Parental Affinities and Environments of Bauxite Genesis in the Salt Range, Northwestern Himalayas, Pakistan
Abstract
1. Introduction
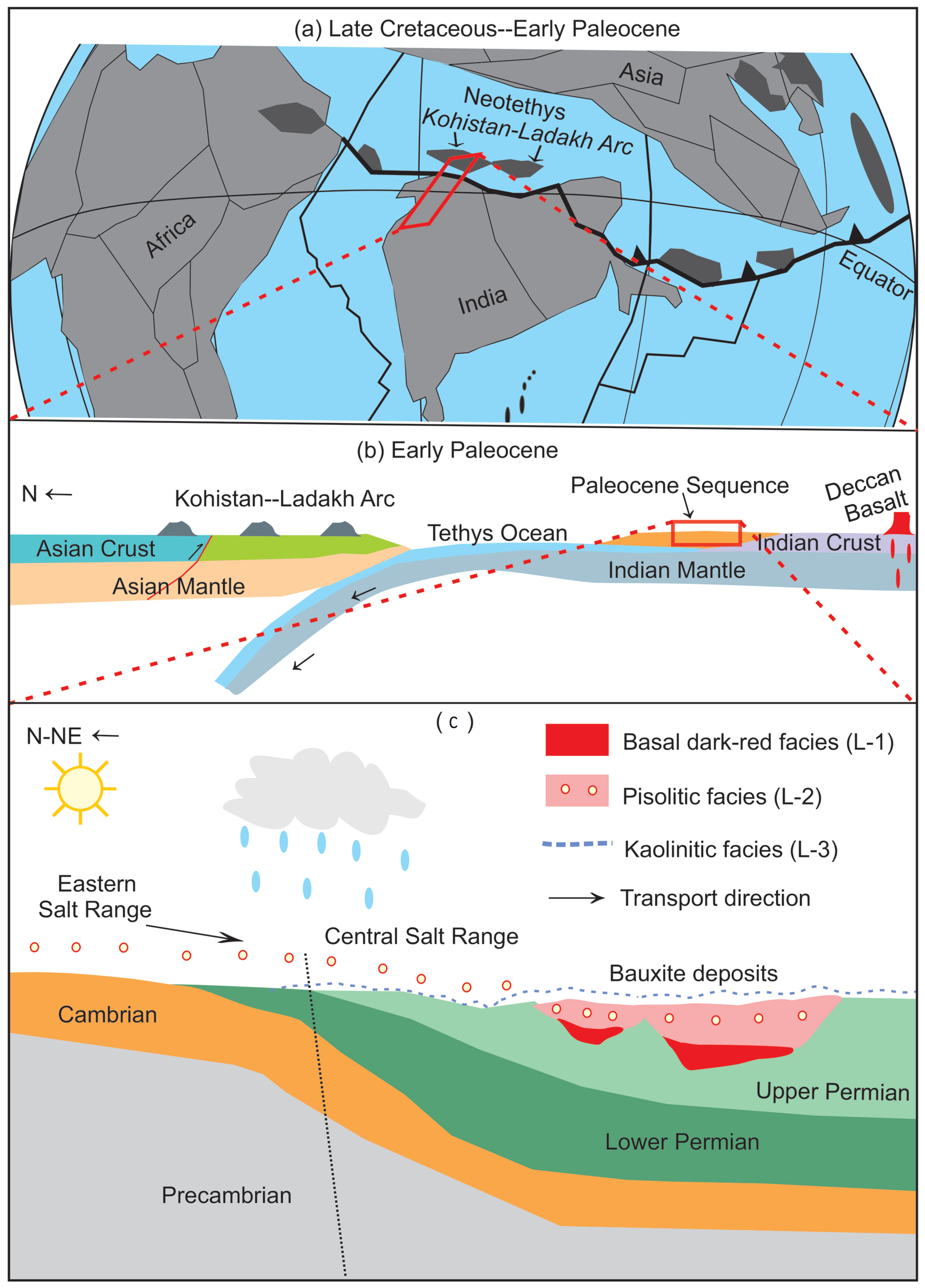
2. Regional Geology and Tectonics of the Salt Range
3. Materials and Analytical Methods
4. Results
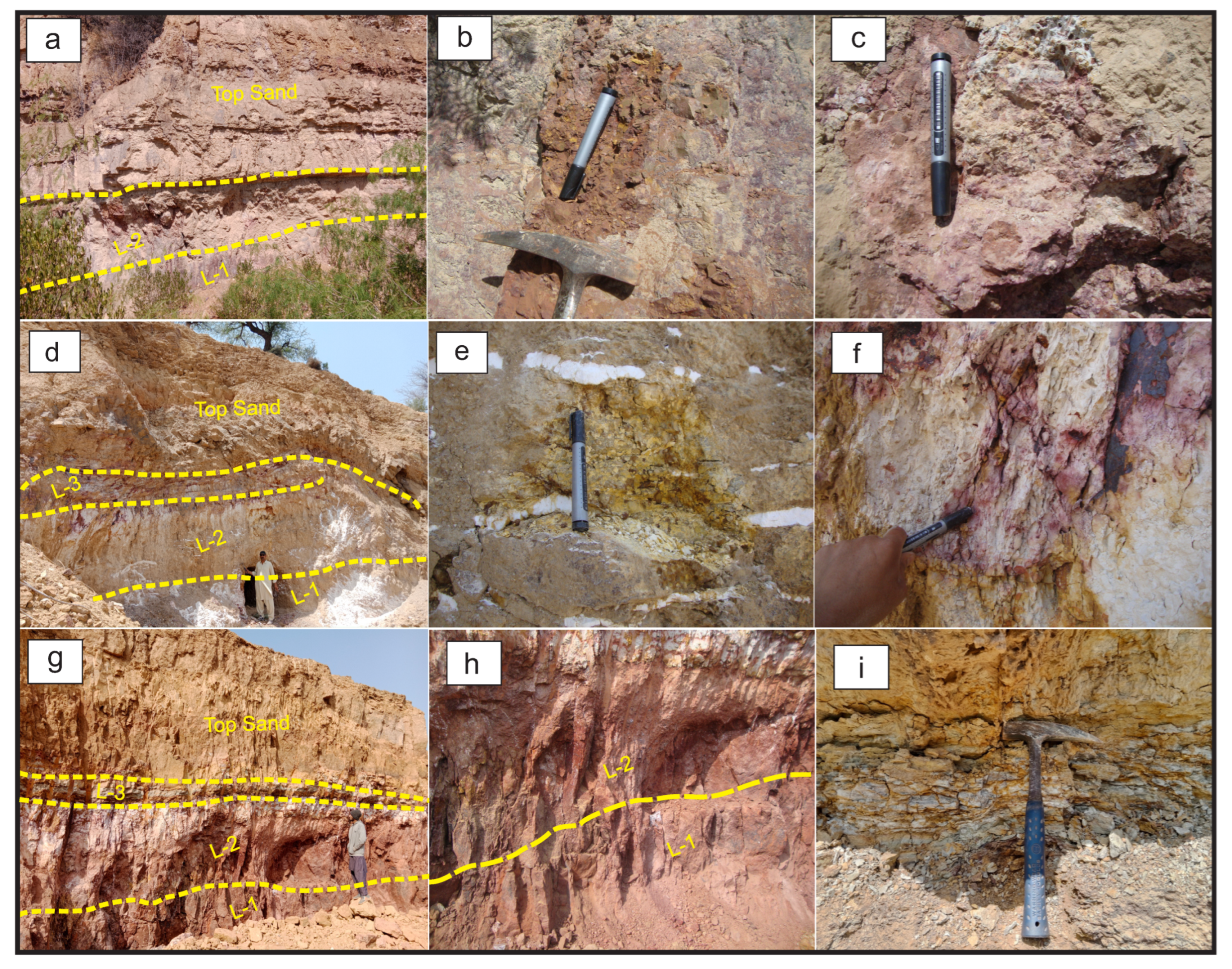
4.1. Outcrop Description
4.2. Mineralogy and Texture
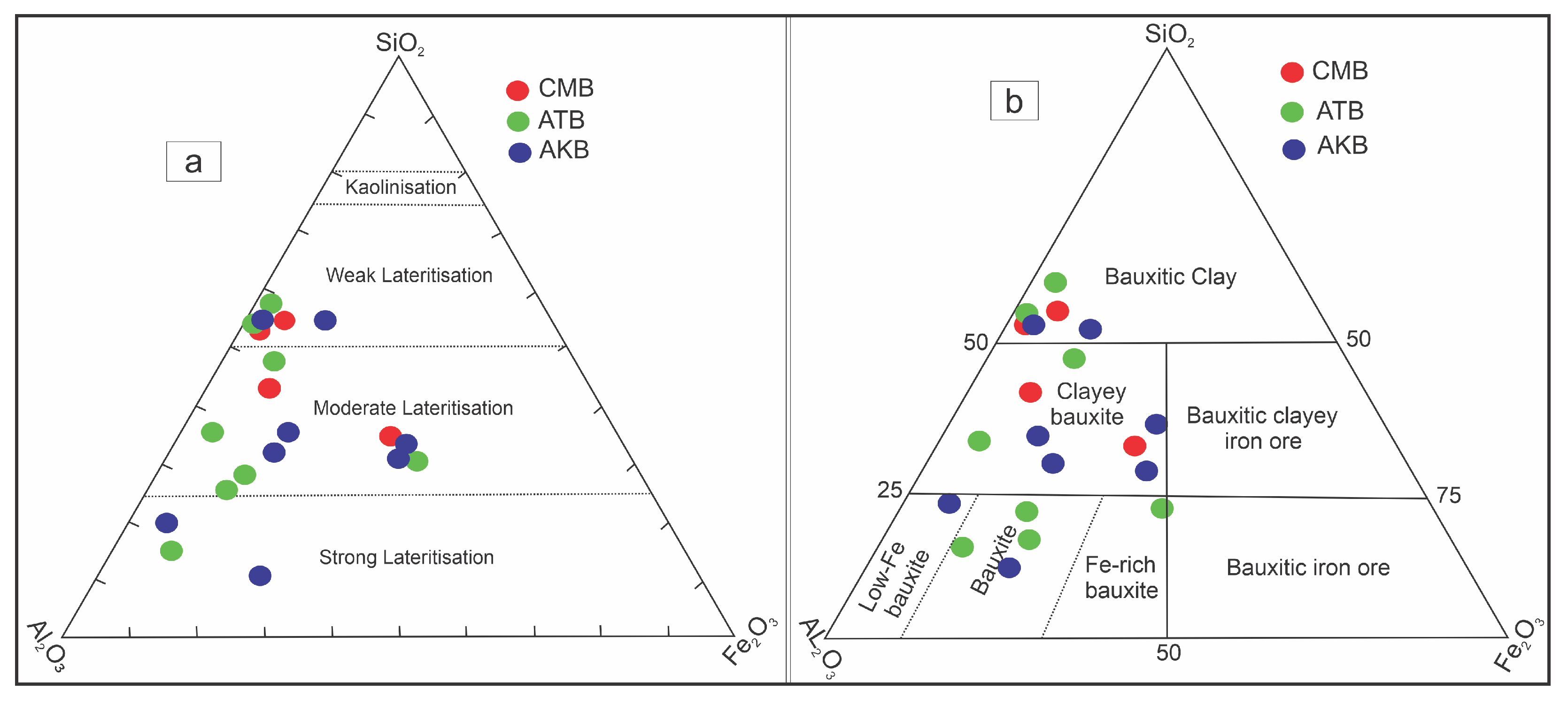
4.3. Major Elements Geochemistry
4.4. Trace Elements Geochemistry
4.5. Rare Earth Elements Geochemistry
5. Discussion
5.1. Bauxite Types and Stratigraphy
5.2. Mineralogy and Texture
5.3. Major Elements Geochemistry
5.4. Trace Elements Geochemistry
5.5. Rare Earth Elements Geochemistry
5.6. Parental Affinity
5.7. Ore Genesis
6. Conclusions
- Field observations, mineralogical analysis, and geochemical data indicate that the bauxites of the Salt Range belong to the karst bauxite category. The ternary diagram of major oxides further classifies them as bauxite/bauxitic clay deposits.
- Hematite, goethite, and kaolinite are the primary constituents of L-1, with minor amounts of mica, quartz, boehmite, rutile, and anatase. L-2 contains boehmite, kaolinite, alunite/natroalunite, and zaherite, along with minor amounts of quartz, mica, rutile, and anatase, while L-3 predominantly comprises kaolinite and quartz, with rutile, goethite, and anatase as accessory minerals.
- Binary diagrams of geochemical proxies (Eu/Eu* vs. Sm/Nd and Eu/Eu* vs. /) suggest a provenance from UCC and cratonic sandstones. Additionally, the Zr-Cr-Ga ternary diagram shows that all samples from ATB and AKB, and half of those from CMB, are derived from acidic and intermediate/argillaceous source rocks.
- Field studies, along with microscopic and SEM/EDS observations, reveal that the bauxite ore formed through multiple stages involving both diagenetic and late epigenetic processes. The L-1 facies reflects an autochthonous-to-para-autochthonous origin, while the L-2 facies are characterized by an allochthonous-to-para-allochthonous origin, pointing to an erosional event that followed a period of relative landscape stability, which previously resulted in the in situ ferrallitic weathering mentioned above.
- Further, geological evidence (including the geochemistry and mineralogy of the studied outcrops) indicates that these bauxite deposits are generally of sub-economic grade, except for a few particular layers within the conglomeratic facies.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bardossy, G. Karst Bauxites; Elsevier: New York, NY, USA, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Bardossy, G.; Aleva, G.J.J. Lateritic Bauxites; Developments in Economic Geology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1990; Volume 27. [Google Scholar]
- Bardossy, G.; Combes, P.J. Karst Bauxites: Interfingering of Deposition and Palaeoweathering. In Palaeoweathering, Palaeosurfaces and Related Continental Deposits; Thiry, M., Simon-Coincon, R., Eds.; Blackwell Publishing Ltd.: Oxford, UK, 1999; pp. 189–206. [Google Scholar]
- Ling, K.Y.; Zhu, X.Q.; Tang, H.S.; Li, S.J. Importance of Hydrogeological Conditions During Formation of the Karstic Bauxite Deposits, Central Guizhou Province, Southwest China: A Case Study at Lindai Deposit. Ore Geol. Rev. 2017, 82, 198–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, G.; Zhou, N.; Guo, W.; Fan, J.; Lei, K.; Zhang, S. Delineation of Sedimentary Bauxite Deposits in Shaanxi Province Using the Gravity and Transient Electromagnetic Methods. Ore Geol. Rev. 2022, 144, 104865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhao, L.; Wang, Q.; Sun, X.; Liu, L.; Yang, S.; Deng, J. Provenance and Genesis of Karstic Bauxite Deposits in China: Implications for the Formation of Super-Large Karstic Bauxite Deposits. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2024, 257, 104882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Argenio, B.; Mindszenty, A. Bauxites and Related Paleokarst: Tectonic and Climatic Event Markers at Regional Unconformities. Eclogae Geol. Helv. 1995, 88, 453–499. [Google Scholar]
- Ozturk, H.; Hein, J.R.; Hanilci, N. Genesis of the Doğankuzu and Mortaş Bauxite Deposits, Taurides, Turkey: Separation of Al, Fe and Mn and Implications for Passive Margin Metallogeny. Econ. Geol. 2002, 97, 1063–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.F.; Wang, Q.F.; Deng, J.; Zhang, Q.Z.; Sun, S.L.; Meng, J.Y. Mineralogical and Geochemical Investigations of the Dajia Salento-Type Bauxite Deposits, Western Guangxi, China. J. Geochem. Explor. 2010, 105, 137–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarasvandi, A.; Carranza, E.J.M.; Ellahi, S.S. Geological, Geochemical, and Mineralogical Characteristics of the Mandan and Dehnow Bauxite Deposits, Zagros Fold Belt, Iran. Ore Geol. Rev. 2012, 48, 125–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mongelli, G.; Buccione, R.; Gueguen, E.; Langone, A.; Sinisi, R. Geochemistry of the Apulian Allochthonous Karst Bauxite, Southern Italy: Distribution of Critical Elements and Constraints on Late Cretaceous Peri-Tethyan Palaeogeography. Ore Geol. Rev. 2016, 77, 246–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Wang, Q.; Liu, X.; Kan, Z.; Santosh, M.; Deng, J. Global Spatio-Temporal Variations and Metallogenic Diversity of Karst Bauxites and Their Tectonic, Paleogeographic and Paleoclimatic Relationship with the Tethyan Realm Evolution. Earth Sci. Rev. 2022, 233, 104184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiaeshkevarian, M.; Calagari, A.A.; Abedini, A.; Shamanian, G. Geochemical and Mineralogical Features of Karst Bauxite Deposits from the Alborz Zone (Northern Iran): Implications for Conditions of Formation, the Behavior of Trace and Rare Earth Elements and Parental Affinity. Ore Geol. Rev. 2020, 125, 103691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, S.; Bibi, M.; Wagreich, M. Geochemistry of the Triassic–Jurassic lateritic bauxites of the Salt Range: Implications for eastward extension of the Tethyan bauxite deposits into Pakistan. Int. J. Earth Sci. 2023, 112, 1527–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanilci, N. Geological and Geochemical Evolution of the Bolkardaği Bauxite Deposits, Karaman, Turkey: Transformation from Shale to Bauxite. J. Geochem. Explor. 2013, 133, 118–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamanian, H.; Ahmadnejad, F.; Zarasvandi, A. Mineralogical and Geochemical Investigations of the Mombi Bauxite Deposit, Zagros Mountains, Iran. Chem. Der Erde-Geochem. 2016, 76, 13–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- d’Argenio, B.; Mindszenty, A. Tectonic and climatic control on paleokarst and bauxites. G. Geol. 1992, 54, 207–218. [Google Scholar]
- Mameli, P.; Mongelli, G.; Oggiano, G.; Dinelli, E. Geological, Geochemical, and Mineralogical Features of Some Bauxite Deposits from Nurra (Western Sardinia, Italy): Insights on Conditions of Formation and Parental Affinity. Int. J. Earth Sci. 2007, 96, 887–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karadağ, M.; Kupeli, S.; Aryk, F.; Ayhan, A.; Zedef, V.; Doyen, A. Rare Earth Element (REE) Geochemistry and Genetic Implications of the Mortaş Bauxite Deposit (Seydişehir/Konya-Southern Turkey). Chem. Der Erde-Geochem. 2009, 69, 143–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondillo, N.; Balassone, G.; Boni, M.; Rollinson, G. Karst Bauxites in the Campania Apennines (Southern Italy): A New Approach. Period. Mineral. 2011, 80, 407–432. [Google Scholar]
- Abedini, A.; Calagari, A.A. REE Geochemical Characteristics of Titanium-Rich Bauxites: The Permian Kanigorgeh Horizon, NW Iran. Turk. J. Earth Sci. 2014, 23, 513–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boni, M.; Rollinson, G.; Mondillo, N.; Balassone, G.; Santoro, L. Quantitative Mineralogical Characterization of Karst Bauxite Deposits in the Southern Apennines, Italy. Econ. Geol. 2013, 108, 813–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mongelli, G.; Boni, M.; Oggiano, G.; Mameli, P.; Sinisi, R.; Buccione, R.; Mondillo, N. Critical Metals Distribution in Tethyan Karst Bauxite: The Cretaceous Italian Ores. Ore Geol. Rev. 2017, 86, 526–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadnejad, F.; Zamanian, H.; Taghipour, B.; Zarasvandi, A.; Buccione, R.; Ellahi, S.S. Mineralogical and Geochemical Evolution of the Bidgol Bauxite Deposit, Zagros Mountain Belt, Iran: Implications for Ore Genesis, Rare Earth Elements Fractionation and Parental Affinity. Ore Geol. Rev. 2017, 86, 755–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abedini, A.; Calagari, A.A.; Azizi, M.R. The Tetrad-Effect in Rare Earth Elements Distribution Patterns of Titanium-Rich Bauxites: Evidence from the Kanigorgeh Deposit, NW Iran. J. Geochem. Explor. 2018, 186, 129–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putzolu, F.; Piccolo Papa, A.; Mondillo, N.; Boni, M.; Balassone, G.; Mormone, A. Geochemical Characterization of Bauxite Deposits from the Abruzzi Mining District (Italy). Minerals 2018, 8, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinhardt, N.; Proenza, J.A.; Villanova-de Benavent, C.; Aiglsperger, T.; Bover-Arnal, T.; Torró, L.; Dziggel, A. Geochemistry and Mineralogy of Rare Earth Elements (REE) in Bauxitic Ores of the Catalan Coastal Range, NE Spain. Minerals 2018, 8, 562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metcalfe, I. Multiple Tethyan Ocean Basins and Orogenic Belts in Asia. Gondwana Res. 2021, 100, 87–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, B.; Chu, Y.; Chen, L.; Liang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Ao, S.; Talebian, M. Paleo-Tethys Subduction Induced Slab-Drag Opening the Neo-Tethys: Evidence from an Iranian Segment of Gondwana. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2021, 221, 103788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malkani, M.S.; Mahmood, Z. Mineral resources of Pakistan: A review. Geol. Surv. Pak. Rec. 2016, 128, 1–90. [Google Scholar]
- Ashraf, M.; Chohan, N.A.; Faruqi, F.A. Bauxite and Clay Deposits in the Kattha Area, Salt Range, Punjab, West Pakistan. Econ. Geol. 1972, 67, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaheen, M. Evaluation of bauxite of Khushab (Pakistan) as a raw material for extraction of aluminum. Pak. J. Sci. 2010, 62, 79–82. [Google Scholar]
- Hussain, S.; Iqbal, M. Extraction of alumina from low grade, highly siliceous bauxite ore from Khushab, Pakistan, using sulfuric acid process. In Mineral Processing on the Verge of the 21st Century; Routledge: Oxford, UK, 2017; pp. 457–460. [Google Scholar]
- Tariq, M.; Mansoor Iqbal, M.; Aziz, A.; Shafiq, M.; Sajid, M.; Mohammad, B. Recovery of Alumina from Khushab Bauxite by Leaching with Sulphuric Acid and Removal of Iron Impurity by Ethanol. J. Chem. Soc. Pak. 2014, 36, 624–629. [Google Scholar]
- Nazirahmedchohan, M.Q.; Faruqi, M.C.F. Evaluation of Kattha Bauxites for Industrial Utilization. Pak. J. Sci. Ind. Res. 1973, 16, 70–74. [Google Scholar]
- Kazmi, A.H.; Abbasi, I.A. Stratigraphy & Historical Geology of Pakistan; Department & National Centre of Excellence in Geology: Peshawar, Pakistan, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Gee, E.R.; Gee, D.G. Overview of the Geology and Structure of the Salt Range, with Observations on Related Areas of Northern Pakistan; Geological Society of America: Boulder, CO, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Yeats, R.S.; Hussain, A. Timing of Structural Events in the Himalayan Foothills of Northwestern Pakistan. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 1987, 99, 161–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazmi, A.H.; Jan, M.Q. Geology and Tectonics of Pakistan; Graphic Publishers: Santa Ana, CA, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Yeats, R.S.; Khan, S.H.; Akhtar, M. Late Quaternary Deformation of the Salt Range of Pakistan. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 1984, 95, 958–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiesmayr, G.; Grasemann, B. Eohimalayan Fold and Thrust Belt: Implications for the Geodynamic Evolution of the NW-Himalaya (India). Tectonics 2002, 21, 8-1–8-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, S.; Wagreich, M.; Bibi, M.; Jan, I.U.; Gier, S. Multi-Proxy Provenance Analyses of the Kingriali and Datta Formations (Triassic-Jurassic Transition): Evidence for Westward Extension of the Neo-Tethys Passive Margin from the Salt Range (Pakistan). Minerals 2021, 11, 573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghazi, S.; Mountney, N.P.; Butt, A.A.; Sharif, S. Stratigraphic and Paleoenvironmental Framework of the Early Permian Sequence in the Salt Range, Pakistan. J. Earth Syst. Sci. 2012, 121, 1239–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, S.K. Regional tectonic framework, structure and evolution of the western marginal basins of India. Tectonophysics 1987, 135, 307–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, P.F.; Duddy, I.R.; Japsen, P.; Bonow, J.M.; Malan, J.A. Post-breakup burial and exhumation of the southern margin of Africa. Basin Res. 2017, 29, 96–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asim, S.; Qureshi, S.N.; Khan, N. Study of an uplift of Sargodha High by stratigraphical and structural interpretation of an east-west seismic profile in Central Indus Basin, Pakistan. Int. J. Geosci. 2014, 5, 1027–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aleva, G.J.J. Laterites: Concepts, Geology, Morphology and Chemistry; International Soil Reference and Information Centre (ISRIC): Wageningen, The Netherlands, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Garzanti, E.; Hu, X. Latest Cretaceous Himalayan Tectonics: Obduction, Collision or Deccan-Related Uplift. Gondwana Res. 2015, 28, 165–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aadil, N.; Sohail, G.M. Stratigraphic Correlation and Isopach Maps of Punjab Platform in Middle Indus Basin, Pakistan; Search and Discovery Article-10364; AAPG: Tulsa, OH, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Storey, M.; Mahoney, J.J.; Saunders, A.D. Cretaceous basalts in Madagascar and the transition between plume and continental lithosphere mantle sources. Geophys.-Monogr.-Am. Geophys. Union 1997, 100, 95–122. [Google Scholar]
- Qayyum, M.; Spratt, D.A.; Dixon, J.M.; Lawrence, R.D. Displacement Transfer from Fault-Bend to Fault-Propagation Fold Geometry: An Example from the Himalayan Thrust Front. J. Struct. Geol. 2015, 77, 260–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudnick, R.L.; Gao, S. Composition of the Continental Crust. In Treatise on Geochemistry, 2nd ed.; Holland, H., Turekian, K., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2003; pp. 1–64. [Google Scholar]
- Anders, E.; Grevesse, N. Abundances of the Elements: Meteoritic and Solar. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1989, 53, 197–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malkani, M.S.; Mahmood, Z. Stratigraphy of Pakistan; Memoir; Geological Survey of Pakistan: Balochistan, Pakistan, 2017; Volume 24, pp. 1–134.
- Valeton, I. Bauxites; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2010; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Schwertmann, U.; Murad, E. Effect of pH on the Formation of Goethite and Hematite from Ferrihydrite. Clays Clay Miner. 1983, 31, 277–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schellmann, W. A New Definition of Laterite. Mem. Geol. Surv. India 1986, 120, 70–74. [Google Scholar]
- Trolard, F.; Tardy, Y. A Model of Fe3+-Kaolinite, Al3+-Goethite, Al3+-Hematite Equilibria in Laterites. Clay Miner. 1989, 24, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nia, R. On the Significance of Methodological Sampling for Genetic Investigations of Bauxite Deposits Using the Example of the Upper Cretaceous Bauxites of the Parnassus-Kiona Zone of Greece. Miner. Depos. 1968, 3, 368–374. [Google Scholar]
- Stoffregen, R.E.; Alpers, C.N.; Jambor, J.L. Alunite-Jarosite Crystallography, Thermodynamics, and Geochronology. Rev. Mineral. Geochem. 2000, 40, 453–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raymahashay, B.C. A Geochemical Study of Rock Alteration by Hot Springs in the Paint Pot Hill Area, Yellowstone Park. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1968, 32, 499–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemley, J.J.; Hostetler, P.B.; Gude, A.J.; Mountjo, W.T. Some Stability Relations of Alunite. Econ. Geol. 1969, 64, 599–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qureshi, K.A.; Shah, M.R.; Meerani, I.A.; Fahad, S.; Hussain, H.; Habib, U. Sedimentology and Economic Significance of Hangu Formation, Northwest Pakistan: Sedimentology and Economic Significance of Hangu Formation, Northwest Pakistan. Int. J. Econ. Environ. Geol. 2020, 11, 48–55. [Google Scholar]
- Schoen, R.; White, D.E.; Hemley, J.J. Argillization by Descending Acid at Steamboat Springs, Nevada. Clays Clay Miner. 1974, 22, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruotsala, A.P.; Babcock, L. Zaherite, a new hydrated aluminum sulfate. Am. Mineral. 1977, 62, 1125–1128. [Google Scholar]
- Maignien, R. Review of Research in Laterites; UNESCO: Paris, France, 1966. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Wang, Q.; Feng, Y.; Li, Z.; Cai, S. Genesis of the Guangou Karstic Bauxite Deposit in Western Henan, China. Ore Geol. Rev. 2013, 55, 162–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cetiner, Z.S.; Wood, S.A.; Gammons, C.H. The Aqueous Geochemistry of the Rare Earth Elements. Part XIV. The Solubility of Rare Earth Element Phosphates from 23 to 150 C. Chem. Geol. 2005, 217, 147–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadnejad, F.; Mongelli, G. Geology, Geochemistry, and Genesis of REY Minerals of the Late Cretaceous Karst Bauxite Deposits, Zagros Simply Folded Belt, SW Iran: Constraints on the Ore-Forming Process. J. Geochem. Explor. 2022, 240, 107030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mongelli, G.; Boni, M.; Buccione, R.; Sinisi, R. Geochemistry of the Apulian Karst Bauxite (Southern Italy): Chemical Fractionation and Parental Affinities. Ore Geol. Rev. 2014, 63, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abedini, A.; Khosravi, M. Geochemical Characteristics of Aluminum-Bearing Iron Ores: A Case Study from the Kolijan Karst-Type Bauxite Deposit, Northwestern Iran. Minerals 2024, 14, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertille Ilalie, M.K.; Véronique, K.K.; Armand, W.; Katte, V. Mineralogy of Lateritic Weathering Profiles Developed on the Rocks under a Sub-equatorial Monsoon Climate: Case of the Bambouto Mountains. J. Geol. Soc. India 2024, 100, 1033–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinis, P.A.; Soares, A.F. Stable and Ultrastable Heavy Minerals of Alluvial to Nearshore Marine Sediments from Central Portugal: Facies Related Trends. Sediment. Geol. 2007, 201, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamley, H. Clay mineralogy. In Clay Sedimentology; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 30–36. [Google Scholar]
- Babechuk, M.G.; Widdowson, M.; Kamber, B.S. Quantifying Chemical Weathering Intensity and Trace Element Release from Two Contrasting Basalt Profiles, Deccan Traps, India. Chem. Geol. 2014, 363, 56–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loughnan, F.C. Chemical Weathering of the Silicate Minerals; Mineralogical Society of America: Chantilly, VA, USA, 1969. [Google Scholar]
- Esmaeily, D.; Rahimpour-Bonab, H.; Esna-Ashari, A.; Kananian, A. Petrography and Geochemistry of the Jajarm Bauxite Ore Deposit, Northeast Iran: Implications for Source Rock Material and Ore Genesis. Turk. J. Earth Sci. 2010, 19, 267–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, K.Y.; Zhu, X.Q.; Tang, H.S.; Wang, Z.G.; Yan, H.W.; Han, T.; Chen, W.Y. Mineralogical Characteristics of the Karstic Bauxite Deposits in the Xiuwen Ore Belt, Central Guizhou Province, Southwest China. Ore Geol. Rev. 2015, 65, 84–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radusinović, S.; Jelenković, R.; Pačevski, A.; Simić, V.; Božović, D.; Holclajtner-Antunović, I.; Životić, D. Content and Mode of Occurrences of Rare Earth Elements in the Zagrad Karstic Bauxite Deposit (Nikšić Area, Montenegro). Ore Geol. Rev. 2017, 80, 406–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abedini, A.; Khosravi, M.; Mongelli, G. Critical Metals Distribution in the Late Triassic-Early Jurassic Nasr-Abad Bauxite Deposit, Irano-Himalayan Karst Bauxite Belt, NW Iran. Geochemistry 2024, 84, 126039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Li, Y.; Yang, H.; Xu, J.; Huang, M. Geochemistry of the Yudong Bauxite Deposit, South-Eastern Guizhou, China: Implications for Conditions of Formation and Parental Affinity. J. Geochem. Explor. 2021, 220, 106676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nesbitt, H.W. Mobility and Fractionation of Rare Earth Elements During Weathering of a Granodiorite. Nature 1979, 279, 206–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronov, A.B. Geochemistry of the Rare Earths in the Sedimentary Cycle. Geochem. Int. 1967, 4, 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Sanematsu, K.; Kon, Y.; Imai, A.; Watanabe, K.; Watanabe, Y. Geochemical and Mineralogical Characteristics of Ion-Adsorption Type REE Mineralization in Phuket, Thailand. Miner. Depos. 2013, 48, 437–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Huang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Deng, J.; Liu, X.; Wang, J. Mineralogical and Geochemical Features of Karst Bauxites from Poci (Western Henan, China), Implications for Parental Affinity and Bauxitization. Ore Geol. Rev. 2019, 105, 295–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun, J.J.; Pagel, M.; Muller, J.P.; Bilong, P.; Michard, A.; Guillet, B. Cerium Anomalies in Lateritic Profiles. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1990, 54, 781–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Condie, K.C. Another Look at Rare Earth Elements in Shales. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1991, 55, 2527–2531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Gong, Z.T. Geochemical Implication of Rare Earth Elements in the Process of Soil Development. J. Rare Earths 2001, 19, 57–62. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, J.L.; Wei, G.J.; Xu, Y.G.; Long, W.G.; Sun, W.D. Mobilization and Re-Distribution of Major and Trace Elements During Extreme Weathering of Basalt in Hainan Island, South China. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2007, 71, 3223–3237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.L.; Zhong, Y.T.; Xu, Y.G.; He, B. The Provenance of Late Permian Karstic Bauxite Deposits in SW China, Constrained by the Geochemistry of Interbedded Clastic Rocks, and U-Pb-Hf-O Isotopes of Detrital Zircons. Lithos 2017, 278, 240–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Liu, X. Metallogenic and Tectonic Implications of Detrital Zircon U-Pb, Hf Isotopes, and Detrital Rutile Geochemistry of Late Carboniferous Karstic Bauxite on the Southern Margin of the North China Craton. Lithos 2019, 350–351, 105222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.H.; Liu, X.F.; Yang, S.J.; Ma, X.L.; Liu, L.; Sun, X.F. Regional Multi-Sources of Carboniferous Karstic Bauxite Deposits in North China Craton: Insights from Multiproxy Provenance Systems. Sediment. Geol. 2021, 421, 105958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunkl, I. Origin of Eocene-Covered Karst Bauxites of the Transdanubian Central Range (Hungary)—Evidence for Early Eocene Volcanism. Eur. J. Mineral. 1992, 4, 581–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boni, M.; Reddy, S.M.; Mondillo, N.; Balassone, G.; Taylor, R. A Distant Magmatic Source for Cretaceous Karst Bauxites of the Southern Apennines (Italy) Revealed by SHRIMP. Terra Nova 2012, 24, 326–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelemen, P.; Dunkl, I.; Csillag, G.; Mindszenty, A.; Józsa, S.; Fodor, L.; von Eynatten, H. Origin, Timing and Paleogeographic Implications of Paleogene Karst Bauxites in the Transdanubian Range, Hungary. Int. J. Earth Sci. 2023, 112, 243–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroll, E.; Sauer, D. Beitrag zur Geochemie von Ti, Cr, Ni Co, V, and Mo in bauxitischen Gestermen und Problem der stofflichen Herkunft des aluminiums. Trav. ICSOBA 1968, 5, 83–96. [Google Scholar]
- Özlü, N. Trace-Element Content of “Karst Bauxites” and Their Parent Rocks in the Mediterranean Belt. Miner. Depos. 1983, 18, 469–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viers, J.; Wasserburg, G.J. Behavior of Sm and Nd in a Lateritic Soil Profile. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2004, 68, 2043–2054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, S.R. Abundance of Chemical Elements in the Continental Crust: A New Table. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1964, 28, 1273–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, S.R. The Continental Crust: Its Composition and Evolution; Geoscience Texts; Blackwell Scientific Publications: Oxford, UK, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong-Altrin, J.S.; Lee, Y.I.; Verma, S.P.; Ramasamy, S. Geochemistry of Sandstones from the Upper Miocene Kudankulam Formation, Southern India: Implications for Provenance, Weathering, and Tectonic Setting. J. Sediment. Res. 2004, 74, 285–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garzanti, E.; Critelli, S.; Ingersoll, R.V. Paleogeographic and Paleotectonic Evolution of the Himalayan Range as Reflected by Detrital Modes of Tertiary Sandstones and Modern Sands (Indus Transect, India and Pakistan). Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 1996, 108, 631–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jadoul, F.; Berra, F.; Garzanti, E. The Tethys Himalayan Passive Margin from Late Triassic to Early Cretaceous (South Tibet). J. Asian Earth Sci. 1998, 16, 173–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, R.I.; Ghazi, S. Dynamics of Sargodha High and its impact on Late Phanerozoic sequence including petroleum system, Indus Basin, Pakistan. Arab. J. Geosci. 2022, 15, 1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qayyum, M. Crustal Shortening and Tectonic Evolution of the Salt Range in Northwest Himalaya, Pakistan. Master’s Thesis, Oregon State University, Corvallis, OR, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Scotese, C.R. Atlas of Paleogene Paleogeographic Maps (Mollweide Projection), Maps 8-15, Volume 1, The Cenozoic, PALEOMAP Atlas for ArcGIS; PALEOMAP Project: Evanston, IL, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Chatterjee, S.; Bajpai, S. India’s Northward Drift from Gondwana to Asia During the Late Cretaceous-Eocene. Proc. Indian Natl. Sci. Acad. 2016, 82, 479–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arif, M.; Jan, M.Q. Petrotectonic significance of the chemistry of chromite in the ultramafic–mafic complexes of Pakistan. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2006, 27, 628–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakar, M.I.; Kerr, A.C.; Mahmood, K.; Collins, A.S.; Khan, M.; McDonald, I. Supra-subduction zone tectonic setting of the Muslim Bagh Ophiolite, northwestern Pakistan: Insights from geochemistry and petrology. Lithos 2014, 202, 190–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qasim, M.; Ding, L.; Khan, M.A.; Baral, U.; Jadoon, I.A.; Umar, M.; Imran, M. Provenance of the Hangu Formation, Lesser Himalaya, Pakistan: Insight from the detrital zircon U-Pb dating and spinel geochemistry. Palaeoworld 2020, 29, 729–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, M.; Klötzli, U.; Rentenberger, C.; Sláma, J.; Younas, M.; Khubab, M.; Goudarzi, M.; Ahmad, T. Unravelling the geochemical and geochronological diversities of the pre-collisional magmatism: Implications for the subduction dynamics in the Kohistan island arc and Karakorum block, Pakistan. Geosci. Front. 2025, 16, 102003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Rad, U.; Exon, N.F.; Boyd, R.; Haq, B.U. Mesozoic Paleoenvironment of the Rifted Margin off NW Australia (ODP Legs 122/123). In Geophysical Monograph Series; AGU Publications: Malden, MA, USA, 1992; Volume 70, pp. 157–184. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, P.; Xie, Y.; Kang, C.; Chi, Y.; Sun, L.; Wei, Z. Effects of provenance, transport processes and chemical weathering on heavy mineral composition: A case study from the Songhua River Drainage, NE China. Front. Earth Sci. 2022, 10, 839745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, K.; Qi, H.W.; Hu, R.Z. Element Mobilization and Redistribution Under Extreme Tropical Weathering of Basalts from the Hainan Island, South China. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2018, 158, 80–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| L-1 | L-2 | L-3 | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample | CMB1 | ATB1 | AKB1 | CMB2 | CMB3 | ATB2 | ATB3/4 | ATB5 | ATB6 | ATB7/1 | ATB7/2 | AKB2 | AKB3 | AKB4 | AKB5 | AKB6 | AKB7 | CMB4 | ATB8 | AKB8 |
| 29.09 | 20.75 | 28.70 | 34.93 | 43.31 | 18.48 | 9.21 | 21.43 | 26.35 | 38.14 | 42.71 | 9.06 | 29.97 | 30.38 | 43.25 | 17.34 | 32.52 | 42.31 | 45.27 | 32.31 | |
| 28.09 | 26.18 | 27.42 | 38.69 | 36.50 | 43.43 | 38.92 | 40.67 | 40.38 | 33.45 | 36.57 | 52.81 | 39.25 | 25.54 | 31.13 | 53.75 | 37.53 | 30.56 | 30.30 | 21.78 | |
| 25.18 | 34.38 | 29.66 | 6.83 | 2.02 | 10.90 | 6.70 | 10.18 | 4.28 | 9.45 | 0.91 | 19.83 | 14.77 | 28.39 | 10.75 | 5.15 | 12.08 | 4.15 | 2.23 | 27.54 | |
| MgO | 1.06 | 0.08 | 0.67 | 0.15 | 0.14 | 0.18 | 0.11 | 0.18 | 0.16 | 0.15 | 0.13 | <0.01 | <0.01 | 0.10 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | 0.95 | 0.70 | 0.63 |
| CaO | 0.22 | 0.01 | 0.22 | 0.12 | 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.06 | 0.04 | 0.09 | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.13 | 0.24 | 0.18 | 0.14 | 0.17 | 0.22 | 0.30 | 0.09 | 0.85 |
| O | 0.10 | 0.04 | 0.06 | 0.13 | 0.09 | 0.15 | 0.14 | 0.06 | 1.21 | 0.07 | 0.19 | 0.01 | 0.07 | 0.05 | 0.04 | 1.13 | 0.15 | 0.26 | 0.14 | 0.08 |
| O | 0.10 | 0.33 | 0.27 | 0.10 | 0.06 | 0.04 | 0.01 | <0.01 | 0.09 | 0.03 | 0.07 | 0.04 | 0.11 | 0.12 | 0.10 | 0.44 | 0.26 | 2.41 | 2.16 | 1.80 |
| 1.95 | 2.56 | 1.46 | 3.83 | 2.95 | 3.59 | 3.03 | 3.22 | 3.11 | 2.96 | 3.24 | 3.49 | 2.20 | 1.84 | 2.17 | 3.25 | 2.97 | 2.01 | 3.02 | 2.07 | |
| 0.05 | 0.04 | 0.06 | 0.04 | 0.02 | 0.11 | 0.04 | 0.08 | 0.04 | 0.05 | 0.01 | 0.12 | 0.06 | 0.13 | 0.05 | 0.34 | 0.07 | 0.19 | 0.10 | 0.35 | |
| MnO | <0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | 0.02 | 0.01 | <0.01 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.03 |
| LOI | 13.70 | 15.10 | 11.27 | 14.60 | 14.50 | 22.50 | 41.40 | 23.70 | 23.90 | 15.30 | 15.80 | 13.80 | 12.74 | 12.80 | 12.06 | 18.04 | 14.10 | 16.30 | 15.30 | 14.35 |
| Sum | 99.66 | 99.58 | 99.80 | 99.66 | 99.78 | 99.56 | 99.65 | 99.58 | 99.63 | 99.65 | 99.69 | 99.31 | 99.44 | 99.53 | 99.68 | 99.61 | 99.91 | 99.54 | 99.38 | 98.63 |
| Ba | 32.00 | 72.00 | 27.20 | 33.00 | 9.00 | 17.00 | 11.00 | 12.00 | 14.00 | 12.00 | 18.00 | 9.50 | 13.00 | 27.00 | 4.80 | 3.10 | 3.40 | 317.00 | 337.00 | 12.20 |
| Ni | 49.00 | 10.00 | 18.50 | 10.00 | 10.00 | 10.00 | 10.00 | 10.00 | 10.00 | 10.00 | 10.00 | 10.10 | 13.70 | 10.00 | 11.00 | 13.30 | 15.50 | 32.00 | 34.00 | 22.10 |
| Cr | 355.00 | 430.00 | 213.00 | 1140.00 | 934.00 | 402.00 | 375.00 | 361.00 | 341.00 | 382.00 | 259.00 | 414.70 | 257.70 | 341.00 | 128.80 | 210.70 | 265.10 | 225.00 | 184.00 | 222.50 |
| Sc | 0.20 | 36.00 | 22.10 | 0.30 | 0.10 | 27.00 | 29.00 | 26.00 | 27.00 | 13.00 | 15.00 | 17.30 | 15.70 | 18.00 | 15.50 | 14.70 | 17.50 | 5.90 | 37.00 | 30.10 |
| Be | 45.80 | 2.00 | 1.80 | 49.80 | 34.10 | 3.00 | 1.00 | 2.00 | 2.00 | <1 | <1 | 1.00 | 0.92 | 1.00 | 0.65 | 0.71 | 0.90 | 54.70 | 3.00 | 1.70 |
| Co | 16.70 | 6.80 | 14.40 | 32.70 | 24.10 | 4.90 | 8.40 | 4.70 | 2.90 | 1.60 | 1.00 | 13.50 | 10.30 | 2.40 | 3.50 | 4.10 | 3.90 | 36.10 | 6.90 | 9.50 |
| Cs | 0.20 | 0.40 | 0.78 | 0.30 | 0.10 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | 0.30 | 0.20 | 0.27 | 0.16 | 5.90 | 6.00 | 4.20 |
| Ga | 45.80 | 41.40 | 53.00 | 49.80 | 34.10 | 76.90 | 60.50 | 65.70 | 64.80 | 39.60 | 31.90 | 28.10 | 23.40 | 20.60 | 22.30 | 25.60 | 21.20 | 54.70 | 50.40 | 27.50 |
| Hf | 16.70 | 33.80 | 16.20 | 32.70 | 24.10 | 50.30 | 40.90 | 46.10 | 45.70 | 43.50 | 44.20 | 21.50 | 23.10 | 22.70 | 24.20 | 20.50 | 18.20 | 36.10 | 76.80 | 42.50 |
| Nb | 35.40 | 39.30 | 24.50 | 80.20 | 60.20 | 51.90 | 42.50 | 48.30 | 44.90 | 47.50 | 51.20 | 29.50 | 30.20 | 31.50 | 33.20 | 35.60 | 31.50 | 44.20 | 53.00 | 36.30 |
| Rb | 3.60 | 12.20 | 13.50 | 3.10 | 1.80 | 1.30 | 0.40 | 0.30 | 3.30 | 0.90 | 2.50 | 4.40 | 4.10 | 4.30 | 3.80 | 5.10 | 4.60 | 93.00 | 85.40 | 51.50 |
| Sn | 5.00 | 9.00 | 8.20 | 10.00 | 7.00 | 12.00 | 10.00 | 10.00 | 9.00 | 7.00 | 7.00 | 6.70 | 5.60 | 7.00 | 3.70 | 6.50 | 7.50 | 7.00 | 8.00 | 9.30 |
| Sr | 245.00 | 86.50 | 166.50 | 115.50 | 43.00 | 52.00 | 94.10 | 24.60 | 78.10 | 16.20 | 40.40 | 153.20 | 154.50 | 155.80 | 148.80 | 161.50 | 158.10 | 597.70 | 203.00 | 198.50 |
| Ta | 2.60 | 3.10 | 2.20 | 5.10 | 4.00 | 6.10 | 3.30 | 3.70 | 3.70 | 4.30 | 4.60 | 2.60 | 1.90 | 2.40 | 2.70 | 2.40 | 1.80 | 2.90 | 4.70 | 2.30 |
| Th | 37.80 | 77.80 | 42.10 | 64.20 | 45.10 | 106.80 | 44.20 | 99.80 | 70.00 | 50.20 | 41.00 | 68.60 | 65.50 | 73.40 | 71.50 | 78.20 | 81.50 | 44.00 | 64.40 | 67.50 |
| U | 13.60 | 8.20 | 9.20 | 10.90 | 6.60 | 11.20 | 8.80 | 10.00 | 8.90 | 7.30 | 7.10 | 6.40 | 5.30 | 4.00 | 4.60 | 5.10 | 4.20 | 12.60 | 17.30 | 15.20 |
| V | 357.00 | 939.00 | 1033.00 | 524.00 | 242.00 | 578.00 | 392.00 | 572.00 | 318.00 | 405.00 | 209.00 | 1127.00 | 1295.00 | 1491.00 | 1305.00 | 1535.00 | 1275.00 | 305.00 | 216.00 | 1523.00 |
| W | 3.70 | 4.90 | 3.10 | 10.50 | 4.20 | 9.20 | 5.50 | 7.30 | 8.10 | 4.00 | 4.10 | 2.63 | 2.45 | 2.50 | 2.30 | 3.50 | 2.70 | 4.30 | 7.50 | 6.20 |
| Zr | 637.10 | 1244.20 | 565.00 | 1234.60 | 953.70 | 1867.20 | 1553.70 | 1775.80 | 1721.90 | 1564.60 | 1650.40 | 1873.00 | 865.00 | 893.20 | 1046.00 | 2150.00 | 1619.00 | 1423.60 | 2946.20 | 2401.00 |
| Y | 73.10 | 43.30 | 33.60 | 56.60 | 40.00 | 52.60 | 41.20 | 53.40 | 44.50 | 42.10 | 45.60 | 31.50 | 28.20 | 29.60 | 32.10 | 35.10 | 30.50 | 67.10 | 113.50 | 47.50 |
| La | 49.70 | 19.10 | 20.50 | 17.40 | 10.00 | 6.50 | 5.60 | 4.10 | 8.60 | 3.60 | 6.90 | 13.20 | 11.80 | 10.50 | 9.70 | 12.10 | 11.40 | 114.00 | 126.50 | 72.00 |
| Ce | 607.50 | 41.40 | 45.10 | 51.00 | 29.40 | 25.90 | 19.20 | 14.30 | 32.50 | 9.40 | 15.70 | 30.10 | 26.10 | 22.90 | 21.40 | 28.10 | 23.10 | 260.80 | 261.20 | 151.80 |
| Pr | 12.27 | 3.28 | 4.70 | 3.90 | 2.08 | 2.44 | 1.45 | 1.26 | 2.40 | 0.96 | 1.47 | 3.10 | 2.70 | 1.97 | 1.80 | 2.70 | 2.20 | 26.45 | 27.69 | 16.50 |
| Nd | 51.50 | 10.80 | 11.80 | 14.10 | 7.50 | 9.60 | 5.40 | 4.80 | 8.20 | 4.00 | 5.50 | 9.60 | 7.30 | 6.30 | 5.80 | 7.80 | 6.40 | 90.00 | 96.40 | 67.34 |
| Sm | 13.46 | 2.69 | 2.40 | 3.83 | 2.04 | 2.24 | 1.72 | 1.68 | 1.92 | 1.50 | 1.80 | 2.10 | 1.70 | 1.54 | 1.40 | 1.75 | 1.20 | 14.65 | 18.52 | 11.10 |
| Eu | 2.86 | 0.68 | 0.61 | 0.81 | 0.48 | 0.56 | 0.43 | 0.47 | 0.46 | 0.43 | 0.46 | 0.53 | 0.37 | 0.36 | 0.28 | 0.41 | 0.32 | 2.43 | 3.21 | 2.49 |
| Gd | 14.87 | 4.24 | 3.20 | 4.94 | 3.06 | 4.02 | 3.14 | 3.78 | 3.31 | 3.09 | 3.28 | 3.10 | 2.20 | 2.33 | 1.90 | 2.20 | 1.64 | 10.83 | 16.84 | 11.10 |
| Tb | 2.11 | 1.00 | 0.75 | 1.04 | 0.73 | 1.00 | 0.79 | 0.99 | 0.79 | 0.75 | 0.80 | 0.71 | 0.63 | 0.55 | 0.43 | 0.52 | 0.40 | 1.76 | 2.85 | 1.80 |
| Dy | 11.84 | 7.33 | 4.80 | 7.79 | 5.53 | 8.06 | 6.00 | 7.93 | 6.31 | 6.10 | 6.46 | 5.30 | 4.30 | 4.20 | 3.30 | 3.90 | 3.30 | 11.23 | 18.57 | 14.20 |
| Ho | 2.41 | 1.63 | 1.45 | 1.78 | 1.26 | 1.95 | 1.44 | 1.92 | 1.55 | 1.45 | 1.58 | 1.30 | 1.14 | 1.05 | 1.01 | 1.08 | 0.90 | 2.40 | 4.08 | 3.20 |
| Er | 7.25 | 5.48 | 4.60 | 5.84 | 4.07 | 6.78 | 5.03 | 6.68 | 5.44 | 5.06 | 5.50 | 4.80 | 3.71 | 3.57 | 2.80 | 3.50 | 2.80 | 7.57 | 13.50 | 8.20 |
| Tm | 0.98 | 0.84 | 0.70 | 0.90 | 0.63 | 1.06 | 0.76 | 1.01 | 0.82 | 0.80 | 0.85 | 0.74 | 0.68 | 0.55 | 0.48 | 0.64 | 0.48 | 1.21 | 2.04 | 1.40 |
| Yb | 6.51 | 5.90 | 4.10 | 6.31 | 4.38 | 7.66 | 5.74 | 7.58 | 6.15 | 5.75 | 6.36 | 5.60 | 4.60 | 3.92 | 3.20 | 4.60 | 3.70 | 8.35 | 14.75 | 8.40 |
| Lu | 0.92 | 0.88 | 0.58 | 0.95 | 0.67 | 1.17 | 0.83 | 1.13 | 0.92 | 0.89 | 0.98 | 0.80 | 0.75 | 0.62 | 0.51 | 0.72 | 0.58 | 1.28 | 2.26 | 1.40 |
| LREE | 737.29 | 77.95 | 85.11 | 91.04 | 51.50 | 47.24 | 33.80 | 26.61 | 54.08 | 19.89 | 31.83 | 58.63 | 49.97 | 43.57 | 40.38 | 52.86 | 44.62 | 508.33 | 533.52 | 321.23 |
| HREE | 46.89 | 27.30 | 20.58 | 29.55 | 20.33 | 31.70 | 23.73 | 31.02 | 25.29 | 23.89 | 25.81 | 22.35 | 18.01 | 16.79 | 13.63 | 17.16 | 13.80 | 44.63 | 74.89 | 49.70 |
| REE | 784.18 | 105.25 | 105.69 | 120.59 | 71.83 | 78.94 | 57.53 | 57.63 | 79.37 | 43.78 | 57.64 | 80.98 | 67.98 | 60.36 | 54.01 | 70.02 | 58.42 | 552.96 | 608.41 | 370.93 |
| La/Y | 0.68 | 0.44 | 0.61 | 0.31 | 0.25 | 0.12 | 0.14 | 0.08 | 0.19 | 0.09 | 0.15 | 0.42 | 0.42 | 0.35 | 0.30 | 0.34 | 0.37 | 1.70 | 1.11 | 1.52 |
| (La/Yb)N | 5.29 | 2.24 | 3.46 | 1.91 | 1.58 | 0.59 | 0.68 | 0.37 | 0.97 | 0.43 | 0.75 | 1.63 | 1.78 | 1.85 | 2.10 | 1.82 | 2.13 | 9.45 | 5.94 | 5.93 |
| Sm/Nd | 0.26 | 0.25 | 0.20 | 0.27 | 0.27 | 0.23 | 0.32 | 0.35 | 0.23 | 0.38 | 0.33 | 0.22 | 0.23 | 0.24 | 0.24 | 0.22 | 0.19 | 0.16 | 0.19 | 0.16 |
| Ce/Ce* | 5.90 | 1.25 | 1.10 | 1.48 | 1.55 | 1.56 | 1.62 | 1.51 | 1.71 | 1.21 | 1.18 | 1.13 | 1.11 | 1.21 | 1.23 | 1.18 | 1.11 | 1.14 | 1.06 | 1.06 |
| Eu/Eu* | 0.61 | 0.61 | 0.67 | 0.57 | 0.58 | 0.57 | 0.56 | 0.57 | 0.55 | 0.61 | 0.57 | 0.63 | 0.58 | 0.58 | 0.52 | 0.63 | 0.69 | 0.59 | 0.55 | 0.68 |
| CaO | O | O | LOI | Ga | Nb | Nd | Gd | Cr | Zr | V | Ni | Sc | Co | |||||
| 1.00 | ||||||||||||||||||
| −0.51 | 1.00 | |||||||||||||||||
| −0.31 | −0.49 | 1.00 | ||||||||||||||||
| CaO | 0.11 | −0.39 | 0.36 | 1.00 | ||||||||||||||
| O | −0.18 | 0.44 | −0.38 | −0.07 | 1.00 | |||||||||||||
| O | 0.40 | −0.38 | −0.09 | 0.53 | 0.01 | 1.00 | ||||||||||||
| −0.26 | 0.72 | −0.59 | −0.46 | 0.25 | −0.27 | 1.00 | ||||||||||||
| LOI | −0.53 | 0.30 | −0.34 | −0.25 | 0.24 | −0.15 | 0.37 | 1.00 | ||||||||||
| Ga | −0.24 | 0.08 | −0.22 | −0.29 | 0.14 | 0.04 | 0.27 | 0.58 | 1.00 | |||||||||
| Nb | 0.31 | 0.11 | −0.57 | −0.29 | 0.01 | 0.03 | 0.63 | 0.18 | 0.41 | 1.00 | ||||||||
| Nd | 0.39 | −0.43 | −0.04 | 0.48 | −0.07 | 0.93 | −0.29 | −0.16 | 0.14 | 0.07 | 1.00 | |||||||
| Gd | 0.31 | −0.44 | 0.04 | 0.36 | −0.12 | 0.73 | −0.22 | −0.12 | 0.22 | 0.14 | 0.92 | 1.00 | ||||||
| Cr | 0.04 | 0.15 | −0.17 | −0.23 | −0.13 | −0.31 | 0.46 | 0.01 | 0.15 | 0.75 | −0.24 | −0.14 | 1.00 | |||||
| Zr | −0.07 | 0.26 | −0.37 | 0.16 | 0.28 | 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.25 | 0.13 | 0.20 | 0.40 | 0.33 | −0.24 | 1.00 | ||||
| V | −0.26 | 0.01 | 0.54 | 0.48 | −0.01 | −0.07 | −0.34 | −0.35 | −0.65 | −0.64 | −0.23 | −0.34 | −0.33 | −0.06 | 1.00 | |||
| Ni | 0.28 | −0.40 | 0.12 | 0.34 | −0.09 | 0.56 | −0.43 | −0.21 | 0.10 | −0.12 | 0.80 | 0.89 | −0.26 | 0.02 | −0.24 | 1.00 | ||
| Sc | −0.34 | −0.12 | 0.23 | 0.03 | 0.05 | 0.20 | 0.03 | 0.35 | 0.26 | −0.25 | 0.08 | 0.06 | −0.48 | 0.54 | 0.15 | −0.18 | 1.00 | |
| Co | 0.22 | −0.08 | −0.10 | 0.18 | −0.17 | 0.34 | −0.08 | −0.16 | 0.16 | 0.40 | 0.40 | 0.32 | 0.55 | −0.28 | −0.29 | 0.34 | −0.59 | 1.00 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Khubab, M.; Wagreich, M.; Mindszenty, A.; Iqbal, S.; Schöpfer, K.; Ullah, M. Parental Affinities and Environments of Bauxite Genesis in the Salt Range, Northwestern Himalayas, Pakistan. Minerals 2025, 15, 993. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15090993
Khubab M, Wagreich M, Mindszenty A, Iqbal S, Schöpfer K, Ullah M. Parental Affinities and Environments of Bauxite Genesis in the Salt Range, Northwestern Himalayas, Pakistan. Minerals. 2025; 15(9):993. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15090993
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhubab, Muhammad, Michael Wagreich, Andrea Mindszenty, Shahid Iqbal, Katerina Schöpfer, and Matee Ullah. 2025. "Parental Affinities and Environments of Bauxite Genesis in the Salt Range, Northwestern Himalayas, Pakistan" Minerals 15, no. 9: 993. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15090993
APA StyleKhubab, M., Wagreich, M., Mindszenty, A., Iqbal, S., Schöpfer, K., & Ullah, M. (2025). Parental Affinities and Environments of Bauxite Genesis in the Salt Range, Northwestern Himalayas, Pakistan. Minerals, 15(9), 993. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15090993









