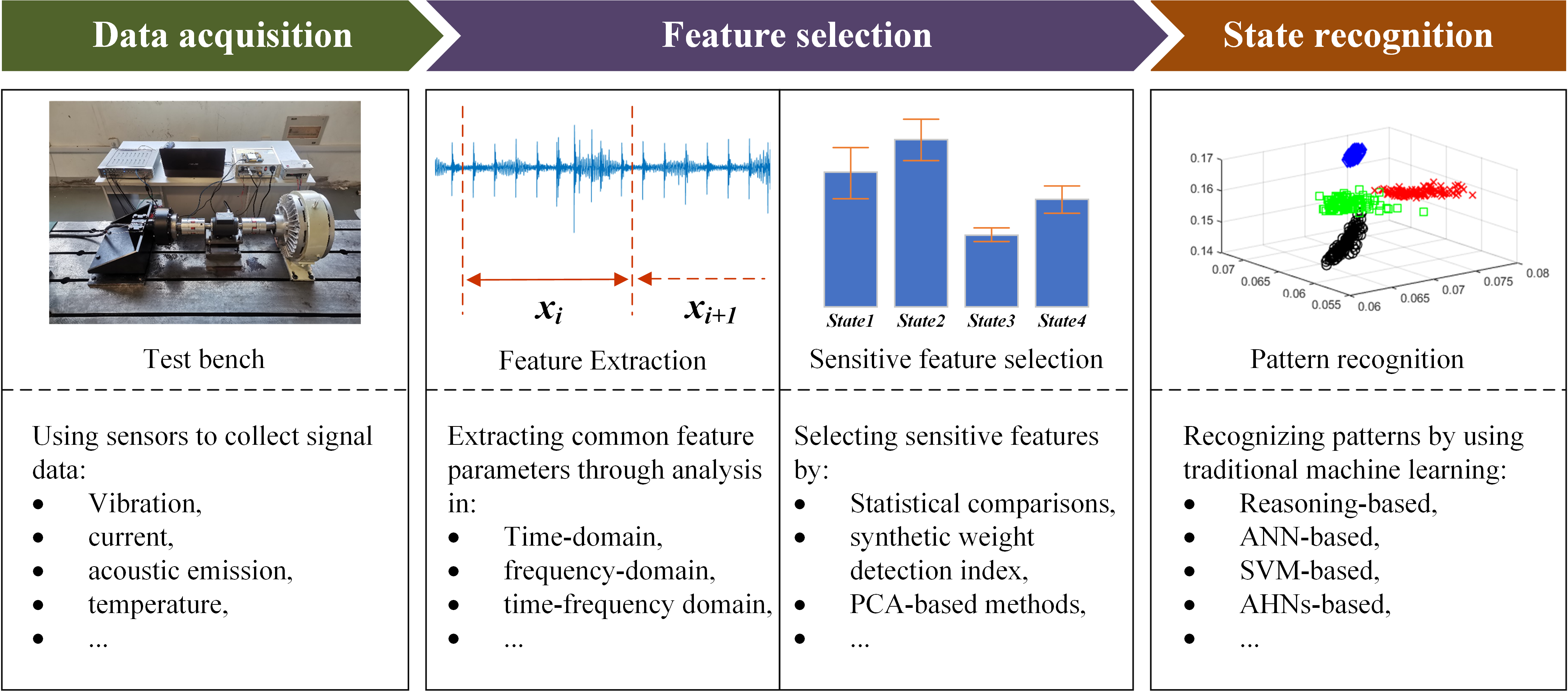
The diagnostic process based on traditional machine learning methods primarily includes data acquisition, manual selection of feature parameters, and state assessment or recognition, as illustrated in Figure 6.
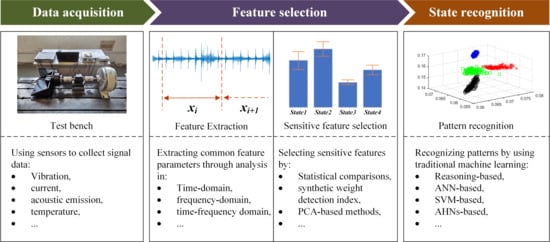
Figure 6.
Diagnostic process based on traditional machine learning methods.
- a.
- Data Acquisition and Feature Selection
Data acquisition is carried out using sensors and data acquisition devices, with the scheme designed according to the specific diagnostic scenario. Multi-sensor data acquisition and information fusion technologies are receiving increasing attention to achieve higher classification accuracy [144,145]. For example, Xue et al. [106] proposed a multi-perspective evaluation of the operating condition of IWMs, incorporating vibration, noise, temperature, current, and voltage signals.
The objective of feature extraction is to manually select feature parameters that are more sensitive to changes in machine states, i.e., those which are more discriminative across different operating states. This process typically leverages time-domain, frequency-domain, and time–frequency analysis methods, as introduced in signal-based diagnosis. Commonly used feature parameters can be found in [146].
The selection of sensitive features plays a critical role in diagnostic performance. Conventional methods rely on statistical comparisons (mean or variance) of feature parameters across various operating states. However, manual selection is time-consuming and labor-intensive, especially when dealing with high-dimensional data. Consequently, increasing attention has been directed toward the development of more efficient and adaptive feature selection techniques. For instance, a synthetic weight detection index built upon the discriminative index [147] and a principal component analysis (PCA)-based method [38] were employed to select the most sensitive parameters under various operating conditions of IWMs.
- b.
- State Recognition
Machine learning-based diagnostic models are used to establish the mapping between sensitive features and state patterns, thereby enabling state recognition. Traditional machine learning methods typically require labeled sample data for input or training, serving as a preparatory step for identifying unknown states during actual operation [143]. According to existing research related to IWMs, the current studies can be broadly classified into the following categories.
- (1)
- Reasoning-based Methods
Reasoning-based machine learning approaches express system uncertainty and inference through mathematical models, making them well-suited for fault diagnosis tasks that involve complex and ambiguous information. Fuzzy logic reasoning and probabilistic reasoning are most commonly used for IWMs.
- Fuzzy Logic Reasoning
Fuzzy logic is grounded in fuzzy set theory and is capable of handling uncertainties and vagueness that traditional binary logic cannot describe [148,149]. The core idea is to map input variables to membership functions ranging from 0 to 1, representing degrees of belonging to fuzzy sets, thereby enabling approximate reasoning of system states. A typical fuzzy inference system consists of fuzzification, rule evaluation, and defuzzification processes [150,151,152]. By constructing a rule base derived from expert knowledge, fuzzy logic systems can perform fault diagnosis effectively, especially when precise models are unavailable but experiential knowledge is abundant. For instance, Yan et al. [150] first extracted fault symptom variables using the average current Park vector method, and then employed a Mamdani-type fuzzy inference system to detect and locate single/multiple open-circuit faults and intermittent faults based on a predefined rule base. Moosakunju et al. [151] utilized DWT to extract the standard deviation features of stator currents. After fuzzification, fault phase identification of inter-turn short-circuit faults was achieved through rule matching and defuzzification processes. Picture fuzzy sets, known for carrying richer information, have also been employed for multi-stage safety assessment [106]: each element is characterized by a triplet < α, β, γ >, representing degrees of positive, negative, and refusal membership, subject to the constraint α + β + γ ≤ 1.
- Probabilistic Reasoning
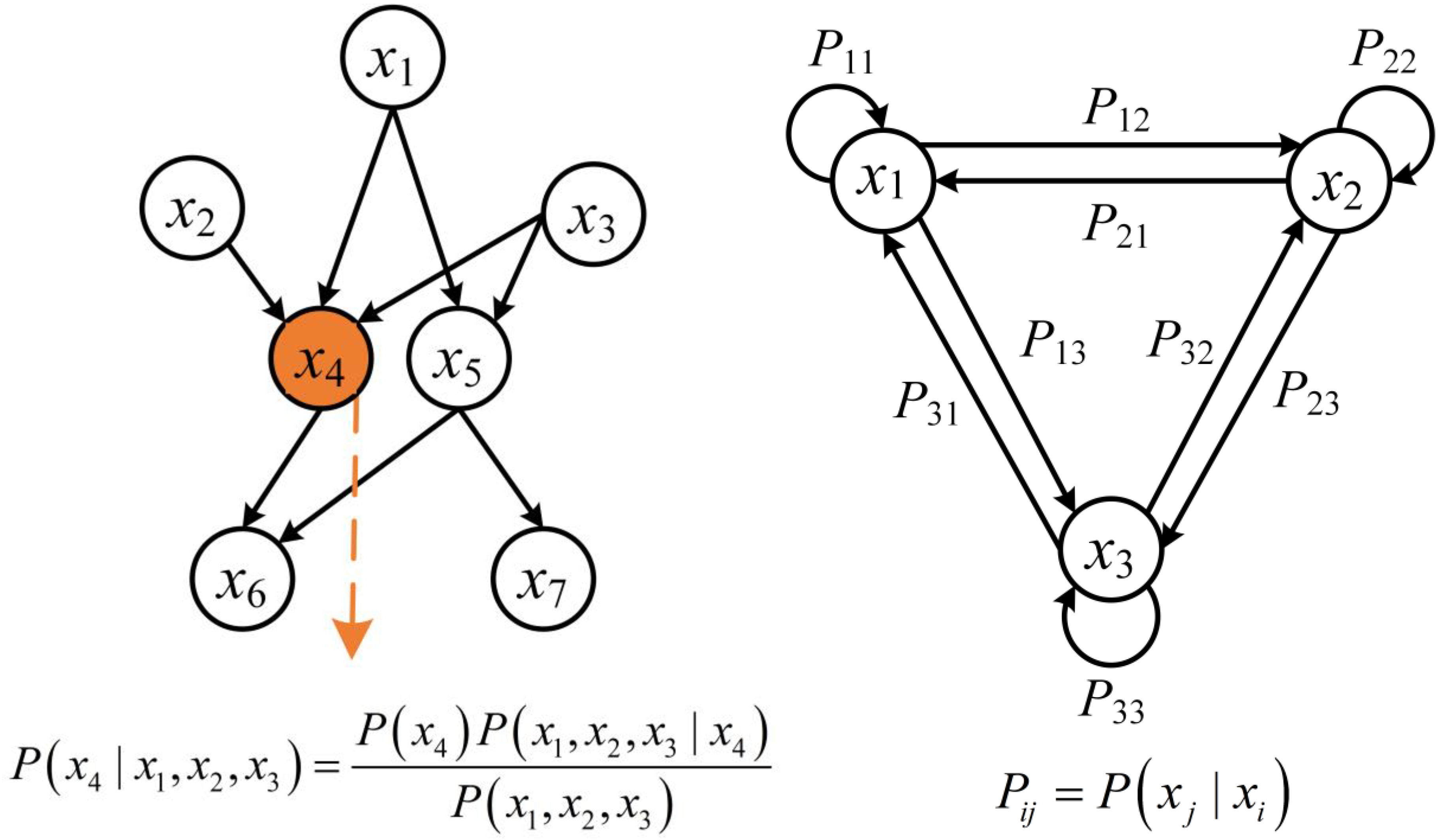
Probabilistic reasoning encompasses a set of approaches that model and infer system states under uncertainty using probability theory. Among these, probabilistic graphical models (PGMs) are widely used due to their ability to represent complex dependencies among variables in a compact and interpretable form [153]. PGMs include two major categories: Bayesian networks (BNs) and Markov models, as shown in Figure 7.
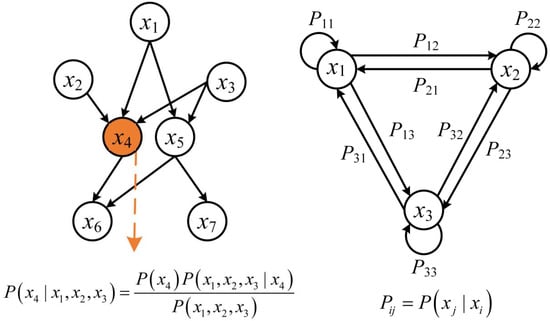
Figure 7.
Illustration of PGMs: (a) Bayesian network, (b) hidden Markov model.
Bayesian networks are directed acyclic graphs in which nodes represent random variables and edges denote conditional dependencies. They encode joint probability distributions and support reasoning under uncertainty via Bayes’ theorem. Cai et al. [154,155,156] achieved efficient diagnosis of multiple faults in PMSMs using BN. An improved Dempster–Shafer (DS) evidence theory, weighted by entropy, was employed to reallocate the conflicting portions of posterior probabilities in the BN-based diagnosis model constructed from vibration and noise data [157]. This process yielded new basic belief assignments, thereby enhancing diagnostic accuracy.
Markov models capture the stochastic evolution of system states over time and are especially useful for modeling sequential or temporal dependencies [153]. The most common forms are the Markov chain (MC) and the hidden Markov model (HMM). In fault diagnosis, HMMs are often employed to model time-series data, such as vibration or current signals, by assuming that the system transitions between hidden fault states with observable emissions [158]. The observation sequences can also be extended using models such as the Weibull mixture model [159]. The inference process involves estimating the most probable sequence of hidden states given a series of observations, typically using algorithms such as the Viterbi algorithm or the Baum–Welch algorithm [159,160,161].
In summary, probabilistic reasoning methods provide a rigorous and interpretable framework for fault diagnosis in uncertain environments. They are particularly advantageous when dealing with incomplete, noisy, or temporally correlated data. However, their performance may degrade in high-dimensional scenarios or when prior probabilities are difficult to estimate accurately.
- (2)
- Artificial Neural Network (ANN)-based Methods
Artificial neural networks (ANNs) are computational models inspired by the structure and function of biological neural systems. They have been widely adopted for state recognition in IWM fault diagnosis due to their ability to approximate nonlinear mappings between inputs (e.g., fault-sensitive features) and outputs (e.g., health states), even under complex and uncertain conditions.
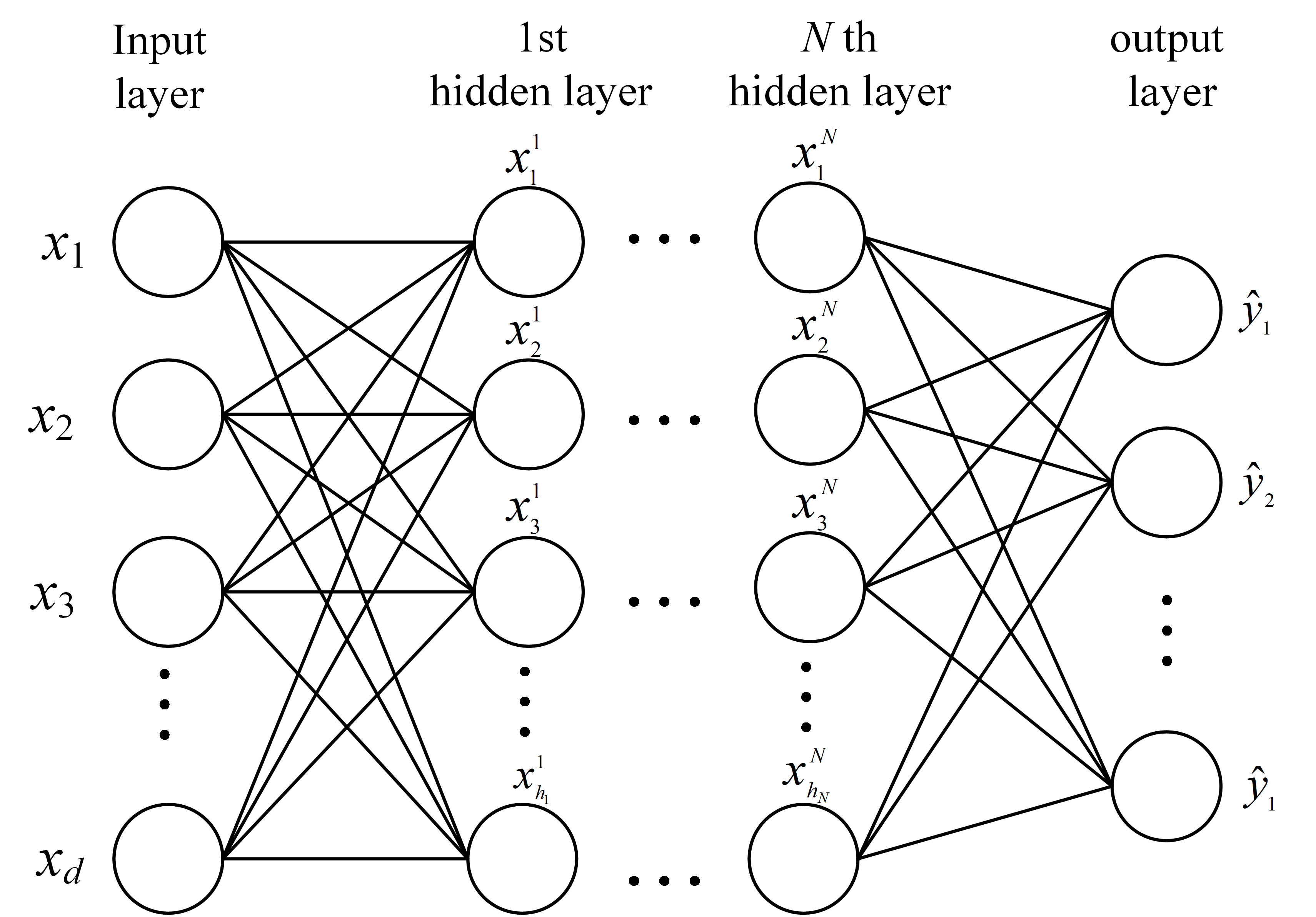
A standard feedforward ANN is typically composed of an input layer, one or more hidden layers, and an output layer, as shown in Figure 8. Each layer consists of interconnected neurons that compute weighted sums of their inputs followed by nonlinear activation functions [162]. The general expression of an ANN mapping can be described as follows:
where x is the input feature vector, W(l) and b(l) are the weight matrix and bias vector of the l-th layer, f(l) is the activation function (commonly ReLU or sigmoid), and y is the output corresponding to the predicted system state. Backpropagation with gradient descent is used to iteratively update weights based on a loss function such as cross-entropy or mean squared error [163,164]. Once trained, the ANN model can efficiently classify or regress unknown states based on new input features.
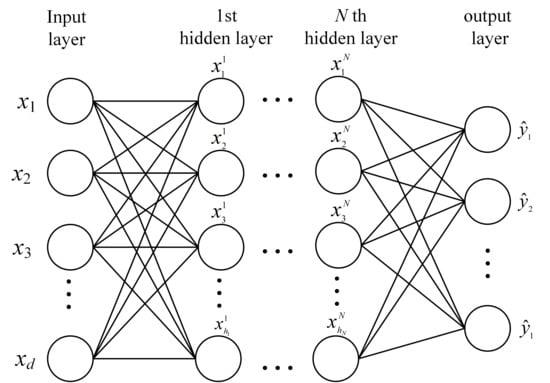
Figure 8.
Schematic diagram of the ANN architecture.
ANNs have demonstrated strong performance in identifying faults such as stator winding inter-turn short circuits [165,166], static and dynamic eccentricities [167,168], and inverter-related faults [169,170]. The weights of ANN nodes determine the network’s responsiveness to input features and its learning capacity. Consequently, many researchers have focused on optimizing weight adjustment strategies for ANNs; for instance, particle swarm optimization (PSO) [171], genetic algorithms [172,173], and the FOX optimizer [174] have been employed as alternatives to traditional backpropagation to enhance synaptic weight adjustment.
Despite their flexibility, conventional ANNs may suffer from overfitting when training data is limited or imbalanced. Additionally, they are typically regarded as “black-box” models, making interpretation and decision traceability challenging in safety-critical applications.
- (3)
- Support Vector Machine (SVM)-based Methods
Support vector machines aim to find the optimal hyperplane that maximizes the margin between different classes in a feature space. For linearly separable data, the decision boundary is defined as follows [175]:
where w is the weight vector and b is the bias term. The objective is to minimize ||w||2 while ensuring all samples are correctly classified with a margin, formulated as follows [176]:
SVM has been proven effective in identifying faults such as inter-turn short circuits, rotor faults, and demagnetization in PMSMs [177,178,179]. However, conventional SVM is inherently a binary classification algorithm, which necessitates tailored diagnostic strategies for handling multiple fault types. For instance, Kong et al. [180] proposed a method where samples are simultaneously input into all fault classifiers, and the diagnosis is made based on a predefined membership threshold using the following rule: “if exactly one classifier exceeds the threshold, assign that fault; if none or more than one do, classify as unknown”—effectively reducing the risk of misclassification. Meanwhile, another study [38], considering computational efficiency, adopted a sequential diagnosis approach, where the first classifier determines whether a fault exists, and then identifies the fault type progressively through other classifiers.
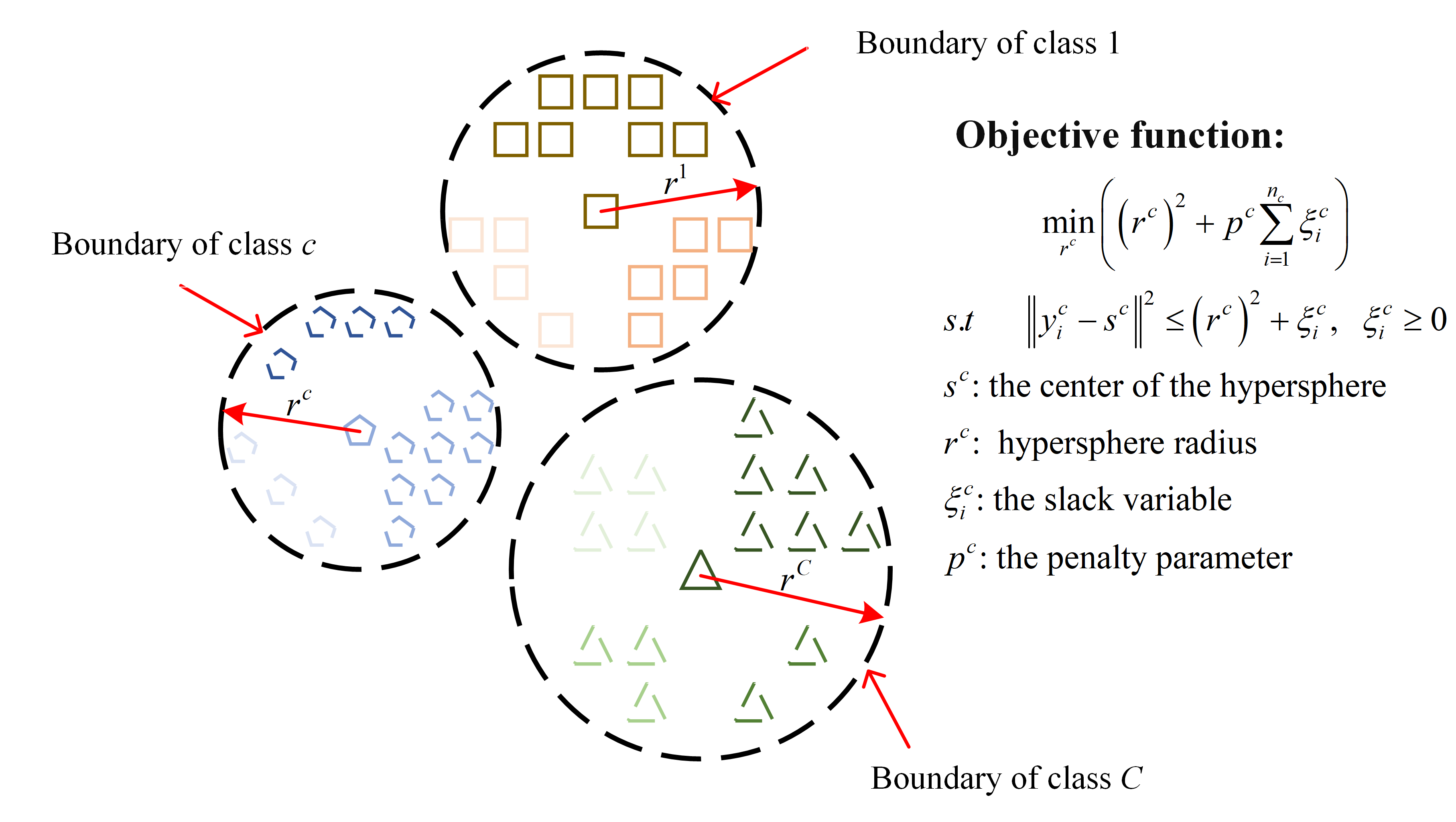
A more robust one-class classification algorithm—support vector data description (SVDD)—has also been applied to fault diagnosis of IWMs [179,181,182]. SVDD is a variant of SVM that constructs a minimum hypersphere enclosing most of the target data in a transformed feature space, allowing the identification of data points that lie outside this boundary as anomalies or unknown states. The idea of its application to multi-class diagnosis is shown in Figure 9. Similar to SVM, SVDD also requires kernel functions K(xi, xj) to map data into higher-dimensional spaces for nonlinearly separable problems. Common kernel choices include polynomial, radial basis function (RBF), and sigmoid kernels [181,183]. Some studies have focused on improving kernel functions, such as combining RBF with Gaussian difference function [182], or developing Weibull kernel functions based on the Weibull distribution [181], in order to enhance the classification performance of the model.
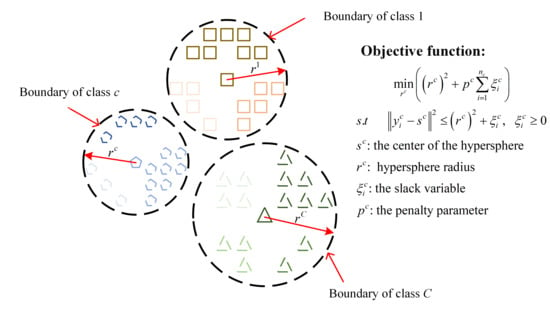
Figure 9.
Multi-class diagnostic approach based on SVDD.
- (4)
- Other Approaches
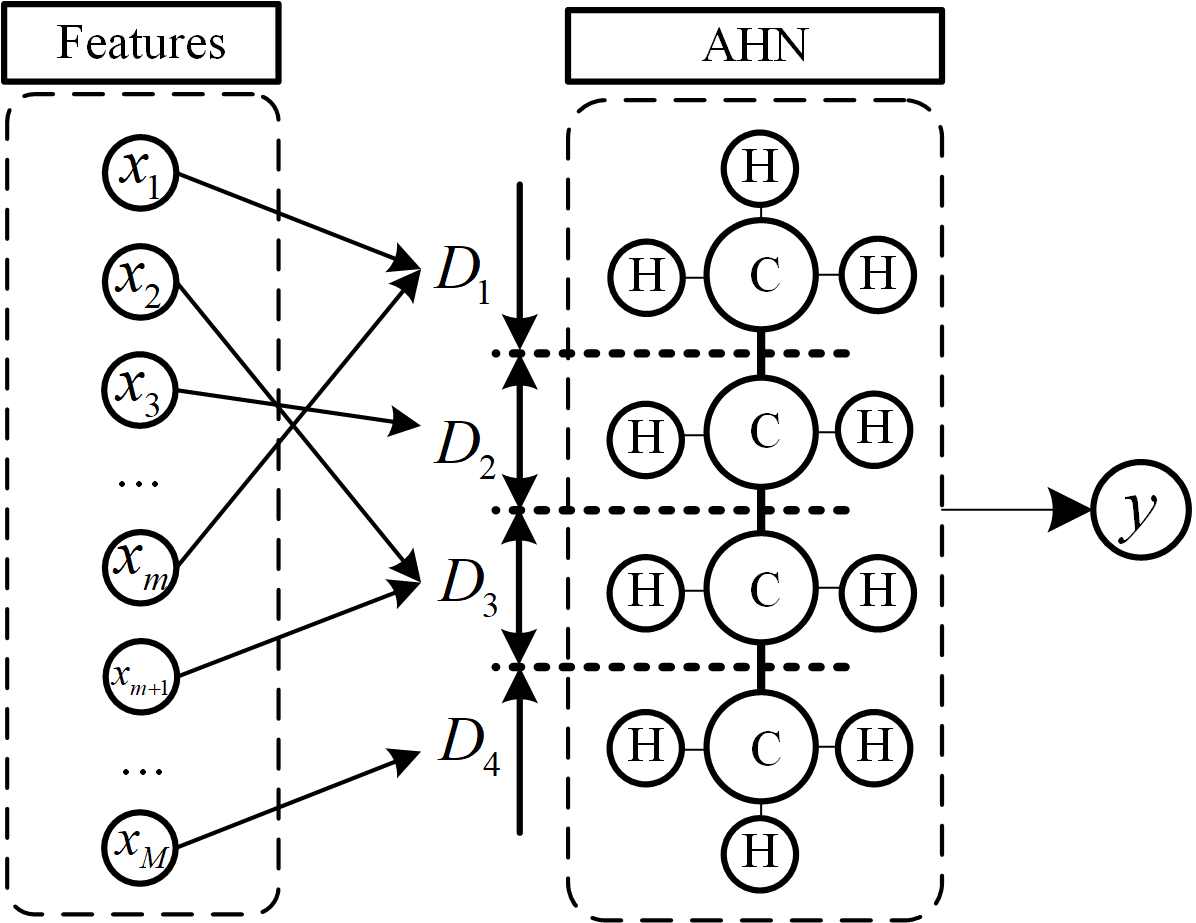
In recent years, artificial hydrocarbon networks (AHNs) have attracted growing attention in the field of IWM fault diagnosis [184,185,186,187]. Inspired by the structure and behavior of hydrocarbon molecules, AHNs simulate the learning process using analogies such as carbon chains and hydrogen atoms to model the relationships between inputs and outputs [185]. The core of the AHN lies in representing input variables as carbon chains and each carbon chain corresponds to the product of these membership degrees across inputs, as shown in Figure 10. The hydrogen atoms Hj act as weighting parameters associated with each carbon chain. The output y of an AHN with m carbon chains and n input variables is mathematically expressed as follows:
where Hj is the weighting coefficient (hydrogen atom) associated with the j-th carbon. xi is the i-th input variable, and denotes the membership degree function of xi.
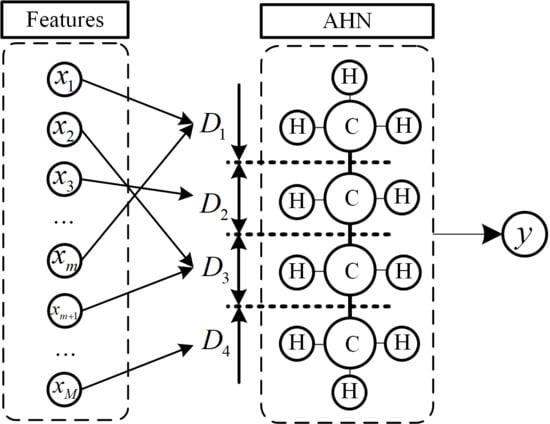
Figure 10.
Illustration of the AHN architecture.
Despite the excellent capabilities of AHNs in information encapsulation and integration, their adaptability to severe external disturbances in IWMs and their rapid response performance remain limited [188]. Improvements of AHNs have mainly focused on two aspects: first, enhancing the classification by refining the error function to capture more informative features [187]; and second, improving the update mechanism of hydrocarbon molecules. For example, algorithms such as K-means clustering [184] or AdaBoost [186] have been employed to optimize the partitioning of molecular intervals and the linear linking strategies among multiple molecules, thereby improving both classification accuracy and computational efficiency.
3.3.2. Deep Learning Methods
Traditional machine learning methods have achieved promising results in IWM fault diagnosis. However, they suffer from several limitations that hinder their applicability in complex and dynamic industrial environments [189]. Specifically, these models typically rely on manual feature extraction and prior expert knowledge, making them sensitive to signal preprocessing and less effective in capturing deep nonlinear relationships. Moreover, their scalability and adaptability to varying operating conditions are constrained, particularly in the presence of nonstationary signals, high-dimensional inputs, and large-scale datasets.
During the evolution of diagnostic techniques, deep learning has emerged as a powerful alternative due to its inherent ability to perform automatic feature extraction, hierarchical representation learning, and end-to-end fault classification [189]. Deep architectures can model intricate dependencies in raw or transformed signals, enabling robust state recognition without extensive manual intervention. Accordingly, deep learning methods have become an increasingly popular research focus in fault diagnosis.
Existing studies have adopted a wide variety of deep learning architectures with numerous variants. Focusing on research related to IWMs and their underlying motor type—PMSMs—this section considers three major perspectives, as shown in Table 5.

Table 5.
Categorization of deep learning-based fault diagnosis methods for IWMs.
- a.
- Representation Learning Models
Representation learning models are primarily designed to automatically extract high-level features from raw or transformed signal data. Typical examples include autoencoders (AEs), deep belief networks (DBNs), and convolutional neural networks (CNNs), among which CNNs are the most widely applied.
CNNs operate by applying convolutional filters to input data, capturing local spatial correlations through hierarchical layers [190,191]. They are particularly effective at processing spatial input formats such as time–frequency matrices or spectrograms [121,125,126,192]. For instance, Pietrzak et al. [193] performed bispectral analysis on stator phase currents and used the resulting data as input to a CNN model. Yu et al. [194] employed VMD to extract component signals for model input. Zhang et al. [195] transformed one-dimensional torque signals into two-dimensional grayscale images based on Gramian angular fields for CNN training. Chen et al. [196] computed two-dimensional spectral representations under normal and faulty states using the generalized frequency response function, from which CNNs were used to extract fault-related features. In terms of architectures, some studies [197,198] have designed multi-scale convolutional kernels to enhance feature extraction capability. Some researchers [197,198,199,200] have introduced residual learning into CNNs, enabling the model to learn the residuals between inputs and outputs, while employing skip connections to alleviate the vanishing gradient problem. For multi-sensor diagnostics, multi-branch CNN architectures have also been proposed to achieve effective information fusion [126,199].
Despite the widespread use and promising performance of CNNs in IWM and PMSM fault diagnosis, several limitations remain. First, CNNs are inherently designed for spatial feature extraction and lack the ability to capture long-term temporal dependencies, making them less effective when dealing with time-series signals without transformation [201]. Second, although incorporating multidimensional and complex signal representations can enhance the ability of convolutional kernels to extract informative features, these methods rely heavily on signal preprocessing procedures, which limits their applicability for end-to-end diagnostic deployment. Furthermore, CNNs can be computationally demanding [202], especially when deeper layers or multi-branch designs are used, posing challenges for real-time and resource-constrained IWM diagnostic applications.
- b.
- Temporal Dynamic Networks
Temporal dynamic networks are designed to capture temporal dependencies in time-series data, making them suitable for modeling the nonstationary behavior of motor systems [203,204]. Recurrent neural networks (RNNs) serve as the foundational architecture, processing input sequences one element at a time while maintaining a hidden state that captures previous information [205,206]. However, standard RNNs suffer from vanishing gradient problems when learning long-term dependencies. Long short-term memory (LSTM) networks address this limitation by introducing memory cells and gating mechanisms (input, output, and forget gates), enabling the model to retain information over longer sequences [207]. They are effective in learning long-term dependencies from current, vibration, or speed signals over multiple cycles. For example, Tang et al. [208] employed LSTM networks to detect motor bearing and stator faults based on sequential current data. Some other studies [209,210,211] have adopted CNNs as front-end feature extractors to reduce data dimensionality, followed by LSTM networks to process the temporal evolution of these features, thereby enhancing the abstraction capability for local patterns embedded in the raw signals. Gated recurrent units (GRUs) networks are applied [212,213,214] to simplify the LSTM architecture by combining the forget and input gates into a single update gate, achieving comparable performance with fewer parameters.
Although these architectures are capable of extracting temporal features across multiple temporal scales, their reliance on sequential processing presents certain limitations. On one hand, they may be vulnerable to irrelevant noise within the sequence, which can obscure critical information. On the other hand, their inherently serial computation is inefficient when dealing with long input sequences.
- c.
- Attention-enhanced Models
Attention mechanisms have recently gained traction in motor fault diagnosis due to their capability to selectively focus on relevant parts of the input sequence or feature space. The core idea is to assign weights to input components based on their contextual relevance [215,216], enabling the model to prioritize critical fault-related information while filtering out irrelevant or noisy features.
- (1)
- Attention Integration
In practical applications, attention mechanisms are often integrated into existing deep learning models to enhance their feature representation [217,218,219]. For application in PMSMs, Wang et al. [220] proposed a frequency attention mechanism and integrated it with discrete wavelet transform (DWT) to form CNN pooling layers for extracting fault-relevant features from different frequency components. Similarly, Jiang et al. [221] combined DWT with an adaptive sparse attention mechanism to enhance the robustness of inverter open-circuit fault diagnosis by filtering out redundant information in the data.
Attention mechanisms also play a key role in multi-channel or multi-branch data fusion [222]. Tang et al. [208] combined CNN with a hybrid attention mechanism for feature extraction from multiple current signals. Wang et al. [223] embedded a channel attention mechanism into a deep residual network, enabling the model to learn the relative importance of different feature channels and adaptively assign weights. Qin et al. [224] applied a multi-channel attention mechanism to LSTM networks by integrating temporal ratio vectors across channels. Ge et al. [126] improved the efficient channel attention mechanism by updating the weight coefficients of each branch based on the contribution of informative content.
- (2)
- Transformer
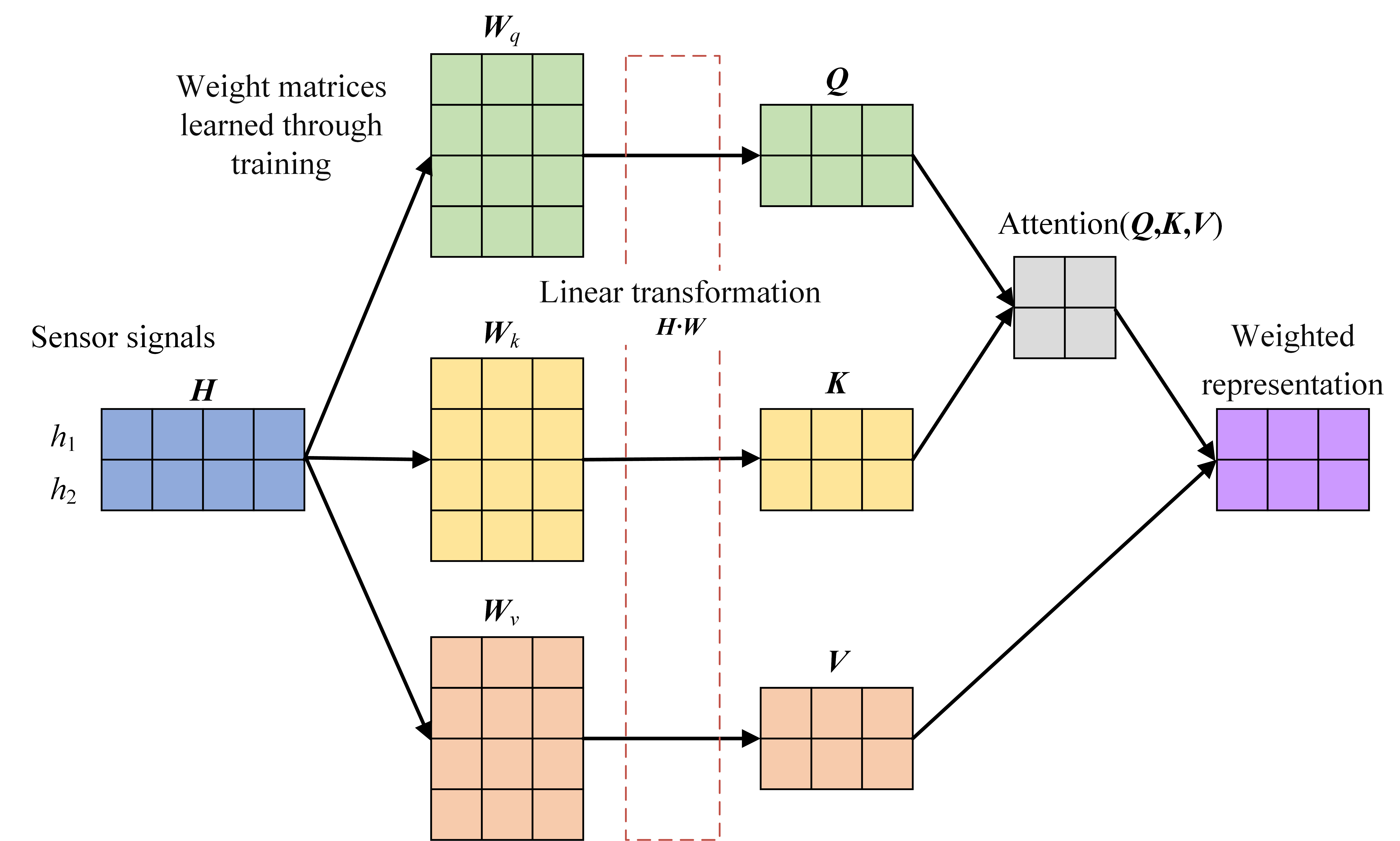
Transformers based on self-attention mechanisms have demonstrated remarkable advantages in fault diagnosis in recent years [225]. Their core strength lies in capturing long-range dependencies and enabling global feature interactions [226], which makes them particularly effective for handling nonstationary and multi-scale fault signals commonly encountered in IWMs. In contrast to RNNs or LSTMs, which may suffer from vanishing gradients when processing long sequences, the self-attention mechanism in Transformers computes pairwise correlations across all time steps [227,228], thereby directly extracting cross-temporal fault features. This is achieved by calculating a weighted sum of all value vectors, where the weights reflect the similarity between the query at a given position and all keys [229], as shown in Figure 11. The classic formulation, known as scaled dot-product attention, is expressed as follows [230]:
In the context of fault diagnosis, the input sequence typically consists of sensor signals collected over time. The query matrix , key matrix , and value matrix are linearly projected from the input features, where each row corresponds to a time step. Specifically, QKT measures the correlation between different time steps, allowing the model to assign attention weights based on temporal relevance. The scaling factor ensures numerical stability during optimization. By applying these weights to the value matrix V, the attention mechanism produces a context-aware representation of each time step, capturing cross-temporal fault signatures critical for accurate diagnosis.
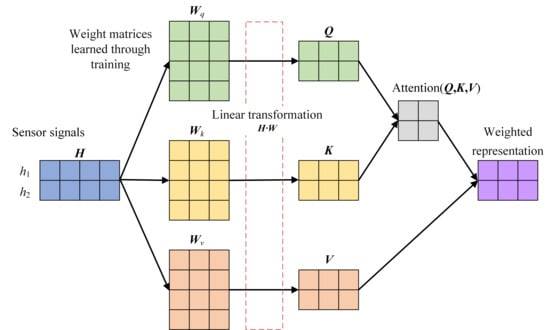
Figure 11.
Brief illustration of scaled dot-product attention mechanism.
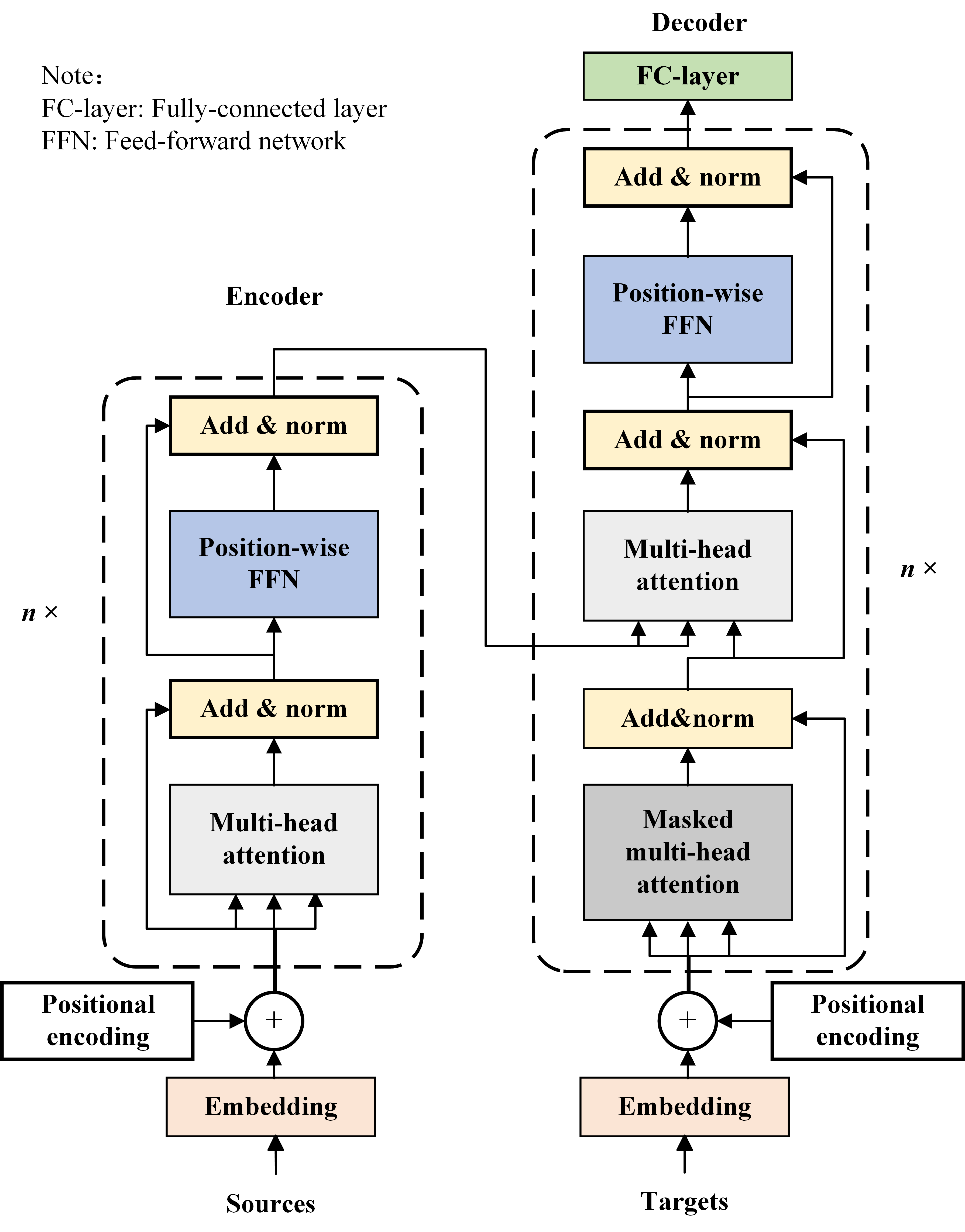
To effectively capture complex temporal dependencies in fault signals, Transformers employ multi-head attention, where multiple attention heads operate in parallel to learn diverse representations from different subspaces of the input [230]. This mechanism enables the model to simultaneously focus on transient disturbances, gradual trends, and periodic patterns, enhancing robustness under nonstationary and noisy conditions. The encoder architecture consists of stacked multi-head attention and feedforward layers, integrated with residual connections and layer normalization [231,232], as demonstrated in Figure 12. To compensate for the lack of inherent sequential order, positional encoding is added to input embeddings, allowing the model to extract temporal fault signatures from sensor data.
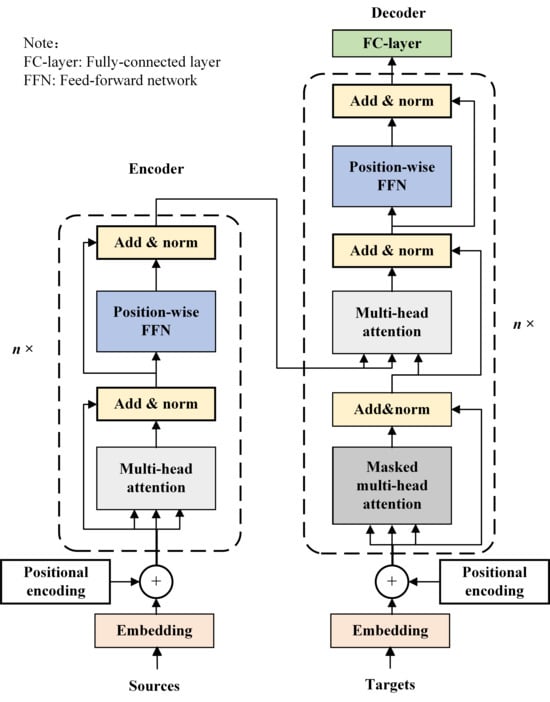
Figure 12.
Schematic diagram of Transformer network.
At present, Transformer-based fault diagnosis for IWMs and PMSMs remains in its early stages. Parvin et al. [233] employed the Transformer architecture to diagnose the severity of inter-turn short circuit faults using only stator current time-series signals. Lang et al. [234] constructed sample pairs by combining current signals with residual signals estimated by observers, and input them into a dual-channel Transformer framework. The results demonstrated robust performance in open-circuit fault diagnosis of inverters under varying operating conditions. There are other researchers focusing on optimizing the self-attention mechanism. For instance, Li et al. [235] introduced an efficient moving window self-attention mechanism for time series by integrating Half-sandwich and Cascaded window group attention operations, effectively reducing computational complexity and network parameters. These advances demonstrate the adaptability of Transformer-based models to motor signal characteristics, especially in capturing complex temporal dependencies and subtle fault signatures.
3.3.3. Limitations and Challenges
Traditional machine learning methods—including reasoning-based models, ANNs, SVMs, and newer approaches like AHNs—have demonstrated effectiveness in fault diagnosis of IWMs by learning the mapping between extracted features and system states. These approaches are especially useful when physical modeling is difficult or when large amounts of condition-monitoring data are available. Most of these methods fall under the category of supervised learning, relying on labeled datasets to train classifiers for specific fault types.
Several limitations also remain. First, their performance is highly dependent on the quality of manually extracted features, which requires substantial domain knowledge and limits generalization to unseen fault patterns. Second, these methods are often sensitive to noise and may struggle to maintain robustness under varying signal quality. Finally, they may perform poorly in nonstationary operating conditions and typically require retraining or adaptation when the data distribution shifts.
Deep learning has significantly advanced the fault diagnosis of IWMs by enabling automatic feature extraction, modeling of complex signal dependencies, and end-to-end classification. Techniques based on CNNs, RNNs, LSTMs, GRUs, and Transformer architectures have each shown unique advantages—ranging from spatial pattern recognition to temporal dynamics modeling and global context learning. Attention-enhanced models, in particular, offer improved robustness under nonstationary and noisy conditions, which are common in IWM applications.
Despite these strengths, deep learning methods face several notable limitations. First, many models—especially deeper or hybrid architectures—are computationally intensive, making real-time deployment on embedded IWM systems challenging. Second, deep models are highly data-dependent; acquiring large-scale, high-quality labeled datasets for fault diagnosis remains difficult in real-world settings. Third, while many current methods operate in a supervised learning framework, the scarcity of labeled fault data limits their scalability and generalization to unseen fault types or new operating conditions.
There is no doubt that deep learning will remain a major research trend. To address these challenges, future studies may benefit from exploring lightweight architectures, such as efficient CNNs or Transformer variants with reduced parameters, to support real-time diagnostics. In addition, semi-supervised, self-supervised, or contrastive learning approaches could help alleviate the dependence on labeled data. Incorporating domain knowledge into network design—through physics-informed learning or hybrid modeling—also holds potential to improve interpretability and reliability. Finally, developing generalizable and adaptive models that remain effective under shifting conditions is key for transitioning deep learning-based fault diagnosis from lab environments to practical IWM applications.
3.4. Section Summary of Fault Diagnosis for IWMs
This section reviewed the fault diagnosis methods for IWMs, which can be broadly categorized into model-based, signal-based, and knowledge-based approaches. Model-based methods rely on mathematical models to estimate system states or parameters and detect faults via residual analysis. They are physically interpretable but are highly dependent on model accuracy and sensitive to noise and parameter uncertainties.
Signal-based methods extract fault-related features directly from measurable signals, using time-domain and frequency-domain analysis, advanced time–frequency analysis and signal decomposition methods. These approaches are less reliant on system modeling and offer good real-time performance, but often require expertise in signal processing and are limited by signal noise and non-stationarity.
Knowledge-based methods, especially those based on machine learning and deep learning, have gained increasing attention for their ability to achieve end-to-end fault classification. Traditional machine learning models depend on manual feature extraction and may struggle with generalization. In contrast, deep learning models can automatically learn hierarchical representations from raw or transformed signals, offering superior adaptability in complex conditions. However, they may require large labeled datasets and face challenges in real-time deployment and model interpretability.
Collectively, each method has its own characteristics, as shown in Table 6. A comprehensive understanding and effectively leveraging these techniques based on specific scenarios is essential for reliable IWM fault diagnosis.

Table 6.
Comparative evaluation of diagnostic methods for IWMs.
4. Diagnostic Challenges and Future Research Directions
Despite significant progress in the development of fault diagnosis techniques for IWMs, several technical and practical challenges remain, limiting their large-scale deployment and industrial applicability. This section outlines the key challenges and potential future research directions.
4.1. Toward More Accurate Modeling: Digital Twin-Driven Diagnosis
A major limitation of model-based diagnosis methods is the difficulty of achieving accurate modeling, along with their sensitivity to parameter variations and environmental disturbances. Advancements in digital twin technology offer a promising direction, enabling the construction of high-fidelity virtual models that mirror the physical behavior of motors in real time. This allows for more precise model-based fault detection and parameter estimation, especially under complex operating conditions.
To support this approach, future research can explore multi-modal sensor fusion frameworks that combine electrical, mechanical, and thermal signals to enhance model accuracy. Additionally, the development of modular and reconfigurable digital twin templates tailored for common IWM configurations would facilitate broader adoption. Embedding such models into real-time diagnostic systems, possibly with cloud-edge hybrid computation, could significantly improve monitoring fidelity and adaptability.
4.2. Handling Noise and Disturbances: Nonstationary Signal Analysis and Multi-Wheel Cooperative Processing
In practical scenarios, diagnostic signals are often contaminated by intermittent disturbances and high levels of noise, which compromises the reliability of conventional signal processing methods. This highlights the need to develop advanced nonstationary signal analysis techniques and robust fault component extraction methods, capable of isolating meaningful fault components under abrupt variations.
Meanwhile, multiple wheels often exhibit dynamic similarity during vehicle operation in terms of working conditions and road inputs. This implies that the external disturbances affecting different motors tend to share common characteristics. However, a faulty motor is expected to present specific deviations from this shared behavior. Therefore, exploring cooperative signal processing across multiple motors to extract locally discriminative fault features represents a promising research direction.
4.3. Coping with Complex Working Conditions: Condition-Invariant Representation Learning
The highly dynamic and complex working conditions of IWMs also pose significant challenges for maintaining diagnostic consistency. Fault features may vary with load, speed, and environment, complicating the identification of invariant fault signatures. Future work should focus on learning representations that are robust to operating condition variations, such as domain-invariant features or condition-agnostic embeddings.
Addressing this issue requires developing condition-invariant or domain-adaptive representation learning techniques. Promising directions include contrastive learning with domain augmentation, adversarial feature alignment, and multi-task learning frameworks that jointly model operating condition attributes and fault states. Establishing shared latent representations disentangled from contextual variation is critical for robust generalization.
To benchmark progress in this area, there is also a growing need for open-access, condition-diverse IWM datasets with well-annotated operating parameters, facilitating reproducible evaluation and model calibration.
4.4. Enhancing Generalization: Transferable and Data-Efficient Diagnostic Knowledge
For real-world IWM applications, diagnostic models must generalize across motors, working conditions, and vehicle platforms. However, distribution shifts often lead to degraded model performance outside the training domain.
To address this, one key direction is the development of transfer learning. Techniques such as domain adaptation, multi-source transfer, and federated learning can help reuse diagnostic knowledge across different systems while minimizing the need for labeled data. For instance, federated frameworks are promising for privacy-preserving collaboration among vehicles, enabling shared model improvement without raw data exchange. Moreover, lifelong learning offers the potential for models to continuously adapt as new fault types or operational regimes emerge, reducing performance degradation over time.
Equally important is improving data efficiency, as high-quality fault data and labels in IWM systems are scarce and costly to obtain. Future research should explore self-supervised and unsupervised representation learning, enabling models to extract meaningful features from unlabeled operational data. In addition, few-shot learning—potentially combined with physical knowledge—can support rapid adaptation to rare or emerging fault types. Integrating meta-learning and reinforcement learning may further enhance adaptability under dynamic conditions or limited supervision.
4.5. Towards Practical Deployment: Efficiency and Interpretability
To be practically deployable, diagnostic models must meet stringent requirements in terms of computational cost, real-time performance, and interpretability. Research should prioritize the development of lightweight diagnostic architectures, such as compressed convolutional networks, transformer variants with reduced complexity, and hardware-friendly model pruning techniques.
At the same time, incorporating explainable AI tools—such as attention maps, saliency-based attribution, or rule-based surrogate models—will be key to building trust in automated diagnosis outcomes, especially for regulatory approval and human-in-the-loop decision-making.
To accelerate deployment and standardized evaluation, it would also benefit from the creation of benchmarking platforms and testbeds for IWM diagnosis. These platforms would help validate algorithm performance across common metrics such as detection latency, computational cost, and fault diagnosis accuracy.
5. Conclusions
This paper presents a systematic review of fault diagnosis for IWMs used in EVs, focusing on their structural uniqueness, typical failure types, and corresponding diagnostic methodologies. Three mainstream diagnostic approaches were reviewed: model-based methods offer physical interpretability but require accurate modeling and are sensitive to uncertainties; signal-based methods are widely applicable and effective in real time, yet limited by non-stationarity and noise; and knowledge-based methods, especially deep learning, have shown great promise in achieving end-to-end diagnosis and feature automation, though issues remain in data dependence, generalization, and interpretability. Recent research trends suggest a shift toward more intelligent and adaptable systems, such as integrating attention mechanisms and Transformer-based models, to better capture nonstationary fault features. Finally, we discuss the challenges of IWM diagnosis and further outline promising research directions. This review is expected to provide researchers and practitioners with a clear understanding of the current state, limitations, and directions in this field.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.T., H.X. and X.W.; methodology, Y.T., H.X. and L.Z.; formal analysis, Y.T. and X.W.; investigation, X.B. and H.Y.; resources, Y.T.; writing—original draft preparation, Y.T., X.W. and L.Z.; writing—review and editing, H.X., H.F. and D.Y.; supervision, H.X. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Jiangsu Province Science and Technology Plan Special Project (International Science and Technology Cooperation Program), grant number BZ2024028 and the Project of Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province, grant number BK20240872.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Cai, S.; Kirtley, J.L.; Lee, C.H.T. Critical review of direct-drive electrical machine systems for electric and hybrid electric vehicles. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2022, 37, 2657–2668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Dai, L.; Niu, S.; Fu, W.; Chau, K.T. Critical review of direct-drive in-wheel motors in electric vehicles. Energies 2025, 18, 1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hori, Y. Future Vehicle Driven by electricity and control-research on four-wheel-motored “UOT Electric March II”. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2004, 51, 954–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deepak, K.; Frikha, M.A.; Benômar, Y.; El Baghdadi, M.; Hegazy, O. In-Wheel Motor Drive Systems for Electric Vehicles: State of the Art, Challenges, and Future Trends. Energies 2023, 16, 3121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Hua, W. Overview of in-wheel traction machine and its key techniques for distributed-driving system. Proc. Chin. Soc. Electr. Eng. 2024, 44, 2871–2885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, T.; Liu, D.; He, Y. Review on development of permanent magnet in-wheel motors. Trans. China Electrotech. Soc. 2024, 39, 378–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Z.; Li, X.; Liu, T.; Zhao, S. Modeling and suppression of unbalanced radial force for in-wheel motor driving System. J. Vib. Control. 2022, 28, 3108–3119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Cong, J. Optimization and Control of Vehicle Vertical system with suspended in-wheel motor. Mechanics 2022, 28, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wan, S.; Zhang, M.; Guo, J. Analysis on coupled vibration characteristics of electric vehicles in-wheel motor with random excitation. J. Mach. Des. 2024, 41, 146–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Taghavifar, H.; Du, H.; Qin, Y.; Dong, M.; Gu, L. In-wheel motor vibration control for distributed-driven electric vehicles: A review. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electr. 2021, 7, 2864–2880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iizuka, S.; Akatsu, K. A Thermal Dissipation Characteristics of Integrated In-Wheel Motor Using SiC Power Module. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE 3rd International Future Energy Electronics Conference and Ecce Asia, Kaohsiung, Taiwan, 3–7 June 2017; pp. 1251–1255. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.; Zhu, G.; Zhao, Y.; Jia, N.; Xue, M.; Li, Y. Design and analysis of different cooling schemes of a flux-modulated permanent magnet in-wheel motor for electric vehicle applications. IET Electr. Power Appl. 2021, 15, 348–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutoh, N.; Nakano, Y. Dynamics of front-and-rear-wheel-independent-drive-type electric vehicles at the time of failure. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2012, 59, 1488–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanner, D.; Drugge, L.; Trigell, A.S. Fault classification method for the driving safety of electrified vehicles. Veh. Syst. Dyn. 2014, 52, 704–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Yan, S.; Shen, Y.; Li, C.; Zhang, Y.; Hussain, F. Model predictive control system based on direct yaw moment control for 4WID self-steering agriculture vehicle. Int. J. Agric. Biol. Eng. 2021, 14, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, F.; Yu, Y.; Pei, Y. State-of-the-art technology and prospects of permanent magnet in-wheel motors for electric drive vehicles. Acta Armamentarii 2022, 42, 2060–2074. [Google Scholar]
- Hang, P.; Chen, X. Towards autonomous driving: Review and perspectives on configuration and control of four-wheel independent drive/steering electric vehicles. Actuators 2021, 10, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Adeleke, O.P.; Xu, X. Methods and applications of energy saving control of in-wheel motor drive system in electric vehicles: A comprehensive review. J. Renew. Sustain. Energy 2019, 11, 062701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Fan, X.; Wang, Q.; Chen, X.; Zhu, S. Review on torque distribution scheme of four-wheel in-wheel motor electric vehicle. Machines 2022, 10, 619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Qiao, X.; Zhang, N.; Feng, J.; Wang, X. Review of intelligent fault diagnosis for permanent magnet synchronous motors in electric vehicles. Adv. Mech. Eng. 2020, 12, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaneghah, M.Z.; Alzayed, M.; Chaoui, H. Fault detection and diagnosis of the electric motor drive and battery system of electric vehicles. Machines 2023, 11, 713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaaraoui, L.; Mansouri, A. New design and optimization of an in-wheel permanent magnet motor with tangentially magnetized magnets and unequal stator teeth. J. Electr. Eng. 2023, 74, 228–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.; Yu, K.; Ding, Y.; Lu, X. Design and optimization of a novel external-rotor axial flux motor for in-wheel application. J. Electr. Eng. Technol. 2024, 19, 2473–2479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saavedra, H.; Romeral, L.; Riba, J.-R. Optimal Design of a Three-Phase AFPM for In-Wheel Electrical Traction. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Electric Vehicle Conference (IEVC), Florence, Italy, 17–19 December 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, J.; Wang, X.; Zhao, B.; Tan, F.; Semail, E.; Nguyen, N.K.; Bracikowski, N. Design, analysis of a seven-phase fault-tolerant bi-harmonic permanent magnet machine with three active air gaps for in-wheel traction applications. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2024, 39, 263–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, J.; Zhao, B.; Huang, Y.; Semail, E.; Nguyen, N.K. Quantitative comparisons of outer-rotor permanent magnet machines of different structures/phases for in-wheel electrical vehicle application. Energies 2022, 15, 6688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishanth, F.N.U.; Van Verdeghem, J.; Severson, E.L. A review of axial flux permanent magnet machine technology. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2023, 59, 3920–3933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandagopal, S.; Chokkalingam, L.N. External rotor permanent magnet-less electric motors for traction application: A review. Int. J. Veh. Des. 2022, 90, 142–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cetinceviz, Y. Optimal design, electromagnetic–thermal analysis and application of in-wheel permanent magnet BLDC motor for e-mobility. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 3258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tashakori, A.; Ektesabi, M.; Hosseinzadeh, N. Characteristics of suitable drive train for electric vehicle. In Proceedings of the 2011 International Conference on Instrumentation, Measurement, Circuits and Systems (ICIMCS 2011), Hong Kong, China, 12–13 December 2011; pp. 51–57. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y. Outer-rotor switched reluctance motor and its control system used in electric vehicles. In Proceedings of the 2011 International Conference on Electrical Machines and Systems, Beijing, China, 20–23 August 2011; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Boldea, I.; Tutelea, L.N.; Parsa, L.; Dorrell, D. Automotive electric propulsion systems with reduced or no permanent magnets: An overview. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2014, 61, 5696–5711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdo, T.M.; Adly, A.A. The outer solid rotor induction motor as an alternative for electric vehicle traction applications. In Proceedings of the 2022 Joint MMM-Intermag Conference (INTERMAG), New Orleans, LA, USA, 10–14 January 2022; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Sui, Y.; Zheng, P.; Wu, F.; Wang, P.; Cheng, L.; Zhu, J. A novel five-phase fault-tolerant modular in-wheel permanent-magnet synchronous machine for electric vehicles. J. Appl. Phys. 2015, 117, 17B521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, P.; Wu, F.; Lei, Y.; Sui, Y.; Yu, B. Investigation of a novel 24-Slot/14-Pole six-phase fault-tolerant modular permanent-magnet in-wheel motor for electric vehicles. Energies 2013, 6, 4980–5002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Yang, J.; Ye, H.; Zhou, W. A Review of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor Fault Diagnosis. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Conference and Expo Transportation Electrification Asia-Pacific (ITEC Asia-Pacific), Beijing, China, 31 August–3 September 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Liang, S.; Li, W.; Liang, H.; Wang, C. Faults and diagnosis methods of permanent magnet synchronous motors: S review. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 2116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, H.; Wang, M.; Li, Z.; Chen, P. Sequential fault detection for sealed deep groove ball bearings of in-wheel motor in variable operating conditions. J. Vibroengineering 2017, 19, 5947–5959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Y.; Ge, C.; Feng, H.; Xue, H.; Yao, M.; Tang, H.; Liao, Z.; Chen, P. A novel approach for adaptively separating and extracting compound fault features of the in-wheel motor bearing. ISA Trans. 2025, 159, 337–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Ji, K.; Zhu, R. A fault diagnosis method for a differential inverse gearbox of a crawler combine harvester based on order analysis. Agriculture 2022, 12, 1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Yu, Y.; Tu, W. Review of research on fault diagnosis of permanent magnet synchronous motor. Chin. J. Eng. Des. 2022, 28, 548–558. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, C.; Gao, Y.; Degano, M.; Wang, Y.; Fang, J.; Gerada, C.; Zhou, S.; Mu, Y. Eccentric position diagnosis of static eccentricity fault of external rotor permanent magnet synchronous motor as an in-wheel motor. IET Electr. Power Appl. 2020, 14, 2263–2272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Zheng, L.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Yu, Y. Robust control for active suspension of hub-driven electric vehicles subject to in-wheel motor magnetic force oscillation. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 3929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Liu, Z.; Yu, Y.; Liu, J. Research on unbalanced characteristics of axial-varying eccentric rotor based on signal demodulation. Mech. Syst. Signal Proc. 2024, 220, 111647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; He, Z.; Cai, J. Study on torque ripple suppression of permanent magnetic in-wheel motor under rotor eccentricity by separated harmonic current injection. Int. J. Appl. Electrom. 2021, 65, 561–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ifedi, C.J.; Mecrow, B.C.; Brockway, S.T.M.; Boast, G.S.; Atkinson, G.J.; Kostic-Perovic, D. Fault-tolerant in-wheel motor topologies for high-performance electric vehicles. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2013, 49, 1249–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumislawska, M.; Gyftakis, K.N.; Kavanagh, D.F.; McCulloch, M.; Burnham, K.J.; Howey, D.A. The Impact of Thermal Degradation on Electrical Machine Winding Insulation. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE 10th International Symposium on Diagnostics for Electrical Machines, Power Electronics and Drives (SDEMPED), Guarda, Portugal, 1–4 September 2015; pp. 232–238. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, D.; Xue, H.; Yang, K.; Li, A.; Wang, H. Study on the thermal characteristics of in-wheel motor drive system based on driving cycles. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 14463–14471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Yuan, C.; Wang, Y.; Qiu, H.; Chen, S.; Lian, Z.; Zhu, Z. Analysis of inter-turn-short fault in high-speed permanent magnet generators considering effect of structure windings. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2025, 61, 3007–3015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabarniarami, Z.; Ghods, M.; Faiz, J.; Abedini, M. Online diagnosis of short-circuit faults of permanent magnet synchronous generator by short-time analysis of the three phase amplitude-phase signal based on analytical modeling. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2024, 10, 10029–10042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavanagh, D.F.; Gyftakis, K.N.; McCulloch, M.D. Thermal degradation phenomena of polymer film on magnet wire for electromagnetic coils. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2021, 57, 458–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Y.; Mollet, Y.; Song, B.; Gyselinck, J. Detection and Isolation of Asymmetrical Short-Circuit Faults in Permanent-Magnet Synchronous Machines. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Energy Conference (ENERGYCON), Leuven, Belgium, 4–8 April 2016; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Zheng, X.; Li, X.; Wang, H.; Jin, S.; Wu, X. An improved mean phase currents method of open-circuited faults diagnosis for nine-phase permanent synchronous motor systems. Proc. Chin. Soc. Electr. Eng. 2023, 43, 1589–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Zhang, X.; Liu, X.; Yuan, X. A new signal-based diagnosis method for current sensor and open-circuited faults of a nine-phase open-end winding PMSM. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2025, 11, 1214–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Zhang, J.; Cheng, M. Common model predictive control for permanent-magnet synchronous machine drives considering single-phase open-circuit fault. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2017, 32, 5862–5872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Chai, F.; Xie, Y.; Cai, W. Design of a modular in-wheel motor with high fault-tolerant performance and low MMF space harmonic. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2023, 70, 6574–6584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Chai, F.; Chen, L. Investigation of open-circuit fault-tolerant strategy in a modular permanent magnet synchronous in-wheel motor based on electromagnetic–thermal analysis. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2022, 8, 1085–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hang, J.; Shu, X.; Ding, S.; Huang, Y. Robust open-circuit fault diagnosis for PMSM drives using wavelet convolutional neural network with small samples of normalized current vector trajectory graph. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2023, 70, 7653–7663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saavedra, H. Detection of inter-turn faults in five-phase permanent magnet synchronous motors. Adv. Electr. Comp. Eng. 2014, 14, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Li, R.; Xu, W.; Zhao, Z.; Liu, S. Evolutionary characteristics of magnetic field for the permanent magnet in-wheel motor under time-dependent demagnetization. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 76673–76681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, J.; Qu, C.; Zhou, C. Temperature field and demagnetization analysis of in-wheel motors based on magneto-thermal two-way coupling. J. Power Electron. 2024, 24, 227–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, J.C.; Cho, H.R.; Yadav, S.; Kim, S.C. Cooling effect of water channel with vortex generators on in-wheel driving motors in electric vehicles. Energies 2022, 15, 722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.; Huang, X.; Ma, J.; Fang, Y. A Comparative Study on Two Outer Rotor PMSMs for In-Wheel Direct Drive Under Short-Circuit Faults. In Proceedings of the 2017 20th International Conference on Electrical Machines and Systems (ICEMS), Sydney, NSW, Australia, 11–14 August 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, S.; Baker, N.J.; Mecrow, B.C.; Smith, D.; Atkinson, G.; Hilton, C.; Perovic, D.K.; Kakavas, I.; Sooriyakumar, G.; Harvey, P. Magnet Losses and Demagnetisation in a Permanent Magnet In-Wheel Electric Vehicle Traction Motor. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Electric Machines & Drives Conference (IEMDC), Coeur d’Alene, ID, USA, 10–13 May 2015; pp. 1831–1837. [Google Scholar]
- Xiang, P.; Yan, L.; Liu, X.; He, X.; Du, N.; Wang, H. Structural topology design for electromagnetic performance enhancement of permanent-magnet machines. Chin. J. Mech. Eng. 2025, 38, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bin Tarek, M.T.; Das, S.; Sozer, Y. Comparative Analysis of Static Eccentricity Faults of Double Stator Single Rotor Axial Flux Permanent Magnet Motors. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Energy Conversion Congress and Exposition (ECCE), Baltimore, MD, USA, 29 September–3 October 2019; pp. 3223–3228. [Google Scholar]
- Ajily, E.; Ardebili, M.; Abbaszadeh, K. Magnet defect and rotor eccentricity modeling in axial flux permanent-magnet machines via 3-D field reconstruction method. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2016, 31, 486–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, B.; Du, Y.; Peng, F.; Huang, Y. Magnetic field calculation in axial flux permanent magnet motor with rotor eccentricity. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2022, 58, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, W.; Dai, S.; Li, S.; Li, J.; Tang, R. Modeling and analysis of axial flux permanent magnet machines with coexistence of rotor radial deviation and angular eccentricity. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2020, 35, 2181–2190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrokh, F.; Vahedi, A.; Torkaman, H.; Banejad, M.; Jafer Mahdi, A.; Jamal Mohammed, M. Demagnetization and fault-tolerance analysis in dual-stator axial-field flux-switching permanent magnet motor. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 102579–102591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rallabandi, V.; Taran, N.; Ionel, D.M. Multilayer concentrated windings for axial flux PM machines. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2017, 53, 8103104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Liang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Tian, J.; Fan, L. Thermal analysis and research of a yokeless and segmented armature axial flux in-wheel motor with an amorphous magnetic metal stator. IEEE Access 2025, 13, 48672–48682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Wang, Y.; Zeng, T.; Wang, H.; Chan, S.-C.; Ran, L. Wind turbine generator failure analysis and fault diagnosis: A review. IET Renew. Power Gener. 2024, 18, 3127–3148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solís, R.; Torres, L.; Pérez, P. Review of methods for diagnosing faults in the stators of BLDC motors. Processes 2023, 11, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Ge, X.; Shen, W.; Yang, R. A soft short-circuit diagnosis method for lithium-ion battery packs in electric vehicles. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2022, 37, 8572–8581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muenchhof, M.; Beck, M.; Isermann, R. Fault-tolerant actuators and drives—Structures, fault detection principles and applications. Annu. Rev. Control. 2009, 33, 136–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Wang, J. Fault-tolerant control with active fault diagnosis for four-wheel independently driven electric ground vehicles. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2011, 60, 4276–4287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Wang, Y.; Yu, S.; Chen, H. Gain-Scheduled Fault Diagnosis of In-Wheel Motor Electric Vehicles. In Proceedings of the 2017 29th Chinese Control and Decision Conference (CCDC), Chongqing, China, 28–30 May 2017; pp. 4093–4098. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.; Moon, S.; Jeong, H.; Kim, S.W. Robust diagnosis method based on parameter estimation for an interturn short-circuit fault in multipole PMSM under high-speed operation. Sensors 2015, 15, 29452–29466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Lin, K.; Zhang, X.; Wang, S.; Ai, J.; Lin, M. An online estimation method for both stator inductance and rotor flux linkage of SPMSM without dead-time influence. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2022, 10, 1627–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, B.-G.; Kim, R.-Y.; Hyun, D.-S. Open circuit fault diagnosis using stator resistance variation for permanent magnet synchronous motor drives. J. Power Electron. 2013, 13, 985–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Jeon, Y.-J.; Choi, D.; Kim, S.; Kim, S.W. Demagnetization Fault Diagnosis Method for PMSM of Electric Vehicle. In Proceedings of the 39th Annual Conference of the IEEE Industrial Electronics Society (IECON 2013), Vienna, Austria, 10–13 November 2013; pp. 2709–2713. [Google Scholar]
- Sarikhani, A.; Mohammed, O.A. Inter-turn fault detection in PM synchronous machines by physics-based back electromotive force estimation. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2013, 60, 3472–3484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, H.; Tao, Y.; Feng, J.; Zhang, Y.; Xue, H.; Wang, T.; Xu, X.; Chen, P. Fault-tolerant collaborative control of four-wheel-drive electric vehicle for one or more in-wheel motors’ faults. Sensors 2025, 25, 1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, N.; Lee, H. Integrated fault diagnosis algorithm for motor sensors of in-wheel independent drive electric vehicles. Sensors 2016, 16, 2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Niu, W.; Guo, Y. Direct torque control for PMSM based on the RBFNN surrogate model of electromagnetic torque and stator flux linkage. Control. Eng. Pract. 2024, 148, 105943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Wang, W.; Zhang, C.; Wang, Z.; Ge, Z.; Yuan, S. Linear active disturbance rejection control system for the travel speed of an electric reel sprinkling irrigation machine. Agriculture 2024, 14, 1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, S.; Ding, S.X.; Zhou, D. Diagnosis and prognosis for complicated industrial systems—Part I. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2016, 63, 2501–2505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Jin, M.; Tian, C.; Qin, F. Molecular diagnostics of copper-transporting protein mutations allows early onset individual therapy of Menkes disease. Int. J. Agric. Biol. Eng. 2019, 12, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.H.; Chen, B.C.; Yin, D.; Huynh, P.S. Active Fault Tolerant Torque Distribution Control of 4 In-Wheel Motors Electric Vehicles Based on Kalman Filter Approach. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on System Science and Engineering (ICSSE), Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam, 21–23 July 2017; pp. 360–364. [Google Scholar]
- Naseri, F.; Schaltz, E.; Lu, K.; Farjah, E. Real-time open-switch fault diagnosis in automotive permanent magnet synchronous motor drives based on Kalman Filter. IET Power Electron. 2020, 13, 2450–2460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romdhane, M.; Naoui, M.; Mansouri, A. PMSM inter-turn short circuit fault detection using the fuzzy-extended Kalman Filter in electric vehicles. Electronics 2023, 12, 3758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dan, L. EKF-based fault detection and isolation for PMSM inverter. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2022, 52, 101846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aboelhassan, A.; El Sayed, W.; Hebala, A.; Galea, M.; Bozhko, S. Fault Tolerant Control Strategy Based on Model Predictive Control and Unscented Kalman Filter for Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE 16th Conference on Industrial Electronics and Applications (ICIEA), Chengdu, China, 1–4 August 2021; pp. 153–159. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, N.; He, H.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, Z. UKF-Based Sensor Fault Diagnosis of PMSM Drives in Electric Vehicles. In Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Applied Energy, Cardiff, UK, 21–24 August 2017; Volume 142, pp. 2276–2283. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, J.; Wang, Z.; Ding, S.; Xia, J.; Xing, G. Adaptive disturbance observer-based fixed time nonsingular terminal sliding mode control for path-tracking of unmanned agricultural tractors. Biosyst. Eng. 2024, 246, 96–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, E.; Ma, Z.; Li, Y.; Xu, L.; Tang, Z. Adaptive backstepping control of tracked robot running trajectory based on real-time slip parameter estimation. Int. J. Agric. Biol. Eng. 2020, 13, 178–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hang, J.; Hu, Q.; Sun, W.; Ren, X.; Ding, S.; Huang, Y.; Hua, W. A voltage-distortion-based method for robust detection and location of interturn fault in permanent magnet synchronous machine. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2022, 37, 11174–11186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoudi, A.; Jlassi, I.; Marques Cardoso, A.J.; Yahia, K.; Sahraoui, M. Inter-turn short-circuit faults diagnosis in synchronous reluctance machines, using the Luenberger state observer and current’s second-order harmonic. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2022, 69, 8420–8429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Liang, D.; Jia, S.; Yang, S. Model-based data normalization for data-driven PMSM fault diagnosis. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2024, 39, 11596–11612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Wang, J. Actuator-redundancy-based fault diagnosis for four-wheel independently actuated electric vehicles. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2014, 15, 239–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Chen, Y.; Tang, H.; Xia, F.; Luo, J.; Du, C. Event-triggered adaptive fault tolerant sliding mode control for FWID-EV. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2024, 10, 9192–9208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehifar, M.; Salehi Arashloo, R.; Moreno-Eguilaz, M.; Sala, V.; Romeral, L. Observer-based open transistor fault diagnosis and fault-tolerant control of five-phase permanent magnet motor drive for application in electric vehicles. IET Power Electron. 2015, 8, 76–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashemi, M.; Stolz, M.; Watzenig, D. Super-Twisting Algorithm-Based Sliding Mode Observer for Open-Circuit Fault Diagnosis in PWM Voltage Source Inverter in an In-Wheel Motor Drive System. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE International Conference on Mechatronics (ICM), Loughborough, UK, 15–17 March 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, K.; Leng, A.; Zhou, R.; Dai, W.; Wu, S.; Li, T. Demagnetization fault reconstruction for six-phase permanent magnet synchronous motor by improved super-twisting algorithm-based sliding-mode observer. Measurement 2021, 172, 108905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, H.; Ding, D.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, M.; Wang, H. A fuzzy system of operation safety assessment using multimodel linkage and multistage collaboration for in-wheel motor. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2022, 30, 999–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, G.; Zhai, X.; Tang, Z.; Wang, B.; Li, P. Response characteristics of harvester bolts and the establishment of the strongest response structure’s kinetic model. Agriculture 2024, 14, 1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Song, Z.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; Xu, L. Durable testing and analysis of a cleaning sieve based on vibration and strain signals. Agriculture 2023, 13, 2232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, A.; Upadhyay, S.H. A review on signal processing techniques utilized in the fault diagnosis of rolling element bearings. Tribol. Int. 2016, 96, 289–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, S.; Tang, Z.; Guo, S.; Ding, Z.; Su, Z. Model and method of fault signal diagnosis for blockage and slippage of rice threshing drum. Agriculture 2022, 12, 1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randall, R.B.; Antoni, J. Rolling element bearing diagnostics-a tutorial. Mech. Syst. Signal Proc. 2011, 25, 485–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandi, S.; Toliyat, H.A.; Li, X. Condition monitoring and fault diagnosis of electrical motors—A review. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2005, 20, 719–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimi, B.M.; Javan Roshtkhari, M.; Faiz, J.; Khatami, S.V. Advanced eccentricity fault recognition in permanent magnet synchronous motors using stator current signature analysis. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2014, 61, 2041–2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinosa, A.G.; Rosero, J.A.; Cusido, J.; Romeral, L.; Ortega, J.A. Fault detection by means of Hilbert–Huang transform of the stator current in a PMSM with demagnetization. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2010, 25, 312–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.; Chen, Y.; Liang, S.; Wang, C. Fault detection of stator inter-turn short-circuit in PMSM on stator current and vibration signal. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skora, M.; Ewert, P.; Kowalski, C.T. Selected rolling bearing fault diagnostic methods in wheel embedded permanent magnet brushless direct current motors. Energies 2019, 12, 4212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tashakori, A.; Ektesabi, M. Fault Diagnosis of In-Wheel BLDC Motor Drive for Electric Vehicle Application. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium (IV), Gold Coast, QLD, Australia, 23–26 June 2013; pp. 925–930. [Google Scholar]
- Oppenheim, A.V.; Willsky, A.S.; Nawab, S.H. Signals & Systems; Pearson Education: London, UK, 1997; ISBN 978-970-17-0116-4. [Google Scholar]
- Maldonado Ruelas, V.A.; Villalobos Pina, F.J.; Alvarez Salas, R.; Morones Alba, J.A.; Ortiz Medina, R.A. Multiple criteria fault detection of BLDC (brushless direct current) motor. Dyna 2018, 93, 556–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallat, S. A Wavelet Tour of Signal Processing; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1999; ISBN 978-0-08-052083-4. [Google Scholar]
- Choudhary, A.; Mian, T.; Fatima, S.; Panigrahi, B.K. Fault diagnosis of electric two-wheeler under pragmatic operating conditions using wavelet synchrosqueezing transform and CNN. IEEE Sens. J. 2023, 23, 6254–6263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, K.; Wu, X.; Wang, D.; Liu, X. Error analysis of instantaneous frequency estimation of second-order SST and its application on analyzing gear meshing stiffness from motor current. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2024, 73, 3507812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Dong, X.; Niu, G.; Ge, X. Fault detection of synchronous motor inter-turn short circuit based on current residual harmonic characteristics. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part C J. Eng. Mech. Eng. Sci. 2025, 239, 6238–6257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, L.; Chen, J.; Liu, D.; Zhen, D. Fault diagnosis of offshore wind turbines based on component separable synchroextracting transform. Ocean Eng. 2024, 291, 116275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.-B.; Luo, L.; Tang, L.; Yang, Z.-X. Automatic representation and detection of fault bearings in in-wheel motors under variable load conditions. Adv. Eng. Inform. 2021, 49, 101321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, C.; Song, Z.; Shang, J.; Xue, H.; Wang, T. MIWF-2DCNN diagnosis method for bearing fault of in-wheel motor. J. Electron. Meas. Instrum. 2024, 38, 127–135. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, D.; Xue, H.; Liu, B. Feature extraction method based on optimized SSD and enhance MOMEDA for bearing faults of in-wheel motor. Proc. CSEE 2024, 43, 9721–9732. [Google Scholar]
- Rosero, J.A.; Romeral, L.; Ortega, J.A.; Rosero, E. Short-circuit detection by means of empirical mode decomposition and Wigner Ville distribution for PMSM running under dynamic condition. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2009, 56, 4534–4547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Gao, J.; Jin, Z. Research on acoustic signal identification mechanism and denoising methods of combine harvesting loss. Agronomy 2024, 14, 1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Li, Y.; Sun, Q. Open-circuit fault diagnosis of six-phase permanent magnet synchronous motor drive system based on empirical mode decomposition energy entropy. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 91137–91147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dogan, Z.; Tetik, K. Diagnosis of inter-turn faults based on fault harmonic component tracking in LSPMSMs working under nonstationary conditions. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 92101–92112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Xu, Q.; Gao, L.; Miao, Y.; Cai, H.; Zhao, Y. ITSC fault diagnosis for PMSM by using adaptive filtering and tree-structured parzen estimator optimized-automated random forest. Electr. Eng. 2025, 107, 4711–4725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, K.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Yu, Z.; Cheng, J. Vibration signal extraction and analysis of combine harvester based on low-pass filter-EEMD combination. Eng. Agric. 2024, 44, e20240006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Li, X.; Luo, Y. Inter-turn short circuit fault detection of PMSM based on wavelet packet energy spectrum and CEEMDAN-HT. J. Electr. Eng. Technol. 2024, 19, 1379–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, T.; Dong, Z.Y.; Ma, J. Integrated optimal active and reactive power control scheme for grid connected permanent magnet synchronous generator wind turbines. IET Electr. Power Appl. 2018, 12, 474–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, D.; Chen, D.; Wang, S.; Li, S.; Mao, X.; Zhang, B.; Wang, Z.; Ma, Z. Compilation and extrapolation of load spectrum of tractor ground vibration load based on CEEMDAN-POT model. Agriculture 2023, 13, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Li, Y.; Du, X.; Liu, Y. Threshing cylinder unbalance detection using a signal extraction method based on parameter-adaptive variational mode decomposition. Biosyst. Eng. 2024, 244, 26–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Wang, J.; Shi, J.; Shen, C.; Huang, W.; Zhu, Z. A coarse-to-fine decomposing strategy of VMD for extraction of weak repetitive transients in fault diagnosis of rotating machines. Mech. Syst. Signal Proc. 2019, 116, 668–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.-K.; Wang, W.-T.; Li, X.-Y. Adaptive parameter selection variational mode decomposition based on Bayesian optimization and its application to the detection of ITSC in PMSM. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 38594–38614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, M.; Liu, M.; Yan, X.; Xu, L. Drive power allocation strategy for electric tractor based on adaptive multiresolution analysis. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2024, 39, 55–66. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, D.; Seung, H.S. Algorithms for Non-Negative Matrix Factorization. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Cambridge, MA, USA; 2000; Volume 13. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, H.; Ding, D.; Li, R.; Xu, X. Feature extraction method based on component weighted reconstruction and sparse NMF for bearing compound faults of in-wheel motor. J. Mech. Eng. 2023, 59, 146–156. [Google Scholar]
- Lei, Y.; Yang, B.; Jiang, X.; Jia, F.; Li, N.; Nandi, A.K. Applications of machine learning to machine fault diagnosis: A review and roadmap. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2020, 138, 106587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Z.; Wu, T.; Guo, S.; Shao, T.; Malekian, R.; Li, Z. Development and trend of condition monitoring and fault diagnosis of multi-sensors information fusion for rolling bearings: A review. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2018, 96, 803–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Xie, S.; Ning, J.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, Z. Evaluating green tea quality based on multisensor data fusion combining hyperspectral imaging and olfactory visualization systems. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2019, 99, 1787–1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Y.; He, Z.; Zi, Y.; Hu, Q. Fault diagnosis of rotating machinery based on multiple ANFIS combination with GAs. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2007, 21, 2280–2294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Chen, Z.; Xue, H.; Yin, S. Online diagnosis method for mechanical fault of in-wheel motor based on DBNs. J. Vib. Meas. Diagn. 2020, 40, 643–649. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Z.; Zeng, L.; Chen, L.; Zou, R.; Cai, Y. Fuzzy adaptive energy management strategy for a hybrid agricultural tractor equipped with HMCVT. Agriculture 2022, 12, 1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Wu, B.; Sun, J.; Yang, N. Classification of apple varieties using near infrared reflectance spectroscopy and fuzzy discriminant c-means clustering model. J. Food Process Eng. 2017, 40, e12355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Xu, Y.; Cai, F.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, W.; Gerada, C. PWM-VSI fault diagnosis for a PMSM drive based on the fuzzy logic approach. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2019, 34, 759–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moosakunju, S.; Mini, V.P.; Ushakumari, S.; Mayadevi, N.; Harikumar, R. A hybrid fault detection and diagnosis algorithm for five-phase PMSM drive. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2023, 48, 6507–6519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Hao, S.; Guo, S.; Tang, Z.; Chen, S. Motor torque distribution strategy for different tillage modes of agricultural electric tractors. Agriculture 2022, 12, 1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Zhao, Y.; Yan, K.; Zhou, K.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, X. Probabilistic graphical models in energy systems: A review. Build. Simul. 2022, 15, 699–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, B.; Wang, Z.; Zhu, H.; Liu, Y.; Hao, K.; Yang, Z.; Ren, Y.; Feng, Q.; Liu, Z. Artificial intelligence enhanced two-stage hybrid fault prognosis methodology of PMSM. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2022, 18, 7262–7273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, B.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, H.; Xie, M. A data-driven fault diagnosis methodology in three-phase inverters for PMSM drive systems. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2017, 32, 5590–5600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, B.; Hao, K.; Wang, Z.; Yang, C.; Kong, X.; Liu, Z.; Ji, R.; Liu, Y. Data-driven early fault diagnostic methodology of permanent magnet synchronous motor. Expert Syst. Appl. 2021, 177, 115000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Qin, X.; Xue, H. In-wheel motor fault diagnosis method based on BN and improved DST. J. Huazhong Univ. Sci. Technol. Nat. Sci. 2021, 49, 27–32. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, H.; Zhou, J.; Tong, P. Mechanical fault diagnosis method of in-wheel motor based on WMM-HMM. J. Huazhong Univ. Sci. Technol. Nat. Sci. 2021, 49, 32–37. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, H.; Liu, B.; Ding, D.; Zhou, J.; Cui, X. Diagnosis method based on hidden Markov model and Weibull mixture model for mechanical faults of in-wheel motors. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2022, 33, 114002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhan, W.; Ehsani, M. Diagnosis and fault-tolerant control of permanent magnet synchronous motors with interturn short-circuit fault. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 2023, 31, 1909–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhan, W.; Ehsani, M. On-line diagnosis of inter-turn short circuit fault for DC brushed motor. ISA Trans. 2018, 77, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Feng, Z.; Dai, S.; Zhang, P.; Wei, X. Using UAV multispectral remote sensing with appropriate spatial resolution and machine learning to monitor wheat scab. Agriculture 2022, 12, 1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X. Detection method for tomato leaf mildew based on hyperspectral fusion terahertz technology. Foods 2023, 12, 535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Yu, S.; Xu, H.; Aheto, J.H.; Bonah, E.; Ma, M.; Wu, M.; Zhang, X. Rapid and nondestructive detection of freshness quality of postharvest spinaches based on machine vision and electronic nose. J. Food Saf. 2019, 39, e12708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lale, T.; Gumus, B. An Effective Torque-based method for automatic turn fault detection and turn fault severity classification in permanent magnet synchronous motor. Electr. Eng. 2024, 106, 2865–2876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moosavi, S.S.; Djerdir, A.; Ait-Amirat, Y.; Khaburi, D.A. ANN based fault diagnosis of permanent magnet synchronous motor under stator winding shorted Turn. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2015, 125, 67–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.-K.; Yoo, D.-W.; Hur, J. Application and verification of voltage angle-based fault diagnosis method in six-phase IPMSM. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2024, 60, 426–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimi, B.M.; Faiz, J.; Roshtkhari, M.J. Static-, dynamic-, and mixed-eccentricity fault diagnoses in permanent-magnet synchronous motors. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2009, 56, 4727–4739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aktas, M.; Aygun, H. Comparison of DC link current and stator phase current in inverter switching faults detection of PMSM drives in HEVs. Eng. Sci. Technol. 2018, 21, 664–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahafzah, K.A.A.; Obeidat, M.A.A.; Mansour, A.M.M.; Al-Shetwi, A.Q.Q.; Ustun, T.S. Artificial-Intelligence-Based Open-Circuit Fault Diagnosis in VSI-Fed PMSMs and a Novel Fault Recovery Method. Sustainability 2022, 14, 16504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyanteh, Y.; Edrington, C.; Srivastava, S.; Cartes, D. Application of artificial intelligence to real-time fault detection in permanent-magnet synchronous machines. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2013, 49, 1205–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belfore, L.A.; Arkadan, A. A methodology for characterizing fault tolerant switched reluctance motors using neurogenetically derived models. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2002, 17, 380–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Y.; Li, H.; Tang, P.; Chen, C. Irrigation scheduling of pressurized irrigation networks for minimizing energy consumption. Irrig. Drain. 2023, 72, 268–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddique, M.F.; Zaman, W.; Ullah, S.; Umar, M.; Saleem, F.; Shon, D.; Yoon, T.H.; Yoo, D.-S.; Kim, J.-M. Advanced Bearing-fault diagnosis and classification using mel-scalograms and FOX-optimized ANN. Sensors 2024, 24, 7303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonah, E.; Huan, X.; Yi, R.; Aheto, J.H.; Osae, R.; Golly, M. Electronic nose classification and differentiation of bacterial foodborne pathogens based on support vector machine optimized with particle swarm optimization algorithm. J. Food Process Eng. 2019, 42, e13236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Zhou, X.; Mao, H.; Wu, X.; Zhang, X.; Li, Q. Discrimination of pesticide residues in lettuce based on chemical molecular structure coupled with wavelet transform and near infrared hyperspectra. J. Food Process Eng. 2017, 40, e12509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.; Chen, Y.; Liang, H.; Li, X. Sparse representation and SVM diagnosis method for inter-turn short-circuit fault in PMSM. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Gao, H.; Zhou, S.; Pan, Y.; Zhang, K.; Liu, P.; Yang, H.; Zhao, Z.; Madyira, D.M. Rotor faults diagnosis in PMSMs based on branch current analysis and machine learning. Actuators 2023, 12, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wang, L.; Wu, Q.; Pei, H.; Diao, L. A data-driven intelligent fault diagnosis framework for permanent magnet in PMSM. Alex. Eng. J. 2025, 113, 331–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, L.; Mao, Y.; Zhang, T.; Chen, X.; Wang, Z.; Wang, X. Online data-driven diagnosis for common electrical and sensor faults in dual three-phase PMSM drives. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2025, 74, 2507510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Xue, H.; Ding, D.; Sun, N.; Chen, P. In-wheel motor fault diagnosis using affinity propagation minimum-distance discriminant projection and weibull-kernel-function-based SVDD. Sensors 2023, 23, 4021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Xi, S.; Xue, H.; Zhu, F. Research on condition recognition method based on DK-SVDD for in-wheel motor bearing. J. Vib. Meas. Diagn. 2023, 43, 1121–1128. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, B.; Tang, Z.; Wang, K.; Li, P. Failure feature identification of vibrating screen bolts under multiple feature fusion and optimization method. Agriculture 2024, 14, 1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, H.; Wu, M.; Zhang, Z.; Zhou, H.; Wang, H. Condition recognition method based on K-AHNs for in-wheel motor. J. Mech. Eng. 2024, 59, 207–214. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, H.; Wang, M.; Li, Z.; Chen, P. Fault Feature Extraction Based on Artificial Hydrocarbon Network for Sealed Deep Groove Ball Bearings of In-Wheel Motor. In Proceedings of the 2017 Prognostics and System Health Management Conference (PHM-Harbin), Harbin, China, 9–12 July 2017; pp. 417–421. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, H.; Song, Z.; Wu, M.; Sun, N.; Wang, H. Intelligent diagnosis based on double-optimized artificial hydrocarbon networks for mechanical faults of in-wheel motor. Sensors 2022, 22, 6316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, H.; Wu, M.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, H. Intelligent diagnosis of mechanical faults of in-wheel motor based on improved artificial hydrocarbon networks. ISA Trans. 2022, 120, 360–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ponce, H.; Miralles-Pechuán, L.; Martínez-Villaseñor, M.D.L. A flexible approach for human activity recognition using artificial hydrocarbon networks. Sensors 2016, 16, 1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, F.; Lei, Y.; Lin, J.; Zhou, X.; Lu, N. Deep Neural Networks: A promising tool for fault characteristic mining and intelligent diagnosis of rotating machinery with massive data. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2016, 72–73, 303–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Pan, T.; Li, Y.; Chen, S.; Li, G. Development of analytical method associating near-infrared spectroscopy with one-dimensional convolution neural network: A case study. Food Meas. 2021, 15, 2963–2973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, Q.; Fan, Z.; Chang, H.; Shoaib, M.; Chen, Q. Analyzing TVB-N in snakehead by Bayesian-optimized 1D-CNN using molecular vibrational spectroscopic techniques: Near-infrared and Raman spectroscopy. Food Chem. 2025, 464, 141701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Deng, J.; Jiang, H. Markov Transition field combined with convolutional neural network improved the predictive performance of near-infrared spectroscopy models for determination of aflatoxin B1 in maize. Foods 2022, 11, 2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pietrzak, P.; Wolkiewicz, M.; Orlowska-Kowalska, T. PMSM stator winding fault detection and classification based on bispectrum analysis and convolutional neural network. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2023, 70, 5192–5202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Yuan, C.; Zeng, D.; Carbone, G.; Hu, Y.; Yang, J. Conceptual approach to permanent magnet synchronous motor turn-to-turn short circuit and uniform demagnetization fault diagnosis. Actuators 2024, 13, 511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Cui, J.; Xiao, W.; Mei, L.; Yu, X. Demagnetization fault diagnosis of a PMSM for electric drilling tools using GAF and CNN. Electronics 2024, 13, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Zhang, Z.; Cao, J. A novel method of combining generalized frequency response function and convolutional neural network for complex system fault diagnosis. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0228324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Q.; Wang, M.; Lai, W.; Zhao, S. Multiscale kernel-based residual CNN for estimation of inter-turn short circuit fault in PMSM. Sensors 2022, 22, 6870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, K.; Wang, D.; Huang, W.; Liu, H.; Jiang, Y.; Hu, J. Multiple fault diagnosis of PMSM based on stator tooth flux and parallel residual convolutional neural network. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2024, 10, 9727–9738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Ouyang, X.; Jiang, Z.; Xu, Y.; Xue, H.; Yue, H.; Feng, H. In-wheel motor fault diagnosis method based on two-stream 2DCNNs with DCBA module. Sensors 2025, 25, 4617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Q.; Wang, M.; Lai, W.; Zhao, S. On bayesian optimization-based residual CNN for estimation of inter-turn short circuit fault in PMSM. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2023, 38, 2456–2468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Yang, H.; Niu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, L.; Chai, X. Wheat biomass, yield, and straw-grain ratio estimation from multi-temporal UAV-based RGB and multispectral images. Biosyst. Eng. 2023, 234, 187–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, M.M.U.; Liu, J.; Nijabat, A.; Faheem, M.; Wang, W.; Zhao, S. Leveraging convolutional neural networks for disease detection in vegetables: A comprehensive review. Agronomy 2024, 14, 2231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lale, T.; Yueksek, G. Identification and classification of turn short-circuit and demagnetization failures in PMSM using LSTM and GRU methods. Bull. Pol. Acad. Sci. Tech. Sci. 2025, 73, e151958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taha, M.F.; Mao, H.; Mousa, S.; Zhou, L.; Wang, Y.; Elmasry, G.; Al-Rejaie, S.; Elwakeel, A.E.; Wei, Y.; Qiu, Z. Deep learning-enabled dynamic model for nutrient status detection of aquaponically grown plants. Agronomy 2024, 14, 2290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shifat, T.A.; Jang-Wook, H. Remaining useful life estimation of BLDC motor considering voltage degradation and attention-based neural network. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 168414–168428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seker, S.; Ayaz, E.; Türkcan, E. Elman’s recurrent neural network applications to condition monitoring in nuclear power plant and rotating machinery. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2003, 16, 647–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Zhu, W.; Steibel, J.; Siegford, J.; Han, J.; Norton, T. Classification of drinking and drinker-playing in pigs by a video-based deep learning method. Biosyst. Eng. 2020, 196, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, M.; Liang, L.; Zheng, H.; Chen, J.; Chen, D. Anomaly detection of permanent magnet synchronous motor based on improved DWT-CNN multi-current fusion. Sensors 2024, 24, 2553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ertargin, M.; Yildirim, O.; Orhan, A. Mechanical and electrical faults detection in induction motor across multiple sensors with CNN-LSTM deep learning model. Electr. Eng. 2024, 106, 6941–6951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, L.; Zhang, Q.; Xie, Y.; Zhang, J.; Ke, J. Research on wind turbine fault detection based on CNN-LSTM. Energies 2024, 17, 4497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eang, C.; Lee, S. Predictive maintenance and fault detection for motor drive control systems in industrial robots using CNN-RNN-based observers. Sensors 2025, 25, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Encalada-Davila, A.; Moyon, L.; Tutiven, C.; Puruncajas, B.; Vidal, Y. Early fault detection in the main bearing of wind turbines based on gated recurrent unit (GRU) neural networks and SCADA data. IEEE-ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2022, 27, 5583–5593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, Z.; Tang, B.; Deng, L.; Liu, W.; Han, Y. Condition monitoring of wind turbines based on spatio-temporal fusion of SCADA data by convolutional neural networks and gated recurrent units. Renew. Energy 2020, 146, 760–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, C.; Zhu, J.; Xu, F. Fault diagnosis of motor vibration signals by fusion of spatiotemporal features. Machines 2022, 10, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, W.; Pan, Y.; Xu, B.; Wang, J. A real-time apple targets detection method for picking robot based on shufflenetV2-YOLOX. Agriculture 2022, 12, 856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, K.; Wang, A.; Shen, Y.; Lu, Z.; Peng, F.; Wei, X. Peach flower density detection based on an improved CNN incorporating attention mechanism and multi-scale feature fusion. Horticulturae 2022, 8, 904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Zhao, Y.; Fan, W.; Liu, J. An improved YOLOv8 model for lotus seedpod instance segmentation in the lotus pond environment. Agronomy 2024, 14, 1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Peng, Y.; Liu, J.; Wu, S. Tomato leaf disease diagnosis based on improved convolution neural network by attention module. Agriculture 2021, 11, 651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Hassan, M.; Yu, J.; Zhu, A.; Han, Z.; He, P.; Chen, Q.; Li, H.; Ouyang, Q. Time series prediction of insect pests in tea gardens. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2024, 104, 5614–5624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Liu, Z.; Peng, D.; Zuo, M.J. Interpretable convolutional neural network with multilayer wavelet for noise-robust machinery fault diagnosis. Mech. Syst. Signal Proc. 2023, 195, 110314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Chen, L.; Wang, M.; Wei, L.; Li, M. Adaptive sparse attention wavelet network for the robust open-circuit fault diagnosis in PMSM drives. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2024, 73, 3514611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Sun, J.; Shi, L.; Dai, C. An effective method fusing electronic nose and fluorescence hyperspectral imaging for the detection of pork freshness. Food Biosci. 2024, 59, 103880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Lai, W.; Sun, P.; Li, H.; Song, Q. Severity estimation of inter-turn short-circuit fault in PMSM for agricultural machinery using Bayesian optimization and enhanced convolutional neural network architecture. Agriculture 2024, 14, 2214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, S.; Tao, J.; Zhao, Z. Fault diagnosis of wind turbine pitch system based on LSTM with multi-channel attention mechanism. Energy Rep. 2023, 10, 4087–4096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Li, S.; Bai, Q.; Zhang, A.; Yang, J.; Shen, M. A Siamese vision transformer for bearings fault diagnosis. Micromachines 2022, 13, 1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, W.; Sun, J.; Wang, S.; Shen, J.; Yang, K.; Zhou, X. Identifying field crop diseases using transformer-embedded convolutional neural network. Agriculture 2022, 12, 1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Zhang, M.; Qiu, L.; Wang, L.; Yu, Y. An arrhythmia classification model based on vision transformer with deformable attention. Micromachines 2023, 14, 1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, F.; Guo, Z.; Li, T.; Feng, Q.; Zhao, C. Dynamic task planning for multi-arm harvesting robots under multiple constraints using deep reinforcement learning. Horticulturae 2025, 11, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zhou, X.; Cai, N.; Zhou, S.; Wang, H. IC packaging material identification via a hybrid deep learning framework with CNN–transformer bidirectional interaction. Micromachines 2024, 15, 418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhandari, B. Comparative study of popular deep learning models for machining roughness classification using sound and force signals. Micromachines 2021, 12, 1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Yu, M.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Yu, L.; Zhang, C.; Ni, Y. Prediction of IGBT gate oxide layer’s performance degradation based on MultiScaleFormer network. Micromachines 2024, 15, 985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, W.; Zhai, K.; Xu, B.; Wu, J. Green apple detection method based on multidimensional feature extraction network model and transformer module. J. Food Prot. 2025, 88, 100397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parvin, F.; Faiz, J.; Qi, Y.; Kalhor, A.; Akin, B. A comprehensive interturn fault severity diagnosis method for permanent magnet synchronous motors based on transformer neural networks. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2023, 19, 10923–10933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, W.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Gan, C.; Si, J.; Wen, H. Few-shot learning with residual current for EV inverter fault diagnosis of EV powertrain. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2024, 10, 9316–9327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Geng, Y.; Wang, W.; Tu, M.; Wu, X. Permanent magnet synchronous motor inter-turn short circuit diagnosis based on physical-data dual model under oil-drilling environment. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2024, 132, 107938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).