Abstract
Surface functionalization is a key enabler that imparts solid materials with excellent chemoselectivity. With this aim, halloysite and sepiolite clay particles were functionalized with carboxyethylsilanetriol sodium salt (CES) and 3-aminopropyltriethoxysilane (APTES), affording carboxy-terminated and amino-terminated clay, respectively. In the case of halloysite, the grafting occurs at Al-OH groups of the lumen surface (tube inner surface) and Al-OH and Si-OH groups at the edges and external surface defects of the nanotubes. For sepiolite, silanol groups located on the edges of the structural channels were at the origin of a chemical reaction between this fibrous clay and the terminal alkoxysilane. The resulting modified clays were examined for removal of Congo red (CR) and malachite green (MG) as anionic and cationic dyes, respectively. Clay bearing only carboxylic groups display more affinity towards cationic dye (MG), recording 926 mg·g−1 and 387 mg·g−1 for HNT-CES and SEP-CES, respectively, while amino-functionalized clays show very high adsorption for anionic dye (CR), reaching 1232 and 1228 mg·g−1 for HNT-APTES and SEP-APTES, respectively. Simultaneous grafting of the two silyl coupling reagents was also attempted through one-pot and sequential grafting method, with the latter being more appropriate to access amphoteric clay featuring both carboxylic and amino groups. The behavior of the bifunctional adsorbents was investigated with respect to pristine and monofunctional clay. The obtained results provide insights to fulfill the requirement for handling complex water effluent containing both anionic and cationic pollutants, towards more sustainable development.
1. Introduction
Water pollution is one of the most serious environmental problems, caused mainly by chemicals and organic products from industrial, agricultural, or domestic activities [1,2,3,4,5]. It is a crucial factor for several industrial processes that have to meet the requirements of sustainable development [6,7]. In this regard, adsorption is considered as a competitive technology for the treatment and purification of wastewater, groundwater, and industrial effluents and has specifically proven to be a very efficient and relatively inexpensive technique for the treatment of contaminated water [8,9,10,11]. Activated carbon, with its oxygenated functional groups, is presently the most widely used adsorbent [12,13,14]. However, the possibilities for further tailoring its surface chemistry through modification are very limited, thereby hindering the targeted uptake of more recalcitrant chemicals. Alternatively, clays stand as very promising adsorbents due to their abundance and low cost, non-toxicity, great stability of their inorganic structure, and the related physicochemical properties [15]. Current studies have shown that the adsorption capacity of clay materials can be enhanced by associating organic functionalities with the mineral phase [16,17,18,19,20]. Such modification can be reached through two main approaches: (i) the exchange of native mineral cations present in the interlayer space of the clay galleries by organic cations and (ii) the covalent grafting of organic molecules carrying chemical functions adapted to the desired application. Although the first approach of cationic surfactants affords exfoliated organo-modified clays, notoriously used as fillers for reinforcing nanocomposites [21,22,23,24,25,26], the implementation of such solid materials in adsorption unfortunately present secondary pollution resulting from leaching of intercalated surfactant out of the galleries [27]. Alternatively, the second route of post-grafting of alkoxysilane derivatives on mineral surfaces enables the creation of stable covalent bonding that definitely preclude the anchored functionalities from leaching back to the solution [28,29,30]. The selectivity of surface-functionalized clays can be consequently improved by introducing special functional groups (ex. NH2, SH, COOH, etc.) in the other side of the organoalkoxysilane coupling reagent [31,32]. To meet the requirement of surface-grafting chemistry, we herein selected halloysite and sepiolite as the most appropriate clay structures to be decorated with organic groups due to their high content of aluminol and silanol groups, respectively. Other clay-based particles (ex. montmorillonites) are less suitable for post-grafting because of the limited anchoring sites on their surface and were rather more explored for non-covalent modification through cationic exchange within the galleries. The hollow tubular structure of halloysite and its large specific surface area have triggered its use in healthcare and environment-related applications [33,34,35,36]. The same also applies for sepiolite, for which its fibrous morphology, high surface area, and porosity provide opportunities for a wide range of applications [37,38,39,40].
While halloysite and sepiolite were already subjected to alkoxysilane grafting, most of these reports involve the anchorage of single functionalities. Although efficient, these adsorbents fail to capture complex effluents containing different chemical species (anionic, cationic, neural, zwitterionic, metallic, and so on) [41,42,43,44]. It is indeed highly desirable to establish synthetic post-grafting methodologies that involve more than a single precursor for designing bi-functional or even multifunctional clay-based adsorbents. Considering the lack of relevant literature on analogs of clay particles featuring acid-base functionalities, we embarked on an investigation of the simultaneous grafting of amine and carboxylic acid-terminated alkoxysilane on halloysite and sepiolite clay to access amphoteric adsorbents. Through a comparative study with the pristine clay and the mono-functionalized clay, we have also assessed their adsorption capacity towards water containing Congo red and malachite green as representative anionic and cationic dye pollutants, respectively.
2. Materials and Methods
General: Organosilane coupling agents, solvents, and dyes used in this study (carboxyethylsilanetriol sodium salt (CES), aminopropyltriethoxysilane (APTES), toluene, Congo red (CR), and malachite green (MG)) were purchased from Across and Sigma-Aldrich (Massachusetts, USA). Sepiolite, referred her ein as Sep, was purchased from TOLSA (Spain). Its degree of purity is superior to 95%, while the remaining impurities <2%–3% consist of interstratified clay particles and a very negligible amount of carbonate. Sep is built from slightly aggregated fibers with a length of a few micrometers. Halloysite nanotubes (high purity: 99%; 1% of Fe2O3 and TiO2, and CaCO3 impurities), referred herein as HNT, with the following parameters (length: 0.2–2 m; outside diameter 50–70 nm; inside diameter 15–45 nm) was made available by Dragonite company (USA). Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectra were obtained with a PerkinElmer Spectrum 100FT-IR spectrometer on neat samples (ATR FT-IR) (resolution of 4 cm−1 with 32 scans, PerkinEmler, Shelton, CT, USA). 13C and 29Si CP MAS NMR spectra were acquired on a Bruker Advance 400 WB spectrometer (Bruker Biospin, Rheinstetten, Germany) operating at 100 MHz and 79 MHz, respectively, under cross-polarization conditions. Thermogravimetric analyses (TGA) were performed on a Q500 (TA instrument, New Castle, DE, USA) using a heating rate of 10 °C/min from room temperature to 900 °C under air. Prior to measurement, the solid sample was heated in an oven at 100 °C for 2 h. Pristine CEP was thermally treated at 100 °C for 12 h prior to the analysis, which could explain its lower water content. X-ray powder diffraction (XRD) patterns were recorded on a D8 Advance Bruker AXS system (Bruker Corp, Billerica, MA, USA) using CuKα radiation (ʎ = 0.1541 nm) with a step size of 0.02° in the 2θ range from 5 to 90°. UV-visible spectra were measured in the 200–800 nm range using spectralon as the reference on a PerkinElmer Lambda 1050 spectrometer (PerkinEmler, Labsphere, North Sutton, NH, USA).
Preparation of carboxy-clay and amino-modified clay (HNT and Sep): A measure of 200 mg of oven-dried (60 °C, 4 h) clay minerals (HNT and Sep) were dispersed in 20 mL of toluene. Then, 4.3 mmol of organosilane agent was added dropwise during vigorous stirring. The mixture was refluxed at 110 ◦C for 24 h. At the end of reaction, the silylated clay was separated by evaporation and washed with toluene to remove excess reagent and next dried at 100 °C for 12 h. The resulting materials will be denoted as HNT-CES and HNT-APTES in the case of Halloysite and Sep-CES and Sep-APTES in the case of Sepiolite.
Preparation of amphoteric carboxylate amino-modified clay: The dual acid and base functionalization of clay was carried out using two synthetic methods. The first method is a one-pot synthesis, which consists of reacting oven-dried sepiolite or halloysite with the two reagents simultaneously (in a single reaction mixture). To do this, 200 mg of clay was dispersed in 20 mL of toluene, followed by adding APTES (2.15 mmol) and CES (2.15 mmol), simultaneously. The reaction was refluxed at 110 °C for 24 h. The bifunctional clay (HNT@APTES-CES_OP and Sep@APTES-CES_OP) was separated by evaporation and washed with toluene to remove excess reagents and then dried at 100 °C for 12 h. The second method is a sequential method, in which the second reagent was introduced in situ after the reaction of the first silylation precursor with the clay surface. Thus, aminopropyltriethoxysilane (APTES: 2.15 mmol) was added to a volume of 20 mL of toluene, in which a quantity of 200 mg of halloysite was dispersed. After one hour of stirring, the second reagent, carboxyethylsilanetriol sodium salt (CES: 2.15 mmol), was added. The reaction was refluxed at 110 °C for 24 h. The obtained material (HNT@APTES-CES_SG) was next recovered in the same way as before.
Dye adsorption experiments: All experiments of adsorption were conducted at room temperature (25 °C) and at neutral pH using distillated water. Please note that a slight variation in the pH of the reaction medium could occurs depending on the dye and surface functional groups of the clays. The adsorption tests were carried out according to the batch technique by dispersing 8 mg of the adsorbent in 10 mL of dye-containing water solution with a concentration of 1000 mg/L under magnetic stirring for two hours. The solution was then centrifuged at 3000 rpm for 15 min to recover the liquid (supernatant) and the residual dye concentration was measured by UV-Vis spectrophotometry at the wavelength corresponding to the maximum absorbance of the dyes used (499 nm for Congo red and 617 nm for malachite green). The amount of adsorbed dye (Qe) on the solids was calculated by following the equation:
where Qe is the adsorption capacity (mg/g), C0 and Ce are the initial and equilibrium concentrations of the dye (mg/L), respectively, V is the volume (L), and m is the mass of adsorbent (g).
3. Results
3.1. Mono-Functional Adsorbents
Surface modification of HNT and Sep was first executed using carboxyethylsilanetriol, denoted herein as CES, and aminopropyltriethoxysilane, denoted as APTES (Scheme 1).
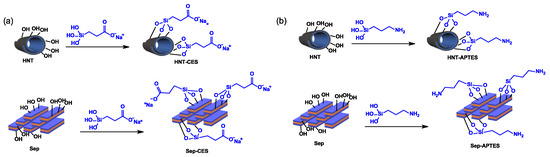
Scheme 1.
Silylation of HNT and Sep with (a) carboxy methyl silanetriol silane (CES) and with (b) aminopropyltriethoxysilane (APTES).
The FTIR spectra of silylated clay reveals the presence of new bands characteristic of the coupling organosilane reagent (Supplementary Material S1). In the case of HNT-CES and Sep-CES, the spectra show the appearance of a new signal at 1309 cm−1 corresponding to Si-C, and at 1407 cm−1 and 1563 cm−1 characteristic of symmetric and symmetric stretching vibrations of the C=O carboxylate group [45]. A low intensity signal was also observed at 2928 cm−1, corresponding to the stretching vibration of C-H. All the carboxyl groups adopt their ionic form (COO−) due to the absence of the signature of COOH acid groups, which generally appear in the interval 1754–1720 cm−1. The spectra of HNT-APTES and Sep-APTES show several new absorption bands. First, we noticed a significant reduction in the intensity of the bands, characteristic of the hydroxyl groups at 3621 cm−1 and 3693 cm−1, which is due to their consumption through reaction with terminal alkoxysilane tethers that form Si-O-Si bridges. New bands appear at 3363 and 3287 cm−1, corresponding to the asymmetric and symmetric stretching vibrations of the NH2 function [46]. The bands at 2930 and 2864 cm−1 correspond to the asymmetric and symmetric stretching vibration of C-H bond, the one resonating at 1580 cm−1 could be assigned to the deformation vibration of the NH [33], while at 1480 cm−1 (1470 cm−1 for Sep-APTES), we also observed the deformation vibration of -NH3+ [47]. Additional signals are also observed, mainly the one at 1378 cm−1, corresponding to the CH2 deformation vibration of the alkyl chain provided by the organosilane [48,49]; the signal at 1322 cm−1, corresponding to Si-C; and the one at 1233 cm−1, attributed to C-N [50]. Notably, the presence of protonated amine NH3+ groups is due to the strong hydrogen bonding interaction of the NH2 tethered arms with the neighboring hydroxyl groups located on the clay surface [51].
Solid-state 13C CP MAS NMR spectra of HNT-CES and Sep-CES show signals at 12.8, 32.6 and 185.7 ppm (184.6 for Sep-CES), attributed to -CH2-Si, -CH2-, and C=O groups of CES, respectively (Figure 1 and Supplementary Material S2). The spectra of HNT-APTES and Sep-APTES show signals at 12.8, 28 (24, 27 for sepiolite), and 46 ppm (45 and 46 ppm for sepiolite), respectively, attributed to C1 carbon atoms (CH2-Si), C2 (C-C), and C3 (CH2-NH2) of the propyl group [49,50]. The similarities between the materials modified using HNT and Sep demonstrate that the two clay surfaces are prone to organic modification through a siloxane grafting route.
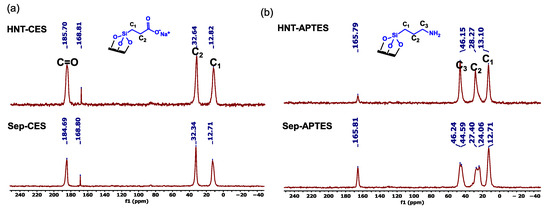
Figure 1.
13C CP MAS NMR spectra of (a) HNT-CES and Sep-CES and (b) HNT-APTES and Sep-APTES.
29Si CP MAS NMR spectra of silylated clay show the expected signals for both the support and the organic tether. Indeed, the signature of the support (−92 ppm for HNT and −92, −95, and −96 ppm for Sep) could be recognized in the silylated version. In addition, a new signal at −66 ppm (T2 signal) was observed for both HNT-CES and Sep-CES, thereby confirming the covalent grafting of CES to the clay surface. Three new signals appear at −51, −60, and −68 ppm for HNT-APTES and Sep-APTES, and are attributed to the silicon atom of the grafted aminosilane, bridged by one (T1), two (T2), and three (T3) Si-O bonds to the clay surface, respectively [33,49]. This clearly indicates the covalent grafting of organic fragments to the clay surface through siloxane (Si-O-Si) bridges (Figure 2).
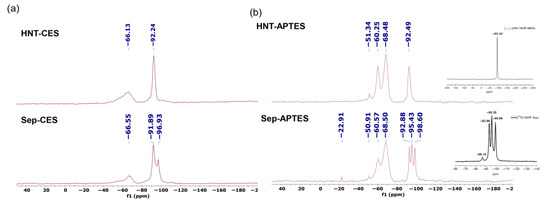
Figure 2.
29Si CP MAS NMR spectra of (a) HNT-CES and Sep-CES and (b) HNT-APTES and Sep-APTES.
Additional insight was also gained from solid-state 27Al CP MAS NMR. Native HNT displays a unique aluminum signal at 2.66 ppm. The 27Al CP MAS NMR spectra of modified halloysite HNT-CES show the persistence of this signal with a small shift to 2.54 ppm in the case of HNT-APTES and to 3.36 HNT-CES, owing to the slight change occurring on the outer sphere of Al species. An additional peak is also observed at 51.92 ppm for HNT-APTES and at 56.45 ppm for HNT-CES (Figure 3). This suggests that some aluminum sites, and more particularly those located at the edges of the halloysite nanotubes, reacted with the organosilane by forming Al-O-Si bonds [33].
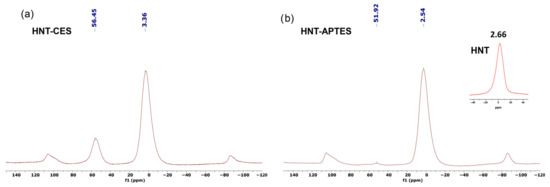
Figure 3.
27Al CP MAS NMR spectra of (a) HNT-CES and (b) HNT-APTES.
Thermogravimetric analyses (TGA) of silylated clay display a different pattern compared to the thermal degradation of native HNT and Sep, with the organomodified clay showing additional weight loss compared to pristine inorganic clays (Figure 4 and Table 1). The additional weight loss is due to the decomposition of the grafting agents. The residues obtained at 900 °C for HNT and Sep are, respectively, 86 and 99%. In contrast, the char residues harvested at the same temperature for HNT-CES, Sep-CES, HNT-APTES, and Sep-APTES were of 67, 73, 62, and 57%, respectively [33,46]. The weight degradation is quite similar for HNT-CES and HNT-APTES until 400 °C, suggesting that the organic functionalities are bonded in a similar way to the clay surfaces. A substantial discrepancy was, however, observed when they were grafted on SEP, with SEP-CES being more stable compared to SEP-APTES. This suggests that CES was strongly embedded within the SEP framework, imparting it with enhanced thermal properties, as corroborated by the weight loss calculated at 450 °C for these materials.
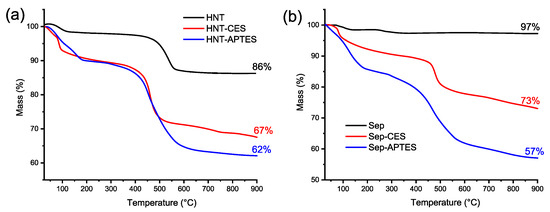
Figure 4.
TGA of (a) HNT, HNT-CES, and HNT-APTES and (b) Sep, Sep-CES, and Sep-APTES.

Table 1.
Organic and inorganic composition of modified versus pristine clay.
X-ray diffraction (XRD) of HNT, HNT-CES, and HNT-APTES shows that the basal distance has not been modified after functionalization, since the main diffraction peak seen at 2θ = 11.8°, corresponding to d = 0.74 nm, was kept intact (Figure 5a). This implies that the grafting does not take place within the galleries, which further consolidate the occurrence of the attachment at the Al–OH groups of the lumen surface (tube inner surface) and the Al–OH and Si–OH groups at the edges and external surface defects of nanotubes [50]. This could be explained by the inaccessibility of the Al-OH groups of the interlayer because of the strong hydrogen bonding interactions between the sheets [33,50]. A similar trend was also observed for sepiolite, since no alteration of the basal distance could be noticed after surface functionalization (Figure 5b) [52,53]. Nevertheless, a decrease in peak intensity was observed for silylated clay. This could be due to the formation of covalent bonds between the hydroxyl groups of clay and the organosilane producing structural distortions and consequently decreasing the layer stacking order [54].
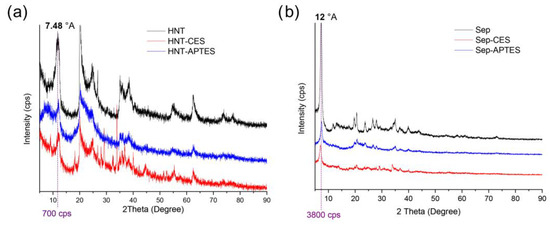
Figure 5.
XRD analyses of (a) HNT, HNT-CES, and HNT-APTES and (b) Sep, Sep-CES, and Sep-APTES.
SEM images show that halloysite and sepiolite display a tubular and fibrillar morphology, respectively, which are inherent to pristine clay minerals (Figure 6). The preserved morphologies after functionalization indicate that the grafting does not take place in the interlayer space of clay but rather on the surface and edges of the particles, in perfect agreement with the results found by XRD. However, the fingerprint of the grafting could be recognized when examining the extended network. In the case of carboxylate clay, a new secondary structure could be observed, which consists of large aggregates with preferential orientation, presumably formed through hydrogen bonding between individual tubes and fibers. In the case of amine-containing clay, significant densification and network compactness is observed instead. In the two cases, the observed morphology can be explained by the interaction of carboxylic or amino groups of the coupling reagent with siloxane or hydroxyl groups of the clay surface [53].
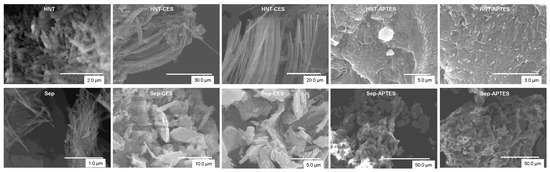
Figure 6.
SEM images of pristine and modified clays. (Top) HNT. (Down) Sep.
EDX analysis was carried out to identify the elemental composition of HNT and Sep before and after functionalization. Halloysite consists mainly of aluminum (Al), silicon (Si), and oxygen (O), while sepiolite features magnesium (Mg), silicon (Si), and oxygen (O). After functionalization, new peaks attributed to carbon (C) and nitrogen (N) are observed, which again confirm the successful surface silylation of the two clay materials (Supplementary Material S3).
Pristine and modified clays were also investigated through nitrogen sorption analysis. A severe decrease in the specific surface area and the pore volume was noticed after functionalization. Indeed, the specific surface area of HNT drops from 48 m2·g−1, with the grafted clay HNT-CES and HNT-APTES being devoid from any appreciable surface. Similarly, the specific surface area of Sep decreases dramatically from 321 m2·g−1 after grafting of CES and APTES (Supplementary Material S4). Surface functionalization of the two clays has therefore caused a serious decrease in the specific surface, which implies that the grafted molecules completely block nitrogen adsorption sites and hinder its access to the pores.
3.2. Amphoteric Carboxy- and Amino-Modified Halloysite
Having ascertained the occurrence of chemical grafting on both HNT and Sep, leading to mono-functional carboxy-decorated or amino-modified clay, we next attempted the preparation of amphoteric acid-base clay that could present much more potential for adsorbing dyes and micro-pollutants from wastewater. As has been mentioned in the experimental section, two strategies were explored to access bifunctional clay materials, namely (i) the simultaneous grafting of the two precursors and (ii) their sequential grafting, which consists of a step-by-step functionalization, as discussed below.
Preparation of HNT@APTES-CES_OP
The first method consists of the simultaneous introduction of carboxysilantriol (CES) and aminopropyltriethoxysilane (APTES). The resulting material was denoted as HNT@APTES-CES_OP, where OP stands for one-pot (Scheme 2).
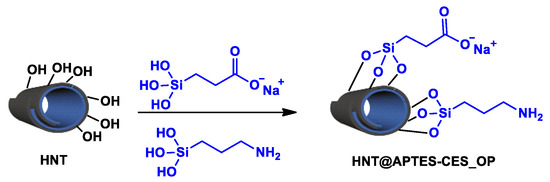
Scheme 2.
Dual functionalization of clay by APTES and CES through one-pot approach.
After the one-pot modification, the harvested solids were dried and then subjected to characterization. FTIR spectra of HNT@APTES-CES_OP and Sep@APTES-CES_OP illustrated in Supplementary Material S5 show bands in the 2868–2969 cm−1 interval, corresponding to the stretching (asymmetric and symmetric) of the C-H bond of the propyl and ethyl group belonging to APTES and CES coupling agents; an overlap of the characteristic bands of stretching vibration (asymmetric) of COO- and deformation of NH at 1570 cm−1; a band at 1456 cm−1 (1485 cm−1 for Sep@APTES-CES_OP), corresponding to the deformation vibration of the NH3+ function; a band at 1407 cm−1, attributed to the carboxylate group (COO−) [55]; and a band at 1302 cm−1, characteristic of the Si-C. This indicates the simultaneous presence of the two grafting agents, APTES and CES, on the surface of the amphoteric clay, thereby confirming their surface modification. Given the absence of signals 1754–1720 cm−1 that could be assigned to neutral COOH, one may also confirm that the grafted carboxylic group exists in its ionic form as carboxylate COO−. In addition, the presence of the signature of protonated amine NH3+ points to the zwitterion character of the resulting materials, due to the presence of both NH3+ and COO- groups on their surface [55].
29Si CP MAS NMR spectra of HNT@APTES-CES_OP shows the appearance of the signal at −92.43 ppm characteristic of the Q3 silicon atom of the pristine clay. A new broad signal was also observed at −65.79 ppm, corresponding to a T3-type silicon atom of the organosilane bonded to the halloysite surface (Figure 7). For sepiolite, a new signal appeared at 68.48 ppm, corresponding to the silicon atom of the organosilanes bonded to the clay surface with three siloxane bonds (T3). The appearance of the T group in the 29Si NMR of bifunctionalized clay clearly demonstrates the successful grafting of organic functional groups into the clay structure [56].
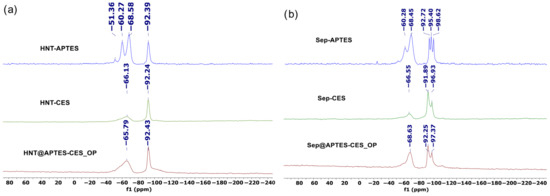
Figure 7.
29Si CP MAS NMR spectra of (a) HNT@APTES-CES_OP and (b) Sep@APTES-CES_OP.
13C CP MAS NMR of HNT@APTES-CES_OP shows a signal at 12.5 ppm, attributed to the CH2-Si group belonging to APTES and CES molecules; signals at 24 and 44.8 ppm, attributed, respectively, to the carbon atom in position 2 (C-C) and 1 (CH2-NH2) of the propyl group of the APTES molecule; and signals at 32 and 185 ppm, corresponding, respectively, to the -CH2- and C=O groups of the CES molecule (Figure 8) [57]. From these results, it is clear that the obtained clays contain two different types of molecules on their surface, namely the CES represented by the chemical shift at 185 ppm, characteristic of the C=O group and by two signals in the aliphatic region, and APTES, also identified by two signals in its aliphatic region. However, the characteristic signals of the APTES molecule are less intense than those of the CES molecule, meaning that the latter was more reactive toward the clay surface compared to APTES.
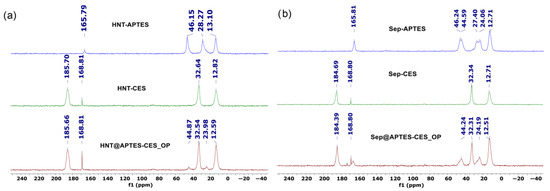
Figure 8.
13C CP MAS NMR of (a) HNT@APTES-CES_OP and (b) Sep@APTES-CES_OP.
The highest reactivity of CES is not surprising given the presence of an already hydrolyzed trisilanol in its extremity compared to triethoxysilyl groups in the case of APTES, that would necessitate additional time for hydrolysis prior to post-grafting. Considering this discrepancy, we envisioned that a more balanced and homogeneous coverage could be reached by reacting APTES first with HNT, followed by the grafting of CES. This post-grafting method is denoted herein as SG.
Preparation and characterization of HNT@APTES-CES_SG
Sequential grafting was undertaken by first reacting the activated clay with APTES, followed by the grafting of CES as a second partner, as illustrated below (Scheme 3). As described in the experimental section, the two-step grafting allowed the harvesting of a new solid material, denoted as HNT@APTES-CES_SG.
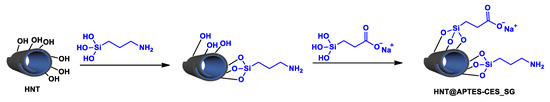
Scheme 3.
Sequential grafting of APTES and CES on HNT.
Akin to the material prepared in one pot, the FTIR spectrum of the latter shows characteristic bands of the two grafting agents (APTES and CES) (Supplementary Material S6). This includes those at 1315, 1383, 1484, and 3344 cm−1, corresponding to the vibration of Si-C, the deformation vibration of CH2, the deformation vibration of the NH3+, and the elongation vibration of the function NH2 [33,46,55,58,59]. The signature of the asymmetric and symmetric C-H bond was moreover observed at 2933–2870 cm−1. In addition, there is an overlap of the characteristic COO- stretching (asymmetric) vibration and N-H strain bands at about 1560 cm−1 [59].
29Si CP MAS NMR of the post-grafted halloysite presents new signals at −60.24 and −68.35 ppm, corresponding, respectively, to T2-type silicon atom of CES and T2-type silicon of APTES linked by two and three Si-O-Si bonds on the clay surface (Figure 9a). The presence of a T-type signal provides salient evidence for the creation of covalent bonds between the two tethers and the clay surface through Si-O-Si bridges.
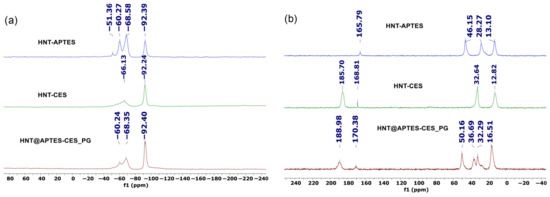
Figure 9.
NMR of HNT@APTES-CES_SG (a) 29Si CP NMR and (b) 13C NMR.
Solid-state 13C CP MAS NMR of the sequentially grafted halloysite HNT@APTES-CES_PG shows characteristic signals of the APTES agent including the ones at 16.51 and 50.16 ppm, attributed to the remaining and non-condensed ethoxyl group. The spectra also display typical signals of CES at 32.3 and 188.9 ppm, attributed, respectively, to -CH2- and C=O belonging to CES (Figure 9b). A substantial increase in the signal of grafted APTES was moreover noticed compared to the one observed during the one-pot method, indicating that sequential post-grafting allows for anchoring more APTES on the surface of halloysite.
3.3. Adsorption of Dyes from Water
We next turned our attention to assess the behavior of mono-functionalized versus amphoteric clay in adsorbing Congo red (CR), as a representative anionic dye, and malachite green (MG) as a cationic dye.
Adsorption using carboxy-functionalized clay
HNT-CES and Sep-CES show no affinity for Congo red compared to pristine HNT and Sep (Figure 10). This consolidates the presence of negatively charged carboxylate groups on the surface of HNT-CES and Sep-CES, resulting in electrostatic repulsion between the adsorbent and the dye. In contrast, HNT-CES and Sep-CES display a high adsorption efficiency towards malachite green compared to unmodified clays. In quantitative terms, the adsorption capacity of HNT-CES and Sep-CES are, respectively, 926 and 387 mg·g−1, being 3.32 and 1.13 times higher than those obtained for HNT and SEP (279 and 344 mg·g−1, respectively). The efficiency of these functionalized clays in adsorbing dye pollutants is illustrated by their impressive performance compared to many already reported materials, presented in Supplementary Material S7.
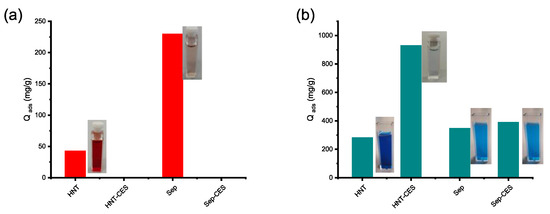
Figure 10.
Adsorption capacity of HNT-CES and Sep-CES for Congo red (a) and malachite green (b).
It is indeed obvious that the introduction of carboxylic groups dramatically changed the adsorption capacity of the resulting clay, maximizing its interaction with cationic dyes, as illustrated in the figure below, and suppressing its retention to anionic dyes because of the electrostatic repulsions (Scheme 4). The highest performance of HNT-CES compared to Sep-CES is noteworthy and should be considered for the selective removal of cationic dyes from water effluent containing a mixture of pollutants.
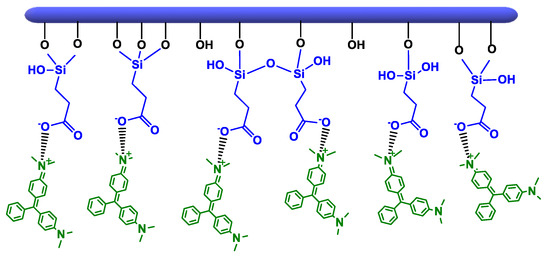
Scheme 4.
Adsorption mechanism of malachite green on clays-CES.
Adsorption with aminopropyl-modified clay
Compared to HNT-CES and Sep-CES, a diverging pattern was instead observed for HNT-APTES and Sep-APTES when comparing their adsorption towards CR and MG. In the two cases, the amino-modified clay exhibits significantly enhanced adsorption capacity towards both the anionic and cationic dyes compared to the parent clay (CR and MG) (Figure 11). Indeed, the adsorption capacities obtained for HNT-APTES and Sep-APTES were 1232 and 1228 mg/g for Congo red, being 29.3 and 5.4 times higher than those achieved for HNT and Sep, respectively, and 1139 and 948 mg/g for malachite green which are, respectively, 4 and 2.8 times higher than those observed for HNT and Sep (Supplementary Material S7).
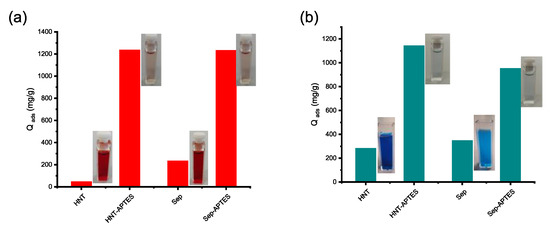
Figure 11.
Adsorption capacity of HNT-APTES and Sep-APTES for Congo red (a) and malachite green (b).
The removal efficiency of anionic dye (CR) obtained by clay-APTES was slightly greater than that of cationic dye (MG). This is due to the basic character of terminal NH2 groups that are prone to protonation to become positively charged (–NH3+), either by interacting with clay surface or once immersed in water solution [60,61,62,63]. The occurrence of electrostatic interactions between protonated amine and negatively charged sulfonate of CR provide the driving force for its uptake from water solution [64]. The adsorption of the cationic dye on HNT-APTES and Sep-APTES occurs rather through the non-protonated amine groups of APTES, which behave as a Lewis base by sharing their non-binding electron doublet with the positively charged dye molecule (Scheme 5).
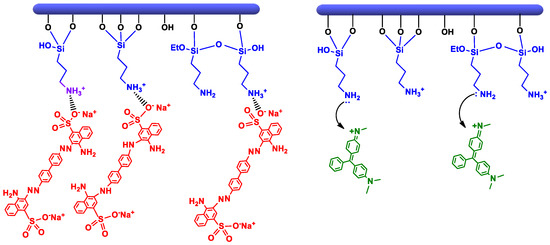
Scheme 5.
Adsorption mechanism of CR and MG on clays–APTES.
Adsorption using amphoteric clay
Amphoteric HNT modified through the one-pot method (HNT@APTES-CES_OP) have no affinity for the anionic Congo red dye (Figure 12a). In contrast, its analog, prepared through sequential-grafting method, (HNT@APTES-CES_SG) displays a noticeable affinity towards the two dyes, anionic and cationic (Figure 12). This could be explained by the difference in the density of tethered carboxylate COO− versus NH2, being much higher in the one-pot compared to the post-grafted surface, as confirmed by solid-state 13C NMR. This functional group is known to repel the CR anionic dyes from the clay surface, resulting in zero uptake of the latter. The slight increase noticed for the sequential-grafted material could be attributed to enhanced amount of immobilized amine groups compared to the one-pot material. The increase in the amine density results in maximizing the interaction of the surface either directly by electrostatic interaction with the anionic part of the dye or through neutralization of carboxylate COO− that is detrimental to anionic dye uptake. Care should be indeed taken as a balance must be reached during grafting, with the surface reactivity of the modified material being dependent on the coverage density and the homogeneous distribution of each functional group.
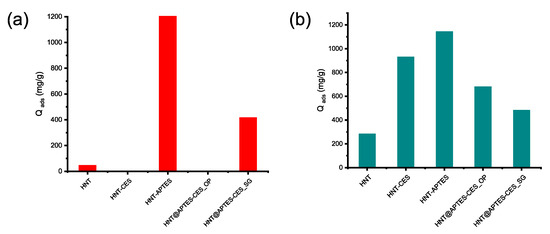
Figure 12.
Adsorption capacity of functional clay for Congo red (a) and malachite green (b).
A comparative study of cationic dye adsorption through modified clay shows the great performance of mono-functional clay with respect to native and amphoteric clay. The decrease in the adsorption performance of the post-grafted material (478 mg/g) compared to the one-pot material (676 mg/g) indicates the predominance of carboxylate groups in the latter as well as their quenching in the post-grafted material by tethering more APTES on the surface.
This further demonstrates that grafting antagonistic species on the clay surface is prone to generating multifunctional solids with tunable properties.
The cohabitation in close proximity (e.g., confined nanospace) of acid and base functionality is of tremendous interest as it could impart novel and unique reactivity to the solid surface. Indeed, the clay modified simultaneously by CES and APTES displays the advantage of being pH-sensitive and responsive, with the possibility to behave as a positively charged particle at an acid pH, due to the protonation of the NH2 groups of the APTES to NH3+, and consequently adsorb negatively charged dyes, and as a negatively charged particle at high pH due to the deprotonation of the COOH group to COO- for adsorbing positively charged dyes (Supplementary Material S8). The zwitterion form of the resulting material could be moreover harnessed for the simultaneous removal of both anionic and cationic dyes.
4. Conclusions
Functionalization of tubular halloysite and fibrous sepiolite enabled access to high-performance dye adsorbents.
The introduction of carboxylate groups on the surface of halloysite and sepiolite resulted in excellent selectivity toward cationic dyes. While electrostatic repulsion occurs between the adsorbent and the anionic Congo red, resulting in zero uptake of the pollutant, the carboxylate adsorbents interact strongly with cationic green malachite, resulting in substantial removal of the latter from water medium, being of 926 mg·g−1 and 387 mg·g−1 for HNT-CES and SEP-CES, respectively. This discriminative behavior could be harnessed later for the separation of cationic and anionic chemicals from liquid solution.
Amine-decorated adsorbents reached through immobilization of aminopropyltriethoxysilane on the surface of halloysite and sepiolite show a very significant improvement in adsorption of the anionic dye, Congo red, owing to the basic nature of the amine functions in that they are prone to protonation into positively charged ammonium species (–NH3+). These groups strongly interact with the negatively charged sulphonate groups of the dye, recording 1232 and 1228 mg·g−1 for HNT-APTES and SEP-APTES, respectively.
The amphoteric absorbents are more versatile owing to their pH-responsive properties. We have shown that the final performance varies depending on the functionalization method that affects the coverage density and site distribution. We consequently call for caution when comparing different materials. We have also evidenced strong interaction between amine and carboxylate moieties during grafting, which impact the uptake of the anionic pollutants. Current work explores the reactivity of the amphoteric adsorbents toward a mixture of pollutants and their pH-switchable reactivity.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/min15080841/s1, S1: Infrared spectra of HNT-CES, Sep-CES, HNT-APTES, and Sep-APTES; S2: 13C CP MAS NMR spectra of HNT-CES, Sep-CES, HNT-APTES, and Sep-APTES; S3: Mapping of Al and Si and EDX analysis of HNT-CES, Sep-CES, HNT-APTES, and Sep-APTES; S4: BET surface area, pore volume, and pore diameter of functionalized clays; S5: Infrared spectra of HNT@ APTES-CES_OP and Sep@ APTES-CES_OP; S6: Infrared spectra of HNT@ APTES-CES_SG; S7: Adsorption of Congo red and malachite green dye from aqueous solutions by different materials; S8: Proposed surface functional groups on Clay@APTES-CES depending on solution pH [65,66,67,68,69,70,71,72,73,74,75,76].
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.E.K. methodology, A.E.K., N.K. and K.D.; software, B.B. and J.E.H.; validation, A.E.K., K.D. and N.K.; formal analysis, B.B. and N.K.; investigation, B.B.; resources, A.E.K., K.D. and J.E.H.; data curation, K.D. and N.K.; writing—original draft preparation, B.B.; writing—review and editing, K.D. and A.E.K.; visualization, N.K.; supervision, K.D., A.E.K. and N.K.; project administration K.D. and N.K.; funding acquisition, K.D. and A.E.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
UEMF is acknowledged for financial support.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article/Supplementary Materials. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
References
- Sultan, M.B.; Anik, A.H.; Rahman, M.M. Emerging contaminants and their potential impacts on estuarine ecosystems: Are we aware of it? Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2024, 199, 115982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Ashokkumar, V.; Amobonye, A.; Bhattacharjee, G.; Sirohi, R.; Singh, V.; Flora, G.; Kumar, V.; Pillai, S.; Zhang, Z.; et al. Current research trends on cosmetic microplastic pollution and its impacts on the ecosystem: A review. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 320, 121106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tijani, J.O.; Fatoba, O.O.; Babajide, O.O.; Petrik, L.F. Pharmaceuticals, endocrine disruptors, personal care products, nanomaterials and perfluorinated pollutants: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2016, 14, 27–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, A.; Chaudhary, P.; Bhushan, B.; Ghai, K.; Singh, S.; Sillanpää, M. Removal of emergent pollutants: A review on recent updates and future perspectives on polysaccharide-based composites vis-à-vis traditional adsorbents. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 258, 129092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Narvaez, O.M.; Peralta-Hernandez, J.M.; Goonetilleke, A.; Bandala, E.R. Treatment technologies for emerging contaminants in water: A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 323, 361–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcamo, J. Water quality and its interlinkages with the Sustainable Development Goals. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sust. 2019, 36, 126–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Janssen, A.B.G.; Bazin, J.; Strokal, M.; Ma, L.; Kroeze, C. Accounting for interactions between Sustainable Development Goals is essential for water pollution control in China. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Worch, E. Adsorption Technology in Water Treatment; De Gruyter: Berlin, Germany; Boston, MA, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Bonilla-Petriciolet, A.; Mendoza-Castillo, D.I.; Reynel-Ávila, H.E. Adsorption Processes for Water Treatment and Purification; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; Volume 256. [Google Scholar]
- Faust, S.D.; Aly, O.M. Adsorption Processes for Water Treatment; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Cooney, D.O. Adsorption Design for Wastewater Treatment; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Mariana, M.; H.P.S., A.K.; Mistar, E.M.; Yahya, E.B.; Alfatah, T.; Danish, M.; Amayreh, M. Recent advances in activated carbon modification techniques for enhanced heavy metal adsorption. J. Water Proc. Eng. 2021, 43, 102221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bansal, R.C.; Goyal, M. Activated Carbon Adsorption; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Li, Z.; Yahyaoui, S.; Hanafy, H.; Seliem, M.K.; Bonilla-Petriciolet, A.; Luiz Dotto, G.; Sellaoui, L.; Li, Q. Effective adsorption of dyes on an activated carbon prepared from carboxymethyl cellulose: Experiments, characterization and advanced modelling. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 417, 128116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deitz, V.R. Bibliography of Solid Adsorbents: An Annotative Bibliographical Survey of the Scientific Literature on Bone Char, Activated Carbons, and Other Technical Solid Adsorbents, for the Years 1900 to 1942 Inclusive; National Bureau of Standards: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 1944. [Google Scholar]
- Celis, R.; HermosÍn, M.C.; Cornejo, J. Heavy Metal Adsorption by Functionalized Clays. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2000, 34, 4593–4599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-Guzmán, M.; Celis, R.; Hermosín, M.C.; Cornejo, J. Adsorption of the Herbicide Simazine by Montmorillonite Modified with Natural Organic Cations. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2004, 38, 180–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alomari, A.D.A. Chemically modified clay for adsorption of contaminants: Trends, advantages and limitations—A concise review. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2024, 105, 2302–2325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kausar, A.; Iqbal, M.; Javed, A.; Aftab, K.; Nazli, Z.-i.-H.; Bhatti, H.N.; Nouren, S. Dyes adsorption using clay and modified clay: A review. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 256, 395–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil, A.; Santamaría, L.; Korili, S.A.; Vicente, M.A.; Barbosa, L.V.; de Souza, S.D.; Marçal, L.; de Faria, E.H.; Ciuffi, K.J. A review of organic-inorganic hybrid clay based adsorbents for contaminants removal: Synthesis, perspectives and applications. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, G.D.; Theng, B.K.G.; Churchman, G.J.; Gates, W.P. Chapter 5.1—Clays and Clay Minerals for Pollution Control. In Developments in Clay Science; Bergaya, F., Lagaly, G., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013; Volume 5, pp. 587–644. [Google Scholar]
- Andrades, M.S.; Rodríguez-Cruz, M.S.; Sánchez-Martín, M.J.; Sánchez-Camazano, M. Effect of the modification of natural clay minerals with hexadecylpyridinium cation on the adsorption–desorption of fungicides. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2004, 84, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamoudi, S.; Srasra, E. Adsorption of organic dyes by HDPy+-modified clay: Effect of molecular structure on the adsorption. J. Mol. Struct. 2019, 1193, 522–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, M.; Sun, D.; Li, Y.; Wu, T. Effective removal of emulsified oil from oily wastewater using surfactant-modified sepiolite. Appl. Clay Sci. 2018, 157, 227–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ennajih, H.; Gueddar, H.; El Kadib, A.; Bouhfid, R.; Bousmina, M.; Essassi, E.M. Intercalation of nickel and cobalt thiabendazole complexes into montmorillonite. Appl. Clay Sci. 2012, 65–66, 139–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chabbi, J.; Jennah, O.; Katir, N.; Lahcini, M.; Bousmina, M.; El Kadib, A. Aldehyde-functionalized chitosan-montmorillonite films as dynamically-assembled, switchable-chemical release bioplastics. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 183, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Zhou, Q.; Martens, W.N.; Kloprogge, T.J.; Yuan, P.; Xi, Y.; Zhu, J.; Frost, R.L. Microstructure of HDTMA+-Modified Montmorillonite and its Influence on Sorption Characteristics. Clays Clay Min. 2006, 54, 689–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margelefsky, E.L.; Zeidan, R.K.; Davis, M.E. Cooperative catalysis by silica-supported organic functional groups. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2008, 37, 1118–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shylesh, S.; Thiel, W.R. Bifunctional Acid–Base Cooperativity in Heterogeneous Catalytic Reactions: Advances in Silica Supported Organic Functional Groups. ChemCatChem 2011, 3, 278–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz, U.; Brunel, D.; Corma, A. Catalysis using multifunctional organosiliceous hybrid materials. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 4083–4097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avila, L.R.; de Faria, E.H.; Ciuffi, K.J.; Nassar, E.J.; Calefi, P.S.; Vicente, M.A.; Trujillano, R. New synthesis strategies for effective functionalization of kaolinite and saponite with silylating agents. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2010, 341, 186–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, H.; Tao, Q.; Zhu, J.; Yuan, P.; Shen, W.; Yang, S. Silylation of clay mineral surfaces. Appl. Clay Sci. 2013, 71, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peixoto, A.F.; Fernandes, A.C.; Pereira, C.; Pires, J.; Freire, C. Physicochemical characterization of organosilylated halloysite clay nanotubes. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2016, 219, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carli, L.N.; Daitx, T.S.; Soares, G.V.; Crespo, J.S.; Mauler, R.S. The effects of silane coupling agents on the properties of PHBV/halloysite nanocomposites. Appl. Clay Sci. 2014, 87, 311–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cataldo, S.; Lazzara, G.; Massaro, M.; Muratore, N.; Pettignano, A.; Riela, S. Functionalized halloysite nanotubes for enhanced removal of lead(II) ions from aqueous solutions. Appl. Clay Sci. 2018, 156, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ressam, I.; El Kadib, A.; Lahcini, M.; Luinstra, G.A.; Perrot, H.; Sel, O. Enhanced proton transport properties of Nafion via functionalized halloysite nanotubes. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2018, 43, 18578–18591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez, A.; Santarén, J.; Esteban-Cubillo, A.; Aparicio, P. Chapter 12—Current Industrial Applications of Palygorskite and Sepiolite. In Developments in Clay Science; Galàn, E., Singer, A., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2011; Volume 3, pp. 281–298. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Liao, L.; Hursthouse, A.; Song, N.; Ren, B. Sepiolite-Based Adsorbents for the Removal of Potentially Toxic Elements from Water: A Strategic Review for the Case of Environmental Contamination in Hunan, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, N.; Hursthouse, A.; McLellan IWang, Z. Treatment of environmental contamination using sepiolite: Current approaches and future potential. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 43, 2679–2697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boumhidi, B.; Katir, N.; El Haskouri, J.; Draoui, K.; El Kadib, A. Phosphorylation triggered growth of metal phosphate on halloysite and sepiolite nanoparticles: Preparation, entrapment in chitosan hydrogels and application as recyclable scavengers. New J. Chem. 2020, 44, 14136–14144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Mello Ferreira Guimarães, A.; Ciminelli, V.S.T.; Vasconcelos, W.L. Smectite organofunctionalized with thiol groups for adsorption of heavy metal ions. Appl. Clay Sci. 2009, 42, 410–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerra, D.L.; Oliveira, S.P.; Silva, R.A.S.; Silva, E.M.; Batista, A.C. Dielectric properties of organofunctionalized kaolinite clay and application in adsorption mercury cation. Ceram. Int. 2012, 38, 1687–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wamba, A.G.N.; Kofa, G.P.; Koungou, S.N.; Thue, P.S.; Lima, E.C.; dos Reis, G.S.; Kayem, J.G. Grafting of Amine functional group on silicate based material as adsorbent for water purification: A short review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 3192–3203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiebault, T.; Brendlé, J.; Augé, G.; Limousy, L. Cleaner Synthesis of Silylated Clay Minerals for the Durable Recovery of Ions (Co2+ and Sr2+) from Aqueous Solutions. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2020, 59, 2104–2112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao L-y Fei J-j Lian H-z Mao, L.; Cui, X.-b. Development of a novel amine- and carboxyl-bifunctionalized hybrid monolithic column for non-invasive speciation analysis of chromium. Talanta 2020, 212, 120799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, J.A.; Sarmento, V.H.; Romão, L.P.; Paranhos, C.M.J.S. Performance of the MCM-41-NH 2 Functionalized Mesoporous Material Synthetized from the Rice Husk Ash on the Removal of the Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons. Silicon 2020, 12, 1913–1923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maria Chong, A.S.; Zhao, X.S. Functionalization of SBA-15 with APTES and Characterization of Functionalized Materials. J. Phys. Chem. B 2003, 107, 12650–12657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasbakhsh, P.; Ismail, H.; Fauzi, M.N.A.; Bakar, A.A. EPDM/modified halloysite nanocomposites. Appl. Clay Sci. 2010, 48, 405–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, D.; Yuan, P.; Annabi-Bergaya, F.; Yu, H.; Liu, D.; Liu, H.; He, H. Natural halloysite nanotubes as mesoporous carriers for the loading of ibuprofen. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2013, 179, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, P.; Southon, P.D.; Liu, Z.; Green, M.E.R.; Hook, J.M.; Antill, S.J.; Kepert, C.J. Functionalization of Halloysite Clay Nanotubes by Grafting with γ-Aminopropyltriethoxysilane. J. Phys. Chem. C 2008, 112, 15742–15751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huynh, J.; Palacio, R.; Safizadeh, F.; Lefèvre, G.; Descostes, M.; Eloy, L.; Guignard, N.; Rousseau, J.; Royer, S.; Tertre, E.; et al. Adsorption of Uranium over NH2-Functionalized Ordered Silica in Aqueous Solutions. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 15672–15684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeniyol, M. Characterization of two forms of sepiolite and related Mg-rich clay minerals from Yenidoğ an (Sivrihisar, Turkey). Clay Miner. 2014, 49, 91–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, M.A.; Ciuffi, K.J.; Rives, V.; Vicente, M.A.; Trujillano, R.; Gil, A.; Korili, S.A.; de Faria, E.H. Effect of chemical modification of palygorskite and sepiolite by 3-aminopropyltriethoxisilane on adsorption of cationic and anionic dyes. Appl. Clay Sci. 2017, 135, 394–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doğan, M.; Turhan, Y.; Alkan, M.; Namli, H.; Turan, P.; Demirbaş, Ö. Functionalized sepiolite for heavy metal ions adsorption. Desalination 2008, 230, 248–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colilla, M.; Izquierdo-Barba, I.; Sánchez-Salcedo, S.; Fierro, J.L.G.; Hueso, J.L.; Vallet-Regí, M. Synthesis and Characterization of Zwitterionic SBA-15 Nanostructured Materials. Chem. Mater. 2010, 22, 6459–6466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.-H.; Deka, J.R.; Wu, C.-E.; Tsai, C.-H.; Saikia, D.; Yang, Y.-C.; Kao, H.-M. Bifunctional Cage-Type Cubic Mesoporous Silica SBA-1 Nanoparticles for Selective Adsorption of Dyes. Chem. Asian J. 2017, 12, 1314–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutmann, T.; Liu, J.; Rothermel, N.; Xu, Y.; Jaumann, E.; Werner, M.; Breitzke, H.; Sigurdsson, S.T.; Buntkowsky, G. Natural Abundance 15N NMR by Dynamic Nuclear Polarization: Fast Analysis of Binding Sites of a Novel Amine-Carboxyl-Linked Immobilized Dirhodium Catalyst. Chem. Eur. J. 2015, 21, 3798–3805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhu, Z.; Zhang, X.; Li, P.; Huang, Y.; Luo, X.; Liang, Z. Amine-functionalized sepiolite: Toward highly efficient palladium nanocatalyst for dehydrogenation of additive-free formic acid. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2019, 44, 16707–16717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Ruan, J.; Li, Y.; Terasaki, O.; Che, S. Synthesis and Characterization of the Amphoteric Amino Acid Bifunctional Mesoporous Silica. Chem. Mater. 2007, 19, 2860–2867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, A.; Zhou, S.; Zhao, Y.; Lu, X.; Han, P. Effective NH2-grafting on attapulgite surfaces for adsorption of reactive dyes. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 194, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanani-Jazi, M.H.; Akbari, S. Amino-dendritic and carboxyl functionalized halloysite nanotubes for highly efficient removal of cationic and anionic dyes: Kinetic, isotherm, and thermodynamic studies. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Errais, E.; Duplay, J.; Elhabiri, M.; Khodja, M.; Ocampo, R.; Baltenweck-Guyot, R.; Darragi, F. Anionic RR120 dye adsorption onto raw clay: Surface properties and adsorption mechanism. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2012, 403, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xia, K.; Liu, X.; Chen, Z.; Du, H.; Zhang, X. Synthesis of cationic-modified silica gel and its adsorption properties for anionic dyes. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2019, 102, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, P.; Southon, P.D.; Liu, Z.; Kepert, C.J. Organosilane functionalization of halloysite nanotubes for enhanced loading and controlled release. Nanotechnology 2012, 23, 375705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vimonses, V.; Lei, S.; Jin, B.; Chow, C.W.; Saint, C. Kinetic study and equilibrium isotherm analysis of Congo Red adsorption by clay materials. Chem. Eng. J. 2009, 148, 354–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vahidhabanu, S.; Karuppasamy, D.; Adeogun, A.I.; Babu, B.R. Impregnation of zinc oxide modified clay over alginate beads: A novel material for the effective removal of congo red from wastewater. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 5669–5678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, C.; Feng, C.; Wei, M.; Wu, Y. Enhanced adsorption of anionic toxic contaminant congo red by activated carbon with electropositive amine modification. Chemosphere 2018, 208, 476–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, C.; Pi, M.; Jiang, C.; Cheng, B.; Yu, J. Synthesis of hierarchical porous zinc oxide (ZnO) microspheres with highly efficient adsorption of Congo red. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 490, 242–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, F.; Gao, M.; Shen, T.; Zeng, H.; Xiang, Y. Comparative study of organo-vermiculite, organo-montmorillonite and organo-silica nanosheets functionalized by an ether-spacer-containing Gemini surfactant: Congo red adsorption and wettability. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 349, 388–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Gao, M.; Shen, T.; Zeng, H. Single and simultaneous adsorption of rhodamine B and congo red from aqueous solution by organo-vermiculites. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 292, 111408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Li, Y.; Li, M.; Zheng, H.; Du, Q.; Li, H.; Wang, Y.; Wang, D.; Wang, C.; Sui, K. Preparation of improved gluten material and its adsorption behavior for congo red from aqueous solution. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 556, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmoubarki, R.; Mahjoubi, F.Z.; Tounsadi, H.; Moustadraf, J.; Abdennouri, M.; Zouhri, A.; El Albani, A.; Barka, N. Adsorption of textile dyes on raw and decanted Moroccan clays: Kinetics, equilibrium and thermodynamics. Water Resour. Ind. 2015, 9, 16–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tehrani-Bagha, A.R.; Nikkar, H.; Mahmoodi, N.M.; Markazi, M.; Menger, F.M. The sorption of cationic dyes onto kaolin: Kinetic, isotherm and thermodynamic studies. Desalination 2011, 266, 274–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, Y.C. Adsorption Characteristics of a Low-Cost Activated Carbon for the Reclamation of Colored Effluents Containing Malachite Green. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2011, 56, 478–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, L.; Zhang, J.; Shi, H.; Li, N.; Ping, Q. Adsorption of malachite green by diatomite: Equilibrium isotherms and kinetic studies. J. Disper. Sci. Technol. 2016, 37, 1059–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, S.; Ur Rahman, A.; Ullah, F.; Rashid, A.; Arshad, T.; Viglašová, E.; Galamboš, M.; Mahmoodi, N.M.; Ullah, H. Adsorption of Malachite Green Dye onto Mesoporous Natural Inorganic Clays: Their Equilibrium Isotherm and Kinetics Studies. Water 2021, 13, 965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).