Transient Vortex Dynamics in Tip Clearance Flow of a Novel Dishwasher Pump
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Numerical Model and Simulation Setup
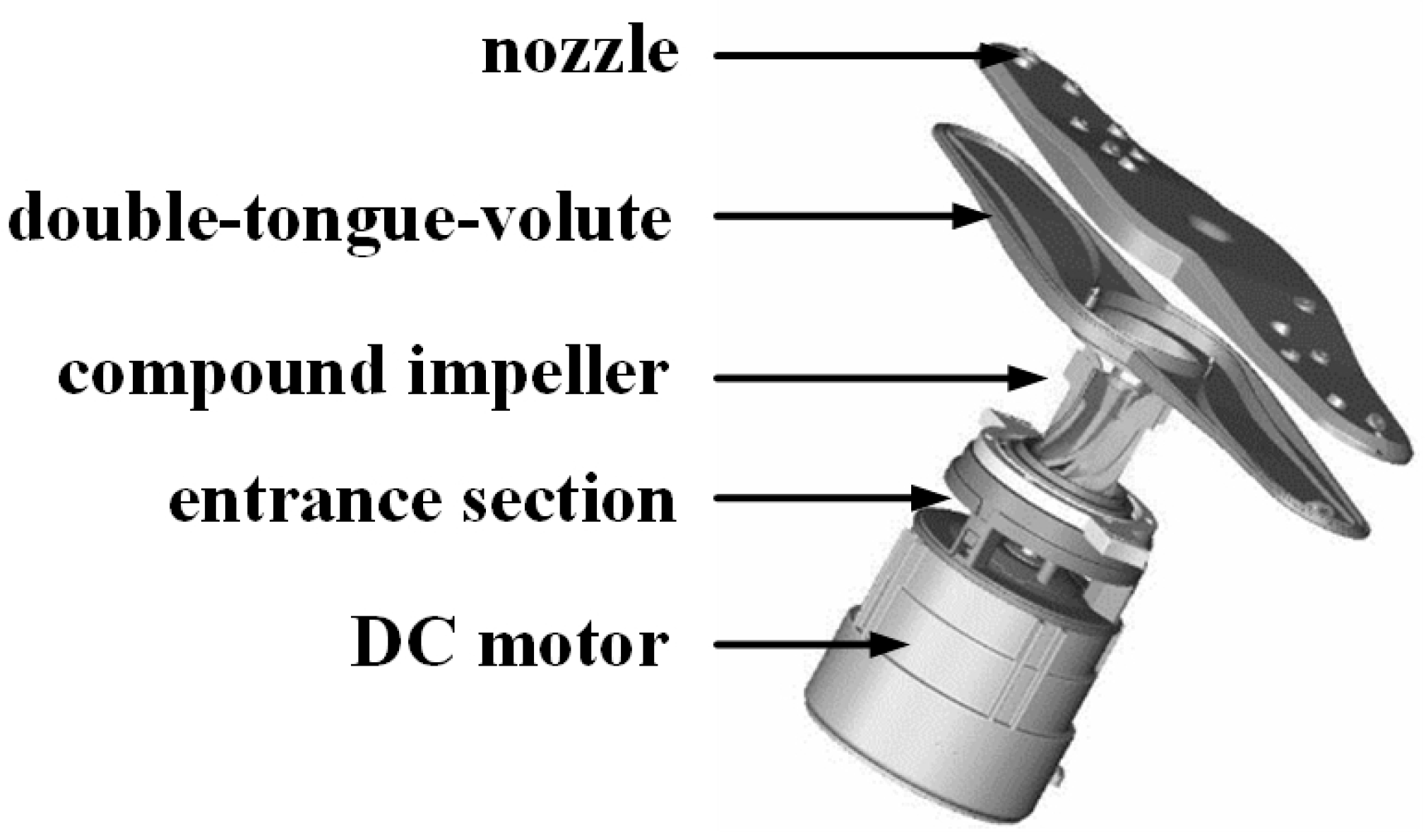
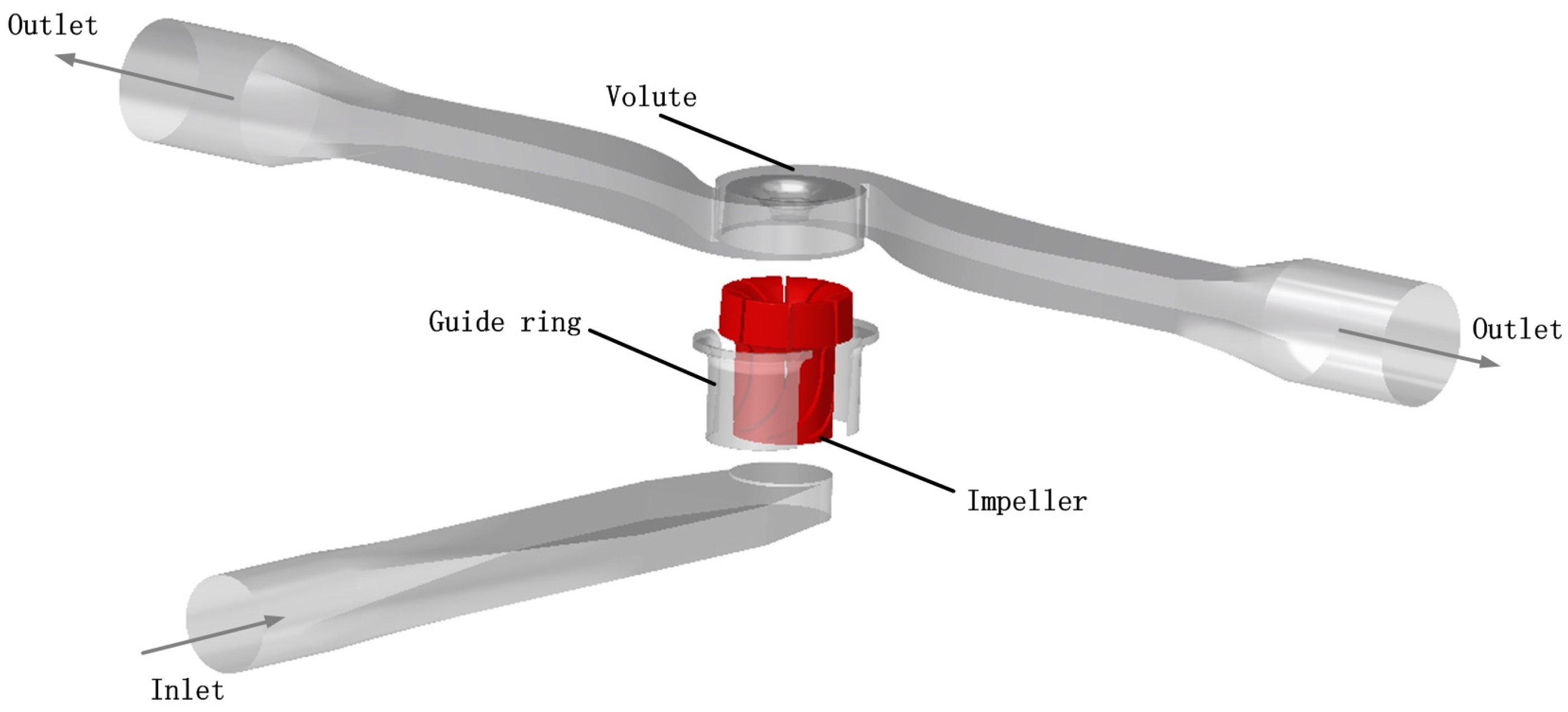
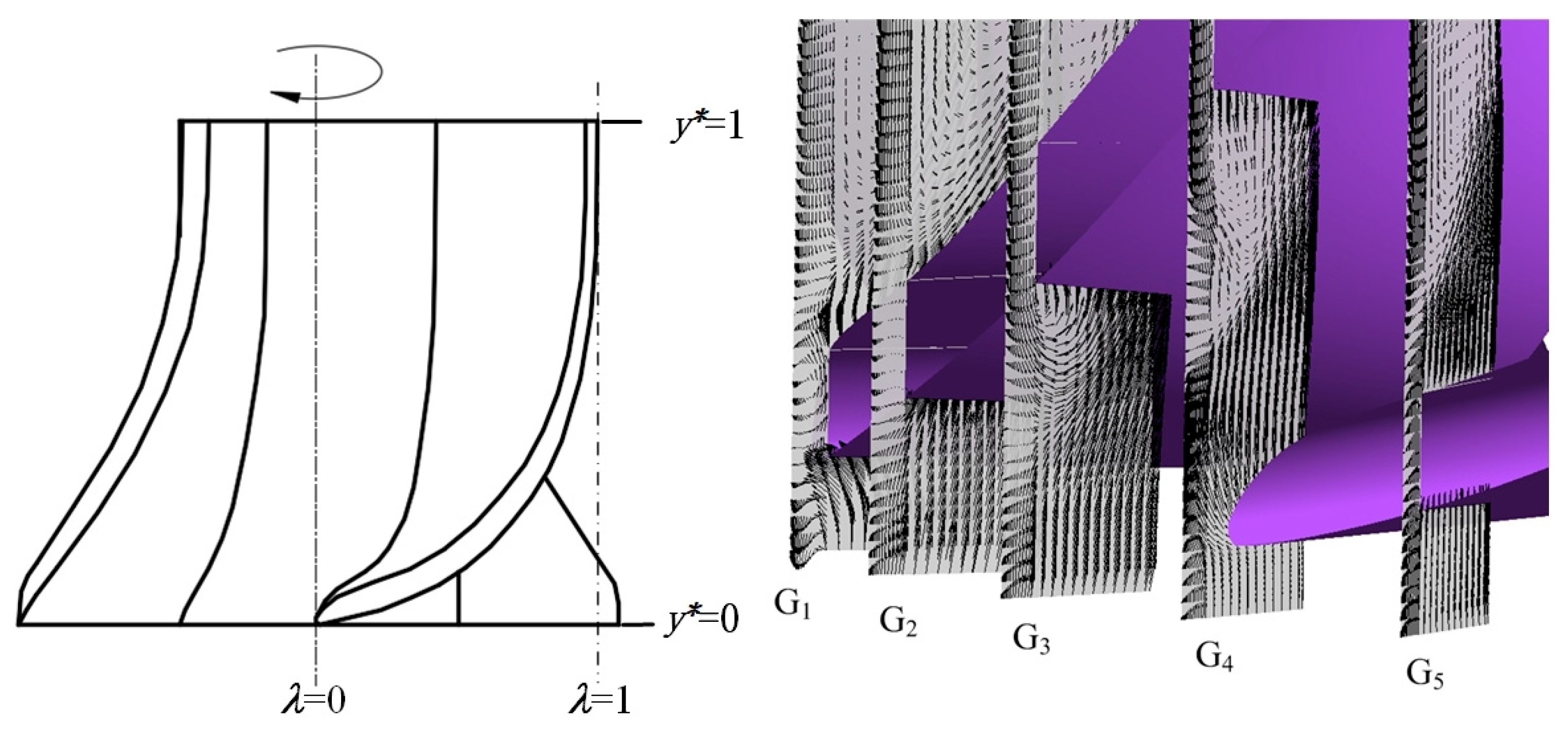
2.1. Computational Domain
2.2. Governing Equations
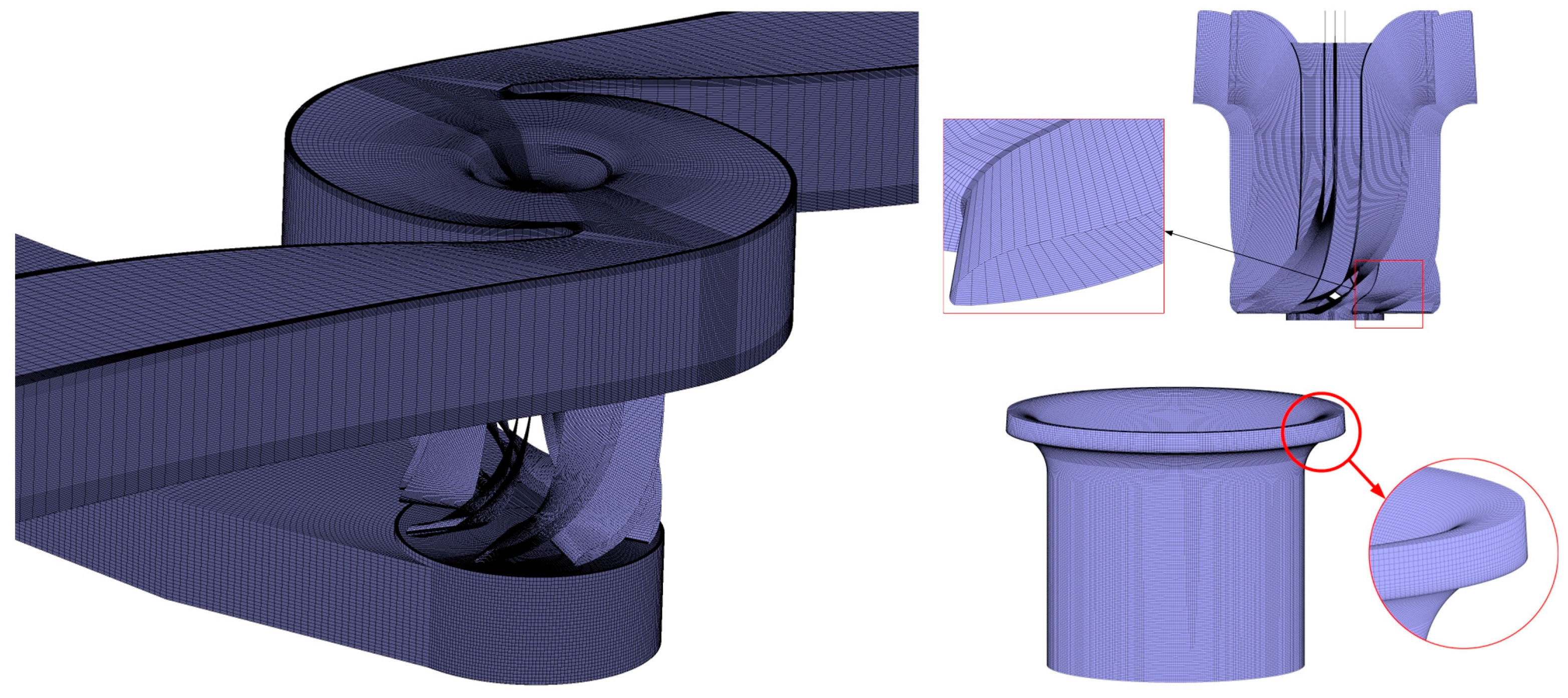
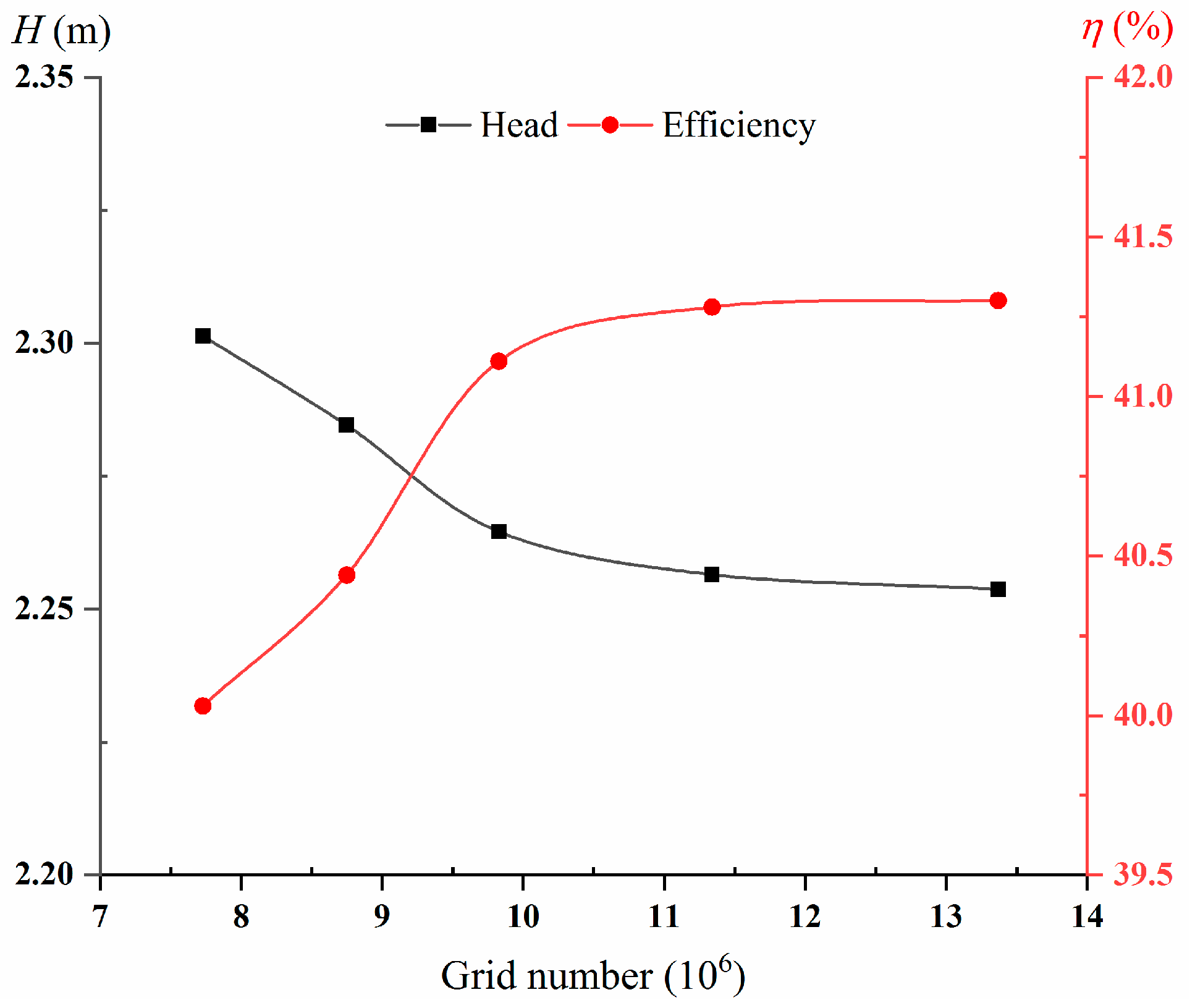
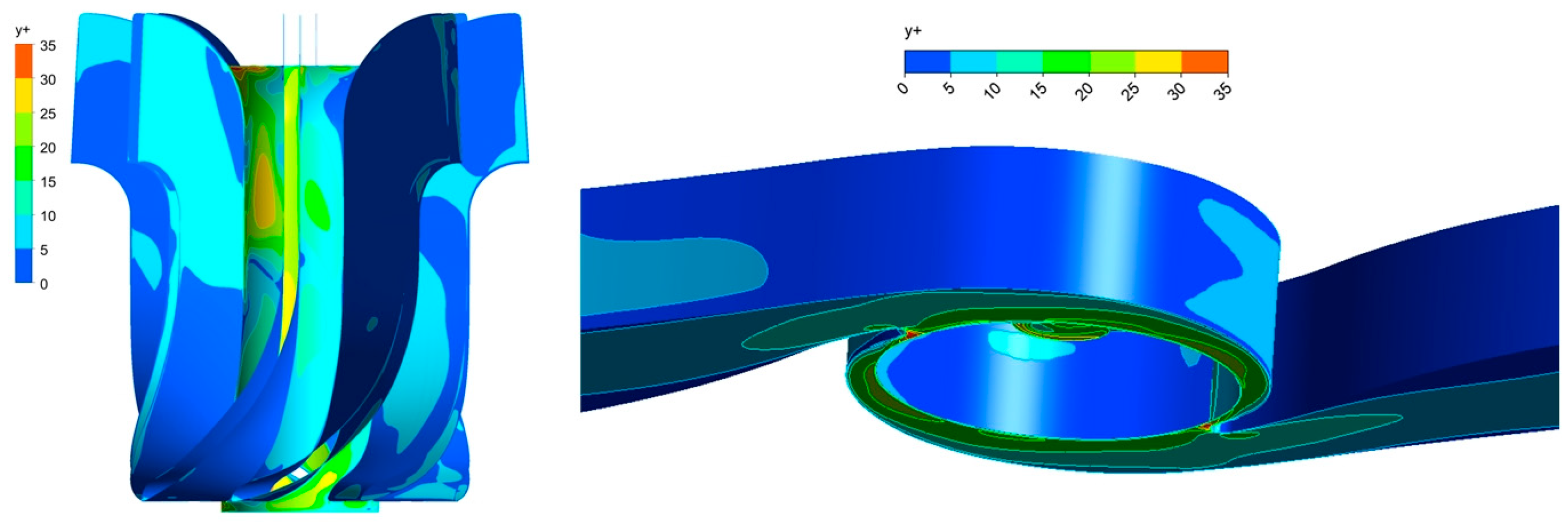
2.3. Mesh Generation
2.4. Numerical Settings and Boundary Conditions
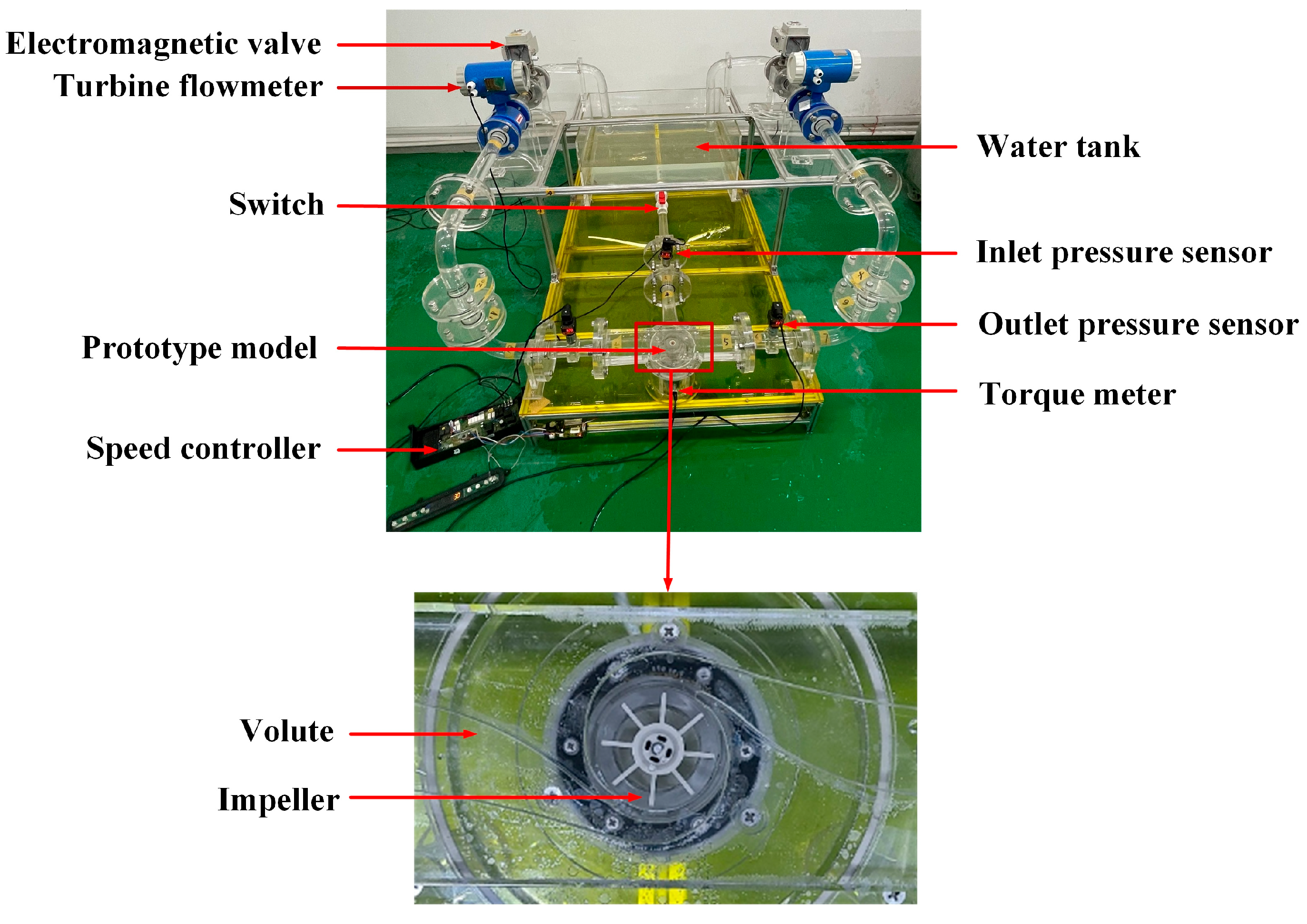
3. Experimental Characterization of Pump Performance
4. Results and Discussion
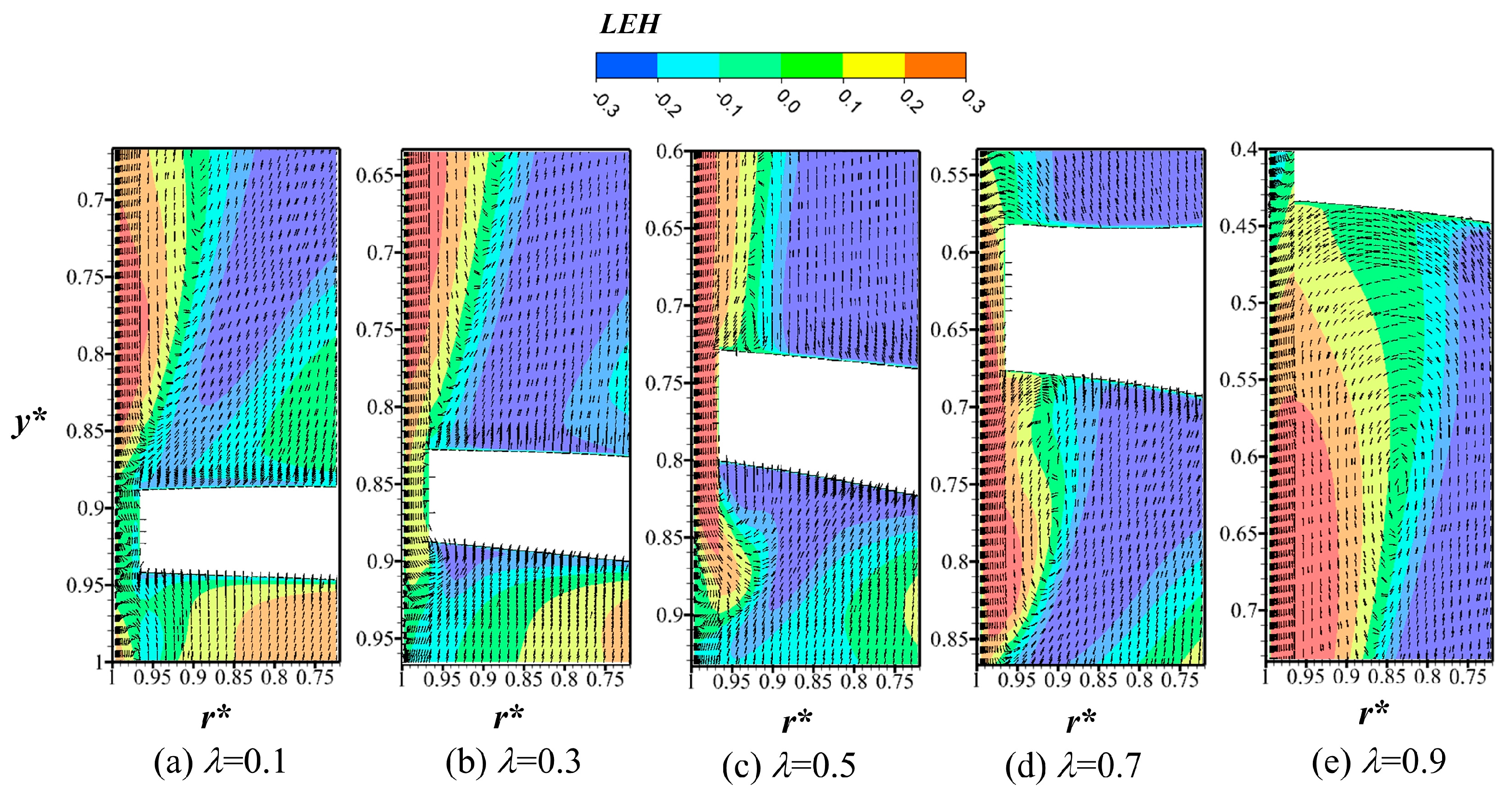
4.1. Structure of Leakage Vortex Flow Field in the Tip Clearance of Composite Impeller Blades
4.2. Evolution of Tip Clearance Vortices in Axial Flow of Composite Impellers
4.3. Evolution Mechanism of Axial Clearance Vortices in Composite Impellers
5. Conclusions
- (1)
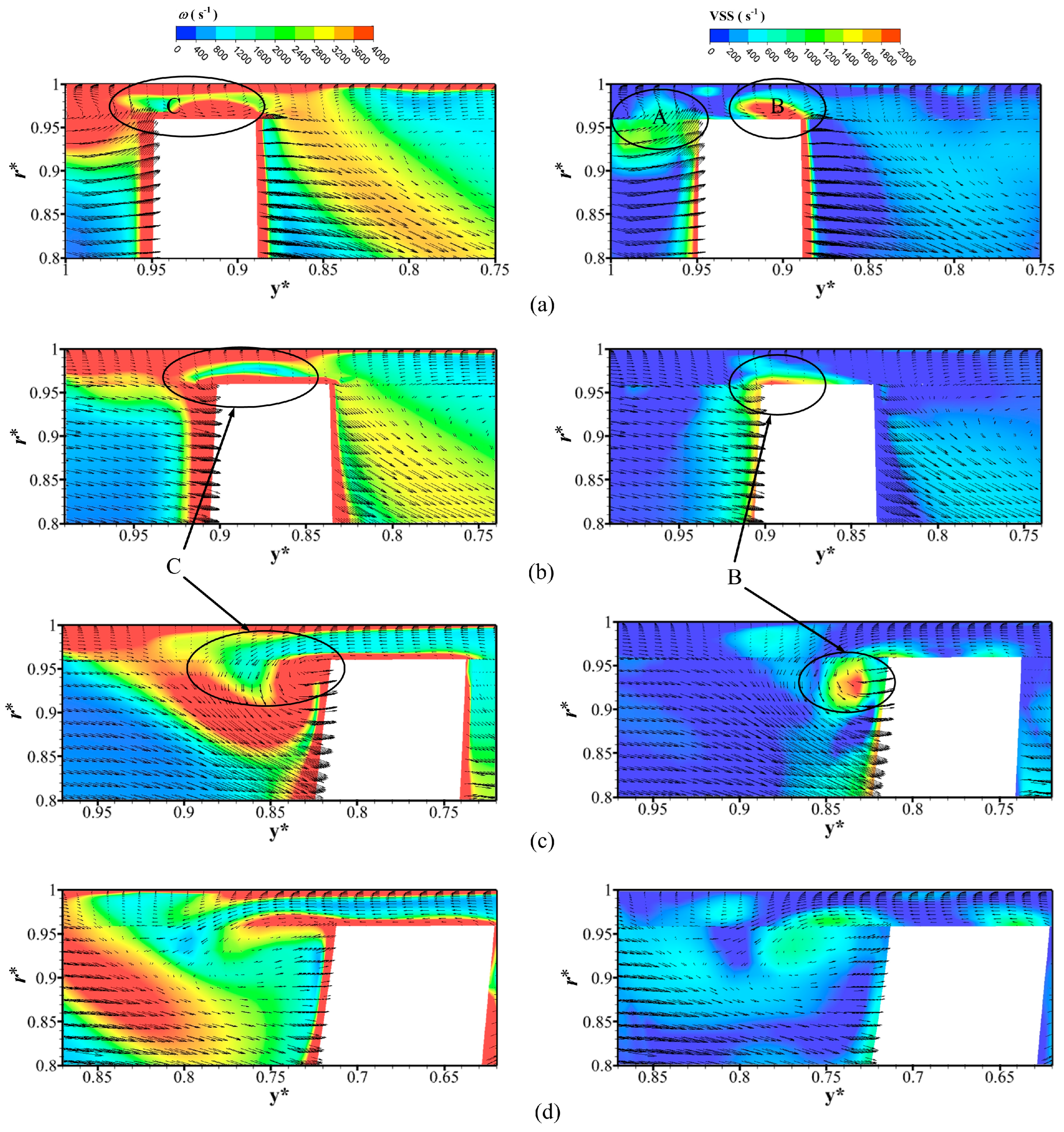
- The clearance leakage vortex in a composite axial flow cascade comprises an initial leakage vortex and a secondary leakage vortex. The initial leakage vortex is further divided into two components: corner vortex A, which originates at the outer edge of the blade inlet and progresses backward along the direction of rotation, and corner vortex B, which emerges within the impeller inlet clearance and ascends along the suction side of the blade. As a portion of the leakage flow enters the flow passage of the subsequent stage blades due to the impeller’s rotation, secondary leakage vortices are formed. These vortices progressively accumulate and stretch within the flow passage, ultimately inducing stall and detachment along with the vortices adhering to the suction side of the blade, before finally reaching the pressure side of adjacent blades.
- (2)
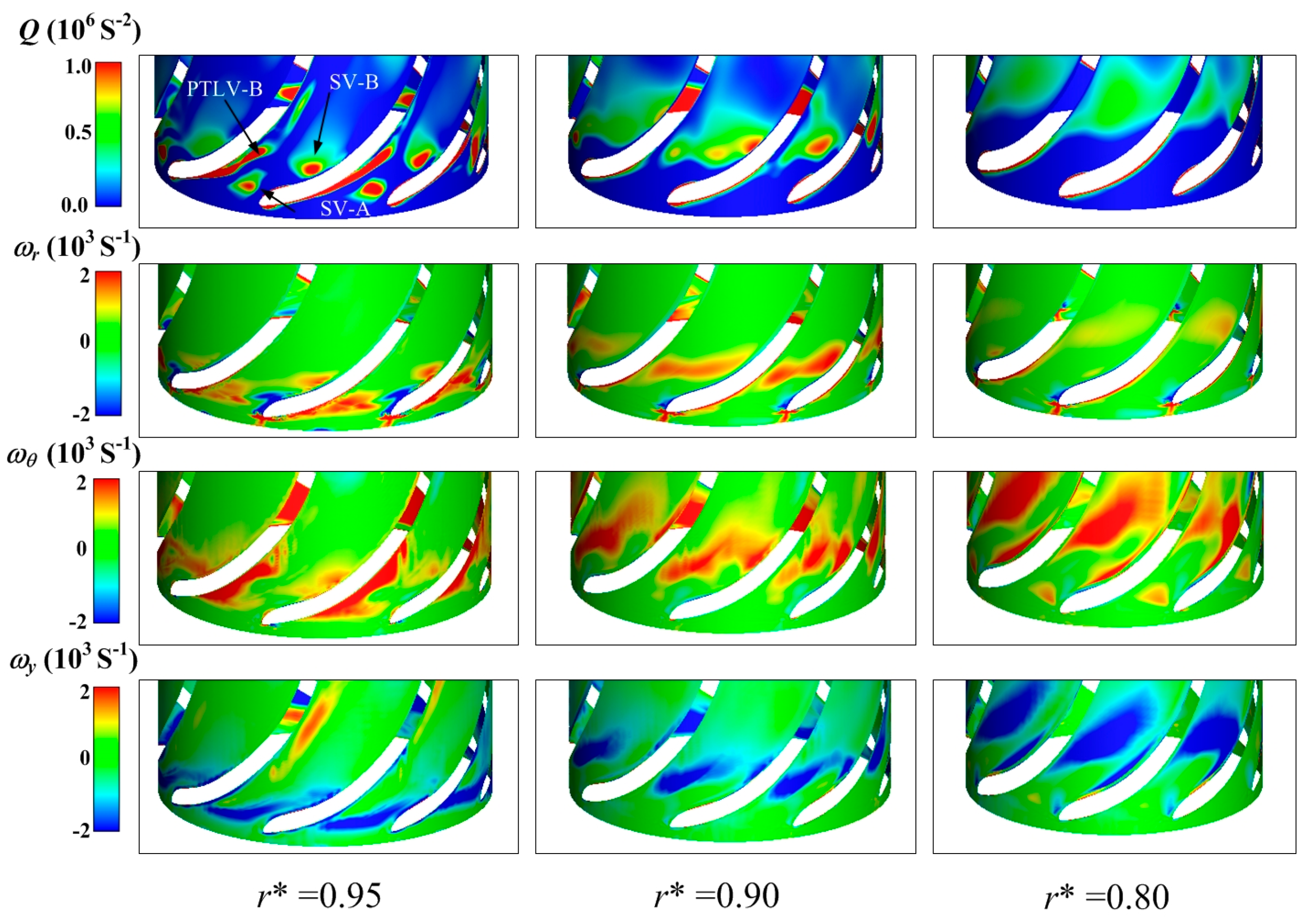
- The leakage vortex within the tip clearance of the blades in the flow passages evolves from the suction side of the blade towards the center of the flow passage. It ultimately detaches and impacts the pressure side of the adjacent blade. The vorticity distribution across the eight flow passages in the impeller demonstrates a predominantly axisymmetric characteristic. Additionally, the double-tongue volute structure influences the flow field within the bottom axial flow cascade.
- (3)
- The trajectory of the shedding vortex (SV) exhibits a notable correlation with vorticity in various directions. The distribution of radial, circumferential, and axial vorticity across different radial heights reveals that the vorticity at the SV generation site is predominantly contributed by the circumferential and axial vorticity components, with the circumferential vorticity being dominant. As the detached SV migrates through the flow channel, the circumferential vorticity contribution gradually diminishes.
- (4)
- The energy loss at the inlet of the impeller is greater than at other regions within the flow passage. The region of energy loss adjacent to the suction surface of the shroud coincides with the area occupied by the leakage vortex, indicating that the oscillation and shedding of the tip leakage vortex are key contributors to localized energy loss within the flow passage.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhu, Y.L.; Zhang, J.F.; Li, Y.L.; Huang, P.; Xu, H.; Zheng, F. Experimental investigation of unsteady pressure pulsation in new type dishwasher pump with special double-tongue volute. Machines 2021, 9, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.F.; Zhu, Y.L.; Li, Y.L.; Huang, P.; Xu, H.; Zheng, F. Investigation of unsteady pressure pulsation in new type dishwasher pump with special double tongue volute. Shock. Vib. 2022, 9, 9349432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Sun, H.; Xu, H.; Wang, X.; Li, Y. Orthogonal optimization design of the compound impeller for a New Type of dishwasher pump. Processes 2022, 10, 1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, C.; Li, Y.L.; Huang, P.; Xu, H.; Zheng, F. Numerical analysis of a new type of dishwasher pump for different rotation speeds of the volute. Front. Energy Res. 2022, 9, 825159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zang, J.; Zhang, D.; Shi, W.; Shen, J. Analysis of the Formation Mechanism of Secondary Tip Leakage Vortex (S-TLV) in an Axial Flow Pump. Machines 2022, 10, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Ji, L.; Shi, W.; Li, E.; Yang, Z. Particle image velocimetry measurement of flow fields in a mixed-flow pump with non-uniform tip clearance. J. Vis. 2021, 24, 29–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Ji, L.; Li, E.; Zhou, L.; Agarwal, R.K. Effect of tip clearance on rotating stall in a mixed-flow pump. J. Turbomach. 2021, 143, 091013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Cheng, L.; Xu, W.; Lei, S. Study on the influence of tip clearance on cavitation performance and entropy production of an axial flow pump. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2024, 12, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, H.; Li, L.; Shi, G.; Ma, H.; Peng, X. Effect of tip clearance on force characteristics of helical axial-flow blade pumps under cavitation conditions. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 2299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, H.; Lv, W.; Shi, G. Study of Tip Clearance on Dynamic and Static Head of a Spiral Axial-Flow Blade Pump under Cavitation Conditions. Water 2023, 15, 4304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.; Wu, H.; Yang, G.; Tang, R.; Chang, C.; Xu, B.; Lin, S.; Zhang, D. Experimental study on the classification and evolution of the tip cavitation morphology in axial waterjet pumps with two different blade numbers. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2024, 12, 1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Jiang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Chen, D. Effect of tip clearance flow on pressure oscillation and vortex patterns of a high-speed centrifugal pump. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part C J. Mech. Eng. Sci. 2024, 238, 822–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Jiang, C.; Qian, H.; Zhu, Z. The influence of tip clearance on the performance of a high-speed inducer centrifugal pump under different flow rates conditions. Processes 2023, 11, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.P.; Shi, L.J.; Tang, F.P.; Sun, Z.-Z.; Zhang, Y. Identification and analysis of the inlet vortex of an axial-flow pump. J. Hydrodyn. 2022, 34, 234–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Lin, Q.; Meng, F.; Zheng, Y.; Xu, X. Research on the influence of tip clearance of axial-flow pump on energy characteristics under pump and turbine conditions. Machines 2022, 10, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, B.; Cai, Y.; Ding, Q.; Zhao, D.; Sun, W.; Wang, L. Investigation of tip leakage vortex structure and trajectory in a centrifugal pump with a new omega vortex identification method. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 5270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kan, K.; Zhang, Q.; Xu, Z.; Zheng, Y.; Gao, Q.; Shen, L. Energy loss mechanism due to tip leakage flow of axial flow pump as turbine under various operating conditions. Energy 2022, 255, 124532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafiee, S.E.; Grnman, A.; Uusitalo, A.; Turunen-Saaresti, T. Comprehensive study on the design and analysis of supercritical carbon dioxide (sCO2) radial outflow turbines (ROTs), focusing on tip clearance effects, loss correlations, and performance evaluation. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2025, 272, 126399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Tang, F.; Shi, L.; Dai, L.; Shen, J.; Liu, J. The Analysis of Cavitation Flow and Pressure Pulsation of Bi-Directional Pump. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, L.; Li, S.; Li, W.; Huang, Y.; Shi, W.; Li, H.; Yang, Y.; Agarwal, R.K. Study on passive suppression method of rotating stall in mixed-flow pump: Using different impeller rim structures. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part A J. Power Energy 2023, 237, 965–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Xu, F.; Cheng, L.; Pan, W.; Ge, Y.; Li, J.; Zhang, J. Simulation of internal flow characteristics of an axial flow pump with variable tip clearance. Water 2022, 14, 1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Tang, F.; Liu, H.; Zhang, X.; Sun, Z.; Wang, F. Investigation of cavitation and flow characteristics of tip clearance of bidirectional axial flow pump with different clearances. Ocean Eng. 2023, 288, 115960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miorini, R.L.; Wu, H.X.; Katz, J. The internal structure of the tip leakage vortex within the rotor of an axial waterjet pump. J. Turbomach. 2012, 134, 031018.1–031018.12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, J.; Wray, A.; Moin, P. Eddies, Stream, and Convergence Zones in Turbulent Flows; Center for Turbulent Research Report CTR-S8; Center for Turbulence Research: Stanford, CA, USA, 1988; pp. 193–208. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, P.; Chu, N.; Wu, D.Z.; Cao, L.; Yang, S.; Wu, P. Computational fluid dynamics-based pump redesign to improve efficiency and decrease unsteady radial forces. J. Fluids Eng. Trans. ASME 2017, 139, 011101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.B.; Tan, L. Spatial-temporal evolution of tip leakage vortex in a mixed-flow pump with tip clearance. J. Fluids Eng. Trans. ASME 2019, 141, 081302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, B.N.; Jeong, H.; Kim, J.H.; Park, J.-S.; Yang, C. Effects of tip clearance size on energy performance and pressure fluctuation of a tidal propeller turbine. Energies 2020, 13, 4055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

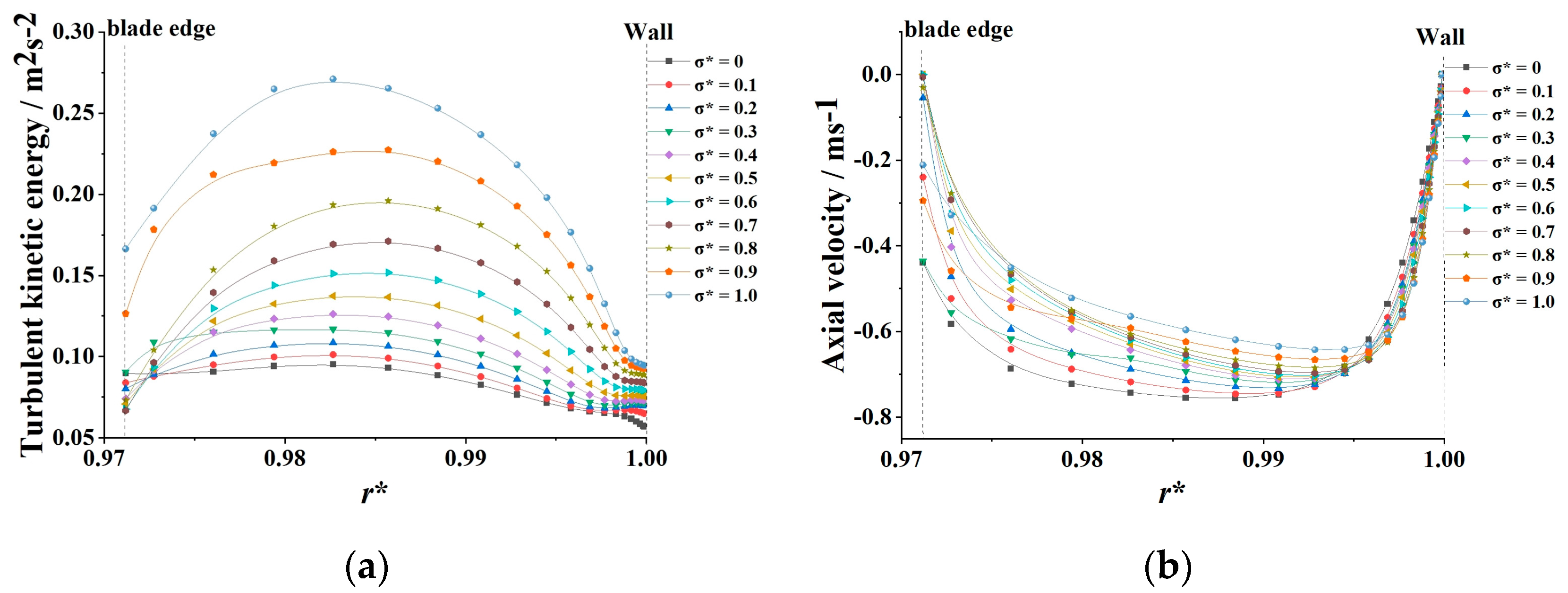
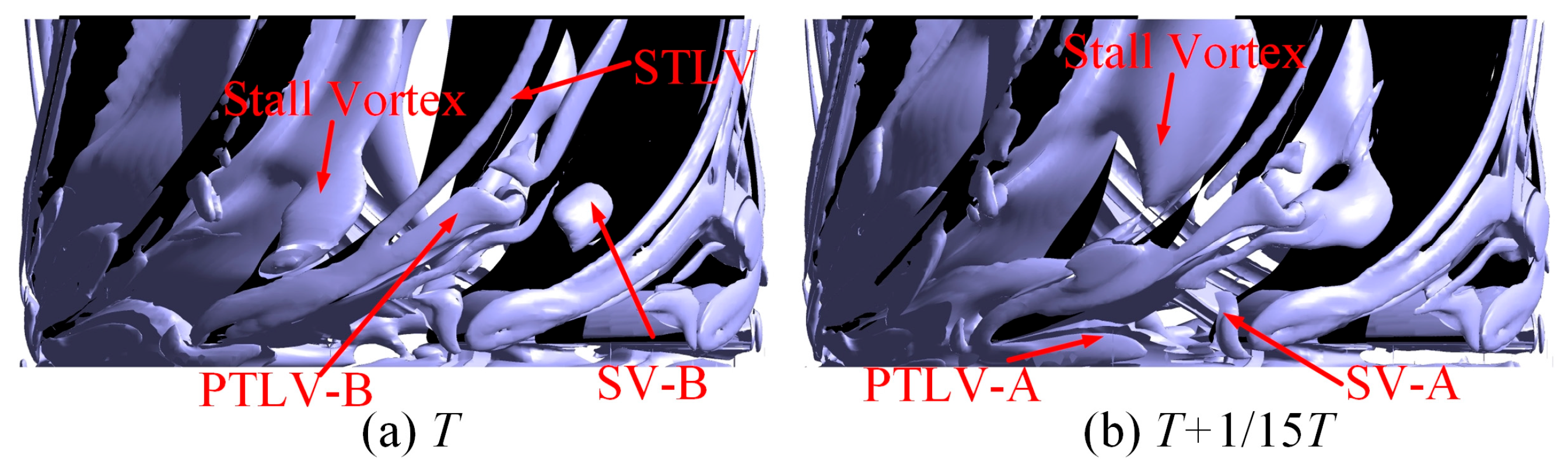
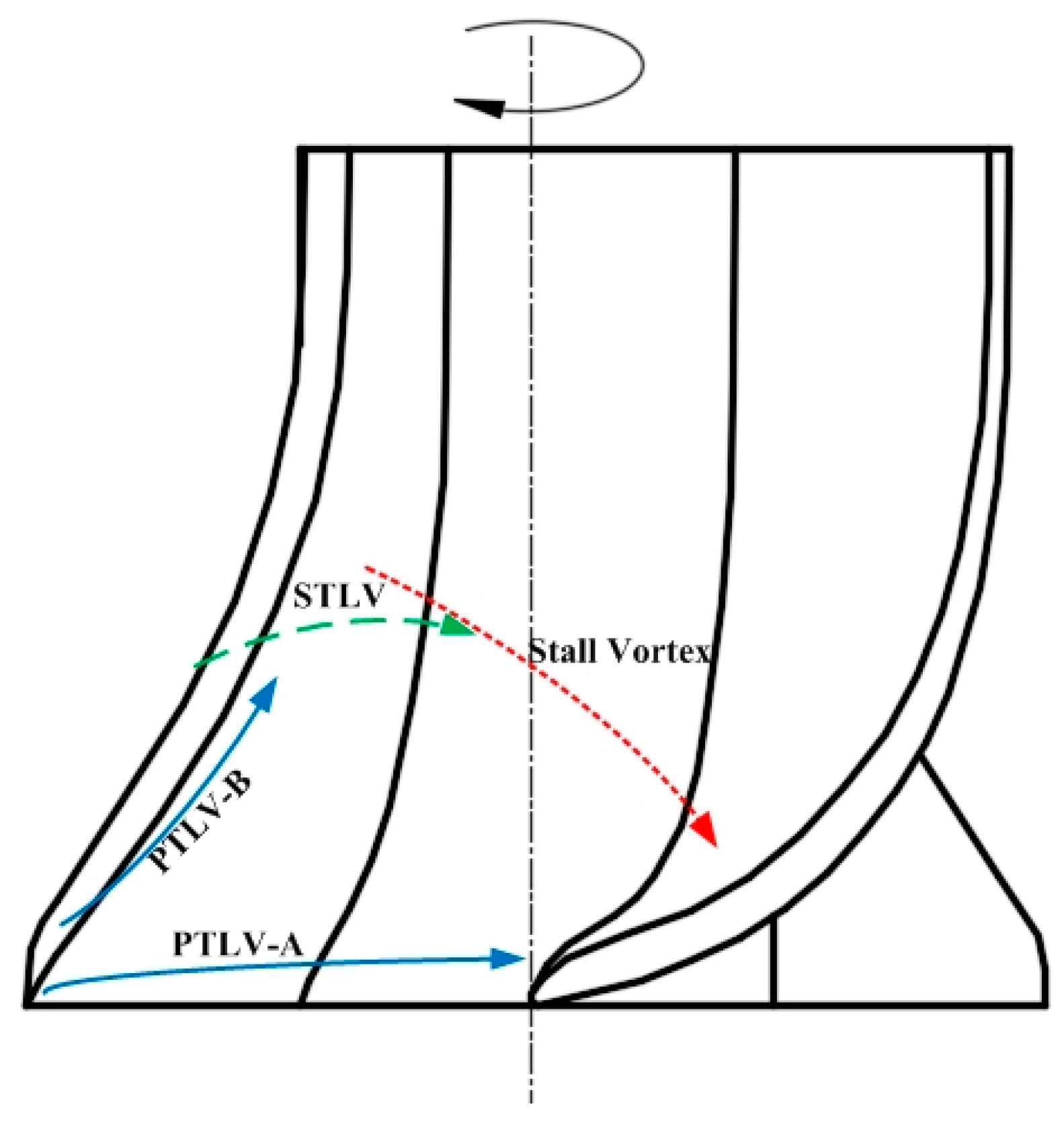


| Parameters | Value |
|---|---|
| Design flow rate (Qd) | 55 L/min |
| Number of impeller blades (Z) | 8 |
| Impeller rotating speed (n) | 3000 rpm |
| Diameter of inlet (Din) | 32 mm |
| Diameter of impeller inlet (D) | 32 mm |
| Delivery head (H) | 1.5 m |
| Diameter of outlet (Dout) | 40 mm |
| Grid Schemes | N1 | N2 | N3 | N4 | N5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Grid number (106) | 7.73 | 8.75 | 9.83 | 11.34 | 13.37 |
| Item | Classification | Setup | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Model | Turbulent model | Standard k-ε | - |
| Physical characteristics | Water | density | 998 kg/m3 |
| dynamic viscosity | 0.001 kg/(m·s) | ||
| Initial condition | Inlet | Mass flow rate | 55 L/min |
| Turbulence intensity | 5% | ||
| Outlet | Outflow | - | |
| Turbulence intensity | 5% | ||
| Wall | No slip | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ning, C.; Li, Y.; Sun, H.; Wang, Y.; Meng, F. Transient Vortex Dynamics in Tip Clearance Flow of a Novel Dishwasher Pump. Machines 2025, 13, 681. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines13080681
Ning C, Li Y, Sun H, Wang Y, Meng F. Transient Vortex Dynamics in Tip Clearance Flow of a Novel Dishwasher Pump. Machines. 2025; 13(8):681. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines13080681
Chicago/Turabian StyleNing, Chao, Yalin Li, Haichao Sun, Yue Wang, and Fan Meng. 2025. "Transient Vortex Dynamics in Tip Clearance Flow of a Novel Dishwasher Pump" Machines 13, no. 8: 681. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines13080681
APA StyleNing, C., Li, Y., Sun, H., Wang, Y., & Meng, F. (2025). Transient Vortex Dynamics in Tip Clearance Flow of a Novel Dishwasher Pump. Machines, 13(8), 681. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines13080681






