Influence of Hydration on Shale Reservoirs: A Case Study of Gulong Shale Oil
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Samples and Method
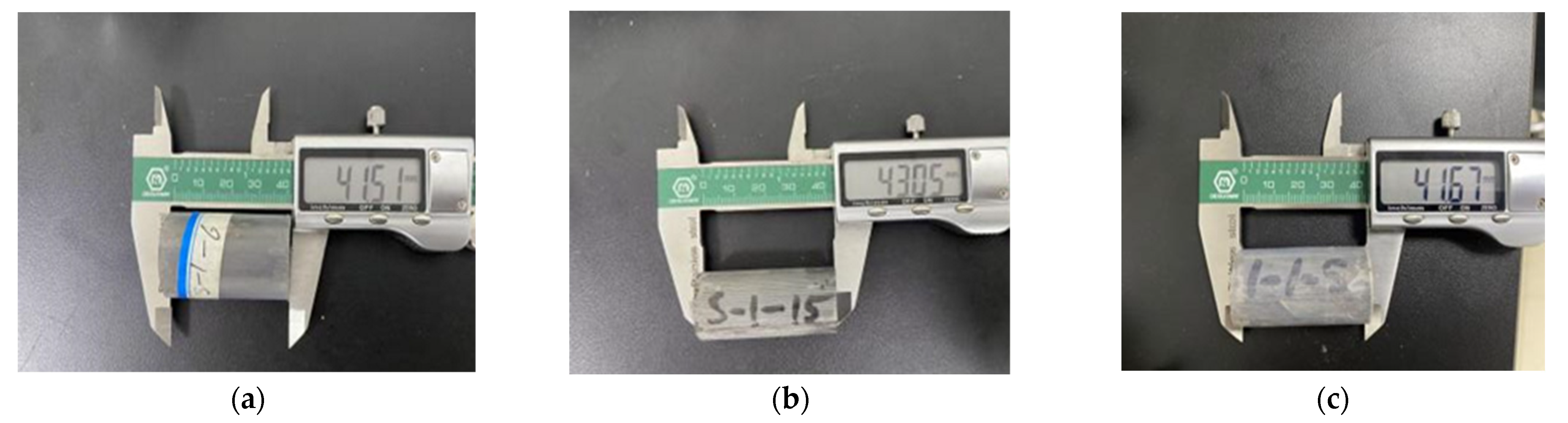
2.1. Experimental Samples
2.2. Experimental Instruments and Principles
2.2.1. X-Ray Diffraction Test
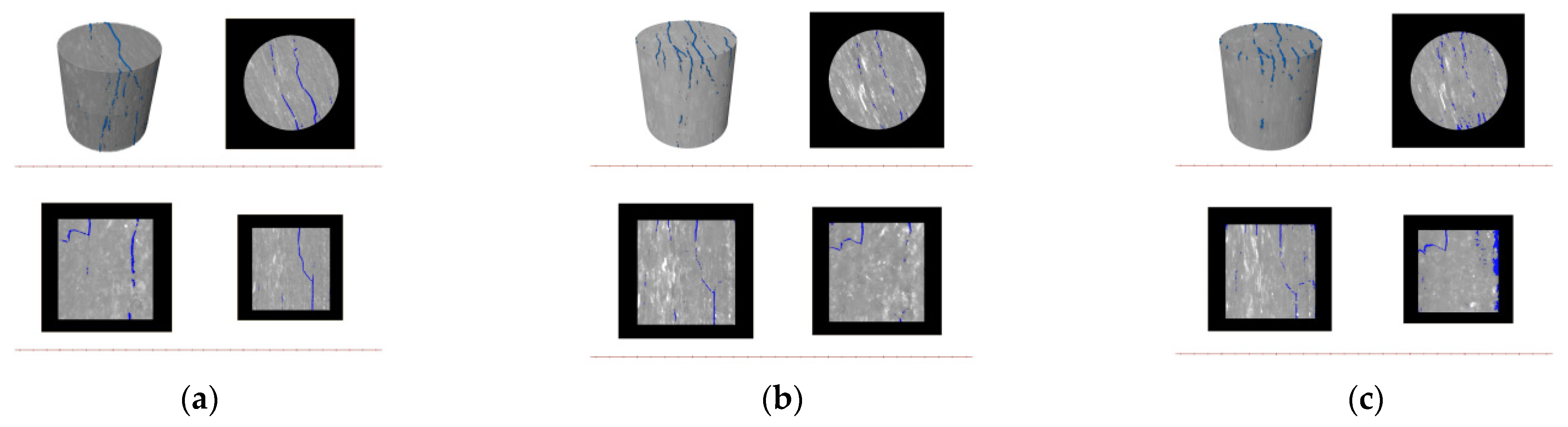
2.2.2. Micron CT Scanning Test
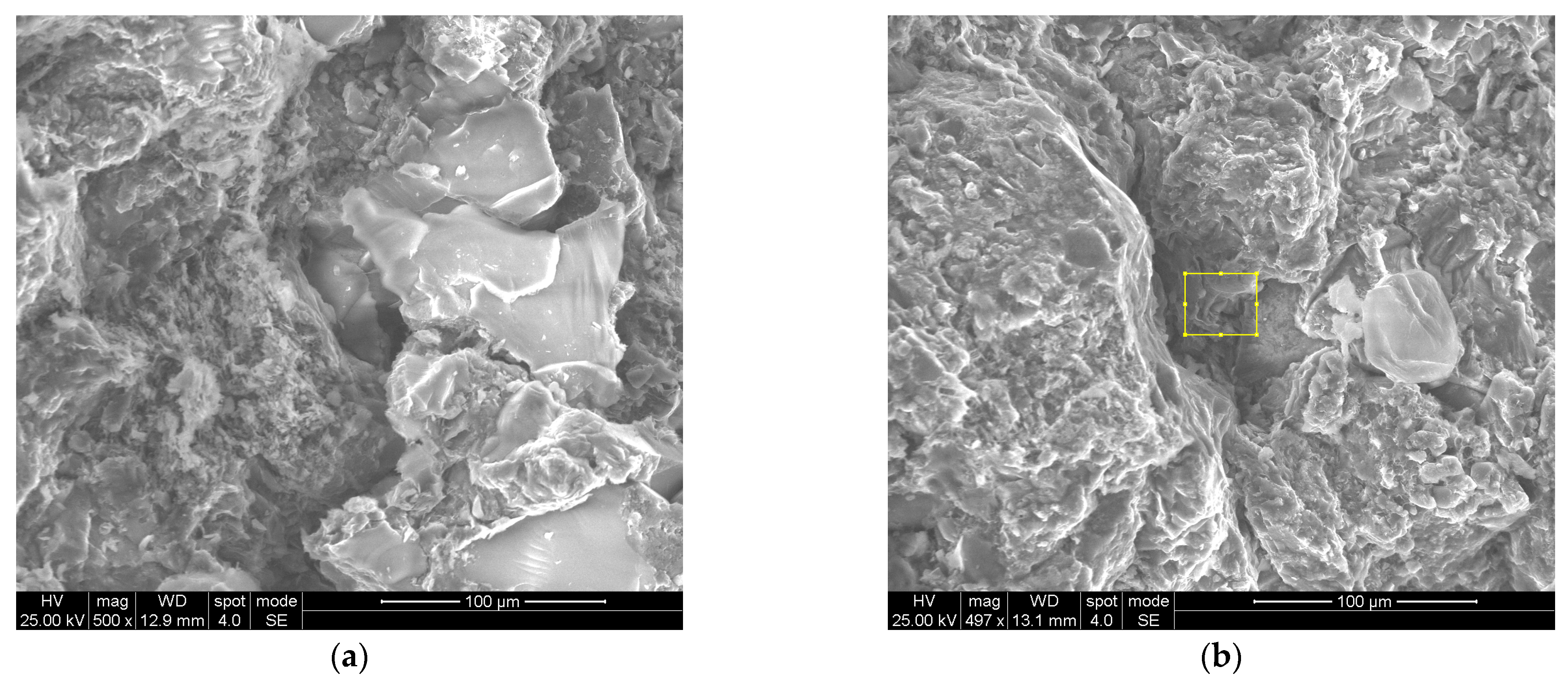
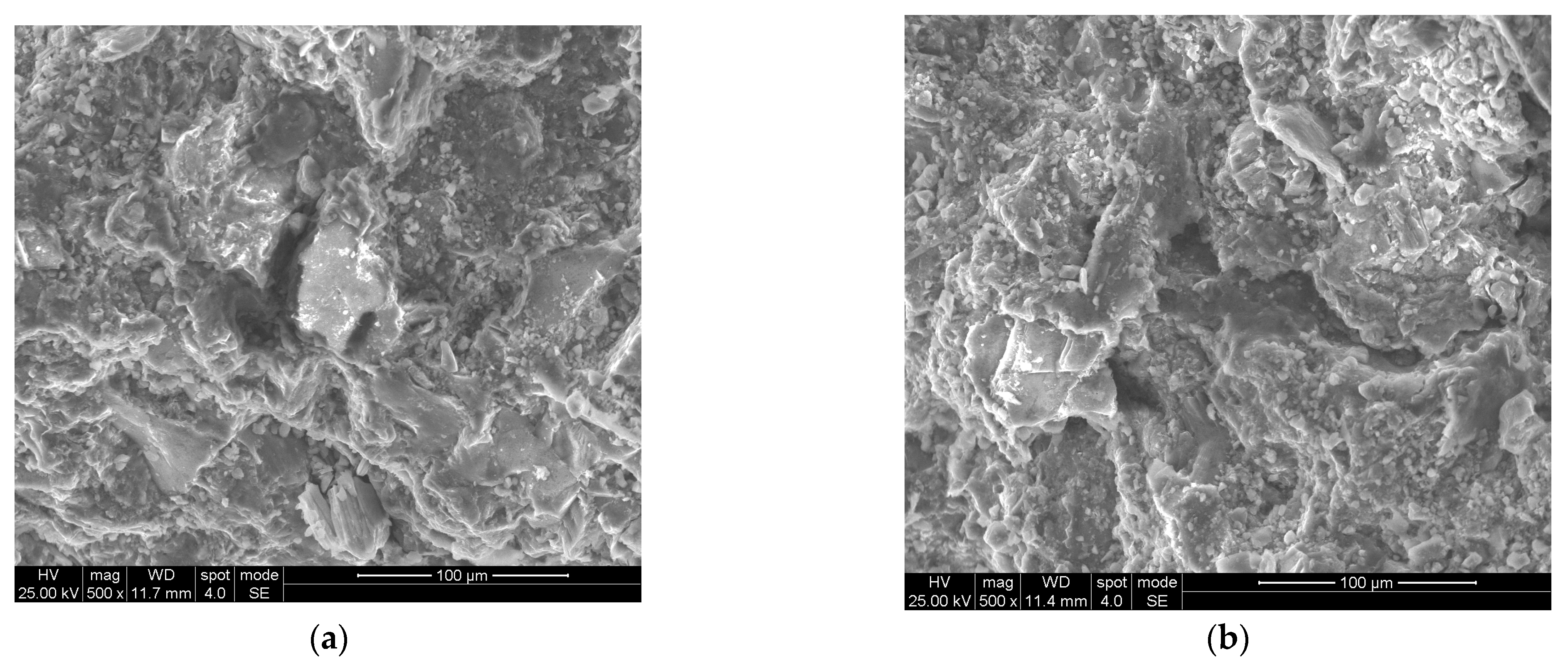
2.2.3. Scanning Electron Microscopy Test
2.3. Experimental Method
2.3.1. X-Ray Diffraction Analysis
2.3.2. Micron CT Scanning Analysis
2.3.3. Scanning Electron Microscopy Analysis
3. Result
3.1. Effect of Hydration on Microstructure and Physical Parameters of Shale
3.1.1. The Differences in Porosity and Permeability Before and After Hydration
3.1.2. Comparison of Shale Hydration Based on Micron CT Scan
3.2. Study on the Influence of Fracturing Fluid Type on Shale Hydration
3.2.1. Effect of Fracturing Fluid Type on Permeability
3.2.2. Comparison of Shale Hydration Based on X-Ray Diffraction
3.2.3. Comparison of Shale Hydration Based on Electron Microscopy Scanning Experiments
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, D.; Meegoda, J.; Goncalves da Silva, B.; Hu, L. Impact of de-ionized water on changes in porosity and permeability of shales mineralogy due to clay-swelling. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 20049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L. Clay Stabilization in Sandstone Reservoirs and the Perspectives for Shale Reservoirs. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 276, 102087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, Y.; Liu, X.; Xiong, H.; Liang, L. Microscopic Mechanism of Clay Minerals on Reservoir Damage during Steam Injection in Unconsolidated Sandstone. Energy Fuels 2018, 32, 4671–4681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, W.; Tian, Y.; Yao, C. Investigation of microscopic pore structure variations of shale due to hydration effects through SEM fixed-point observation experiments. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2018, 45, 894–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Sun, X.; Yuan, Y.; Lai, X.; Qu, H.; Luo, C. Experimental investigation on the dynamic volume changes of varied-size pores during shale hydration. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2022, 101, 104506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, J.; Wu, T.; Yu, X.; Zhou, C.; Chen, H.; Gao, J. The Effect of Water–Rock Interaction on Shale Reservoir Damage and Pore Expansion. Processes 2025, 13, 1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Fan, X.; Zhang, Q.; Yao, B.; Zhang, M.; He, L.; Qiang, Y.; Liu, J. Characteristics of hydration damage and its influence on permeability of lamellar shale oil reservoirs in Ordos Basin. Geofluids 2021, 2021, 6646311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; You, L.; Kang, Y.; Jia, C.; Xiao, B. Influencing Factors and Application of Spontaneous Imbibition of Fracturing Fluids in Lacustrine and Marine Shale Gas Reservoir. Energy Fuels 2022, 36, 3606–3618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, H.; Zhou, S.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, F.; Dong, Z.; Guo, W. Effects of hydration on the microstructure and physical properties of shale. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2018, 45, 1146–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, W.; Tian, J.; Chen, Q.; Wang, P.; Han, T.; Zhai, Y.; Jiang, D. Relationship between shale hydration and shale collapse. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 42524–42536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, B.; Dong, E.; Yao, Z.; Song, Y.; Xiong, Z.; Huang, Y.; Gou, X.; Hu, X. Strategies for Optimizing Shut-In Time: New Insights from Shale Long-Term Hydration Experiments. Processes 2024, 12, 1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, F.; Zhang, Q.; Guo, J.; Zeng, B.; Zhang, Y.; He, S. Mechanisms of shale hydration and water block removal. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2021, 48, 646–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Wang, H.; Li, F.; Wang, D.; Li, N.; He, S. Effects of Hydration during Drilling on Fracability of Shale Oil Formations: A Case Study of Da’anzhai Section Reservoir in Sichuan Basin, China. Processes 2022, 10, 2313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zhou, P.; Lan, B. Study of wellbore instability in shale formation considering the effect of hydration on strength weakening. Front. Earth Sci. 2024, 12, 1403902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, T.; Chen, P. Study of meso-damage characteristies of shale hydration based on CT scanning technology. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2014, 41, 227–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Cui, B.; Feng, Z.; Shao, H.; Huo, Q.; Zhang, B.; Gao, B.; Zeng, H. In-situ hydrocarbon formation and accumulation mechanisms of micro- and nano-scale pore-fracture in Gulong shale, Songliao Basin, NE China. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2023, 50, 1269–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.; Zhu, R.; Cui, B.; Zhang, S.; Meng, Q.; Bai, B.; Feng, Z.; Lei, Z.; Wu, S.; He, K.; et al. The Geoscience Frontier of Gulong Shale Oil: Revealing the Role of Continental Shale from Oil Generation to Production. Engineering 2023, 28, 79–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, S.; Tao, J.; Li, T.; Li, D.; Wang, S.; Yang, L.; Liu, X.; Liang, L.; Liu, H. Mechanical characteristics and reservoir stimulation mechanisms of the Gulong shale oil reservoirs, the northern Songliao Basin. Pet. Sci. 2024, 21, 2023–2036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Liang, K.; Wang, C.; Wang, Y.; Jiao, Y.; Zhu, X.; Wang, C. Study of wellbore instability and collapse mechanism for a layered continental shale oil horizontal well. Energies 2022, 15, 4538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, W.; Yuan, J.; Li, P.; Ge, X.; Ge, X.; Liu, P.; Wu, H.; Yu, X.; Huang, B. Lithofacies Characteristics of the Lower Cretaceous Qing 1 Member in the Heiyupao Depression, Northern Binbei Area of the Songliao Basin. Minerals 2025, 15, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.; Zhu, R.; Liu, K.; Zhang, J.; Liu, C. Pore Fractal and Structure Analysis of Pore-Filling Chlorite in Continental Shales: A Case Study from the Qingshankou Formation in the Gulong Sag. Fractal Fract. 2025, 9, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, X. Genetic Mechanisms and Multiparameter Logging Identification of Low-Resistivity Oil Pay: A Case Study of the Triassic Chang 6 Member, Zhidan Area, Ordos Basin, China. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 23425–23445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huo, J.; Zhang, S.; Liu, J.; Wei, C.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, X.; Li, S. Synthesis, Investigation of Temperature and Salt Resistant Polyacrylamide Microspheres Used for Deep Sealing and Profile Control and Function Strengthening Mechanism. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2024, 141, e55620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Huang, B.; Zhan, C.; Jiang, C.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, X.; Zhao, M. Mechanical Properties and Mechanisms of Soda Residue and Fly Ash Stabilized Soil. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Guo, Y.; Hu, X.; Wang, T.; Wang, R.; Chen, X.; Fan, W.; Deng, Z. Pore Structure and Heterogeneity Characteristics of Deep Coal Reservoirs: A Case Study of the Daning–Jixian Block on the Southeastern Margin of the Ordos Basin. Minerals 2025, 15, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Zhou, G.; Fan, L.; Zhang, D.; Shao, M.; Ding, R.; Li, Y.; Hu, H.; Deng, Z. Full-Scale Pore and Microfracture Characterization of Deep Coal Reservoirs: A Case Study of the Benxi Formation Coal in the Daning–Jixian Block, China. Int. J. Energy Res. 2024, 2024, 5772264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, R.; Zhang, X.; Yang, H.; Ren, H.; Guo, H.; Zhou, H. Micropore structure and fractal characteristics of shale in Midwest China. J. Pet. Explor. Prod. Technol. 2024, 14, 867–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, T.; Chen, S.; Hu, Y.; Wei, Q.; Zhuang, D. Pore Structure and Its Fractal Dimension: A Case Study of the Marine Shales of the Niutitang Formation in Northwest Hunan, South China. Fractal Fract. 2025, 9, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehghanpour, H.; Lan, Q.; Saeed, Y.; Fei, H.; Qi, Z. Spontaneous imbibition of brine and oil in gas shales: Effect of water adsorption and resulting microfractures. Energy Fuels 2013, 27, 3039–3049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B.; Meng, J.; Song, C.; Pan, R.; Zhu, Z.; Jin, J. Complexity and Heterogeneity Evaluation of Pore Structures in the Deep Marine Shale Reservoirs of the Longmaxi Formation, China. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Shi, X.; Yin, C.; Liang, X.; Zhao, J.; Li, J.; Zhu, J.; Geng, Z.; Wu, Z.; Li, R. Brazilian tensile failure characteristics of marine shale under the hydration effect of different fluids. Nat. Gas Ind. 2020, 40, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, B.; Xia, B.; Lin, Y.; Xu, J. CT imaging and mechanism analysis of crack development by hydration in hard-brittle shale formations. Acta Pet. Sin. 2012, 33, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Ning, X.; Kang, Y.; Wu, J.; Li, B.; Shi, Y.; Lai, Z.; Bai, J.; Yan, M. Effect of Fracturing Fluid Properties on the Flowback Efficiency of Marine and Continental Transitional Shale Gas Reservoirs in Ordos Basin. Processes 2025, 13, 1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Liu, B.; Yang, J.; Bai, L.; Li, S. Compatibility characteristics of fracturing fluid and shale oil reservoir: A case study of the first member of Qingshankou Formation, northern Songliao Basin, Northeast China. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2022, 211, 110161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Number | TOC | Mineral Content (%) | Relative Content of Clay Mineral (%) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Quartz | Potash Feldspar | Plagioclase | Pyrite | Clay Mineral | Mixed-Layer Illite | Illite | Chlorite | ||
| S-1-6 | 2.33 | 30.2 | 0.6 | 11.4 | 7.3 | 50.5 | 35 | 44 | 21 |
| S-1-15 | 2.24 | 33.1 | 0.8 | 15.3 | 8.2 | 42.6 | 25 | 32 | 43 |
| S-1-1 | 2.21 | 35.7 | 0.6 | 17.5 | 4.9 | 41.3 | 30 | 42 | 28 |
| Experimental Scheme | Permeability (Before Hydration)/mD | Permeability (After Hydration)/mD | Rate of Change/% | Porosity (Before Hydration)/% | Porosity (After Hydration)/% | Rate of Change/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1-A | 0.005 | 0.0076 | 55.12 | 1.80 | 2.17 | 20.56 |
| 1-B | 0.0051 | 0.00422 | −20.85 | 1.81 | 1.71 | −5.81 |
| 1-C | 0.0055 | 0.004175 | −31.74 | 1.82 | 1.55 | −17.65 |
| 1-D | 0.0053 | 0.004164 | −27.28 | 1.80 | 1.58 | −13.64 |
| 2-A | 0.003 | 0.00482 | 60.58 | 0.95 | 1.14 | 20.32 |
| 2-B | 0.0032 | 0.00268 | −19.40 | 0.96 | 0.86 | −11.11 |
| 2-C | 0.0033 | 0.002405 | −37.21 | 0.95 | 0.82 | −16.65 |
| 2-D | 0.0038 | 0.002944 | −29.08 | 0.97 | 0.85 | −12.64 |
| 3-A | 0.001 | 0.00154 | 54.32 | 0.83 | 0.97 | 15.85 |
| 3-B | 0.0011 | 0.00089 | −23.60 | 0.82 | 0.73 | −12.11 |
| 3-C | 0.0013 | 0.000955 | −36.13 | 0.82 | 0.69 | −18.65 |
| 3-D | 0.0012 | 0.000956 | −25.52 | 0.81 | 0.71 | −14.64 |
| Number | Experimental Scheme | Relative Content of Clay Minerals (%) | Ratio of Mixed Layer (%S) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mixed-Layer Illite | Illite | Chlorite | Mixed-Layer Illite | ||
| 1 | 1-0-A | 34 | 41 | 25 | 10 |
| 2 | 1-0-B | 33 | 40 | 24 | 10 |
| 3 | 1-0-C | 32 | 39 | 23 | 10 |
| 4 | 1-0-D | 33 | 40 | 22 | 10 |
| 5 | 2-0-A | 24 | 33 | 43 | 10 |
| 6 | 2-0-B | 24 | 31 | 45 | 10 |
| 7 | 2-0-C | 23 | 34 | 43 | 10 |
| 8 | 2-0-D | 23 | 32 | 45 | 10 |
| 9 | 3-0-A | 33 | 45 | 22 | 10 |
| 10 | 3-0-B | 30 | 42 | 28 | 10 |
| 11 | 3-0-C | 28 | 43 | 29 | 10 |
| 12 | 3-0-D | 32 | 43 | 25 | 10 |
| Number | Experimental Scheme | Relative Content of Clay Minerals (%) | Ratio of Mixed Layer (%S) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mixed-Layer Illite | Illite | Chlorite | Mixed-Layer Illite | ||
| 1 | 1-0-A | 35 | 40 | 25 | 10 |
| 2 | 1-0-B | 35 | 39 | 26 | 10 |
| 3 | 1-0-C | 38 | 37 | 25 | 10 |
| 4 | 1-0-D | 36 | 41 | 23 | 10 |
| 5 | 2-0-A | 26 | 31 | 43 | 10 |
| 6 | 2-0-B | 27 | 29 | 44 | 10 |
| 7 | 2-0-C | 26 | 30 | 44 | 10 |
| 8 | 2-0-D | 29 | 29 | 42 | 10 |
| 9 | 3-0-A | 35 | 42 | 23 | 10 |
| 10 | 3-0-B | 32 | 43 | 25 | 10 |
| 11 | 3-0-C | 29 | 42 | 29 | 10 |
| 12 | 3-0-D | 30 | 41 | 29 | 10 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fang, F.; Xu, K.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Xu, Z.; He, S.; Huang, H.; Wang, H.; Jin, W.; Gong, Y. Influence of Hydration on Shale Reservoirs: A Case Study of Gulong Shale Oil. Minerals 2025, 15, 878. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15080878
Fang F, Xu K, Zhang Y, Wang Y, Xu Z, He S, Huang H, Wang H, Jin W, Gong Y. Influence of Hydration on Shale Reservoirs: A Case Study of Gulong Shale Oil. Minerals. 2025; 15(8):878. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15080878
Chicago/Turabian StyleFang, Feifei, Ke Xu, Yu Zhang, Yu Wang, Zhimin Xu, Sijie He, Hui Huang, Hailong Wang, Weixiang Jin, and Yue Gong. 2025. "Influence of Hydration on Shale Reservoirs: A Case Study of Gulong Shale Oil" Minerals 15, no. 8: 878. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15080878
APA StyleFang, F., Xu, K., Zhang, Y., Wang, Y., Xu, Z., He, S., Huang, H., Wang, H., Jin, W., & Gong, Y. (2025). Influence of Hydration on Shale Reservoirs: A Case Study of Gulong Shale Oil. Minerals, 15(8), 878. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15080878








