Abstract
This study attempted to test whether the use of computer-assisted language learning (CALL) and innovative collaborative learning could be more effective than the use of traditional collaborative learning in improving students’ English proficiencies. A true experimental design was used in the study. Four randomly-assigned groups participated in the study: a traditional collaborative learning group (TCLG, 34 students), an innovative collaborative learning group (ICLG, 31 students), a CALL traditional collaborative learning group (CALLTCLG, 32 students), and a CALL innovative collaborative learning group (CALLICLG, 31 students). TOEIC (Test of English for International Communication) listening, reading, speaking, and writing pre-test and post-test assessments were given to all students at an interval of sixteen weeks. Multivariate analysis of covariance (MANCOVA), multivariate analysis of variance (MANOVA), and analysis of variance (ANOVA) were used to analyze the data. The results revealed that students who used CALL had significantly better learning performance than those who did not. Students in innovative collaborative learning had significantly better learning performances than those in traditional collaborative learning. Additionally, students using CALL innovative collaborative learning had better learning performances than those in CALL collaborative learning, those in innovative collaborative learning, and those in traditional collaborative learning.
1. Introduction
Classes in Taiwan usually consist of the teacher lecturing while the students sit still, listening attentively and taking notes. The students do not dare to ask questions or speak up in class, rarely interacting with their teachers or classmates. They willingly fall into rote, reticent, and passive learning [1,2]. The passive learning style is quite a contrast to active engagement in class, which is promoted in college education [3,4].
College education creates a more learner-centered environment, in which only a small amount of lecturing information is presented in each class period, accompanied by active learning exercises that enable students to learn individually, independently, and critically [5]. Since college education is much more career-oriented, focusing more on professional knowledge and specialized skills, the hours in the classroom are reduced, though more material is packed into each class period. With the shift from teacher- to learner-centered learning, and the constraint of instruction time, teachers should seek assistance from instructional strategies, media, or technologies, and further integrate them into classroom instruction to facilitate students to learn English [6]. When students encounter learning difficulties, they may seek help through learning technologies, such as computers, learning websites, etc., to access useful language resources or interact with learning technologies, or they may seek help from their classmates to generate collaborative dialogues, building interdependence among students.
This study attempted to investigate whether the use of computer-assisted language learning (CALL), a kind of teaching/learning technology as a language tool in language acquisition, in different collaborative learning groups could enhance students’ English learning proficiencies in terms of listening, reading, speaking, and writing.
2. Literature Review
2.1. Collaborative Learning
Collaborative learning is defined as using small learning groups to work together, stimulating students to help one other and maximizing their ability to learn [7,8]. It is based on the constructivist learning theory and on the premise that people can actively construct knowledge for themselves via interaction with their personal experience and their environment [9]. The benefit of collaborative learning is that students can acquire and share knowledge or experience by learning from one other.
Steendam et al.’s study [10] demonstrated that using collaborative learning in English as a foreign language (EFL) acquisition can help students become more independent and autonomous. Through participating in EFL collaborative learning activities, students have an opportunity to develop communication and interaction skills, and can use these skills to master the English language. While actively participating in learning groups, students get more involved in their learning process and are more capable of comprehending learning material effectively, hence, easily attaining their learning goals [11]. Aminloo [12] studied the effect of using group work and collaborative writing on elementary-level EFL students. Results showed that the students writing collaboratively have better writing performance than those writing individually. Ghaith’s study [13] demonstrated that learning English through collaboration can bring students a more positive learning experience; they are more willing to share their experiences with other students.
Another of Ghaith’s studies [14] showed that learning English through collaboration can improve the perception of social support and academic achievement in EFL learning, maximizing positive interdependence. Davoudi and Mahinpo [15] recommended using the Kagan learning model to empower language learners to work together collaboratively for foreign language acquisition. Situated in a collaborative learning environment, students are not alone, but are supported by each other, using multiple ways to overcome language learning problems, therefore, increasing their language achievement, as well as their social skills. Alijanian [16] developed a Student Teams Achievement Division (STAD) approach, emphasizing team goals and success dependent on the collaboration of all groupmates. The results also showed that students using the STAD approach based on collaboration demonstrated better English learning performance than those using traditional methods.
Chan, et al. [17] proposed grouping students into learning groups based on the group complementary score. Those who had mutual complementary strengths were grouped together to learn from each other, avoiding situations where all the students in one group had the same strengths and weaknesses. The proposed collaborative learning strategies provided students with a collaborative learning environment and offered complementary assistance to students to facilitate the learning process. Wang, Li, and Liao [18] proposed an innovative strategy of using a genetic algorithm to determine optimal complementary learning clusters for English learning in Taiwan, taking students’ complementary characteristics into consideration. In the complementary learning groups, students with distinct English competencies and skills were assigned to the same group to teach and learn from each other, exchanging their learning methods and experiences in English speaking, reading, and writing. For instance, those better at speaking English were grouped with others who were better at English writing or reading but worse at speaking. The results showed that students situated in optimal complementary learning environments had higher English performances.
Although collaborative learning is considered an effective teaching/learning strategy for EFL instruction, large class sizes and limited time are also challenges for EFL teachers in Taiwan. Therefore, in order to increase students’ learning outcomes, it is necessary to use teaching/learning technologies to facilitate the English learning process. Collaborative learning can be used in face-to-face language learning, and can be adapted for distance language learning or computer-assisted language learning (CALL).
2.2. Computer-Assisted Language Learning (CALL)
With the development of computer assisted language learning (CALL), there comes an increasing emphasis on integrating computer technology into English-language instructional material to help students achieve the desired learning outcomes, as well as provide them with learning tools and resources that would otherwise be unavailable. CALL is defined as any kind of language learning activity making use of computers [19]. Levy [20] defined CALL as the use of computers in language teaching and learning. It can also be broadly defined as the application of any media, computational method, or technique in language acquisition [21].
Researchers have investigated the advantages of using computers as language tools in language instruction [22,23,24,25,26]. CALL technology allows students to access any learning website to learn a language at their own pace, at any time, and in any location. Through the Internet, students can access a virtual learning environment without being physically present in a classroom; they are also provided immediate feedback, helping students to have their questions answered in real-time. In addition, CALL can be used in place of tutors and tools, checking and testing students’ learning progress [20,23]. Blankenship’s study [27] demonstrated the effectiveness of CALL technology in writing acquisition. After comparing the difference between computer-assisted instruction and lecture-based instruction for college students’ writing courses, the results showed that the performances of students who received computer-assisted writing instruction were better than those who did not.
Liu, Chen, and Chang [28] used a computer-assisted concept-mapping learning strategy to improve English reading comprehension among EFL college students. They found that this strategy improved English reading proficiency among low-level groups, but was not as effective among high-level groups. Marzban [29] studied Iranian intermediate EFL students who used CALL in teaching reading comprehension: the students who used CALL significantly outperformed those who used traditionally-taught reading comprehension methods. Barani [30] explored the difference between CALL users and non-users among Iranian EFL learners in listening skills and activities, finding that CALL significantly enhanced students’ listening skills.
E-learning systems, such as Blackboard, WebCT, Moodle, etc., have proven to be powerful platforms for management and progress in the education sector [31,32]. Teachers may use the system to develop web-based lecture notes and online quizzes and to monitor students’ progress; students may use the system to download course materials, check course announcements or syllabi, submit assignments, take quizzes, and check course grades [31]. In addition, they can use forums, wikis, and chat rooms to support collaborative learning.
Looking at the literature discussed above, it is obvious that collaborative learning and CALL can enhance students’ English learning performance. However, it is worthwhile to explore different learning methods and strategies using CALL and collaborative learning to improve students’ learning outcomes. Considering that most EFL collaborative learning groups were arranged according to similar, rather than complementary, characteristics, the study attempted to test whether the use of CALL in different collaborative learning groups (here innovative collaborative learning groups and traditional collaborative learning groups) could enhance students’ English learning proficiencies in terms of listening, reading, speaking, and writing.
3. Methodology
3.1. Participants
One hundred and thirty-one college freshmen participated in the study, all of whom had studied English for at least six years, beginning in junior high school. Based on English placement test results from the beginning of the academic year, they were randomly assigned into either the control or experimental groups, all at the intermediate level of English proficiency. Additionally, all participants had to take the TOEIC (Test of English for International Communication) pre-test and post-test one week before and one week after the intervention.
3.2. Measures
3.2.1. TOEIC Listening, Reading, Speaking, and Writing Tests
The TOEIC listening, reading, speaking, and writing pre-test and post-test were used to measure students’ ability to use English in everyday communication activities at an interval of sixteen weeks. The pre-test and post-test were not the same, but had similar items. TOEIC was developed by Educational Testing Service (ETS) in 1979, the largest private educational testing organization, with tests including TOEFL, SAT, GMAT, etc. Based on the TOEIC Examinee Handbook [33], the reliability of the TOEIC scores has been around 0.90 and higher. There is a moderately strong correlation (0.40–0.50) between test-takers’ TOEIC scores and their assessment of their own ability to accomplish certain English listening, reading, speaking, and writing tasks. Since the test was first administered in 1979, TOEIC has gone through a series of validity and reliability tests, becoming more popular among organizations, companies, and academic instructions as a measure of how well the student can communicate in English [34,35,36].
In the TOEIC pre-test and post-test, the listening section contained 100 multiple-choice questions, totaling 495 points, with 10 questions relating to photographs, 30 question-response questions, 30 questions about short conversations, and 30 questions about short lectures. The reading section contained 100 multiple-choice questions, totaling 495 points, with 40 questions about incomplete sentences, 12 questions requiring the student to complete a text, 28 questions about single passages, and 20 questions about double passages [37]. There were 11 questions in the speaking section, totaling 200 points, with two questions requiring the student to read a text aloud, one question requiring the student to describe a picture, three free-response questions, three questions about the information provided, one question requiring the student to propose a solution to a problem, and one question requiring the student to express an opinion. There were eight questions in the writing section, totaling 200 points, with five questions requiring the student to write a sentence based on a picture, two questions requiring the student to respond to a request, and one opinion essay [38].
3.2.2. In-Depth Student Interviews with Individuals and Groups
Interviews allowed for greater depth of data collection [39]. In-depth student interviews with individuals or groups were also used to triangulate the quantitative results, as well as to assess possible advantages or difficulties in using CALL in different collaborative learning groups. Pseudonyms were used to encourage honest responses and to protect the students’ privacy. All the interviews were conducted in Mandarin Chinese and tape-recorded to help the researchers understand the students’ opinions and reflections upon the class. In order to generate accurate interpretations, after translating the interviews into English, the researchers asked a bilingual teacher to review the translated data.
3.3. Experimental Design
A true experimental design was used in the study. To determine whether the use of CALL and innovative collaborative learning could increase students’ English proficiencies, four groups were used in the study: one control group and three experimental groups. The control group (TCLG) underwent traditional collaborative learning not using CALL; Experimental Group 1/ICLG underwent innovative collaborative learning not using CALL; Experimental Group 2/CALLTCLG underwent traditional collaborative learning using CALL; and Experimental Group 3/CALLICLG underwent innovative collaborative learning using CALL.
The groups using CALL (CALLTCLG and CALLICLG) had to go to the Moodle website [40] and Pearson Longman’s MyTopNotchLab website [41] for self-study and were required to do assignments to post articles and use discussion forums to discuss and interact with their cluster mates, while the groups not using CALL (TCLG and ICLG) had to spend at least two hours of self-study on the Top Notch 2 Workbook. The groups using traditional collaborative learning methods (TCLG and CALLTCLG) were allowed to form their own learning clusters. The Control Group/TCLG formed eight clusters, six clusters of four students and two clusters of five. Experimental Group 2/CALLTCLG formed eight clusters, and each cluster had four students. For those situated in the innovative learning groups (Experimental Group 1/ICLG and Experimental Group 3/CALLICLG), they had to undergo the following three steps discussed in the following section to derive the innovative collaborative learning clusters. Experimental Group 1/ICLG comprised seven clusters, four clusters of four students and three clusters of five) and Experimental Group 3/CALLICLG comprised eight clusters, six clusters of four students and two clusters of five). Each student was only arranged into one group.
A one-way MANOVA (multivariate analysis of variance) was applied here for the pre-test. The pre-test results (see Table 1) showed that there were no significant differences among the mean scores of the TCLG (means (M) = 225.42, 189.59, 43.53, and 34.18), ICLG (M = 227.03, 168.90, 47.84, and 37.55), CALLTCLG (M = 237.44, 199.84, 48.66, and 37.75), and CALLICLG (M = 249.68, 185.18, 49.65, and 39.27). In other words, they were all homogeneous on the listening, reading, speaking, and writing sections.

Table 1.
One-way MANOVA results on the TOEIC pre-test.
After a sixteen-week intervention covering six instructional units, four groups were compared in the TOEIC post-test to evaluate their English learning performance. Table 2 shows the research design.

Table 2.
Research design.
3.4. The Three Steps Used to Arrange Learning Clusters for the Innovative Collaborative Learning Groups
In order to arrange the learning clusters for the innovative collaborative learning groups (ICLG and CALLICLG), pre-test scores in the four categories of proficiency were evaluated and the students in the two groups were organized into clusters based on the following three steps:
Step 1. Using pre-test English scores to normalize the listening, speaking, reading, and writing scores via Equation (1):
- m = 1 for listening proficiency, 2 for speaking proficiency, 3 for reading proficiency, and 4 for writing proficiency.
- : the lth student in the mth normalization score in listening, speaking, reading, and writing scores.
- : the lth student in the mth initial score in listening, speaking, reading, and writing scores.
- : the maximal scores in the mth initial score in listening, speaking, reading, and writing scores.
Step 2. Reaching the agreement to arrange innovative learning groups based on students’ complementary differences in pre-test listening, speaking, reading, and writing scores.
Viewing that most EFL collaborative learning groups were arranged according to similar rather than complementary characteristics, the study intended to group students based on their mutual complementary strengths in order to help them learn from each other, exchanging their learning methods and experiences. Listening and speaking belonged to oral communication, while reading and writing belonged to written communication. Research has shown that listening and speaking proficiencies were highly correlated with, and complementary to, each other; reading and writing proficiencies were highly correlated with, and complementary to, each other [42,43]. Hence, the researchers convened a panel of experts from universities and reached an agreement that listening and speaking proficiencies were complementary to each other, and reading and writing proficiencies were complementary to each other. For example, if Student A had good English listening proficiency and poor English speaking proficiency, while Student B had poor English listening proficiency and good English speaking proficiency, Student A could help Student B in his/her English listening learning and Student B could help Student A in his/her English speaking learning. Additionally, because English reading and writing proficiencies could demonstrate students’ vocabulary and grammatical abilities, the expert panel determined that the English reading and writing proficiencies were complementary to each other. The clusters could be derived via Equation (2):
and : the weights ; : the threshold.
Step 3. Deriving the innovative learning clusters for Experimental Group 1/ICLG and Experimental Group 3/CALLICLG.
To derive the innovative collaborative learning clusters in Experimental Group 1/ICLG and Experimental Group 3/CALLICLG, the teacher computed the complementary value and determined whether the value was less than or equal to the threshold. In this study, listening, reading, speaking, and writing scores on the TOEIC pre-test were taken into consideration as complementary competencies when the researchers arranged the clusters of students for the course. The and values were set at 0.5, and the value was set at 0.2.
3.5. Procedure
The teaching material used in these four groups was taken mainly from an intermediate-level textbook, Top Notch 2, published by Pearson Longman, which was developed for young adults learning to speak and communicate in English confidently and fluently [44]. The teacher, teaching activities, materials, assignment, and instruction time were the same for each group to avoid confounding effects on the experiment. The treatment lasted sixteen weeks with classes taking place two times per week, plus at least two hours of self-study per week.
During the 16-week experiment, the groups using CALL (Experimental Group 2/CALLTCLG and Experimental Group 3/CALLICLG) had to go to the Pearson Longman MyTopNotchLab website and Moodle website for self-study and were required to do assignments, such as those indicated with the sign “ Movies and Entertainment”, to post articles for sharing, and to use the discussion forums (such as those indicated with the sign “
Movies and Entertainment”, to post articles for sharing, and to use the discussion forums (such as those indicated with the sign “ Movies and Entertainment” to discuss topics and interact with their cluster mates. There were six topics in the experiment; for each topic, each student in both Experimental Group 2/CALLTCLG and Experimental Group 3/CALLICLG had to post at least one article that he or she had read and was interested in. After reading and posting an article for sharing, the student had to go to the same discussion forums to give at least two replies, opinions, or reflections to the threads and messages posted by other cluster mates (each a minimum of 150 words).
Movies and Entertainment” to discuss topics and interact with their cluster mates. There were six topics in the experiment; for each topic, each student in both Experimental Group 2/CALLTCLG and Experimental Group 3/CALLICLG had to post at least one article that he or she had read and was interested in. After reading and posting an article for sharing, the student had to go to the same discussion forums to give at least two replies, opinions, or reflections to the threads and messages posted by other cluster mates (each a minimum of 150 words).
 Movies and Entertainment”, to post articles for sharing, and to use the discussion forums (such as those indicated with the sign “
Movies and Entertainment”, to post articles for sharing, and to use the discussion forums (such as those indicated with the sign “ Movies and Entertainment” to discuss topics and interact with their cluster mates. There were six topics in the experiment; for each topic, each student in both Experimental Group 2/CALLTCLG and Experimental Group 3/CALLICLG had to post at least one article that he or she had read and was interested in. After reading and posting an article for sharing, the student had to go to the same discussion forums to give at least two replies, opinions, or reflections to the threads and messages posted by other cluster mates (each a minimum of 150 words).
Movies and Entertainment” to discuss topics and interact with their cluster mates. There were six topics in the experiment; for each topic, each student in both Experimental Group 2/CALLTCLG and Experimental Group 3/CALLICLG had to post at least one article that he or she had read and was interested in. After reading and posting an article for sharing, the student had to go to the same discussion forums to give at least two replies, opinions, or reflections to the threads and messages posted by other cluster mates (each a minimum of 150 words).3.6. Computer-Assisted Language Learning (CALL) Tools
3.6.1. Moodle (Modular Object-Oriented Dynamic Learning Environment)
To carry out the research, a General English course was set up in Moodle. Additional teaching resources and online activities for students accompanied each unit as an extension of face-to-face course instruction. Moodle is an easy-access and learner-centered online course management system that students can work with to build their knowledge. Moodle’s General English course offered syllabi access, quizzes, notices, and lecture resources. Additionally, assignments and discussion forums were added as an online learning space for group discussion and the sharing of ideas.
3.6.2. Pearson Longman’s MyTopNotchLab Website
Pearson Longman’s MyTopNotchLab is an online learning website for the Top Notch series English course. Students used the code provided with the Top Notch 2 coursebook to register and log on to the e-lab course. It offered students additional learning resources, online exercises, and web-based homework from the Top Notch 2 Student’s Book to master each learning unit. Students were allowed to complete the learning activities anywhere with access to the Internet.
3.7. Data Analysis
The collected data was analyzed quantitatively and qualitatively. The statistical package used to analyze the quantitative data was SPSS (Statistical Packages for the Social Science). The descriptive statistics included means and standard deviations. Moreover, two-way MANCOVA (multivariate analysis of covariance), two-way MANOVA, and three-way ANOVA (analysis of variance) were used to explore the differences.
4. Results
4.1. Quantitative Results
The study investigated whether the use of CALL and innovative collaborative learning could be more effective than traditional collaborative learning. Pre- and post-intervention results for four groups’ English listening, reading, speaking, and writing proficiencies were examined. As shown in Table 1, the difference on the pre-test was not statistically significant at a = 0.05; the four groups were assumed to be equivalent. However, after intervention, a two-way MANCOVA was used in order to illustrate whether pre-test results would affect the results of post-test. Hence, the researchers used the listening, reading, speaking, and writing variables in the pre-test as covariates to analyze whether there were any significant effects on the post-test. The results showed that the pre-test were not significantly related to the post-test in listening (Wilks’ Lambda: p = 0.651), reading (Wilks’ Lambda: 0.995; p = 0.967), speaking (Wilks’ Lambda: 0.947; p = 0.156), and writing (Wilks’ Lambda: 0.992; p = 0.914). Instead, the researchers further used a two-way MANOVA to identify the level of significance and differences in means between the groups that used CALL learning technology (CALLTCLG and CALLICLG) and the groups that did not (ICLG and TCLG), and between the groups situated in innovative collaborative learning (CALLICLG and ICLG) and the groups in traditional collaborative learning (CALLTCLG and TCLG).
Since the interaction effect between the learning technology factor and the collaborative learning factor was not significant, the learning technology factor and the collaborative learning factor were further analyzed (see Table 3). In terms of learning technology, there were significant differences between the groups that used CALL (CALLTCLG and CALLICLG) and the groups that did not (ICLG and TCLG), at the 0.05 significance level in all proficiencies. Regarding the collaborative learning factor, there were significant differences in the groups in innovative collaborative learning (CALLICLG and ICLG) and the groups in traditional collaborative learning (CALLTCLG and TCLG), at the 0.05 significance level in all proficiencies.

Table 3.
Two-way MANOVA results on the TOEIC post-test.
Furthermore, the results showed that the experimental groups improved more than the control group; in the listening, reading, speaking, and writing sections, the mean scores of CALLICLG (M = 281.18, 240.44, 91.59, and 93.35) were all higher than those of CALLTCLG (M = 274.84, 215.63, 83.66, and 85.31), ICLG (M = 271.84, 214.90, 78.81, and 96.94), and TCLG (M = 240.41, 202.26, 74.53, and 58.35). The sequence of score increases for the four groups from high to low is CALLICLG > CALLTCLG > ICLG > TCLG.
After a two-way MANOVA, while further investigating the differences between the students using CALL and those who, via the post hoc analysis of the Fisher’s LSD (least significant difference) test, the researchers found that in the reading section, the mean score of those students using CALL (CALLICLG and CALLTCLG) (M = 228.41) was statistically significantly higher than that of students not using CALL (ICLG and TCLG) (M = 208.29) at the 0.05 significance level. Notably, in the listening, speaking, and writing sections, the mean scores of the students using CALL (M = 278.11, 87.74, and 89.46) were significantly higher than those of the students not using CALL (M = 255.40, 76.57, and 67.22) at the 0.01 significance level (see Table 4).

Table 4.
Post hoc analysis—Fisher’s LSD test results on the English proficiency post-test for the students using CALL and the students not using CALL.
Using Cohen’s d formula, effect sizes of the post-tests of the students using CALL and the students not using CALL were also calculated to indicate the practical significances of the results (see Table 4). As Cohen [45] indicated, the larger the effect size, the greater the impact of intervention. An effect size between 0.2 and 0.5 indicates a small effect size; an effect size between 0.5 and 0.8, a moderate effect size; an effect size greater than 0.8, a large effect size. The effect sizes on listening and speaking were 0.55 and 0.76, indicating moderate effect sizes. The effect size on reading was 0.37, indicating a small effect size. The effect size on writing was 1.12, indicating a large effect size.
As for the comparison between the groups in traditional collaborative learning and those in innovative collaborative learning (see Table 5), the mean scores on the reading and speaking sections of those groups in innovative collaborative learning (ICLG and CALLICLG) (M = 228.26 and 85.49) were statistically significantly higher than those of the students in traditional collaborative learning (TCLG and CALLTCLG) (M = 208.74 and 78.96) at the 0.05 significance level. Notably, in the listening and writing sections, the mean scores of the groups in innovative collaborative learning (M = 276.72 and 85.52) were significantly higher than those of the groups in traditional collaborative learning (M = 257.11 and 71.42; p < 0.01).

Table 5.
Post hoc analysis—Fisher’s LSD test results on the English proficiency post-test for students in traditional collaborative learning and students in innovative collaborative learning.
Using Cohen’s d formula, effect sizes of the post-tests of the students in traditional collaborative learning and those in innovative collaborative learning were calculated to indicate the practical significances of the results. The effect sizes for listening, reading, and speaking were small (Cohen’s d = 0.47, 0.36, and 0.42). The effect size for writing were moderate (Cohen’s d = 0.65).
Therefore, in order to explore which factors would affect listening, reading, speaking, and reading. Figure 1 shows the improvement of English proficiencies in CALLICLG, CALLTCLG, ICLG, and TCLG students in terms of listening, reading, speaking, and writing. Three-way ANOVA (two independent factors and one dependent factor) was used here. The authors performed an analysis for repeated measurements with pre-test and post-test as the dependent variable (hereafter called test factor). Two independent variables were the learning technology factor and the collaborative learning factor. One dependent factor was the test factor, including pre-test and post-test. Table 6 shows the analysis results in listening. There was no significance between the two factors or among the three factors. The two main effects—learning technology and collaborative learning—were significant (p < 0.000, p = 0.019). That is, to affect the listening scores, learning technology and collaborative learning were the main contribution factors. Therefore, as shown in Figure 1, the slopes of the lines for English listening proficiency in ICLG, CALLTCLG, and CALLICLG were steeper and more positive than the slope of TCLG.
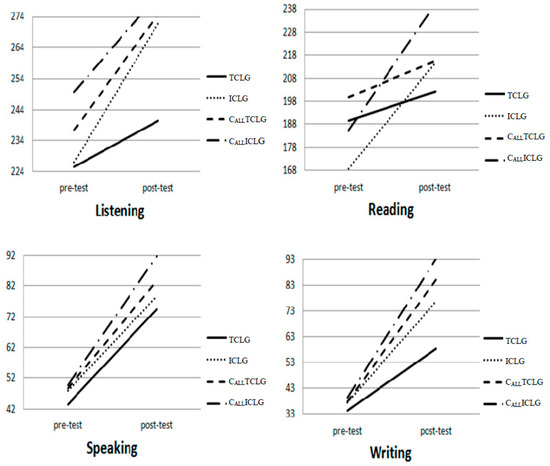
Figure 1.
The improvement of English proficiencies in different learning groups. Pre: pre-test; Post: Post-test.

Table 6.
Three-way ANOVA for dependent variable in listening.
Table 7 shows that in English reading proficiency, there is a significant interaction effect (collaborative learning * test, p = 0.007) in within-subjects. The main effect of learning technology was significant (p = 0.011). This means that in the reading scores, learning technology had a stronger effect than collaborative learning because the main effect of collaborative learning was not significant (p = 0.930). Hence, as shown in Figure 1, for the groups not using CALL—TCLG and ICLG, there is an interaction between the slopes of the lines for English reading proficiency; for the group using CALL—CALLTCLG and CALLICLG, there is also an interaction between the slopes. Therefore, it can be assumed that learning technology can bring a positive effect on English reading proficiency.

Table 7.
Three-way ANOVA for the dependent variable in reading.
Table 8 shows that, in English speaking proficiency, there was no significant interaction between the two factors or among the three factors. Only the main effect leaning technology was significant (p = 0.001). Hence, learning technology is the main factor to affect the speaking scores. Therefore, as shown in Figure 1, the slopes of the lines for English speaking proficiency in CALLTCLG, and CALLICLG were more positive, with minor steep slopes, than those of TCLG and ICLG.

Table 8.
Three-way ANOVA for the dependent variable in speaking.
Table 9 shows that in English writing proficiency, There were significant interaction effects on learning technology * test (p < 0.000) and on collaborative * test (p = 0.008) in within-subjects. The two main effects—learning technology and collaborative learning—are also significant (p < 0.000; p < 0.000). Hence, learning technology and collaborative learning were the main factors to affect writing scores. As shown in Figure 1, learning technology and collaborative learning can bring a positive effect to the slopes of the lines for English writing proficiency.

Table 9.
Three-way ANOVA for the dependent variable in writing.
4.2. Qualitative Results
As the quantitative results showed that the CALLICLG group outperformed the other three groups, four male and four female students in the CALLICLG group were randomly chosen and interviewed to gather more in-depth feedback in order to triangulate the quantitative data obtained in the post-experimental results. Five students in CALLICLG reflected that, as compared with traditional collaborative learning, they enjoyed staying in the innovative collaborative learning group because they could contribute something to the group. Additionally, they enjoyed interacting with their cluster mates in online discussions (M1, M9, F2, F18, F19; M: male student; F: female student). Six students felt more comfortable with online practice exercises, particularly in speaking and pronunciation, because they knew they would not be scolded or corrected in front of their classmates.
Furthermore, in listening practice they were able to listen to the passage repeatedly until they grasped the idea (M8, M9, M13, F10, F18, F19). They consequently became more active and motivated in their English language acquisition, willing to share experiences with their cluster mates and teachers (M1, M9, M13, F2, F18). All students felt that CALL in innovative collaborative learning made their English classes more interesting, and that it was easier to maintain their focus. They enjoyed contributing to the class and getting more involved in the learning process (M1, M8, M9, M13, F2, F10, F18, F19). With the assistance of CALL, students could learn and communicate with each other at any time or in any place. Students also felt that computers were a very useful tool for independent learning. Since they could learn at their own pace and in their own way, they became much more autonomous in their English language learning (M1, M8, M9, M13, F2, F10, F18, F19).
5. Discussion
The quantitative and qualitative results suggested that CALL in innovative collaborative learning was more effective than CALL in traditional collaborative learning, innovative collaborative learning, and traditional collaborative learning.
In the study, the learning technology of CALL and two different collaborative learning methods were designed to be incorporated into regular class instruction. Since there was no interaction between the learning technology and collaborative learning methods, and there were significant differences between the scores of the students using CALL and the students not using CALL in English proficiency tests, it could be concluded that the use of CALL could improve students’ abilities to learn English. The research results correspond with Tseng and Liou’s finding [46] that online practice can increase students’ learning performance. The use of CALL in collaborative learning can help students control their learning process, not only because CALL is independent of both time and place, but because the content can be adapted to students’ needs. The use of online tutorials and the assistance of teachers and peers can help students in mastering the learning unit, correcting mistakes, and understanding material [47]. In CALL, students actively participate in and, to some degree, control the building of their knowledge [48]. When getting tired or bored, they may pause in the middle of learning, or may stop and shift to another learning activity [47]. When students are able to control their learning pace and content, they feel less stressed and, in turn, feel more confident in their English language acquisition [48]. Therefore, the students who use CALL can have greater proficiency in English than those who do not. The results shown in Table 3 and Table 4 and Figure 1 reveal that the use of computer technology can have a positive effect on English language learning. Additionally, Table 6, Table 7, Table 8 and Table 9 show that learning technology can bring a stronger effect to English listening, reading, speaking, and writing proficiencies.
Furthermore, compared with the students in CALL collaborative learning (CALLTCLG), the students who took part in CALL innovative collaborative learning (CALLICLG) had better English learning outcomes. What makes CALL innovative collaborative learning successful is that people in the CALLICLG group feel that they are needed by their cluster mates since, with different complementary competencies, they can contribute to the learning community, equally participating in the construction of knowledge and sharing of ideas with each other. Additionally, when they need help, the students stronger in certain competencies may explain, elaborate, or give examples of the answer, which may increase interaction among mates and also foster deeper understanding of the learning material. When people contribute equally to their learning clusters, they build interdependence among their group or cluster mates. Accordingly, they are encouraged to help each other contribute a greater effort to the success of the class as a whole [49]. Yet, those lower achievers in the CALL traditional collaborative learning group may gain more from the learning group even though they contribute less than their high-achieving counterparts [50].
Moreover, in traditional cooperative or collaborative learning groups, low-achieving students may be teased and criticized by their mates, which may discourage them from getting actively involved in collaborative learning activities [23]. However, students in CALL innovative collaborative learning may prevent mistreatment of those needing special learning assistance, for each student in the CALLICLG group has a certain strong competency and can make a certain contribution to the group. Therefore, students can collaborate with one another equally to achieve learning goals, which also leads to mutual improvement among group or cluster mates [49]. In brief, CALL in innovative collaborative learning is worth recommending for all students.
Though the results revealed that the use of computer technology and innovative collaborative learning can be more effective than the use of traditional collaborative learning in improving students’ English proficiencies in listening, reading, speaking, and writing, there are limitations to this study. While arranging the learning clusters for the innovative collaborative learning groups, the study only took students’ pre-test scores in the four categories of proficiency into consideration. Furthermore, any individual differences in students that were not identified or measured might have contributed to the treatment effect. Future studies may take students’ characteristics related to performance and social features into consideration, such as cognitive styles or learning styles, in order to form more comprehensive innovative collaborative learning groups for students situated in CALL or non-CALL environments.
6. Conclusions
This study attempted to determine whether the use of CALL and innovative collaborative learning could be more effective than traditional collaborative learning in improving students’ English proficiencies in listening, reading, speaking, and writing. The results revealed that students who used CALL had significantly better learning performances than those who did not, and that students in innovative collaborative learning had significantly better learning performances than those in traditional collaborative learning. Additionally, students in CALL innovative collaborative learning had better learning performances than those in CALL collaborative learning, those in innovative collaborative learning, and those in traditional collaborative learning.
The research results may indicate that the learning technology CALL was worth recommending for students in Taiwan, either in traditional collaborative learning or innovative collaborative learning. Furthermore, students in the CALL innovative learning group would have better learning performances. This study outlined an alternative for using CALL innovative collaborative learning in English-language acquisition. It is noteworthy that the most significant contribution of this paper involves the creation of CALL innovative collaborative learning alongside class instruction that explicitly reflects how innovative collaborative learning clusters can optimally facilitate learning through teaching. In these learning clusters, students can both teach and learn from each other in conventional face-to-face class learning or online learning, contributing equally to their clusters according to their competencies. Future studies may take students’ other characteristics into consideration, such as gender, personality, learning styles, cognitive styles, etc.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge the participants and expert professionals who made this study possible.
Author Contributions
Both authors designed the research and co-chaired the research program. Y.-H.W. was responsible for conducting the research, collecting and analyzing the data, and writing the manuscript. H.-C.L. was responsible for analyzing and interpreting the data, and helping improve the manuscript. Both Y.-H.W. and H.-C.L. read and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interests.
References
- Rendon, L. Realizing a transformed pedagogical dreamfield: Recasting agreements for teaching and learning. Spirit. High. Educ. 2005, 2, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, A. An action research of exploring the effect of story summarizing on English writing. Hsiuping J. Humanit. Soc. Sci. 2009, 13, 173–192. [Google Scholar]
- Michael, J. Where’s the evidence that active learning works? Adv. Physiol. Educ. 2006, 30, 159–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moravec, M.; Williams, A.; Aguilar-Roca, N.; O’Dowd, D.K. Learn before lecture: A strategy that improves learning outcomes in a large introductory biology class. CBE Life Sci. Educ. 2010, 9, 473–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaplin, S. Assessment of the impact of case studies on student learning gains in an introductory biology course. J. Coll. Sci. Teach. 2009, 20, 72–79. [Google Scholar]
- Lai, C.; Gu, M. Self-regulated out-of-class language learning with technology. Comput. Assist. Lang. Learn. 2011, 24, 317–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, D.W.; Johnson, R.T. An educational psychology success story: Social interdependence theory and cooperative learning. J. Educ. Res. 2009, 38, 365–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popov, V.; Noroozi, O.; Barrett, J.; Biemans, H.; Teasley, S.; Slof, B.; Mulder, M. Perceptions and experiences of, and outcomes for, university students in culturally diversified dyads in a computer-supported collaborative learning environment. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2014, 32, 186–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schunk, D.H. Learning Theories; Prentice-Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Steendam, E.; Rijlaarsdam, G.; Sercu, L.; Bergh, H. The effect of instruction type and dyadic or individual emulation on the quality of higher-order peer feedback in EFL. Learn. Instr. 2010, 20, 316–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chenga, H.; Linb, N.C. Exploring students’ perceptions of self-access English learning. Proced. Soc. Behav. Sci. 2010, 2, 2676–2680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aminloo, M.S. The effect of collaborative writing on EFL learners writing ability at elementary level. J. Lang. Teach. Res. 2013, 4, 801–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaith, G.M. Learners’ perceptions of their STAD cooperative experience. System 2001, 29, 289–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaith, G.M. The relationship between cooperative learning, perception of social support, and academic achievement. System 2002, 30, 263–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davoudi, A.H.M.; Mahinpo, B. Kagan cooperative learning Model: The Bridge to Foreign Language Learning in the Third Millennium. Theory Pract. Lang. Stud. 2012, 12, 1134–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alijanian, E. The effect of student teams achievement division technique on English achievement of Iranian EFL learners. Theory Pract. Lang. Stud. 2012, 2, 1971–1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, T.; Chen, C.; Wu, Y.; Jong, B.; Hsia, Y.; Lin, T. Applying the genetic encoded conceptual graph to grouping learning. Expert Syst. Appl. 2010, 37, 4103–4118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.H.; Li, Y.C.; Liao, H.C. Using a genetic algorithm to determine optimal complementary learning clusters for ESL in Taiwan. Expert Syst. Appl. 2011, 38, 14832–14837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arikan, A.; Khezerlou, E. Prospective English language teachers’ views on computer and paper-based instruction materials in developing language components. Proced. Soc. Behav. Sci. 2010, 2, 2006–4009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, H. Computer-Assisted Language Learning; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Gamper, J.; Knapp, J. A review of intelligent CALL systems. Comput. Assist. Lang. Learn. 2002, 15, 329–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Chen, Y. Technology-enhanced language learning: A case Study. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2007, 23, 860–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, Y.; Sung, Y.; Chang, K. Let us read together: Development and evaluation of a computer-assisted reciprocal early English reading system. Comput. Educ. 2009, 53, 1188–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kessler, G.; Bikowski, D. Developing collaborative autonomous learning abilities in computer mediated language learning: Attention to meaning among students in wiki space. Comput. Assist. Lang. Learn. 2010, 23, 41–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.F. Engaging students in an online situated language learning environment. Comput. Assist. Lang. Learn. 2011, 24, 182–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Monasour, N.S.; Al-Shorman, R.A. The effect of computer-assisted instruction on Saudi University students’ learning of English. J. King Saud Univ. Lang. Transl. 2012, 24, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blankenship, J.R. The use of computers in the composition—An aid or a hindrance to the learning process. Diss. Abstr. Int. 1999, 34, 9–15. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, P.L.; Chen, C.J.; Chang, Y.J. Effects of a computer-assisted concept mapping learning strategy on EFL college students’ English reading comprehension. Comput. Educ. 2010, 54, 436–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzban, A. Improvement of reading comprehension through computer-assisted language learning in Iranian intermediate EFL students. Proced. Comput. Sci. 2011, 3, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barani, G. The relationship between computer assisted language learning (CALL) and listening skill of Iranian EFL learners. Proced. Soc. Behav. Sci. 2011, 15, 4059–4063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, A.; Areal, N.; Silva, J. Students’ perceptions of Blackboard and Moodle in a Portuguese university. Br. J. Educ. Technol. 2011, 42, 824–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raman, A.; Don, Y. Preservice teachers’ acceptance of learning management software: An application of the UTAUT2 model. Int. Educ. Stud. 2013, 6, 1913–9039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Educational Testing Service. TOEIC Examinee Handbook; Educational Testing Service: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Woodford, P.E. An Introduction to TOEIC: The Initial Validity Study; Educational Testing Service: Princeton, NJ, USA, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Gilfert, S. A Review of TOEIC. Internet TESL 1996, 2, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Stoynoff, S.J. Recent developments in language assessment and the case of four large-scale tests of ESOL ability. Lang. Teach. 2009, 42, 1–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Educational Testing Service. TOEIC Examine Handbook Listening & Reading; Educational Testing Service: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- English Testing Service. TOEIC Examine Handbook Speaking & Writing; Educational Testing Service: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen, L.; Manion, L. Research Method in Education; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.H. Moodle. Available online: 140.128.137.41/moodle (accessed on 12 February 2013).
- Saslow, J. Pearson Longman’s MyTopNotchLab. Available online: www.mytopnotchlab.com (accessed on 15 February 2013).
- Graham, S.; Perin, D. Writing Next: Effective Strategies to Improve Writing of Adolescents in Middle and High Schools—A Report to Carnegie Corporation of New York; Alliance for Excellent Education: Washington, DC, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Budianto, A. The Correlation Between Listening and Speaking Ability of the Fifth Semester Students of English Education Department of Muria Kudus University in the Academic Year 2010/2011. Bachelor’s Thesis, UPT Perpustakaan UMK, Kudus Jawa Tengah, Indonesia, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Saslow, J.; Ascher, A. Top Notch 2; Pearson Longman: New York, NY, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen, J. Statistical Power Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences, 2nd ed.; Lawrence Erlbaum Associates: Hillsdale, NJ, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Tseng, Y.C.; Liou, H.C. The effects of online conjunction materials on college EFL students’ writing. System 2006, 34, 270–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, T.J.F.; Chen, S.Y.; Macredie, R.D. The relationship between Web enjoyment and student perceptions and learning using a Web-based tutorial. Learn. Media Technol. 2005, 30, 27–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.Y. iLED: Interactive learning experience design. J. Online Learn. Teach. 2007, 4, 358–370. [Google Scholar]
- Jalilifar, A. The effect of cooperative learning techniques on college students’ reading comprehension. System 2010, 38, 96–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaith, G.M.; Yaghi, H.M. Effect of cooperative learning on the acquisition of second language rules and mechanics. System 1998, 26, 223–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).