Gardens Fire Detection Based on the Symmetrical SSS-YOLOv8 Network
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Work
2.1. Two-Stage Models
2.2. One-Stage Models
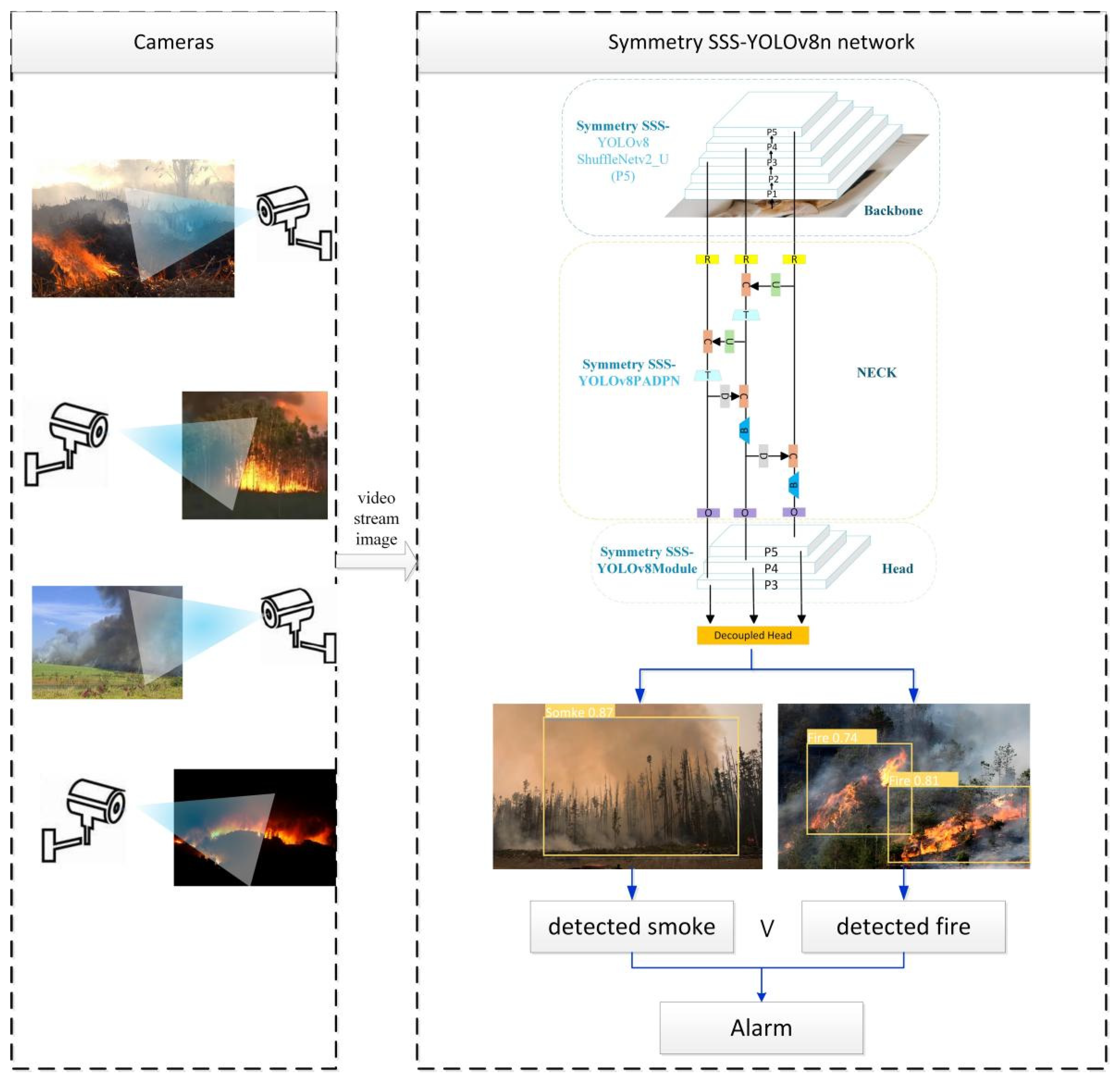
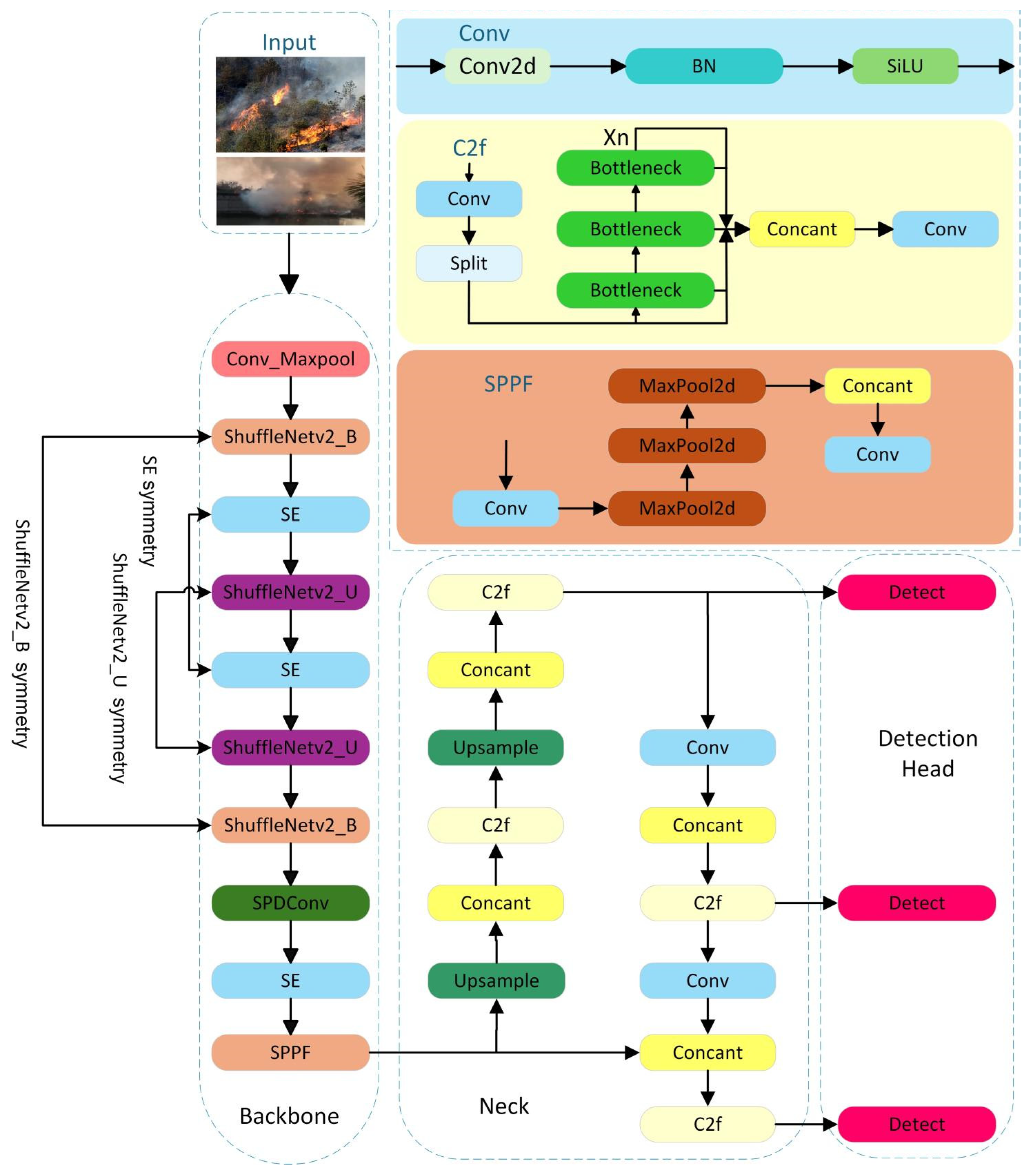
3. Proposed Method
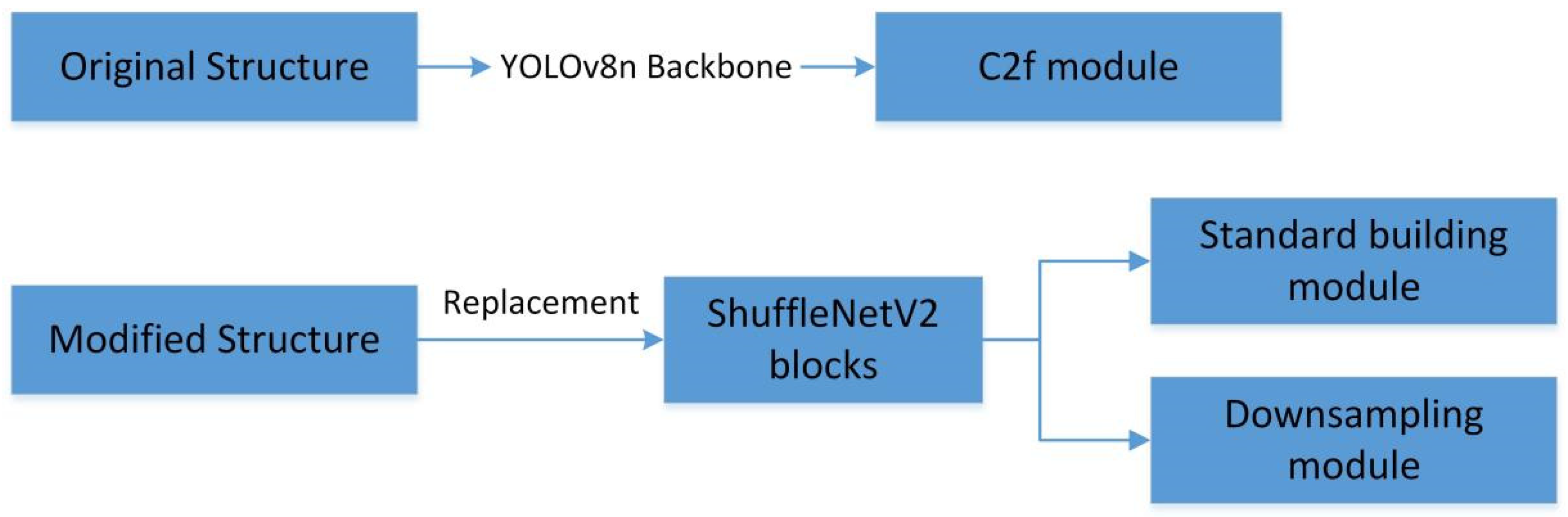
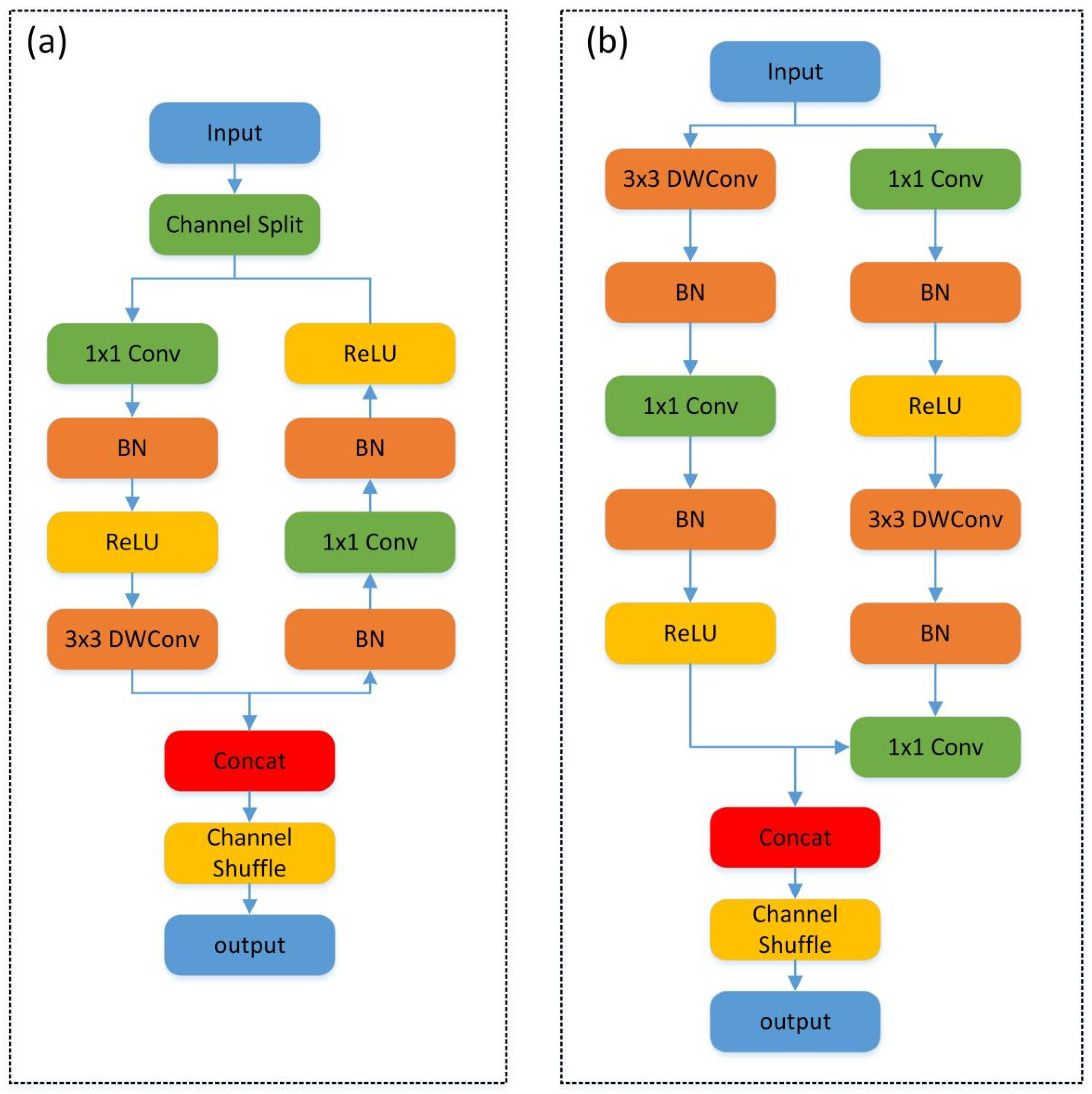
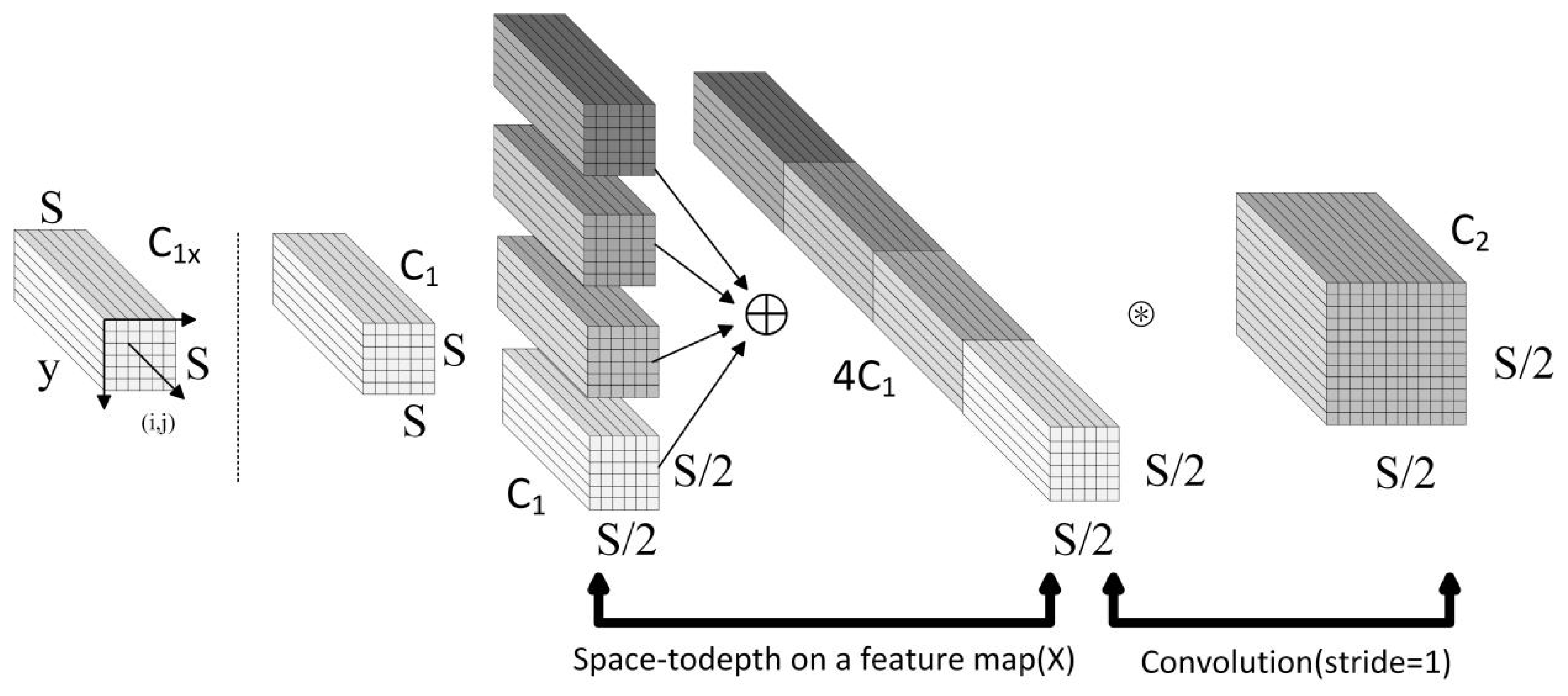
- Lightweight Design: A lightweight design was implemented for the Backbone. The C2f modules were substituted with lightweight symmetry ShuffleNetV2 modules, which include symmetry ShuffleNetv2_B, symmetry ShuffleNetv2_U, and symmetry SE. Additionally, the initial two convolutional layers and the final convolutional layer within the feature extraction network were replaced with Conv-Maxpool layers and an SPDConv layer, respectively.
- SE module: It can establish a dynamic inter-channel relationship model, which adaptively recalibrates channel-wise feature responses to enhance representational power. Therefore, we propose a repeated symmetric deployment strategy for the SE module, which significantly enhances the model’s capability to focus on flame and smoke characteristics.
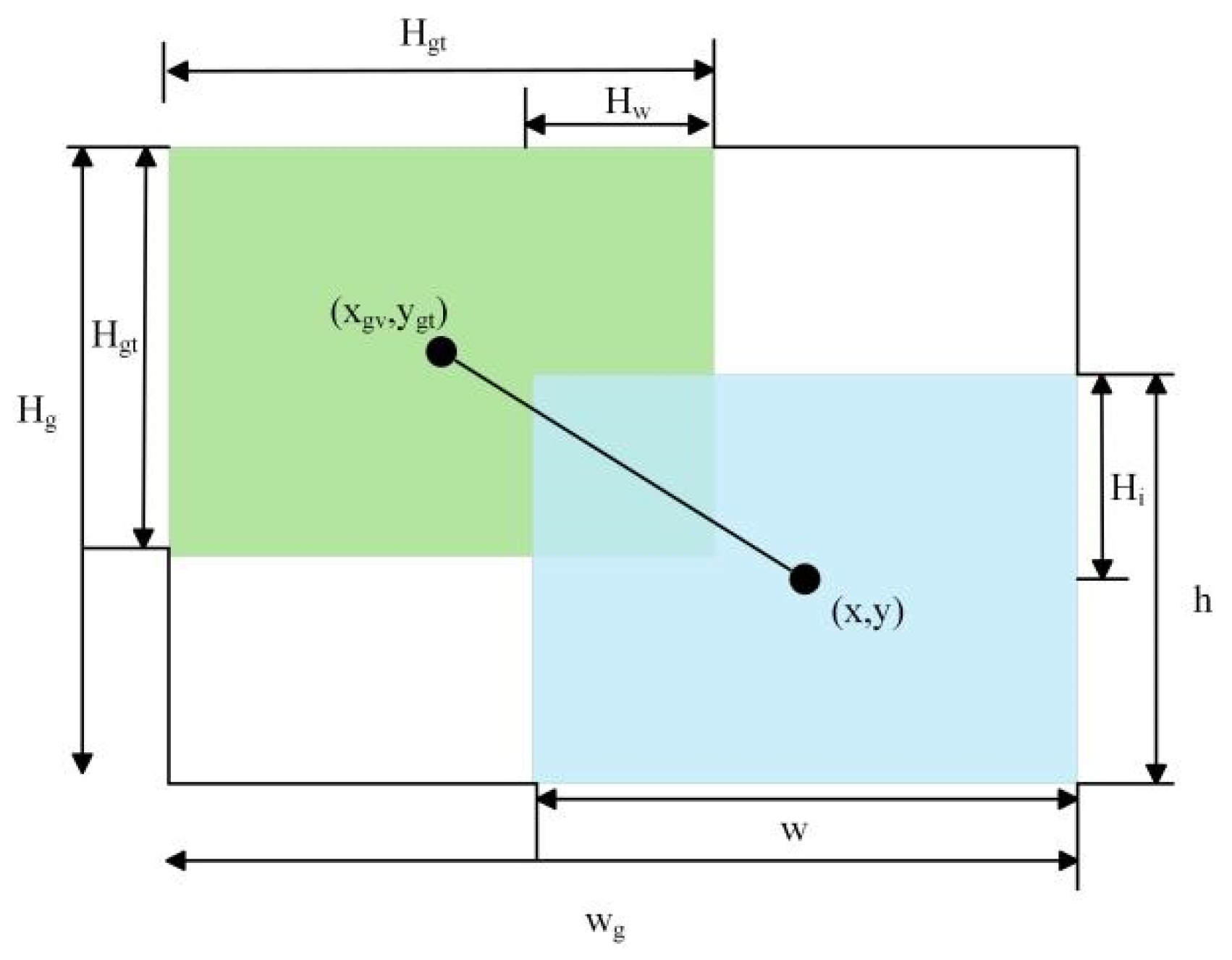
- WIoU: The original Soft IoU (SIoU) loss function was replaced with WIoU. This substitution addresses two key limitations: (1) it mitigates the convergence slowdown caused by the SIoU loss’s inability to simultaneously adjust the aspect ratio of bounding boxes during training, and (2) it effectively reduces the adverse impact of low-quality examples on the model’s generalization ability.
3.1. Lightweight Module SSS-Neck
3.2. Integration of the SE Module
3.3. Selection of Loss Function
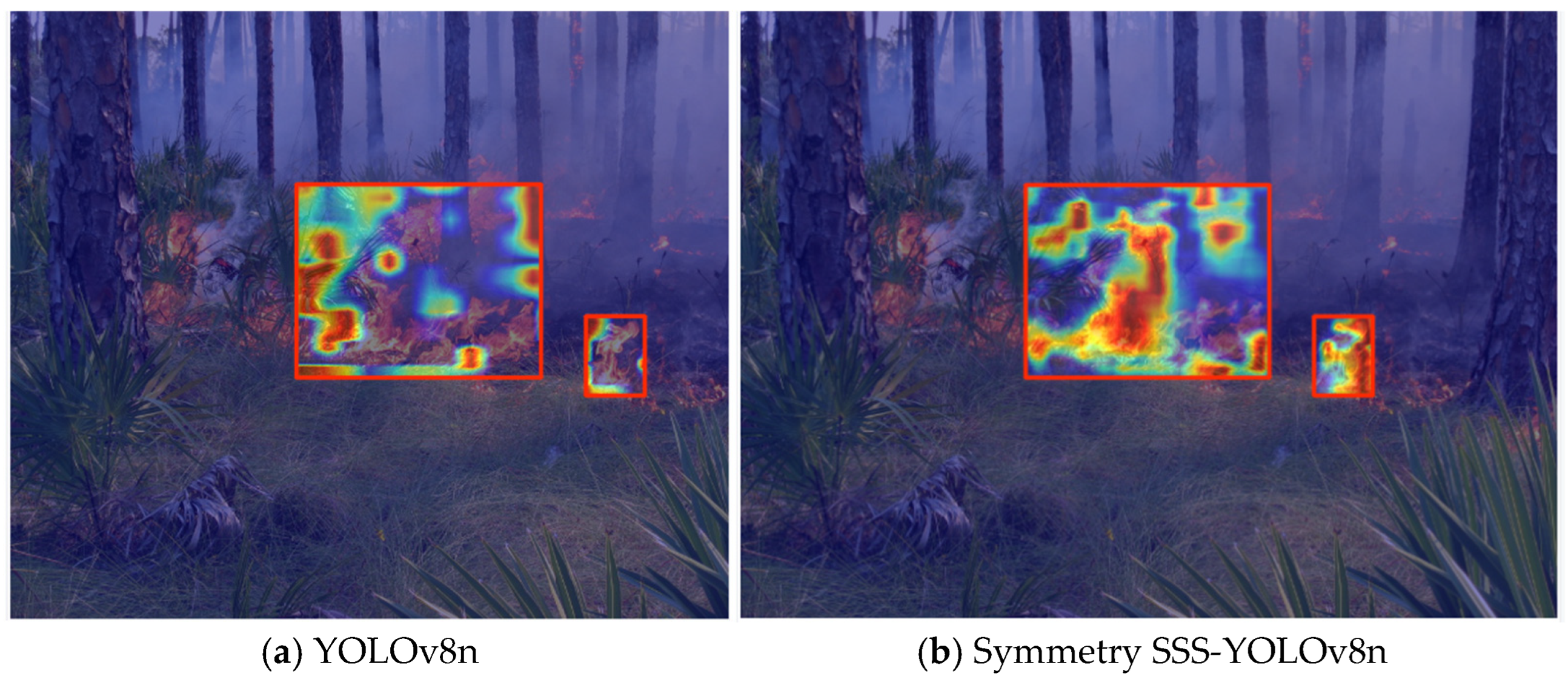
3.4. The Grad-CAM Algorithm Visualizes the Heatmap Features of the Model
4. Experiment Analysis
4.1. Dataset
4.2. Evaluation Metrics
4.3. Ablation Experiment
4.4. Comparison of Different Attention Mechanisms
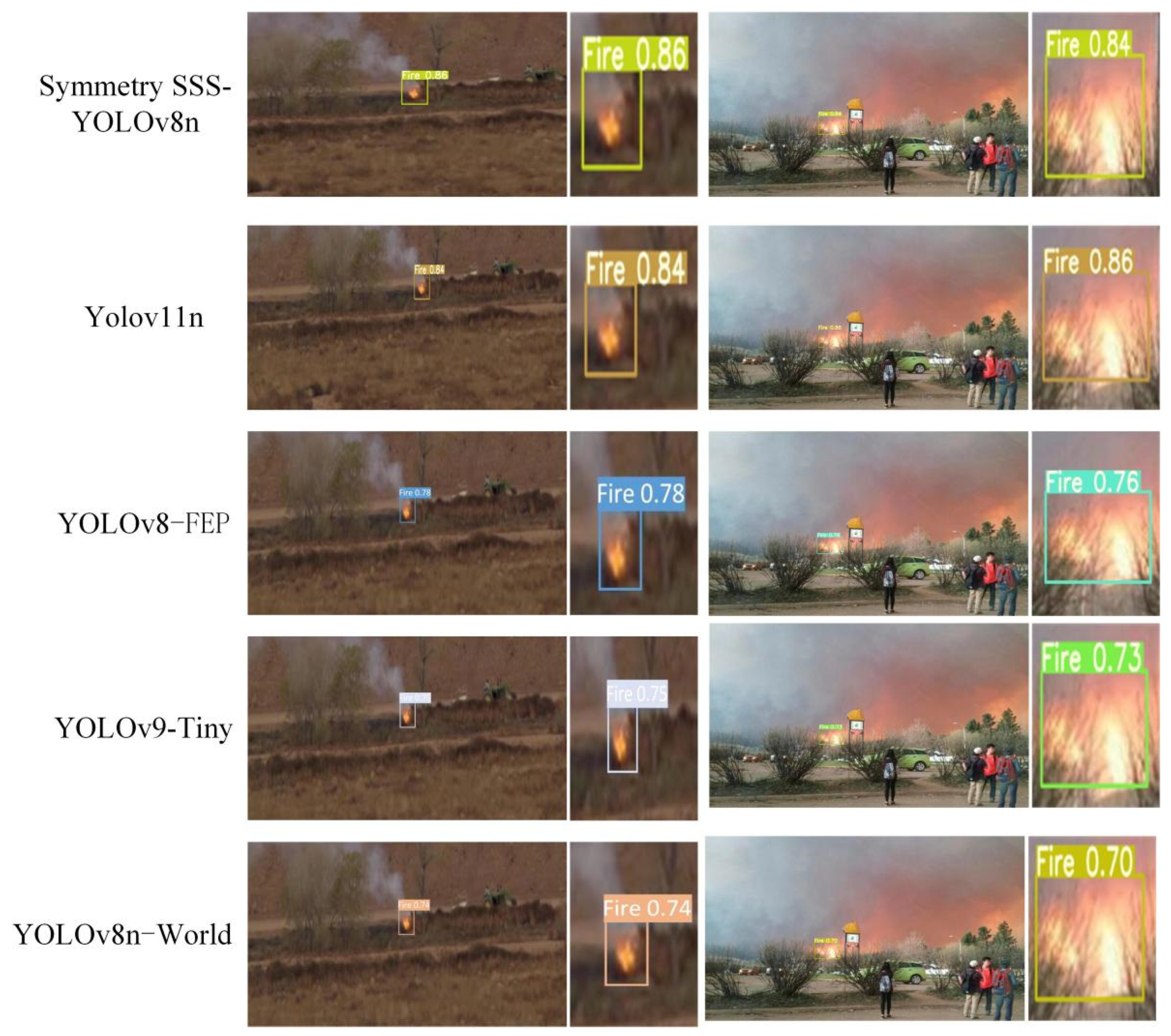
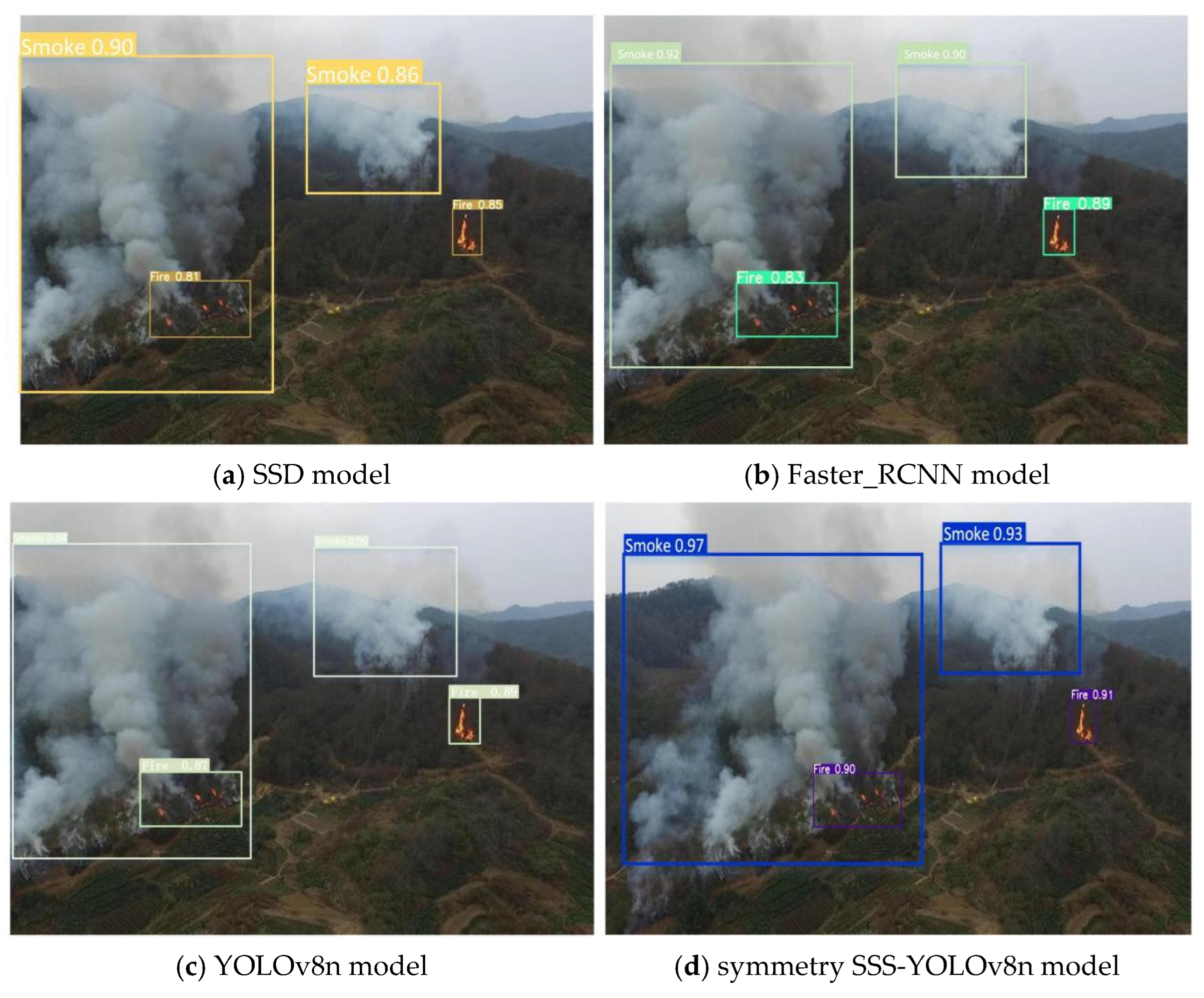
4.5. Comparison Experiment
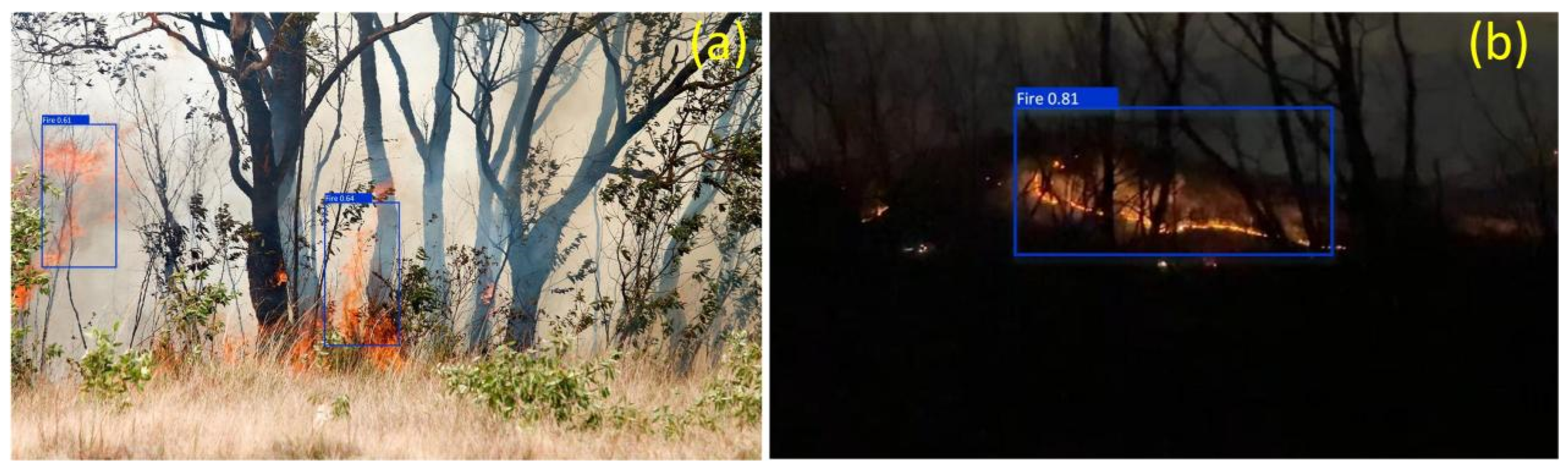
5. Application
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yuan, Z.; Tang, X.; Ning, H.; Yang, Z. LW-YOLO: Lightweight Deep Learning Model for Fast and Precise Defect Detection in Printed Circuit Boards. Symmetry 2024, 16, 418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.J.; Sui, B.W.; Wang, S.T.; Zhang, Y.Y. The video fire detection and location method onboard ship based on an improved MF-SSD deep learning algorithm. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2020, 126, 127–128. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, X.; Wu, Y.; Dong, F.; Zhang, J.; Sun, S. Developing an Image Manipulation Detection Algorithm Based on Edge Detection and Faster R-CNN. Symmetry 2019, 11, 1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Bi, K.; Wang, Q. YOLOv7-FIRE: A tiny-fire identification and detection method applied on UAV. AIMS Math. 2024, 9, 10775–10801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeCun, Y.; Bengio, Y.; Hinton, G. Deep learning. Nature 2015, 521, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Pan, X.; Shen, H.-B. Recent Deep Learning Methodology Development for RNA–RNA Interaction Prediction. Symmetry 2022, 14, 1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.W.; Sahoo, D.; Hoi, S.C.H. Recent advances in deep learning for object detection. Neurocomputing 2020, 396, 39–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, J.; Singh, W. Tools, techniques, datasets and application areas for object detection in an image: A review. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2022, 81, 38297–38351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girshick, R. Fast R-CNN. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 7–13 December 2015; pp. 1440–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.X.; Lin, G.H.; Zhang, Y.M.; Xu, G.; Wang, J.J. Wildland forest fire smoke detection based on faster R-CNN using synthetic smoke Images. Procedia Eng. 2018, 211, 441–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Khan, A. FFireNet: Deep Learning Based Forest Fire Classification and Detection in Smart Cities. Symmetry 2022, 14, 2155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pincott, J.; Tien, P.W.; Wei, S.; Calautit, J.K. Indoor fire detection utilizing computer vision-based strategies. J. Build. Eng. 2022, 61, 105154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheknane, M.; Bendouma, T.; Boudouh, S.S. Advancing fire detection: Two-stage deep learning with hybrid feature extraction using faster R-CNN approach. Signal Image Video Process. 2024, 18, 5503–5510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaman, K.; Sun, Z.; Shah, S.M.; Shoaib, M.; Pei, L.; Hussain, A. Driver Emotions Recognition Based on Improved Faster R-CNN and Neural Architectural Search Network. Symmetry 2022, 14, 687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahul, M.; Shiva Saketh, K.; Sanjeet, A.; Srinivas Naik, N. Early detection of forest fire using deep learning. In Proceedings of the IEEE Region 10 Annual International Conference, Osaka, Japan, 16–19 November 2020; pp. 1136–1140. [Google Scholar]
- Fernandes, A.M.; Utkin, A.B.; Chaves, P. Automatic early detection of wildfire smoke with visible-light cameras and EfficientDet. J. Fire Sci. 2023, 41, 122–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, Z.T.; Zhang, Y.M.; Xin, J.; Mu, L.X.; Yi, Y.M.; Liu, H.; Liu, D. A deep learning based forest fire detection approach using Uav and Yolov3. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Industrial Artificial Intelligence, Shenyang, China, 23–27 July 2019; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.S.; Chu, M.H.; Zhang, L. A detection network for small defects of steel surface based on YOLOv7. Digit. Signal Process. 2024, 149, 104484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, R.X.; Pei, M.T. Lightweight forest fire detection based on deep learning. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Workshop on Machine Learning for Signal Processing, MLSP. Electr Network, Gold Coast, Australia, 25–28 October 2021; pp. 2–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.K.; Xu, R.Z.; Zheng, X.W.; Zhang, L.F.; Zhang, Y. A forest fire detection method based on improved YOLOv5. Signal Image Video Process. 2025, 19, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chetoui, M.; Akhloufi, M.A. Fire and Smoke Detection Using Fine-Tuned YOLOv8 and YOLOv7 Deep Models. Fire 2024, 7, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkhammash, E.H. A Comparative Analysis of YOLOv9, YOLOv10, YOLOv11 for Smoke and Fire Detection. Fire 2025, 8, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.L.; Jiang, Y.; Sun, Y.P.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z. Improvements based on shuffleNetV2 model for bird identification. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 101823–101832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunkara, R.; Luo, T. No more strided convolutions or pooling: A new CNN building block for low-resolution images and small objects. In Proceedings of the Machine Learning and Knowledge Discovery in Databases, ECML PKDD 2022, PT III, Grenoble, France, 19–23 September 2023; Volume 13715, pp. 443–459. [Google Scholar]
- Su, K.K.; Cao, L.H.; Zhao, B.T.; Li, N.; Wu, D.; Han, X.Y. N-IoU: Better IoU-based bounding box regression loss for object detection. Neural Comput. Appl. 2024, 36, 3049–3063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.Q.; Wang, J.; Zhao, H. Research on apple recognition algorithm in complex orchard environment based on deep learning. Sensors 2023, 23, 5425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, Z.J.; Chen, Y.H.; Xu, Z.W.; Yu, R. Wise-IoU: Bounding box regression loss with dynamic focusing mechanism. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2301.10051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.X.; Wang, F.W.; Wang, W.M.; Zhao, Q.H.; Ning, W.J.; Wu, H.D. Research on Fire Smoke Detection Algorithm Based on Improved YOLOv8. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 117354–117362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.; Yang, T.Y.; Xiao, Y.F.; Yao, H.C.; Adeli, H. Vision-based real-time structural vibration measurement through deep-learning-based detection and tracking methods. Eng. Struct. 2023, 281, 115676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.Y.; Chen, Y.J.; Xiao, C.; You, L.X.; Li, R.Z. YOLOv5s-DSD: An Improved Aerial Image Detection Algorithm Based on YOLOv5s. Sensors 2023, 23, 6905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Hua, Z.X.; Wen, Y.C.; Zhang, S.J.; Xu, X.S.; Song, H.B. E-YOLO: Recognition of estrus cow based on improved YOLOv8n model. Expert Syst. Appl. 2024, 238, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, T.H.; Song, L.; Ge, Y.X.; Liu, W.Y.; Wang, X.G.; Shan, Y. YOLO-World: Real-Time Open-Vocabulary Object Detection. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 16–22 June 2024; pp. 16901–16911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro-Bello, M.; Roman-Padilla, D.B.; Morales-Morales, C.; Campos-Francisco, W.; Marmolejo-Vega, C.V.; Marmolejo-Duarte, C.; Evangelista-Alcocer, Y.; Gutiérrez-Valencia, D.E. Convolutional Neural Network Models in Municipal Solid Waste Classification: Towards Sustainable Management. Sustainability 2025, 17, 3523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, H.W.; Pei, X.Y.; Zhang, T.H.; Zhang, L.Q. Research on flame detection method based on improved SSD algorithm. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. 2023, 45, 6501–6512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Ou, X.M.; Xu, L. A Collaborative Region Detection and Grading Framework for Forest Fire Smoke Using Weakly Supervised Fine Segmentation and Lightweight Faster-RCNN. Forests 2021, 12, 768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Evaluation Metrics | Role |
|---|---|
| mAP@0.5 | The mean Average Precision (mAP) calculated at a single IoU threshold of 0.5. |
| mAP@0.5:0.95 | The mAP averaged over multiple IoU thresholds ranging from 0.5 to 0.95 in increments of 0.05. |
| Precision | The ratio of correctly predicted positive observations to the total predicted positive observations. |
| Recall | The ratio of correctly predicted positive observations to all actual positive instances. |
| F1-score | A harmonic mean of Precision and Recall. |
| Model | mAP@0.5 (Val) | mAP@0.5:0.95 (Val) | mAP@0.5 (Test) | mAP@0.5:0.95 (Test) | Parameters/ M |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YOLOv8n | 0.762 | 0.550 | 0.723 | 0.445 | 3.03 |
| YOLOv8n+SE | 0.774 | 0.562 | 0.729 | 0.454 | 3.03 |
| YOLOv8n+SSS-Neck | 0.761 | 0.550 | 0.721 | 0.444 | 1.96 |
| YOLOv8n+WIoU | 0.769 | 0.559 | 0.727 | 0.449 | 3.03 |
| SSS-YOLOv8n | 0.783 | 0.573 | 0.736 | 0.464 | 1.99 |
| Model | Category | Precision | Recall | F1-Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| YOLOv8n | Smoke | 0.8195 | 0.7025 | 0.7565 |
| Flame | 0.7725 | 0.6820 | 0.7244 | |
| YOLOv8n+SE | Smoke | 0.8390 | 0.7135 | 0.7712 |
| Flame | 0.7900 | 0.6980 | 0.7412 | |
| YOLOv8n+SSS-Neck | Smoke | 0.8196 | 0.7024 | 0.7565 |
| Flame | 0.7727 | 0.6813 | 0.7241 | |
| YOLOv8n+WIoU | Smoke | 0.8212 | 0.7130 | 0.7633 |
| Flame | 0.7824 | 0.6945 | 0.7358 | |
| Symmetry SSS-YOLOv8n | Smoke | 0.8489 | 0.7212 | 0.7799 |
| Flame | 0.7987 | 0.7010 | 0.7467 |
| Models | Precision | Recall | Parameters/M | Model Size/MB |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| YOLOv8n | 0.7725 | 0.6820 | 3.03 | 6.3 |
| YOLOv8n+CBAM | 0.7555 | 0.6400 | 3.12 | 6.5 |
| YOLOv8n+SE | 0.7900 | 0.6980 | 3.03 | 6.3 |
| Models | Precision(%) | Recall(%) | mAP50(%) | FPS |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| YOLOv3-Tiny | 63.4 | 62.8 | 63.5 | 69 |
| YOLOv5s | 74.5 | 65.7 | 72.9 | 67 |
| YOLOv7-Tiny | 71.1 | 66.9 | 71.4 | 97 |
| YOLOv8n | 77.3 | 68.2 | 74.8 | 230 |
| YOLOv8n-World | 77.9 | 68.8 | 75.9 | 223 |
| YOLOv9-Tiny | 78.1 | 67.8 | 77.2 | 93 |
| YOLOv8-FEP | 78.8 | 70.8 | 77.9 | 213 |
| YOLOv11n | 79.5 | 71.8 | 78.7 | 253 |
| Symmetry SSS-YOLOv8n | 79.9 | 70.1 | 78.3 | 226 |
| Models | SSD | Faster_RCNN | Symmetry SSS-YOLOv8n |
|---|---|---|---|
| TP | 1160 | 1197 | 1322 |
| FP | 394 | 357 | 332 |
| FN | 518 | 481 | 356 |
| Models | mAP@0.5(%) | Precision(%) | Recall(%) | F1-Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SSD | 72.9 | 74.6 | 69.1 | 71.8 |
| Faster_RCNN | 74.4 | 77.0 | 71.3 | 74.1 |
| symmetry SSS-YOLOv8n | 78.3 | 79.9 | 78.8 | 79.4 |
| Total | TP | FN | Recall |
|---|---|---|---|
| 30 | 28 | 2 | 93.3% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, B.; Wang, J.; An, Q.; Wan, Y.; Zhou, J.; Chen, X. Gardens Fire Detection Based on the Symmetrical SSS-YOLOv8 Network. Symmetry 2025, 17, 1269. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17081269
Liu B, Wang J, An Q, Wan Y, Zhou J, Chen X. Gardens Fire Detection Based on the Symmetrical SSS-YOLOv8 Network. Symmetry. 2025; 17(8):1269. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17081269
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Bo, Junhua Wang, Qing An, Yanglu Wan, Jianing Zhou, and Xijiang Chen. 2025. "Gardens Fire Detection Based on the Symmetrical SSS-YOLOv8 Network" Symmetry 17, no. 8: 1269. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17081269
APA StyleLiu, B., Wang, J., An, Q., Wan, Y., Zhou, J., & Chen, X. (2025). Gardens Fire Detection Based on the Symmetrical SSS-YOLOv8 Network. Symmetry, 17(8), 1269. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17081269








