Effect of Roundness Error of the Grooves on the Inner Ring Runout of Angular Contact Ball Bearings
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. The Prediction Model of the Inner Ring Runout of the Bearing
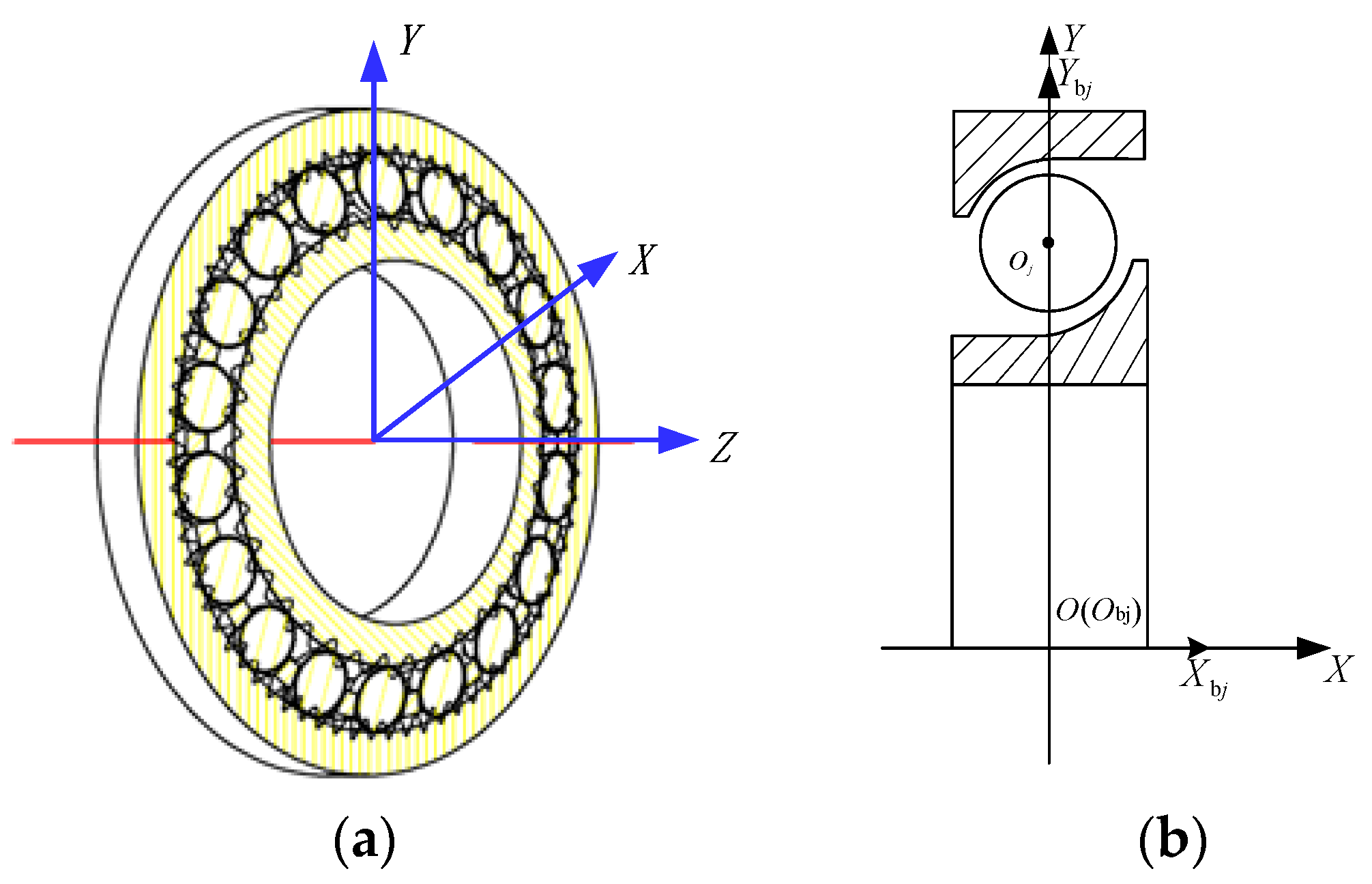
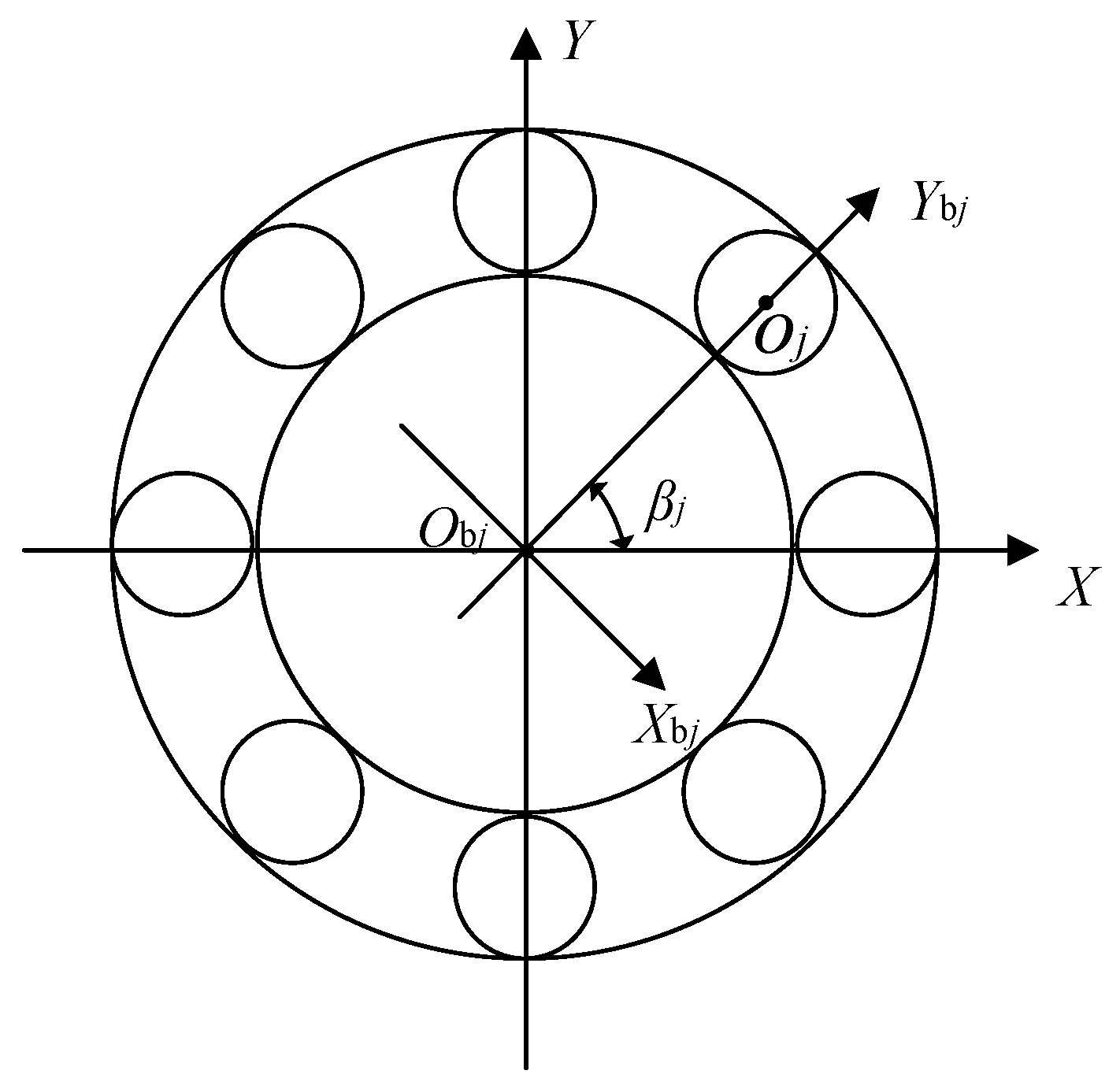
2.1. The Geometric and Kinematic Relationships of the Bearing
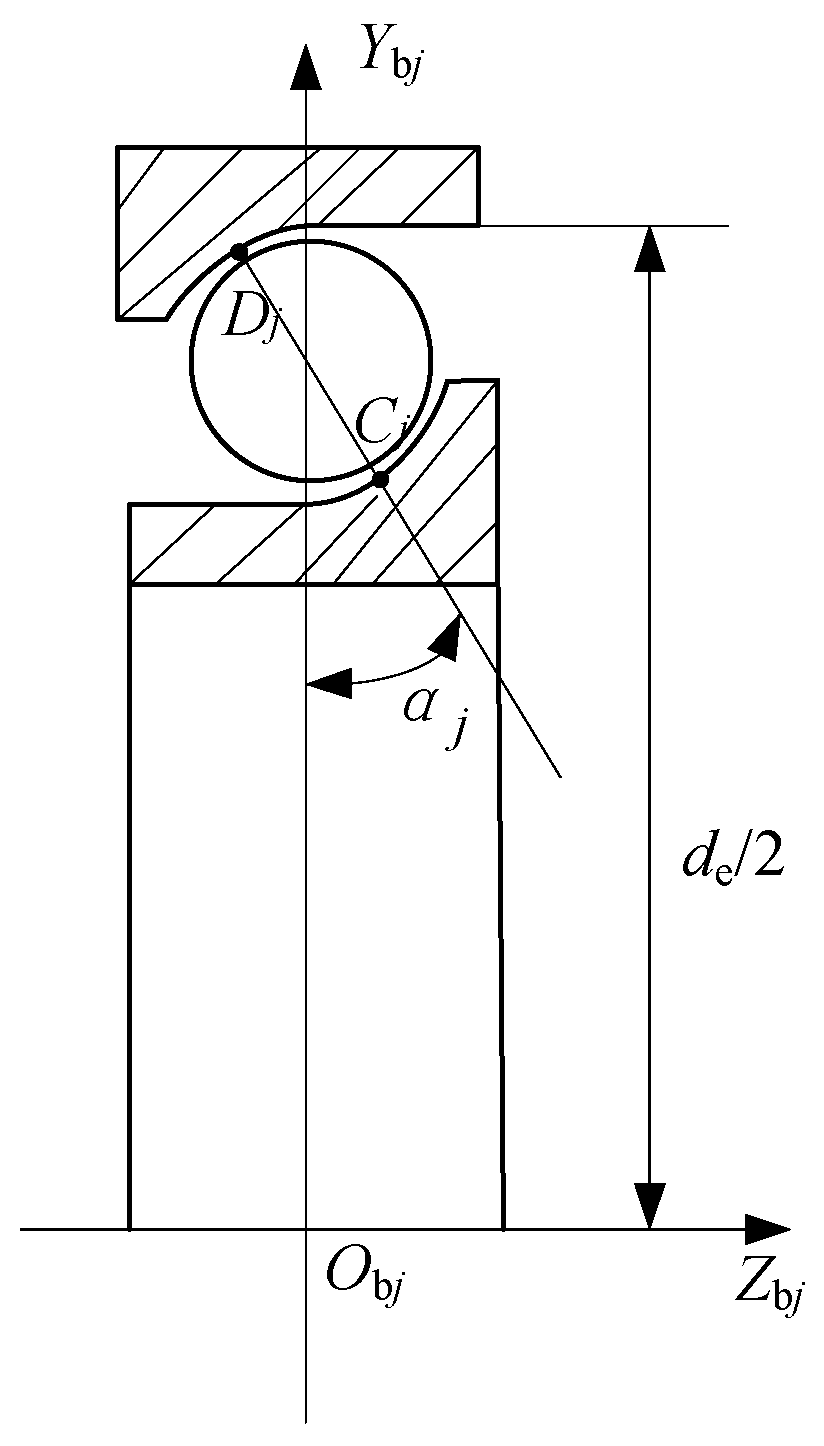
2.2. Equations of the Contour Curves of the Grooves
2.3. Coordinates of Contact Points on Grooves
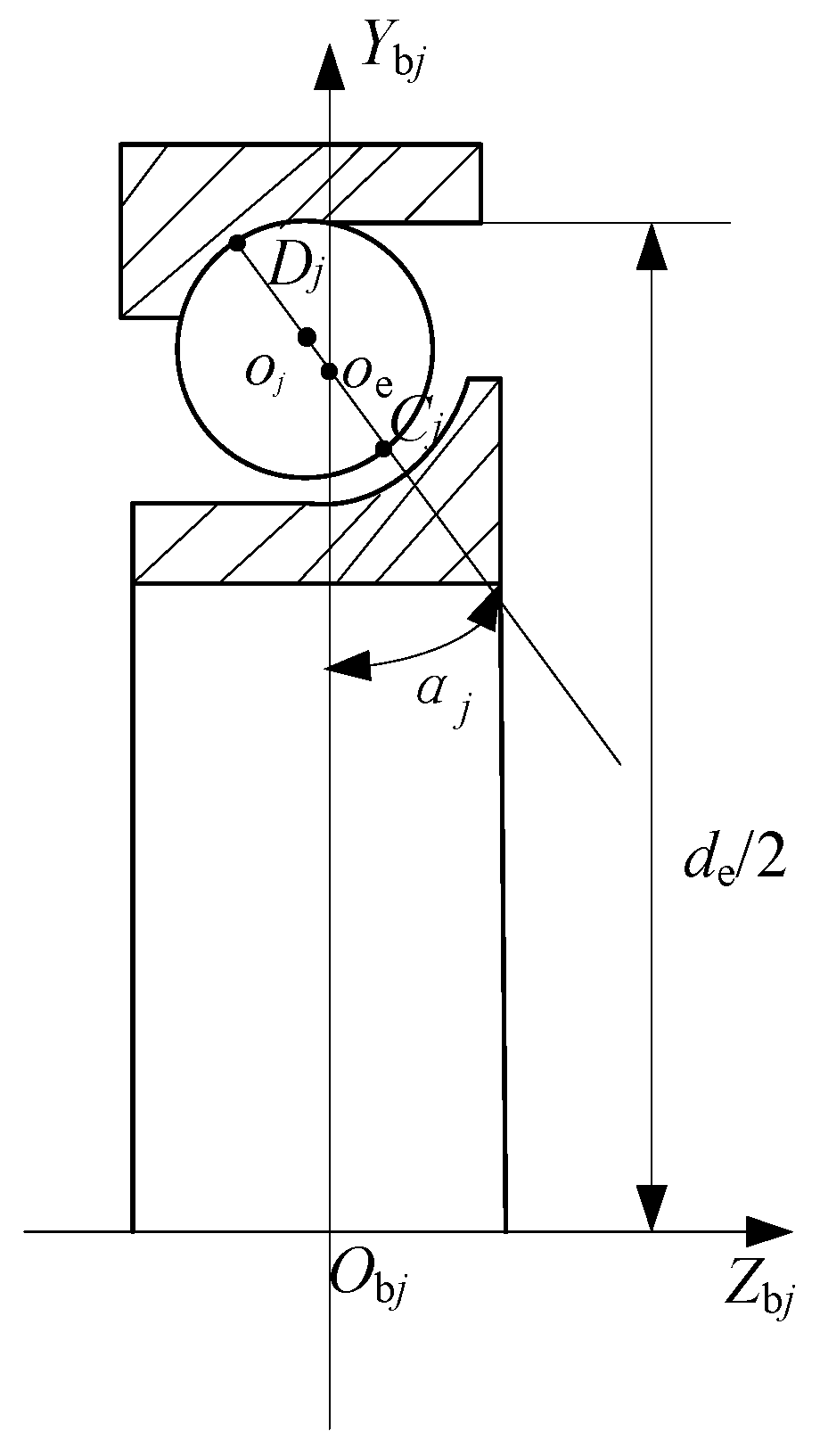
2.4. Coordinates of the Center of the Balls
2.5. Coordinates of the Rotation Center of the Inner Ring
- None of the balls interfered with the inner groove. When one ball interferes with the inner ring groove, it indicates that the position of the inner ring is not the stable position of the inner ring;
- The number of balls that contacted the inner groove is not less than three. Owing to the point contact between the ball and the inner ring groove, the number of balls contacted in the inner groove must be more than or equal to three when the inner groove is in a stable state. Otherwise, the force on the inner ring will not be able to keep the inner ring stable.
- The balls that made contact with the inner groove were distributed in at least three different quadrants or two symmetrical quadrants. When the contact balls are distributed in three different quadrants, each ball that made contact with the inner groove is equivalent to a fulcrum; three fulcrums located in three quadrants cause the inner ring to be in a stable state. When the contact ball is located in two quadrants, these quadrants must be symmetrical, i.e., either quadrants one and three or quadrants two and four.
3. Experimental Validation of the Prediction Model of the Inner Ring Runout of the Bearing
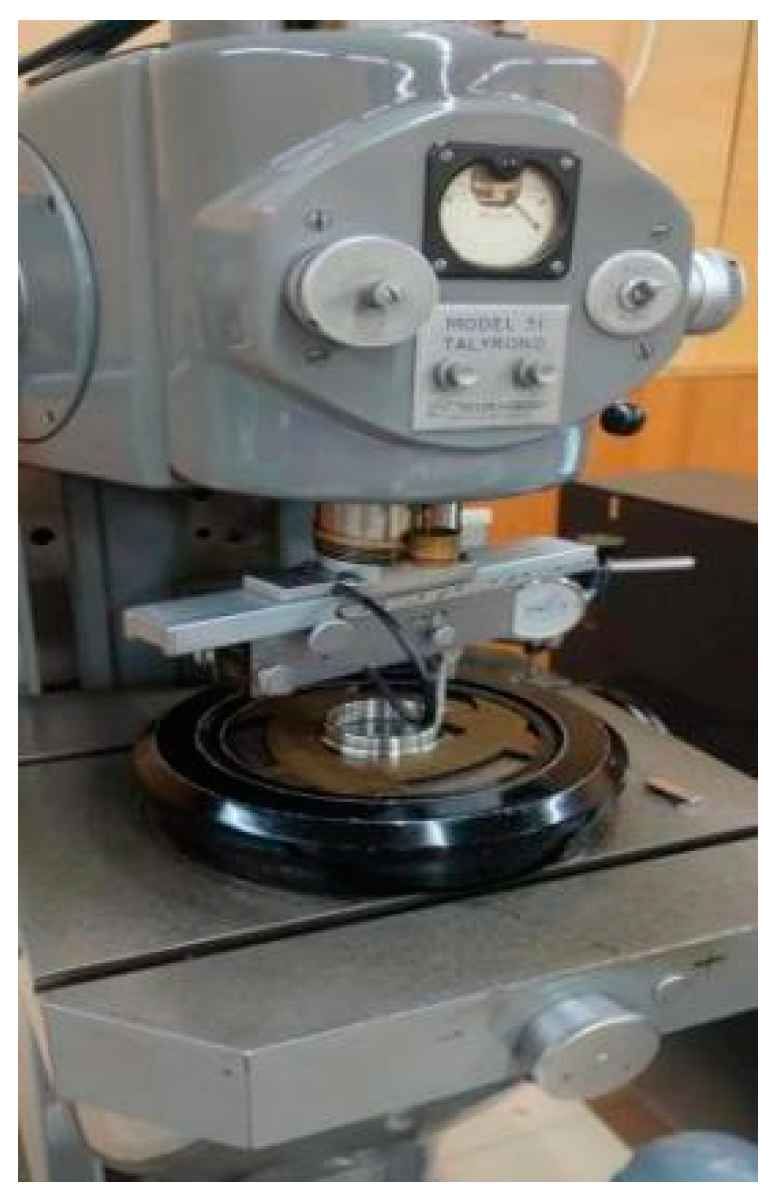
3.1. Measurement of the Contours and Roundness of the Grooves
3.2. Measurement of the Inner Ring Runout and Validation of the Prediction Model
4. Results and Analysis
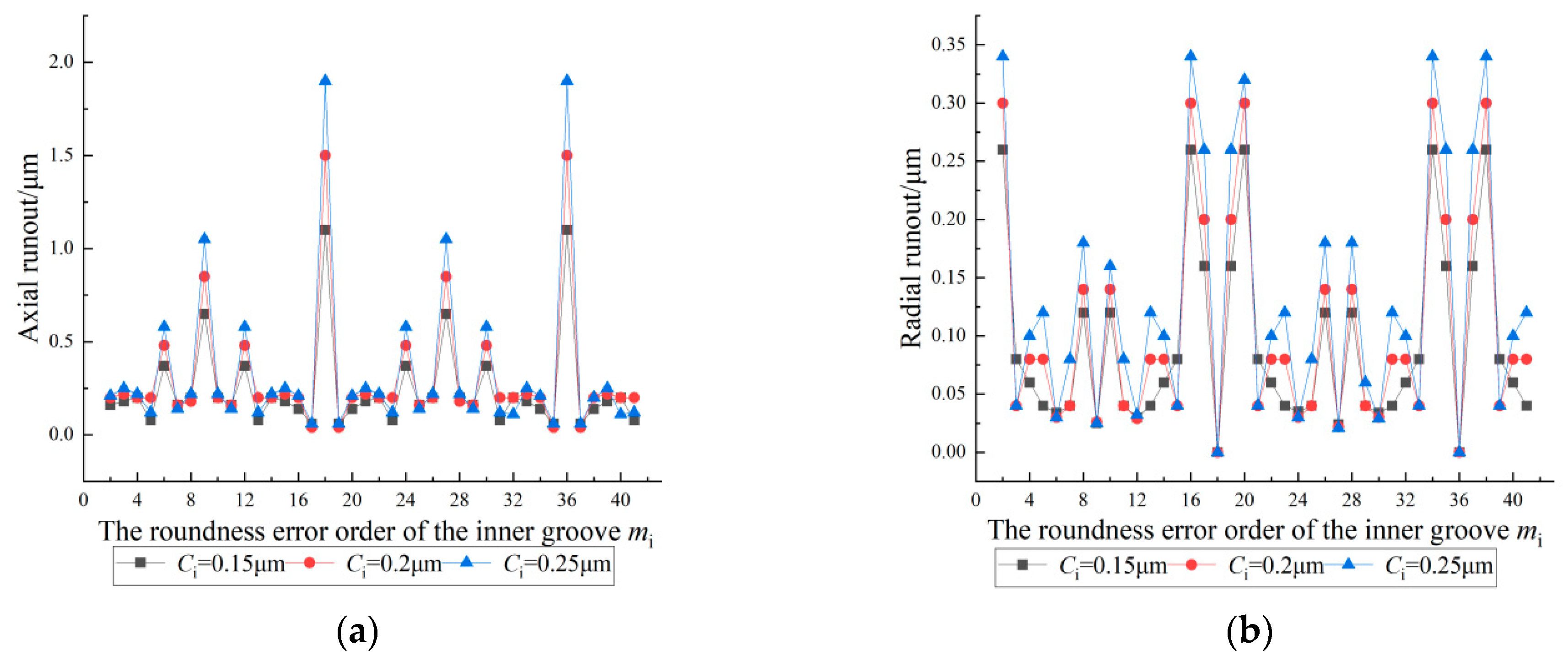
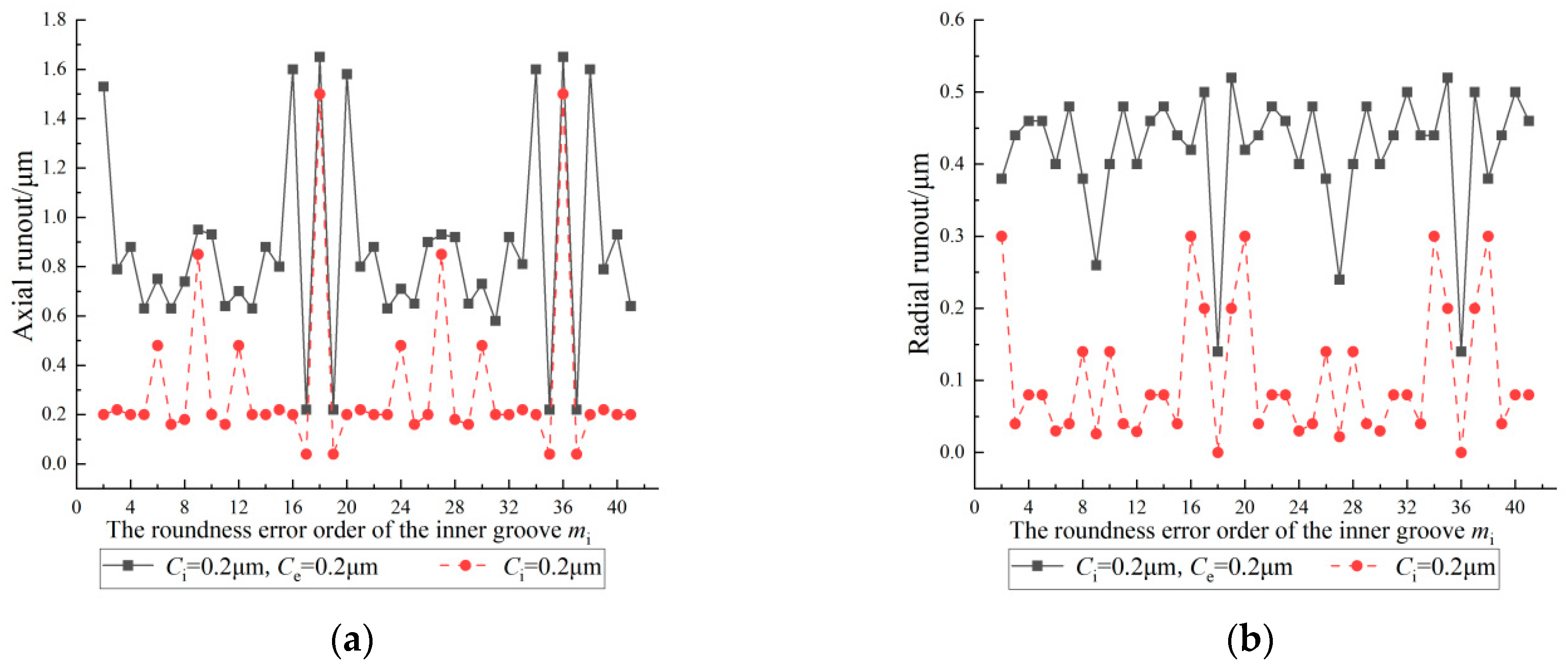
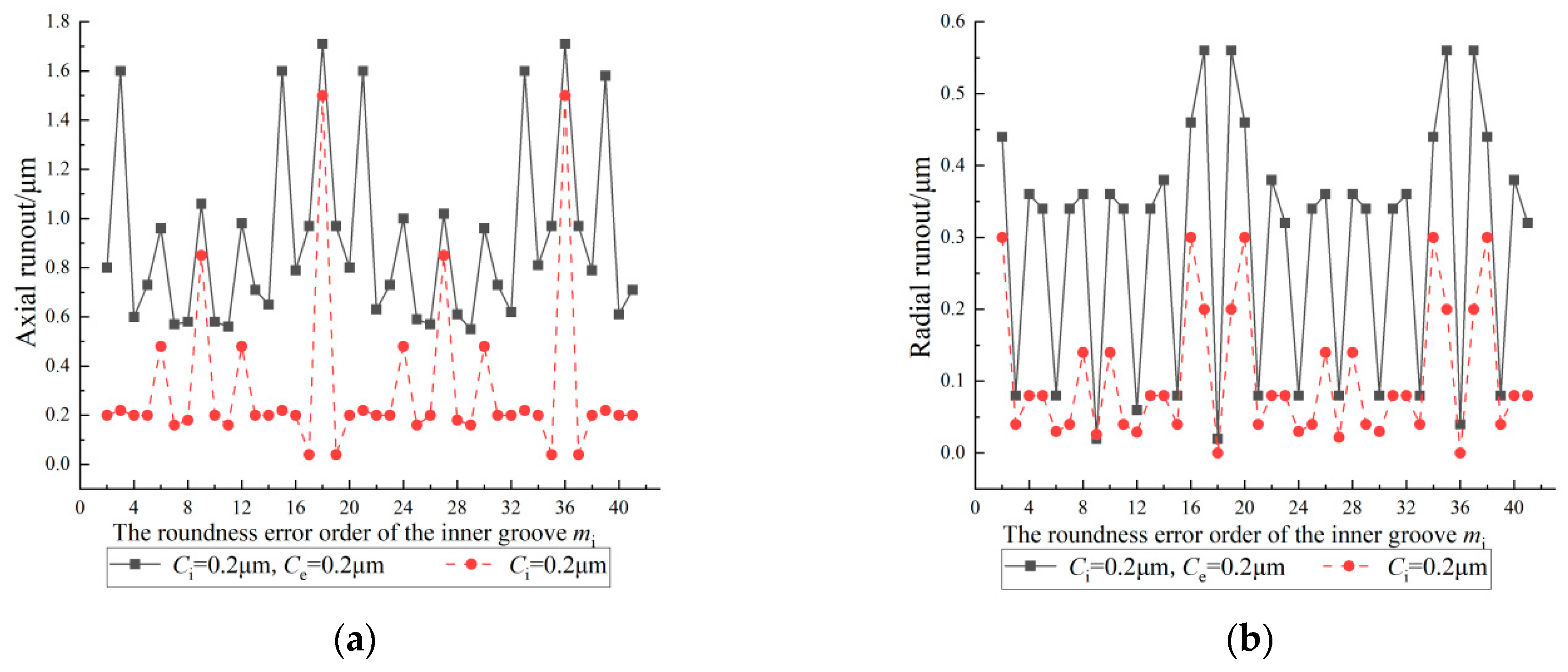
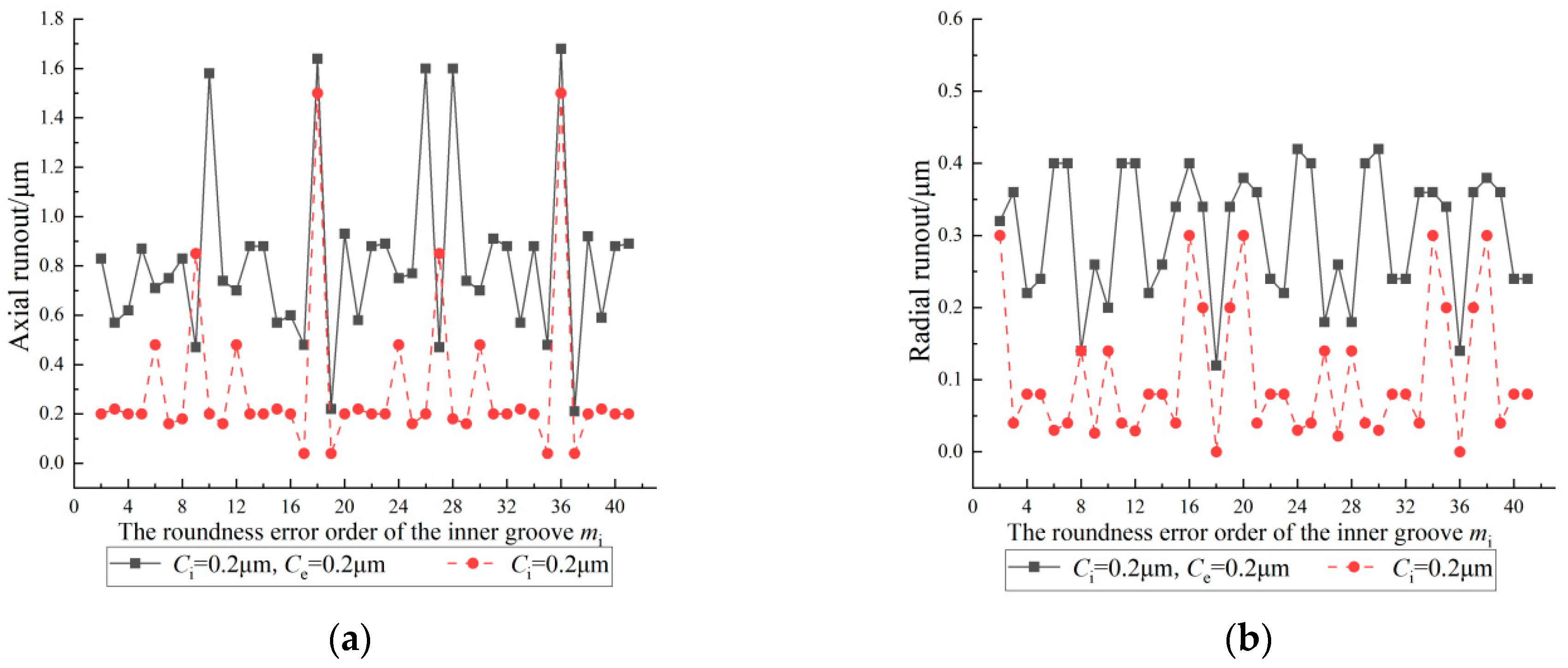
4.1. Effect of the Roundness Error Order of the Inner Groove on the Inner Ring Runout
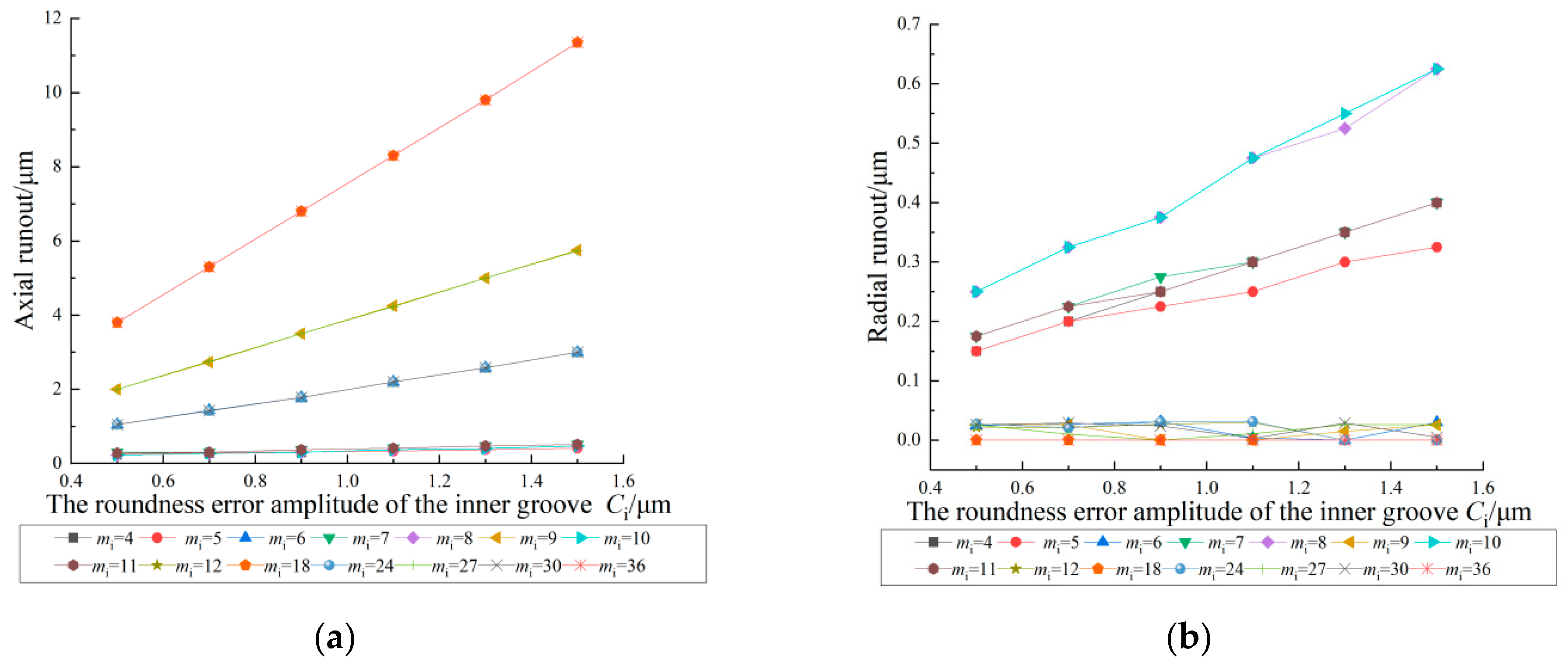
4.2. Effect of the Roundness Error Amplitude of the Inner Groove on the Inner Ring Runout
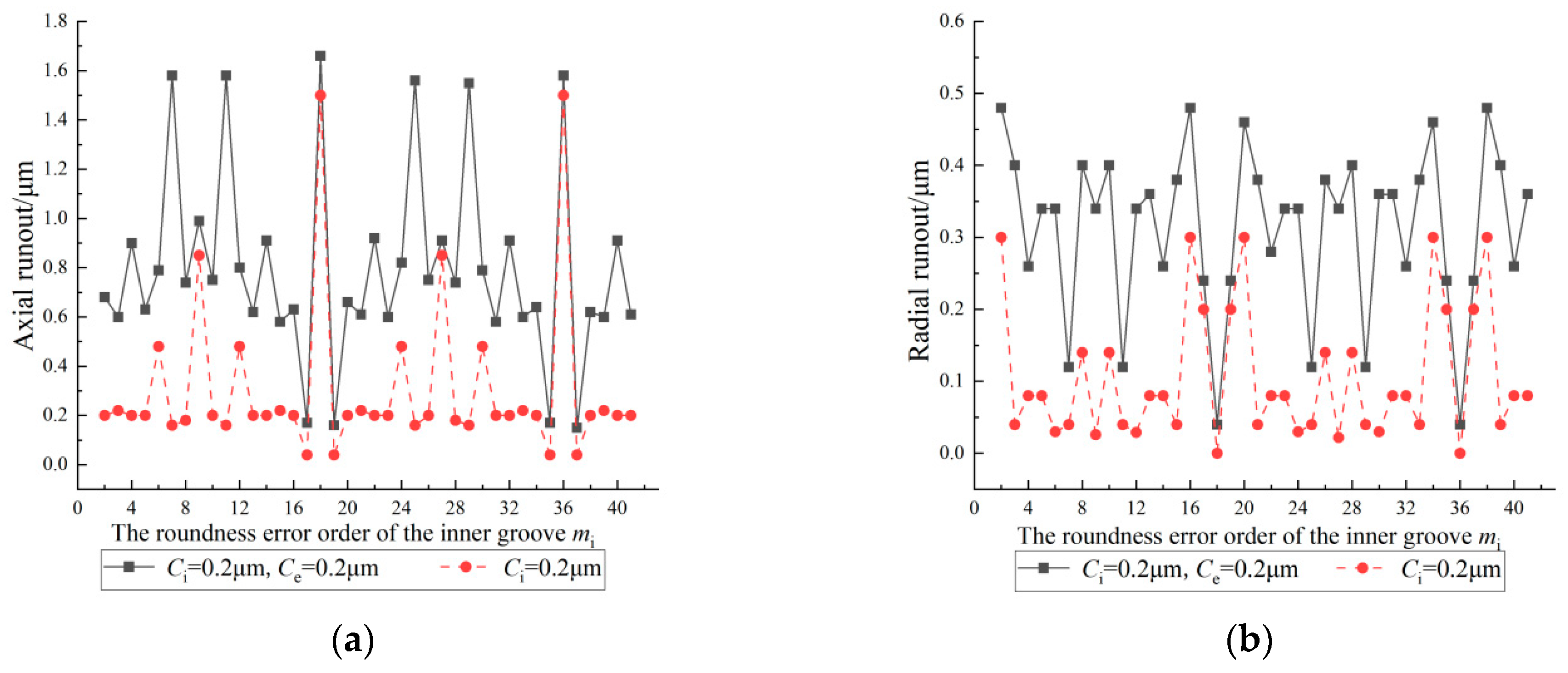
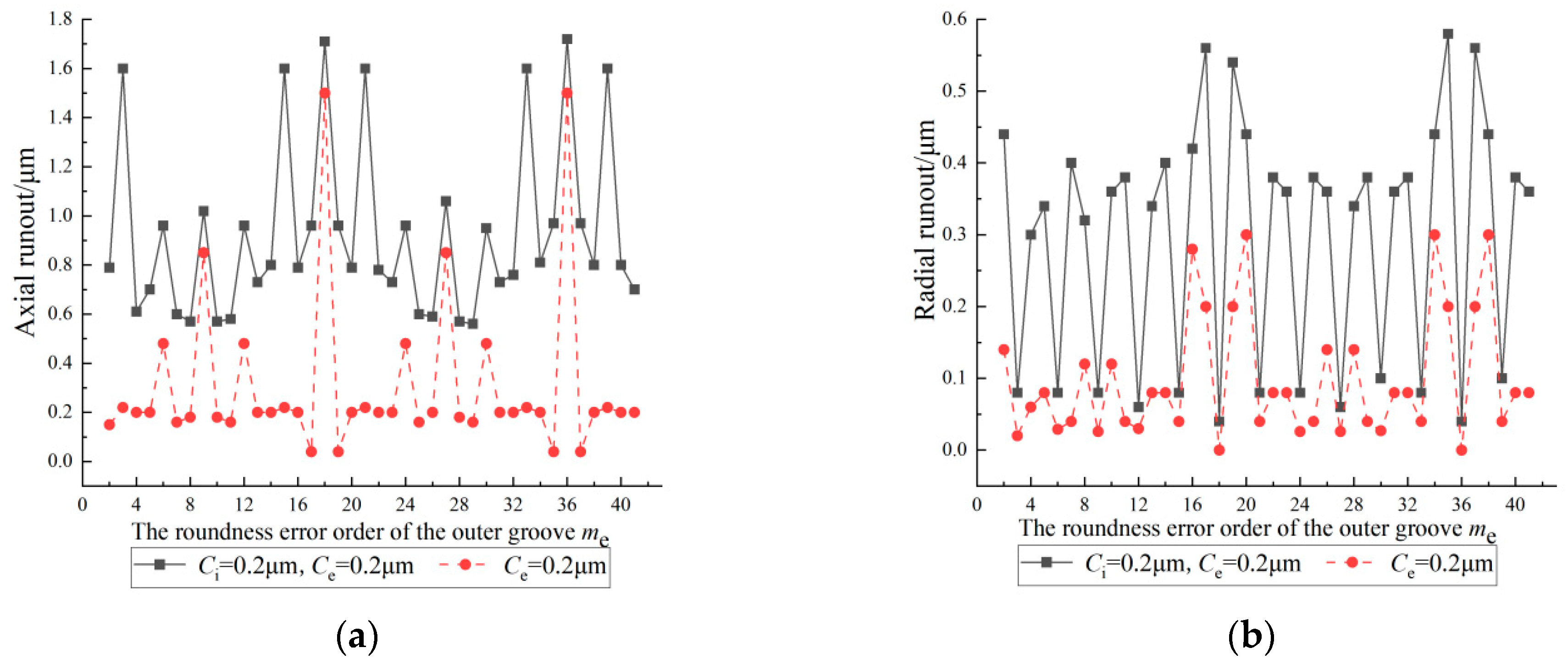
4.3. Effect of the Roundness Error Order of the Outer Groove on the Inner Ring Runout
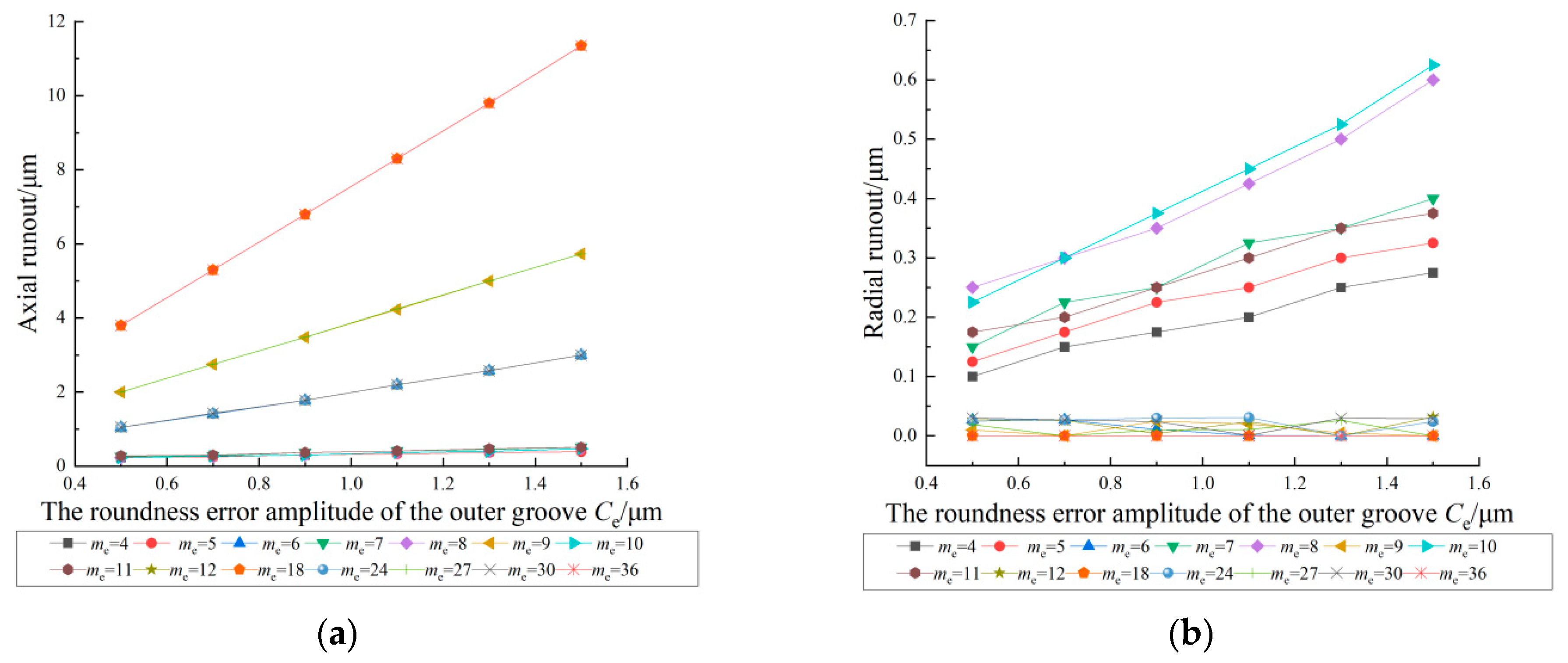
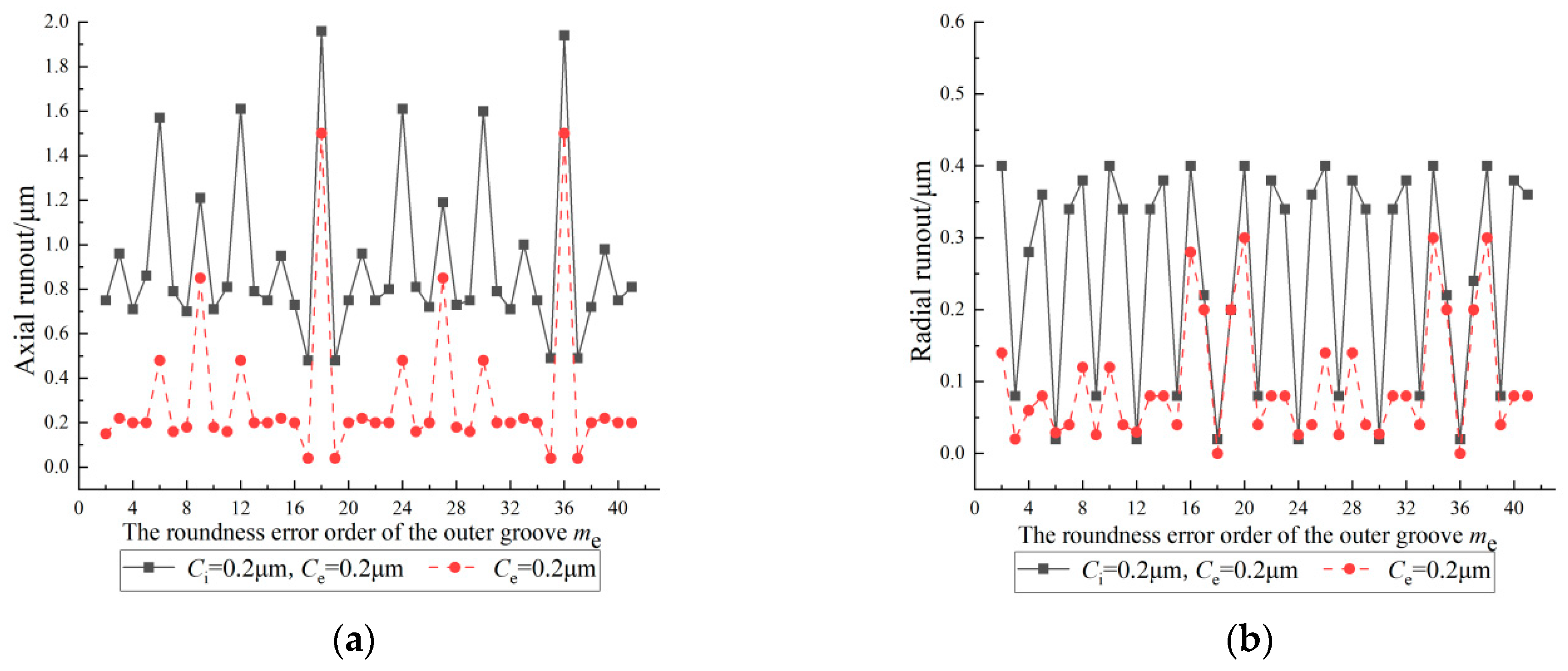
4.4. Effect of the Roundness Error Amplitude of the Outer Groove on the Inner Ring Runout
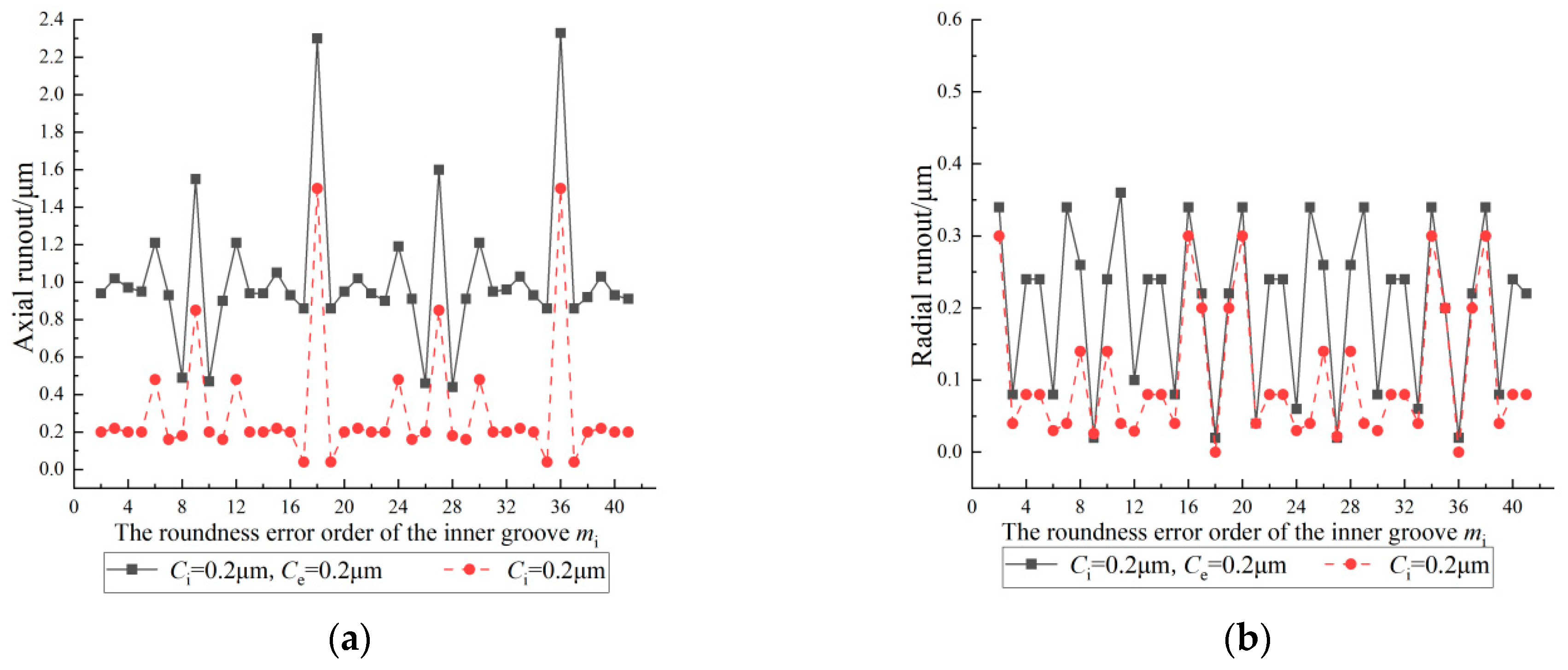
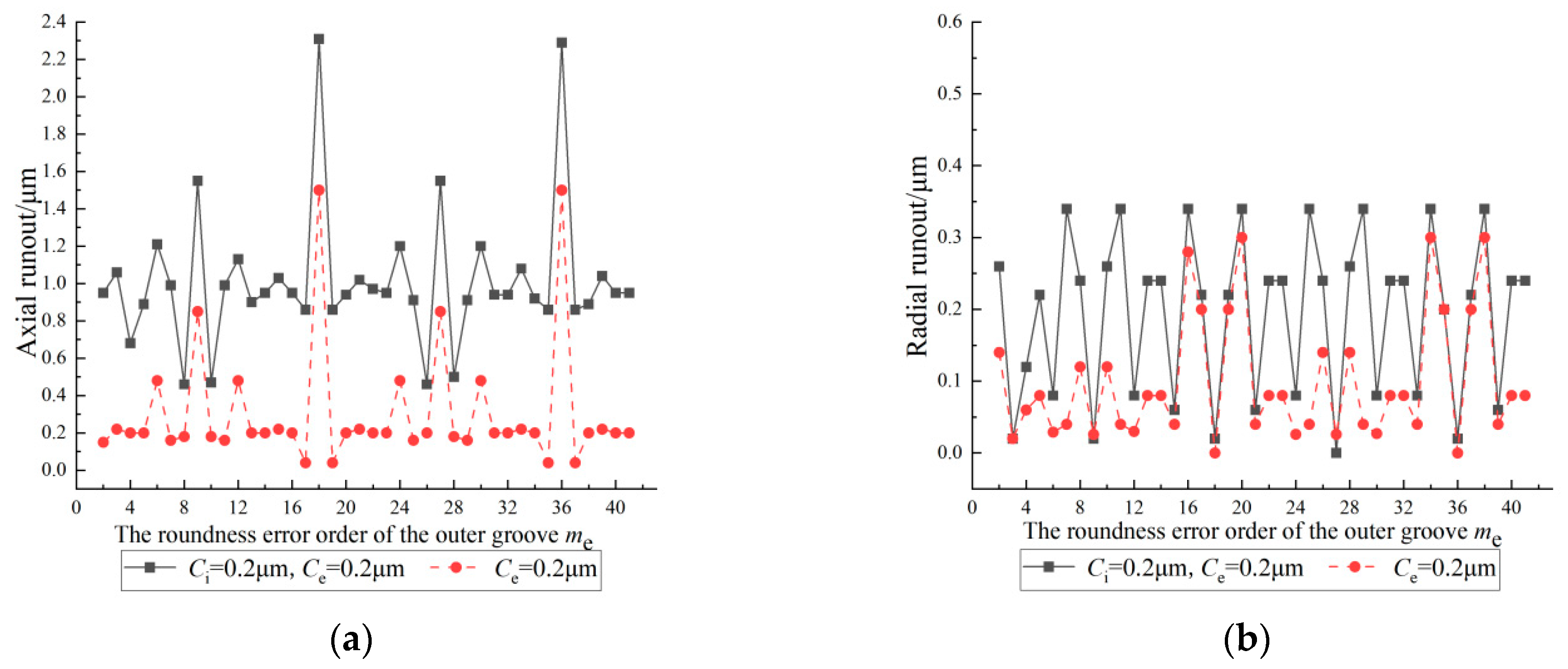
4.5. Coupling Effect of the Roundness Error of the Inner and Outer Grooves on the Inner Ring Runout
5. Conclusions
- The inner ring runout changes periodically with a change in the roundness error order of the grooves; the period is the number of balls.
- The inner ring runout increases with an increase in the roundness error amplitude and the roundness error order affects the magnitude of the increase.
- Under the coupling of the roundness error of the inner and outer grooves, the magnification of the inner ring runout increases as a whole.
- When there are specific relationships between the roundness error orders of the grooves and the number of balls, the magnification of the axial or radial runout changes significantly.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, X.; Yu, K.; Ma, H.; Cao, L.; Luo, Z.; Li, H.; Che, L. Analysis of varying contact angles and load distributions in defective angular contact ball bearing. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2018, 91, 449–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodewig, A.H.; Pape, F.; Poll, G. Optimizing Stainless Steel Bearings: Enhancement of Stainless Steel Bearing Fatigue Life by Low-Temperature Forming. Metals 2024, 14, 512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pape, F.; Coors, T.; Wang, Y.; Poll, G. Fatigue Life Calculation of Load-Adapted Hybrid Angular Contact Ball Bearings; Springer: Singapore, 2019; pp. 401–414. [Google Scholar]
- Takabi, J.; Khonsari, M. On the thermally-induced seizure in bearings: A review. Tribol. Int. 2015, 91, 118–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Y. Modeling and dynamic characteristic analysis of high speed angular contact ball bearing with variable clearance. Tribol. Int. 2023, 182, 108330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Howard, C.Q.; Hansen, C.H. An extensive review of vibration modelling of rolling element bearings with localised and extended defects. J. Sound Vib. 2015, 357, 300–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rejith, R.; Kesavan, D.; Chakravarthy, P.; Murty, S.N. Bearings for aerospace applications. Tribol. Int. 2023, 181, 108312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noguchi, S.; Tanaka, K.; Ono, K. Theoretical analysis of a ball bearing used in HDD spindle motors for reduction of NRRO. IEEE Trans. Magn. 1999, 35, 845–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noguchi, S.; Ono, K. Reduction of NRRO in ball bearings for HDD spindle motors. Precis. Eng. 2004, 28, 409–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noguchi, S.; Obinata, S.; Saito, Y.; Akamatsu, Y.; Sakaguchi, T. The influence of the unequal orbital intervals of balls on the NRRO of rotational frequency of the cage in a ball bearing. Toraibarojisuto/J. Jpn. Soc. Tribol. 2005, 50, 90–96. [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto, J. Study on run-out of ball bearings-relation between unroundness of race and locus of shaft in rotation. J. Jpn. Soc. Tribol. 2001, 46, 578–584. [Google Scholar]
- Tada, S. Three-dimensional analysis of non-repeatable runout (NRRO) in ball bearing. KOYO Eng. J. 2002, 161, 31–37. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.; Hong, J.; Liu, J.; Zhu, Y. Theoretical model to analyze the non-repetitive run-out (NRRO) of ball bearings. Adv. Sci. Lett. 2011, 4, 2522–2527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Hong, J.; Liu, J.; Ding, Y.; Wang, M.Y. Theoretical method to reduce the non-repetitive run-out (NRRO) of angular contact ball bearings. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Symposium on Assembly and Manufacturing (ISAM), Tampere, Finland, 25–27 May 2011; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, G.; Wang, B.; Mao, F. Effects of raceway roundness and roller diameter errors on clearance and runout of a cylindrical roller bearing. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part J J. Eng. Tribol. 2013, 227, 275–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, F.; Ji, P.; Li, Z.; Wu, B.; An, Q. Influences of off-sized rollers on mechanical performance of spherical roller bearings. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part K J. Multi-Body Dyn. 2015, 229, 344–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Chen, G.; Li, J.; Xue, Y.; Pang, B. Prediction Method for the Radial Runout of Inner Ring in Cylindrical Roller Bearings. Math. Probl. Eng. 2017, 2017, 6584561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Chen, G.; Li, J.; Xue, Y. A method to predict the radial runout of outer ring in cylindrical roller bearings. Adv. Mech. Eng. 2017, 9, 168781401773325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Li, J.; Xue, Y. Influence of roundness errors of bearing components on rotational accuracy of cylindrical roller bearings. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 6794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zha, J.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, P. Relationship between elliptical form error and rotation accuracy of hydrostatic journal bearing. Ind. Lubr. Tribol. 2017, 69, 905–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, G.; Chen, Y.; Cui, L.; Jin, G.; Wang, T.; Qi, H.; Tian, Y. Investigation on modeling and formation mechanism of dynamic rotational error for spindle-rolling bearing system. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 5753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Meng, Q.; Ma, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wen, B.; Guo, Z. Rotation Accuracy Analysis of High-speed Angular Contact Ball Bearings. Des. Eng. 2020, 38–49. Available online: https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/Rotation-Accuracy-Analysis-of-High-speed-Angular-Xu-Qingguo/b91bb1ee79a91c732b734927e9f3f4bef1605dae (accessed on 31 July 2024). [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P. Accuracy prediction and roller number optimization of journal roller bearing based on averaging coefficient considering raceway roundness error. J. Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng. 2023, 45, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Hu, L.; Zhang, S.; Zhao, Z.; Ai, S. Modeling angular contact ball bearing without raceway control hypothesis. Mech. Mach. Theory 2014, 82, 154–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, N.; Tu, J. Roundness modeling of machined parts for tolerance analysis. Precis. Eng. 2001, 25, 35–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viitala, R.; Widmaier, T.; Hemming, B.; Tammi, K.; Kuosmanen, P. Uncertainty analysis of phase and amplitude of harmonic components of bearing inner ring four-point roundness measurement. Precis. Eng. 2018, 54, 118–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

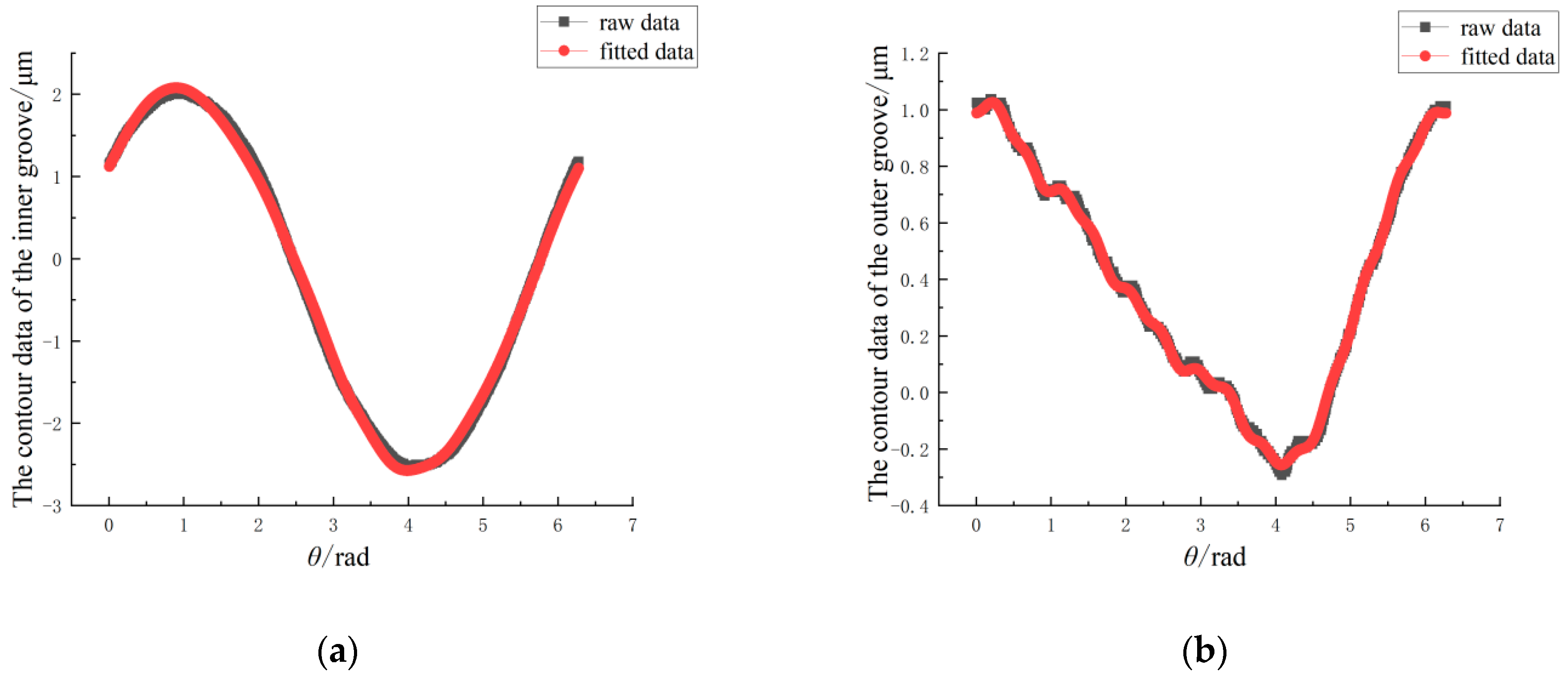







| Orders | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amplitudes/μm | 0.378 | 0.555 | 0.144 | 0.034 | 0.023 | 0.010 | 0.014 | 0.014 | 0.009 | 0.003 | 0.001 |
| Phase/rad | 0 | −0.463 | 0.491 | 2.008 | −0.582 | 0.189 | −1.376 | 3.070 | 3.019 | −0.871 | −0.817 |
| Orders | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amplitudes/μm | 0.708 | 1.688 | 0.251 | 0.037 | 0.030 | 0.009 | 0.011 | 0.004 | 0.004 | 0.010 | 0.002 |
| Phase/rad | 3.142 | 0.689 | 0.364 | 2.008 | −2.075 | −2.087 | 0.351 | −2.480 | −1.646 | −1.727 | −1.979 |
| Bearing Number | B7008C-1 | B7008C-2 | B7008C-3 | B7008C-4 | B7008C-5 | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Radial cross-sections | 1 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| Roundness value of the outer groove/μm | 0.4 | 0.35 | 0.53 | 0.37 | 0.33 | 0.44 | 0.35 | 0.28 | 0.39 | 0.54 | 0.55 | 0.53 | 0.56 | 0.42 | 0.57 |
| Roundness value of the inner groove/μm | 0.53 | 0.57 | 0.56 | 0.36 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.22 | 0.15 | 0.16 | 0.21 | 0.15 | 0.2 | 0.18 | 0.18 | 0.15 |
| Parameters | Numerical Value |
|---|---|
| The bottom diameter of the inner groove /mm | 46.964 |
| The bottom diameter of the outer groove /mm | 61.019 |
| The radius of curvature of the inner groove /mm | 3.99 |
| The radius of curvature of the outer groove /mm | 3.78 |
| Original contact angle | 15 |
| Diameter of the balls /mm | 7.001 () |
| Number of balls | 18 |
| The Inner Ring Runout/μm | B7008C-1 | B7008C-2 | B7008C-3 | B7008C-4 | B7008C-5 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Measured Value | Predicted Value | Measured Value | Predicted Value | Measured Value | Predicted Value | Measured Value | Predicted Value | Measured Value | Predicted Value | |
| 1 | 1.12 | 1 | 0.96 | 1 | 0.88 | 1 | 1.20 | 1 | 1.20 | |
| 2 | 2.00 | 2 | 1.95 | 2 | 1.75 | 3 | 3.30 | 2 | 1.92 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cui, D.; Yu, Y.; Xue, Y.; Guo, P.; Han, H.; Cai, H. Effect of Roundness Error of the Grooves on the Inner Ring Runout of Angular Contact Ball Bearings. Machines 2024, 12, 532. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines12080532
Cui D, Yu Y, Xue Y, Guo P, Han H, Cai H. Effect of Roundness Error of the Grooves on the Inner Ring Runout of Angular Contact Ball Bearings. Machines. 2024; 12(8):532. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines12080532
Chicago/Turabian StyleCui, Di, Yongjian Yu, Yujun Xue, Pengge Guo, Hongbiao Han, and Haichao Cai. 2024. "Effect of Roundness Error of the Grooves on the Inner Ring Runout of Angular Contact Ball Bearings" Machines 12, no. 8: 532. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines12080532
APA StyleCui, D., Yu, Y., Xue, Y., Guo, P., Han, H., & Cai, H. (2024). Effect of Roundness Error of the Grooves on the Inner Ring Runout of Angular Contact Ball Bearings. Machines, 12(8), 532. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines12080532







