Zircon U-Pb-Hf Isotopes, Whole-Rock Geochemistry and Sr-Nd Isotopes of Early Neoproterozoic Intrusion in the Erguna Block, NE China: Petrogenesis and Tectonic Implications
Abstract
1. Introduction
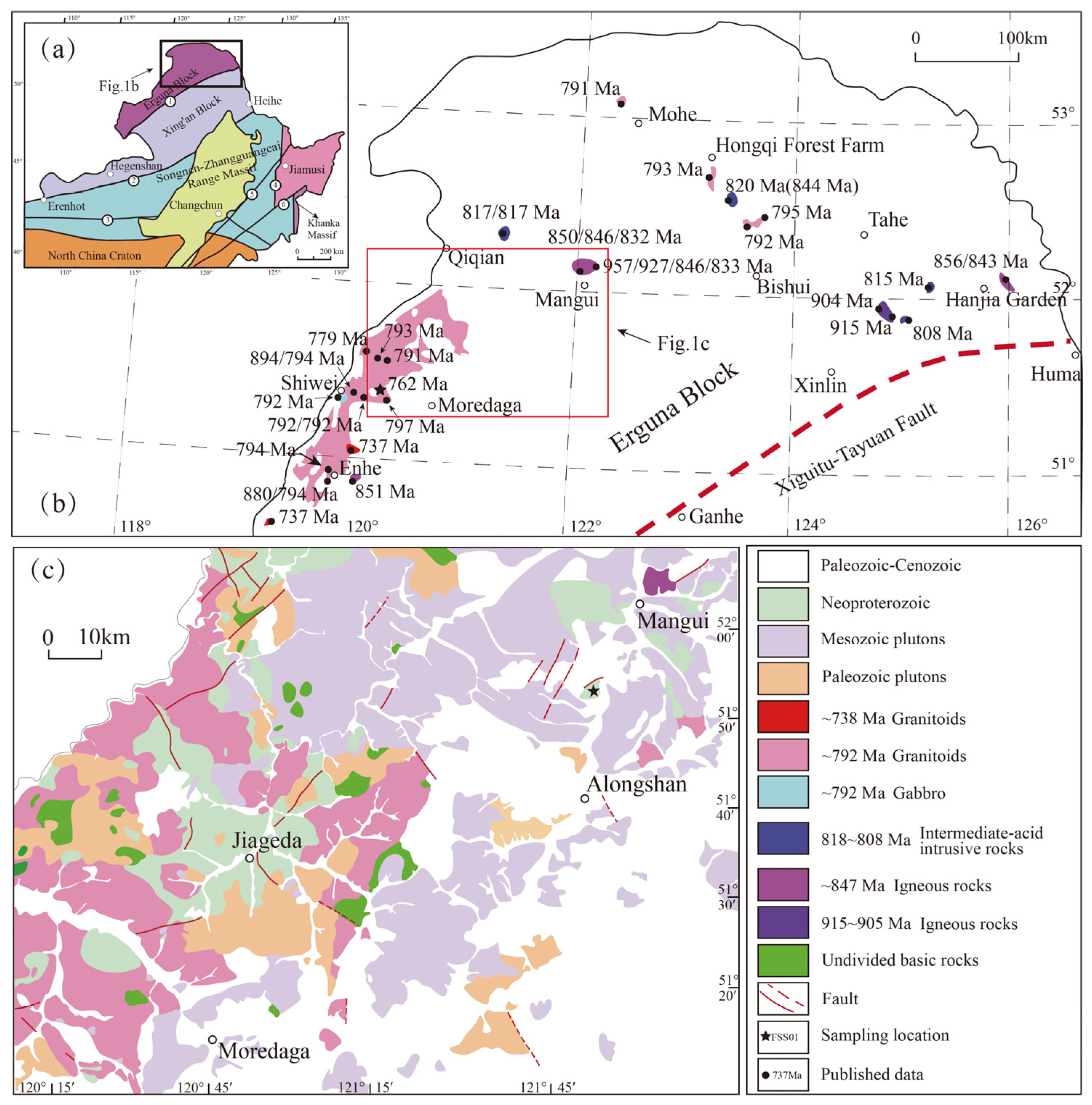
2. Geological Background and Samples
3. Analytical Methods
3.1. Zircon U-Pb Geochronology
3.2. Zircon Lu-Hf Isotopes
3.3. Whole-Rock Geochemistry
3.4. Whole-Rock Sr-Nd Isotopic Analyses
4. Results
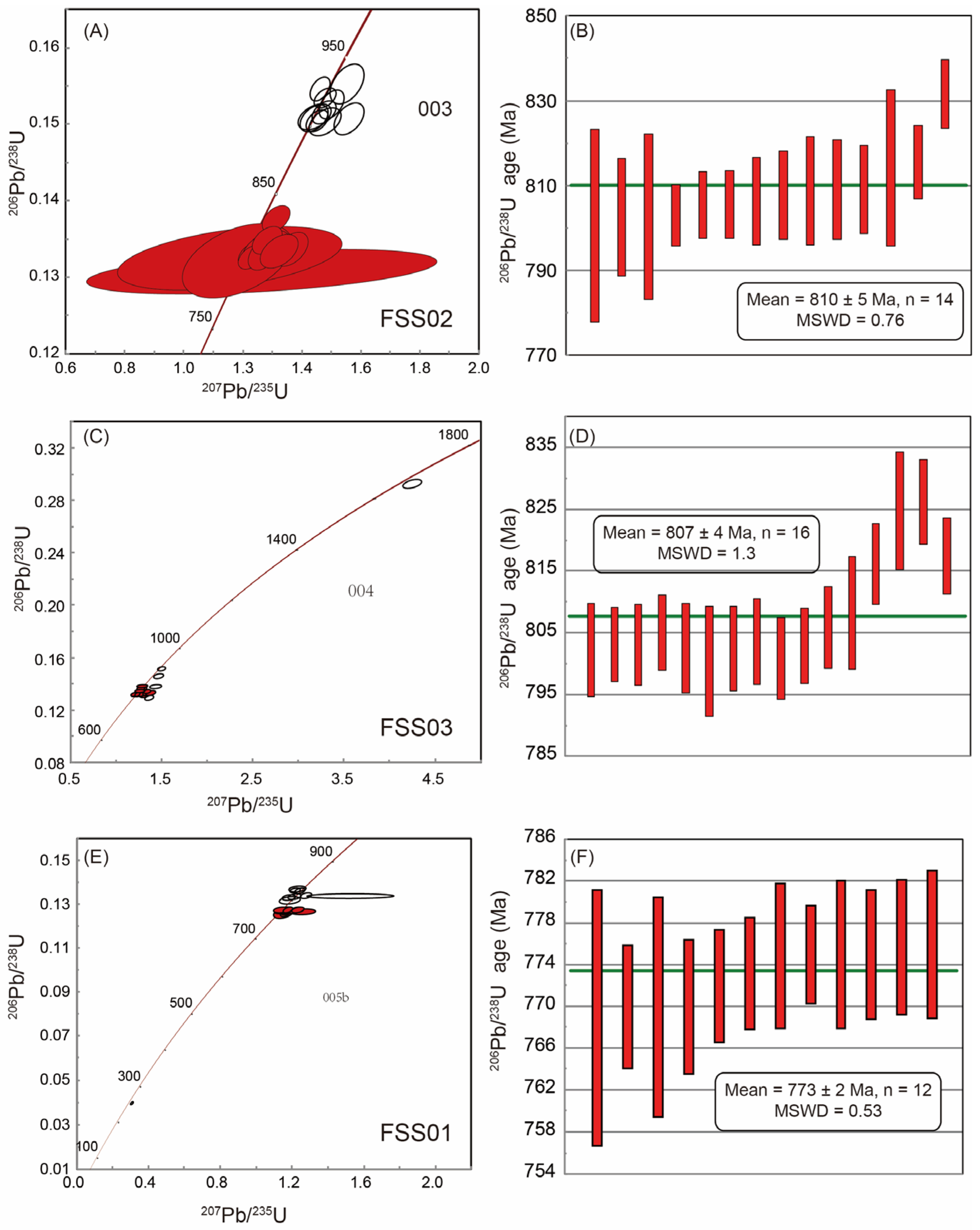
4.1. Zircon U-Pb Geochronology
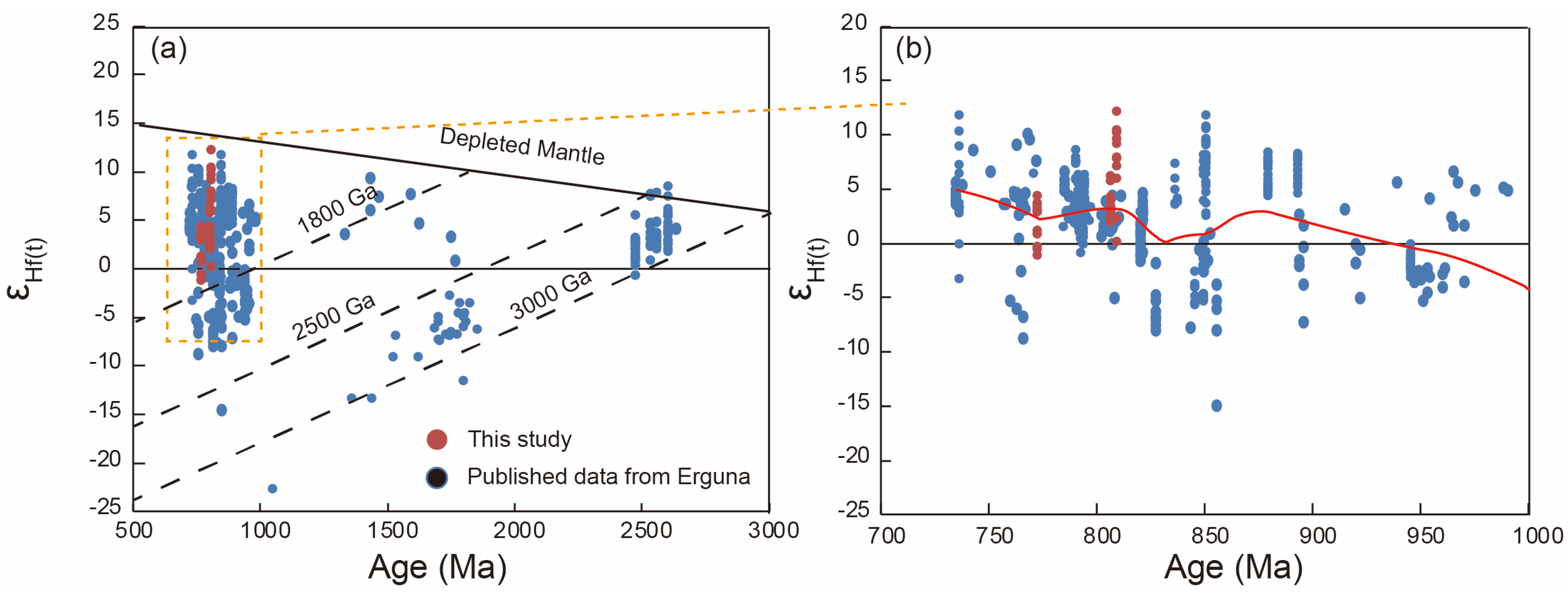
4.2. Zircon Lu-Hf Isotopic Data
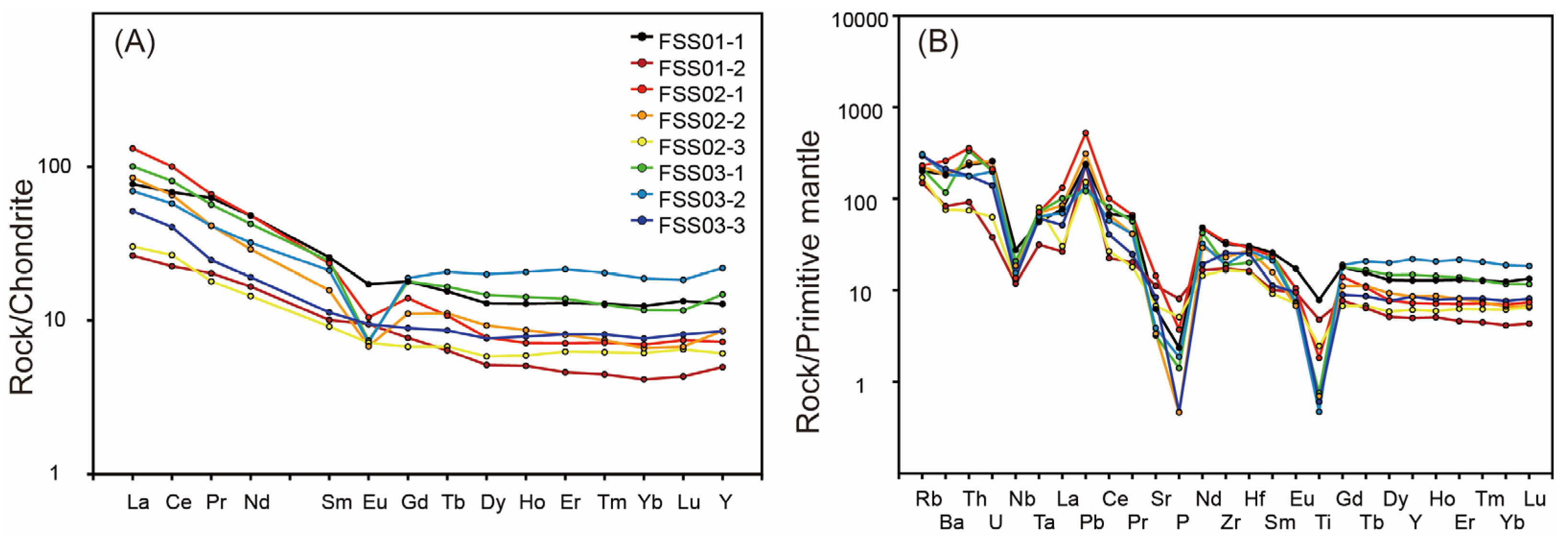
4.3. Whole-Rock Geochemistry
4.4. Whole-Rock Sr-Nd Isotope
5. Discussion
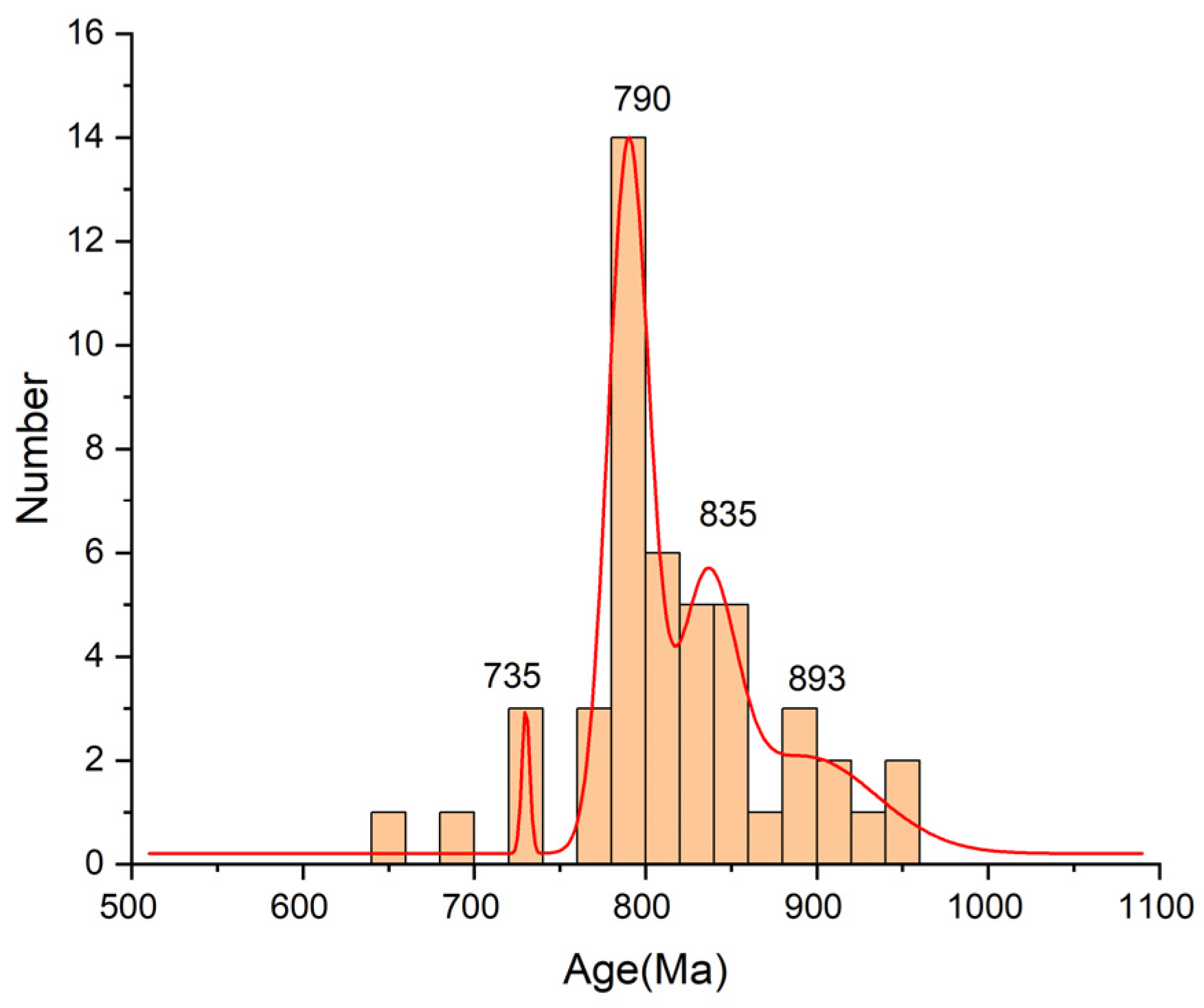
5.1. Neoproterozoic Magmatic Events in the Erguna Block and Adjacent Area
5.2. Source Regions and Petrogenesis of the Magmas
5.2.1. ca. 810–807 Ma A-Type Granite
5.2.2. ca. 770 Ma Gabbroic Diorites
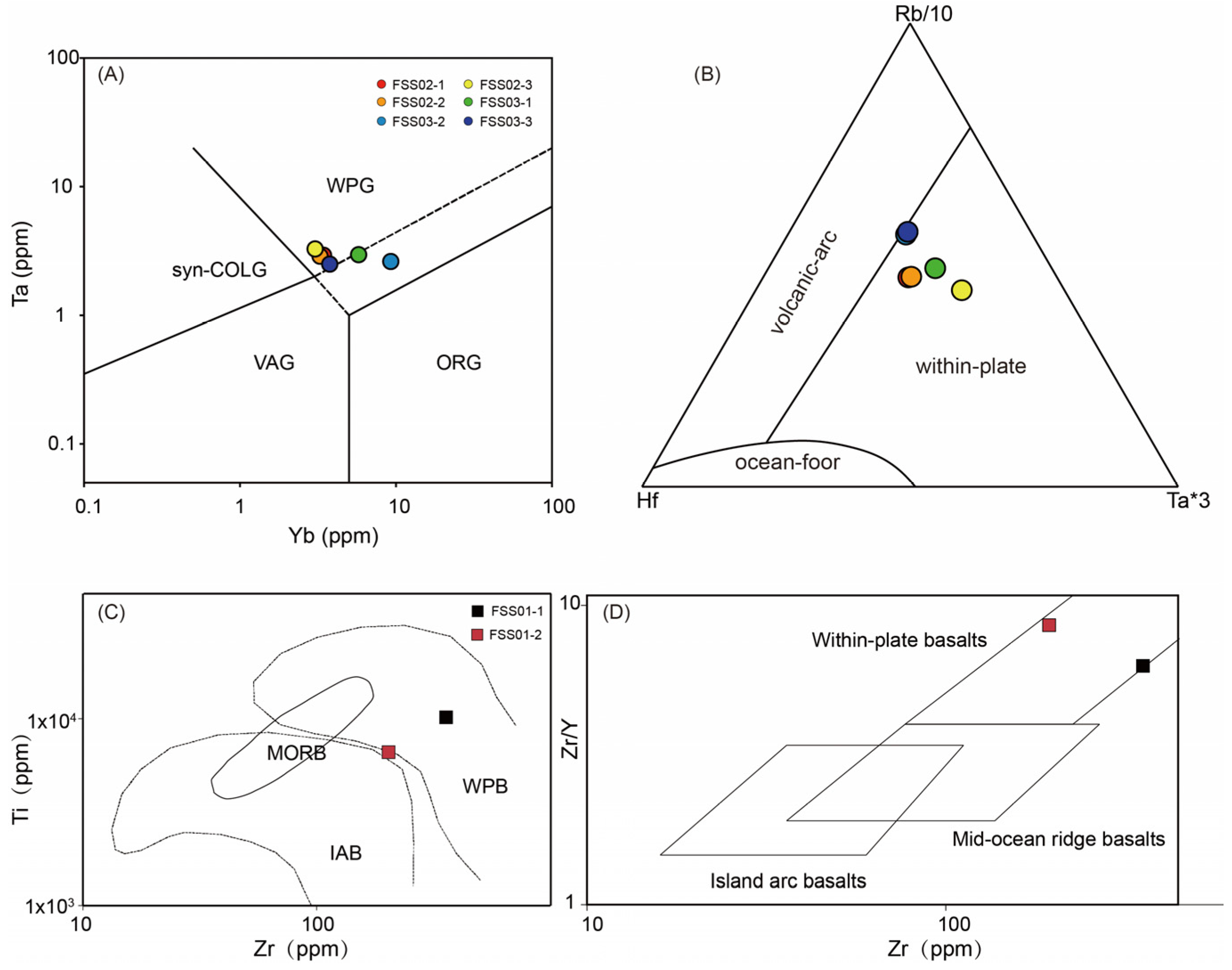
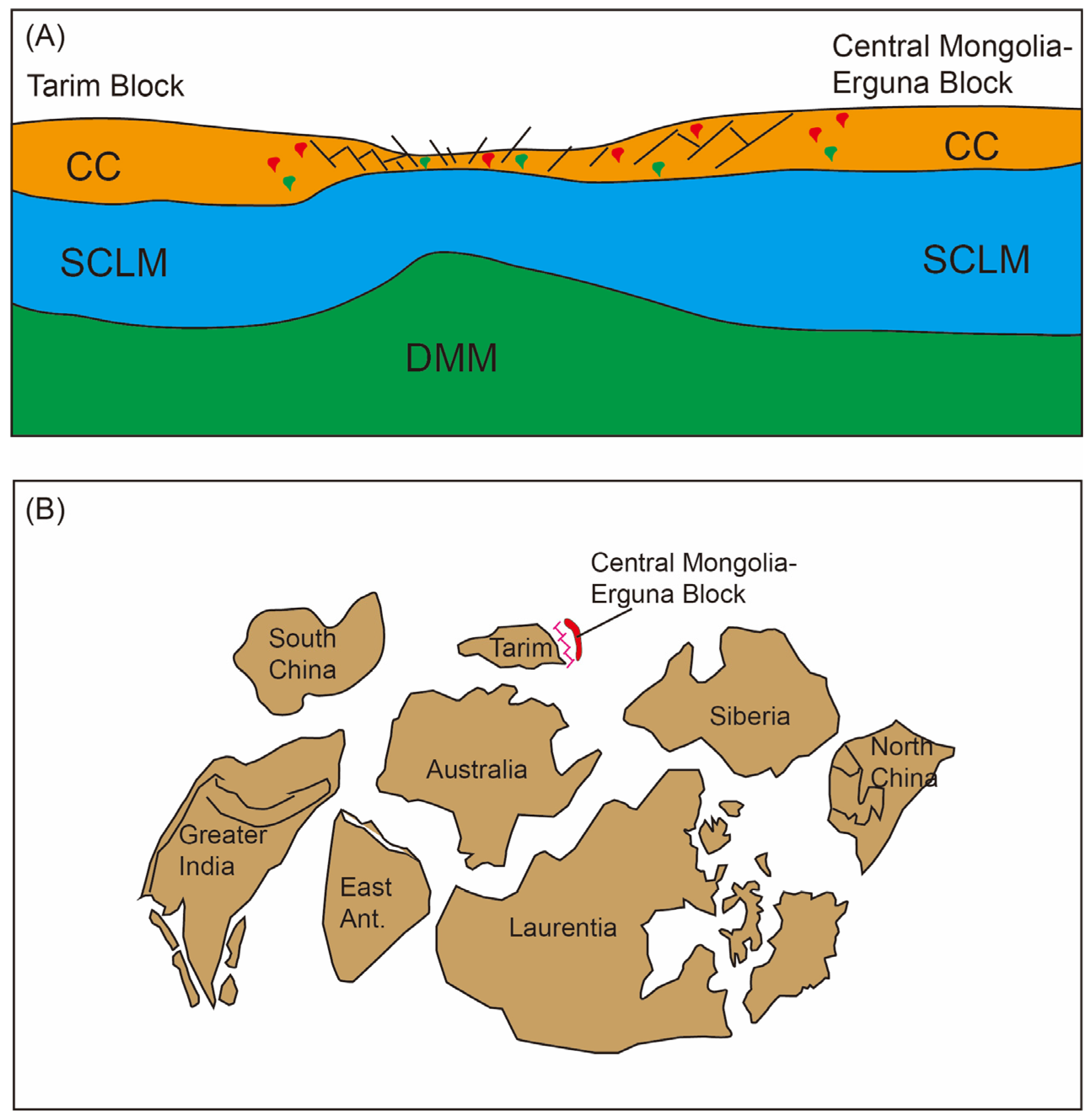
5.3. Tectonic Setting
5.4. Tectonic Evolution of the Erguna Block During Early Neoproterozoic
6. Conclusions
- The Fengshuishan intrusion in the Erguna Block was emplaced during the early Neoproterozoic (810–773 Ma), representing an important magmatic event in the region.
- The 810–807 Ma Fengshuishan granites belong to the A2-type granite and are interpreted to have formed mainly through partial melting of Mesoproterozoic juvenile lower crust with limited mantle contribution. In contrast, the ca. 770 Ma gabbroic diorites originated from the partial melting of an enriched mantle source.
- Geochemical, isotopic, and tectonic evidence indicates that the Fengshuishan intrusion formed within an intracontinental extensional or continental rift setting, associated with the early fragmentation of the Rodinia supercontinent.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Windley, B.F.; Alexeiev, D.; Xiao, W.; Kröner, A.; Badarch, G. Tectonic Models for Accretion of the Central Asian Orogenic Belt. JGS 2007, 164, 31–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, W.J.; Li, J.L.; Song, D.F.; Han, C.M.; Wan, B.; Zhang, J.E.; Ao, S.J.; Zhang, Z.Y. Structural Analyses and Spatio-Temporal Constraints of Accretionary Orogens. Earth Sci. 2019, 44, 1661–1687. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, G.; Wang, Y.; Huang, B.; Dong, Y.; Li, S.; Zhang, G.; Yu, S. Geological Reconstructions of the East Asian Blocks: From the Breakup of Rodinia to the Assembly of Pangea. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2018, 186, 262–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Sun, S.; Santosh, M.; Hui, B.; Sun, J.; Zhang, F.; Cheng, B.; Yang, Z.; Shi, X.; He, D.; et al. Cross Orogenic Belts in Central China: Implications for the Tectonic and Paleogeographic Evolution of the East Asian Continental Collage. Gondwana Res. 2022, 109, 18–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, P.; Kröner, A.; Jahn, B.; Windley, B.F.; Shi, Y.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, F.; Miao, L.; Tomurhuu, D.; Liu, D. Zircon Dating of Neoproterozoic and Cambrian Ophiolites in West Mongolia and Implications for the Timing of Orogenic Processes in the Central Part of the Central Asian Orogenic Belt. Earth Sci. Rev. 2014, 133, 62–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, B.; Li, Y.; Tian, Y.; Wang, Y.; Peng, J. Linking∼1.4–0.8 Ga Volcano-Sedimentary Records in Eastern Central Asian Orogenic Belt with Southern Laurentia in Supercontinent Cycles. Gondwana Res. 2022, 105, 416–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Yang, X.; Ma, Y.; Sun, S.; Han, X.; Zheng, Y.; Li, S. A Synthesis of Geochemistry of Mesozoic Igneous Rocks in NE China and Tectonic Superposition and Transformation of the Easternmost Central Asian Orogenic Belt. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2022, 227, 105032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, Z.; Xu, B.; Zou, H.; Zhao, P.; Zhang, H. Neoproterozoic–Early Cambrian Igneous and Sedimentary Sequences in the Songliao Block, NE China: Records of Rodinia Supercontinent Evolution in Eastern Central Asian Orogenic Belt. Precambrian Res. 2022, 381, 106865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradley, D.C. Secular Trends in the Geologic Record and the Supercontinent Cycle. Earth Sci. Rev. 2011, 108, 16–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Wang, B.; Sun, Z.; Liu, J.; He, Z.; Zhong, L. Detrital Zircon Ages of the Mesoproterozoic Metasedimentary Rocks in the Southern Yili Block: Implications for Tectonic Affinities of the Microcontinents in SW Central Asian Orogenic Belt. Precambrian Res. 2020, 350, 105926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.; Cawood, P.A.; Zi, J.-W.; Wang, K.; Feng, Q.; Tran, D.M.; Trinh, H.D.; Dang, C.M.; Nguyen, Q.M. Locating the Yangtze Block in Nuna: Constraints from Age and Isotopic Data from Paleoproterozoic Sedimentary Rocks in the Phan Si Pan Zone, Northwest Vietnam. Precambrian Res. 2023, 397, 107193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, D.H.; Betts, P.G.; Hall, M. Fragmented Tasmania: The Transition from Rodinia to Gondwana. Aust. J. Earth Sci. 2015, 62, 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unrug, R.; Castaing, C.; Feybesse, J.L.; Gresse, P.G.; Powell, M.C.; Sadowski, G.R.; Tack, L. The geodynamic map of Gondwana Supercontinent Assembly (IGCP Project 288: Gondwanaland Sutures and Fold Belts). In Geological Society of Australia Abstracts; Geological Society of Australia: Townsville, Australia, 1998; Volume 50, pp. 63–64. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, S.; Zhang, J.; Li, J.; Xu, W.; Qu, J.; Liu, J.; Zheng, R.; Ge, M. Titanite LA-ICP-MS U-Pb Dating of the Neoproterozoic Granites in the Erguna Massif and Their Geological Significance. Acta Geol. Sin. 2020, 94, 757–767, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Feng, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Li, L.; Jiang, L.; Zhou, J.; Li, W.; Ma, Y. Reconstruction of Rodinia Supercontinent: Evidence from the Erguna Block (NE China) and Adjacent Units in the Eastern Central Asian Orogenic Belt. Precambrian Res. 2022, 368, 106467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, W.-C.; Chen, J.-S.; Yang, H.; Zhao, G.-C.; Zhang, Y.-L.; Tian, D.-X. Tectonic Implications of New Zircon U–Pb Ages for the Xinghuadukou Complex, Erguna Massif, Northern Great Xing’an Range, NE China. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2015, 106, 169–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gou, J.; Sun, D.-Y.; Ren, Y.-S.; Liu, Y.-J.; Zhang, S.-Y.; Fu, C.-L.; Wang, T.-H.; Wu, P.-F.; Liu, X.-M. Petrogenesis and Geodynamic Setting of Neoproterozoic and Late Paleozoic Magmatism in the Manzhouli–Erguna Area of Inner Mongolia, China: Geochronological, Geochemical and Hf Isotopic Evidence. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2013, 67–68, 114–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Li, Y.; Wan, Z.; Lai, C.-K. Early Neoproterozoic Tectonic Evolution of the Erguna Terrane (NE China) and Its Paleogeographic Location in Rodinia Supercontinent: Insights from Magmatic and Sedimentary Record. Gondwana Res. 2020, 88, 185–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Ge, W.; Zhao, G.; Bi, J.; Wang, Z.; Dong, Y.; Xu, W. Zircon U–Pb Ages and Geochemistry of Newly Discovered Neoproterozoic Orthogneisses in the Mishan Region, NE China: Constraints on the High-Grade Metamorphism and Tectonic Affinity of the Jiamusi–Khanka Block. Lithos 2017, 268–271, 16–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Xu, W.; Tang, J.; Li, Y.; Guo, P. Timing of Formation and Tectonic Nature of the Purportedly Neoproterozoic Jiageda Formation of the Erguna Massif, NE China: Constraints from Field Geology and U–Pb Geochronology of Detrital and Magmatic Zircons. Precambrian Res. 2016, 281, 585–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Liu, Y.; Li, L.; She, H.; Jiang, L.; Du, B.; Liu, Y.; Li, W.; Wen, Q.; Liang, C. Subduction, Accretion, and Collision during the Neoproterozoic-Cambrian Orogeny in the Great Xing’an Range, NE China: Insights from Geochemistry and Geochronology of the Ali River Ophiolitic Mélange and Arc-Type Granodiorites. Precambrian Res. 2018, 311, 117–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khain, E.; Kröner, A.; Gibsher, A.; Fedotova, A. The Fate of Rodinia in the Light of the Discovery of ca. 1000 Ma Old Ophiolites in the Central Asian Orogenic Belt of Siberia. Gondwana Res. 2001, 4, 656–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Li, Y.; Xiao, W.; Zhang, H.; Bai, X.; Zheng, J.; Brouwer, F.M. An 807–763 Ma Continental Arc Records Crust-Mantle Interaction in the Erguna Block during the Breakup of Rodinia. Precambrian Res. 2025, 426, 107833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Li, Y.; Xiao, W.; Zhang, H.; Wang, G.; Zheng, J.; Bai, X.; Yang, G.; Zhang, G.; Brouwer, F.M. An Arc Terrane Separated from the Yangtze Craton during Rodinia Breakup: Insights from Neoproterozoic Sedimentary Successions of the Erguna Block, Northeast China. Precambrian Res. 2024, 410, 107497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Li, J.; Zhao, S.; Ge, M.; Che, Y. A Late Neoproterozoic to Early Paleozoic Accretionary Orogenic Belt in the Eastern Central Asian Orogenic Belt: Evidence from the Irshi Ophiolite Mélange in the Middle Segment of the Great Xing’an Range. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2023, 251, 105657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gou, J.; Sun, D.; Deng, C.; Feng, Z.; Tang, Z. Petrogenesis of the Neoproterozoic Xinlin Ophiolite, Northern Great Xing’an Range, Northeastern China: Implications for the Evolution of the Northeastern Branch of the Paleo-Asian Ocean. Precambrian Res. 2020, 350, 105925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.-Z.; Qin, K.-Z.; Li, G.-M.; Jin, L.-Y.; Song, G.-X. Neoproterozoic and Early Paleozoic Magmatic Records from the Chalukou Ore District, Northern Great Xing’an Range, NE China: Implications for Tectonic Evolution and Mesozoic Mo Mineralization. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2018, 165, 96–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Zhang, W.; Liu, Y.; Gao, S.; Li, M.; Zong, K.; Chen, H.; Hu, S. “Wave” Signal-Smoothing and Mercury-Removing Device for Laser Ablation Quadrupole and Multiple Collector ICPMS Analysis: Application to Lead Isotope Analysis. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 1152–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Gao, S.; Hu, Z.; Gao, C.; Zong, K.; Wang, D. Continental and Oceanic Crust Recycling-Induced Melt-Peridotite Interactions in the Trans-North China Orogen: U-Pb Dating, Hf Isotopes and Trace Elements in Zircons from Mantle Xenoliths. J. Petrol. 2010, 51, 537–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Hu, Z.; Gao, S.; Günther, D.; Xu, J.; Gao, C.; Chen, H. In Situ Analysis of Major and Trace Elements of Anhydrous Minerals by LA-ICP-MS without Applying an Internal Standard. Chem. Geol. 2008, 257, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludwig, K.R. User’s Manual for IsoPlot 3.0. A Geochronological Toolkit Microsoft Excel; Berkeley Geochronology Center Special Publication; Berkeley Geochronology Center: Berkeley, CA, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Gao, S.; Liu, W.; Zhang, W.; Tong, X.; Lin, L.; Zong, K.; Li, M.; Chen, H.; et al. Improved in Situ Hf Isotope Ratio Analysis of Zircon Using Newly Designed X Skimmer Cone and Jet Sample Cone in Combination with the Addition of Nitrogen by Laser Ablation Multiple Collector ICP-MS. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2012, 27, 1391–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Hu, Z. Estimation of Isotopic Reference Values for Pure Materials and Geological Reference Materials. At. Spectrosc. 2020, 41, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, W.A.; Papanastassiou, D.A.; Tombrello, T.A. Ca Isotope Fractionation on the Earth and Other Solar System Materials. Geochim. Cosmochim. Ac. 1978, 42, 1075–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Liu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Hu, Z. Calibration and Correction of LA-ICP-MS and LA-MC-ICP-MS Analyses for Element Contents and Isotopic Ratios. Solid Earth Sci. 2016, 1, 5–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Xu, W.-L.; Wang, F.; Wang, W.; Xu, M.-J.; Zhang, Y.-H. Geochronology and Geochemistry of Neoproterozoic Magmatism in the Erguna Massif, NE China: Petrogenesis and Implications for the Breakup of the Rodinia Supercontinent. Precambrian Res. 2013, 224, 597–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q. Tectonic evolution of Rodinia: Evidence from Neoproterozoic magmatism in northern Greater Khingan. Master’s Thesis, Taiyuan University of Technology, Taiyuan, China, 2024; pp. 3017–3047, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Xue, Y. Neoproterozoic Sedimentary Formations and Magmatism in Eastern Songnen Massif: Constraints on Basement Composition and Tectonic Attribution. Master’s Thesis, Jilin University, Jilin, China, 2024. (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Whalen, J.B.; Currie, K.L.; Chappell, B.W. A-Type Granites: Geochemical Characteristics, Discrimination and Petrogenesis. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 1987, 95, 407–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frost, B.R.; Barnes, C.G.; Collins, W.J.; Arculus, R.J.; Ellis, D.J.; Frost, C.D. A Geochemical Classification for Granitic Rocks. J. Petrol. 2001, 42, 2033–2048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Middlemost, E.A.K. Naming Materials in the Magma/Igneous Rock System. Earth Sci. Rev. 1994, 37, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frost, C.D.; Frost, B.R. On Ferroan (A-Type) Granitoids: Their Compositional Variability and Modes of Origin. J. Petrol. 2011, 52, 39–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.S.; McDonough, W.F. Chemical and Isotopic Systematics of Oceanic Basalts: Implications for Mantle Composition and Processes. Geol. Soc. London Spec. Publ. 1989, 42, 313–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.Y.; Sun, D.Y.; Ge, W.C.; Zhang, Y.B.; Grant, M.L.; Wilde, S.A.; Jahn, B.M. Geochronology of the Phanerozoic Granitoids in Northeastern China. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2011, 41, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.H.; Xu, W.L.; Tang, J.; Wang, F.; Xu, M.J.; Wang, W. Age and Provenance of the Ergunahe Group and the Wubinaobao Formation, Northeastern Inner Mongolia, NE China: Implications for Tectonic Setting of the Erguna Massif. Int. Geol. Rev. 2014, 56, 653–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Xu, W.; Pei, F.; Wang, F.; Guo, P. Geochronology and Geochemistry of Early Paleozoic Igneous Rocks of the Lesser Xing’an Range, NE China: Implications for the Tectonic Evolution of the Eastern Central Asian Orogenic Belt. Lithos 2016, 261, 144–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Xu, W.; Sorokin, A.A.; Ovchinnikov, R.O.; Ge, W. Geochronology and Geochemistry of Neoproterozoic Magmatism in the Bureya Block, Russian Far East: Petrogenesis and Implications for Rodinia Reconstruction. Precambrian Res. 2020, 342, 105676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Ge, W.; Bi, J.; Wang, Z.; Tian, D.; Dong, Y.; Chen, H.-J. The Neoproterozoic-Early Paleozoic Evolution of the Jiamusi Block, NE China and Its East Gondwana Connection: Geochemical and Zircon U–Pb–Hf Isotopic Constraints from the Mashan Complex. Gondwana Res. 2018, 54, 102–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Liang, C.; Neubauer, F.; Zheng, C.; Zhou, J.; Xu, X. A Review of Neoproterozoic to Early Palaeozoic Rocks of the Jiamusi–Khanka Massif, NE China: A Rifted Fragment from the Siberian Craton? Int. Geol. Rev. 2023, 65, 1289–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Liu, B. Characteristics of U-Pb Chronology and Geochemistry of Neoproterozoic Granitic Gneiss in Dongfengjingyingsuo of Yichun Area. Glob. Geol. 2014, 33, 780–786, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Sun, D.Y.; Gou, J.; Wang, T.H.; Ren, Y.S.; Liu, Y.J.; Guo, H.Y.; Liu, X.M.; Hu, Z.C. Geochronological and Geochemical Constraints on the Erguna Massif Basement, NE China–Subduction History of the Mongol–Okhotsk Oceanic Crust. Int. Geol. Rev. 2013, 55, 1801–1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Jiang, S.; Bagas, L.; Ji, G.; Liu, Y. Discovery of Neoproterozoic Highly Fractionated Syenogranite in the Southwestern Part of the Erguna Massif in NE China and Its Geological Implication. Int. Geol. Rev. 2021, 63, 1863–1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Li, C.; Alam, M.; Song, Z.; Zhu, X.; Fu, A.; Yang, W. Geochronology and Geochemistry of the Neoproterozoic–Mesozoic Intrusive Rocks in the Xinlin Area, Northeastern China: New Constraints on the Tectonic Evolution of the Erguna Block. Front. Earth Sci. 2025, 12, 1514658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, J.-P.; Xu, W.-L.; Wang, F.; Wang, Z.-W.; Guo, P. Age and Geochemistry of Neoproterozoic Granitoids in the Songnen–Zhangguangcai Range Massif, NE China: Petrogenesis and Tectonic Implications. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2017, 148, 265–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chappell, B.W.; White, A.J.R. I- and S-Type Granites in the Lachlan Fold Belt. Trans. R. Soc. Edinb. Earth Sci. 1992, 83, 1–26. [Google Scholar]
- Loiselle, M.C.; Wones, D.R. Characteristics and Origin of Anorogenic Granites. Geol. Soc. Am. Abstr. Programs. 1979, 11, 468. [Google Scholar]
- Eby, G.N. The A-Type Granitoids: A Review of Their Occurrence and Chemical Characteristics and Speculations on Their Petrogenesis. Lithos 1990, 26, 115–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, W.J.; Beams, S.D.; White, A.J.R.; Chappell, B.W. Nature and Origin of A-Type Granites with Particular Reference to Southeastern Australia. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 1982, 80, 189–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eby, G.N. Chemical Subdivision of the A-Type Granitoids: Petrogenetic and Tectonic Implications. Geology 1992, 20, 641–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patiño Douce, A.E. Generation of Metaluminous A-Type Granites by Low-Pressure Melting of Calc-Alkaline Granitoids. Geology 1997, 25, 743–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.-Q.; Li, X.-H.; Li, W.-X.; Li, Z.-X. Formation of High 18O Fayalite-Bearing A-Type Granite by High-Temperature Melting of Granulitic Metasedimentary Rocks, Southern China. Geology 2011, 39, 903–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, B.B.; Bartoli, O.; Cesare, B.; Satish-Kumar, M.; Petrelli, M.; Kawakami, T.; Hokada, T.; Gilio, M. Revealing the Link between A-Type Granites and Hottest Melts from Residual Metasedimentary Crust. Geology 2023, 51, 845–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, Y.; Li, J.; Ratschbacher, L.; Zhao, G.; Zhang, Y.; Dong, S.; Xia, X.-P.; Yu, Y. Early Devonian (415–400 Ma) A-Type Granitoids and Diabases in the Wuyishan, Eastern Cathaysia: A Signal of Crustal Extension Coeval with the Separation of South China from Gondwana. GSA Bull. 2020, 132, 2295–2317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.; Cawood, P.A.; Zi, J.W.; Wang, K.; Feng, Q.; Tran, D.M.; Trinh, H.D.; Dang, C.M.; Nguyen, Q.M. Positioning the Yangtze Block within Nuna: Constraints from Paleoproterozoic Granitoids in North Vietnam. Precambrian Res. 2023, 391, 107059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.-F.; Zhou, M.-F.; Li, J.-W.; Wu, F.-Y. Association of Neoproterozoic A- and I-Type Granites in South China: Implications for Generation of A-Type Granites in a Subduction-Related Environment. Chem. Geol. 2008, 257, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Condie, K.C.; Pisarevsky, S.A.; Puetz, S.J.; Roberts, N.M.W.; Spencer, C.J. A-Type Granites in Space and Time: Relationship to the Supercontinent Cycle and Mantle Events. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2023, 610, 118125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Xia, X.P.; Wang, Q.; Spencer, C.J.; He, B.; Lai, C.K. Low-δ18O A-Type Granites in SW China: Evidence for the Interaction between the Subducted Paleotethyan Slab and the Emeishan Mantle Plume. GSA Bull. 2022, 134, 81–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, X.T.; Zhang, C.L.; Wang, Q.; Wang, G.D. Subduction Initiation of Proto-Tethys Ocean and Back-Arc Extension in the Northern Altun Mountains, Northwestern China: Evidence from High-Mg Diorites and A-Type Rhyolites. Lithos 2020, 376–377, 105748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.; Cawood, P.A.; Zi, J.W.; Wang, K.; Feng, Q.; Nguyen, Q.M.; Tran, D.M. Early Paleoproterozoic Magmatism in the Yangtze Block: Evidence from Zircon U-Pb Ages, Sr-Nd-Hf Isotopes and Geochemistry of ca. 2.3 Ga and 2.1 Ga Granitic Rocks in the Phan Si Pan Complex, North Vietnam. Precambrian Res. 2019, 324, 253–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dall’Agnol, R.; de Oliveira, D.C. Oxidized, Magnetite-Series, Rapakivi-Type Granites of Carajás, Brazil: Implications for Classification and Petrogenesis of A-Type Granites. Lithos 2007, 93, 215–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misra, S.; Reinhardt, J.; Wilson, A.H. Petrochemical Evolution of the White Mfolozi Granite Pluton: Evidence for a Late Palaeoarchaean A-Type Granite from the SE Kaapvaal Craton, South Africa. Lithos 2017, 286, 480–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuttle, O.F.; Bowen, N.L. Origin of Granite in the Light of Experimental Studies in the System NaAlSi3O8-KAlSi3O8-SiO2-H2O; Geological Society of America: Boulder, CO, USA, 1958; Volume 74, pp. 1–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grove, T.L.; Elkins-Tanton, L.T.; Parman, S.W.; Chatterjee, N.; Montener, O.; Gaetani, G.A. Fractional Crystallization and Mantle-Melting Controls on Calc-Alkaline Differentiation Trends. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 2003, 145, 515–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annen, C.; Blundy, J.D.; Sparks, R.S.J. The Genesis of Intermediate and Silicic Magmas in Deep Crustal Hot Zones. J. Petrol. 2006, 47, 505–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, S.; Hoernes, S.; Mezger, K. Synorogenic Melting of Mafic Lower Crust: Constraints from Geochronology, Petrology and Sr, Nd, Pb and O Isotope Geochemistry of Quartz Diorites (Damara Orogen, Namibia). Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 2022, 143, 551–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmichael, I.S. The Andesite Aqueduct: Perspectives on the Evolution of Intermediate Magmatism in West-Central (105–99 W) Mexico. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 2002, 143, 641–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parman, S.W.; Grove, T.L. Harzburgite Melting with and without H2O: Experimental Data and Predictive Modeling. J. Geophys. Res.-Solid Earth 2004, 109, B02201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatsumi, Y.; Ishizaka, K. Origin of High-Magnesian Andesites in the Setouchi Volcanic Belt, Southwest Japan, I. Petrographical and Chemical Characteristics. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1982, 60, 293–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rapp, R.P. Amphibole-out Phase Boundary in Partially Melted Metabasalt, Its Control over Liquid Fraction and Composition, and Source Permeability. J. Geophys. Res-sol. Ea. 1995, 100, 15601–15610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rapp, R.P.; Watson, E.B. Dehydration Melting of Metabasalt at 8–32 Kbar: Implications for Continental Growth and Crust-Mantle Recycling. J. Petrol. 1995, 36, 891–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.; Cawood, P.A.; Wang, K.; Zi, J.-W.; Feng, Q.; Nguyen, Q.M.; Tran, D.M. Neoarchean and Paleoproterozoic K-Rich Granites in the Phan Si Pan Complex, North Vietnam: Constraints on the Early Crustal Evolution of the Yangtze Block. Precambrian Res. 2019, 332, 105395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwana, J.K.; Kaur, P.; Chaudhri, N. Association of A- and I-type Granitoids in the Central Aravalli Orogen, Rajasthan: Implications for the Neoproterozoic Tectonic Evolution of North-west India. Geol. J. 2022, 57, 3267–3291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yao, X.; Wang, S.; Zhu, X.; Wang, J.; Wang, C. Intraplate Extension of the Indochina Plate Deduced from 26 to 24 Ma A-Type Granites and Tectonic Implications. Int. Geol. Rev. 2019, 61, 1691–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenan, J.M.; Shaw, H.F.; Ryerson, F.J.; Phinney, D.L. Mineral-Aqueous Fluid Partitioning of Trace Elements at 900 °C and 2.0 GPa: Constraints on the Trace Element Chemistry of Mantle and Deep Crustal Fluids. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta. 1995, 59, 3331–3350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devine, J.D. Petrogenesis of the Basalt-Andesite-Dacite Association of Grenada, Lesser Antilles Island Arc, Revisited. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 1995, 69, 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, D.; Liu, K.; Mo, X.; Wang, S.; Zhao, Z.; He, X.; Yu, T. Geological Significance of Neoproterozoic Intrusive Rocks in the South Section of the Ailaoshan Orogenic Belt, SW China: Insights from Petrology, Geochemistry, and Geochronology. Minerals 2023, 13, 349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.Q.; Wang, Y.L.; Zhang, C.J. Discrimination of the Tectonic Settings of Basalts by Th, Nb and Zr. Geol. Rev. 2003, 49, 40–47. [Google Scholar]
- Pearce, J.A.; Harris, N.B.W.; Tindle, A.G. Trace Element Discrimination Diagrams for the Tectonic Interpretation of Granitic Rocks. J. Petrol. 1984, 25, 956–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, N.B.W.; Pearce, J.A.; Tindle, A.G. Geochemical Characteristics of Collision-Zone Magmatism. Geol. Soc. Lond. Spec. Publ. 1986, 19, 67–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearce, J.A. Trace Element Characteristics of Lavas from Destructive Plate Boundaries. In Orogenic Andesites and Related Rocks; Thorpe, R.S., Ed.; Wiley: Chichester, UK, 1982; pp. 528–548. [Google Scholar]
- Pearce, J.A.; Norry, M.J. Petrogenetic Implications of Ti, Zr, Y, and Nb Variations in Volcanic Rocks. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 1979, 69, 33–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; McKenzie, N.R.; Colleps, C.L.; Chen, W.; Ying, Y.; Stockli, L.; Sardsud, A.; Stockli, D.F. Zircon Isotope–Trace Element Compositions Track Paleozoic–Mesozoic Slab Dynamics and Terrane Accretion in Southeast Asia. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2022, 578, 117298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.H.; Li, W.X.; Li, Z.X.; Liu, Y. 850–790 Ma Bimodal Volcanic and Intrusive Rocks in Northern Zhejiang, South China: A Major Episode of Continental Rift Magmatism during the Breakup of Rodinia. Lithos 2008, 102, 341–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Condie, K. Continental Growth During Formation of Rodinia at 1.35-0.9 Ga. Gondwana Res. 2001, 4, 5–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, N.M.W.; Slagstad, T. Continental Growth and Reworking on the Edge of the Columbia and Rodinia Supercontinents; 1.86–0.9 Ga Accretionary Orogeny in Southwest Fennoscandia. Int. Geol. Rev. 2015, 57, 1582–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, B.; Evans, D.A.D.; Li, Y.X. Neoproterozoic Paleogeography of the Tarim Block: An Extended or Alternative “Missing-Link” Model for Rodinia? Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2017, 458, 92–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.C.; Zou, H.; Chen, H.F.; Pirajno, F.; Lan, Z.W.; Yu, H.D.; Xiao, B.; Liu, C.M.; Wu, J.H.; Zhong, Y.J.; et al. The Last Neoproterozoic Rift Magmatism on the Western Margin of Yangtze Block, South China: New Insights of Marinoan Onset from Low-δ18O Magmatic Events. Precambrian Res. 2023, 390, 107037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.C.; Li, X.H.; Li, W.X.; Li, Z.X. Ca. 825 Ma Komatiitic Basalts in South China: First Evidence For> 1500 C Mantle Melts by a Rodinian Mantle Plume. Geology 2007, 35, 1103–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cawood, P.A.; Strachan, R.A.; Pisarevsky, S.A.; Gladkochub, D.P.; Murphy, J.B. Linking Collisional and Accretionary Orogens during Rodinia Assembly and Breakup: Implications for Models of Supercontinent Cycles. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2016, 449, 118–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Shu, L.; Liu, H.; Gong, H.; Ma, Y.; Mu, L.; Zhong, L. First Evidence for ca. 780 Ma Intra-Plate Magmatism and Its Implications for Neoproterozoic Rifting of the North Yili Block and Tectonic Origin of the Continental Blocks in SW of Central Asia. Precambrian Res. 2014, 254, 258–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarrow, J. The Late Neoproterozoic Enganepe Ophiolite, Polar Urals, Russia: An Extension of the Cadomian Arc? Precambrian Res. 2001, 110, 255–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kröner, A.; Fedotova, A.A.; Khain, E.V.; Razumovskiy, A.A.; Orlova, A.V.; Anosova, M.O.; Perelyaev, V.I.; Nekrasov, G.E.; Liu, D.Y. Neoproterozoic Ophiolite and Related High-Grade Rocks of the Baikal–Muya Belt, Siberia: Geochronology and Geodynamic Implications. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2015, 111, 138–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
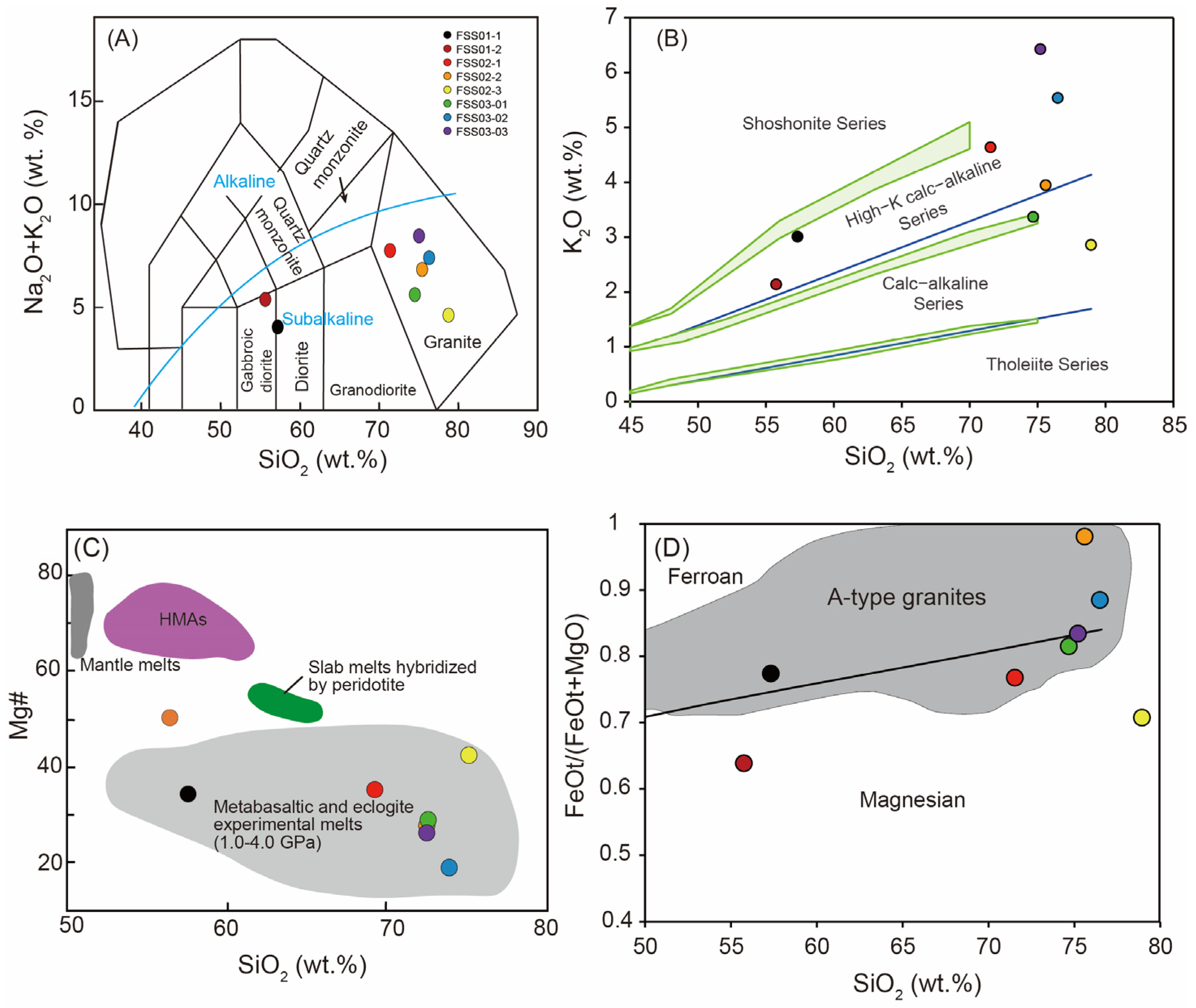
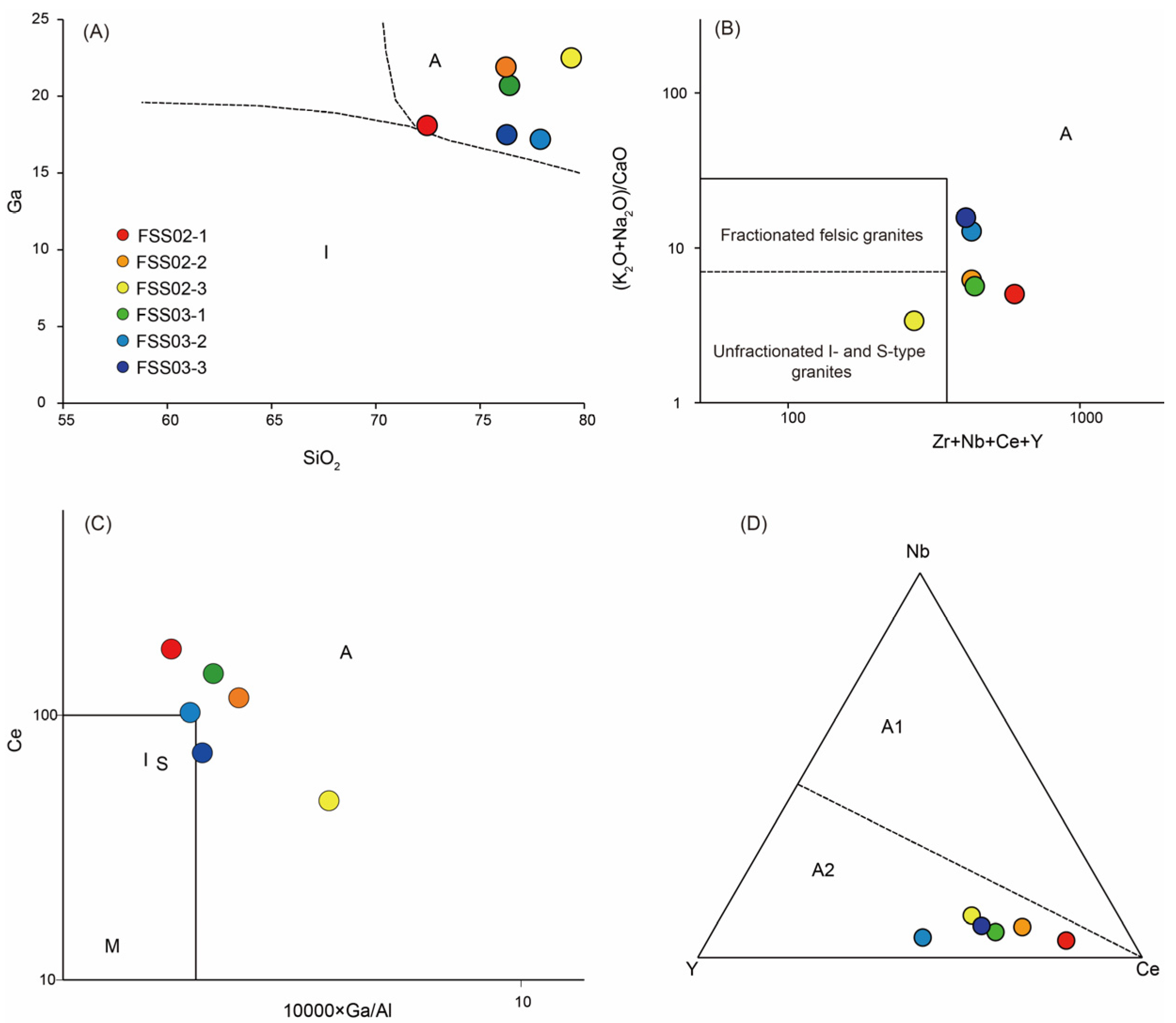
| Index | Typical A-Type Characteristic | Observation in Fengshuishan Granites |
|---|---|---|
| FeOt/(FeOt + MgO) | >0.7 (ferroan affinity) | 0.74–0.90 |
| High SiO2 content | >70% | 74–79% |
| 10,000·Ga/Al | >2.6 | 2.6–4.5 (except one 2.35) |
| Zr + Nb + Ce + Y (ppm) | >350 | 406–597 (except one 270) |
| P2O5 | Low P2O5 | 0.01–0.11 |
| FeOT | >1.00% | 1.69%–3.15% (except one 0.93) |
| Zr saturation temperature (°C) | >800 °C | 818–948 °C |
| REE pattern | Low La/Yb and negative Eu anomaly | (La/Yb)n = 4.5–7.8; Eu/Eu* = 0.37–0.69 |
| Tectonic discrimination | Intraplate/post-collisional fields | Within-plate field |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Z.; Feng, J.; Zhao, T.; Liu, Y.; Wang, R.; Zhang, Y.; Fan, F. Zircon U-Pb-Hf Isotopes, Whole-Rock Geochemistry and Sr-Nd Isotopes of Early Neoproterozoic Intrusion in the Erguna Block, NE China: Petrogenesis and Tectonic Implications. Minerals 2025, 15, 1245. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15121245
Li Z, Feng J, Zhao T, Liu Y, Wang R, Zhang Y, Fan F. Zircon U-Pb-Hf Isotopes, Whole-Rock Geochemistry and Sr-Nd Isotopes of Early Neoproterozoic Intrusion in the Erguna Block, NE China: Petrogenesis and Tectonic Implications. Minerals. 2025; 15(12):1245. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15121245
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Zhanlong, Ji Feng, Tianyu Zhao, Yang Liu, Rui Wang, Yanan Zhang, and Fuling Fan. 2025. "Zircon U-Pb-Hf Isotopes, Whole-Rock Geochemistry and Sr-Nd Isotopes of Early Neoproterozoic Intrusion in the Erguna Block, NE China: Petrogenesis and Tectonic Implications" Minerals 15, no. 12: 1245. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15121245
APA StyleLi, Z., Feng, J., Zhao, T., Liu, Y., Wang, R., Zhang, Y., & Fan, F. (2025). Zircon U-Pb-Hf Isotopes, Whole-Rock Geochemistry and Sr-Nd Isotopes of Early Neoproterozoic Intrusion in the Erguna Block, NE China: Petrogenesis and Tectonic Implications. Minerals, 15(12), 1245. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15121245