Forgery-Aware Guided Spatial–Frequency Feature Fusion for Face Image Forgery Detection
Abstract
1. Introduction
- We propose a novel forgery-aware guided spatial–frequency feature fusion network that jointly utilizes spatial semantics, frequency patterns, and forgery-aware cues. This unified framework enhances the detection of fine-grained tampering and strengthens the complementarity between spatial and frequency domains.
- We design a lightweight forgery-aware module (FAM) based on U-Net to generate pixel-level saliency maps. These maps, guided by a symmetry analysis mechanism and semantic consistency modeling, help the network concentrate on manipulated facial regions, improving regional discrimination without requiring ground-truth masks.
- We enhance feature extraction by incorporating an improved Swin Transformer with dynamic windowing and spatial pyramid pooling for capturing multi-scale spatial features. Additionally, we utilize Haar wavelet transforms to extract high-frequency forgery artifacts. A cross-domain interaction mechanism, along with channel recalibration and spatial gating, is employed to effectively fuse and refine features from both domains.
2. Related Work
3. Methods
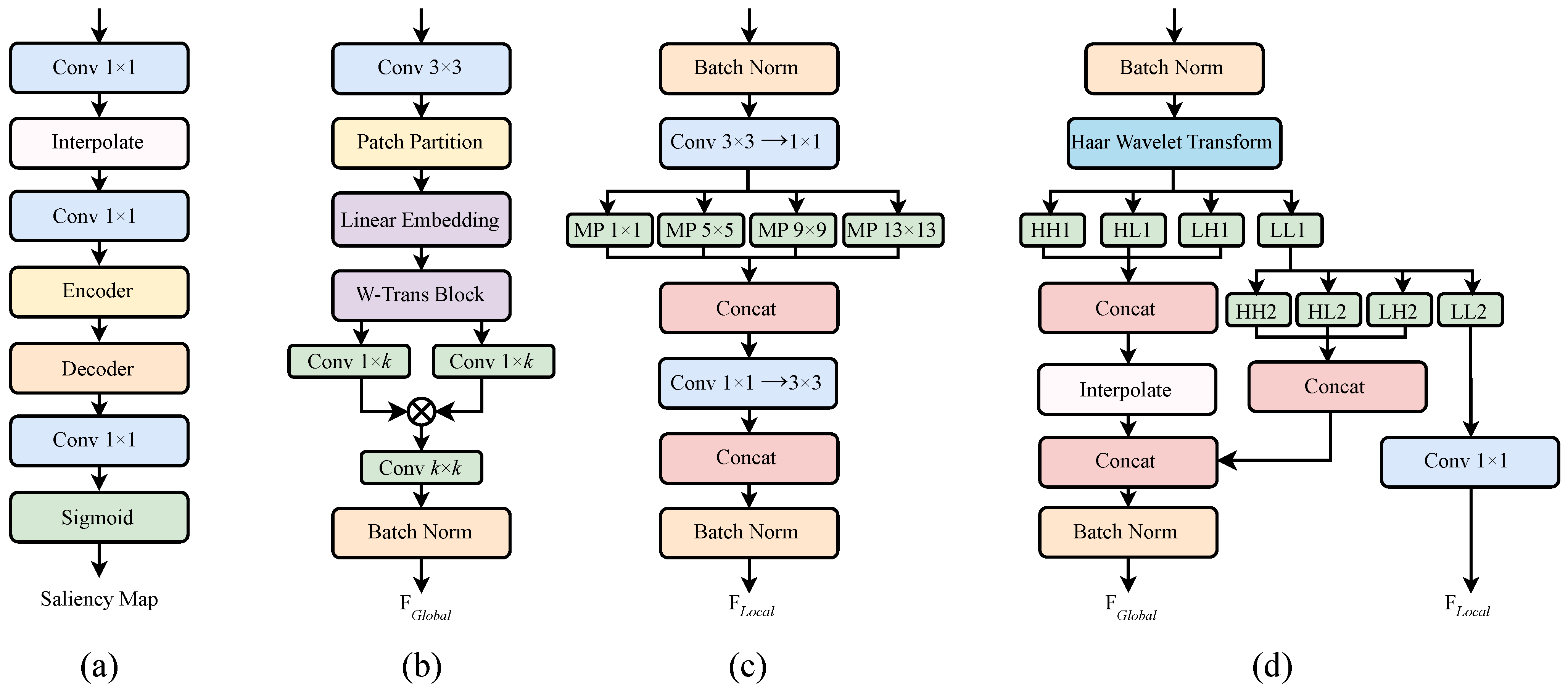
3.1. Forgery-Aware Module Guided by Facial Symmetry and Semantic Consistency
3.1.1. Symmetry-Aware Modeling of Facial Structure
3.1.2. Semantic Consistency-Aware Modeling of Facial Expressions
3.1.3. Saliency Map Generation and Guided Feature Fusion
3.2. Spatial-Domain Feature Extraction Module
3.2.1. Global Feature Extraction Module
3.2.2. Local Feature Extraction Module
3.3. Frequency-Domain Feature Extraction Module
3.4. Forgery-Aware Guided Spatial–Frequency Fusion Module
3.4.1. Cross-Domain Interaction Fusion Module
3.4.2. Channel Recalibration Attention
3.4.3. Spatial Gating Attention
4. Experiments
4.1. Experimental Setup
4.1.1. Datasets
4.1.2. Data Preprocessing
4.1.3. Training and Evaluation Settings
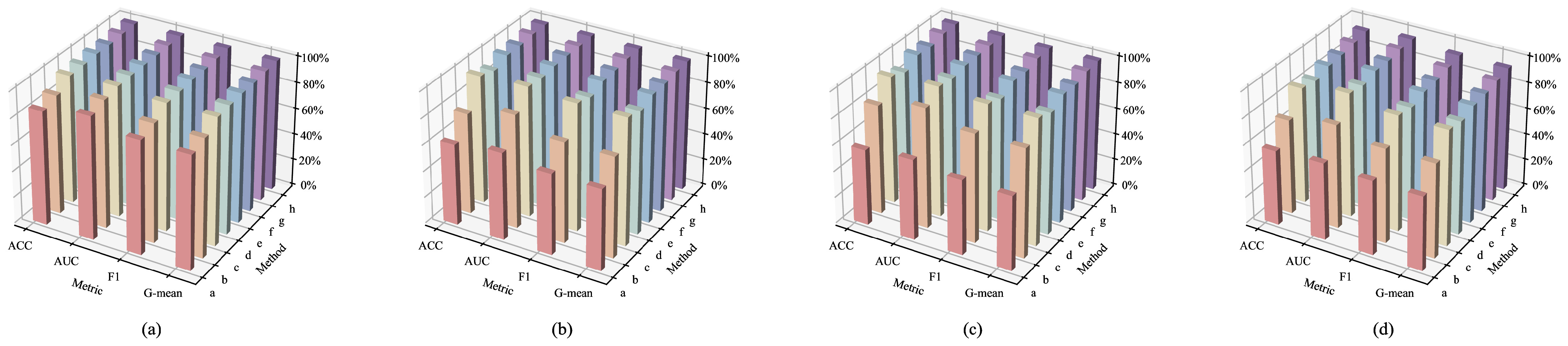
4.2. Comparative Evaluation
4.2.1. Evaluation and Comparison on FF++ and Celeb-DFv2
4.2.2. Cross-Dataset Evaluation and Comparison
4.3. Ablation Study
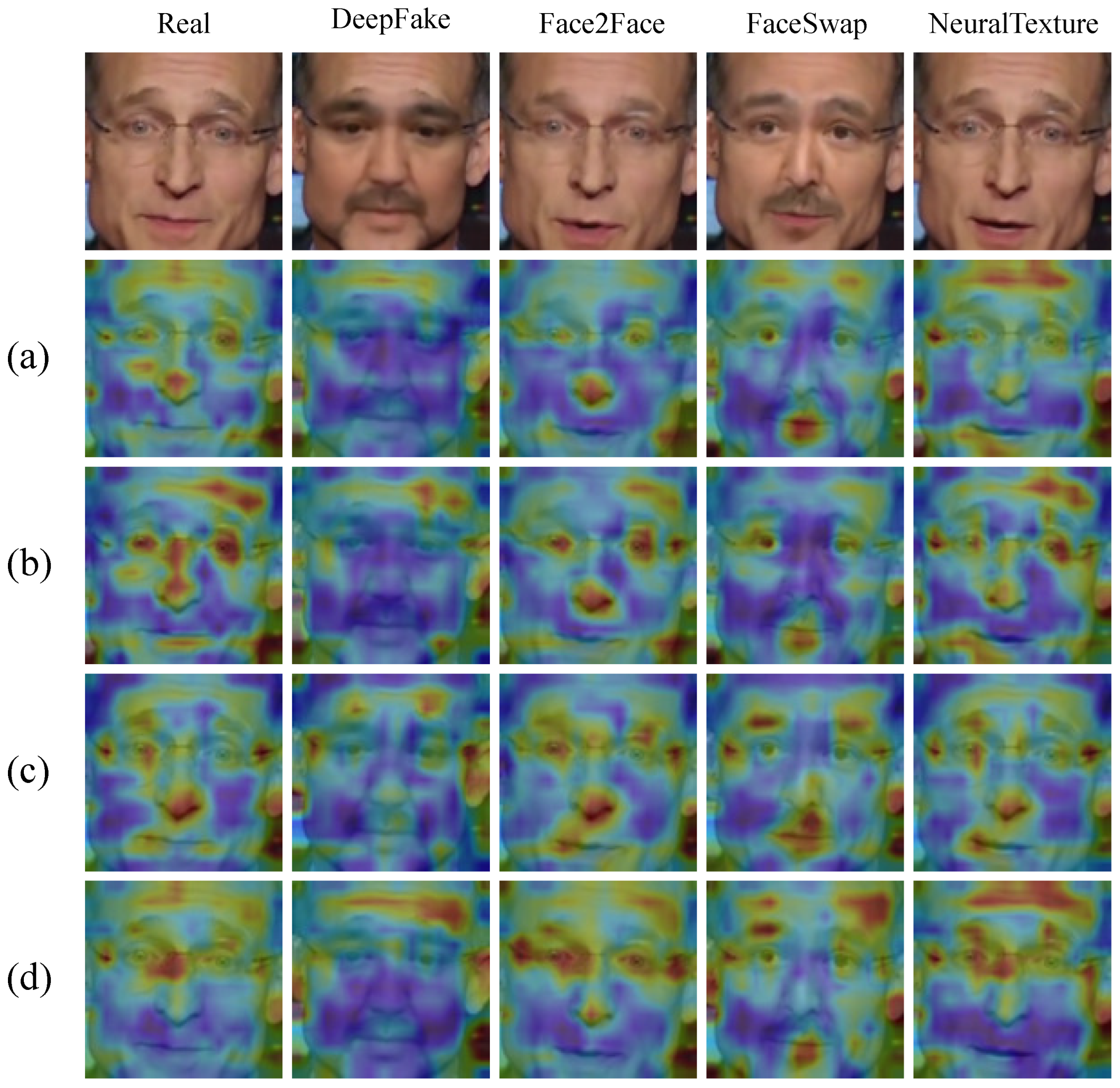
4.4. Visualization Analysis
4.5. Symmetry Analysis Under Non-Frontal Poses
5. Discussion
- Developing more robust modeling approaches to improve detection accuracy under compression and quality degradation;
- Incorporating temporal modeling by leveraging dependencies across video frames;
- Extending the framework to multi-modal forgery detection tasks, such as voice–face matching verification and synthetic speech detection.
- Conducting comprehensive technical comparisons (e.g., parameter count, model complexity, and inference latency) to further assess the computational efficiency and deployment feasibility of the proposed method in comparison with state-of-the-art baselines.
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gao, J.; Xia, Z.; Marcialis, G.L.; Dang, C.; Dai, J.; Feng, X. DeepFake detection based on high-frequency enhancement network for highly compressed content. Expert Syst. Appl. 2024, 249, 123732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyagi, S.; Yadav, D. A detailed analysis of image and video forgery detection techniques. Vis. Comput. 2023, 39, 813–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, L.; Feng, G.; Qian, Z. Image Inpainting Anti-Forensics Network via Attention-Guided Hierarchical Reconstruction. Symmetry 2023, 15, 393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossler, A.; Cozzolino, D.; Verdoliva, L.; Riess, C.; Thies, J.; Nießner, M. Faceforensics++: Learning to detect manipulated facial images. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Yang, X.; Sun, P.; Qi, H.; Lyu, S. Celeb-df: A large-scale challenging dataset for deepfake forensics. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 3207–3216. [Google Scholar]
- Tolosana, R.; Vera-Rodriguez, R.; Fierrez, J.; Morales, A.; Ortega-Garcia, J. Deepfakes and beyond: A survey of face manipulation and fake detection. Inf. Fusion 2020, 64, 131–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popescu, A.C.; Farid, H. Exposing digital forgeries by detecting traces of resampling. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2005, 53, 758–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Jin, X.; Gao, S.; Wu, L.; Yao, S.; Jiang, Q. Tan-gfd: Generalizing face forgery detection based on texture information and adaptive noise mining. Appl. Intell. 2023, 53, 19007–19027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukáš, J.; Fridrich, J.; Goljan, M. Detecting digital image forgeries using sensor pattern noise. In Proceedings of the Security, Steganography, and Watermarking of Multimedia Contents VIII, San Jose, CA, USA, 16–19 January 2006; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2006; Volume 6072, pp. 362–372. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, W.; Huang, J.; Qiu, G. JPEG error analysis and its applications to digital image forensics. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2010, 5, 480–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, P.; Han, X.; Morariu, V.I.; Davis, L.S. Two-stream neural networks for tampered face detection. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 1831–1839. [Google Scholar]
- Dang, L.M.; Hassan, S.I.; Im, S.; Moon, H. Face image manipulation detection based on a convolutional neural network. Expert Syst. Appl. 2019, 129, 156–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, A.; Cai, R.; Kong, C.; Ju, Y.; Kang, X.; Huang, J.; Life, A.C.K. Forgery-aware Adaptive Learning with Vision Transformer for Generalized Face Forgery Detection. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2024, 35, 4116–4129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawar, D.; Gowda, R.; Chandra, K. Image forgery classification and localization through vision transformers. Int. J. Multimed. Inf. Retr. 2025, 14, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.C.; Lu, T.C.; Zhu, Z.H.; Tian, H. An effective authentication scheme using DCT for mobile devices. Symmetry 2018, 10, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Y.; Yin, G.; Sheng, L.; Chen, Z.; Shao, J. Thinking in frequency: Face forgery detection by mining frequency-aware clues. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 86–103. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Xie, H.; Yu, L.; Gao, X.; Zhang, Y. Discriminative feature mining based on frequency information and metric learning for face forgery detection. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 2021, 35, 12167–12180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Yao, T.; Chen, Y.; Ding, S.; Li, J.; Ji, R. Local relation learning for face forgery detection. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Online, 2–9 February 2021; Volume 35, pp. 1081–1088. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Li, X.; Zhou, W.; Chen, Y.; He, Y.; Xue, H.; Zhang, W.; Yu, N. Spatial-phase shallow learning: Rethinking face forgery detection in frequency domain. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 772–781. [Google Scholar]
- Miao, C.; Tan, Z.; Chu, Q.; Liu, H.; Hu, H.; Yu, N. F 2 trans: High-frequency fine-grained transformer for face forgery detection. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2023, 18, 1039–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chollet, F. Xception: Deep learning with depthwise separable convolutions. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 1251–1258. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, M.; Le, Q. Efficientnet: Rethinking model scaling for convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Long Beach, CA, USA, 9–15 June 2019; PMLR: New York, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 6105–6114. [Google Scholar]
- Dosovitskiy, A.; Beyer, L.; Kolesnikov, A.; Weissenborn, D.; Zhai, X.; Unterthiner, T.; Dehghani, M.; Minderer, M.; Heigold, G.; Gelly, S.; et al. An image is worth 16x16 words: Transformers for image recognition at scale. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2010.11929. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Lin, Y.; Cao, Y.; Hu, H.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, S.; Guo, B. Swin transformer: Hierarchical vision transformer using shifted windows. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021; pp. 10012–10022. [Google Scholar]
- Ganguly, S.; Ganguly, A.; Mohiuddin, S.; Malakar, S.; Sarkar, R. ViXNet: Vision Transformer with Xception Network for deepfakes based video and image forgery detection. Expert Syst. Appl. 2022, 210, 118423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Zhang, B.; Li, Z.; Pang, G.; Teng, Z.; Fan, J. Interactive two-stream network across modalities for deepfake detection. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2023, 33, 6418–6430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, C.; Tan, Z.; Chu, Q.; Yu, N.; Guo, G. Hierarchical frequency-assisted interactive networks for face manipulation detection. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2022, 17, 3008–3021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Liu, G.; Yuan, Y. F3-Net: Multiview scene matching for drone-based geo-localization. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 61, 5610611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, C.; Zhao, Y.; Wei, S.; Gu, G.; Liu, P.; Wei, Y. Frequency-aware deepfake detection: Improving generalizability through frequency space domain learning. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 20–27 February 2024; Volume 38, pp. 5052–5060. [Google Scholar]
- Uddin, M.; Fu, Z.; Zhang, X. Deepfake face detection via multi-level discrete wavelet transform and vision transformer. Vis. Comput. 2025, 41, 7049–7061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, L.; Fang, Z.; Li, X.; Dong, X.; Jin, Z.; Chen, Y.; Lyu, S. Adaptive face forgery detection in cross domain. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Tel Aviv, Israel, 23–27 October 2022; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; pp. 467–484. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Peng, C.; Liu, D.; Wang, N.; Gao, X. Spatial-temporal frequency forgery clue for video forgery detection in VIS and NIR scenario. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2023, 33, 7943–7956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Chen, Q.; Jing, B.; Tang, Y.; Song, Z.; Wang, B. Deepfake Detection Based on the Adaptive Fusion of Spatial-Frequency Features. Int. J. Intell. Syst. 2024, 2024, 7578036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, C.; Zhao, Y.; Wei, S.; Gu, G.; Liu, P.; Wei, Y. Rethinking the up-sampling operations in cnn-based generative network for generalizable deepfake detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 16– 22 June 2024; pp. 28130–28139. [Google Scholar]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention–MICCAI 2015: 18th International Conference, Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015; proceedings, part III 18. Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, J.; Shen, L.; Sun, G. Squeeze-and-excitation networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 7132–7141. [Google Scholar]
- Selvaraju, R.R.; Cogswell, M.; Das, A.; Vedantam, R.; Parikh, D.; Batra, D. Grad-cam: Visual explanations from deep networks via gradient-based localization. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 618–626. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Z.; Yang, G.; Zhang, D.; Xia, M. Rethinking gradient operator for exposing AI-enabled face forgeries. Expert Syst. Appl. 2023, 215, 119361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yan, J.; Liu, W. Generalizing face forgery detection with high-frequency features. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 16317–16326. [Google Scholar]



| Parameters | Value |
|---|---|
| Batch Size | 32 |
| Input Size | 224 |
| Dropout | 0.1 |
| Optimizer | adamw |
| Optimizer Epsilon | 1 × 10−8 |
| Gradient Clipping | 0.05 |
| Weight Decay | 0.03 |
| Learning Rate Scheduler | cosine |
| Learning Rate | 1 × 10−3 |
| Warmup Learning Rate | 1 × 10−5 |
| Color Jitter | 0.4 |
| Smoothing | 0.1 |
| Mixup | 0.8 |
| Methods | FF++ (C23) | FF++ (C40) | Celeb-DFv2 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ACC | AUC | F1 | Gm | ACC | AUC | F1 | Gm | ACC | AUC | F1 | Gm | |
| ViT [23] | 59.57 | 63.50 | 59.50 | 59.43 | 56.40 | 58.87 | 56.39 | 56.39 | 86.09 | 92.30 | 86.09 | 86.08 |
| MLFFE_ViT [30] | 71.43 | 79.25 | 73.40 | 71.35 | 66.47 | 72.71 | 66.28 | 66.04 | 77.29 | 85.49 | 77.12 | 76.83 |
| NPR [34] | 90.74 | 96.42 | 90.73 | 90.69 | 73.08 | 80.40 | 73.06 | 73.03 | 95.33 | 99.24 | 95.33 | 95.33 |
| EfficientNet-B4 [22] | 92.77 | 97.71 | 92.77 | 92.77 | 75.16 | 84.04 | 75.16 | 75.16 | 97.20 | 99.52 | 97.20 | 97.19 |
| Xception [21] | 94.04 | 97.62 | 94.04 | 94.00 | 75.78 | 83.89 | 75.75 | 75.71 | 97.40 | 99.65 | 97.40 | 97.40 |
| GocNet [38] | 94.79 | 98.46 | 94.79 | 94.79 | 73.51 | 81.55 | 73.49 | 73.43 | 97.05 | 99.36 | 97.05 | 97.05 |
| GFFD [39] | 96.59 | 98.26 | 96.62 | 96.61 | 75.39 | 84.16 | 75.39 | 75.39 | 97.77 | 99.63 | 97.77 | 97.77 |
| Ours | 96.68 | 98.98 | 96.68 | 96.67 | 77.06 | 84.52 | 77.06 | 77.05 | 98.61 | 99.71 | 98.61 | 98.60 |
| Methods | Deepfake | Face2Face | FaceSwap | NeuralTexture | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ACC | AUC | F1 | Gm | ACC | AUC | F1 | Gm | ACC | AUC | F1 | Gm | ACC | AUC | F1 | Gm | |
| ViT [23] | 86.71 | 93.63 | 86.71 | 86.69 | 61.82 | 66.37 | 61.81 | 61.80 | 57.71 | 61.20 | 57.21 | 56.68 | 56.89 | 58.66 | 56.63 | 56.36 |
| MLFFE_ViT [30] | 90.61 | 97.42 | 90.59 | 90.52 | 76.82 | 86.49 | 76.82 | 76.81 | 83.07 | 91.50 | 83.07 | 83.07 | 71.92 | 78.80 | 71.92 | 71.91 |
| NPR [34] | 97.50 | 99.69 | 97.50 | 97.50 | 97.18 | 99.38 | 97.18 | 97.16 | 96.64 | 99.49 | 96.64 | 96.64 | 88.29 | 94.39 | 88.25 | 88.13 |
| EfficientNet-B4 [22] | 98.00 | 99.78 | 98.00 | 98.00 | 93.64 | 98.02 | 93.64 | 93.64 | 92.50 | 97.58 | 92.50 | 92.50 | 86.18 | 92.51 | 86.16 | 86.08 |
| Xception [21] | 98.86 | 99.88 | 98.86 | 98.85 | 97.86 | 99.26 | 97.86 | 97.86 | 97.96 | 99.57 | 97.96 | 97.96 | 89.75 | 95.80 | 89.73 | 89.66 |
| GocNet [38] | 98.61 | 99.87 | 98.61 | 98.60 | 98.00 | 99.49 | 98.00 | 98.00 | 97.14 | 99.59 | 97.14 | 97.14 | 90.54 | 95.64 | 90.52 | 90.45 |
| GFFD [39] | 99.54 | 99.99 | 99.54 | 99.54 | 99.29 | 99.58 | 99.29 | 99.29 | 99.61 | 99.99 | 99.61 | 99.61 | 92.71 | 97.16 | 92.74 | 92.64 |
| Ours | 99.82 | 99.99 | 99.82 | 99.82 | 99.43 | 99.81 | 99.43 | 99.43 | 99.75 | 99.99 | 99.75 | 99.75 | 94.39 | 97.45 | 94.39 | 94.33 |
| Methods | Training Set | Testing Set (Celeb-DFv2) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ACC | AUC | F1 | G-Mean | ||
| ViT [23] | FF++ (C23) | 49.92 | 49.77 | 62.12 | 38.14 |
| MLFFE_ViT [30] | FF++ (C23) | 61.16 | 68.28 | 66.73 | 58.82 |
| NPR [34] | FF++ (C23) | 63.11 | 68.15 | 54.28 | 60.08 |
| EfficientNet-B4 [22] | FF++ (C23) | 71.48 | 79.61 | 72.18 | 71.44 |
| Xception [21] | FF++ (C23) | 70.86 | 77.94 | 70.25 | 70.83 |
| GocNet [38] | FF++ (C23) | 68.84 | 76.10 | 70.47 | 68.62 |
| GFFD [39] | FF++ (C23) | 67.43 | 74.84 | 71.93 | 65.50 |
| Ours | FF++ (C23) | 69.63 | 79.66 | 73.44 | 68.14 |
| Component Configuration | ACC | AUC | F1 | G-Mean | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spatial | Global Only | 60.54 | 64.64 | 60.15 | 59.72 |
| Local Only | 60.62 | 64.60 | 59.84 | 59.00 | |
| Full Spatial Branch | 95.28 | 98.19 | 95.28 | 95.17 | |
| Frequency | First-Stage Haar Only | 57.71 | 60.17 | 57.53 | 57.35 |
| High-Frequency Only | 58.17 | 60.57 | 58.00 | 57.85 | |
| Low-Frequency Only | 51.55 | 51.40 | 51.19 | 50.82 | |
| Full Frequency Branch | 95.12 | 98.07 | 95.10 | 95.09 | |
| Spatial + Frequency | 95.66 | 98.43 | 95.66 | 95.65 | |
| Spatial + Frequency + | Symmetry-Aware Module | 95.73 | 98.30 | 95.73 | 95.72 |
| Semantic Consistency Module | 95.90 | 98.46 | 95.91 | 95.88 | |
| Saliency-Guided Fusion Only | 96.29 | 98.71 | 96.29 | 96.28 | |
| Full FAM (with saliency) | 96.68 | 98.97 | 96.68 | 96.67 | |
| Group | Yaw Range | ACC | AUC | F1 | G-Mean | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Strict Frontal | 0.03528 | 96.68 | 98.98 | 96.68 | 96.67 | |
| Mild Profile | 0.03603 | 94.81 | 97.75 | 94.81 | 94.81 | |
| Moderate Profile | 0.03666 | 93.03 | 97.68 | 93.03 | 93.03 | |
| Large Profile | 0.03985 | 91.80 | 96.40 | 91.80 | 91.78 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
He, Z.; Liu, Z.; Zhao, Z. Forgery-Aware Guided Spatial–Frequency Feature Fusion for Face Image Forgery Detection. Symmetry 2025, 17, 1148. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17071148
He Z, Liu Z, Zhao Z. Forgery-Aware Guided Spatial–Frequency Feature Fusion for Face Image Forgery Detection. Symmetry. 2025; 17(7):1148. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17071148
Chicago/Turabian StyleHe, Zhenxiang, Zhihao Liu, and Ziqi Zhao. 2025. "Forgery-Aware Guided Spatial–Frequency Feature Fusion for Face Image Forgery Detection" Symmetry 17, no. 7: 1148. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17071148
APA StyleHe, Z., Liu, Z., & Zhao, Z. (2025). Forgery-Aware Guided Spatial–Frequency Feature Fusion for Face Image Forgery Detection. Symmetry, 17(7), 1148. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17071148





