Advances in Distribution Pattern and Enrichment Mechanism of Associated Cobalt Resources in Skarn-Type Deposits, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
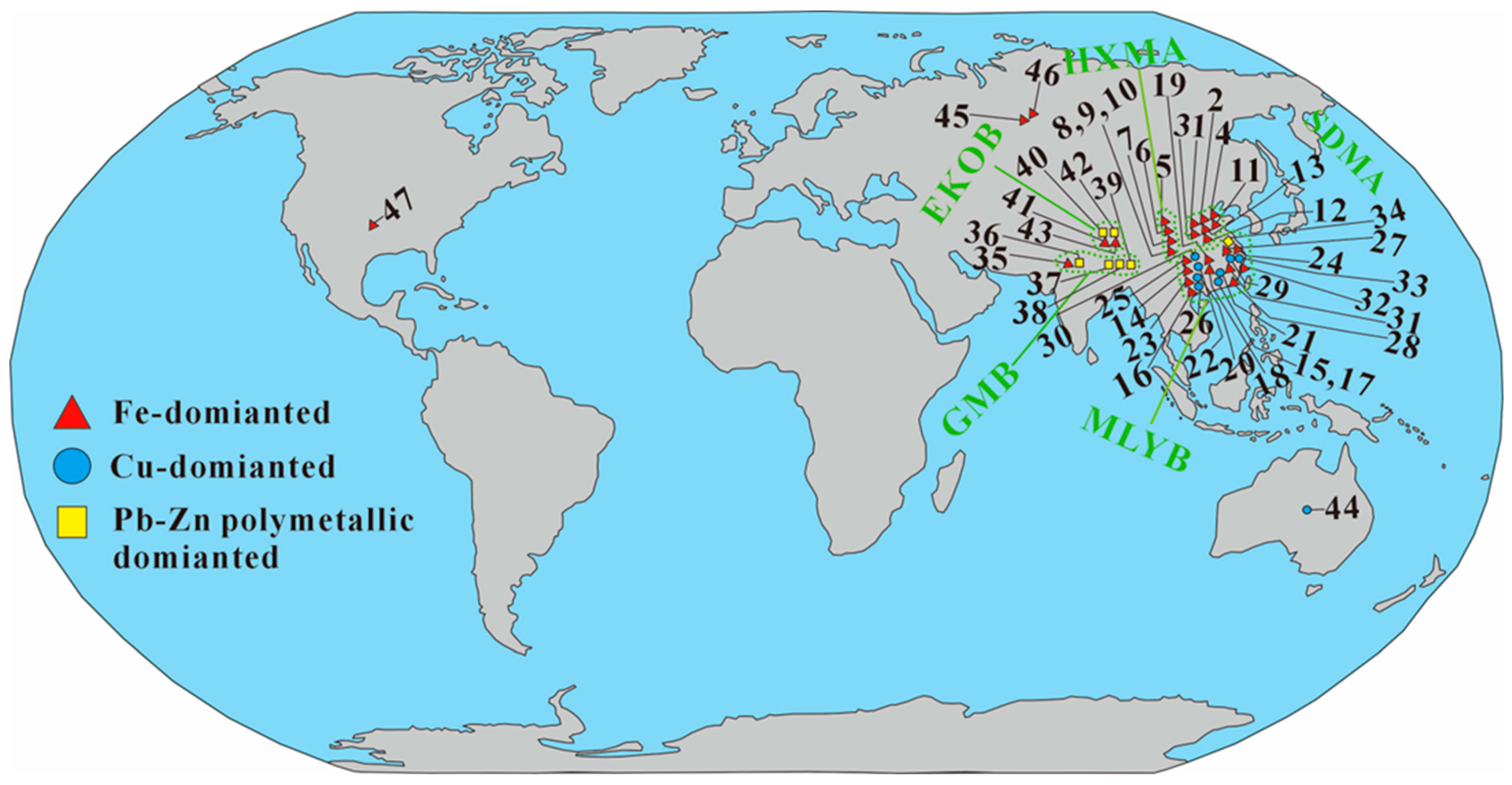
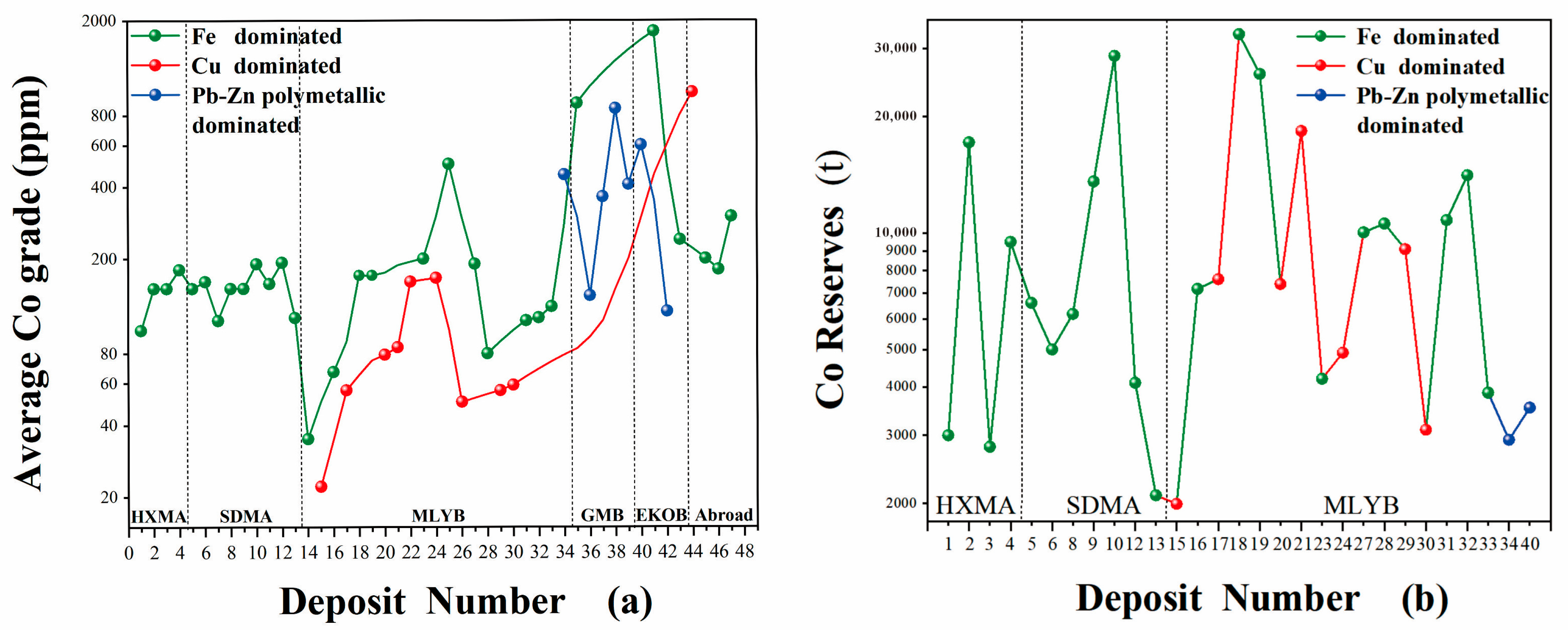
2. Grade and Reserves of Associated Cobalt Resources in Skarn-Type Deposits
2.1. Fe-Dominated Skarn-Type Cobalt Deposits
2.2. Cu-Dominated Skarn-Type Cobalt Deposits
2.3. Pb-Zn Polymetallic-Dominated Skarn-Type Cobalt Deposits
| No. | Name | Location | Type | Average Co Grade (ppm) | Co Reserves (t) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Henghui | Xingtai, Hebei Province, China | Fe | 100 | 3000 | [55] |
| 2 | Baijian | Xingtai, Hebei Province, China | Fe | 150 | 17,186 | [35] |
| 3 | Yushiwa | Handan, Hebei Province, China | Fe | 150 | 2800 | [33] |
| 4 | Zhongguan | Xingtai, Hebei Province, China | Fe | 180 | 9489 | [32,33] |
| 5 | Xishangzhuang | Laiwu, Shandong Province, China | Fe | 150 | 6600 | [33] |
| 6 | Gujiatai | Laiwu, Shandong Province, China | Fe | 160 | 5000 | [33] |
| 7 | Chuiyang | Laiwu, Shandong Province, China | Fe | 110 | —— | [38] |
| 8 | Zhangjiawa I Mining Area | Laiwu, Shandong Province, China | Fe | 150 | 6180 | [38] |
| 9 | Zhangjiawa II Mining Area | Laiwu, Shandong Province, China | Fe | 150 | 13,612 | [38] |
| 10 | Zhangjiawa III Mining Area | Laiwu, Shandong Province, China | Fe | 190 | 28,757 | [38] |
| 11 | Xinzhuang | Zibo, Shandong Province, China | Fe | 157 | —— | [56] |
| 12 | Jinzhao | Zibo, Shandong Province, China | Fe | 193 | 4100 | [33] |
| 13 | Houjiazhuang | Zibo, Shandong Province, China | Fe | 113 | 2100 | [33] |
| 14 | Tonglvshan Fe Ore | Daye, Hubei Province, China | Fe | 35 | —— | [57] |
| 15 | Wushan South Ore Zones | Ruichang, Jiangxi Province, China | Cu | 22 | 1995 | [44] |
| 16 | Jinshandian | Daye, Hubei Province, China | Fe | 67 | 7178 | [58] |
| 17 | Wushan North Ore Zones | Ruichang, Jiangxi Province, China | Cu | 56 | 7603 | [44] |
| 18 | Chengchao | Ezhou, Hubei Province, China | Fe | 170 | 32,717 | [59] |
| 19 | Tieshan | Huangshan, Hubei Province, China | Fe | 170 | 25,818 | [57] |
| 20 | Fengshandong | Huangshan, Hubei Province, China | Cu | 79 | 7384 | [60] |
| 21 | Chengmenshan | Jiujiang, Jiangxi Province, China | Cu | 85 | 18,382 | [22,47] |
| 22 | Xujiazu | Daye, Hubei Province, China | Cu | 160 | —— | [57] |
| 23 | Daguangshan | Daye, Hubei Province, China | Fe | 200 | 4200 | [33] |
| 24 | Anqing Cu Ore | Anqing, Anhui Province, China | Cu | 166 | 4905 | [43] |
| 25 | Zhangsizhu | Daye, Hubei Province, China | Fe | 500 | —— | [57] |
| 26 | Tonglvshan Cu Ore | Daye, Hubei Province, China | Cu | 50 | —— | [57] |
| 27 | Zhuchong | Anqing, Anhui Province, China | Fe | 190 | 10,045 | [61] |
| 28 | Baixiangshan | Maan, Anhui Province, China | Fe | 80 | 10,584 | [62] |
| 29 | Dongguashan | Tongling, Anhui Province, China | Cu | 56 | 9093 | [63] |
| 30 | Tongshankou | Daye, Hubei Province, China | Cu | 59 | 3099 | [64,65] |
| 31 | Longqiao | Hefei, Anhui Province, China | Fe | 110 | 10,810 | [19] |
| 32 | Xinqiao | Tongling, Anhui Province, China | Fe | 113 | 14,129 | [66,67] |
| 33 | Anqing Fe Ore | Anqing, Anhui Province, China | Fe | 126 | 3864 | [43] |
| 34 | Yaojialing | Wuhu, Anhui Province, China | Pb-Zn polymetallic | 450 | 2920 | [53] |
| 35 | Chunzhe | Rikeze, Xizang Province, China | Fe | 898 | —— | [68] |
| 36 | Pusangguo | Rikeze, Xizang Province, China | Pb-Zn polymetallic | 140 | —— | [20] |
| 37 | Bangpu | Lasa, Xizang Province, China | Pb-Zn polymetallic | 363 | —— | [68] |
| 38 | Jiama | Lasa, Xizang Province, China | Pb-Zn polymetallic | 853 | —— | [68] |
| 39 | Zhibula | Lasa, Xizang Province, China | Pb-Zn polymetallic | 410 | —— | [17] |
| 40 | Galinge | Geermu, Qinghai Province, China | Pb-Zn polymetallic | 600 | 3538 | [49] |
| 41 | Haisi | Dulan, Qinghai Province, China | Fe | 1800 | —— | [69] |
| 42 | Niukutou | Geermu, Qinghai Province, China | Pb-Zn polymetallic | 120 | —— | [70] |
| 43 | Zhanbuzhale IV Mining Area | Dulan, Qinghai Province, China | Fe | 240 | —— | [71] |
| 44 | Mount Elliott | Queensland, Australia | Cu | 1000 | —— | [48] |
| 45 | Goroblagodat | Middle Urals, Russia | Fe | 200 | —— | [15] |
| 46 | Magnitogorsk | Baimak-Buribai, Russia | Fe | 180 | —— | [42] |
| 47 | Cornwall | Pennsylvania, America | Fe | 300 | —— | [40] |
3. Distribution Patterns of Associated Cobalt Resources in Skarn-Type Deposits
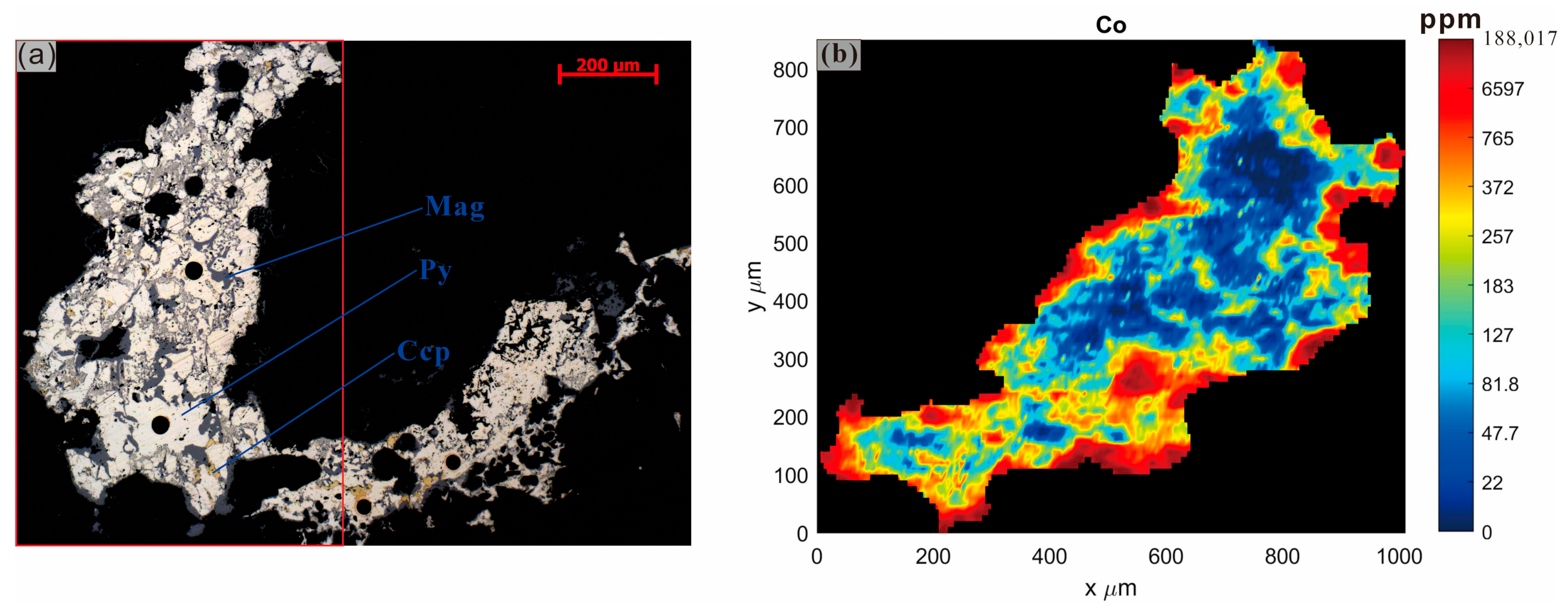
3.1. Distribution Patterns of Cobalt in Host Minerals
| Name | Type | Cobalt-Bearing Minerals | Main Cobalt-Bearing Minerals and the Average Content (ppm) | Independent Cobalt Minerals | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zhongguan | Fe | Pyrite, Magnetite, Pyrrhotite, Hematite | Pyrite (1750), Magnetite (42.8) | [34] | |
| Baijian | Fe | Pyrite, Magnetite | Pyrite (4251), Magnetite (47.6) | Cobaltite | [35] |
| Henghui | Fe | Pyrite | Pyrite (5233) | [55] | |
| Yushiwa | Fe | Pyrite, Magnetite | Pyrite (2800), Magnetite (320) | [75,81] | |
| Zhangjiawa | Fe | Pyrite | Pyrite (6300) | [38] | |
| Jinshandian | Fe | Pyrite, Magnetite | Pyrite (590), Magnetite (52) | [58] | |
| Baixiangshan | Fe | Pyrite, Magnetite | Pyrite (785), Magnetite (17) | [62] | |
| Chengchao | Fe | Pyrite, Magnetite | Pyrite (1550) | [57,59] | |
| Tieshan | Fe | Pyrite, Magnetite | Pyrite (1580), Magnetite (1046) | [57] | |
| Zhuchong | Fe | Pyrite, Magnetite, Pyrrhotite, Chalcopyrite | Pyrite (2138), Magnetite (72.1) | Grimmite | [43] |
| Longqiao | Fe | Pyrite, Magnetite | Pyrite (1115), Magnetite (30) | Cobaltite, Carrollite, Glaucodot | [19,82] |
| Goroblagodat | Fe | Pyrite | Pyrite (220) | [15] | |
| Cornwall | Fe | Pyrite | Pyrite (13,000) | [40] | |
| Peña Colorada | Fe | Pyrite | Pyrite (1200) | [83] | |
| Dongguashan | Cu | Pyrite, Magnetite, Chalcopyrite, Pyrrhotite | Pyrite (626) | Carrollite, Cobaltite, Glaucodot | [63] |
| Tongshankou | Cu | Pyrite, Chalcopyrite | Pyrite (629), Chalcopyrite (253) | [64,65] | |
| Fengshandong | Cu | Pyrite, Chalcopyrite | Pyrite (689) | [60] | |
| Anqing | Cu | Pyrite, Magnetite, Chalcopyrite, Pyrrhotite | Pyrite (1358), Chalcopyrite (260) | Siegenite | [43,77,78] |
| Chengmenshan | Cu | Pyrite, Chalcopyrite | Pyrite (790) | [47] | |
| Tonglvshan | Cu | Pyrite, Magnetite, Chalcopyrite, Bornite | Pyrite (1365), Chalcopyrite (500) | Carrollite, Cobaltite, Safflorite | [84] |
| Pusangguo | Pb-Zn polymetallic | Pyrite, Sphalerite, Chalcopyrite, Galena | Pyrite (490.9), Sphalerite (1102) | Cobaltite, Carrollite, Linnaeite | [20,85] |
| Niukutou | Pb-Zn polymetallic | Pyrite, Arsenopyrite, Pyrrhotite, Sphalerite, Chalcopyrite, | Pyrite (42.5), Sphalerite (230.7), Arsenopyrite (3755.9) | Cobaltite, Glaucodot | [70] |
| Yaojialing | Pb-Zn polymetallic | Pyrite, Sphalerite, Chalcopyrite | Pyrite (193.2), Sphalerite (733.9) | Carrollite | [53] |
| Lalingzaohuo | Pb-Zn polymetallic | Pyrite, Chalcopyrite, Pyrrhotite, Sphalerite | Pyrite (27,400), Sphalerite (8100) | Cobaltite | [18] |
| Zhibule | Pb-Zn polymetallic | Pyrite, Magnetite, Galena, Sphalerite | Pyrite (2454), Magnetite (228) | Siegenite | [17] |
| Galinge | Pb-Zn polymetallic | Pyrite, Arsenopyrite, Sphalerite, Pyrrhotite, Chalcopyrite | Pyrite (194), Sphalerite (471), Arsenopyrite (34,077) | Skutterudite, Cobaltite | [73] |
3.2. Distribution Patterns of Cobalt in Metallogenic Regions
| Metallogenic Region | Geotectonic Settings | Main Mineralization Ages of Deposits | Main Rock Types of Deposits | Magmatic Source | Main Types of Deposits | Typical Deposits | Distribution Patterns of Co Resources | Influencing Factors | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Han–Xing Mining Area in China | Subduction of the Paleo-Siberian, Yangtze, and Pacific Plates | 135–125 Ma | Diorite, Monzonite, Monzodiorite | Predominantly mantle-derived with minor crustal or mixed crust-mantle sources | Fe | Baijian, Henghui, Zhongguan | High Co grade and abundant Co reserves | Multi-stage magmatic activities, relatively developed fault structures, ordovician carbonate strata | [12,21,34,35,55,88] |
| Gangdese Metallogenic Belt in China | Subduction of the Neo-Tethyan oceanic crust | 65–41 Ma and 33–13 Ma | Granodiorite, Quartz Mozonite, Monzogranite | Predominantly mantle-derived with minor mixed crust-mantle sources | Pb-Zn polymetallic | Jiama, Zhibula | East segment Co-enriched, west segment Co-poor | Eastern Co-enriched deposits with adakitic ore-forming intrusions, young mineralization age, and intense magmatic activity | [23,68,93,94,103] |
| East Kunlun Metallogenic Belt in China | Collision between the Bayan Har or Qiangtang terrane and the Qaidam Basin | 237–212 Ma | Granodiorite, Monzogranite | Mantle-derived, mixed crust-mantle sources | Pb-Zn polymetallic | Galinge, Niukutou | Significant variation in Co grade | “Trench–island arc–back arc basin” tectonic system, intense magmatic activity | [49,69,70,111,112,113,114,115,118,119] |
| Middle-Lower Yangtze Metallogenic Belt in China | Subduction and collision of the Yangtze and North China blocks | 145–127 Ma | Granodiorite, Diorite, Quartz diorite | Mantle-derived, mixed crust-mantle sources | Fe, Cu | Zhuchong, Anqing | Extremely abundant Co reserves | ———— | [19,22,43,54,120,121,122,123] |
| Cornwall mining district in America | Variscan orogeny | 295–270 Ma | Granite | ———— | Fe | Cornwall | Relatively high Co grade | ———— | [39,41,125] |
| Cloncurry mining district (Mount Isa Eastern Fold Belt) in Australia | Late tectonism | 1510 Ma | Granite | ———— | Cu | Mount Elliott | Extremely high Co grade | ———— | [48] |
| Magnitogorsk zone in Russia | Island arc | Late-Devonian to Early Carboniferous | Gabbroid | Mantle-derived | Fe | Magnitogorsk | Relatively high Co grade | ———— | [126,127,128] |
3.3. Distribution Patterns of Cobalt in Metallogenic Process
4. Enrichment Mechanism of Associated Cobalt Resources in Skarn-Type Deposits
4.1. Magmatic Source
| Controlling Factors | Specific Mechanisms | Representative Examples | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mantle-derived magma sources | High Co content in mantle-derived magmas provides the additional Co source | Handan–Xingtai Ming Area, Gangdese Metallogenic Belt | [23,151,152,153,154] |
| Mafic magma injection | Inherited high Co content from mantle-derived magmas and mixed with felsic magmas | Baijian deposit, Henghui deposit | [21,55,110] |
| Assimilation of evaporite sequences | Extensive assimilation of evaporite sequences with magmatic–hydrothermal fluids alter fluid composition and metallogenic environment | Baijian deposit, Zhuchong deposit | [35,54] |
| Dissolution and re-precipitation mechanism of hydrothermal fluids | Enhanced activity of late-stage hydrothermal fluids drives the reprecipitation and enrichment of Co | Henghui deposit, Zhongguan deposit, Baijian deposit | [35,55] |
4.2. Injection of Mafic Magmas
4.3. Assimilation of Evaporite Sequences
4.4. Dissolution–Reprecipitation Mechanism of Hydrothermal Fluids
5. Exploration Strategy of Associated Cobalt Recourses in Skarn-Type Deposits
6. Conclusions
- Fe-dominated skarn-type cobalt deposits are characterized by a widespread distribution, high Co grades, and abundant reserves, exhibiting significantly superior cobalt resource potential compared to Cu-dominated or Pb-Zn polymetallic-dominated skarn-type deposits.
- In skarn-type cobalt deposits, cobalt mainly occurs in sulfide minerals, particularly pyrite, while independent cobalt minerals occur only in specific deposits.
- Associated cobalt resources in skarn-type deposits are observed to exhibit regionally zonal distribution features.
- Associated cobalt resources in skarn-type deposits are characterized by stage-specific differential enrichment, with effective enrichment particularly exhibited during the sulfide stage.
- Mantle-derived magmas provide additional cobalt sources for enrichment in associated skarn-type cobalt deposits.
- The injection of mafic magmas creates favorable conditions for cobalt enrichment in skarn-type cobalt deposits.
- The assimilation of evaporite sequences alters hydrothermal fluid composition, thereby affecting cobalt enrichment in skarn-type cobalt deposits.
- The dissolution–reprecipitation mechanism of hydrothermal fluids drives the secondary enrichment of cobalt in skarn-type cobalt deposits, significantly contributing to cobalt enrichment.
- The formation of skarn-type cobalt deposits is a complex process. Mantle-derived magmatic sources represent the primary condition for mineralization, while the injection of mafic magmas and the dissolution–reprecipitation mechanism of hydrothermal fluids play crucial roles in promoting cobalt enrichment.
- Cobalt exploration should emphasize mantle-derived magmatic rocks (primarily mafic-intermediate lithologies) in convergent plate tectonic settings such as subduction or collision zones.
- Given the multiple factors influencing cobalt enrichment, multidimensional data analysis under AI-aided frameworks will significantly enhance cobalt exploration efficiency.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hitzman, M.W.; Bookstrom, A.A.; Slack, J.F.; Zientek, M.L. Cobalt-Styles of Deposits and the Search for Primary Deposits; Open-File Report 2017-1155; U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2017; p. 47.
- Zhang, H.R.; Hou, Z.Q.; Yang, Z.M.; Song, Y.C.; Liu, Y.C.; Chai, P. A new division of genetic types of cobalt deposits: Implications for Tethyan cobalt-rich belt. Miner. Depos. 2020, 39, 501–510. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, J.; Xu, G.; Tang, Z.L.; Yan, H.Q.; Liu, J.Q.; Chen, Y.Y.; Liu, Q. Analysis of development of China’s cobalt industry: Current status, problems and countermeasures. Eng. Sci. 2024, 26, 98–107. [Google Scholar]
- European Commission. Report on Critical Raw Materials for the EU; Report of the Ad Hoc Working Group on Defining Critical Raw Materials; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2014; p. 41. [Google Scholar]
- European Commission. Study on the Review of the List of Critical Raw Materials; Report of the Ad Hoc Working Group on Defining Critical Raw Materials; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2017; p. 93. [Google Scholar]
- Schulz, K.J.; DeYoung, J.H.; Seal, R.R.; Bradley, D.C. (Eds.) Critical Mineral Resources of the United States—Economic and Environmental Geology and Prospects for Future Supply; U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2017.
- Li, P.; He, L.; Liang, T. Geochemical behavior, genetic type, resource distribution, and research prospects of the cobalt deposits. Xinjiang Geol. 2023, 41, 210–217. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Feng, C.Y.; Zhang, M.Y. Characteristics of global cobalt resources and research progress in exploration. Miner. Depos. 2019, 38, 739–750. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.B.; Ye, J.H.; Chen, X.F.; Li, N.; He, X.Y.; Chen, X.F.; Liu, Y.F. Global cobalt resource distribution and exploration potential. Resour. Ind. 2018, 20, 56–61. [Google Scholar]
- Roberts, S.; Gunn, G. Cobalt. In Critical Metals Handbook; Gunn, G., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Oxford, UK, 2014; pp. 122–149. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, C.G. Always the bridesmaid, never the bride: Cobalt geology and resources. Appl. Earth Sci. 2001, 110, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, G. Formation mechanism and key controlling factors of skarn-type rich iron deposits in Han-Xing area. China Univ. Geosci. 2017, 1–227. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, J. Geological characteristics and prospecting indicators of Zhuchong skarn iron-copper deposit in Anqing-Guichi ore concentration area, Anhui. Anhui Geol. 2023, 33, 113–115, 185. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, J.X.; Li, G.M.; Qin, K.Z.; Tang, D.M. A review of the types and ore mechanism of the cobalt deposits. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2019, 64, 2484–2500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slack, J.F.; Kimball, B.E.; Sheed, K.B. Cobalt. No. 1802-F; US Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2017.
- Wang, F.; Guo, Y.; Yan, H.; Gu, H.; Sun, H.; Ge, C. Geochronology and geochemistry of the W-Mo-ore-related granitic rocks from eastern Ningzhen, lower Yangtze river belt, eastern China. Acta Geochim. 2022, 41, 288–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Cao, M.; Li, G.; Evans, N.J.; Silang, W.; Qin, K. Tracing the genesis of the Zhibula skarn deposit, Tibet, using Co, Te, Au and Ag occurrence. Ore Geol. Rev. 2023, 160, 105601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wu, H.; Niu, X.; Niu, S.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, Z. Geology and geochronology of the Lalingzaohuo cobalt-bearing copper polymetallic skarn deposit, East Kunlun. Ore Geol. Rev. 2023, 154, 105349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Fan, Y.; Liu, Y. The occurrence and spatial distribution of cobalt in Longqiao iron deposit in Luzong Basin, Anhui Province. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2021, 37, 2778–2796. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Cao, M.; Li, G.; Silang, W.; Shan, P.; Qin, K. The occurrence of cobalt and implications for genesis of the Pusangguo cobalt-rich skarn deposit in Gangdese, Tibet. Ore Geol. Rev. 2022, 150, 105193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, C. Study on occurrence state and enrichment mechanism of associated cobalt in Han-xing type iron deposits. Hebei GEO Univ. 2022, 1–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Zhou, T.F.; Fan, Y.; Zhang, Y.F.; Yan, L.; Liang, X. Resource status and comprehensive utilization potential evaluation of associated cobalt in the Middle-Lower Yangtze River Metallogenic Belt. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2023, 39, 1144–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Cao, M.J.; Shan, P.F. Study on cobalt enrichment and genesis of the (porphyry-) skarn deposits in Gangdese metallogenic belt, Tibet. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2025, 41, 492–509. [Google Scholar]
- Meinert, L.D.; Dipple, G.M.; Nicolescu, S. World skarn deposits. Econ. Geol. 2005, 100, 299–336. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, T.F.; Fan, Y. Enrichment mechanisms, mineral exploration, and comprehensive utilization of critical metals: Preface. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2021, 37, 2599–2603. [Google Scholar]
- GB/T 25283-2023; Specification for Comprehensive Exploration and Evaluation of Mineral Resources. Ministry of Land and Resources: Beijing, China, 2023.
- Tretiakova, I.G.; Borisenko, A.S.; Lebedev, V.I.; Pavlova, G.G.; Goverdovsky, V.A.; Travin, A.V. Cobalt mineralization in the Altai-Sayan orogen: Age and correlation with magmatism. Russ. Geol. Geophys. 2010, 51, 1078–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebedev, V.I.; Lebedeva, M.F. Cobalt mineralization of Tuva, South-East Altai and North-West Mongolia. Int. Multidiscip. Sci. Geo. Conf. Surv. Geol. Min. Ecol. Manag. 2013, 2, 567–571. [Google Scholar]
- Nagashima, M.; Akasaka, M.; Morifuku, Y. Ore and skarn mineralogy of the Yamato mine, Yamaguchi prefecture, Japan, with emphasis on silver-, bismuth-, cobalt-, and tin-bearing sulfides. Resour. Geol. 2016, 66, 37–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nimis, P.; Dalla Costa, L.; Guastoni, A. Cobaltite-rich mineralization in the iron skarn deposit of Traversella (Western Alps, Italy). Mineral. Mag. 2014, 78, 11–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, N.J.; Ciobanu, C.L. Paragenesis of Cu-Fe ores from Ocna de Fier-Dognecea (Romania), typifying fluid plume mineralization in a proximal skarn setting. Mineral. Mag. 2001, 65, 351–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, A.M.; Wang, S.G. Experimental study on cobalt recovery from Zhongguan iron deposit. China New Technol. Prod. 2014, 32, 137. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, D.S.; Wang, X.Q.; Chen, Y.Y.; Zhang, B.M.; Zhou, J.; Liu, H.L.; Wang, W.; Nie, L.S.; Chi, Q.H. Cobalt distribution and its relationship with bedrocks and cobalt mineralizations in China. Ore Geol. Rev. 2024, 167, 105992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.Y.; Cao, C.; Wang, S.Z.; Cao, Q.; Dong, B.X.; Li, Y.; Dong, G.Y.; Wang, L. Distribution patterns and precipitation mechanisms of cobalt in Zhongguan skarn iron deposit, Hebei: Implications for mineralization. Geol. Explor. 2024, 60, 244–264. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, X.; Wang, F.Y.; Zhang, J.Q.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, T.F.; Fan, Y.; Qin, C.; Zhang, J.W. Enrichment of cobalt at Baijian skarn Fe–Co deposit in the Handan—Xingtai region, North China Craton: Insights from mineral trace elements and pyrite sulfur isotopes. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2024, 273, 106265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.F.; Fan, Y.; Chen, J.; Liu, L.H.; Li, M.M. Establishment of a research workflow for occurrence state of critical metal in ore concentrate power: A case study of the cobalt-rich sulfide ore concentrate from the Middle-Lower Yangtze River Valley Metallogenic Belt, China. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2021, 37, 2791–2804. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, Z. The Mineralization and Mechanism of the Iron Skarn Deposits in Laiwu District, Shandong Province. China Univ. Geosci. 2019, 1–148. [Google Scholar]
- Zong, X.D.; Li, W.; Wang, J.; Qiao, W.; Zhang, J.F.; Liu, J.T. Study on rich iron ore for martin steel and the by-products of Cu and Co in Zhangjiawa iron deposit of Shandong province. Contrib. Geol. Miner. Resour. Res. 2012, 27, 60–65. [Google Scholar]
- Rollinson, G.; Le Boutillier, N.; Selley, R. Cobalt mineralisation in Cornwall—A new discovery at Porthtowan. Proc. Ussher Soc. 2018, 14, 176–187. [Google Scholar]
- Meinert, L.D. Skarns and Skarn Deposits. Geosci. Can. 1992, 19, 145–162. [Google Scholar]
- Robinson, G.P., Jr. Magnetite skarn deposits of the Cornwall (Pennsylvania)type—A potential cobalt, gold, and silver resource. In Proceedings of the Second U.S. Geological Survey Workshop on the Early Mesozoic Basins of the Eastern United States, Reston, VA, USA, 11–14 May 1985; Volume 946, pp. 126–128. [Google Scholar]
- Herrington, R.J.; Zaykov, V.V.; Maslennikov, V.V.; Brown, D.; Puchkov, V.N. Mineral Deposits of the Urals and Links to Geodynamic Evolution. In Economic Geology, One Hundredth Anniversary Volume; Society of Economic Geologists: Littleton, CO, USA, 2005; pp. 1069–1095. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, Z.H.; Wang, S.W.; Zhou, T.F.; Wang, B.; Wu, S.; Shu, Y. Study on the occurrence, distribution and enrichment of cobalt in Anqing copper-iron deposit, Anhui Province. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2024, 40, 629–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.Q.; Zhou, T.F.; Wang, B.; Liu, X.; Peng, K. Distribution, occurrence and enrichment mechanism of key metals of selenium, tellurium and cobalt in Wushan copper deposit, Jiurui ore concentration area, Jiangxi Province. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2023, 39, 3121–3138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.M.; Lu, J.J.; Zhang, R.Q.; Xu, Z.W. Textural characteristics of pyrrhotite ore and their genetic significance in the Dongguashan deposit, Tongling, Anhui. Miner. Depos. 2010, 29, 405–414. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, J.W.; Peng, X.L. Microscopic Identification Manual for Metallic Minerals; Geological Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2010; pp. 1–320. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, J.A.; Yang, G.C. Geological characteristics and genesis of the Chengmenshan copper deposit, Jiangxi Province. Miner. Resour. Geol. 2007, 21, 284–288. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.Q.; Williams, P.J. Geochemistry and origin of Proterozoic skarns at the Mount Elliott Cu-Au(-Co-Ni) deposit, Cloncurry district, NW Queensland, Australia. Mineral. Depos. 2001, 36, 109–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, D.X. Study on Occurrence State and Enrichment Mechanism of Cobalt in the Galinge Iron Polymetallic Deposit, East Kunlun Mountains, Qinghai Province. Ph.D. Dissertation, Yunnan University, Kunming, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.L.; Li, Z.Q.; Zhang, C.J.; Hu, T.; Zhang, Z.Z. Discussion on the genesis of the Pusangguo lead-zinc deposit, Tibet. Yunnan Geol. 2011, 30, 122–126. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Lang, X.H.; Zhang, Q.Z.; He, L. Petrogenesis and geodynamic setting of intermediate-acidic rocks in the Pusangguo copper polymetallic deposit, Tibet: Constraints from geochronology, geochemistry and Sr-Nd-Pb-Hf isotopes. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2019, 35, 737–759. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, S.G. Exploration on the metallogenic model of the Yaojialing deposit. World Nonferrous Met. 2020, 2, 81–82. [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, Y.; Zhou, T.; Fan, Y.; Chen, J.; Wang, B.; Liu, J.; Wang, F. Enrichment mechanisms and occurrence regularity of critical minerals resources in the Yaojialing Zn skarn polymetallic deposit, Tongling district, eastern China. Ore Geol. Rev. 2022, 144, 104822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Wang, F.Y.; Zhou, T.F.; Wei, C.; Zhang, L.; Guo, X.; Zhang, K. Metallogenic mechanism of cobalt in the Zhuchong cobalt-rich skarn iron deposit in the Middle-Lower Yangtze River Valley Metallogenic Belt: Constrained by in-situ sulfur isotopes and zircon U-Pb dating. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2023, 39, 3015–3030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, R.; Hu, J.; Wang, S.G.; Yu, D.S.; Guo, R.T.; Yan, Q.H.; Gao, S.P.; Guo, W.M. Mineralogy and geochemistry of the pyrite from the Henghui skarn iron deposit in central North China craton: Insights into cobalt mineralization. Ore Geol. Rev. 2024, 168, 106053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.T.; Hu, Z.G.; Mei, Z.H.; Wang, X.W.; Wei, Z.Y.; Zheng, Y.Y.; Zhao, X.B.; Chen, L.; Hu, C.Y. Geological and geophysical characteristics and deep prospecting prediction of Xinzhuang iron deposit in Jinling area, Zibo, Shandong. Geol. Rev 2022, 68, 2259–2268. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, K.T.; Xu, J.Y.; Wu, C.X.; Liu, D.Q.; Yan, F. Discussion on the current status and comprehensive utilization prospects of cobalt resources in ore-concentrated area of Southeast Hubei. Resour. Environ. Eng. 2021, 35, 777–781. [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, Q. Geological and Geochemical Characteristics and Fluid Inclusion Study of the Jinshandian Iron Deposit in Southeast Hubei Province. Master’s Thesis, Yangtze University, Jingzhou, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W. Discussion on the Formation-Mechanism of Chengchao Iron Skarn Deposit, Southeast Hubei Province. Ph.D. Dissertation, China University of Geosciences, Beijing, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, J.R.; Chen, S.Y.; Zhao, S.L.; Cheng, Q.F. Geochemical characteristics and magmatic evolution processes of intrusive rock bodies in the Fengcheng-Ruichang-Jiujiang area. Bull. Nanjing Inst. Geol. Miner. Res 1985, 6, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, X.; Wang, F.Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, J.W.; Wei, C.S.; Fan, Y.; Guo, X.Z.; Zhou, T.F.; Zhang, J.Q.; Lü, Q.T. Cobalt distribution and enrichment in skarn iron deposits: A case study of the Zhuchong skarn iron deposit, Eastern China. Ore Geol. Rev. 2023, 163, 105778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di, S.W. Geological and Geochemical Characteristics and Genesis of the Baixiangshan Iron Deposit in the Ningwu Basin. Master’s Thesis, Hefei University of Technology, Hefei, China, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, S. Metallogenic Geological Characteristics and Mineralization Regularity of the Dongguashan Copper Deposit in Tongling, Anhui Province. Master’s Thesis, Central South University, Changsha, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, K.D. Discussion on diagenetic and metallogenic evolution mechanism of the Tongshankou copper deposit. Geol. Explor. 1994, 5, 7–13. [Google Scholar]
- Hubei Geological Survey. Resource reserve verification report for the Tongshankou copper mine verification area, Daye City, Hubei Province. Geol. Surv. Rep. 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, H. Geological Characteristics and Genesis of the Xinqiao Copper-Iron-Sulfur Deposit in Tongling, Anhui Province. Master’s Thesis, China University of Geosciences, Beijing, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Hua Dong Bureau of Metallurgical Geology and Exploration. Resource reserve utilization status verification report for the Xinqiao copper-iron-sulfur deposit verification area, Tongling County, Anhui Province. Geol. Surv. Rep. 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Xu, Y.; Shan, P.F.; Silang, W.D.; Li, G.M.; Cao, M.J. Occurrence state and enrichment characteristics of cobalt in skarn deposits of the Gangdese Metallogenic Belt, Tibet. Acta Geol. Sin. 2024, 98, 163–180. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, J.X.; Zeng, X.G.; Fang, G.; Luo, M.; Fan, L.K. Geological characteristics of cobalt deposits in east part of East Kunlun and its potential. Miner. Resour. Geol. 2006, 20, 4. [Google Scholar]
- Che, Y.Y.; Su, H.M.; Liu, T.; Li, H.; He, S.Y. The occurrence and enrichment of cobalt in skarn Pb-Zn deposits: A case study of the Niukutou Co-rich deposit, East Kunlun metallogenic belt, western China. Ore Geol. Rev. 2024, 172, 106210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.C.; Liu, H.C. Geological characteristics and preliminary discussion on genesis of the Zhanbuzhale iron deposit, Qinghai. Min. Technol. 2005, 5, 2. [Google Scholar]
- Nadoll, P.; Angerer, T.; Mauk, J.L.; French, D.; Walshe, J. The chemistry of hydrothermal magnetite: A review. Ore Geol. Rev. 2014, 61, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Jiang, S.Y.; Cao, S.; Wang, W.; Su, H.M.; Yang, D.; Li, H.; He, S. Cobalt enrichment and metallogenic mechanism of the Galinge skarn iron deposit in the Eastern Kunlun metallogenic belt, western China. Ore Geol. Rev. 2024, 170, 106147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, G.; Deng, X.D.; Zhou, R.J.; Duan, Z.; Cui, B.Z.; Li, J.W. Geology, geochronology and stable isotope studies at the Baijian Fe-(Co) skarn deposit, eastern China, with implications for ore genesis and regional Fe skarn metallogeny. Ore Geol. Rev. 2024, 166, 105935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.Y. Geochemical characteristics of co-occurring cobalt in skarn iron (copper) deposits in China. Geol. Explor. 1979, 23, 24–29. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.F.; Fan, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, T.F.; Ou, B.G. Distribution and enrichment processes of cobalt in the Longqiao iron skarn deposit in Eastern China. Ore Geol. Rev. 2024, 174, 106277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, W.S. Characteristics and Genesis of the Anqing Copper-Iron Deposit, Anhui Province. Master’s Thesis, China University of Geosciences, Beijing, China, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.Q. Genesis and Metallogenic Regularity of the Anqing Copper-Iron Deposit, Anhui Province. Master’s Thesis, Central South University, Changsha, China, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Rezazadeh, S.; Hosseinzadeh, M.R.; Raith, J.G.; Moayyed, M. Mineral Chemistry and Phase Relations of Co-Ni Arsenides and Sulfarsenides from the Baycheh-Bagh Deposit, Zanjan Province, Iran. Ore Geol. Rev. 2020, 127, 103836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Qi, C.M. The Occurrence State of Cobalt and Its Significance in Prospecting and Resource Assessment. J. Chang. Univ. Sci. Technol. 2001, 31, 217–218. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, P.G.; Long, Y.Z.; Li, P.Z. Occurrence state and comprehensive utilization of associated cobalt in Yushiwai iron deposit. Hunan Geol. 2000, 19, 54–57. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, C. Geological and Geochemical Characteristics and Genesis of Longqiao Iron Deposit in Luzong Basin, Anhui Province. Hefei Technol. Univ. 2009, 1–120. [Google Scholar]
- Zuicher, L.; Ruiz, J.; Barton, M.D. Paragenesis, elemental distribution, and stable isotopes at the Peña Colorada iron skarn, Colima, Mexico. Econ. Geol. 2001, 96, 535–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.B. Geochemical Characteristics and Genesis of Tonglushan Cu-Fe Deposit in Hubei Province. China Univ. Geosci. 2012, 1–110. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Tan, H.; Zhao, F.; Xiang, Z.; Wu, H.; Zhang, P. Sphalerite and Pyrite Geochemistry from the Pusangguo Co-Rich Cu–Zn–Pb Skarn Deposit, Tibet: Implications for Element Occurrence and Mineralization. Minerals 2023, 13, 1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.M.; Mao, J.W.; Chen, M.H.; Li, G.D.; Ban, C.Y. Geological characteristics and metallogenic model of skarn iron deposits in the Handan-Xingtai area, southern Hebei, China. Geol. Bull. China 2007, 26, 150–154. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.M. Ore-controlling structural factors of Handan-Xingtai type iron deposits. Geol. Explor. 1986, 22, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, L.L.; Lu, J.; Zhang, J.Q.; Jin, Y.N.; Bai, F.S.; Tang, Y.Y.; Qin, C. The zoning and its geological significance of texture of amphibole from the Qicun porphyritic quartz monzonite in the southern Hebei. Bull. Mineral. Petrol. Geochem. 2021, 40, 903–913. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, K.Z.; Xia, D.X.; Li, G.M.; Duo, J.; Jiang, G.W.; Zhao, J.X. Qulong Porphyry-Skarn Cu-Mo Deposit. Sci. Press. 2014, 1–316. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, Z.Q.; Cook, N.J.; Zaw, K. Metallogenesis of the Tibetan Collisional Orogen: A Review and Introduction to the Special Issue. Ore Geol. Rev. 2009, 36, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.-C.; Zhao, Z.-D.; Niu, Y.; Mo, X.-X.; Chung, S.-L.; Hou, Z.-Q.; Wang, L.-Q.; Wu, F.-Y. The Lhasa Terrane: Record of a Microcontinent and Its Histories of Drift and Growth. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2011, 301, 241–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Zhu, D.-C.; Wang, Q.; Hou, Z.-Q.; Yang, Z.-M.; Zhao, Z.-D.; Mo, X.-X. Porphyry Mineralization in the Tethyan Orogen. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2020, 63, 2042–2067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, A.; Harrison, T.M. Geologic evolution of the Himalayan-Tibetan orogen. Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 2000, 28, 211–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.B.; Chen, Y.C.; Tang, J.X.; Chang, Z.S.; Wang, X.W.; Ying, L.J.; Li, F.J.; Wang, H.; Tang, X.Q. Discovery of tubular ore body in Jiama ore district, Tibet and its geological significance. Miner. Depos. 2011, 30, 12. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, W.Q.; Wu, F.Y.; Chung, S.L.; Li, J.X.; Liu, C.Z. Zircon U-Pb geochronology and Hf isotopic constraints on petrogenesis of the Gangdese batholith, southern Tibet. Chem. Geol. 2009, 262, 229–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, W.Q.; Wu, F.Y.; Liu, C.Z.; Chung, S.L. Geochronology and petrogenesis of granitic rocks in Gangdese batholith, southern Tibet. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2009, 52, 1240–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.T.A.; Luffi, P.; Chin, E.J.; Bouchet, R.; Dasgupta, R.; Morton, D.M.; Le Roux, V.; Yin, Q.Z.; Jin, D. Copper systematics in arc magmas and implications for crust-mantle differentiation. Science 2012, 336, 64–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, D.C.; Zhao, Z.D.; Pan, G.T.; Lee, H.Y.; Kang, Z.Q.; Liao, Z.L.; Wang, L.Q.; Li, G.M.; Dong, G.C.; Liu, B. Early Cretaceous subduction-related adakite-like rocks of the Gangdese belt, southern Tibet: Products of slab melting and subsequent melt-peridotite interaction? J. Asian Earth Sci. 2009, 34, 298–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Z.Q.; Xu, J.F.; Wilde, S.A.; Feng, Z.H.; Chen, J.L.; Wang, B.D.; Fu, W.C.; Pan, H.B. Geochronology and geochemistry of the Sangri Group volcanic rocks, southern Lhasa Terrane: Implications for the early subduction history of the Neo-Tethys and Gangdese magmatic arc. Lithos 2014, 200–201, 157–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.X.; Xu, Z.Q.; Meert, J.G. Eocene slab breakoff of Neotethys as suggested by dioritic dykes in the Gangdese magmatic belt, southern Tibet. Lithos 2016, 248–251, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, K. Study on Geological and Geochemical Characeristics and Genesis of Bangbule Pb-Zn-Cu-Fe Deposit, Western Gangdese, Tibet. Ph.D. Thesis, China University of Geosciences, Wuhan, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, S.B.; Zheng, Y.Y.; Tian, L.M.; Zhang, Z.; Qu, W.J.; Liu, M.Y.; Zheng, H.T.; Zheng, L.; Zhu, J.H. Geochronology of magmatic intrusions and mineralization of Chagele Copper-Lead-Zinc Deposit in Tibet and its implications. Earth Sci. China Univ. Geosci. 2012, 37, 507–514. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, F.W.; Lang, X.H.; Tang, J.X.; He, Q.; Deng, Y.L.; Wang, X.H.; Wang, Y. Metallogenic Regularity of Gangdese Metallogenic Belt, Tibet. Miner. Depos. 2022, 41, 952–974. [Google Scholar]
- Li, G.M.; Liu, B.; Qu, W.J.; Lin, F.C.; She, H.Q.; Feng, C.Y. The Porphyry-Skarn Metallogenic System in the Gangdese Metallogenic Belt, Tibet: Re-Os Isotopic Age Evidence from Porphyry and Skarn-Type Cu Polymetallic Deposits. Geotecton. Met. 2005, 29, 60–68. [Google Scholar]
- Qu, T.; He, R.Z.; Yu, P.L.; Wang, S.F.; Chen, X.L.; Liu, J.L. Statistics and Application of Rock Physical Properties in Jiama Mining Area, Tibet. Geophys. Geochem. Explor. 2021, 45, 661–668. [Google Scholar]
- Shu, Q.H.; Deng, J.; Chang, Z.S.; Wang, Q.F.; Niu, X.D.; Xing, K.; Sun, X.; Zhang, Z.K.; Zeng, Q.W.; Zhao, H.S.; et al. Skarn Zonation of the Giant Jiama Cu-Mo-Au Deposit in Southern Tibet, SW China. Econ. Geol. 2024, 119, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Qin, K.Z.; Li, G.M.; Li, J.X.; Xiao, B.; Jiang, H.Z.; Zhao, J.X.; Fan, X.; Jiang, S.Y. Geological Characteristics and Skarn Mineralogy of the Nuri Cu-W-Mo Deposit in the Southern Margin of Gangdese, Tibet. Mineral. Depos. 2012, 31, 417–437. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, K.J.; Zhang, Y.X.; Tang, X.C.; Xia, B. Late Mesozoic Tectonic Evolution and Growth of the Tibetan Plateau Prior to the Indo-Asian Collision. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2012, 114, 236–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, L.J.; Wang, D.H.; Tang, J.X.; Chang, Z.S.; Qu, W.J.; Zheng, W.B.; Wang, H. Re-Os dating of molybdenite from the Jiama Cu-polymetallic deposit in Tibet and its metallogenic significance. Acta Geol. Sin. 2010, 84, 1165–1174. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, M.J.; Qin, K.Z.; Evans, N.J.; Li, G.M.; Ling, X.X.; McInnes, B.I.A.; Zhao, J.X. Titanite in situ SIMS U-Pb geochronology, elemental and Nd isotopic signatures record mineralization and fluid characteristics at the Pusangguo skarn deposit, Tibet. Min. Depos. 2021, 56, 907–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.F.; Wang, Z.Q.; Li, J.Y. Opening-Closing Tectonics of Central Orogenic Belt; Geological Publishing Housing: Beijing, China, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, Y.P.; He, D.F.; Sun, S.S.; Liu, X.M.; Zhou, X.H.; Zhang, F.F.; Yang, Z.; Cheng, B.; Zhao, G.C.; Li, J.H. Subduction and accretionary tectonics of the East Kunlun orogen, western segment of the Central China Orogenic System. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2018, 186, 231–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Zhai, Y.S.; Mo, X.X.; Wang, Q.F. Temporal-spatial distribution of metallic ore deposits in China and their geodynamic settings. Econ. Geol. Spec. Publ. 2019, 22, 103–132. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, P.; Zhao, G.C.; Liu, Q.; Yao, J.L.; Han, Y.G. Evolution of the Paleo-Tethys Ocean in Eastern Kunlun, North Tibetan Plateau: From continental rift-drift to final closure. Lithos 2022, 422–423, 106717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Dick, J.M.; Feng, C.Y.; Li, B.; Wang, H. The tectonic evolution of the East Kunlun Orogen, northern Tibetan Plateau: A critical review with an integrated geodynamic model. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2020, 191, 104168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.P.; Sun, S.S.; Santosh, M.; Zhao, J.; Sun, J.P.; He, D.F.; Shi, X.H.; Hui, B.; Cheng, C.; Zhang, G.W. Central China Orogenic Belt and Amalgamation of East Asian Continents. Gondwana Res. 2021, 100, 131–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.M.; Song, X.Y.; Hu, R.Z.; Yu, S.Y.; Yi, J.N.; Kang, J.; Huang, K.J. Mg-Sr-Nd isotopic insights into petrogenesis of the Xiarihamu mafic-ultramafic intrusion, northern Tibetan Plateau. J. Petrol. 2021, 62, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Li, G.M.; Li, Z.S.; Su, H.M.; Shan, P.F.; Huang, X.S.; Cao, M.J. Occurrence and enrichment characteristics of cobalt in typical skarn deposits of the Qimantagh ore-concentrated area, East Kunlun, Qinghai. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2025, 41, 2648–2665. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.D.; Ma, Y.W.; Cao, C.G. Geological Characteristics of the East Kunlun Metallogenic Belt in Qinghai Province. West. Resour. 2022, 5, 166–168. [Google Scholar]
- Faure, M.; Lin, W.; Le Breton, N. Where is the North China-South China Block Boundary in Eastern China? Geology 2001, 29, 119–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.J. Early Cretaceous Magmatism and Porphyrite Iron Mineralization in the Middle-Lower Yangtze River Region Under Ridge Subduction. Ph.D. Dissertation, Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Qingdao, China, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, L.; Zhou, T.F.; Xiao, X. Distribution patterns, occurrence states and enrichment mechanisms of critical metals (Co-Se-Te) in the Xinqiao deposit, Tongling ore district, Anhui Province. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2023, 39, 3031–3047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Lü, Q.T.; Man, Z.H.; Lan, X.Y.; Guo, D.; Tao, L.; Zhao, J.H. Electrical constraints on the deep setting and process of magma-mineral system in the Middle-Lower Reaches of Yangtze River Metallogenic Belt. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2022, 38, 573–583. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.F. Genetic Study of Stratiform Sulfide Deposits in the Northern Ore Belt of Wushan Copper Deposit, Jiurui Area, Jiangxi Province. Ph.D. Dissertation, Chang’an University, Xi’an, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Ehser, A.; Borg, G.; Pernicka, E. Provenance of the Gold of the Early Bronze Age Nebra Sky Disk, Central Germany: Geochemical Characterization of Natural Gold from Cornwall. Eur. J. Mineral. 2011, 23, 895–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seravkin, I.B.; Kosarev, A.M.; Puchkov, V.N. Geodynamic Conditions of Formation of Massive Sulfide Deposits in the Magnitogorsk Megazone, Southern Urals, and Prospection Criteria. Geol. Ore Depos. 2017, 59, 227–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plotinskaya, O.Y.; Grabezhev, A.I.; Tessalina, S.; Seltmann, R.; Groznova, E.O.; Abramov, S.S. Porphyry Deposits of the Urals: Geological Framework and Metallogeny. Ore Geol. Rev. 2017, 85, 153–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabezhev, A.I.; Kuznetsov, N.S.; Puzhakov, B.A. Ore and Alteration Zoning of Sodium Type Copper-Porphyry Column (Paragonite-Bearing Aureoles, the Urals); IGG Publisher: Yekaterinburg, Russia, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Zhai, Y.S.; Yao, S.Z.; Cai, K.Q. Ore Deposit Geology, 3rd ed.; Geological Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2011; pp. 1–440. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.J.; Cao, L.M.; Li, Z.L. Element Geochemistry; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1984; pp. 113–137. [Google Scholar]
- Williams-Jones, A.E.; Vasyukova, O.V. Constraints on the Genesis of Cobalt Deposits: Part I. Theoretical Considerations. Econ. Geol. 2022, 117, 513–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.Q.; Li, S.R.; Santosh, M.; Wang, J.Z.; Li, Q. Mineral chemistry of high-Mg diorites and skarn in the Han-Xing Iron deposits of South Taihang Mountains, China: Constraints on mineralization process. Ore Geol. Rev. 2015, 64, 200–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.Q.; Yan, L.N.; Santosh, M.; Li, S.R.; Lu, J.; Wang, D.X.; Liang, X.; Wang, L.X.; Li, Y.Q. Tracing the genesis of skarn-type iron deposit in central North China Craton: Insights from mineral zoning textures in ore-forming intrusion. Geol. J. 2020, 55, 6280–6295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.L.; Su, S.G.; Wang, N.; Wang, W.B. Deep magmatic processes and shallow responses during the lithospheric thinning of North China Craton: Taking Tanling intrusive complex as an example. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2019, 35, 2873–2892. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, G.; Li, J.; Hofstra, A.H.; Harlov, D.E.; Zhao, X.; Lowers, H.A.; Koenig, A.E. Trace element fractionation in magnetite as a function of Fe depletion from ore fluids at the Baijian Fe-(Co) skarn deposit, eastern China: Implications for Co mineralization in Fe skarns. Am. Miner. 2024, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.M. The Ore-Forming Fluid and Mineralization of Skarn Fe Deposits in Handan-Xingtai, South Hebei. China Univ. Geosci. 2007, 1–150. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Y.; Jiang, S.Y.; Frimmel, H.E.; Zhu, L.Y. In situ chemical and isotopic analyses and element mapping of multiple-generation pyrite: Evidence of episodic gold mobilization and deposition for the Qiucun epithermal gold deposit in Southeast China. Am. Miner. 2022, 107, 1133–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.H.; Borg, S.J.; Testemale, D.; Etschmann, B.; Hazemann, J.L.; Brugger, J. Speciation and thermodynamic properties for cobalt chloride complexes in hydrothermal fluids at 35–440 °C and 600 bar: An in-situ XAS study. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2011, 75, 1227–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, M.J.; Shan, P.F.; Qin, K.Z. Cobalt-rich characteristics and existing problems of porphyry gold-copper deposit: A case study of Jinchang deposit in Heilongjiang Province. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2022, 67, 3708–3723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kretschmar, U.; Scott, S.D. Phase relations involving arsenopyrite in the system Fe-As-S and their application. Can. Miner. 1976, 14, 364–386. [Google Scholar]
- Sharp, Z.D.; Essene, E.J.; Kelly, W.C. A re-examination of the arsenopyrite geothermometer: Pressure considerations and applications to natural assemblages. Can. Miner. 1985, 23, 517–534. [Google Scholar]
- Vasyukova, O.V.; Williams-Jones, A.E. Constraints on the genesis of Cobalt deposits: Part II. Applications to Natural Systems. Econ. Geol. 2022, 117, 529–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Feng, C.Y.; Bao, G.Y.; Liu, H.C.; Zhao, Y.M.; Li, D.X.; Xiao, Y.; Liu, J.N. Mineralogy and alteration zoning of skarn in the Galinge iron deposit, Qinghai Province. Miner. Depos. 2013, 32, 55–76. [Google Scholar]
- Rudnick, R.L.; Gao, S.; Holland, H.D.; Turekian, K.K. Composition of the continental crust. Treat. Crust 2003, 4, 1–51. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, D.Z.; Zheng, R.F. Preliminary Study on Migration Forms and Metallogenic Mechanism of Cobalt. Acta Geol. Sichuan 2010, 30, 364–368. [Google Scholar]
- Richards, J.P. Tectono-magmatic precursors for porphyry Cu-(Mo-Au) deposit formation. Econ. Geol. 2003, 98, 1515–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sillitoe, R.H. Porphyry copper systems. Econ. Geol. 2010, 105, 3–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T. Chemical Element Abundances in the Earth and Its Major Shells. Geochimica 1976, 3, 167–174. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Zhong, H.; Cao, Y.H.; Wei, B.; Chen, C. Genetic classification, distribution and ore genesis of major PGE, Co and Cr deposits in China: A critical review. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2020, 65, 3825–3838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Bai, M.; Zhu, D.; Dong, L.; Liu, S.; Li, X.; Lu, L. Study of Ore Features and Occurrence Status of Cobalt in the Hanxing Type Iron Deposit, Hebei Province. Nonferrous Met. Miner. Process. Sect. 2024, 1, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, X.L. Mineralogical characteristics and genesis of amphibole in intermediate-mafic intrusive complex from Wu’an, Hebei Province. China Univ. Geosci. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, F.S.; Jin, Y.N.; Fan, L.L.; Tang, Y.Y.; Qin, C.; Zhang, J.Q. Genetic mineralogy of Ziquan diorite in eastern Han-Xing area. J. Hebei GEO Univ. 2021, 44, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, L.L. Genetic Mineralogy of Amphiboles in Mesozoic Intrusive Rocks from Handan-Xingtai Area, Southern Hebei Province, China. Hebei GEO Univ. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.Y.; Zhang, J.Q.; Wang, Y.Q.; Sun, T.Q.; Zhao, K.C.; Wang, L.X.; Li, Y.Q.; Xu, C. Formation and Mineralogy of Porphyritic Biotite Hornblende Diorite in Qicun Pluton, Southern Hebei. Geoscience 2019, 33, 738–750. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Wang, L.Q.; Li, H.F.; DanZhen, W.X.; Shi, S. Sulfur and Lead Isotopic Compositions of the Pusangguo Cu-Pb-Zn Polymetallic Deposit in Tibet: Implications for the Source of Ore-forming Material. Geoscience 2018, 32, 56–65. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y. Characteristics and Evolution of Ore-Forming Fluids in the Jiama Cu Polymetallic Deposit, Mozhugongka County, Tibet. Ph.D. Dissertation, Chengdu University of Technology, Chengdu, China, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.S. Geological Characteristics and Genesis of the Jiama Cu Polymetallic Deposit in Tibet. Ph.D. Dissertation, China University of Geosciences, Wuhan, China, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Qu, X.M.; Hou, Z.Q.; Li, Y.G. S and Pb Isotopes as Indicators of Ore-Forming Material Sources and Orogenic Belt Material Cycling in the Gangdese Porphyry Copper Belt. Geol. Bull. Chin. 2002, 21, 768–775. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, P.; Zheng, M.H.; Peng, Y.M.; Li, J.G.; Li, D.K.; Fan, W.Y. Study on the Sources of Ore-Forming Material and Genesis of the Jiama Copper and Polymetallic Deposit in Gangdese Island-arc Belt, Xizang. J. Geol. Rev. 2002, 48, 468–478. [Google Scholar]
- She, H.Q.; Feng, C.Y.; Zhang, D.Q.; Pan, G.T.; Li, G.M. Characteristics and Metallogenic Prospective Analysis of Skarn Cu-Pb-Zn Polymetallic Deposits in the Middle-Eastern Gangdese Belt, Tibet. Miner. Depos. 2005, 24, 508–520. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, X.F.; Tang, J.X.; Ding, S.; Zheng, W.B.; Yang, H.H.; Zhang, W.Y.; Feng, Y.F. Petrography, Geochronology and Hf Isotope Constraints on Origin of the of Ore-bearing Granodiorite in Zhibula copper Deposit, Tibet. Geotecton. Met. 2015, 39, 315–324. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Huang, Y.; Dong, S.L.; Yan, G.Q.; You, Q.; Jiang, H.Z.; Zhang, K. Zicron LA-ICP-MS U-Pb Geochronology, Geochemistry and implications of Ore-Forming Porphyry in Nuri skarn Cu-Mo-W Deposit, Eastern Gangdise. Miner. Depos. 2018, 37, 571–586. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, F. Magmatic Evolution and Genesis of the Jiama Superlarge Porphyry-Skarn Deposit, Southern Tibet. Ph.D. Dissertation, China University of Geosciences, Wuhan, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Esser, B.K.; Turekian, K.K. The osmium isotopic composition of the continental crust. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1993, 57, 3093–3104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.P.; Zheng, Y.C.; Xu, B.; Fu, Q.; Ma, W.; Wu, C.D.; Zhang, C.; Shen, Y.; Fei, F. Metallogeny of the Lietinggang-Leqingla Fe-Cu-(Mo)-Pb-Zn polymetallic deposit, evidence from geochronology, petrogenesis, and magmatic oxidation state, Lhasa terrane. Ore Geol. Rev. 2019, 106, 318–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Zheng, Y.Y.; Wu, S.; You, Z.M.; Wu, X.; Li, M.; Zhou, T.C.; Dong, J. Metallogenic epoch and genesis of ore-bearing rocks in the Mingze-Chengba porphyry-skarn Mo-Cu deposit, Gangdese. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2013, 29, 1392–1406. [Google Scholar]
- Marsh, E.; Anderson, E.; Gray, F. Nickel-Cobalt Laterites: A Deposit Model: Chapter H in Mineral Deposit Models for Resource Assessment; U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2013.
- Shu, L.S. General Geology; Geological Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, L.L.; Jin, Y.N.; Bai, F.S.; Liang, X.; Wu, W.Z.; Li, Q.; Zhang, J.Q. Genetic mineralogical study of dioritic complex in Wu’an pluton, southern Hebei province. J. Hebei GEO Univ. 2020, 43, 16–21. [Google Scholar]
- Shan, P.F.; Cao, M.J.; Tang, D.M.; Qiu, Z.J.; Evans, N.J.; Lazarov, M.; Wang, D.C.; Hu, W.; Qin, K.Z.; Horn, I.; et al. Cobalt-rich porphyry deposits derived from multiple mafic magma injections. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2025, 399, 125–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barton, M.D.; Johnson, D.A. An evaporitic source model for igneous-related Fe oxide-(REE-Cu-Au-U) mineralization. Geology 1996, 24, 259–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sillitoe, R.H.; Burrows, D.R. New field evidence bearing on the origin of the El Laco magnetite deposit, Northern Chile. Econ. Geol. 2002, 75, 1101–1109. [Google Scholar]
- Sillitoe, R.H. Iron oxide copper gold deposits: An Andean view. Miner. Depos. 2003, 38, 787–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jami, M.; Dunlop, A.C.; Cohen, D.R. Fluid inclusion and stable isotope study of the Esfordi apatite-magnetite deposit, Central Iran. Econ. Geol. 2007, 102, 1111–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Xie, G.; Duan, C.; Han, D.; Wang, C. Effect of sulfate evaporate salt layer over the formation of skarn-type iron ores. Acta Geol. Sin. 2013, 87, 1324–1334. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.H.; Duan, C.; Han, D.; Chen, X.W.; Wang, C.L.; Yang, B.Y.; Zhang, C.; Liu, F. Role of evaporite layers as oxidation barriers in the mineralization of porphyrite iron deposits in the Middle-Lower Yangtze River Belt. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2014, 30, 1355–1368. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.H.; Duan, C.; Wang, C.L.; Yang, B.Y.; Hou, K.J.; Zhang, C.; Liu, J.L. Mineralization of Porphyrite Iron Deposits in the Ningwu District: Case Study of the Washan Deposit, Anhui; Geological Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2021; pp. 1–124. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, C.; Li, Y.H.; Mao, J.W.; Zhu, Q.Q.; Xie, G.Q.; Wan, Q.; Jian, W.; Hou, K.J. The role of evaporite layers in the ore-forming processes of iron oxide-apatite and skarn Fe deposits: Examples from the Middle-Lower Yangtze River Metallogenic Belt, East China. Ore Geol. Rev. 2021, 138, 104352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, C.; Li, Y.H.; Mao, J.W.; Wan, Q.; He, S.; Wang, C.L.; Yang, B.Y.; Hou, K.J. Zircon U-Pb ages, Hf-O isotopes and trace elements of the multi-volcanism in the Ningwu ore district, Eastern China: Implications for the magma evolution and fertility of iron oxide-apatite (IOA) deposits. Gondwana Res. 2023, 116, 149–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Li, Y.H.; Li, H.M.; Hou, K.J.; Zhang, Z.J. Paleoproterozoic hydrothermal overprinting over Neoarchean banded iron formation produced high-grade iron ores in the giant Gongchangling deposit of North China: Evidence from O-S-B isotopes. Ore Geol. Rev. 2024, 165, 105911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.H.; Duan, C.; Fan, C.F.; Hu, B.; Hou, K.J.; Zhu, Q.Q.; Wang, Q.; Guo, D.W. Study on the Role of Gypsum-Salt Layers in the Mineralization of Endogenic Metal Deposits. Miner. Explor. 2024, 15, 1391–1408. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, T.F.; Fan, Y.; Yuan, F.; Wu, M.A.; Zhao, W.G.; Qian, B.; Ma, L.; Wang, W.C.; Liu, Y.N.; Noel, W. The metallogenic model of Nihe iron deposit in Luzong basin and genetic relationship between Gypsum-Salt layer and deposit. Acta Geol. Sin. 2014, 88, 562–573. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.; Qin, Y.J.; Zhang, K. Metallogenic Geological Characteristics and Genesis of Skarn-Type Iron Deposits: A Review. China Met. Bull. 2018, 11, 252–253. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, J.F.; Hu, Y.L.; Li, R.J. Skarn type iron ore ore-forming geological characteristics and genesis of review. West. Resour. 2016, 4, 21–23. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Q.Q.; Xie, G.Q.; Wang, J.; Li, W.; Yu, B.F. The Relationship between the Evaporate and Skarn-Type Iron Deposits: A Case Study of the Jinshandian Iron Deposit in Hubei. Acta Geol. Sin. 2013, 87, 1419–1429. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, B.M.; Zhao, G.L.; Ma, G.X. The Metallogenetic System and Ore-Forming Models of the Main Metallogenic Belts in Hebei Province; Petroleum Industrial Publishing House: Beijing, China, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, B.; Li, X.; Wei, S.; Cui, Y.; He, J. The Control of the Evaporite Beds in the Middle Ordovician Series over the Endogenic Iron (Sulfur) Ores of Han-Xing Type. Mineral. Petrol. 1983, 4, 31–44. [Google Scholar]
- Zhai, Y.S.; Shi, Z.L.; Lin, X.D.; Xiong, P.F.; Wang, D.Y.; Yao, S.Z.; Jin, Z.M. Genesis of “Daye-Type” iron ore deposits in eastern Hubei, China. Earth Sci. 1982, 3, 239–251. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.M.; Wu, J.S.; Han, F.; Luo, Z.K.; Feng, Y.M. Mineralization and Alteration Characteristics of Magnesian Skarn-Type Iron Deposits in Luonan Area, Shaanxi Province: Prospecting Indicators. Bull. Inst. Miner. Resour. Chin. Acad. Geol. Sci. 1982, 1, 29–50. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.H.; Duan, C.; Han, D.; Liu, F.; Wan, D.F.; Wang, C.Y. Oxygen Isotope Discrimination Marker of Magmatic Iron Deposits: Ningwu Porphyry Iron ore as an Example. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2017, 33, 3411–3421. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, T.F.; Yuan, F.; Yue, S.C.; Liu, X.D.; Zhang, X.; Fan, Y. Geochemistry and Evolution of Ore-Forming Fluids of the Yueshan Cu-Au Skarn- and Vein-Type Deposits, Anhui Province, South China. Ore Geol. Rev. 2007, 31, 279–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.F.; Yue, S.C.; Yuan, F. Petrogenesis and Metallogenesis of the Yueshan Ore District, Anhui Province; Geological Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2005; pp. 1–146. [Google Scholar]
- Li, F.J.; Qi, Y.Q.; Gong, H.T. A Review of Researches on Mineral Dissolution and Reprecipitation Processes. Bull. Mineral. Petrol. Geochem. 2024, 43, 240–258. [Google Scholar]
- Davey, J.; Roberts, S.; Wilkinson, J.J. Copper- and Cobalt-Rich, Ultrapotassic Bittern Brines Responsible for the Formation of the Nkana-Mindola Deposits, Zambian Copperbelt. Geology 2021, 49, 341–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulrich, T.; Gunther, D.; Heinrich, C.A. The Evolution of a Porphyry Cu-Au Deposit Based on LA-ICP-MS Analysis of Fluid Inclusions: Bajo de la Alumbrera, Argentina. Econ. Geol. 2001, 96, 1743–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putnis, A. Mineral Replacement Reactions. Rev. Mineral. Geochem. 2009, 70, 87–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Agudo, E.; Putnis, C.V.; Putnis, A. Coupled Dissolution and Precipitation at Mineral-Fluid Interfaces. Chem. Geol. 2014, 383, 132–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putnis, A. Mineral Replacement Reactions: From Macroscopic Observations to Microscopic Mechanisms. Mineral. Mag. 2002, 66, 689–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Name | Main Metallogenic Stage | Enrichment Degree of Co Element | Influencing Factors | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zhongguan | Wet skarn | Depleted | Continuous high-temperature oxidation conditions prevent the decomposition of cobalt complexes | [34] |
| Oxide | Enriched | Decreased fluid temperature, elevated oxygen fugacity | ||
| Henghui | Early sulfide | Enriched | Magnetite crystallization and multi-stage mafic magmatism causing decreased fluid temperature and salinity | [55] |
| Late sulfide | Depleted | Hydrothermal alterations release Co into fluid | ||
| Carbonate | Re-enriched | Meteoric water injection causes fluid cooling and dilution | ||
| Anqing | Early quartz–sulfide | Enriched | Meteoric water injection causes fluid temperature and chloride complex concentration to decrease | [43] |
| Late quartz–sulfide | Depleted | Continuous meteoric water injection causes further fluid cooling and dilution | ||
| Zhuchong | Sulfide | Enriched | Magnetite crystallization and wall-rock Mg-Ca strata cause fluid temperature and oxygen fugacity to decrease | [54] |
| Wushan | Quartz–sulfide I | Depleted | Formation of limited pyrite amount | [44] |
| Quartz–sulfide II | Enriched | Elevated fluid temperature, the massive formation of pyrite | ||
| Xinqiao | Quartz–sulfide | Enriched | Elevated fluid temperature | [122] |
| Galinge | Early sulfide I | Enriched | ———— | [73] |
| Early sulfide II | Re-enriched | Elevated fluid temperature and pH, fluid–rock interaction | ||
| Late sulfide | Depleted | Decreased fluid temperature | ||
| Zhibula | Quartz–sulfide | Enriched | ———— | [17] |
| Yaojialing | Early sulfide | Enriched | ———— | [53] |
| Late sulfide | Depleted | Decreased fluid temperature | ||
| Niukutou | Pyrrhotite | Depleted | ———— | [70] |
| Chalcopyrite | Enriched | Decreased fluid temperature and oxygen fugacity | ||
| Sphalerite–Galena | Depleted | ———— |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, R.; Cao, C.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Yuan, Z.; Dong, B.; Cao, Q.; Zuo, W.; Guo, Z. Advances in Distribution Pattern and Enrichment Mechanism of Associated Cobalt Resources in Skarn-Type Deposits, China. Minerals 2025, 15, 913. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15090913
Zhang R, Cao C, Zhang Y, Wang S, Zhang Y, Yuan Z, Dong B, Cao Q, Zuo W, Guo Z. Advances in Distribution Pattern and Enrichment Mechanism of Associated Cobalt Resources in Skarn-Type Deposits, China. Minerals. 2025; 15(9):913. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15090913
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Rongfang, Chong Cao, Yanbo Zhang, Shuzhi Wang, Yang Zhang, Zhaokang Yuan, Boxiao Dong, Qing Cao, Wenzhe Zuo, and Zhihua Guo. 2025. "Advances in Distribution Pattern and Enrichment Mechanism of Associated Cobalt Resources in Skarn-Type Deposits, China" Minerals 15, no. 9: 913. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15090913
APA StyleZhang, R., Cao, C., Zhang, Y., Wang, S., Zhang, Y., Yuan, Z., Dong, B., Cao, Q., Zuo, W., & Guo, Z. (2025). Advances in Distribution Pattern and Enrichment Mechanism of Associated Cobalt Resources in Skarn-Type Deposits, China. Minerals, 15(9), 913. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15090913







