Abstract
Understanding diagenetic processes is fundamental to characterizing heterogeneous carbonate reservoirs, where variations in pore structures and mineralogy significantly influence reservoir quality and fluid flow behavior. This study presents an integrated diagenetic classification approach applied to the upper Dalan and Kangan formations in the Persian Gulf. Utilizing extensive core analyses, petrographic studies, scanning electron microscopy (SEM) imaging, and petrophysical data, six distinct diagenetic classes were identified based on the quantification of key processes such as dolomitization, dissolution, cementation, and compaction. The results reveal that dolomitization and dissolution enhance porosity and permeability, particularly in high-energy shoal facies, while cementation and compaction tend to reduce reservoir quality. A detailed petrographic examination and rock typing, including pore type classification and hydraulic flow unit analysis using flow zone indicator methods, allowed the subdivision of the reservoir into hydraulically meaningful units with consistent petrophysical characteristics. The application of the Stratigraphic Modified Lorenz Plot facilitated large-scale reservoir zonation, revealing the complex internal architecture and significant heterogeneity controlled by depositional environments and diagenetic overprints. This diagenetic classification framework improves predictive modeling of reservoir behavior and fluid distribution, supporting the optimization of exploitation strategies in heterogeneous carbonate systems. The approach demonstrated here offers a robust template for similar carbonate reservoirs worldwide, emphasizing the importance of integrating diagenetic quantification with multi-scale petrophysical and geological data to enhance reservoir characterization and management.
1. Introduction
An examination of geological heterogeneity and diagenetic processes plays a critical role in understanding the complexities of subsurface reservoirs [1,2]. Variations in rock properties such as porosity, texture, composition, and permeability directly influence the behavior and movement of fluids, including water, hydrocarbons, and gases [3,4]. These factors are particularly significant in the context of resource exploration and extraction, where predicting reservoir quality and performance is essential [5]. Furthermore, heterogeneity affects groundwater flow and contaminant transport, making its study equally important for environmental management and remediation [6]. Diagenetic processes, encompassing the physical, chemical, and biological changes that sediments undergo after deposition, further alter the original characteristics of rocks [7]. These processes influence lithification, mineralogy, and pore structures, thereby enhancing or diminishing the storage and transmissive capacities of reservoir rocks [8]. An in-depth understanding of these transformations is key to developing accurate geological models, optimizing resource recovery strategies, and interpreting the geological history of sedimentary basins [9,10].
Various methods are used to assess subsurface heterogeneity and understand diagenetic changes [11,12,13,14]. Well-logging methods, including sonic, resistivity, and gamma-ray logs, generate continuous borehole data, offering insights into porosity and rock composition [15]. Geophysical surveys, such as seismic reflection and ground-penetrating radar, expand the spatial understanding of rock variability, while geostatistical tools like kriging model and predict heterogeneity patterns [16]. A laboratory-based petrophysical analysis provides quantitative measurements of porosity, permeability, and mechanical strength [17]. Additional tools, such as remote sensing and field investigations of outcrops, help detect surface indicators of subsurface variations [18]. Among these methods, core analysis and petrography remain some of the most direct techniques, providing detailed data on rock lithology and texture [19]. Diagenetic processes are often classified to better understand the sediment-to-rock transformation [20]. This classification remains widely used in sedimentary petrology and reservoir geology for predicting fluid behavior and evaluating economic viability [21,22,23,24,25].
The present study investigates the upper Dalan and Kangan Formations in a supergiant gas field situated in the Persian Gulf, an area that holds over 60% of the global oil reserves and about 30% of gas resources [26]. Given the economic and strategic significance of this region, a detailed geological and reservoir analysis of these formations remains crucial. This study aims to identify and quantitatively analyze the diagenetic processes affecting the upper Dalan and Kangan Formations, determine the types of reservoir rocks and flow units present, and examine the relationships between diagenetic classes and reservoir properties. By integrating a geological core analysis with modern characterization techniques, this research contributes new insights into the diagenetic history and reservoir architecture of one of the world’s most important hydrocarbon provinces, thereby enhancing predictive models and resource management strategies.
2. Geological Background
During the Permian–Triassic, the Middle East and Persian Gulf region were located along the northern passive margin of the Gondwana supercontinent, adjacent to the Paleo-Tethys Ocean [27]. The Arabian Plate, situated along the northern rim of Gondwana, was tectonically stable during much of the Permian, allowing for the development of widespread carbonate–evaporite platforms [28]. This setting favored the deposition of cyclic shallow marine carbonates, such as those preserved in the upper Dalan and Kangan Formations [29,30,31]. These formations were deposited in a broad, shallow, and gradually subsiding shelf environment and represent alternating high-energy oolitic/bioclastic shoals and evaporitic interbeds [29,32,33]
A prominent paleogeographic feature during this time was the Qatar–South Fars Arch (Q-SF Arch), a structural high that played a key role in the localization of shallow marine carbonate deposition during the Late Permian–Early Triassic [34]. This arch served as a substrate for the accumulation of oolitic shoals and widespread tidal flat deposits [35]. The onset of carbonate–evaporite sedimentation was further driven by a regional marine transgression that affected the eastern Arabian Plate during the Late Permian [29]. Although this transgression led to extensive carbonate deposition, global eustatic sea-level curves indicate that the relative sea level was near its lowest during this period [36,37].
Mineralogically, the marine carbonates deposited in the Permian–Triassic interval were initially aragonitic, reflecting warm, supersaturated marine conditions [38]. These aragonitic carbonates are represented by the oolitic reservoir facies of the Khuff Formation, which is the stratigraphic equivalent of the upper Dalan and Kangan Formations across much of the Arabian Plate [39]. Recent geochemical studies suggest that these aragonitic deposits began transitioning to calcite during the middle Wuchiapingian stage and this trend continued into the Changhsingian [40]. The high content of unstable allochems, such as ooids composed of aragonite or high-Mg calcite, led to early diagenetic dissolution, significantly enhancing the reservoir quality of these formations [41].
The climate during the Late Permian to Early Triassic underwent dramatic transitions [42]. The cold, glacial conditions of the Late Paleozoic gave way to a warmer, non-glacial Mesozoic climate [43]. A warming phase in the Sakmarian led to rapid melting of glacial ice, and by the Kazanian, high-latitude regions experienced temperate conditions [44]. A second, more intense global warming event occurred near the Permian–Triassic boundary (PTB), producing temperate–warm conditions even in high northern latitudes and marking one of the most extreme greenhouse intervals in Earth’s history [45,46]. This shift had significant implications for both marine carbonate production and biotic turnover, as the PTB coincided with the largest mass extinction in Earth’s history [47].
Stratigraphically, the upper Dalan Formation (Late Permian) and the overlying Kangan Formation (Early Triassic) correlate laterally with the Khuff Formation in Saudi Arabia, Qatar, and the United Arab Emirates [48,49] (Figure 1). These units form a transboundary reservoir system that contains some of the world’s largest non-associated gas accumulations, especially within the South Pars/North Dome field (Figure 1). Their depositional continuity, favorable facies distribution, and diagenetic porosity enhancement make them highly significant targets for hydrocarbon exploration and production [50]. Stratigraphically, the upper Dalan Formation is subdivided into the K3 and K4 units and the Kangan Formation includes the K1 and K2 units (Figure 1C).
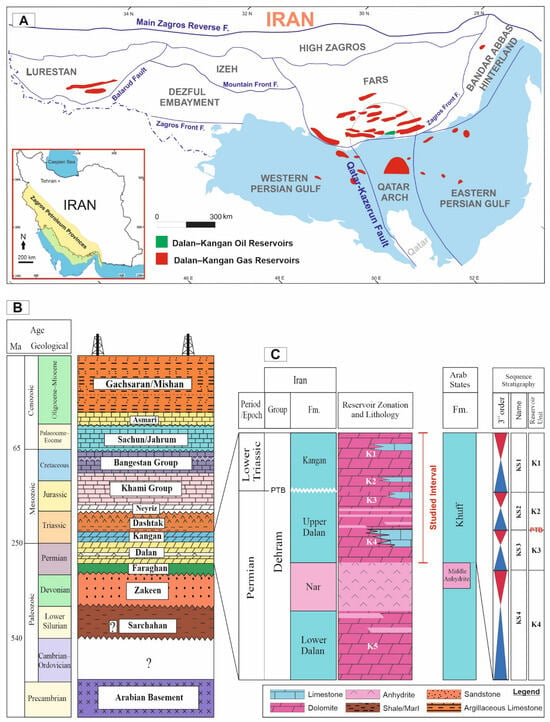
Figure 1.
(A) Map showing the locations of oil and gas fields producing in the Dalan–Kangan reservoirs in the Zagros area of SW Iran [35]. (B) Stratigraphic column of the studied field [50]. (C) Detailed stratigraphy of the Dalan–Kangan reservoirs in the central part of the Persian Gulf.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Dataset
A total of 406.7 m of core samples from the studied field were analyzed, covering the Kangan and upper Dalan Formations in the central Persian Gulf. From these intervals, 1683 thin sections were prepared from both horizontal and vertical plugs, with samples taken approximately every 0.3 m. Thin sections were used for the sedimentological analysis, with Alizarin Red-S staining techniques applied to distinguish between calcite and dolomite. Additionally, ten samples from mud-dominated facies were selected for scanning electron microscopy (SEM) to investigate micro-pore structures. Petrophysical data, including core porosity and permeability measurements and wireline logs, were integrated with geological core descriptions and petrographic observations to support reservoir characterization. All analyses were performed at the National Iranian Oil Company (NIOC) laboratories in Tehran.
3.2. Petrographic and Petrophysical Methods
The geological reservoir characterization of the Permian–Triassic upper Dalan and Kangan Formations was conducted through a structured methodological approach. Core-log depth matching was performed using gamma-ray (GR) outputs, including potassium, thorium, and uranium logs, plotted at multiple scales and compared with wireline CGR logs for accurate correlations. Macroscopic core descriptions were conducted in two stages, beginning with visual logging of un-slabbed cores to identify sedimentary and diagenetic features such as stylolites and laminations. Detailed lithological and structural descriptions followed slab preparation and the thin section analysis. Thin sections were microscopically analyzed to assess mineralogy, microfacies, diagenetic alterations, pore types, and the fossil content. The sequence stratigraphic interpretation was based on the core description, facies and diagenesis studies, petrophysical logs, and fossil assemblages. Sequence boundaries and maximum flooding surfaces were identified using sedimentological and diagenetic indicators and interpreted within a modified Embry [51] sequence stratigraphic framework, distinguishing transgressive and regressive (T–R) system tracts.
3.3. Reservoir Rock Typing and Zonation Methods
In this study, an integrated geological-based reservoir characterization and rock typing was applied on the Permian–Triassic reservoirs. Based on the available data, several rock-typing methods were used and the results were integrated into a comprehensive “reservoir characterization and rock-typing” log.
Pore Typing
This method utilizes the results from petrographic and SEM studies, combined with the standard diagram of Ahr [1], to categorize pore types.
Hydraulic Flow Units (HFUs)
This methodology enables the subdivision of heterogeneous carbonate reservoirs into discrete rock units with consistent petrophysical and pore structure properties [52]. The Flow Zone Indicator (FZI) method calculates key parameters: the Reservoir Quality Index (RQI), normalized porosity (ϕz), and FZI derived from permeability, porosity, and rock fabric data. Prior to analysis, data filtration was conducted to remove samples with a permeability below 0.01 mD, which can distort FZI calculations.
A total of 1153 valid samples were analyzed through a combination of a histogram analysis, probability plots, and RQI versus ϕz cross plots to define distinct HFUs. These statistical techniques were integrated with geological observations to refine unit boundaries and account for facies variability and diagenetic effects. The principal equations governing the HFU method are outlined below (Equations (1)–(3)):
where K is permeability (mD) and φ is porosity (fraction).
RQI = 0.0314(K/φ)1/2
φz= φ/(1 − φ)
FZI = RQI/φz
Reservoir Zonation by the Lorenz Plot
The internal zonation of the Permian–Triassic reservoirs was established by utilizing continuous core poroperm data in conjunction with the Stratigraphic Modified Lorenz (SML) approach [53]. The implementation of the SMLP technique involved arranging continuous core porosity and permeability data in stratigraphic order and calculating the respective flow capacity (Kh) and storage capacity (Φh) (Equations (4) and (5)):
where k is permeability (in millidarcies), Φ is the fractional porosity, and h is the thickness of the sample interval (in meters).
(kh)cum = k1(h1 − h0) + k2(h2 − h1) + … + ki(hi − hi − 1)
(Φh)cum = Φ1(h1 − h0) + Φ2(h2 − h1) + … + Φki(hi − hi − 1)
3.4. Diagenetic Classification Method
In most geological studies, the impacts of diagenetic processes on reservoir parameters are often addressed through qualitative descriptions. However, achieving a precise and comprehensive understanding of how diagenetic events influence the petrophysical and reservoir characteristics of carbonate rocks requires both quantification and a systematic classification of these processes. The concepts of diagenetic classes and pore formation categories aim to advance our understanding of how sedimentary and diagenetic mechanisms govern reservoir development and porosity preservation in carbonate sequences [1,54,55].
In this study, a detailed effort was made to identify and quantify all diagenetic processes affecting the reservoir quality of the upper Dalan and Kangan Formations in the Persian Gulf. This was accomplished through a petrographic analysis of thin sections, enabling the documentation of various diagenetic phases.
The relative abundance of processes such as cementation, dissolution, and dolomitization was expressed as a percentage of occurrence. For diagenetic features where a percentage estimation was not feasible, such as mechanical compaction and fracturing, a semi-quantitative intensity scale ranging from 1 to 4 was applied. These quantified data were then visualized using rhombic diagrams to classify the samples into distinct diagenetic classes (see Section 4.2 for details).
4. Results
4.1. Facies Analysis
A detailed facies analysis of the upper Dalan–Kangan Formations was not the target of this study and is discussed in previous research published from the Persian Gulf [29,30,56,57]. In this study, summarized facies characteristics of the formations are provided in Table 1. They will be used as a basis for detailed interpretation of diagenetic classes (see Section 4.2, Section 4.3, Section 4.4 and Section 4.5).

Table 1.
Summarized facies characteristics of the Permian–Triassic sequences in the Persian Gulf.
The upper Dalan and Kangan Formations exhibit a diverse range of microfacies, each indicative of distinct depositional environments. The supratidal setting is represented by FG1, characterized by anhydrite, reflecting arid conditions with high evaporation. Intertidal environments include FG2 (dolomudstone/fenestral-nodular dolomudstone/dolo-breccia), FG3 (stromatolite boundstone), and FG4 (thrombolite boundstone), which indicate microbial activity and periodic subaerial exposure.
Lagoon settings are marked by FG5 (bioturbated benthic foraminifera bioclast peloid mudstone/wackestone), FG6 (bioclast intraclast ooid wackestone), and FG7 (intraclast oncoid wackestone), suggesting low-energy, shallow waters with abundant organic activity. Shoal environments are represented by FG8 (peloid oncoid packstone), FG9 (bioclast ooid packstone/grainstone), and FG10 (oncoid intraclast packstone/grainstone), reflecting higher-energy conditions with grain-supported textures.
Off-shoal settings include FG11 (microbioclast mudstone/wackestone), indicating quieter, deeper waters. Overall, these microfacies illustrate a transition from tidal flats to lagoonal, shoal and off-shoal (open marine) environments, highlighting a ramp-like depositional model for the Permian–Triassic sequences in the Persian Gulf.
4.2. Diagenetic Processes
The key diagenetic processes that influenced the reservoir quality of the upper Dalan and Kangan Formations include dolomitization, dissolution, cementation, and compaction (Figure 2).
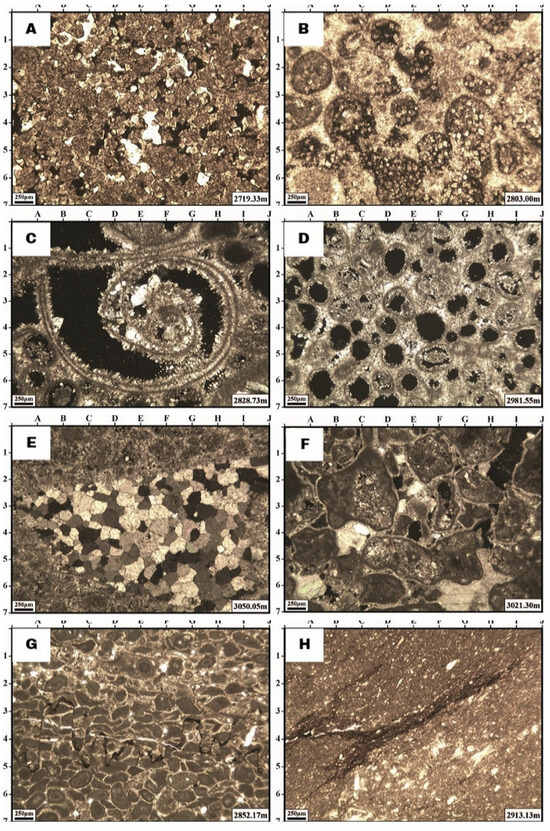
Figure 2.
Microscopic images of dolomitization as an important diagenetic feature in the Permian–Triassic reservoirs. (A) Coarse crystalline dolomitization destroying fabric. (B) Fabric-selective dolomitization from coarse to fine crystalline in shoal facies. (C) Vuggy porosity resulting from dissolution in muddy tidal facies. (D) Bioclastic and ooid moldic pores. (E) Isopachous cement and blocky calcite cement in shoal facies. (F) Drusy calcite cement in a skeletal mold. (G) Grain deformation and formation of stylolites. (H) Dissolution vugs in open marine wackestone facies.
Dolomitization is a dominant diagenetic process, occurring in over 60% of the cored intervals, in a range of mud- to grain-dominated facies of intertidal to shoal settings (Table 1). In the high-energy shoal facies, the process is fabric-selective, preserving the original textures and structures of carbonate grains (Figure 2). This is particularly evident in the middle parts of the K1 and K2 units, where fabric-selective dolomitization is common (Figure 3). In contrast, in lower-energy facies (i.e., dolomudstones of intertidal and lagoon settings), dolomitization becomes non-fabric-selective, forming larger dolomite crystals (Figure 2), especially in the upper K3 and K4 units (Figure 3). These non-fabric-selective dolostones, characterized by coarse and sucrosic dolomite crystals, exhibit evidence of later dolomitization stages, possibly resulting from burial recrystallization (Figure 2).
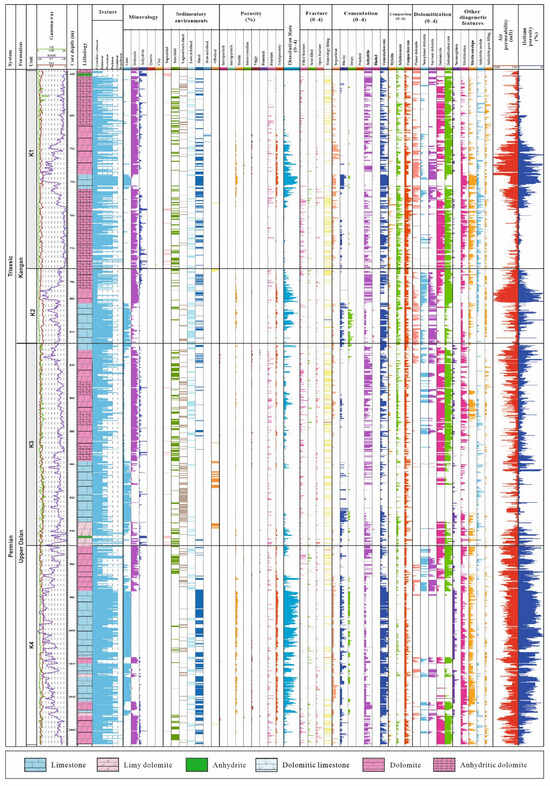
Figure 3.
Sedimentological log of the Permian–Triassic reservoirs in the studied field, Persian Gulf.
Dissolution is another key process that contributes to porosity, particularly in the shoal complex facies (Table 1). The dissolution of originally aragonitic and high-Mg calcite grains creates moldic and vuggy pores, leaving pores filled with calcite spar cement (Figure 2). The dissolution features are most prominent in the middle parts of the K1, K2, and K4 units (Figure 3). Dissolution is less evident in the K3 unit, which is substantially composed of mud-dominated facies of intertidal, lagoon and off-shoal (open marine) settings (Table 1 and Figure 3).
The cementation process involves the precipitation of calcite or aragonite, which reduces the pore volume in the shoal facies (Figure 2B). Isopachous cementation is the main type of cement within the high-energy shoal facies. The intensity of isopachous cementation diminishes from shoal settings toward offshore and landward facies. Later-stage burial cementation, including calcite (drusy and blocky), anhydrite (pore-filling and poikilotopic), and saddle dolomite (mostly fracture-filling), is recorded in the whole K1, lower K2, upper K3, and whole K4 units (Figure 3).
Compaction, both mechanical and chemical, varies across the facies and stratigraphic units. Mechanical compaction is more intense in the finer-grained, less-cemented intervals, such as the mud-supported facies, where the grains are rearranged or crushed under the pressure of overlying sediments (Figure 2). In contrast, compaction is less pronounced in the dolomitized, grain-supported facies due to early cementation, which provide a rigid framework against compaction (Figure 2). Chemical compaction is recorded in the forms of stylolites and solution seams, and is most intense in the fine-grained mud-supported facies of the K1 to K3 units (Figure 3). These features are less prominent in the coarser-grained and well-cemented facies of the K4 unit (Figure 3).
4.3. Diagenetic Classification
In this study, the diagenetic processes of dolomitization, dissolution, cementation, and compaction were examined to assess their impacts on the reservoir characteristics of the upper Dalan and Kangan Formations. Dolomitization and dissolution are processes that enhance reservoir quality, while cementation and compaction tend to reduce it. To quantify these processes, rhombus-shaped diagrams were used, with cementation and compaction rated from an intensity of one (lowest) to four (highest), and dolomitization and dissolution expressed as percentages. The percentages were calculated through an image analysis of thin sections. The relative intensities of cementation and compaction are determined throughout petrographic studies as one (0–25%), two (25–50%), three (50–75%), and four (75–100%). Based on these processes, six diagenetic classes (DCs) were identified:
DC-I—cemented and compacted anhydrite, stromatolites, and mudstone facies;
DC-II—dolomitized stromatolites and mudstone facies;
DC-III—dolomitized or dissolved wackestone and packstone facies;
DC-IV—cemented and compacted wackestone and packstone facies;
DC-V—dolomitized (DC-V-Dol) or dissolved (DC-V-Dis) grainstone facies;
DC-VI—cemented and compacted grainstone facies.
In each reservoir unit, the distribution of these diagenetic classes varies according to the specific lithological and diagenetic conditions present.
4.3.1. K1 Unit
In reservoir unit K1, the porosity distribution exhibits distinct trends across its different sections. This unit was subdivided into five sub-units according to the general porosity–permeability trends and dominant diagenetic classes (Figure 4). Sub-unit K1_A corresponds to DC-I represented by anhydrites, stromatolites, and mudstone facies with high compaction and cementation. Sub-unit K1_B mostly includes the DC-V-Dol class in which dolomitized grainstone facies dominate. Sub-unit K1_C has a limestone lithology and resembles DC-VI, indicating cemented and compacted grainstone facies. Sub-unit K1_D corresponds to DC-V-Dis, representing dissolved grainstone facies. Sub-unit K1_E has a dolomite lithology and includes anhydrite, stromatolites, and mudstone facies with high compaction and cementation (i.e., DC-I) (Figure 4). The upper (K1_A) and lower (K1_E) sections display low porosity, characterized primarily by intergranular and fenestral pores. In contrast, the middle section exhibits high porosity and can be subdivided into three distinct parts: the upper (K1_B) and lower (K1_D) portions are predominantly dolomitic, while the middle portion (K1_C) is limestone.
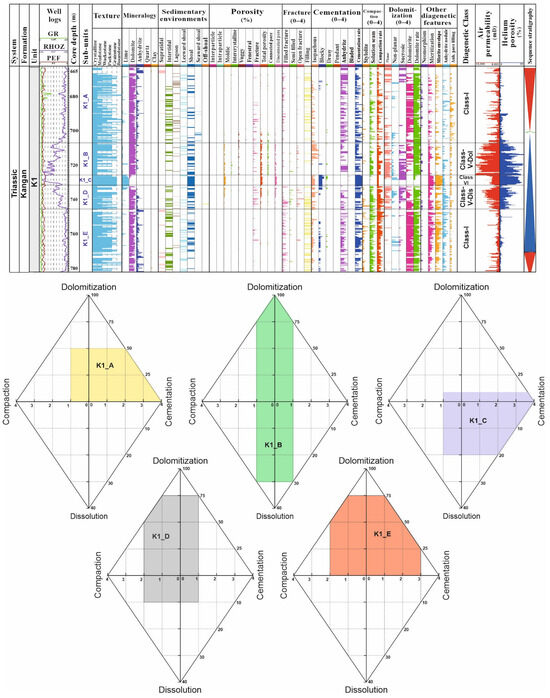
Figure 4.
Diagenetic classes and subunits of the K1 reservoir unit of the Kangan Formation in the studied well, Persian Gulf.
Within the dolomitized sections, intercrystalline porosity is the most prevalent, whereas the middle section primarily exhibits vuggy and moldic porosities resulting from dissolution processes (Figure 4). The cement types present in the K1 unit vary across sections. In the K1_A and K1_E sections, where porosity is lower, anhydritic cements are commonly found, often in the form of pore-filling or poikilotopic cements. Conversely, the middle section (K1_B to K1_D) contains carbonate cements, such as blocky calcite and isopachous aragonite, which are subsequently stabilized into calcite through fabric preservation. Sucrosic dolomites are most pronounced in the K1_B to K1_D sub-units, where sugary and non-laminated dolomites are observed. In contrast, dolomicrites are prominent within the K1_A and K1_E units. In these units, cementation and the formation of anhydrite nodules are predominant, while the middle section (K1_B to K1_D sub-units) is marked by significant recrystallization and micritization (Figure 2 and Figure 4).
4.3.2. K2 Unit
Reservoir unit K2 is lithologically divided into an upper dolomitic section (K2_A and K2_B) and a lower limestone section (K2_C, K2_D, and K2_E) (Figure 5). K2_A corresponds to DC-III, indicating the dominance of dolomitized wackestone and packstone facies. The K2_B sub-unit includes the DC-V diagenetic class that indicates the domination of dolomitized and dissolved grainstone facies. K2_C encompasses DC-IV, representing cemented and compacted wackestone and packstone facies. The K2_D sub-unit corresponds to DC-III, indicating the dominance of dissolved wackestone and packstone facies. K2_E includes cemented and compacted wackestone and packstone facies represented by DC-IV (Figure 5).

Figure 5.
Diagenetic classes and subunits of the K2 reservoir unit of the Kangan Formation in the studied field, Persian Gulf.
The K2 unit is dominantly composed of high-energy facies associated with shoal setting. In the upper dolomitic section (K2_A and K2_B), the dominant pore types are intergranular and intercrystalline, with vuggy and moldic porosities also being notably abundant due to dissolution processes. In contrast, the lower limestone section (K2_C, K2_D, and K2_E) is primarily characterized by moldic porosity, with other pore types being relatively scarce. Cementation in the upper section is more intense and predominantly anhydritic in nature. Meanwhile, the lower section contains a variety of carbonate cements exhibiting bladed, drusy, blocky, and isopachous fabrics. The texture of dolomite crystals in the upper section is mainly fine-crystalline dolomicrite, with sucrosic fabric occurring in euhedral, subhedral, and anhedral crystal forms. In the lower section, dolomites are less prevalent and are typically euhedral. The upper section displays the extensive development of anhydritic cements and anhydrite nodules, whereas the lower section is more affected by micritization and recrystallization, although some pore-filling anhydritic cements are also present (Figure 2 and Figure 5).
4.3.3. K3 Unit
Reservoir unit K3 (Figure 6), with an approximate thickness of 120 m in the studied well, comprises back-shoal, lagoonal, and intertidal facies. Lithologically, it is subdivided into an upper dolomitic section (i.e., K3_A and K3_B), a middle limestone section (K3_C), and a lower dolomitic section (K3_D). The K3_A sub-unit corresponds to DC-II, which includes dolomitized stromatolites and mudstone to grainstone facies. K3_B is dominantly composed of intertidal, lagoon, and leeward shoal facies with intense dolomitization and dissolution. These properties indicate the prevalence of DC-III (dolomitized/dissolved wackestone and packstone facies). The K3_C sub-unit is mainly composed of mud-dominated facies of intertidal to off-shoal facies in which carbonate (calcite) cementation and compaction are dominant diagenetic features, representing DC-I (Figure 6). The K3_D sub-unit is marked by DC-II, indicating the dominance of dolomitized intertidal to leeward shoal facies with high levels of anhydrite cementation (Figure 6).
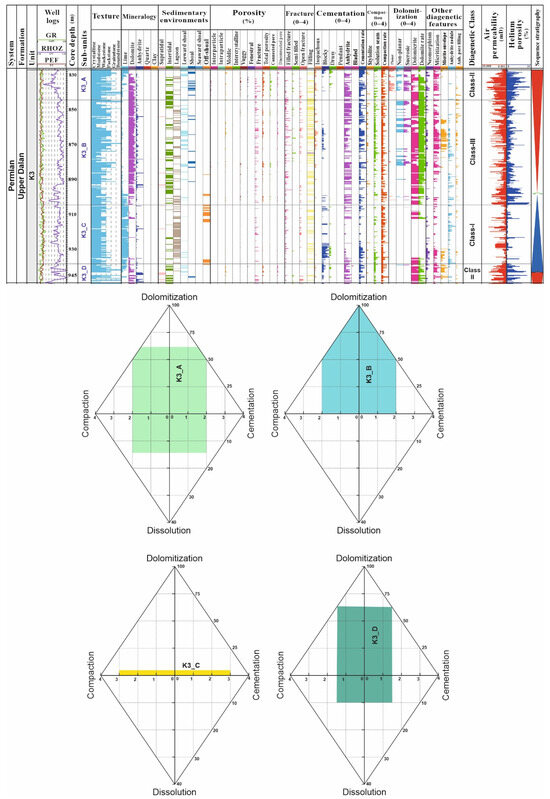
Figure 6.
Diagenetic classes and subunits of the K3 reservoir unit of the upper Dalan Formation in the studied field, Persian Gulf.
Compared to other reservoir units within the upper Dalan and Kangan Formations, the K3 unit exhibits a lower reservoir quality, as indicated by its reduced porosity and permeability (Figure 6). In the dolomitized sections, intercrystalline porosity is dominant, while the limestone section displays intergranular, vuggy, moldic, and fenestral porosities (Figure 6). Anhydritic cementation is pervasive throughout the unit (i.e., K3_A, K3_B, and K3_D) and plays a critical role in reducing porosity and permeability by extensively filling intergranular spaces and cavities. In the limestone intervals (K3_C), blocky and drusy calcite cements are abundant, with minor occurrences of thin-section calcite and aragonite cements. Dolomite types in K3 are primarily fine-crystalline dolomicrites, with sucrosic dolomites occurring in lesser quantities. These dolomites are generally euhedral and fabric-selective. Additional diagenetic features include the development of anhydrite nodules, anhydrite pore-fillings and nodules, micritization—particularly in leeward shoal facies—and recrystallization processes (Figure 2 and Figure 6).
4.3.4. K4 Unit
Reservoir unit K4 (Figure 7), with a thickness of 120 m, consists of two dolomitic sections (upper K4_A and lower K4_D) and a thick limestone middle section (K4_B), which also contains thinly-laminated dolomitic units (K4_C). The K4_A sub-unit is composed of a range of intertidal, lagoonal to leeward shoal facies with intensive dolomitization and moderate anhydrite cementation. Therefore, it is assigned to the DC-V-Dol. (Figure 7). The K4_B sub-unit is substantially composed of grain-dominated (grainstone and packstone) facies of the shoal setting in which dissolution and calcite cementation are predominant diagenetic features and vuggy to moldic pores are the major pore types. Accordingly, this sub-unit is classified as DC-V-Dis. referring to the dissolved grain-dominated facies (Figure 7). The K4_C sub-unit has similar facies characteristics but different diagenetic alterations than the K4_B sub-unit. In K4_C, there are some dolomitic inter-layers showing higher rates of dolomitization and anhydrite cementation. However, dissolution is still dominant diagenetic process within the limestone intervals. Consequently, K4_C is assigned to DC-V (i.e., dolomitized or dissolved grainstone facies). The K4_D sub-unit is basically a dolomitized interval in which intertidal, lagoonal, and shoal facies are dominant (Figure 7). Anhydrite cementation is also present. This sub-unit corresponds to DC-III—dolomitized wackestone and packstone facies (Figure 7).
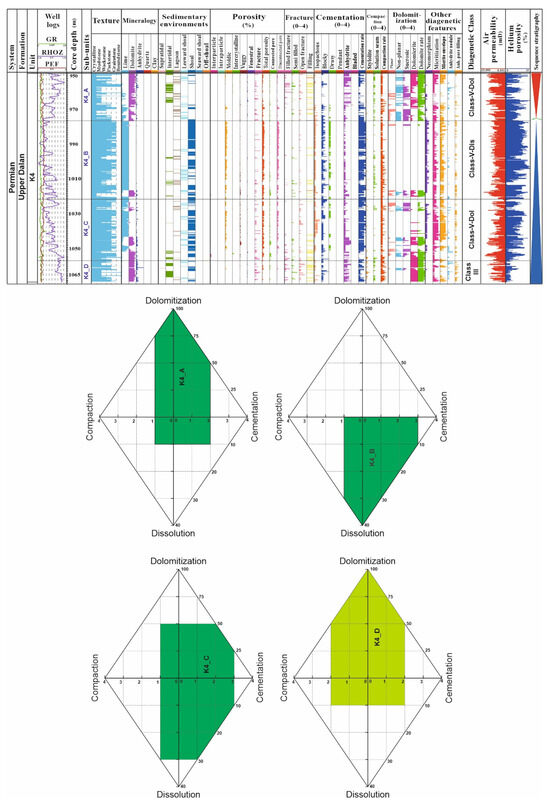
Figure 7.
Diagenetic classes and subunits of the K4 reservoir unit of the upper Dalan Formation in the studied field, Persian Gulf.
The K4 unit is the most important reservoir unit of the upper Dalan and Kangan Formations, and is primarily formed by high-energy facies of the shoal setting. The dissolution and dolomitization processes have enhanced its porosity and permeability, making it a significant reservoir zone. The key pore types in this unit are moldic, vuggy, and interparticle pores, with intercrystalline porosity being significant in the dolomitized sections (Figure 7). The dissolution of ooid grainstone facies, the predominant facies, has contributed to the development of moldic porosity, improving reservoir quality. Anhydritic cement is dominant in the dolomitized sections, while blocky and drusy calcitic cements, along with pendant cements, are most common in the limestone intervals (Figure 7). The cementation intensity is higher in the dolomitized sections, where it affects reservoir quality more significantly. Dolomitization is limited to the upper section, lower section, and some parts of the middle section (Figure 7). Micritic and sucrosic dolomites, formed in grain-supported facies, enhance permeability. Additional diagenetic processes include recrystallization, micritization, the formation of anhydrite nodules, and pore-filling anhydrite (Figure 2). Cementation and anhydrite nodules are more abundant in the dolomitized horizons, while micritization and recrystallization are more prevalent in the limestone sections (Figure 7).
4.4. Genetical Classification of Pores
Among the various pore classification frameworks developed for carbonate reservoirs, the genetic classification proposed by Ahr (2008) [1] is adopted in this study to categorize the pore types within the Permian–Triassic reservoirs of the studied well (Figure 8). Accordingly, the pore spaces identified within the studied intervals can be genetically classified into three principal categories: depositional pores, diagenetic pores, and tectonically induced pores (Figure 8). These pore types are recorded in the macroscopic (core), mesoscopic (thin-section), and microscopic (SEM) scales (Figure 9).
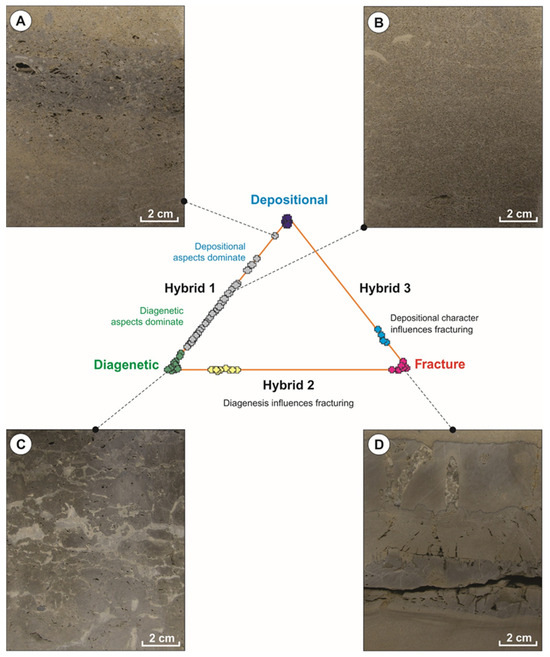
Figure 8.
(A): Genetic pore type classification diagram of Ahr (2008) [1]. Photos of slabbed core surfaces illustrating genetic pore-types of the upper Dalan–Kangan Formations. (A) Fenestral and intra-skeletal pores; (B) oomoldic pores; (C) vuggy pores; and (D) open fractures.
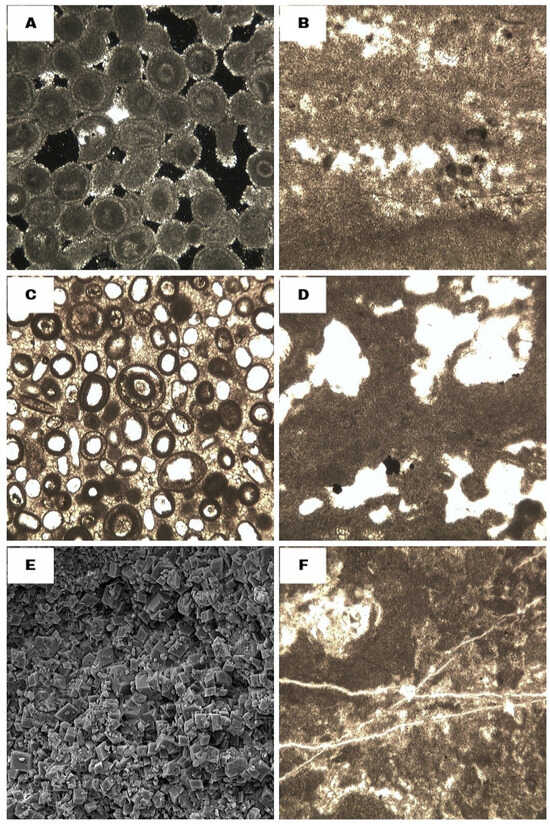
Figure 9.
Genetic pore types of the upper Dalan and Kangan Formations in the studied well. (A) Interparticle pores (depositional); (B) fenestral pores (depositional); (C) oomoldic pores (hybrid-I); (D) vuggy pores (diagenetic); (E) intercrystalline pores (diagenetic); and (F) fracture pores (tectonic).
Statistical analyses were conducted on 100 samples selected from various facies and reservoir units within the targeted sequences to evaluate pore genesis (Figure 8). The analysis reveals that diagenetic pores constitute more than 68% of the total pore spaces, with over 80% of these diagenetic pores exhibiting a strong correlation with the facies characteristics. A representative example is the oomoldic porosity resulting from the dissolution of aragonitic ooids in high-energy shoal environments. These are categorized as facies-controlled diagenetic pores. Additionally, fabric-selective dolomitization and associated intercrystalline porosity are included within this group.
Samples exhibiting vuggy and non-fabric-selective intercrystalline porosity, accounting for approximately 14% of the dataset, are assigned to a purely diagenetic category (Figure 8). Meanwhile, pores such as interparticle, intraparticle, and fenestral types—representing 8% of the samples—are classified as purely depositional pore types (Figure 8). Fracture porosity was analyzed using core plug samples, which are typically not visible in thin sections. Approximately 10% of the samples contain open or partially open fractures, which are placed in a distinct category.
By including the samples assigned to hybrid-II—diagenetic–fracture (8 samples) and hybrid-III—depositional–fracture (4 samples), it is evident that fractures constitute a significant pore type in the upper Dalan and Kangan Formations of the studied field (Figure 8). Their importance is further underscored by their influences on pore network connectivity and, consequently, reservoir permeability. Furthermore, notable associations are observed between fracture development and both the depositional and diagenetic attributes of the rock. Specifically, fractures are more prevalent in mud-dominated facies and dolomitized intervals, corresponding to Ahr’s hybrid-III class [1].
4.5. Porosity–Permeability Trends
The impacts of diagenetic processes on petrophysical properties of the upper Dalan and Kangan Formations were evaluated using the porosity–permeability cross plots depicted in Figure 10. Accordingly, fracturing has resulted in a shift toward extremely high permeability values (Figure 10A). Dissolution has positive effects on the both porosity and permeability, especially within the grain-supported shoal facies (Figure 10B). Two different trends were recorded from dissolved shoal facies:
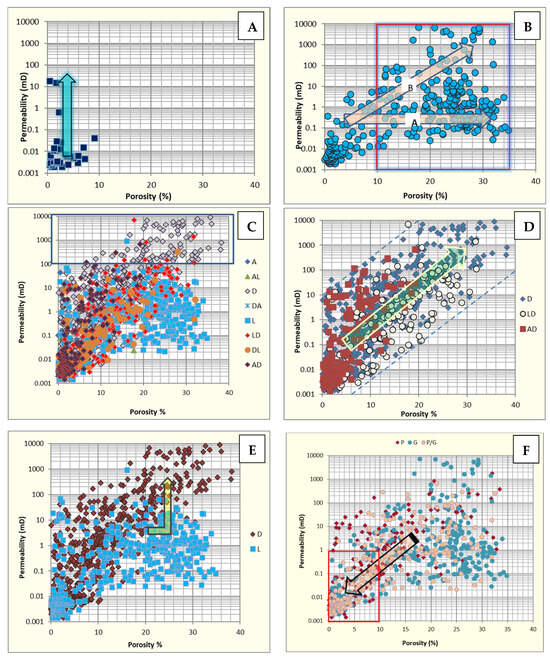
Figure 10.
(A) Impact of fracturing (blue arrow) on the reservoir quality in low-energy off-shoal facies. (B) Influence of dissolution on high-energy shoal facies, with increased K–Φ values due to both fabric-selective (arrow A) and non-fabric-selective (arrow B) dissolution. (C) Porosity–permeability relationship highlighting that over 90% of samples with permeability >100 mD are dolomitic (blue box). (D,E) Poro-perm plots showing that dolomitic facies typically exhibit higher permeability than limestones (yellow arrows). (F) Despite their favorable depositional characteristics, many high-energy shoal samples exhibit low poro-perm values (black arrow), primarily due to diagenetic cementation and compaction. Abbreviations: A, anhydrite; L, limestone; D, dolomite; DL, dolomitic limestone; AL, anhydritic limestone; LD, limy dolostone; AD, anhydritic dolomite.
- (a)
- Fabric-selective dissolution in ooid grainstone facies has resulted in the formation of isolated (oomoldic) pores with high porosity but low permeability. Consequently, a horizontal shift toward higher porosity values was recorded from these samples (marked as A in Figure 10B).
- (b)
- Fabric-destructive dissolution formed large touching vuggy pores within the shoal facies that increased both porosity and permeability (marked as B in Figure 10B).
Porosity–permeability cross plots are also depicted for various lithologies recorded in the studied formations (Figure 10C–E). As shown, dolomitic facies show higher permeabilities than limestones (Figure 10C). The presence of anhydrite (commonly as nodules, cements, and rare inter-layers) has extreme negative effects on the porosity and permeability (Figure 10C,D).
There is a clear increasing trend of porosity–permeability from anhydritic dolostones/limestones toward limy dolostones and dolostones (Figure 10D). A general comparison between the dolomitized and limestone facies indicates that, for similar facies, dolomitized samples have higher permeabilities that limestones (Figure 10E). Cementation and compaction have negative effects on the reservoir quality of the studied formations. Intensively cemented and compacted facies show lower porosity and permeability values in the upper Dalan and Kangan Formations (Figure 10F). Among the various types of cements, anhydritic cements (poikilotopic, pore-filling, and fracture-filling) have the most negative effect on reservoir properties of these formations.
4.6. Reservoir Quality
4.6.1. Hydraulic Flow Units (HFUs)
All samples with permeability values below 0.01 mD were removed from further analysis and categorized as HFU1, representing the lowest reservoir quality. This filtration step excluded 418 samples, and the remaining 1153 core measurements were subjected to a detailed statistical evaluation. To define HFUs within the upper Dalan and Kangan Formations of the studied well, a combination of statistical and petrophysical techniques was applied, which include a histogram analysis, probability plotting, and cross-plotting of reservoir quality indicators. The histogram analysis of FZI values revealed a multimodal distribution indicative of eight potential HFUs (Figure 11A).
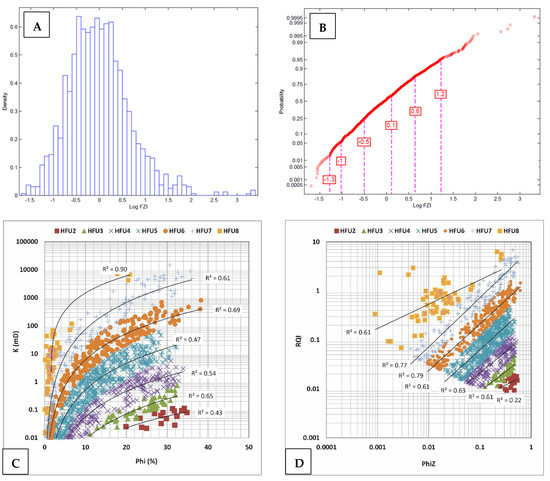
Figure 11.
(A) Histogram (frequency) of log FZI values for the total samples from the upper Dalan and Kangan Formations in the studied well. (B) Probability plot of log FZI values for filtered samples from the targeted reservoirs in the studied well. Based on the marked 6 inflection points, 7 hydraulic flow units have been identified. Together with filtered data of HFU1, there are 8 HFUs in this well. Defined HFUs on the poroperm cross plot (C) and RQI-PhiZ plot (D) of the studied well. Samples of HFU1 (K < 0.01 mD) are not included in these diagrams.
However, due to the inherent overlap in log-normal distributions, this result was further validated using a cumulative probability plot of log FZI values, which exhibited six inflection points, corresponding to seven HFUs in the filtered dataset (Figure 11B). Additionally, log-log plots of the Reservoir Quality Index (RQI) versus normalized porosity (ϕz) and porosity versus permeability were employed (Figure 11C,D). In these plots, samples sharing similar FZI values are aligned along straight lines with a unit slope, confirming consistency in pore throat attributes within individual flow units (Figure 11D). As a result, eight distinct hydraulic flow units were identified within the studied formations (Table 2). While the FZI-based HFU classification provides a useful framework for reservoir zonation, the boundaries between HFUs may exhibit some overlap due to natural geological variability, measurement errors, or subjective threshold selection, introducing interpretive uncertainty; similarly, diagenetic class assignments can be influenced by pore network heterogeneity and the limitations of discrete categorization in continuous rock properties.

Table 2.
Geological and petrophysical characteristics of the defined hydraulic flow units of the Permian–Triassic reservoirs in studied well, Persian Gulf.
4.6.2. Reservoir Characterization Using the Lorenz Plot (SMLP)
To achieve a large-scale zonation of the carbonate reservoir, the Stratigraphic Modified Lorenz Plot (SMLP) technique was employed. In the studied well, the application of the SMLP technique resulted in the subdivision of the Kangan and upper Dalan Formations into distinct flow units (Figure 12 and Table 3). The cumulative Kh% versus Φh% plot, commonly referred to as the modified Lorenz plot, is presented in Figure 12A for the upper Dalan and Kangan Formations. This plot reveals 18 significant inflection points, which delineate 19 distinct flow zones.
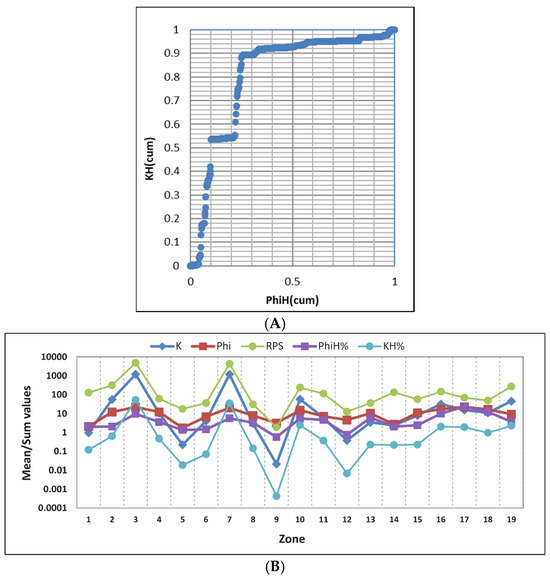
Figure 12.
(A) Plot of the cumulative storage capacity (KH) versus cumulative flow capacity (PhiH) in the studied well. Based on the inflection points on this diagram, 19 zones have been differentiated in the Permian–Triassic reservoirs. (B) Diagram of mean and sum values of K, Phi, RPS, KH%, and PhiH% in defined zones in the Permian–Triassic reservoirs of the studied well.

Table 3.
Statistical parameters in defined barrier, baffle, and reservoir zones in the upper Dalan and Kangan Formations in the studied well, Persian Gulf. Abbreviations: Br—barrier, Bf—baffle, Rs—reservoir, RPS—reservoir process speed, PhiH—storage capacity, KH—flow capacity.
These subdivisions were corroborated through integration with geological (particularly facies and diagenetic characteristics) and petrophysical data, supporting the validity of the zonation scheme (Figure 13). Detailed statistical parameters for these zones are provided in Table 3. Specifically, the Kangan Formation was divided into nine zones (five within the K1 unit and four within the K2 unit) while the upper Dalan Formation was subdivided into ten zones (six in K3 and four in K4) (Table 3). These zones were classified as barrier, baffle, or reservoir units based on their flow characteristics, and their statistical parameters were documented in the reservoir evaluation log (Figure 13).
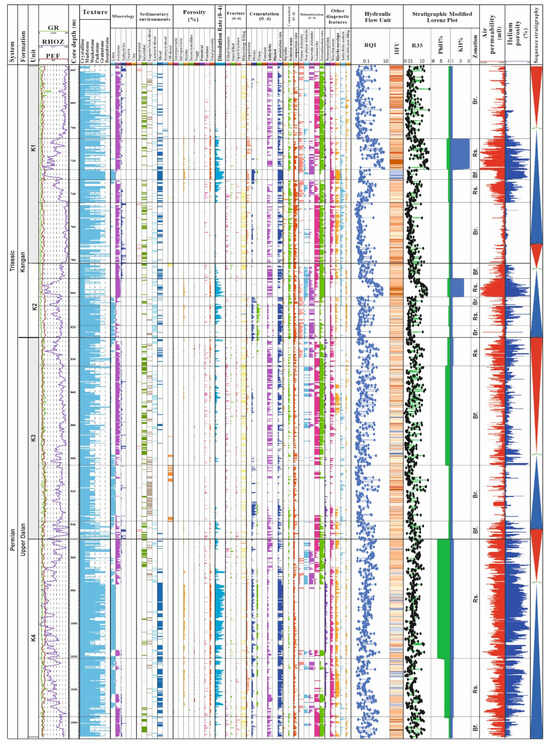
Figure 13.
Reservoir quality evaluation log of the upper Dalan and Kangan Formations in the studied well, Persian Gulf.
5. Discussion
5.1. Paragenesis
Depositional facies of the Permian–Triassic reservoirs of the studied well experienced several diagenetic modifications just after their deposition in the carbonate platform to the burial realm. Based on the presented description and interpretation of diagenetic alterations, the upper Dalan–Kangan intervals seem to have a relatively complex diagenesis history. This included their modification in marine, hypersaline, and shallow environments to deep burial in diagenetic environments (Figure 14).
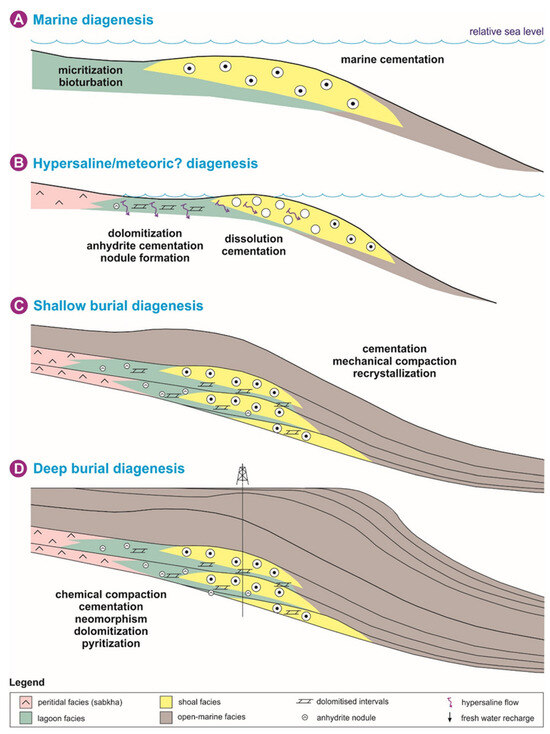
Figure 14.
Schematic cartoons illustrating the diagenetic history of the upper Dalan–Kangan Formations in the studied well, Persian Gulf.
The paragenetic sequence (relative timing) of diagenetic processes was acquired by studying their textural relationships in petrographic studies, combined with our previous knowledge on diagenesis of carbonate intervals, especially the Permian–Triassic reservoirs of the Persian Gulf [39,41,50,55,58,59,60]. The paragenetic sequence of Permian–Triassic reservoirs is presented in Figure 15. In this sequence, all of the diagenetic processes are arranged based on their occurrence time relative to their subsequent alterations. They are also grouped based upon their diagenetic environments and their controls on reservoir properties. The proposed conceptual diagenetic model of the studied reservoirs is presented in Figure 14. As shown, this model illustrates passing through marine, hypersaline (meteoric), shallow, and deep burial realms. During early (near-surface) diagenesis, the primary mineralogy of carbonate sediments, their facies characteristics, governing paleoclimatic conditions, and relative sea-level fluctuations were the main factors controlling the type, development, and intensity of diagenetic alterations [7,61].
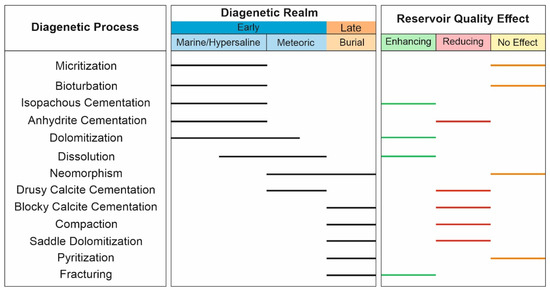
Figure 15.
Paragenesis of diagenetic processes recorded in the upper Dalan–Kangan Formations (Permian–Triassic) in the central Persian Gulf.
5.2. Diagenetic Impact on Reservoir Quality
Considering the impact of diagenetic processes on reservoir characteristics (porosity and permeability), the types of diagenetic processes that occurred in the upper Dalan and Kangan Formations can be categorized into three groups: (a) diagenetic processes enhancing reservoir quality, (b) diagenetic processes reducing reservoir quality, and (c) diagenetic processes with a minimal or unknown impact on reservoir quality.
5.2.1. Diagenetic Processes Enhancing Reservoir Quality
This group of diagenetic processes includes dissolution and dolomitization as two important diagenetic features of the studied formations, leading to improved reservoir properties (porosity–permeability) (Figure 10). Another significant feature from this perspective is fracturing.
Open, partially filled, and filled fractures were distinguished in the core samples and in thin sections of the upper Dalan–Kangan Formations. Fractures are more frequent in the dolomitized intervals (Figure 13). They are commonly filled by anhydrite cements. Open micro-fractures have increased the flow capacity (i.e., permeability values of up to 100 mD), especially within the dolomitized mud-dominated facies of intertidal, lagoon, and open marine settings (Figure 10).
The intense dissolution of unstable grains (such as ooids and aragonitic bioclasts) has resulted in substantial porosity (up to 40%) and permeability (up to 10,000 millidarcy). Such diagenetic processes have created moldic and vuggy porosity, especially in the shoal facies belt, providing the main reservoir rocks for K2 (in the Kangan Formation) and K4 (in the upper Dalan Formation) (Figure 13). These correspond to the diagenetic classes II, III and V, HFUs 5 to 8 and reservoir zones 7, 16, 17, and 18 (Table 2 and Table 3; Figure 13).
Depending on factors such as the intensity of dissolution, the textural and mineralogical characteristics of the host rocks, and the types of porosity, two different types of dissolution features can be identified (Figure 10B):
- (a)
- Fabric-selective dissolution of aragonitic allochems (mainly ooids) that forms substantial moldic and separate vuggy porosity (isolated pores) but does not significantly increase permeability. High porosity (up to 35%) and low to moderate permeability values (0.1–1 mD) were recorded from samples in which fabric-selective (moldic) dissolution was predominant.
- (b)
- Non-fabric selective dissolution of high-energy facies that leads to the development of touching (interconnected) vuggy porosity. It resulted in high porosity (up to 30%) and permeability (1 to 100 mD) (Figure 10).
On the other hand, dolomitization has improved the reservoir quality in some sections of the studied sequences. As shown in Figure 10, the dolomitic sequences of the studied formations exhibit higher porosity–permeability (mainly permeability) compared to other sequences. These correspond to the diagenetic classes II, III and V. Theoretically, dolomitization can enhance the reservoir properties of carbonate sequences under certain conditions [62]: (a) dolomite crystals can create an integrated and robust framework in the rock, (b) the consumable elements for dolomitization (especially magnesium) are sourced from the host rock, and (c) over-dolomitization does not occur.
Additionally, a porosity–permeability chart for samples with a predominantly dolomitic lithology shows a relatively linear relationship between porosity and permeability in dolomitized facies, attributed to the effect of dolomitization (Figure 10D,E). As noted in previous research, increased dolomitization tends to homogenize the pore network distribution of carbonate rocks [63].
In this context, this process generally improves permeability [62,64,65]. In the Persian Gulf, samples from various facies groups are plotted in a cross plot of porosity–permeability and divided into two categories: limestone and dolomite rock groups (Figure 10E). As shown, there is a positive shift toward higher permeability values in dolomitized facies. The trend lines corresponding to these classes also indicate that dolomitic samples generally have higher permeability values.
5.2.2. Diagenetic Processes Reducing Reservoir Quality
The major diagenetic processes in this group are compaction and cementation. Intensively cemented and compacted facies formed diagenetic classes I, IV, and VI in the upper Dalan and Kangan Formations. Compaction (mechanical and chemical) deteriorates the reservoir properties of carbonate sequences due to a decreased pore volume (i.e., porosity) and their connectivity (i.e., permeability) [66]. Cementation blocks pore spaces and consequently reduces reservoir quality [67]. The best example of this event is pervasive anhydrite cementation. Facies containing intense anhydrite cementation have experienced severe reductions in porosity and permeability. In contrast, the development of isopachous marine cement is suitable for preserving reservoir quality by providing a rigid framework against post-depositional changes in burial environments [22].
Compaction is another important diagenetic process that has a major control over the properties of the Permian–Triassic reservoirs. This process includes both mechanical and chemical compaction. The features of chemical compaction include dissolution seams and stylolites, which are common features in the studied sequences and have affected their reservoir quality [59]. Chemically compacted carbonate sequences typically act as potential vertical barriers on a small scale and contribute to reservoir heterogeneity [68]. In contrast, stylolites may act as flow paths parallel to the stylolite plane in the horizontal direction [59,69]. They can also be considered flow paths associated with fractures [70]. In the studied units, stylolite-related fractures often have varying lengths (<5 to >15 cm), are perpendicular to stylolite planes, and are usually filled with various types of cement (especially anhydrite cements). However, in cases where they remain unfilled, they can play a role in fluid flow through their host rocks [68]. The impacts of reducing diagenesis on reservoir quality were recorded from HFUs 1 to 4 and barrier to baffle zones 1, 4 to 6, 8, 9, 11 to 15 (Table 2 and Table 3; Figure 13).
5.2.3. Diagenetic Processes with a Minimal or Unknown Impact on Reservoir Quality
Some diagenetic processes do not have a major control over the reservoir quality of carbonate sequences, or their roles are not yet fully understood [71]. The main diagenetic processes in this group include bioturbation, micritization, pyritization, and neomorphism (recrystallization). Micritization of allochems usually occurs due to the presence of microscopic burrowing organisms during or immediately after deposition in low-energy sedimentary environments (e.g., lagoons) [72]. This process does not significantly influence reservoir characteristics (i.e., porosity and permeability) [73]. In contrast, neomorphism refers to a process in which diagenetic changes systematically convert minerals into their different forms [74]. The control of this process on the reservoir quality of carbonate sequences is still not fully understood. Recrystallization of dolomites can improve reservoir properties [75].
The proposed diagenetic-based reservoir classification method, grounded in the quantification of key processes (dissolution, dolomitization, cementation, and compaction), is not only relevant to the upper Dalan and Kangan Formations but also applicable to their stratigraphic equivalents, such as the Khuff Formation in Arabian countries. Furthermore, this approach can be extended to other analogous carbonate sequences in the Middle East (e.g., the Arab Formation) and globally, where similar diagenetic overprints control reservoir quality. By integrating petrographic, geochemical, and petrophysical data, this method offers a robust framework for reservoir characterization in heterogeneous carbonate systems worldwide, aiding in the prediction of flow units and compartmentalization.
6. Conclusions
The diagenetic history of the Permian–Triassic reservoirs in the studied field reveals a complex interplay of processes across marine, hypersaline, and burial environments. Paragenetic sequences, established through a petrographic analysis and existing knowledge, highlight the temporal and environmental controls on diagenetic alterations. Early diagenesis was strongly influenced by primary mineralogy and facies–textural characteristics, providing a foundation for subsequent diagenetic modifications.
Diagenetic processes were categorized based on their impacts on reservoir quality. Dissolution and dolomitization significantly enhanced porosity and permeability, particularly in shoal facies, creating moldic and vuggy porosity (diagenetic classes II, III, and V). Fracturing further improved the reservoir properties, with dolomitization homogenizing pore networks and increasing permeability under specific conditions. Conversely, compaction and cementation, especially anhydrite cementation, reduced the reservoir quality by diminishing the pore volume and connectivity (diagenetic classes I, IV, and VI).
Stylolites and dissolution seams introduced heterogeneity, acting as barriers or localized flow paths, depending on their orientation and cementation. Processes such as bioturbation, micritization, and neomorphism had minimal or uncertain effects on the reservoir characteristics. While micritization showed a negligible impact, the role of neomorphism, particularly in dolomite recrystallization, warrants further investigation.
This study underscores the importance of integrating diagenetic classifications with reservoir characterization to predict heterogeneity and fluid flow in carbonate reservoirs. The findings provide a framework for understanding the Permian–Triassic successions in the Persian Gulf, with implications for similar carbonate reservoirs globally.
Future researches should focus on (i) quantifying the impact of less-understood processes and refining predictive models for reservoir quality and (ii) incorporating well test or production data to validate whether the defined hydraulic flow units (HFUs) and diagenetic classes correlate with actual reservoir performance.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, H.M., S.S.G. and K.R.; methodology, H.M. and K.R.; software, H.M., S.S.G. and Y.H.; validation, H.M., S.S.G. and Y.H.; formal analysis, H.M.; investigation, H.M., S.S.G. and Y.H.; resources, H.M.; data curation, H.M.; writing—original draft preparation, H.M., S.S.G. and Y.H.; writing—review and editing, H.M., S.S.G. and Y.H.; visualization, H.M. and K.R.; supervision, H.M.; project administration, H.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
All data used in this study will be made available upon request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
The University of Tehran provided facilities for this research, for which the authors are grateful. The National Iranian Oil Company is acknowledged for data support.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Ahr, W.M. Geology of Carbonate Reservoirs; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavakoli, V. Carbonate Reservoir Heterogeneity; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isah, A.; Arif, M.; Hassan, A.; Mahmoud, M.; Iglauer, S. Fluid–rock interactions and its implications on EOR: Critical analysis, experimental techniques and knowledge gaps. Energy Rep. 2022, 8, 6355–6395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozotta, O.; Saberi, M.R.; Kolawole, O.; Malki, M.L.; Rasouli, V.; Pu, H. Pore morphology effect on elastic and fluid flow properties in Bakken formation using rock physics modeling. Geomech. Geophys. Geo-Energy Geo-Resour. 2022, 8, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shalaby, M.R.; Thota, S.T.; Norsahminan, D.N.P.; Kamalrulzaman, K.N.; Matter, W.S.; Al-Awah, H. Reservoir quality evaluation using petrophysical, well-log analysis and petrographical description: A case study from the Carboniferous–Permian Kulshill group formations, southern Bonaparte Basin, Australia. Geoenergy Sci. Eng. 2023, 226, 211738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathania, T.; Bottacin-Busolin, A.; Eldho, T.I. Evaluating the effect of aquifer heterogeneity on multiobjective optimization of in-situ groundwater bioremediation. Eng. Anal. Bound. Elem. 2023, 148, 336–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehrabi, H. Deposition, diagenesis, and geochemistry of Upper Cretaceous carbonates (Sarvak Formation) in the Zagros Basin and the Persian Gulf, Iran. Minerals 2023, 13, 1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, J.; Wang, G.; Chai, Y.; Ran, Y.; Zhang, X. Depositional and diagenetic controls on pore structure of tight gas sandstone reservoirs: Evidence from Lower Cretaceous Bashijiqike Formation in Kelasu Thrust Belts, Kuqa Depression in Tarim Basin of West China. Resour. Geol. 2015, 65, 55–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Overare, B.; Azmy, K.; Garzanti, E.; Avwenagha, E.O.; Emudianughe, J.E. Diagenetic imprints in the reservoirs of Agbada Formation, Niger Delta Basin: Implication for reservoir quality and appraisal of calcite cement. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2024, 163, 106746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, T.; Chu, M.; Zhang, X.; Wang, B.; Li, J.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, X. Quantitative analysis of pore evolution and its application in basin simulation: A case study of Chang 6 reservoir in Heshui area, Ordos Basin, NW China. Energy Geosci. 2025, 6, 100403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavoosi Iraj, P.; Mehrabi, H.; Rahimpour-Bonab, H.; Ranjbar-Karami, R. Quantitative analysis of geological attributes for reservoir heterogeneity assessment in carbonate sequences; a case from Permian–Triassic reservoirs of the Persian Gulf. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2021, 200, 108356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foroshani, J.S.; Mehrabi, H.; Rahimpour-Bonab, H. Reservoir heterogeneity of Upper Cretaceous Sarvak Formation in the Dezful Embayment, SW Iran: Implications of flow unit distribution, electrofacies analysis and geological-based reservoir zonation. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2023, 200, 104882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafarian, A.; Kakemem, U.; Husinec, A.; Mehrabi, H.; Javanbakht, M.; Wang, C.; Chen, X.; Li, Y. Depositional facies and diagenetic control on reservoir quality of the Aptian Dariyan Formation, NW Persian Gulf. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2024, 165, 106895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafarian, A.; Kakemem, U.; Husinec, A.; Mehrabi, H.; Pouyafard, Z.; Ghasemi, M.; Senemari, S.; Saboor, A.; Wang, C. Syn- and post-depositional influences on reservoir quality of the Aptian Dariyan Formation, eastern Persian Gulf. Pet. Geosci. 2025, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, J.; Su, Y.; Xiao, L.; Zhao, F.; Bai, T.; Li, Y.; Li, H.; Huang, Y.; Wang, G.; Qin, Z. Application of geophysical well logs in solving geologic issues: Past, present and future prospect. Geosci. Front. 2024, 15, 101779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Liang, Y.; Wang, P.; Yeh, T.J.; Dai, L.; Xia, R.; Zhang, H.; Xu, B.; Zhang, S. Incorporating electrical sounding survey into geostatistical electrical resistivity tomography for high-resolution characterization of karst aquifer. J. Hydrol. 2025, 656, 133018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lis-Śledziona, A. Petrophysical rock typing and permeability prediction in tight sandstone reservoir. Acta Geophys. 2019, 67, 1895–1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metawee, M.; Araffa, S.A.S.; Othman, A.; Alfy, M.E. Geophysical and geospatial insights into surface and subsurface characteristics for groundwater potential analysis, Ras Sudr, West Sinai, Egypt. Environ. Earth Sci. 2024, 83, 616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavakoli, V. Core analysis: An introduction. In Core Analysis; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, F.; Hussein, D.; Glover, P.W.J.; Lorinczi, P.; Lawrence, J.A. Quantitative diagenesis: Methods for studying the evolution of the physical properties of tight carbonate reservoir rocks. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2022, 139, 105603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bukar, M.; Worden, R.H.; Bukar, S.; Shell, P. Diagenesis and its controls on reservoir quality of the Tambar oil field, Norwegian North Sea. Energy Geosci. 2021, 2, 10–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worden, R.H.; Armitage, P.J.; Butcher, A.R.; Churchill, J.M.; Csoma, A.E.; Hollis, C.; Lander, R.H.; Omma, J.E. Petroleum reservoir quality prediction: Overview and contrasting approaches from sandstone and carbonate communities. Geol. Soc. Lond. Spec. Publ. 2018, 435, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehrabi, H.; Yahyaei, E.; Navidtalab, A.; Rahimpour-Bonab, H.; Abbasi, R.; Omidvar, M.; Assadi, A.; Honarmand, J. Depositional and diagenetic controls on reservoir properties along the shallow-marine carbonates of the Sarvak Formation, Zagros Basin: Petrographic, petrophysical, and geochemical evidence. Sediment. Geol. 2023, 454, 106457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehrabi, H.; Fakhar-Shahreza, N.; Karami, F.; Honarmand, J. Controls of tectonics and paleoclimate on depositional–diagenetic evolution and pore types of Upper Cretaceous successions (Sarvak Formation) in the Abadan plain, Iran. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2024, 170, 107118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, R.; Mehrabi, H.; Yahyaei, E.; Rahimpour-Bonab, H. Diagenetic evolution of Upper Cretaceous carbonate sequences (Sarvak Formation) in the Abadan Plain, Iran: Evidence from petrographic, elemental, stable, and strontium isotopic data. Int. Geol. Rev. 2024, 66, 3793–3813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabbani, A.R.; Kotarba, M.J.; Baniasad, A.R.; Hosseiny, E.; Wieclaw, D. Geochemical characteristics and genetic types of the crude oils from the Iranian sector of the Persian Gulf. Org. Geochem. 2014, 70, 29–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orang, K.; Motamedi, H.; Azadikhah, A.; Royatvand, M. Structural framework and tectono-stratigraphic evolution of the eastern Persian Gulf, offshore Iran. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2018, 91, 89–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziegler, A.M. Late Permian to Holocene Paleofacies Evolution of the Arabian Plate and its Hydrocarbon Occurrences. GeoArabia 2001, 6, 445–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Insalaco, E.; Virgone, A.; Courme, B.; Gaillot, J.; Kamali, M.; Moallemi, A.; Lotfpour, M.; Monibi, S. Upper Dalan Member and Kangan Formation between the Zagros Mountains and offshore Fars, Iran: Depositional system, biostratigraphy and stratigraphic architecture. GeoArabia 2006, 11, 75–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakemem, U.; Ghasemi, M.; Adabi, M.H.; Husinec, A.; Mahmoudi, A.; Anderskouv, K. Sedimentology and sequence stratigraphy of automated hydraulic flow units—The Permian Upper Dalan Formation, Persian Gulf. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2023, 147, 105965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavakoli, V.; Barfizadeh, H. The role of plate movements on reservoir development of the Iranian carbonate formations: A review of the interplay between tectonics, paleoclimate, and diagenesis. Results Earth Sci. 2024, 2, 100037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehrabi, H.; Rahimpour-Bonab, H.; Enayati, A.; Esrafili-Dizaji, B. Impact of contrasting paleoclimate on carbonate reservoir architecture: Cases from arid Permo-Triassic and humid Cretaceous platforms in the south and southwestern Iran. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2015, 126, 262–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esrafili-Dizaji, B.; Rahimpour-Bonab, H. Carbonate reservoir rocks at giant oil and gas fields in SW Iran and the adjacent offshore: A review of stratigraphic occurrence and poro-perm characteristics. J. Pet. Geol. 2019, 42, 343–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perotti, C.R.; Carruba, S.; Rinaldi, M.; Bertozzi, G.; Feltre, L.; Rahimi, M. The Qatar–South Fars Arch Development (Arabian Platform, Persian Gulf): Insights from Seismic Interpretation and Analogue Modelling. In New Frontiers in Tectonic Research—At the Midst of Plate Convergence; InTech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esrafili-Dizaji, B.; Rahimpour-Bonab, H. A review of Permo-Triassic reservoir rocks in the Zagros area, SW Iran: Influence of the Qatar-Fars arch. J. Pet. Geol. 2013, 36, 257–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vail, P.R.; Mitchum, R.M.; Thompson, S. Seismic stratigraphy and global changes of sea level, parts 3 and 4. In Seismic Stratigraphy—Applications to Hydrocarbon Exploration; Payton, C.E., Ed.; AAPG Memoir 26; American Association of Petroleum Geologists: Tulsa, OK, USA, 1977; pp. 63–97. [Google Scholar]
- Kiessling, W.; Flügel, E.; Golonka, J. (Eds.) Phanerozoic Reef Patterns; SEPM Special Publication No. 72; Society for Sedimentary Geology (SEPM): Tulsa, OK, USA, 2002; 775p. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bots, P.; Benning, L.G.; Rickaby, R.E.M.; Shaw, S. The role of SO4 in the switch from calcite to aragonite seas. Geology 2011, 39, 331–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafarian, A.; Fallah-Bagtash, R.; Mattern, F.; Heubeck, C. Reservoir quality along a homoclinal carbonate ramp deposit: The Permian Upper Dalan Formation, South Pars Field, Persian Gulf Basin. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2017, 88, 587–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heydari, E.; Arzani, N.; Safaei, M.; Hassanzadeh, J. Ocean’s response to a changing climate: Clues from variations in carbonate mineralogy across the Permian–Triassic boundary of the Shareza Section, Iran. Glob. Planet. Change 2013, 105, 79–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fallah-Bagtash, R.; Jafarian, A.; Husinec, A.; Adabi, M.H. Diagenetic stabilization of the Upper Permian Dalan Formation, Persian Gulf Basin. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2020, 189, 104144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourquin, S.; Bercovici, A.; López-Gómez, J.; Diez, J.B.; Broutin, J.; Ronchi, A.; Durand, M.; Arché, A.; Linol, B.; Amour, F. The Permian–Triassic transition and the onset of Mesozoic sedimentation at the northwestern peri-Tethyan domain scale: Palaeogeographic maps and geodynamic implications. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2011, 299, 265–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viaretti, M.; Crippa, G.; Brombin, V.; della Porta, G.; Griesshaber, E.; Jurikova, H.; Posenato, R.; Bottini, C.; Angiolini, L. Duration and intensity of the Late Permian (early Wuchiapingian) cool climate episode: Sclerochemical evidence from brachiopod assemblages in Iran. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2025, 659, 112654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbs, M.T.; Rees, P.M.; Kutzbach, J.E.; Ziegler, A.M.; Behling, P.J.; Rowley, D.B. Simulations of Permian Climate and Comparisons with Climate-Sensitive Sediments. J. Geol. 2002, 110, 33–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parrish, J.T. Climate of the supercontinent Pangea. J. Geol. 1993, 101, 215–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winguth, A.M.E.; Shields, C.A.; Winguth, C. Transition into a Hothouse World at the Permian–Triassic boundary—A model study. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2015, 440, 316–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davydov, V.I.; Karasev, E.V.; Nurgalieva, N.G.; Schmitz, M.D.; Budnikov, I.V.; Biakov, A.S.; Kuzina, D.M.; Silantiev, V.V.; Urazaeva, M.N.; Zharinova, V.V.; et al. Climate and biotic evolution during the Permian-Triassic transition in the temperate Northern Hemisphere, Kuznetsk Basin, Siberia, Russia. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2021, 573, 110432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konert, G.; Afifi, A.; Al-Hajri, S.; Droste, H. Paleozoic Stratigraphy and Hydrocarbon Habitat of the Arabian Plate. Geoarabia 2001, 6, 407–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lashin, A.; AlQuraishi, A.A.; AlKhidir, K.; Kinawy, M.M.; al Jawder, A. Characterization of the Permo-Triassic upper Khuff reservoir, central Saudi Arabia: An integrated core plugs, petro-fabrics and mercury injection analysis. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2018, 145, 284–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esrafili-Dizaji, B.; Rahimpour-Bonab, H. Effects of depositional and diagenetic characteristics on carbonate reservoir quality: A case study from the South Pars gas field in the Persian Gulf. Petrol. Geosci. 2009, 15, 325–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Embry, A.F. Transgressive-Regressive (T-R) Sequence Stratigraphy. In Sequence Stratigraphic Models for Exploration and Production: Evolving Methodology, Emerging Models and Application Histories; Armentrout, J.M., Rosen, N.C., Eds.; SEPM Society for Sedimentary Geology: Claremore, OK, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Amaefule, J.-O.; Altunbay, M.; Tiab, J.; Kersey, D.-G.; Keelan, D.-K. Enhanced reservoir description: Using core and log data to identify hydraulic (flow) units and predict permeability in uncored intervals/wells. In Proceedings of the Society of Petroleum Engineers, Oklahoma City, OK, USA, 21–23 March 1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunter, G.W.; Finneran, J.M.; Hartmann, D.J.; Miller, J.D. Early determination of reservoir flow units using an integrated petrophysical method. In Proceedings of the SPE Annual Technical Conference and Exhibition, San Antonio, TX, USA, 5–8 October 1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopaska-Merkel, D.; Mann, S. Classification of lithified carbonates using ternary plots of pore facies: Examples from the Jurassic Smackover Formation. In Carbonate Microfabrics; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1993; pp. 265–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavakoli, V.; Rahimpour-Bonab, H.; Esrafili-Dizaji, B. Diagenetic controlled reservoir quality of South Pars gas field, an integrated approach. Comptes Rendus Geosci. 2011, 343, 55–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amel, H.; Jafarian, A.; Husinec, A.; Koeshidayatullah, A.; Swennen, R. Microfacies, depositional environment and diagenetic evolution controls on the reservoir quality of the Permian Upper Dalan Formation, Kish Gas Field, Zagros Basin. Mar. Petrol. Geol. 2015, 67, 57–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakemem, U.; Jafarian, A.; Husinec, A.; Adabi, M.H.; Mahmoudi, A. Facies, sequence framework, and reservoir quality along a Triassic carbonate ramp: Kangan Formation, South Pars Field, Persian Gulf Superbasin. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2021, 198, 108166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enayati-Bidgoli, A.H.; Rahimpour-Bonab, H.; Mehrabi, H. Flow unit characterisation in the Permian-Triassic carbonate reservoir succession at South Pars Gas Field, Offshore Iran. J. Pet. Geol. 2014, 37, 205–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehrabi, H.; Mansouri, M.; Rahimpour-Bonab, H.; Tavakoli, V.; Hassanzadeh, M. Chemical compaction features as potential barriers in the Permian-Triassic reservoirs of Southern Iran. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2016, 145, 95–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enayati-Bidgoli, A.H.; Rahimpour-Bonab, H. A geological based reservoir zonation scheme in a sequence stratigraphic framework: A case study from the Permo-Triassic gas reservoirs, Offshore Iran. Mar. Petrol. Geol. 2016, 73, 36–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messadi, A.M.; Mardassi, B.; Ouali, J.A.; Touir, J. Sedimentology, diagenesis, clay mineralogy and sequential analysis model of Upper Paleocene evaporite-carbonate ramp succession from Tamerza area (Gafsa Basin: Southern Tunisia). J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2016, 118, 205–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machel, H. Concepts and models of dolomitization: A critical reappraisal. Geol. Soc. Lond. Spec. Publ. 2004, 235, 7–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehrabi, H.; Pouyafard, Z.; Bahrehvar, M.; Al-Aasm, I.S. Diverse dolomitization models in the Aptian Dariyan (Shu’aiba) Formation in the Persian Gulf, Iran: Evidence from petrography, geochemistry and impact on reservoir quality. Mar. Petrol. Geol. 2025, 172, 107229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, C.H. Carbonate Reservoirs: Porosity Evolution and Diagenesis in a Sequence Stratigraphic Framework; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Saller, A.H. Paleozoic dolomite reservoirs in the Permian Basin, SW USA: Stratigraphic distribution, porosity, permeability and production. Geol. Soc. Lond. Spec. Publ. 2004, 235, 309–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croizé, D.; Renard, F.; Gratier, J.-P. Compaction and porosity reduction in carbonates: A review of observations, theory, and experiments. In Advances in Carbonate Sedimentology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 181–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed Sajed, O.K.; Glover, P.W.J. Dolomitisation, cementation and reservoir quality in three Jurassic and Cretaceous carbonate reservoirs in north-western Iraq. Mar. Petrol. Geol. 2020, 115, 104256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afroogh, A.; Mehrabi, H. How geomechanical attributes control the morphology of stylolites in carbonate sequences? A case from Permian–Triassic gas reservoirs in the Persian Gulf. Geomech. Energy Environ. 2023, 33, 100424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heap, M.J.; Baud, P.; Reuschlé, T.; Meredith, P. Stylolites in limestones: Barriers to fluid flow? Geology 2013, 42, 51–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toussaint, R.; Aharonov, E.; Koehn, D.; Gratier, J.-P.; Ebner, M.; Baud, P.; Rolland, A.; Renard, F. Stylolites: A review. J. Struct. Geol. 2018, 114, 163–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahrehvar, M.; Mehrabi, H.; Akbarzadeh, S.; Rahimpour-Bonab, H. Depositional and diagenetic controls on reservoir quality of the uppermost Jurassic–Lower Cretaceous sequences in the Persian Gulf; a focus on J–K boundary. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2021, 201, 108512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garuglieri, E.; Marasco, R.; Odobel, C.; Chandra, V.; Teillet, T.; Areias, C.; Sánchez-Román, M.; Vahrenkamp, V.; Daffonchio, D. Searching for microbial contribution to micritization of shallow marine sediments. Environ. Microbiol. 2024, 26, e16573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wadood, B.; Khan, S.; Wagreich, M.; Vennemann, T.; Li, H.; Ullah, M.; Schöpfer, K. Diagenetic history and porosity evolution of the Middle Permian clastic-carbonate mixed system, Indus Basin, Pakistan: Implications for reservoir development. Energy Geosci. 2024, 5, 100317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, K.V.; Hardisty, D.S. Modeling the impacts of diagenesis on carbonate paleoredox proxies. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2022, 337, 123–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blinkenberg, K.H.; Rameil, N.; Hodgskiss, M.S.W.; Polonio, I.; Riber, L.; Gianotten, I.P.; Roberts, N.M.W.; Lepland, A.; Stemmerik, L. Widespread dolomite recrystallization and porosity modification of upper Permian Zechstein carbonates, Symra discovery, Utsira High, Norwegian North Sea. Mar. Petrol. Geol. 2024, 170, 107064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).