Symmetry-Aware Advances in Multimodal Large Language Models: Architectures, Training, and Evaluation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Mainstream Model Architectures
2.1. Modality Encoders
- Direct Scaling: feeding higher-resolution images directly into the encoder.
- Image Partitioning: Splitting high-resolution images into smaller patches, which are then processed individually by a lower-resolution encoder. For example, Monkey [16] divides large images into multiple patches and combines them with a downsampled global image, allowing the patches to capture local features while the low-resolution image retains global context.
2.2. Pretrained LLMs
2.3. Modality Connectors
2.3.1. Learnable Connectors
2.3.2. Expert Models
2.4. Representative MLLMs
- Encoding: LLaVA employs the pretrained Vicuna model as the language backbone and uses the ViT-L/14 encoder from CLIP as the vision encoder.
- Modality Alignment: For the image , a visual encoder is first employed to encode the input image into the visual feature representation , which is subsequently transformed via a linear projection layer into . For the language instruction , it is converted into a textual feature representation through a tokenizer, which can be written as the following equation:
- Connection: The visual feature and textual representation are concatenated and fed into the language model to produce the final output . This process can be formally expressed as
2.5. Classification of MLLM Architectures
3. Training and Fine-Tuning Strategies
3.1. Pretraining
3.1.1. Single-Stage Pretraining
3.1.2. Multi-Stage Pretraining
3.2. Fine-Tuning
3.2.1. Instruction Tuning
3.2.2. Parameter-Efficient Fine-Tuning (PEFT)
3.2.3. Alignment Tuning
3.2.4. Representative Model Case Studies
4. Task Taxonomy and Evaluation Methods for MLLMs
4.1. Task Taxonomy
4.1.1. Understanding Tasks
- Deep Visual Content Analysis: This focuses on a comprehensive understanding of images and videos. In visual question answering (VQA), the model is required to respond accurately to natural language questions based on the given image or video content. For example, BLIP [92] significantly improves performance on VQA tasks through an innovative joint training strategy of vision-language models, enabling the model to better capture the semantic association between vision and language. GLaMM [93] introduces a region encoder to support fine-grained visual grounding in question answering, interpreting, and responding to specific regions within an image. Image captioning tasks aim to generate precise and descriptive text for input images. Region understanding and visual grounding tasks focus on locating specific regions in images and extracting their semantic content. VistaLLM [94] and LLaFS adopt unique point-sequence encoding approaches to process polygonal regions, providing key technical support for precise region localization.
- Cross-modal Association and Retrieval: This focuses on establishing tight correlations between different modalities within a shared embedding space and enabling efficient bidirectional retrieval. In cross-modal retrieval, CLIP leverages contrastive learning to align image–text features, laying a solid foundation for image-to-text and text-to-image retrieval. ImageBind further expands these capabilities by incorporating images, videos, and audio, significantly enriching the application scenarios and possibilities of cross-modal retrieval.
4.1.2. Generation Tasks
- Image-related Generation and Editing: Image generation tasks aim to create high-quality images based on text descriptions. GILL [53] maps frozen MLLMs to diffusion models to achieve multimodal image generation, offering new paradigms for such tasks. DALL·E 2 [95], based on advanced diffusion models, enables high-resolution image generation, significantly advancing visual quality. Image editing tasks modify images locally or globally according to instructions or text. InstructPix2Pix [96] combines LLMs to generate editing instructions, offering more intelligent and flexible editing capabilities. MLLM-Guided Editing [97] further utilizes multimodal dialogue understanding to refine editing requirements, allowing personalized and precise modifications.
- Cross-modal and Domain-specific Generation: Multimodal generation tasks aim to generate content across modalities, such as text-to-video or image-to-text. NExT-GPT [98], a major breakthrough in this domain, supports arbitrary modality-to-modality generation, expanding the application scope and innovation potential. VITA-1.5 [10] enables interactive generation across speech and vision modalities, supporting speech output from both speech and image inputs, and exemplifies an end-to-end approach to multimodal generation tasks. Domain-specific generation focuses on areas like healthcare and design, leveraging domain knowledge and multimodal data. For instance, Medical Image Synthesis [99] combines medical knowledge bases to generate high-quality diagnostic images, serving as a valuable tool in medical diagnosis. Robot Action Generation [100] translates visual inputs into robotic action commands, enabling intelligent decision-making and control in complex environments, driving real-world deployment of robotic technologies.
4.2. Evaluation Methods
4.2.1. Closed-Ended Evaluation
4.2.2. Open-Ended Evaluation
5. Key Challenges in MLLM Research
5.1. Multimodal Hallucination
- Existence hallucination: the most fundamental type, where the model incorrectly claims the presence of objects that do not actually exist in the image, leading to fundamental misinterpretations.
- Attribute hallucination: This refers to incorrect descriptions of object attributes, such as misidentifying the color of a dog. Since attribute descriptions are based on object existence, this type is often closely related to existence hallucination.
- Relation hallucination: a more complex type where the model misrepresents relationships between objects—such as relative positions or interactions—misleading the understanding of spatial and contextual relationships within a scene.
- Pre-generation mitigation: This involves fine-tuning with curated data. For instance, LLaVA-RLHF [108] leverages human preference data and reinforcement learning to reduce hallucinations and generate more expected responses. LRV-Instruction [109] introduces a fine-grained visual instruction tuning dataset with negative instructions to guide models toward image-faithful outputs.
- In-process correction: Architectural design or feature representations are modified to reduce hallucinations. For example, VCD [110] attributes hallucinations to dataset bias and strong language priors, proposing a decode-then-contrast design. HACL [111] explores visual and language embedding spaces using contrastive learning to pull aligned cross-modal pairs closer and push apart hallucinated representations.
- Post-generation correction: Methods like Woodpecker provide hallucination correction after the output is generated. Woodpecker is a training-free, general hallucination correction framework that integrates expert models to supplement image context and employs a stepwise correction pipeline with intermediate result inspection.
5.2. Challenges of Noisy Data
5.3. Computational and Storage Costs
5.4. Safety and Ethics
6. Future Research Directions for MLLMs
6.1. Enhancing Long-Range Cross-Modal Reasoning
6.2. Finer-Grained Cross-Modal Interaction
6.3. New Application Paradigms
6.4. Expansion Toward Omni-MLLMs
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| LLMs | Large Language Models |
| MLLMs | Multimodal Large Language Models |
| MLPs | Multi-layer perceptrons |
| PEFT | Parameter-Efficient Fine-Tuning |
| LoRA | Low-Rank Adaptation |
| RLHF | Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback |
| DPO | Direct Preference Optimization |
| GRPO | Group-based Reinforcement Policy Optimization |
| SFT | Supervised Fine-Tuning |
| VQA | Visual Question Answering |
Appendix A. Specifications Table
| Subject | Computer Science |
| Specific subject area | Artificial intelligence |
| Type of data | Figures (processed) |
| Data collection | All data used in this review were manually extracted from peer-reviewed literature, open-access research articles, and official technical reports. Figures were compiled and reorganized by the authors for clarity and comparative purposes. No experimental instruments were involved. |
| Data source location | The data were collected from publicly available literature sources and open-access repositories; no new data were generated by the authors. |
| Data accessibility | No new raw data were generated in this study. All data used are available in the original publications cited in the References section. Repository name: not applicable Data identification number: not applicable Direct URL to data: not applicable Instructions for accessing these data: refer to cited articles in the References section. |
| Related research article | None |
| Previously published dataset or data descriptor | This review did not reuse any previously published dataset. All referenced datasets are described and cited in the original works reviewed in this article. |
References
- Radford, A.; Kim, J.W.; Hallacy, C.; Ramesh, A.; Goh, G.; Agarwal, S.; Sastry, G.; Askell, A.; Mishkin, P.; Clark, J.; et al. Learning Transferable Visual Models from Natural Language Supervision. In Proceedings of the 38th International Conference on Machine Learning, PMLR, Vienna, Austria, 1 July 2021; pp. 8748–8763. [Google Scholar]
- Alayrac, J.-B.; Donahue, J.; Luc, P.; Miech, A.; Barr, I.; Hasson, Y.; Lenc, K.; Mensch, A.; Millican, K.; Reynolds, M. Flamingo: A Visual Language Model for Few-Shot Learning. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2022, 35, 23716–23736. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, C.; Yang, Y.; Xia, Y.; Chen, Y.-T.; Parekh, Z.; Pham, H.; Le, Q.; Sung, Y.-H.; Li, Z.; Duerig, T. Scaling up Visual and Vision-Language Representation Learning with Noisy Text Supervision. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, PMLR, Vienna, Austria, 18–24 July 2021; pp. 4904–4916. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, P.; Yang, A.; Men, R.; Lin, J.; Bai, S.; Li, Z.; Ma, J.; Zhou, C.; Zhou, J.; Yang, H. Ofa: Unifying Architectures, Tasks, and Modalities through a Simple Sequence-to-Sequence Learning Framework. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, PMLR, Baltimore, MD, USA, 25–27 July 2022; pp. 23318–23340. [Google Scholar]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, Ł.; Polosukhin, I. Attention Is All You Need. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1706.03762. [Google Scholar]
- Bao, H.; Wang, W.; Dong, L.; Liu, Q.; Mohammed, O.K.; Aggarwal, K.; Som, S.; Piao, S.; Wei, F. Vlmo: Unified Vision-Language Pre-Training with Mixture-of-Modality-Experts. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2022, 35, 32897–32912. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, D.; Yang, D.; Zhang, H.; Song, J.; Zhang, R.; Xu, R.; Zhu, Q.; Ma, S.; Wang, P.; Bi, X. Deepseek-R1: Incentivizing Reasoning Capability in Llms via Reinforcement Learning. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2501.12948. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, A.; Feng, B.; Xue, B.; Wang, B.; Wu, B.; Lu, C.; Zhao, C.; Deng, C.; Zhang, C.; Ruan, C.; et al. DeepSeek-V3 Technical Report. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2412.19437. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, B.; Li, K.; Cheng, Z.; Hu, Z.; Yuan, Y.; Chen, G.; Leng, S.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Li, X.; et al. VideoLLaMA 3: Frontier Multimodal Foundation Models for Image and Video Understanding 2025. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2501.13106. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, C.; Lin, H.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.-F.; Shen, Y.; Liu, X.; Cao, H.; Long, Z.; Gao, H.; Li, K.; et al. VITA-1.5: Towards GPT-4o Level Real-Time Vision and Speech Interaction. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2501.01957. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, W.; Son, B.; Kim, I. ViLT: Vision-and-Language Transformer Without Convolution or Region Supervision. In Proceedings of the 38th International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML 2021), Virtual Event, 18–24 July 2021; pp. 5583–5594. [Google Scholar]
- Kan, K.B.; Mun, H.; Cao, G.; Lee, Y. Mobile-Llama: Instruction Fine-Tuning Open-Source Llm for Network Analysis in 5g Networks. IEEE Netw. 2024, 38, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Li, C.; Wu, Q.; Lee, Y.J. Visual Instruction Tuning. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2023, 36, 34892–34916. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, Y.; Li, W.; Liu, J.; Tang, D.; Luo, X.; Qin, C.; Zhang, L.; Zhu, J. Osprey: Pixel Understanding with Visual Instruction Tuning. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 16–22 June 2024; pp. 28202–28211. [Google Scholar]
- Cherti, M.; Beaumont, R.; Wightman, R.; Wortsman, M.; Ilharco, G.; Gordon, C.; Schuhmann, C.; Schmidt, L.; Jitsev, J. Reproducible Scaling Laws for Contrastive Language-Image Learning. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 2818–2829. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Yang, B.; Liu, Q.; Ma, Z.; Zhang, S.; Yang, J.; Sun, Y.; Liu, Y.; Bai, X. Monkey: Image Resolution and Text Label Are Important Things for Large Multi-Modal Models. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 16–22 June 2024; pp. 26763–26773. [Google Scholar]
- Deshmukh, S.; Elizalde, B.; Singh, R.; Wang, H. Pengi: An Audio Language Model for Audio Tasks. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2023, 36, 18090–18108. [Google Scholar]
- Elizalde, B.; Deshmukh, S.; Al Ismail, M.; Wang, H. Clap Learning Audio Concepts from Natural Language Supervision. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2023-2023 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Rhodes, Greece, 4–10 June 2023; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2023; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Girdhar, R.; El-Nouby, A.; Liu, Z.; Singh, M.; Alwala, K.V.; Joulin, A.; Misra, I. Imagebind: One Embedding Space to Bind Them All. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 15180–15190. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, T.; Mann, B.; Ryder, N.; Subbiah, M.; Kaplan, J.D.; Dhariwal, P.; Neelakantan, A.; Shyam, P.; Sastry, G.; Askell, A. Language Models Are Few-Shot Learners. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2020, 33, 1877–1901. [Google Scholar]
- Chung, H.W.; Hou, L.; Longpre, S.; Zoph, B.; Tay, Y.; Fedus, W.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Dehghani, M.; Brahma, S. Scaling Instruction-Finetuned Language Models. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2024, 25, 1–53. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Li, D.; Savarese, S.; Hoi, S. Blip-2: Bootstrapping Language-Image Pre-Training with Frozen Image Encoders and Large Language Models. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, PMLR, Honolulu, HI, USA, 23–29 July 2023; pp. 19730–19742. [Google Scholar]
- Touvron, H.; Lavril, T.; Izacard, G.; Martinet, X.; Lachaux, M.-A.; Lacroix, T.; Rozière, B.; Goyal, N.; Hambro, E.; Azhar, F. Llama: Open and Efficient Foundation Language Models. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2302.13971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, A.; Dao, T. Mamba: Linear-Time Sequence Modeling with Selective State Spaces. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2312.00752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Han, J.; Liu, C.; Zhou, A.; Lu, P.; Qiao, Y.; Li, H.; Gao, P. LLaMA-Adapter: Efficient Fine-Tuning of Large Language Models with Zero-Initialized Attention. In Proceedings of the Twelfth International Conference on Learning Representations, Vienna, Austria, 7–11 May 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Li, C.; Li, Y.; Lee, Y.J. Improved Baselines with Visual Instruction Tuning. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 16–22 June 2024; pp. 26296–26306. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Lv, Q.; Yu, W.; Hong, W.; Qi, J.; Wang, Y.; Ji, J.; Yang, Z.; Zhao, L.; XiXuan, S. Cogvlm: Visual Expert for Pretrained Language Models. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2024, 37, 121475–121499. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.; Chen, X.; Zhang, C.; Li, M.; Yu, G.; Fei, H.; Zhu, H.; Fan, J.; Chen, T. Ll3da: Visual Interactive Instruction Tuning for Omni-3d Understanding Reasoning and Planning. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR 2024), Seattle, WA, USA, 17–21 June 2024; pp. 26428–26438. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, J.; Yin, H.; Ping, W.; Molchanov, P.; Shoeybi, M.; Han, S. VILA: On Pre-training for Visual Language Models. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR 2024), Seattle, WA, USA, 17–21 June 2024; pp. 26689–26699. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, G.; Shen, L.; Shao, R.; Deng, X.; Nie, L. Lion: Empowering Multimodal Large Language Model with Dual-Level Visual Knowledge. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR 2024), Seattle, WA, USA, 17–21 June 2024; pp. 26540–26550. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, W.; Xu, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, W.; Chen, Z.; Tu, Z. Bliva: A Simple Multimodal Llm for Better Handling of Text-Rich Visual Questions. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence (AAAI 2024), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 20–27 February 2024; Volume 38, pp. 2256–2264. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, Q.; Xu, H.; Ye, J.; Yan, M.; Hu, A.; Liu, H.; Qian, Q.; Zhang, J.; Huang, F. mPLUG-Owl2: Revolutionizing Multi-modal Large Language Model with Modality Collaboration. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR 2024), Seattle, WA, USA, 17–21 June 2024; pp. 13040–13051. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, P.; Bai, S.; Tan, S.; Wang, S.; Fan, Z.; Bai, J.; Chen, K.; Liu, X.; Wang, J.; Ge, W.; et al. Qwen2-VL: Enhancing Vision-Language Model’s Perception of the World at Any Resolution. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2409.12191. [Google Scholar]
- Jaegle, A.; Gimeno, F.; Brock, A.; Vinyals, O.; Zisserman, A.; Carreira, J. Perceiver: General Perception with Iterative Attention. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML 2021), Virtual Event, 18–24 July 2021; Volume 139, pp. 4651–4664. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, D.; Liu, J.; Dai, W.; Wang, B. Visual Instruction Tuning with Polite Flamingo. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence (AAAI 2024), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 20–27 February 2024; Volume 38, pp. 17745–17753. [Google Scholar]
- Laurençon, H.; Saulnier, L.; Tronchon, L.; Bekman, S.; Singh, A.; Lozhkov, A.; Wang, T.; Karamcheti, S.; Rush, A.; Kiela, D. Obelics: An Open Web-Scale Filtered Dataset of Interleaved Image-Text Documents. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2023, 36, 71683–71702. [Google Scholar]
- Li, K.; He, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, W.; Luo, P.; Wang, Y.; Wang, L.; Qiao, Y. VideoChat: Chat-Centric Video Understanding. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2305.06355. [Google Scholar]
- Van Gansbeke, W.; Vandenhende, S.; Georgoulis, S.; Proesmans, M.; Van Gool, L. SCAN: Learning to Classify Images Without Labels. In Computer Vision—ECCV 2020; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 268–285. ISBN 978-3-030-58606-5. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, P.; Ding, N.; Goodman, S.; Soricut, R. Conceptual Captions: A Cleaned, Hypernymed, Image Alt-Text Dataset For Automatic Image Captioning. In Proceedings of the 56th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Melbourne, Australia, 15–20 July 2018; Volume 1, pp. 2556–2565. [Google Scholar]
- Perez, E.; Strub, F.; de Vries, H.; Dumoulin, V.; Courville, A. FiLM: Visual Reasoning with a General Conditioning Layer. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence (AAAI 2018), New Orleans, LA, USA, 2–7 February 2018; Volume 32, pp. 3942–3951. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.-C.; Li, L.; Yu, L.; El Kholy, A.; Ahmed, F.; Gan, Z.; Cheng, Y.; Liu, J. UNITER: UNiversal Image-TExt Representation Learning. In Computer Vision—ECCV 2020; Vedaldi, A., Bischof, H., Brox, T., Frahm, J.-M., Eds.; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; Volume 12375, pp. 104–120. ISBN 978-3-030-58576-1. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Z.; Zeng, Z.; Liu, B.; Fu, D.; Fu, J. Pixel-BERT: Aligning Image Pixels with Text by Deep Multi-Modal Transformers. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2004.00849. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, Q.; Xu, H.; Xu, G.; Ye, J.; Yan, M.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, J.; Hu, A.; Shi, P.; Shi, Y.; et al. mPLUG-Owl: Modularization Empowers Large Language Models with Multimodality. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2304.14178. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, D.; Chen, J.; Shen, X.; Li, X.; Elhoseiny, M. MiniGPT-4: Enhancing Vision-Language Understanding with Advanced Large Language Models. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2304.10592. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, W.; Li, J.; Li, D.; Tiong, A.; Zhao, J.; Wang, W.; Li, B.; Fung, P.N.; Hoi, S. Instructblip: Towards General-Purpose Vision-Language Models with Instruction Tuning. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2023, 36, 49250–49267. [Google Scholar]
- Li, B.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, L.; Wang, J.; Pu, F.; Cahyono, J.A.; Yang, J.; Li, C.; Liu, Z. Otter: A Multi-Modal Model with in-Context Instruction Tuning. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2025, 47, 7543–7557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Zhang, Z.; Zeng, W.; Zhang, R.; Zhu, F.; Zhao, R. Shikra: Unleashing Multimodal LLM’s Referential Dialogue Magic. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2306.15195. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Zhu, D.; Shen, X.; Li, X.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, P.; Krishnamoorthi, R.; Chandra, V.; Xiong, Y.; Elhoseiny, M. MiniGPT-v2: Large Language Model as a Unified Interface for Vision-Language Multi-Task Learning. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2310.09478. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Djolonga, J.; Padlewski, P.; Mustafa, B.; Changpinyo, S.; Wu, J.; Ruiz, C.R.; Goodman, S.; Wang, X.; Tay, Y.; et al. PaLI-X: On Scaling up a Multilingual Vision and Language Model. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2305.18565. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, L.; Yu, E.; Ge, Z.; Yang, J.; Wei, H.; Zhou, H.; Sun, J.; Peng, Y.; Dong, R.; Han, C.; et al. ChatSpot: Bootstrapping Multimodal LLMs via Precise Referring Instruction Tuning. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2307.09474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, K.; He, X.; Wang, X.E. MiniGPT-5: Interleaved Vision-and-Language Generation via Generative Vokens. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2310.02239. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, Y.; Xu, K.; Xu, K.; Chen, L.; Liao, C.; Tan, J.; Huang, Q.; Chen, B.; Lei, C.; Liu, A.; et al. Unified Language-Vision Pretraining in LLM with Dynamic Discrete Visual Tokenization. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2309.04669. [Google Scholar]
- Koh, J.Y.; Fried, D.; Salakhutdinov, R.R. Generating Images with Multimodal Language Models. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2023, 36, 21487–21506. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Wong, C.; Zhang, S.; Usuyama, N.; Liu, H.; Yang, J.; Naumann, T.; Poon, H.; Gao, J. Llava-Med: Training a Large Language-and-Vision Assistant for Biomedicine in One Day. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2023, 36, 28541–28564. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Chen, Z.; Chen, X.; Wu, J.; Zhu, X.; Zeng, G.; Luo, P.; Lu, T.; Zhou, J.; Qiao, Y. Visionllm: Large Language Model Is Also an Open-Ended Decoder for Vision-Centric Tasks. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2023, 36, 61501–61513. [Google Scholar]
- Koh, J.Y.; Salakhutdinov, R.; Fried, D. Grounding Language Models to Images for Multimodal Inputs and Outputs. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML 2023), Honolulu, HI, USA, 23–29 July 2023; Volume 202, pp. 17283–17300. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Bao, H.; Dong, L.; Bjorck, J.; Peng, Z.; Liu, Q.; Aggarwal, K.; Mohammed, O.K.; Singhal, S.; Som, S.; et al. Image as a Foreign Language: BEiT Pretraining for Vision and Vision-Language Tasks. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR 2023), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 18–22 June 2023; pp. 19175–19186. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Li, J.; Dong, X.; Zhang, P.; He, C.; Wang, J.; Zhao, F.; Lin, D. ShareGPT4V: Improving Large Multi-Modal Models with Better Captions. In Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer Nature Switzerland: Cham, Switzerland, 2025; pp. 370–387. ISBN 978-3-031-72642-2. [Google Scholar]
- Antol, S.; Agrawal, A.; Lu, J.; Mitchell, M.; Batra, D.; Zitnick, C.L.; Parikh, D. VQA: Visual Question Answering. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV 2015), Santiago, Chile, 7–13 December 2015; pp. 2425–2433. [Google Scholar]
- Karpathy, A.; Fei-Fei, L. Deep Visual-Semantic Alignments for Generating Image Descriptions. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR 2015), Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 3128–3137. [Google Scholar]
- Huynh, N.D.; Bouadjenek, M.R.; Razzak, I.; Hacid, H.; Aryal, S. SVLA: A Unified Speech-Vision-Language Assistant with Multimodal Reasoning and Speech Generation. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2503.24164. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Kordi, Y.; Mishra, S.; Liu, A.; Smith, N.A.; Khashabi, D.; Hajishirzi, H. Self-Instruct: Aligning Language Models with Self-Generated Instructions. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2212.10560. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zheng, J.; Xia, J.; Wei, G.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Kong, T.; Song, R. What Matters in Training a Gpt4-Style Language Model with Multimodal Inputs? In Proceedings of the 2024 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies (NAACL-HLT 2024), Mexico City, Mexico, 16–21 June 2024; Volume 1, pp. 7930–7957. [Google Scholar]
- Yue, T.; Guo, L.; Tang, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Zhu, X.; Huang, H.; Liu, J. LaVi: Efficient Large Vision-Language Models via Internal Feature Modulation. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2506.16691. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, P.-Y. Model Reprogramming: Resource-Efficient Cross-Domain Machine Learning. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence (AAAI 2024), Honolulu, HI, USA, 20–27 February 2024; Volume 38, pp. 22584–22591. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Zheng, Y.; Du, Z.; Ding, M.; Qian, Y.; Yang, Z.; Tang, J. GPT Understands, Too. AI Open 2024, 5, 208–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, E.J.; Shen, Y.; Wallis, P.; Allen-Zhu, Z.; Li, Y.; Wang, S.; Wang, L.; Chen, W. Lora: Low-Rank Adaptation of Large Language Models. ICLR 2022, 1, 3. [Google Scholar]
- Dettmers, T.; Pagnoni, A.; Holtzman, A.; Zettlemoyer, L. Qlora: Efficient Finetuning of Quantized Llms. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2023, 36, 10088–10115. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Z.; Shen, S.; Cao, S.; Liu, H.; Li, C.; Shen, Y.; Gan, C.; Gui, L.-Y.; Wang, Y.-X.; Yang, Y.; et al. Aligning Large Multimodal Models with Factually Augmented RLHF. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2309.14525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dosovitskiy, A.; Beyer, L.; Kolesnikov, A.; Weissenborn, D.; Zhai, X.; Unterthiner, T.; Dehghani, M.; Minderer, M.; Heigold, G.; Gelly, S. An Image Is Worth 16 × 16 Words: Transformers for Image Recognition at Scale. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2010.11929. [Google Scholar]
- Marino, K.; Rastegari, M.; Farhadi, A.; Mottaghi, R. OK-VQA: A Visual Question Answering Benchmark Requiring External Knowledge. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR 2019), Long Beach, CA, USA, 16–20 June 2019; pp. 3195–3204. [Google Scholar]
- Zellers, R.; Bisk, Y.; Farhadi, A.; Choi, Y. From Recognition to Cognition: Visual Commonsense Reasoning. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR 2019), Long Beach, CA, USA, 16–20 June 2019; pp. 6720–6731. [Google Scholar]
- Masry, A.; Long, D.X.; Tan, J.Q.; Joty, S.; Hoque, E. ChartQA: A Benchmark for Question Answering about Charts with Visual and Logical Reasoning. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2203.10244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Duan, H.; Zhang, Y.; Li, B.; Zhang, S.; Zhao, W.; Yuan, Y.; Wang, J.; He, C.; Liu, Z.; et al. MMBench: Is Your Multi-Modal Model an All-Around Player? In Computer Vision—ECCV 2024; Leonardis, A., Ricci, E., Roth, S., Russakovsky, O., Sattler, T., Varol, G., Eds.; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer Nature Switzerland: Cham, Switzerland, 2025; Volume 15064, pp. 216–233. ISBN 978-3-031-72657-6. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Li, J.; Dong, X.; Zhang, P.; Zang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Duan, H.; Wang, J.; Qiao, Y.; Lin, D. Are We on the Right Way for Evaluating Large Vision-Language Models? Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2024, 37, 27056–27087. [Google Scholar]
- Yue, X.; Ni, Y.; Zhang, K.; Zheng, T.; Liu, R.; Zhang, G.; Stevens, S.; Jiang, D.; Ren, W.; Sun, Y.; et al. MMMU: A Massive Multi-Discipline Multimodal Understanding and Reasoning Benchmark for Expert Agi. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR 2024), Seattle, WA, USA, 17–21 June 2024; pp. 9556–9567. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, P.; Bansal, H.; Xia, T.; Liu, J.; Li, C.; Hajishirzi, H.; Cheng, H.; Chang, K.-W.; Galley, M.; Gao, J. MathVista: Evaluating Mathematical Reasoning of Foundation Models in Visual Contexts. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2310.02255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Yang, Z.; Li, L.; Wang, J.; Lin, K.; Liu, Z.; Wang, X.; Wang, L. MM-Vet: Evaluating Large Multimodal Models for Integrated Capabilities. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2308.02490. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Fan, H.; Wu, Y.; Xie, S.; Girshick, R. Momentum Contrast for Unsupervised Visual Representation Learning. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR 2020), Seattle, WA, USA, 14–19 June 2020; pp. 9726–9735. [Google Scholar]
- Cho, J.; Zala, A.; Bansal, M. Dall-Eval: Probing the Reasoning Skills and Social Biases of Text-to-Image Generation Models. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV 2023), Paris, France, 2–6 October 2023; pp. 3043–3054. [Google Scholar]
- Bakr, E.M.; Sun, P.; Shen, X.; Khan, F.F.; Li, L.E.; Elhoseiny, M. Hrs-Bench: Holistic, Reliable and Scalable Benchmark for Text-to-Image Models. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV 2023), Paris, France, 2–6 October 2023; pp. 20041–20053. [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh, D.; Hajishirzi, H.; Schmidt, L. Geneval: An Object-Focused Framework for Evaluating Text-to-Image Alignment. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2023, 36, 52132–52152. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, X.; Wang, R.; Fang, Y.; Fu, B.; Cheng, P.; Yu, G. ELLA: Equip Diffusion Models with LLM for Enhanced Semantic Alignment. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2403.05135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Saharia, C.; Montgomery, C.; Pont-Tuset, J.; Noy, S.; Pellegrini, S.; Onoe, Y.; Laszlo, S.; Fleet, D.J.; Soricut, R. Imagen Editor and Editbench: Advancing and Evaluating Text-Guided Image Inpainting. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR 2023), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 18–22 June 2023; pp. 18359–18369. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, X.; Yu, D.; Huang, Y.; Russakovsky, O.; Arora, S. Conceptmix: A Compositional Image Generation Benchmark with Controllable Difficulty. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2024, 37, 86004–86047. [Google Scholar]
- Sheynin, S.; Polyak, A.; Singer, U.; Kirstain, Y.; Zohar, A.; Ashual, O.; Parikh, D.; Taigman, Y. Emu Edit: Precise Image Editing via Recognition and Generation Tasks. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR 2024), Seattle, WA, USA, 17–21 June 2024; pp. 8871–8879. [Google Scholar]
- Basu, S.; Saberi, M.; Bhardwaj, S.; Chegini, A.M.; Massiceti, D.; Sanjabi, M.; Hu, S.X.; Feizi, S. EditVal: Benchmarking Diffusion Based Text-Guided Image Editing Methods. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2310.02426. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.; Xie, L.; Wang, X.; Yuan, Z.; Cun, X.; Ge, Y.; Zhou, J.; Dong, C.; Huang, R.; Zhang, R. Smartedit: Exploring Complex Instruction-Based Image Editing with Multimodal Large Language Models. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR 2024), Seattle, WA, USA, 17–21 June 2024; pp. 8362–8371. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Q.; Chow, W.; Yue, Z.; Pan, K.; Wu, Y.; Wan, X.; Li, J.; Tang, S.; Zhang, H.; Zhuang, Y. AnyEdit: Mastering Unified High-Quality Image Editing for Any Idea. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Conference (CVPR 2025), Nashville, TN, USA, 11–15 June 2025; pp. 26125–26135. [Google Scholar]
- Heusel, M.; Ramsauer, H.; Unterthiner, T.; Nessler, B.; Hochreiter, S. Gans Trained by a Two Time-Scale Update Rule Converge to a Local Nash Equilibrium. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1706.08500. [Google Scholar]
- Salimans, T.; Goodfellow, I.; Zaremba, W.; Cheung, V.; Radford, A.; Chen, X. Improved Techniques for Training Gans. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1606.03498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, D.; Xiong, C.; Hoi, S. BLIP: Bootstrapping Language-Image Pre-training for Unified Vision-Language Understanding and Generation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML 2022), Baltimore, MD, USA, 17–23 July 2022; Volume 162, pp. 12888–12900. [Google Scholar]
- Rasheed, H.; Maaz, M.; Shaji, S.; Shaker, A.; Khan, S.; Cholakkal, H.; Anwer, R.M.; Xing, E.; Yang, M.-H.; Khan, F.S. GlaMM: Pixel Grounding Large Multimodal Model. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR 2024), Seattle, WA, USA, 17–21 June 2024; pp. 13009–13018. [Google Scholar]
- Pramanick, S.; Han, G.; Hou, R.; Nag, S.; Lim, S.-N.; Ballas, N.; Wang, Q.; Chellappa, R.; Almahairi, A. Jack of All Tasks Master of Many: Designing General-Purpose Coarse-to-Fine Vision-Language Model. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR 2024), Seattle, WA, USA, 17–21 June 2024; pp. 14076–14088. [Google Scholar]
- Ramesh, A.; Dhariwal, P.; Nichol, A.; Chu, C.; Chen, M. Hierarchical Text-Conditional Image Generation with Clip Latents. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2204.06125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, T.; Holynski, A.; Efros, A.A. InstructPix2Pix: Learning to Follow Image Editing Instructions. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR 2023), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 18–22 June 2023; pp. 18392–18402. [Google Scholar]
- Kubota, K.; Togo, R.; Maeda, K.; Ogawa, T.; Haseyama, M. MLLM-Based Automatic Exploration of Editing Prompt for High Engagement Image Generation. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE 13th Global Conference on Consumer Electronics (GCCE), Kitakyushu, Japan, 29 October–1 November 2024; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2024; pp. 1165–1166. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, S.; Fei, H.; Qu, L.; Ji, W.; Chua, T.-S. NExT-GPT: Any-to-Any Multimodal LLM. In Proceedings of the Forty-first International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML 2024), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 21–27 July 2024; Volume 235, pp. 53366–53397. [Google Scholar]
- Nie, D.; Trullo, R.; Lian, J.; Wang, L.; Petitjean, C.; Ruan, S.; Wang, Q.; Shen, D. Medical Image Synthesis with Deep Convolutional Adversarial Networks. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2018, 65, 2720–2730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshino, K.; Wakimoto, K.; Nishimura, Y.; Nakamura, S. Caption Generation of Robot Behaviors Based on Unsupervised Learning of Action Segments. In Conversational Dialogue Systems for the Next Decade; Lecture Notes in Electrical Engineering; Springer: Singapore, 2021; pp. 227–241. ISBN 978-981-15-8394-0. [Google Scholar]
- Vedantam, R.; Lawrence Zitnick, C.; Parikh, D. CIDEr: Consensus-based Image Description Evaluation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR 2015), Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 4566–4575. [Google Scholar]
- Li, B.; Ge, Y.; Ge, Y.; Wang, G.; Wang, R.; Zhang, R.; Shan, Y. Seed-Bench: Benchmarking Multimodal Large Language Models. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR 2024), Seattle, WA, USA, 17–21 June 2024; pp. 13299–13308. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, R.; Zhang, B.; Huang, J.; Long, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zou, T.; Wu, Y.; Su, S.; Xu, Y.; Zeng, W.; et al. LENS: Multi-Level Evaluation of Multimodal Reasoning with Large Language Models. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2505.15616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Du, Y.; Zhou, K.; Wang, J.; Zhao, W.X.; Wen, J.-R. Evaluating Object Hallucination in Large Vision-Language Models. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2305.10355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Song, L.; Li, Y.; Zhao, S.; Ge, Y.; Li, X.; Shan, Y. Gpt4tools: Teaching Large Language Model to Use Tools via Self-Instruction. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2023, 36, 71995–72007. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, S.; Fu, C.; Zhao, S.; Xu, T.; Wang, H.; Sui, D.; Shen, Y.; Li, K.; Sun, X.; Chen, E. Woodpecker: Hallucination Correction for Multimodal Large Language Models. Sci. China Inf. Sci. 2024, 67, 220105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raza, S.; Narayanan, A.; Khazaie, V.R.; Vayani, A.; Chettiar, M.S.; Singh, A.; Shah, M.; Pandya, D. HumaniBench: A Human-Centric Framework for Large Multimodal Models Evaluation. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2505.11454. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, T.; Yao, Y.; Zhang, H.; He, T.; Han, Y.; Cui, G.; Hu, J.; Liu, Z.; Zheng, H.-T.; Sun, M. RLHF-V: Towards Trustworthy Mllms via Behavior Alignment from Fine-Grained Correctional Human Feedback. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR 2024), Seattle, WA, USA, 17–21 June 2024; pp. 13807–13816. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, F.; Lin, K.; Li, L.; Wang, J.; Yacoob, Y.; Wang, L. Mitigating Hallucination in Large Multi-Modal Models via Robust Instruction Tuning. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2306.14565. Available online: https://arxiv.org/abs/2306.14565 (accessed on 21 August 2025).
- Leng, S.; Zhang, H.; Chen, G.; Li, X.; Lu, S.; Miao, C.; Bing, L. Mitigating Object Hallucinations in Large Vision-Language Models through Visual Contrastive Decoding. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR 2024), Seattle, WA, USA, 17–21 June 2024; pp. 13872–13882. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, C.; Xu, H.; Dong, M.; Chen, J.; Ye, W.; Yan, M.; Ye, Q.; Zhang, J.; Huang, F.; Zhang, S. Hallucination Augmented Contrastive Learning for Multimodal Large Language Model. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR 2024), Seattle, WA, USA, 17–21 June 2024; pp. 27036–27046. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Selvaraju, R.; Gotmare, A.; Joty, S.; Xiong, C.; Hoi, S.C.H. Align before Fuse: Vision and Language Representation Learning with Momentum Distillation. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2021, 34, 9694–9705. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, S.; He, K.; Girshick, R.; Sun, J. Faster R-CNN: Towards Real-Time Object Detection with Region Proposal Networks. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2016, 39, 1137–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schramowski, P.; Brack, M.; Deiseroth, B.; Kersting, K. Safe Latent Diffusion: Mitigating Inappropriate Degeneration in Diffusion Models. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR 2023), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 18–22 June 2023; pp. 22522–22531. [Google Scholar]
- Poppi, S.; Poppi, T.; Cocchi, F.; Cornia, M.; Baraldi, L.; Cucchiara, R. Safe-CLIP: Removing NSFW Concepts from Vision-and-Language Models. In Computer Vision—ECCV 2024; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2025; pp. 340–356. ISBN 978-3-031-73667-4. [Google Scholar]
- You, H.; Zhang, H.; Gan, Z.; Du, X.; Zhang, B.; Wang, Z.; Cao, L.; Chang, S.-F.; Yang, Y. Ferret: Refer and Ground Anything Anywhere at Any Granularity. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2310.07704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, X.; Tian, Z.; Chen, Y.; Li, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Liu, S.; Jia, J. Lisa: Reasoning Segmentation via Large Language Model. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR 2024), Seattle, WA, USA, 17–21 June 2024; pp. 9579–9589. [Google Scholar]
- Figure AI. Helix: A Vision-Language-Action Model for Generalist Humanoid Control. Fig. AI News 2024. Available online: https://www.figure.ai/news/helix (accessed on 21 August 2025).
- NVIDIA; Bjorck, J.; Castañeda, F.; Cherniadev, N.; Da, X.; Ding, R.; Fan, L.J.; Fang, Y.; Fox, D.; Hu, F.; et al. GR00T N1: An Open Foundation Model for Generalist Humanoid Robots. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2503.14734. [Google Scholar]
- Team, G.R.; Abeyruwan, S.; Ainslie, J.; Alayrac, J.-B.; Arenas, M.G.; Armstrong, T.; Balakrishna, A.; Baruch, R.; Bauza, M.; Blokzijl, M.; et al. Gemini Robotics: Bringing AI into the Physical World. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2503.20020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, W.; Wang, W.; Lv, Q.; Xu, J.; Yu, W.; Ji, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Dong, Y.; Ding, M. Cogagent: A Visual Language Model for Gui Agents. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR 2024), Seattle, WA, USA, 17–21 June 2024; pp. 14281–14290. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, D.; Li, S.; Zhang, X.; Zhan, J.; Wang, P.; Zhou, Y.; Qiu, X. SpeechGPT: Empowering Large Language Models with Intrinsic Cross-Modal Conversational Abilities. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2503.14734. [Google Scholar]
- Su, Y.; Lan, T.; Li, H.; Xu, J.; Wang, Y.; Cai, D. PandaGPT: One Model To Instruction-Follow Them All. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2305.16355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Zhang, R.; Shao, W.; Gao, P.; Xu, P.; Xiao, H.; Zhang, K.; Liu, C.; Wen, S.; Guo, Z.; et al. ImageBind-LLM: Multi-Modality Instruction Tuning. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2309.03905. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, Z.; Yang, Z.; Khademi, M.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, C.; Bansal, M. CoDi-2: In-Context Interleaved and Interactive Any-to-Any Generation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR 2024), Seattle, WA, USA, 17–21 June 2024; pp. 27425–27434. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, Z.; Wu, C. Mini-Omni2: Towards Open-Source GPT-4o with Vision, Speech and Duplex Capabilities. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2410.11190. [Google Scholar]
- Ge, Z.; Huang, H.; Zhou, M.; Li, J.; Wang, G.; Tang, S.; Zhuang, Y. WorldGPT: Empowering LLM as Multimodal World Model. In Proceedings of the 32nd ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Melbourne, VIC, Australia, 28 October 2024; ACM: Melbourne, VIC, Australia, 2024; pp. 7346–7355. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Xie, J.; Hu, C.; Zou, H.; Fan, J.; Tong, W.; Wen, Y.; Wu, S.; Deng, H.; Li, Z.; et al. DriveMLM: Aligning Multi-Modal Large Language Models with Behavioral Planning States for Autonomous Driving. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2312.09245. [Google Scholar]

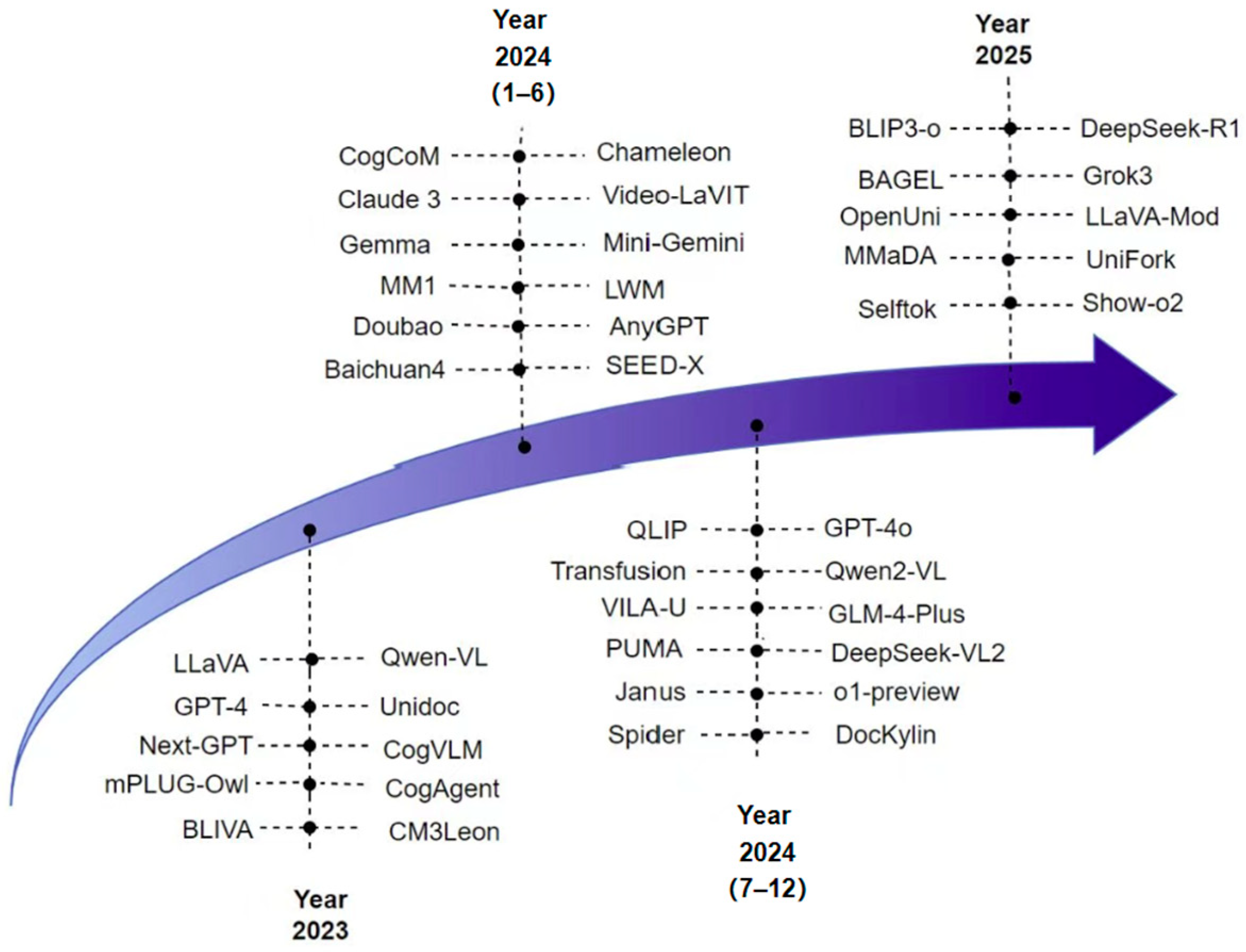

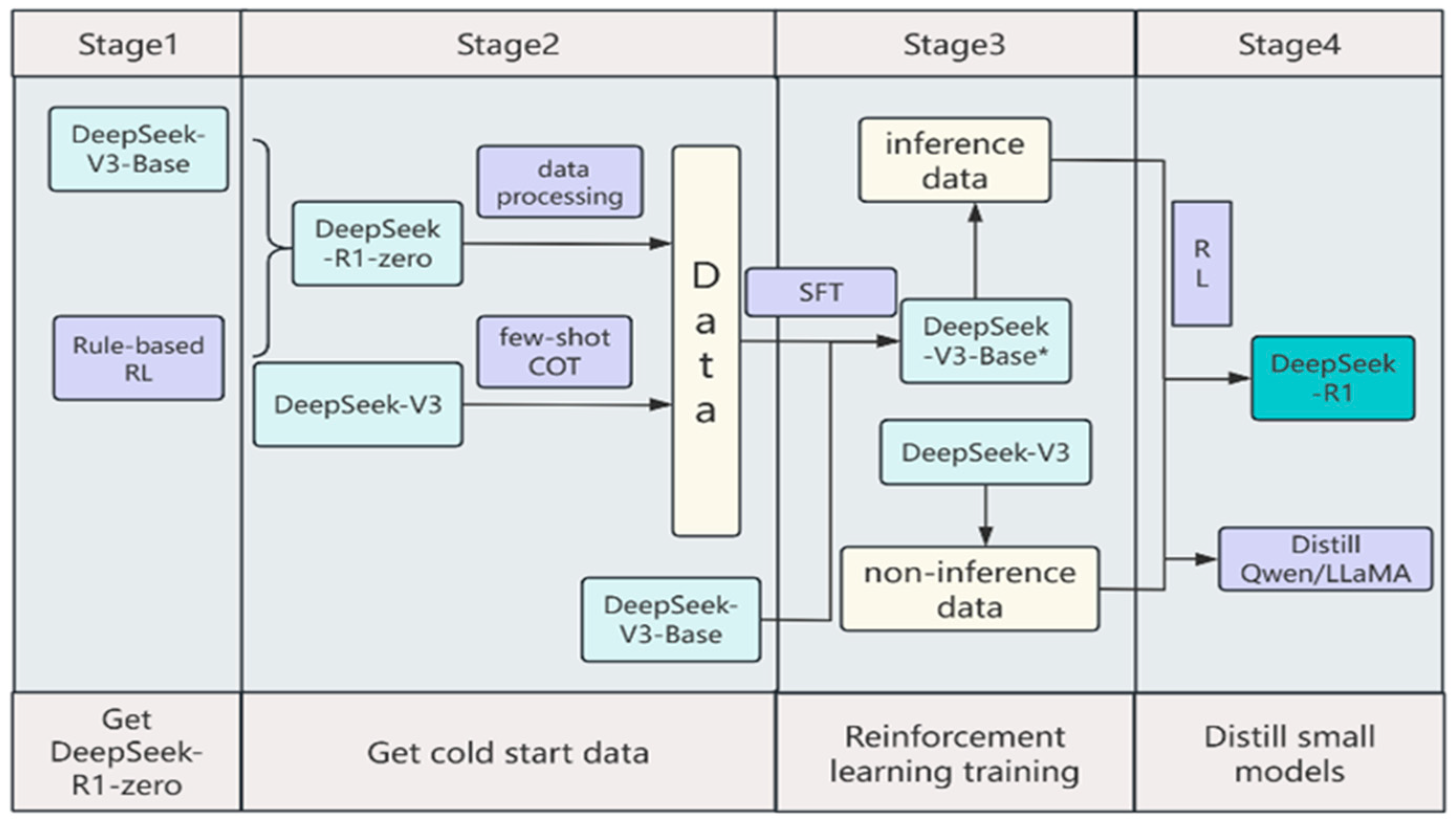
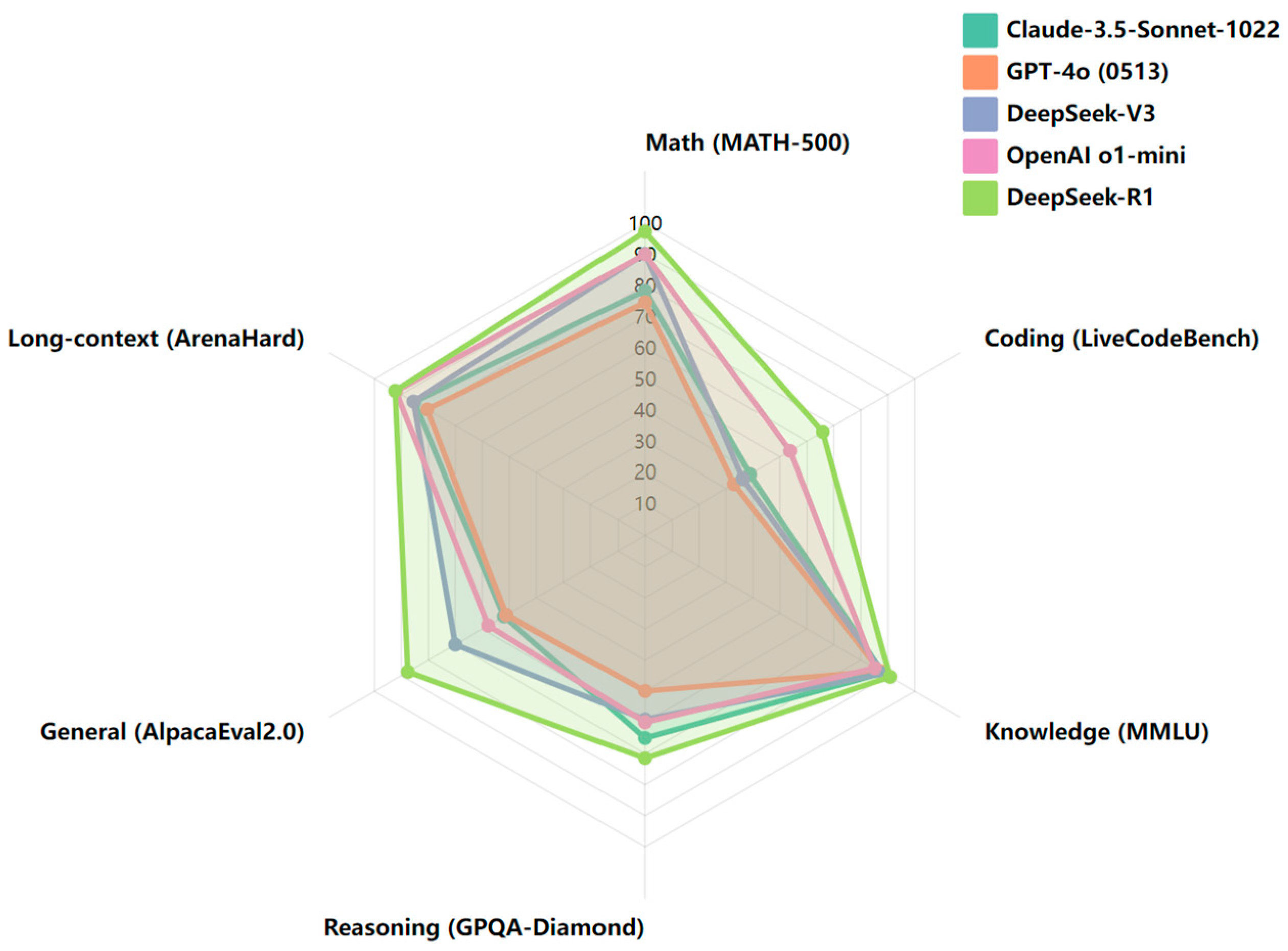
| Model | Visual Encoder | Adapter | LLM Backbone | I→O | Main Tasks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BLIP-2 [22] | EVA ViT-g | Q-Former | Flan-T5/OPT | I + T→T | VQA, Captioning, Retrieval |
| Flamingo [2] | NFNet-F6 | LLM MH-Attn | Chinchilla-1.4B/7B/70B | I + V + T→T | VQA, Captioning |
| LLaVA [35] | CLIP ViT-L | Linear | Vicuna-7B/13B | I + T→T | VQA, Captioning |
| mPLUG-Owl [43] | CLIP ViT-L | Q-Former | LLaMA-7B | I + T→T | Visual Dialogue, VQA |
| MiniGPT-4 [44] | EVA ViT-g | Linear | Vicuna-13B | I + T→T | VQA, Captioning |
| InstructBLIP [45] | EVA ViT-g | Q-Former | Flan-T5/Vicuna | I + V + T→T | VQA, Captioning |
| Otter [46] | CLIP ViT-L | LLM MH-Attn | LLaMA-7B | I + T→T | VQA, Captioning |
| Shikra [47] | CLIP ViT-L | Linear | Vicuna-7B/13B | I + T→T + I | VQA, Captioning, Referring |
| CogVLM [27] | EVA ViT-E | MLP | Vicuna-v1.5-7B | I + T→T | VQA, Captioning, REC |
| VILA [29] | CLIP ViT-L | Linear | LLaMA-2-7B/13B | I + T→T | VQA, Captioning |
| LLaVA-1.5 [26] | CLIP ViT-L | MLP | Vicuna-v1.5-7B/13B | I + T→T | VQA, Captioning |
| MiniGPT-v2 [48] | EVA ViT-g | Linear | LLaMA-2-Chat-7B | I + T→T | VQA, Captioning, Referring |
| PaLI-X [49] | ViT-22B | LLM MH-Attn | UL2-32B | I + T→T | Multilingual, VQA |
| ChatSpot [50] | CLIP ViT-L | Linear | Vicuna-7B/LLaMA | I + T→T | VQA, Captioning, Referring |
| MiniGPT-5 [51] | EVA ViT-g | Q-Former | Vicuna-7B | I + T→I + T | Image Generation |
| LaVIT [52] | EVA ViT-g | LLM MH-Attn | LLaMA-7B | I + T→I + T | Captioning, Image Generation |
| GILL [53] | CLIP ViT-L | Linear | OPT-6.7B | I + T→I + T | Retrieval, Image Generation |
| Task Taxonomy | Benchmark | Evaluation Metrics |
|---|---|---|
| Understanding Tasks | VQA [59] OK-VQA [71] VCR [72] ChartQA [73] VSR [13] MMBench [74] MMStar [75] MMMU [76] MathVista [77] MM-Vet [78] | Accuracy Top-k Accuracy [79] Precision F1 Score mAP NDCG |
| Generation Tasks | PaintSkills [80] HRS-Bench [81] GenEval [82] DPG-Bench [83] EditBench [84] ConceptMix [85] Emu-Edit [86] EditVal [87] Reason-Edit [88] AnyEdit [89] | CIDEr SPICE FID [90] IS [91] Relevance Faithfulness GPTScore |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, X.; Liu, H. Symmetry-Aware Advances in Multimodal Large Language Models: Architectures, Training, and Evaluation. Symmetry 2025, 17, 1400. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17091400
Liu X, Liu H. Symmetry-Aware Advances in Multimodal Large Language Models: Architectures, Training, and Evaluation. Symmetry. 2025; 17(9):1400. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17091400
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Xinran, and Haojie Liu. 2025. "Symmetry-Aware Advances in Multimodal Large Language Models: Architectures, Training, and Evaluation" Symmetry 17, no. 9: 1400. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17091400
APA StyleLiu, X., & Liu, H. (2025). Symmetry-Aware Advances in Multimodal Large Language Models: Architectures, Training, and Evaluation. Symmetry, 17(9), 1400. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17091400





