Data Acquisition Network Configuration and Real-Time Energy Consumption Characteristic Analysis in Intelligent Workshops for Social Manufacturing
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
2.1. Data Acquisition and Analysis of IM Workshops
2.2. Energy Consumption Data Processing and Evaluation
3. Energy-Conservation Production Architecture and Data Acquisition Network Configuration
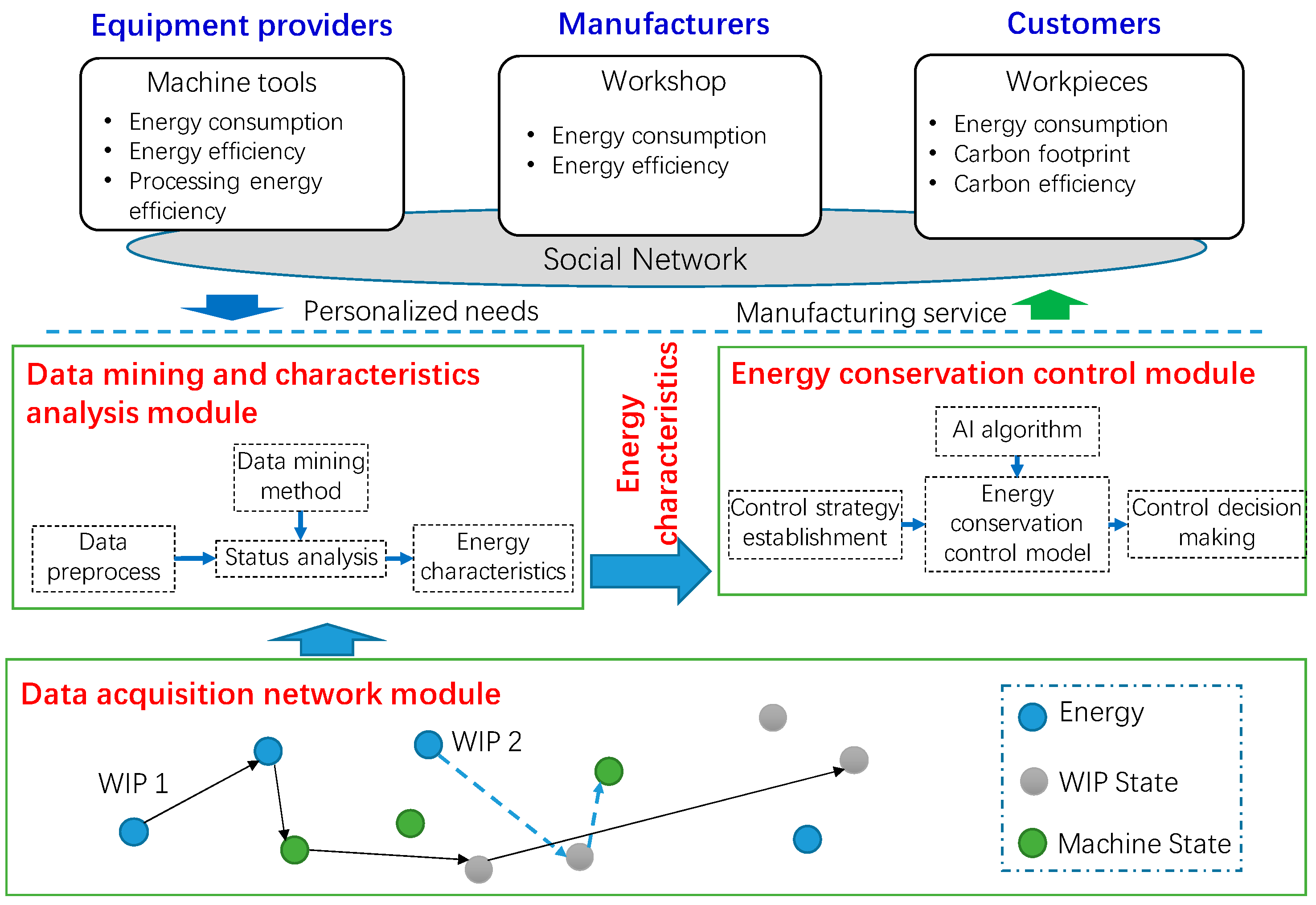
3.1. Energy-Conservation Production Architecture for IM Processes
3.1.1. Data Acquisition Network Module
3.1.2. Energy Characteristic Analysis and Energy-Conservation Control Module
3.1.3. Energy Consumption Service Module
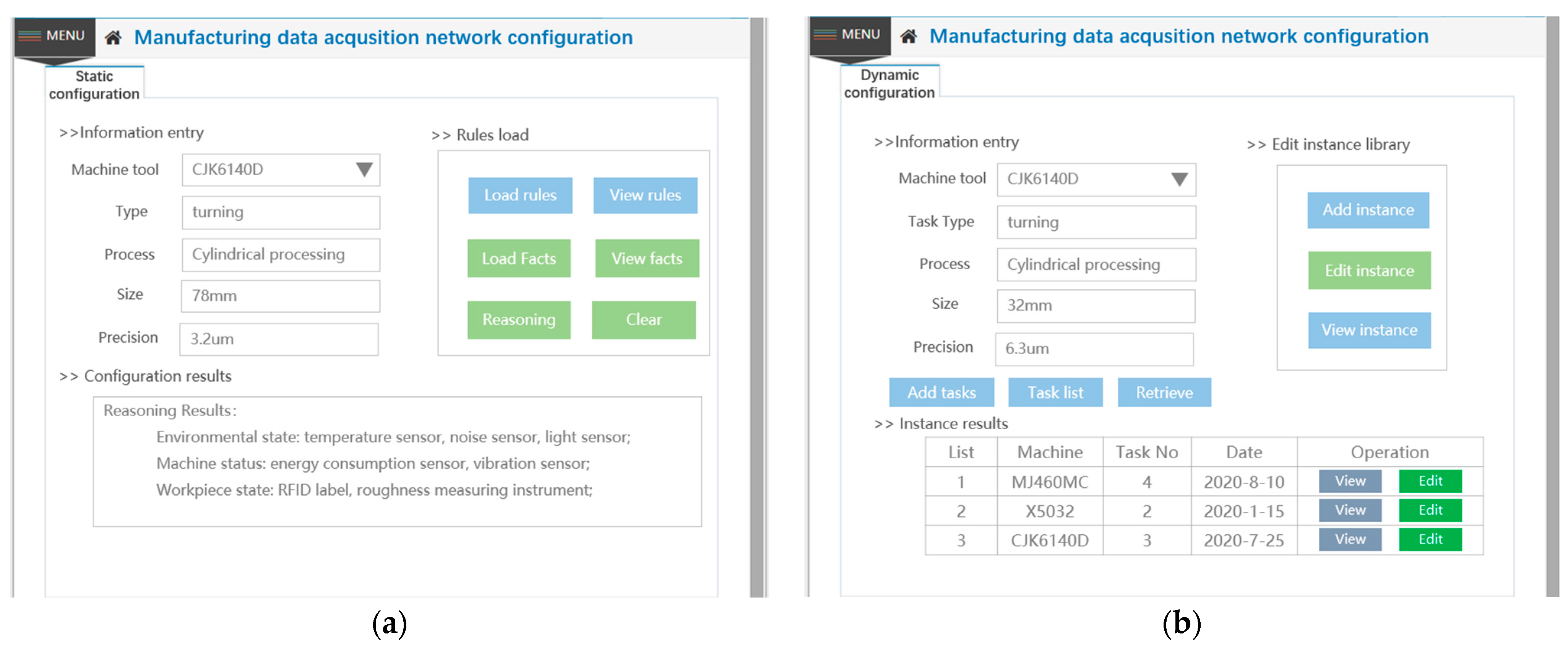
3.2. Configuration of Manufacturing Data Acquisition Network
3.2.1. The Static Sensor Network Configuration
3.2.2. Dynamic Network Construction for a Certain Production Task
4. Energy Consumption Characteristic Analysis Based on Process Time Window
4.1. Data Modeling of Discrete Manufacturing Processes
4.2. Energy Consumption Data-Partition Method Based on Process Time Window
| Algorithm 1: Energy Data Partition Method |
| Input: the power of air cutting |
| Output: the time window node of each steps and |
| Algorithm flow: |
| 1. According to process planning, obtain the starting time and ending time |
| 2. For each process |
| 3. For each energy data of this process |
| 4. The starting time of the first step is , obtain the mean value |
| 5. If |
| 6. The step is in cutting state, and obtain the mean power value |
| 7. Else |
| 8. Obtain the time point |
| 9. End if |
| 10. If |
| 11. This is the next step, and the above is the starting time of the next step |
| 12. End if |
| 13. End For |
| 14. End For |
| 15. Return and |
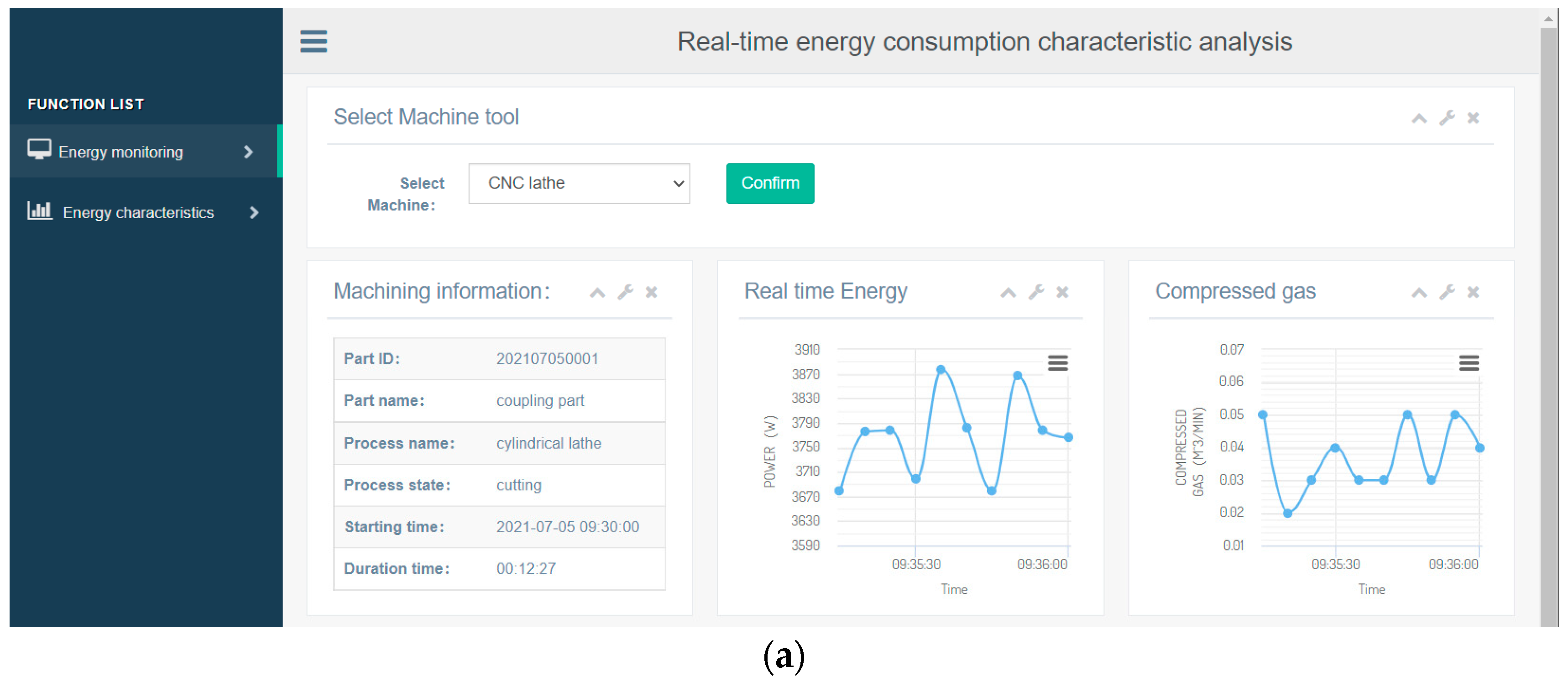
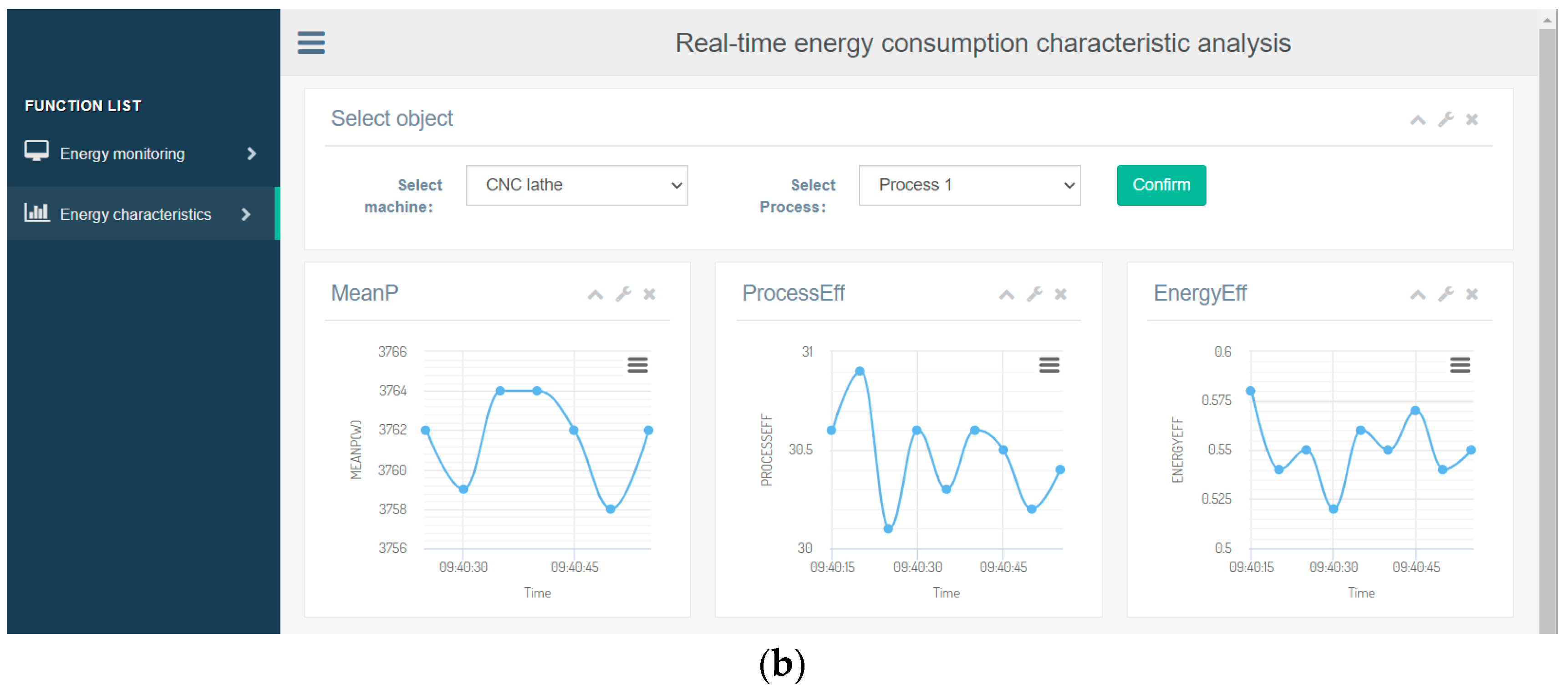
4.3. Real-Time Energy Consumption Characteristic Analysis
5. Case Study
5.1. Case Description
5.2. Energy Consumption Monitoring and Characteristic Analysis
6. Conclusions and Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tian, G.; Liu, Y. Energy-Efficient Models of Sustainable Location for a Vehicle Inspection Station With Emission Constraints. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. 2015, 12, 238–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Liang, Y.; Li, W.; Cai, X. Big Data enabled Intelligent Immune System for energy efficient manufacturing management. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 195, 507–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, G.; Ren, Y.; Feng, Y.; Zhou, M.; Zhang, H.; Tan, J. Modeling and Planning for Dual-Objective Selective Disassembly Using and/or Graph and Discrete Artificial Bee Colony. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2019, 15, 2456–2468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.Y.; Li, W.D.; Jiang, P.Y.; Gu, P.H. Experimental Investigation and Multi-objective Optimization Approach for Low-Carbon Milling Operation of Aluminum. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part C J. Mech. Eng. Sci. 2017, 231, 2753–2772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frigerio, N.; Matta, A. Energy-Efficient Control Strategies for Machine Tools With Stochastic Arrivals. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. 2015, 12, 50–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Newman, S.; Nassehi, A.; Imani-Asrai, R.; Dhokia, V. Energy efficient process planning for CNC machining. CIRP J. Manuf. Sci. Technol. 2012, 5, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, C.; Gu, P.; Jiang, P. Low-carbon scheduling and estimating for a flexible job shop based on carbon footprint and carbon efficiency of multi-job processing. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part B J. Eng. Manuf. 2015, 229, 328–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, P.; Leng, J.; Ding, K. Social manufacturing: A survey of the state-of-the-art and future challenges. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on Service Operations and Logistics, and Informatics (SOLI), Beijing, China, 10–12 July 2016; pp. 12–17. [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, G.; Wang, F.-Y.; Nyberg, T.R.; Shang, X.; Zhou, M.; Shen, Z.; Li, S.; Guo, C. From mind to products: Towards social manufacturing and service. IEEE/CAA J. Autom. Sin. 2018, 5, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, P.; Leng, J.; Ding, K.; Gu, P.; Koren, Y. Social manufacturing as a sustainable paradigm for mass individualization. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part B: J. Eng. Manuf. 2016, 230, 1961–1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, G.; Tamir, T.S.; Shen, Z.; Shang, X.; Wu, H.; Wang, F.-Y. A Survey on Social Manufacturing: A Paradigm Shift for Smart Prosumers. IEEE Trans. Comput. Soc. Syst. 2022, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, K.; Zhang, Y.; Chan, F.T.; Zhang, C.; Lv, J.; Liu, Q.; Leng, J.; Fu, H. A cyber-physical production monitoring service system for energy-aware collaborative production monitoring in a smart shop floor. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 297, 126599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zheng, P.; Lv, Y.; Bao, J.; Zhang, J. Fog-IBDIS: Industrial Big Data Integration and Sharing with Fog Computing for Manufacturing Systems. Engineering 2019, 5, 662–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carletti, M.; Masiero, C.; Beghi, A.; Susto, G.A. A deep learning approach for anomaly detection with industrial time series data: A refrigerators manufacturing case study. Procedia Manuf. 2019, 38, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouzon, G.C.; Yildirim, M.B.; Twomey, J.M. Operational methods for minimization of energy consumption of manufacturing equipment. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2007, 45, 4247–4271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mashaei, M.; Lennartson, B. Energy Reduction in a Pallet-Constrained Flow Shop Through On–Off Control of Idle Machines. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. 2013, 10, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamalainen, M.; Mohajeri, B.; Nyberg, T. Removing barriers to sustainability research on personal fabrication and social manufacturing. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 180, 666–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egger, J.; Masood, T. Augmented reality in support of intelligent manufacturing—A systematic literature review. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2020, 140, 106195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Li, H.; Feng, Y.; Tian, G. Big Data Analytics for System Stability Evaluation Strategy in the Energy Internet. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2017, 13, 1969–1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.; Tian, Y.; Yu, Y. A Real-Time Big Data Gathering Algorithm Based on Indoor Wireless Sensor Networks for Risk Analysis of Industrial Operations. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2016, 12, 1232–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Ardakani, H.D.; Yang, S.; Bagheri, B. Industrial Big Data Analytics and Cyber-physical Systems for Future Maintenance & Service Innovation. Procedia CIRP 2015, 38, 3–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, R.Y.; Xu, C.; Chen, C.; Huang, G.Q. Big Data Analytics for Physical Internet-based intelligent manufacturing shop floors. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2017, 55, 2610–2621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, W.; Wang, L. Big data analytics based fault prediction for shop floor scheduling. J. Manuf. Syst. 2017, 43, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, S.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Sakao, T.; Huisingh, D.; Almeida, C.M.V.B. A comprehensive review of big data analytics throughout product lifecycle to support sustainable smart manufacturing: A framework, challenges and future research directions. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 210, 1343–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kuo, Y.-H.; Kusiak, A. From data to big data in production research: The past and future trends. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2018, 57, 4828–4853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ghahramani, M.; Qiao, Y.; Zhou, M.C.; O’Hagan, A.; Sweeney, J. AI-based modeling and data-driven evaluation for smart manufacturing processes. IEEE/CAA J. Autom. Sin. 2020, 7, 1026–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, A.; Karimoddini, A.; Karimadini, M. Resilient fault diagnosis under imperfect observations—A need for Industry 4.0 era. IEEE/CAA J. Autom. Sin. 2020, 7, 1279–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, K.; Jiang, P. RFID-based production data analysis in an IoT-enabled smart job-shop. IEEE/CAA J. Autom. Sin. 2018, 5, 128–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.; Li, X.; Wu, D.; Ban, X.; Wu, N.-Q.; Dai, H.-N.; Wang, H. Continuous-Time Prediction of Industrial Paste Thickener System With Differential ODE-Net. IEEE/CAA J. Autom. Sin. 2022, 9, 686–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, Y.; Tao, F.; Nee, A. An Internet of things and cloud-based approach for energy consumption evaluation and analysis for a product. Int. J. Comput. Integr. Manuf. 2018, 31, 337–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, S.; Tang, R.; Lv, J.; Yuan, Q.; Peng, T. Energy consumption modeling of machining transient states based on finite state machine. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2017, 88, 2305–2320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, W.; Liu, F.; Xie, J.; Liu, P.; Tuo, J. A tool for assessing the energy demand and efficiency of machining systems: Energy benchmarking. Energy 2017, 138, 332–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finkbeiner, M.; Schau, E.M.; Lehmann, A.; Traverso, M. Towards Life Cycle Sustainability Assessment. Sustainability 2010, 2, 3309–3322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saxena, P.; Stavropoulos, P.; Kechagias, J.; Salonitis, K. Sustainability Assessment for Manufacturing Operations. Energies 2020, 13, 2730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swarnakar, V.; Singh, A.R.; Antony, J.; Jayaraman, R.; Tiwari, A.K.; Rathi, R.; Cudney, E. Prioritizing Indicators for Sustainability Assessment in Manufacturing Process: An Integrated Approach. Sustainability 2022, 14, 3264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Yang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, J. IoT-enabled real-time energy efficiency optimisation method for energy-intensive manufacturing enterprises. Int. J. Comput. Integr. Manuf. 2018, 31, 362–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Li, C.; Tang, Y.; Xiao, Q. An Internet of Things based energy efficiency monitoring and management system for machining workshop. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 199, 957–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Q.; Li, C.; Tang, Y.; Chen, X. Energy Efficiency Modeling for Configuration-Dependent Machining via Machine Learning: A Comparative Study. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. 2020, 18, 717–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Ji, W. Big Data Analysis Approach for Real-Time Carbon Efficiency Evaluation of Discrete Manufacturing Workshops. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 107730–107743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Zhang, Y.; Lv, J.; Yang, H.; Wu, J. Energy-cyber-physical system enabled management for energy-intensive manufacturing industries. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 226, 892–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Tian, G.; Fathollahi-Fard, A.M.; Ahmadi, A.; Zhang, C. Stochastic multi-objective modelling and optimization of an energy-conscious distributed permutation flow shop scheduling problem with the total tardiness constraint. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 226, 515–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.; Zhou, M.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, X.; Qi, L.; Wang, Y. Hybrid Scatter Search Algorithm for Optimal and Energy-Efficient Steelmaking-Continuous Casting. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. 2020, 17, 1814–1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Xing, K.; Zhou, M.; Wang, X.; Wu, Y. Modified Dynamic Programming Algorithm for Optimization of Total Energy Consumption in Flexible Manufacturing Systems. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. 2019, 16, 691–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenny, L.D.C.; Ocampo-Martinez, C. Energy efficiency in discrete-manufacturing systems: Insights, trends, and control strategies. J. Manuf. Syst. 2019, 52, 131–145. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Jiang, P.; Cheng, K.; Xu, X.W.; Ma, Y. Configuration Design of the Add-on Cyber-physical System with CNC Machine Tools and its Application Perspectives. Procedia CIRP 2016, 56, 360–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ren, L.; Wei, Y.; Cui, J.; Du, Y. A sliding window-based multi-stage clustering and probabilistic forecasting approach for large multivariate time series data. J. Stat. Comput. Simul. 2017, 87, 2494–2508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Jiang, P. Sustainability Evaluation of Process Planning for Single CNC Machine Tool under the Consideration of Energy-Efficient Control Strategies Using Random Forests. Sustainability 2019, 11, 3060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, W.; Tian, G.; Chen, M.; Tao, F.; Zhang, C.; Ai-Ahmari, A.; Li, Z.; Jiang, Z. Dual-objective program and improved artificial bee colony for the optimization of energy-conscious milling parameters subject to multiple constraints. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 245, 118714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Wang, Z.; Ding, K.; Chan, F.T.; Ji, W. An energy-aware cyber physical system for energy Big data analysis and recessive production anomalies detection in discrete manufacturing workshops. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2020, 58, 7059–7077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabassian, M.; Verbeke, R.; Tourwe, T.; Tsiporkova, E. Data-Driven Divide-and-Conquer for Estimating Build Times of 3D Objects. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Conference on Data Mining Workshops (ICDMW), Auckland, New Zealand, 7–10 December 2021; pp. 268–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


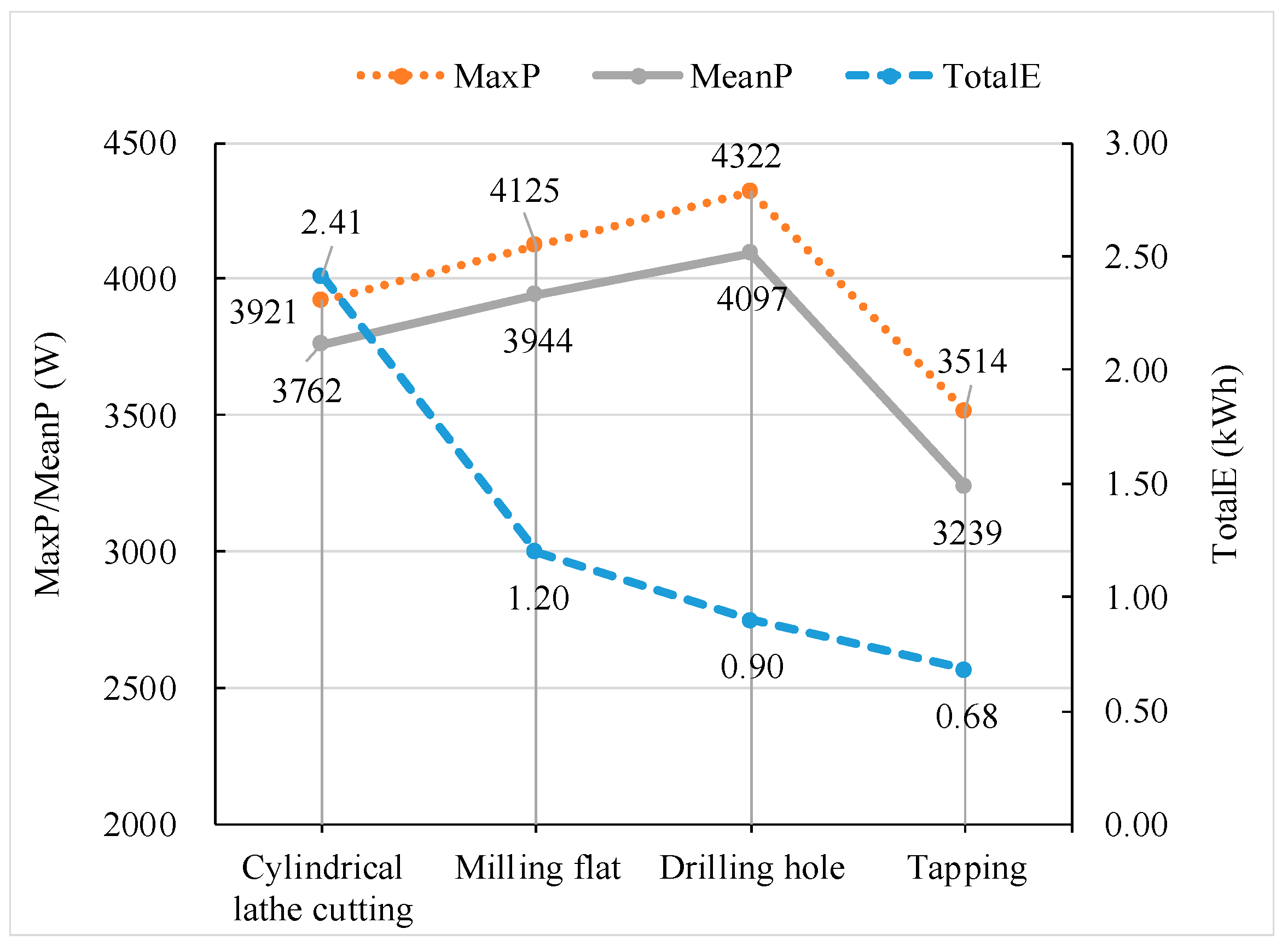
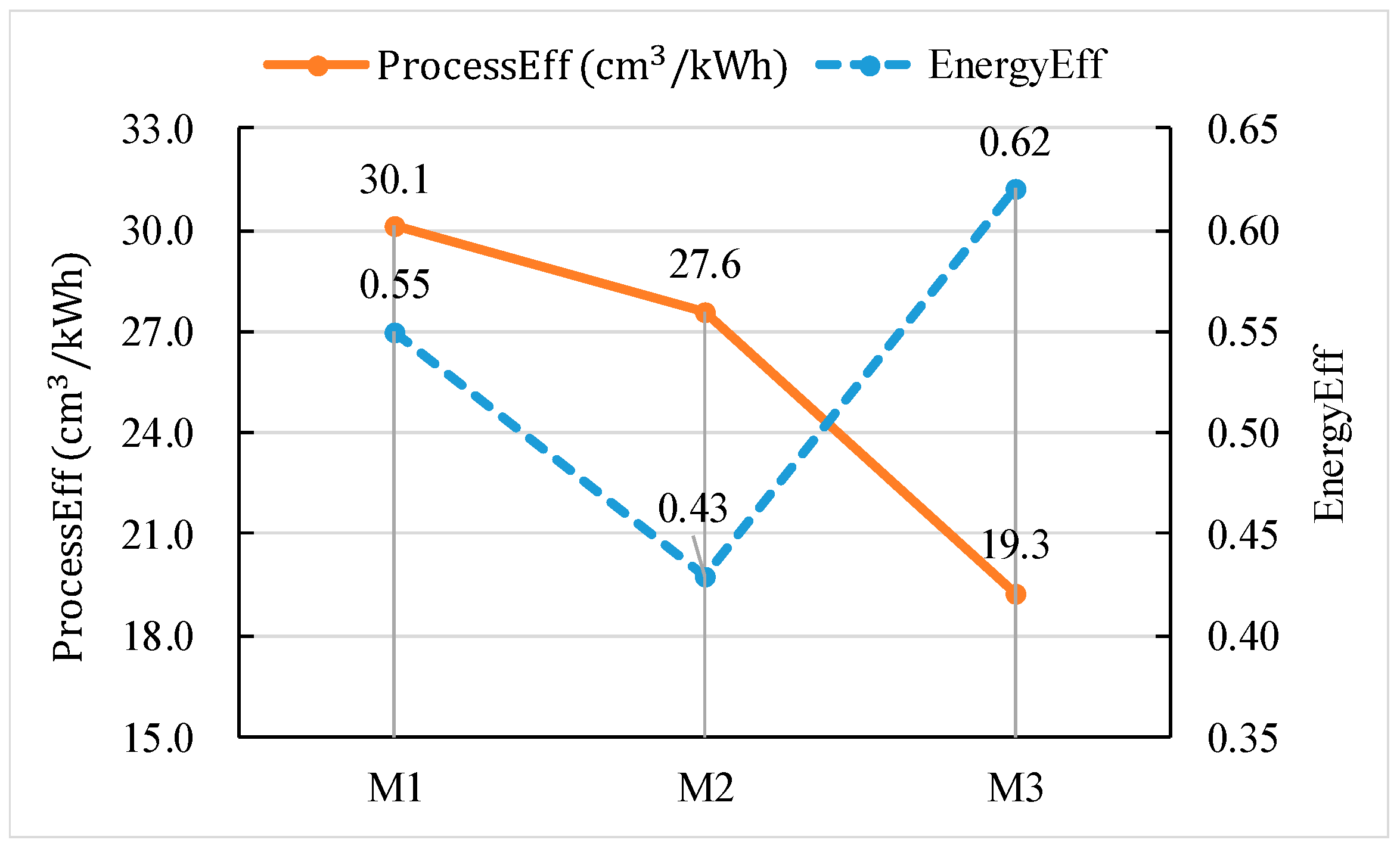
| No. | Processes | Machine Tool | Machine No. | Power of Air Cutting (W) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Cylindrical lathe cutting | CNC lathe | M1 | 2411 |
| 2 | Milling flat | Milling center | M2 | 2941 |
| 3 | Drilling hole | |||
| 4 | Tapping | Drilling machine | M3 | 2182 |
| Test No. | 1 | 2 | 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Machining time (min) | 15 | 30 | 45 |
| Sample size | 2700 | 5400 | 8100 |
| Partition accuracy (%) | 99.5 | 98.6 | 98.4 |
| Accuracy of clustering approach (%) | 98.7 | 97.8 | 97.1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, C.; Zhang, J.; Ji, W.; Peng, W. Data Acquisition Network Configuration and Real-Time Energy Consumption Characteristic Analysis in Intelligent Workshops for Social Manufacturing. Machines 2022, 10, 923. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines10100923
Zhang C, Zhang J, Ji W, Peng W. Data Acquisition Network Configuration and Real-Time Energy Consumption Characteristic Analysis in Intelligent Workshops for Social Manufacturing. Machines. 2022; 10(10):923. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines10100923
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Chaoyang, Juchen Zhang, Weixi Ji, and Wei Peng. 2022. "Data Acquisition Network Configuration and Real-Time Energy Consumption Characteristic Analysis in Intelligent Workshops for Social Manufacturing" Machines 10, no. 10: 923. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines10100923
APA StyleZhang, C., Zhang, J., Ji, W., & Peng, W. (2022). Data Acquisition Network Configuration and Real-Time Energy Consumption Characteristic Analysis in Intelligent Workshops for Social Manufacturing. Machines, 10(10), 923. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines10100923






