Expert System Based on Autoencoders for Detection of Broken Rotor Bars in Induction Motors Employing Start-Up and Steady-State Regimes
Abstract
1. Introduction
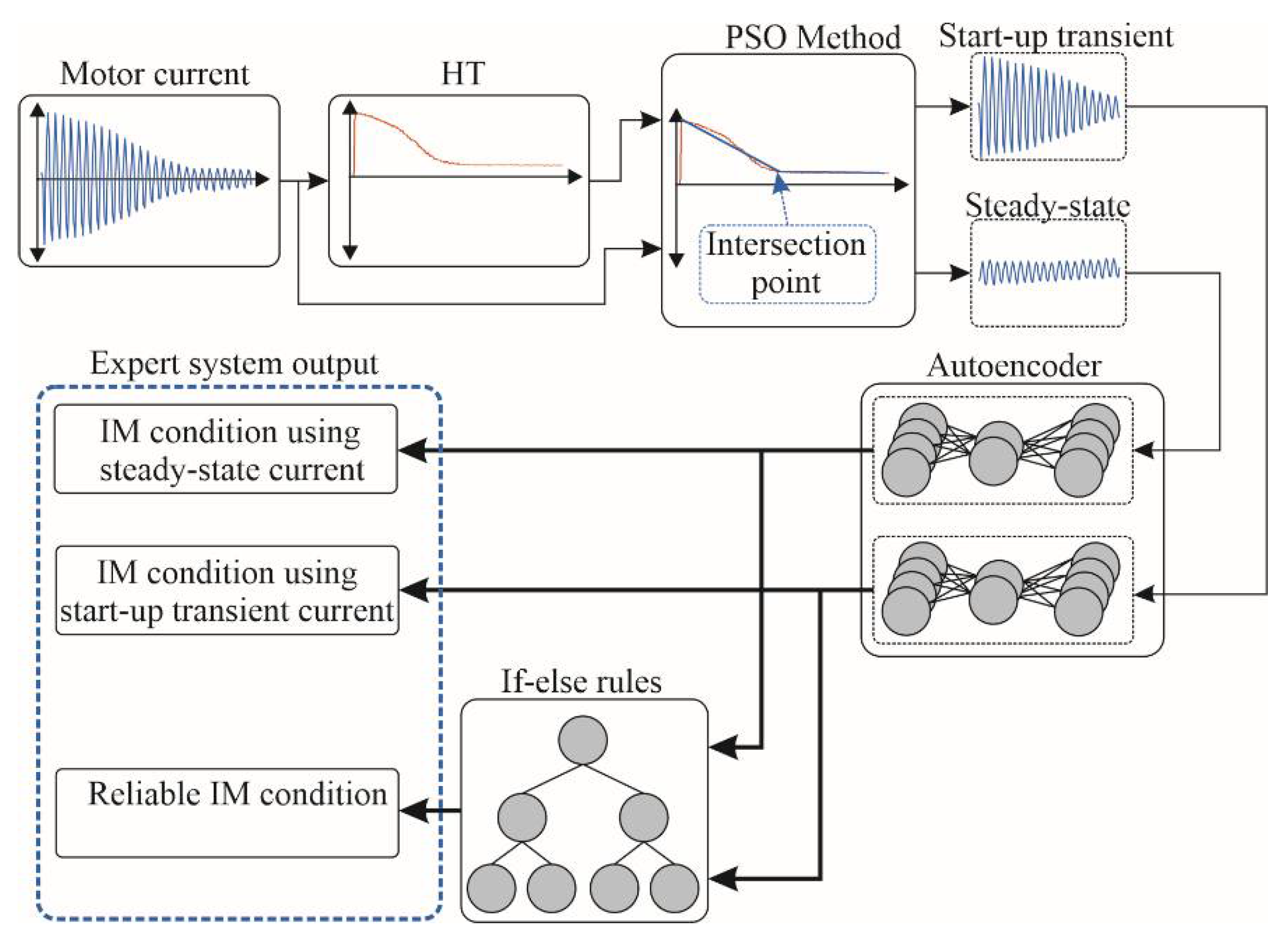
2. Proposed Methodology
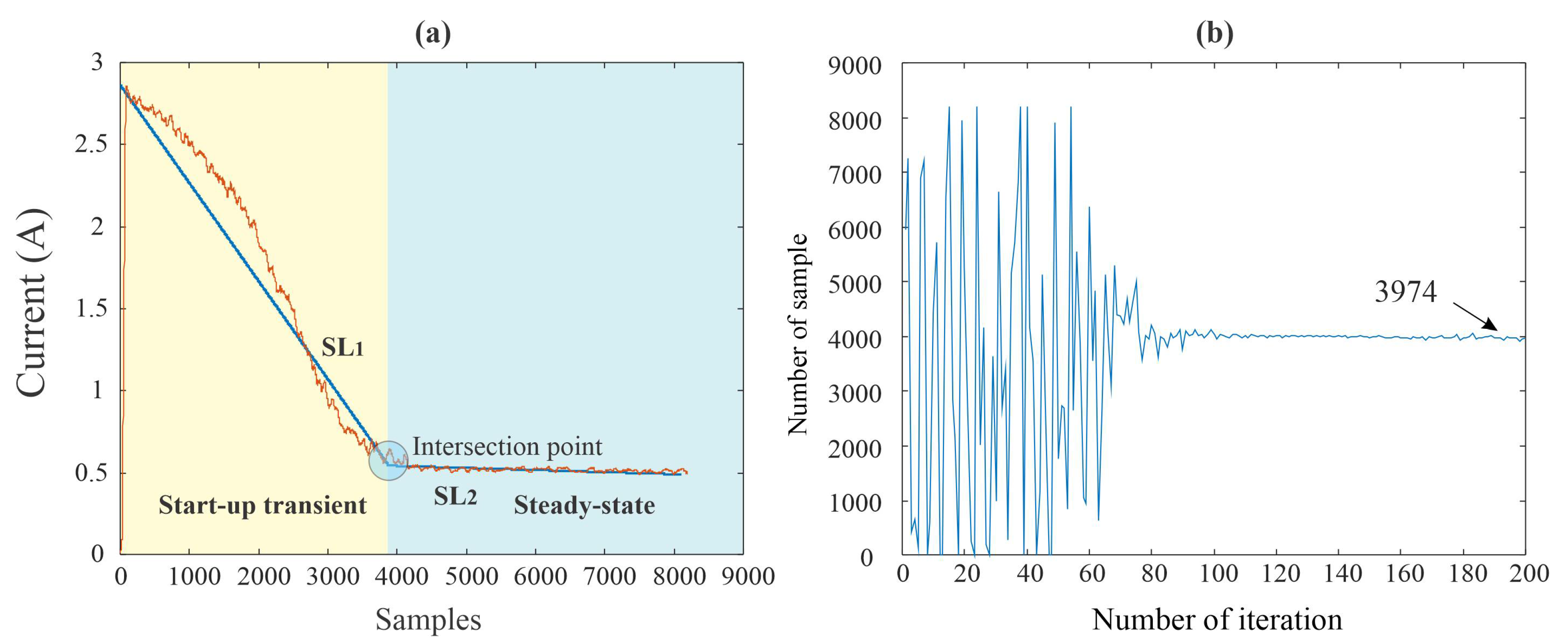
2.1. Hilbert Transform
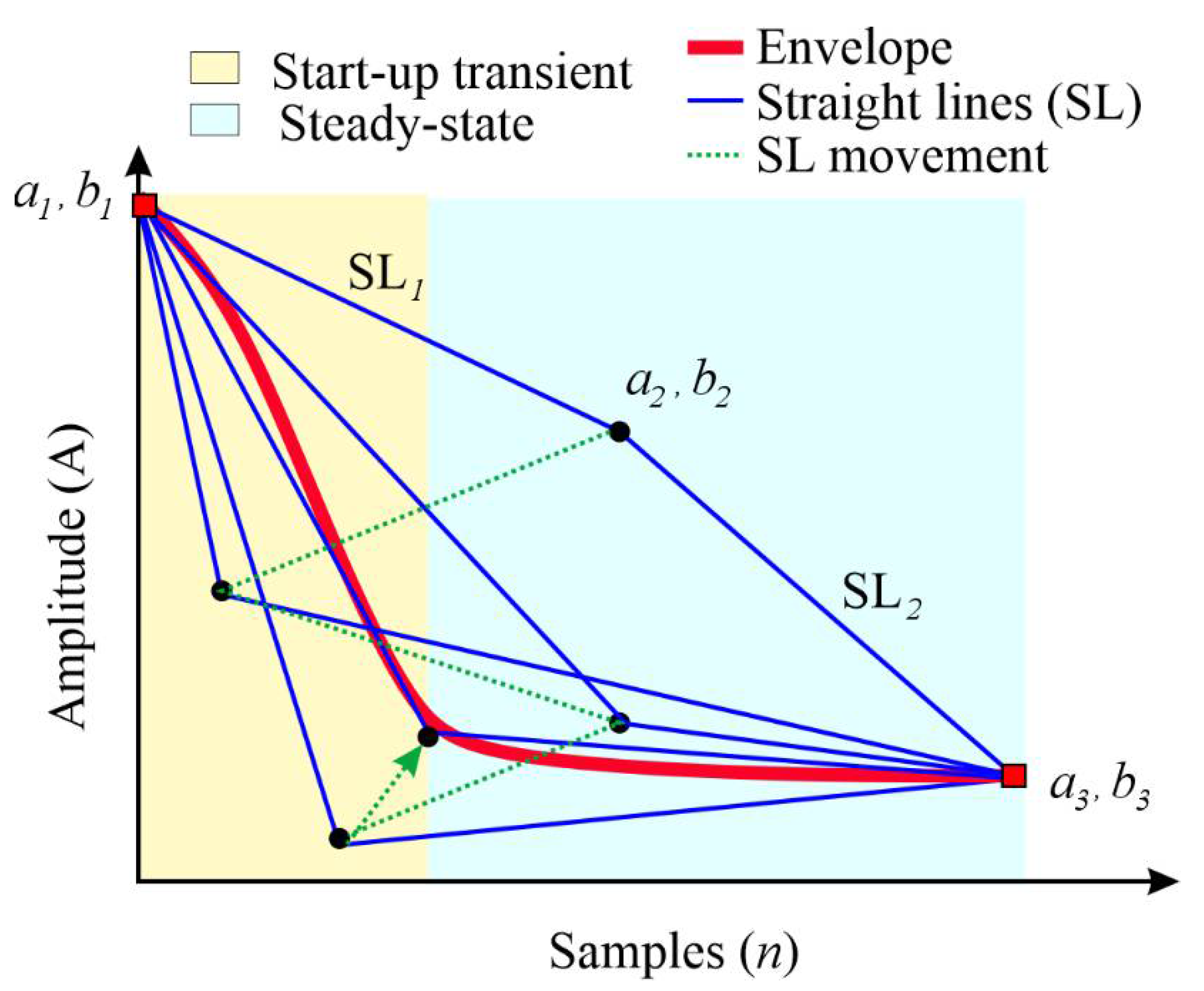
2.2. PSO
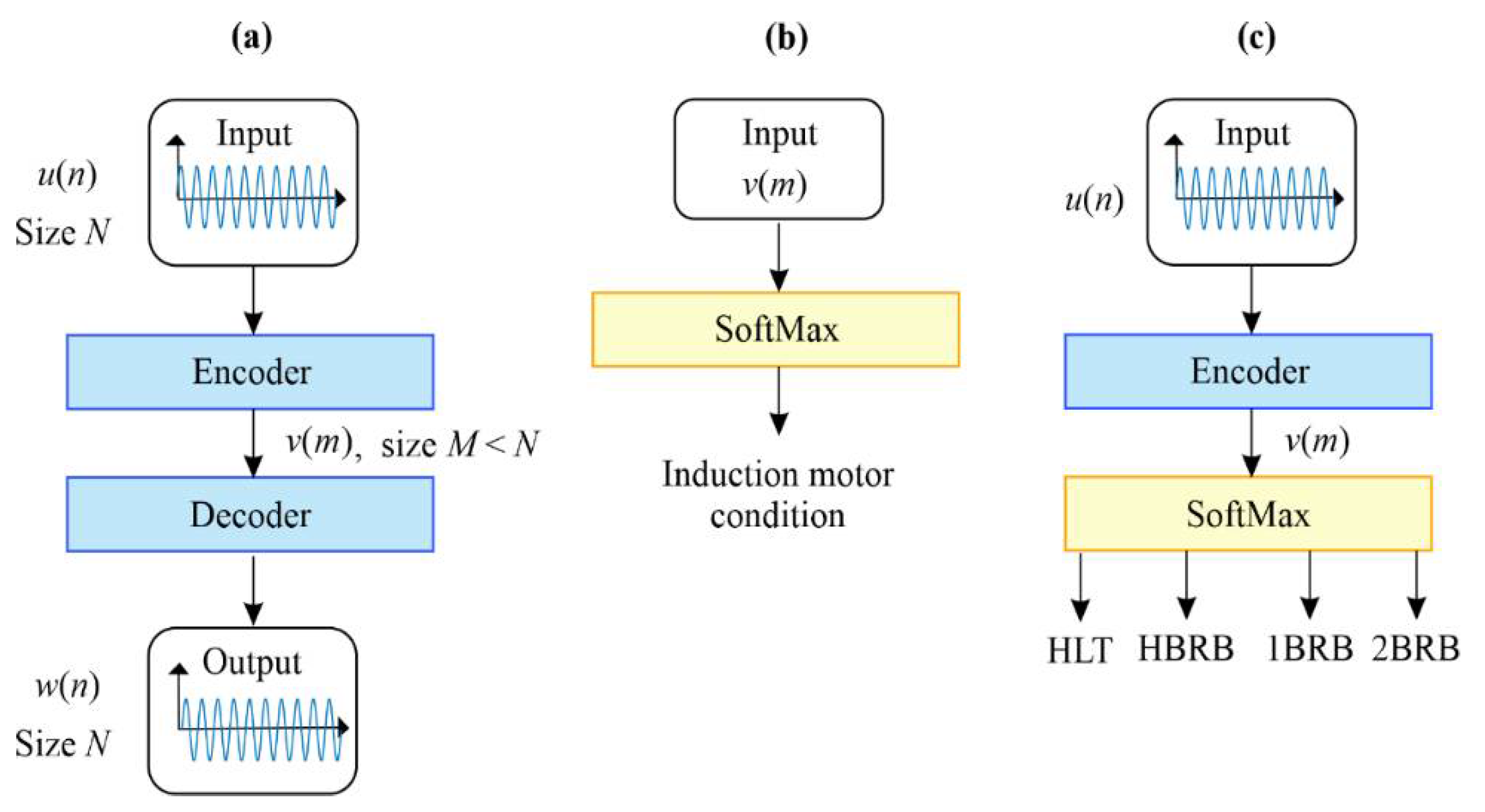
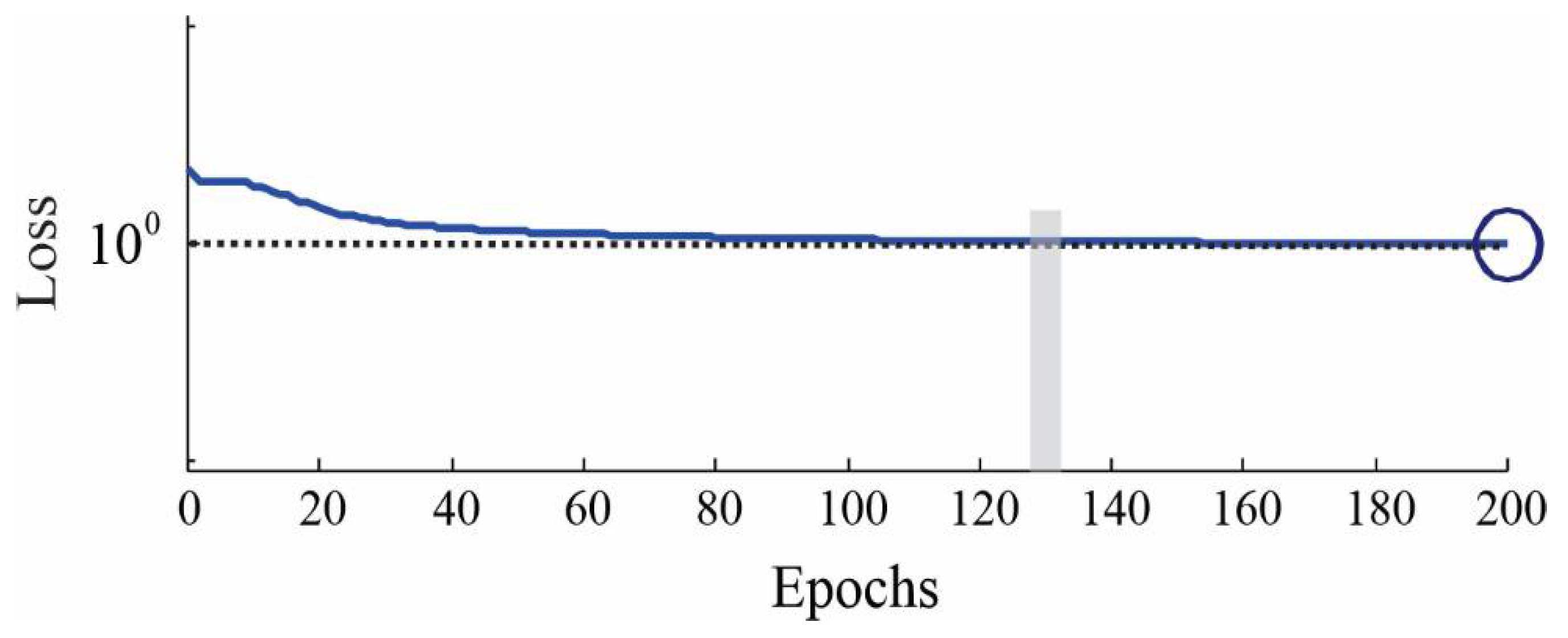
2.3. Autoencoder
2.4. Rules for Determining the IM Condition
- Rule 1. If both diagnoses are equal, the IM condition corresponds to any autoencoder output.
- Rule 2. If both diagnoses indicate a fault but with a different level of severity, the diagnosis is the presence of a fault, and it is recommended to repeat the analysis.
- Rule 3. If one diagnosis indicates a healthy IM condition and the other one indicates IM damage, the expert system indicates an unknown motor condition but recommends repeating the analysis in a more detailed way.
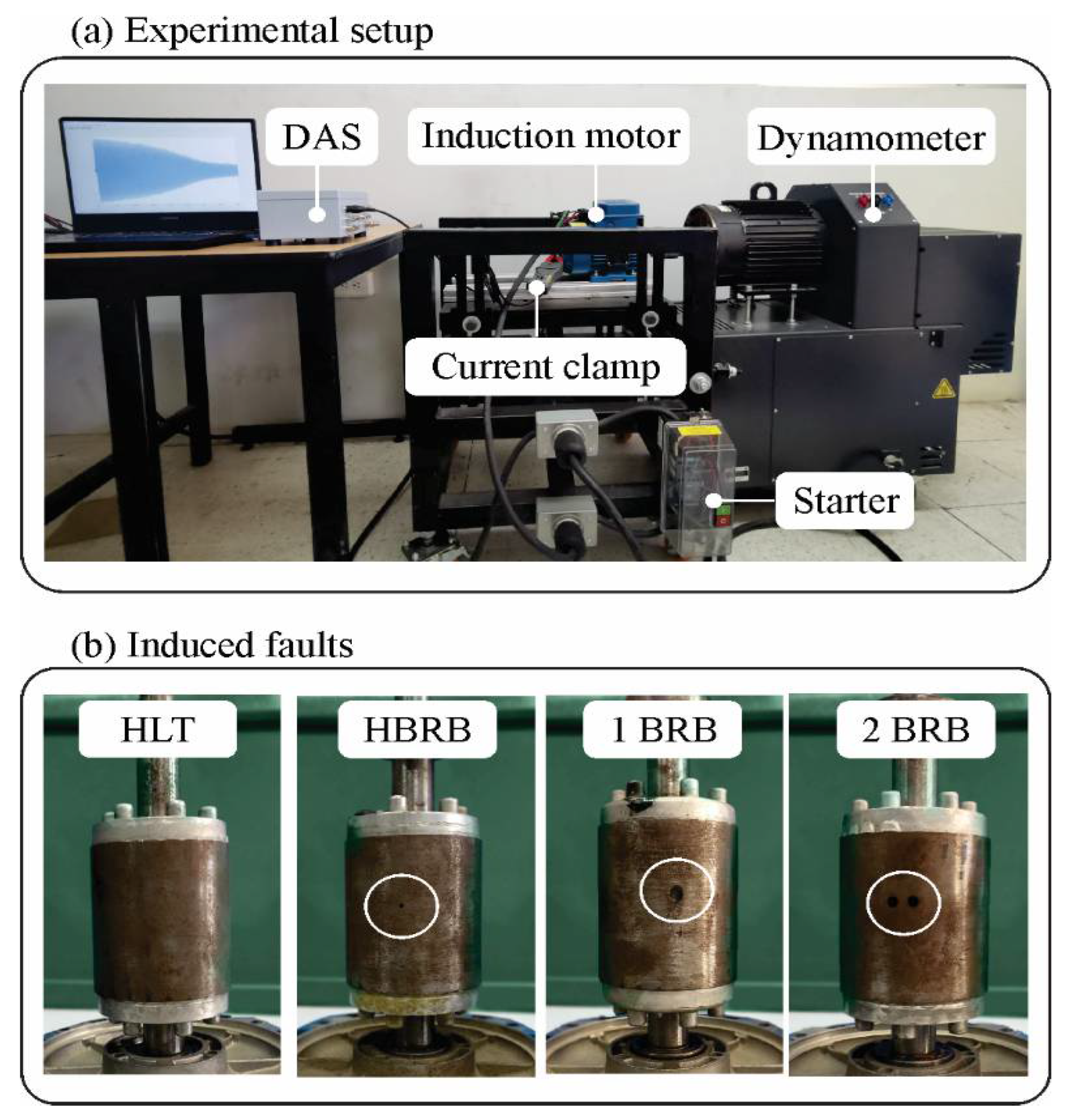
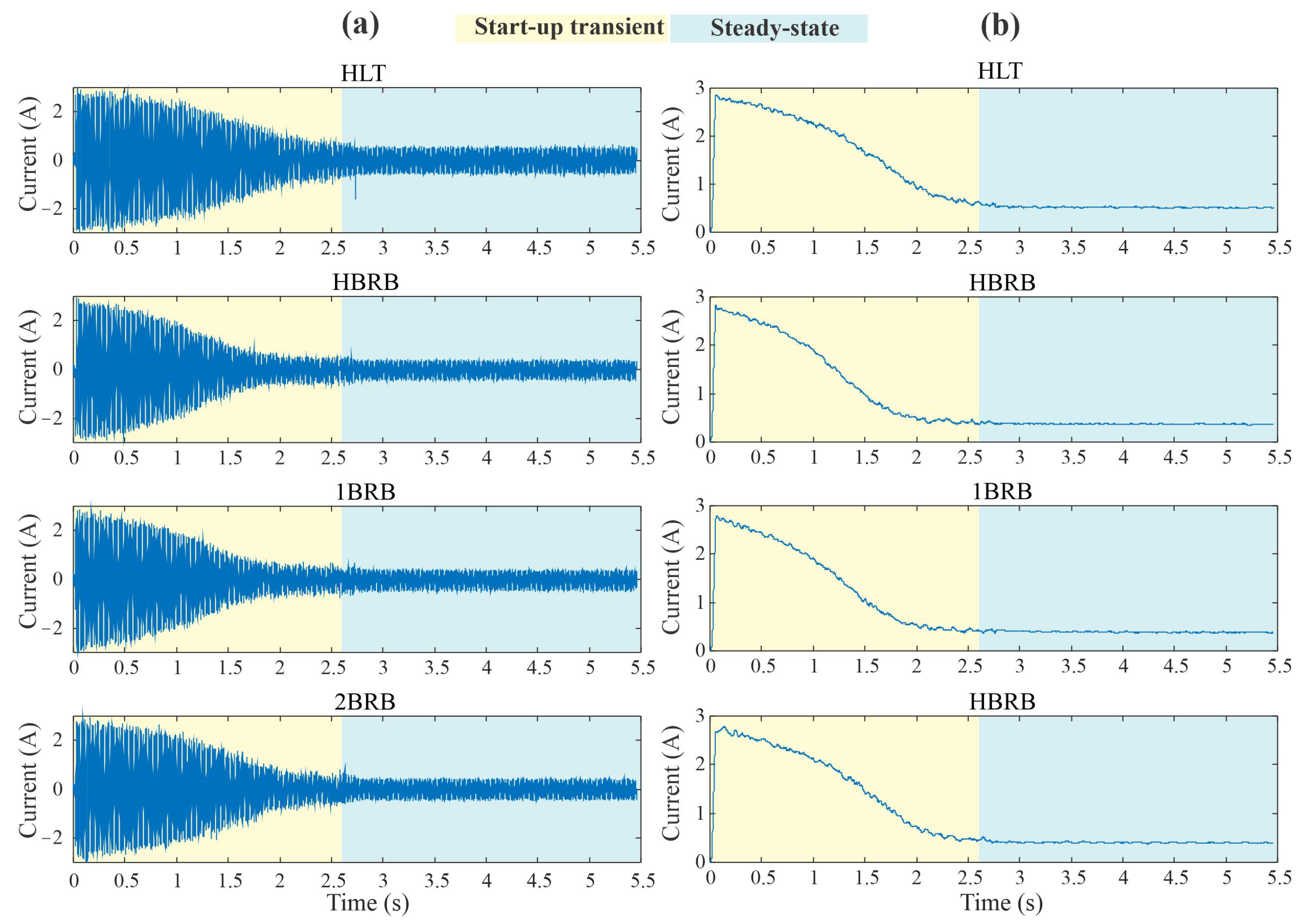
3. Experimental Setup
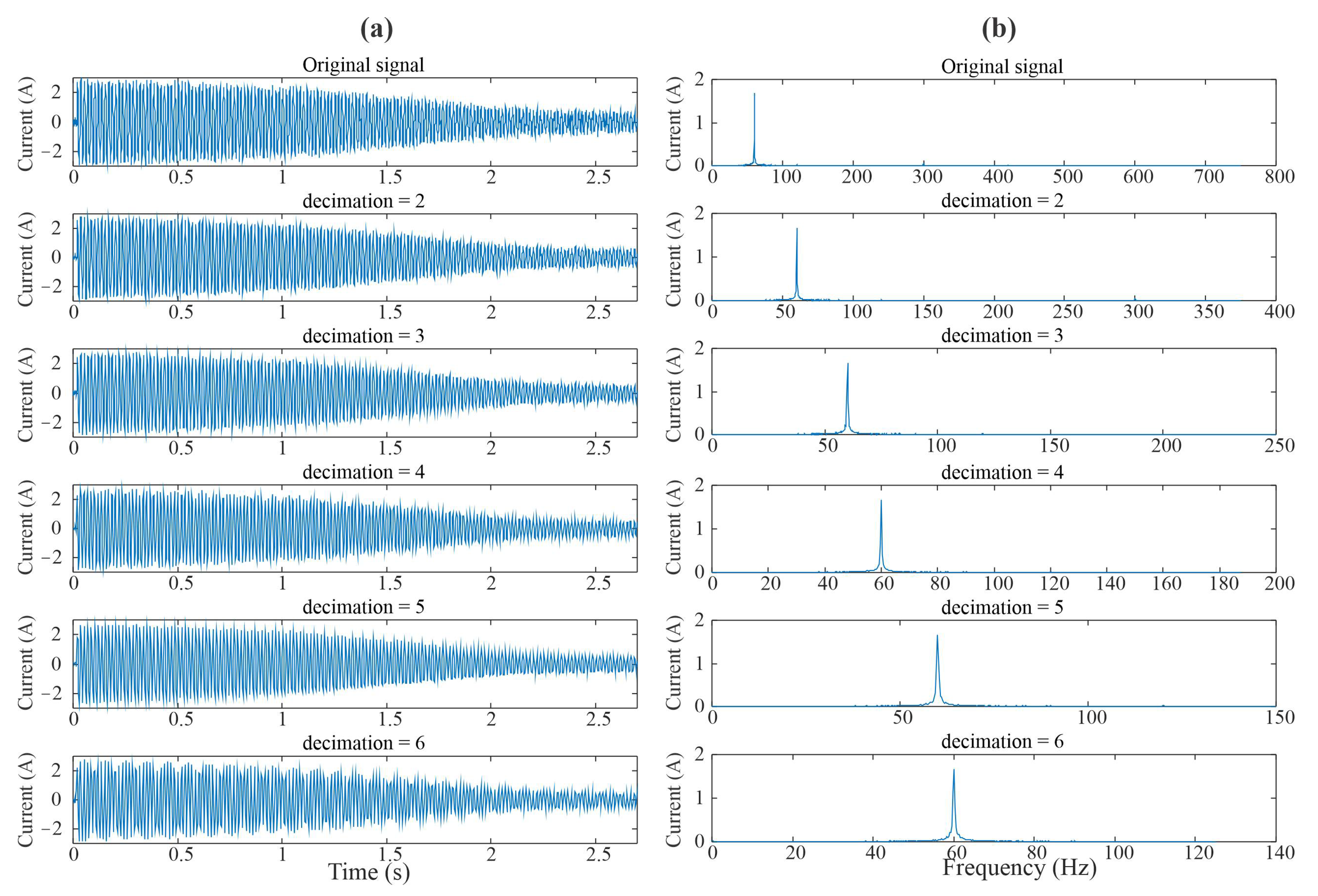
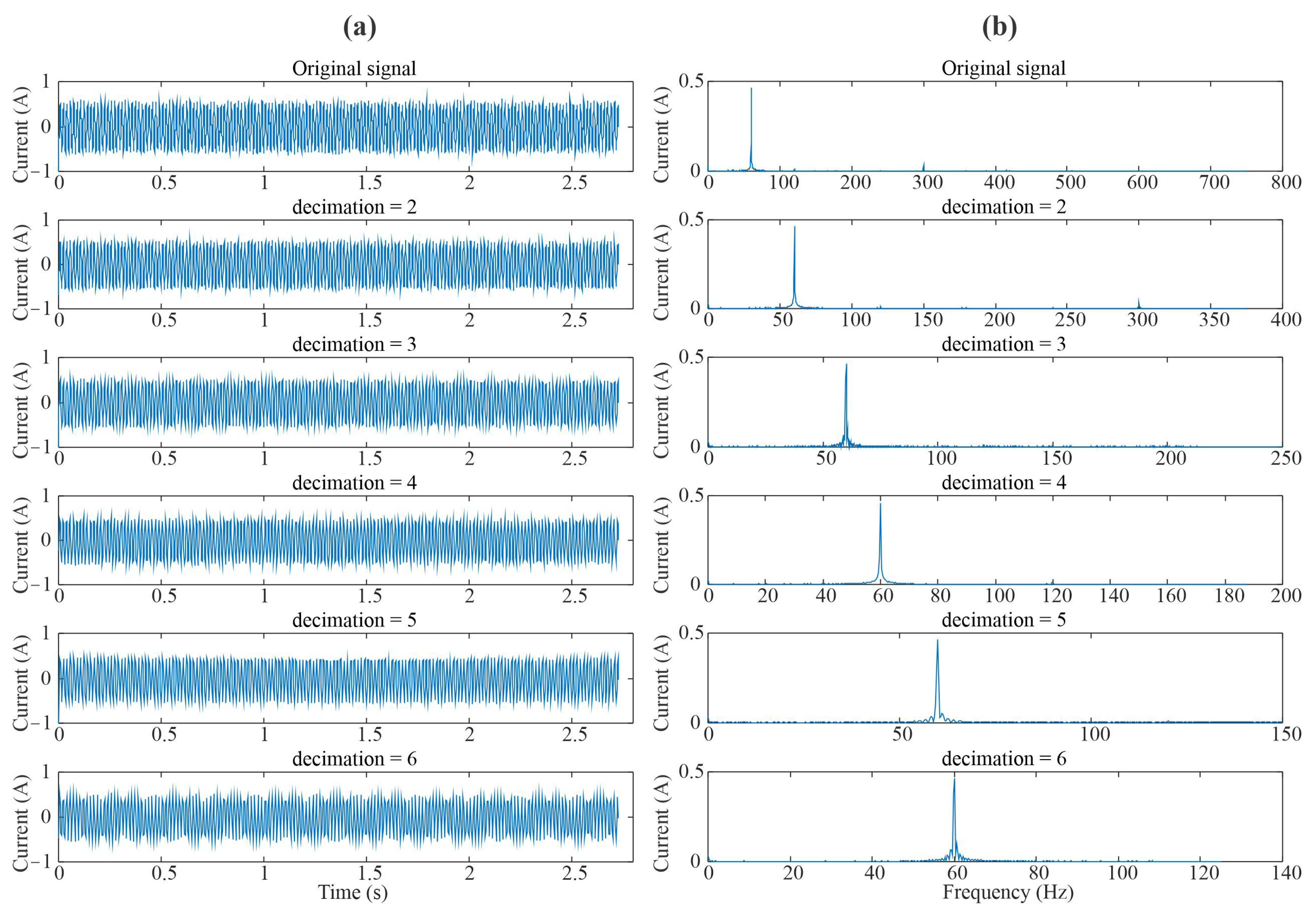
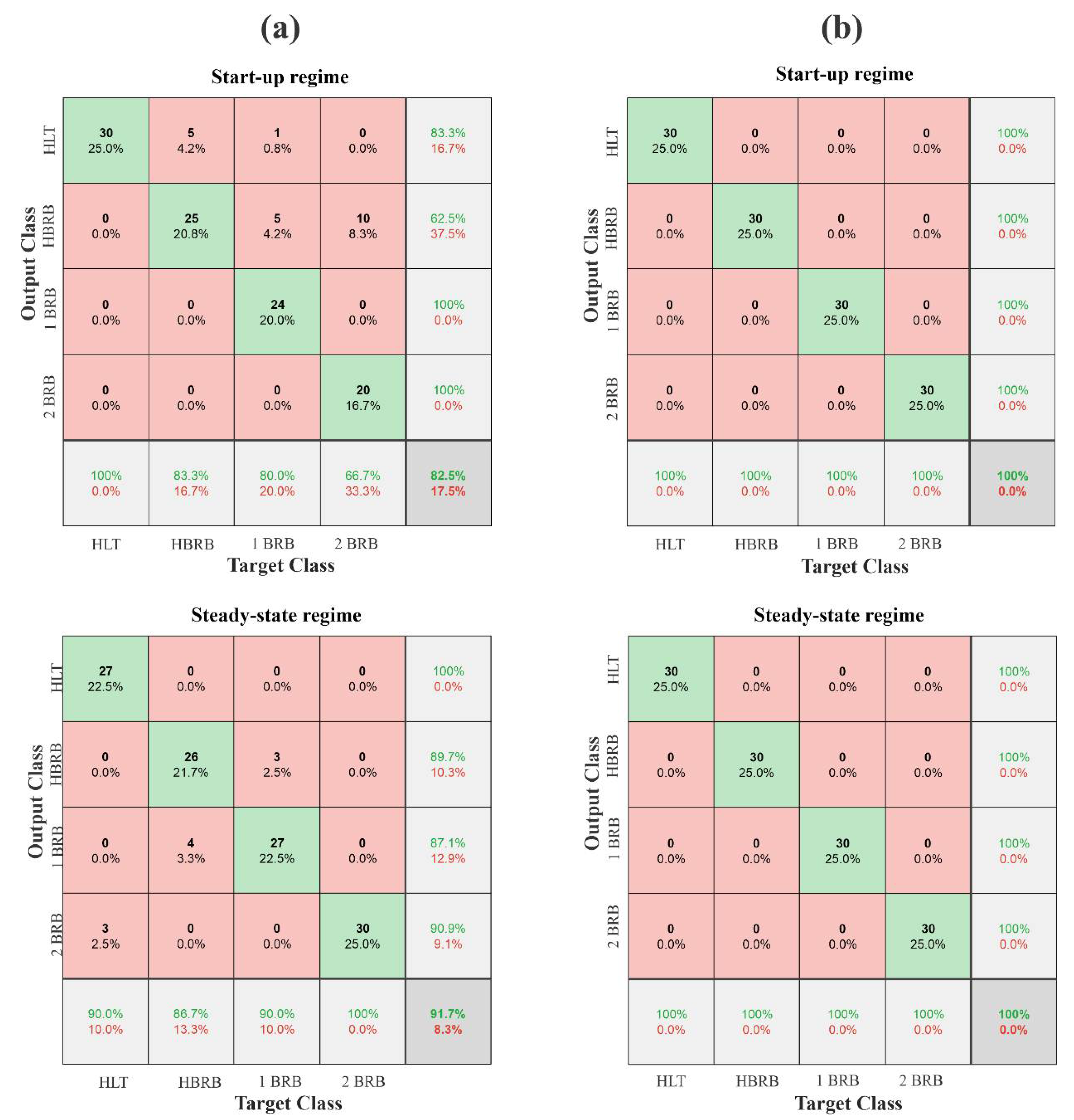
4. Results
Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abd-el-Malek, M.; Abdelsalam, A.K.; Hassan, O.E. Induction motor broken rotor bar fault location detection through envelope analysis of start-up current using Hilbert transform. Mech. Syst. Signal Proc. 2017, 93, 332–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Herrera, A.L.; Ferrucho-Alvarez, E.R.; Ledesma-Carrillo, L.M.; Mata-Chavez, R.I.; Lopez-Ramirez, M.; Cabal-Yepez, E. Multiple fault detection in induction motors through Homogeneity and Kurtosis computation. Energies 2022, 15, 1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drakaki, M.; Karnavas, Y.L.; Karlis, A.D.; Chasiotis, I.D.; Tzionas, P. Study on fault diagnosis of broken rotor bars in squirrel cage induction motors: A multiagent system approach using inteligente classifiers. IET Electr. Power Appl. 2020, 14, 245–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amezquita-Sanchez, J.P.; Valtierra-Rodriguez, M.; Perez-Ramirez, C.A.; Camarena-Martinez, D.; Garcia-Perez, A.; Romero-Troncoso, R.J. Fractal dimension and fuzzy logic systems for broken rotor bars detection in induction motors at start-up and steady-state. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2017, 28, 075001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahkola, M.; Szucs, A.; Halme, J.; Zeb, A.; Keranen, J. A Novel Machine Learning-Based Approach for Induction Machine Fault Classifier Development—A Broken Rotor Bar Case Study. Energies 2022, 15, 3317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera-Guillen, J.R.; De Santiago-Perez, J.J.; Amezquita-Sanchez, J.P.; Valtierra-Rodriguez, M.; Romero-Troncoso, R.J. Enhanced FFT-based method for incipient broken rotor bar detection in induction motors during the startup transient. Measurement 2018, 124, 277–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kafeel, A.; Aziz, S.; Awais, M.; Khan, M.A.; Afaq, K.; Idris, S.A.; Alshazly, H.; Mostafa, S.M. An expert system for rotating machine fault detection using vibration signal analysis. Sensors 2021, 21, 7587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seera, M.; Lim, C.P.; Nahavandi, S.; Loo, C.K. Condition monitoring of induction motors: A review and an application of an ensemble of hybrid intelligent models. Expert Syst. Appl. 2014, 41, 4891–4903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asad, B.; Vaimann, T.; Belahcen, A.; Kallaste, A.; Rassolkin, A.; Iqbal, M.N. Broken rotor bar fault detection of the grid and inverter-fed induction motor by effective attenuation of the fundamental component. IET Electr. Power Appl. 2019, 13, 2005–2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burriel-Valencia, J.; Puche-Panadero, R.; Martinez-Roman, J.; Sapena-Bano, A.; Pineda-Sanchez, M.; Perez-Cruz, J.; Riera-Guasp, M. Automatic fault diagnostic system for induction motors under transient regime optimized with expert systems. Electronics 2018, 8, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro-Navarro, A.; Zamudio-Ramirez, I.; Biot-Monterde, V.; Osornio-Rios, R.A.; Antonino-Daviu, J.A. Current and stray flux combined analysis for the automatic detection of rotor faults in soft-started induction motors. Energies 2022, 15, 2511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misra, S.; Kumar, S.; Sayyad, S.; Bongale, A.; Jadhav, P.; Kotecha, K.; Abraham, A.; Gabralla, L.A. Fault detection in induction motor using time domain and spectral imaging-based transfer learning approach on vibration data. Sensors 2022, 22, 8210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Yan, Y.; Hu, K.; Zhang, S.; Li, H.; Zhang, Z.; Shi, T. Fault diagnosis of rotor broken bar in induction motor based on successive variational mode decomposition. Energies 2022, 15, 1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atta, M.E.E.-D.; Ibrahim, D.K.; Gilany, M.A. Broken bar faults detection under induction motor starting conditions using the optimized Stockwell Transform and adaptive time-frequency filter. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2021, 70, 3518110. [Google Scholar]
- Lopez-Ramirez, M.; Ledesma-Carrillo, L.M.; Garcia-Guevara, F.M.; Munoz-Minjarez, J.; Cabal-Yepez, E.; Villalobos-Pina, F.J. Automatic early broken-rotor-bar detection and classification using otsu segmentation. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 112624–112632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales-Perez, C.; Rangel-Magdaleno, J.; Peregrina-Barreto, H.; Amezquita-Sanchez, J.P.; Valtierra-Rodriguez, M. Incipient broken rotor bar detection in induction motors using vibration signals and the orthogonal matching pursuit algorithm. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2018, 67, 2058–2068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Feng, G.; Zhen, D.; Gu, F.; Ball, A.D. A normalized frequency domain energy operator for broken rotor bar fault diagnosis. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2020, 70, 3500110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Cavero, V.; Pons-Llinares, J.; Duque-Perez, O.; Morinigo-Sotelo, D. Detection of broken rotor bars in nonlinear startups of inverter-fed induction motors. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2021, 57, 2559–2568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panagiotou, P.A.; Arvanitakis, I.; Lophitis, N.; Antonino-Daviu, J.A.; Gyftakis, K.N. A new approach for broken rotor bar detection in induction motors using frequency extraction in stray flux signals. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2019, 55, 3501–3511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrucho-Alvarez, E.R.; Martinez-Herrera, A.L.; Cabal-Yepez, E.; Rodriguez-Donate, C.; Lopez-Ramirez, M.; Mata-Chavez, R.I. Broken rotor bar detection in induction motors through contrast estimation. Sensors 2021, 21, 7446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messaoudi, M.; Flah, A.; Alotaibi, A.A.; Althobaiti, A.; Sbita, L.; El-Bayeh, C.Z. Diagnosis and fault detection of rotor bars in squirrel cage induction motors using combined Park’s vector and extended Park’s vector approaches. Electronics 2022, 11, 380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.-Y.; Wen, M.-S.; Zhuo, G.-L.; Le, T.-A. Application of ANN in induction-motor fault-detection system established with MRA and CFFS. Mathematics 2022, 10, 2250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guajardo, L.A.T.; Garza, M.A.P.; Maldonado, J.R.; Vazquez, M.A.G.; Alfaro, L.H.R.; Salinas, F.S. Prony method estimation for motor current signal analysis diagnostics in rotor cage induction motors. Energies 2022, 15, 3513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feldman, M. Hilbert transform in vibration analysis. Mech. Syst. Signal Proc. 2011, 25, 735–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amezquita-Sanchez, J.P.; Park, H.S.; Adeli, H. A novel methodology for modal parameters identification of large smart structures using MUSIC, empirical wavelet transform, and Hilbert transform. Eng. Struct. 2017, 147, 148–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mezura-Montes, E.; Coello, C.A.C. Constraint-handling in nature-inspired numerical optimization: Past, present and future. Swarm Evol. Comput. 2011, 1, 173–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marini, F.; Walczak, B. Particle swarm optimization (PSO). A tutorial. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2015, 149, 153–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.Y.; Cheng, Y.H. Motor fault detection using wavelet transform and improved PSO-BP neural network. Processes 2020, 8, 1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, B.; Xiong, W.; Wu, J.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, L.; Tao, D. Stacked convolutional denoising auto-encoders for feature representation. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2016, 47, 1017–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Zheng, P.; Chen, Z. Deep learning with stacked denoising auto-encoder for short-term electric load forecasting. Energies 2019, 12, 2445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwala, A.; Pennington, J.; Dauphin, Y.; Schoenholz, S. Temperature check: Theory and practice for training models with softmax-cross-entropy losses. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2010.07344. [Google Scholar]
- Romero-Troncoso, R.J.; Garcia-Perez, A.; Morinigo-Sotelo, D.; Duque-Perez, O.; Osornio-Rios, R.A.; Ibarra-Manzano, M.A. Rotor unbalance and broken rotor bar detection in inverter-fed induction motors at start-up and steady-state regimes by high-resolution spectral analysis. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2016, 133, 142–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Work | Method | Analyzed Regime | Detected Fault | Accuracy Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Burriel-Valencia et al. [10] |
| Start-up and Steady-state regimes | 1 BRB | 98.89 |
| Morales-Perez et al. [16] |
| Steady-state regime | HBRB and 1BRB | 90 |
| Abd-el-Malek et al. [1] |
| Start-up regime | HBRB and 1BRB | 99 |
| Navarro-Navarro et al. [11] |
| Start-up regime | 1 and 2 BRB | 94.4 |
| Rivera-Guillen et al. [6] |
| Start-up regime | HBRB, 1BRB, and 2BRB | 97.5 |
| Martinez-Herrera et al. [2] |
| Start-up regime | 1BRB and 2BRB | 100 |
| Proposed work |
| Start-up and steady-state regimes | HBRB, 1BRB, and 2BRB | 100 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Valtierra-Rodriguez, M.; Rivera-Guillen, J.R.; De Santiago-Perez, J.J.; Perez-Soto, G.I.; Amezquita-Sanchez, J.P. Expert System Based on Autoencoders for Detection of Broken Rotor Bars in Induction Motors Employing Start-Up and Steady-State Regimes. Machines 2023, 11, 156. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines11020156
Valtierra-Rodriguez M, Rivera-Guillen JR, De Santiago-Perez JJ, Perez-Soto GI, Amezquita-Sanchez JP. Expert System Based on Autoencoders for Detection of Broken Rotor Bars in Induction Motors Employing Start-Up and Steady-State Regimes. Machines. 2023; 11(2):156. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines11020156
Chicago/Turabian StyleValtierra-Rodriguez, Martin, Jesus Rooney Rivera-Guillen, J. Jesus De Santiago-Perez, Gerardo Israel Perez-Soto, and Juan Pablo Amezquita-Sanchez. 2023. "Expert System Based on Autoencoders for Detection of Broken Rotor Bars in Induction Motors Employing Start-Up and Steady-State Regimes" Machines 11, no. 2: 156. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines11020156
APA StyleValtierra-Rodriguez, M., Rivera-Guillen, J. R., De Santiago-Perez, J. J., Perez-Soto, G. I., & Amezquita-Sanchez, J. P. (2023). Expert System Based on Autoencoders for Detection of Broken Rotor Bars in Induction Motors Employing Start-Up and Steady-State Regimes. Machines, 11(2), 156. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines11020156










