Accelerated Gradient-CQ Algorithms for Split Feasibility Problems
Abstract
1. Introduction
- -
- -
- We adopt double non-Lipschitz step sizes [9], which remove the restrictions imposed by the condition and the requirement . The structures of our proposed step sizes are similar symmetry, and they have positive lower bounds and grow with the iterative count, leading to accelerated convergence;
- -
- We propose inertial gradient-CQ algorithms with double non-Lipschitz step sizes for solving the , and we establish their weak and strong convergence without requiring Lipschitz continuity of or firm nonexpansiveness of , respectively;
- -
- We apply our methods to the LASSO problem to demonstrate and validate the theoretical results.
2. Preliminaries
- Then, there exists , such that converges weakly to
- Then, is a converging sequence and where (for any ).
3. Weak Convergence
| Algorithm 1: A weakly convergent algorithm for SFP. |
| Step 0. Take , , , and |
| . The sequence satisfies |
| . |
| Step n. Compute |
| where the stepsizes and are updated via |
| and |
|
4. Strong Convergence
| Algorithm 2: A strongly convergent algorithm for SFP. |
| Step 0. Take , , , and |
| , u is a fixed vector. The sequence satisfies |
| . |
| Step n. Compute |
| where the step sizes and are updated via |
| and |
|
- From Lemma 2 (i), we obtain
5. Numerical Experiments
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Censor, Y.; Elfving, T. A multiprojection algorithm using Bregman projection in a product space. Numer. Algorithms 1994, 8, 221–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrne, C. A unified treatment of some iterative algorithms in signal processing and image reconstruction. Inverse Probl. 2004, 20, 103–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrne, C. Iterative oblique projection onto convex sets and the split feasibility problem. Inverse Probl. 2002, 18, 441–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Censor, Y.; Elfving, T.; Kopf, N.; Bortfeld, T. The multiple-sets split feasibility problem and its applications for inverse problems. Inverse Probl. 2005, 21, 2071–2084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, Y.; Sun, J.; Xu, H. Inertial accelerated algorithm for solving a split feasibility problem. J. Ind. Manag. Optim. 2017, 13, 1383–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibali, A.; Mai, D.T.; Vinh, N.T. A new relaxed CQ algorithm for solving split feasibility problems in Hilbert spaces and its applications. J. Ind. Manag. Optim. 2019, 15, 963–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, G.; Martin, V.; Wang, F.; Xu, H.K. Solving the split feasibility problem without prior knowledge of matrix norms. Inverse Probl. 2012, 28, 085004. [Google Scholar]
- Shehu, Y.; Gibali, A. New inertial relaxed method for solving split feasibilities. Optim. Lett. 2020, 15, 2109–2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, D.R.; Cho, Y.J.; Dong, Q.L.; Kashyap, M.R.; Li, X.H. Inertial relaxed CQ algorithms for solving a split feasibility problem in Hilbert spaces. Numer. Algorithms 2020, 87, 1075–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suantai, S.; Pholasa, N.; Cholamjiak, P. The modified inertial relaxed CQ algorithm for solving the split feasibility problems. J. Ind. Manag. Optim. 2018, 23, 1595–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Liu, H. An inertial Halpern-type CQ algorithm for solving split feasibility problems in Hilbert spaces. J. Appl. Math. Comput. 2021, 68, 1699–1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reich, S.; Tuyen, T.M.; Ha, M.T.N. An optimization approach to solving the split feasibility problem in Hilbert spaces. J. Glob. Optim. 2021, 79, 837–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Q.L.; He, S.; Rassias, M.T. General splitting methods with linearization for the split feasibility problem. J. Glob. Optim. 2021, 79, 813–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yen, L.H.; Huyen, N.T.T.; Muu, L.D. A subgradient algorithm for a class of nonlinear split feasibility problems: Application to jointly constrained Nash equilibrium models. J. Glob. Optim. 2019, 73, 849–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Pong, T.K.; Tan, L.; Zeng, L. A difference-of-convex approach for split feasibility with applications to matrix factorizations and outlier detection. J. Glob. Optim. 2020, 78, 107–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Hu, Y.; Yu, C.K.W.; Zhuang, X. A Family of Projection Gradient Methods for Solving the Multiple-Sets Split Feasibility Problem. J. Optim. Theory Appl. 2019, 183, 520–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, B.; Wang, C.; Xiu, N. Analysis on Newton projection method for the split feasibility problem. Comput. Optim. Appl. 2017, 67, 175–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, X.; Wang, L. A fixed point method for solving a split feasibility problem in Hilbert spaces. RACSAM 2019, 113, 315–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q. On variable-step relaxed projection algorithm for variational inequalities. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 2005, 302, 166–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Q.L.; Tang, Y.C.; Cho, Y.J.; Rassias, T.M. “Optimal” choice of the step length of the projection and contraction methods for solving the split feasibility problem. J. Glob. Optim. 2018, 71, 341–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibali, A.; Liu, L.W.; Tang, Y.C. Note on the modified relaxation CQ algorithm for the split feasibility problem. Optim. Lett. 2018, 12, 817–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kesornprom, S.; Pholasa, N.; Cholamjiak, P. On the convergence analysis of the gradient-CQ algorithms for the split feasibility problem. Numer. Algorithms 2020, 84, 997–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, B.; Xiu, N. A note on the CQ algorithm for the split feasibility problem. Inverse Probl. 2005, 21, 1655–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Chi, E.C.; Yang, M.; Lange, K. A majorization–Cminimization algorithm for split feasibility problems. Comput. Optim. Appl. 2018, 71, 795–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halpern, B. Fixed points of nonexpanding maps. Bull. Am. Math. Soc. 1967, 73, 957–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polyak, B.T. Some methods of speeding up the convergence of iteration methods. Ussr Comput. Math. Math. Phys. 1964, 4, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saejung, S.; Yotkaew, P. Approximation of zeros of inverse strongly monotone operators in Bachna spaces. Nolinear Anal. 2012, 75, 742–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, F.; Attouch, H. An inertial proximal method for maximal monotone operators via discretization of a nonlinear oscillator with damping. Set-Valued Anal. 2001, 9, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maingé, P.E.; Gobinddass, M.L. Convergence of one-step projected gradient methods for variational inequalities. J. Optim. Theory Appl. 2016, 171, 146–168. [Google Scholar]
- Alvarez, F. Weak convergence of a relaxed and inertial hybrid projection-proximal point algorithm for maximal monotone operators in Hilbert space. SIAM J. Optim. 2004, 14, 773–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nesterov, Y. A method for solving the convex programming problem with convergence rate O(1/k2). Dokl. Akad. Nauk. SSSR 1983, 269, 543–547. [Google Scholar]
- Bauschke, H.H.; Combettes, P.L. Convex Analysis and Monotone Operator Theory in Hilbert Spaces; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Agarwal, R.P.; Regan, D.O.; Sahu, D.R. Fixed Point Theory for Lipschitzian-Type Mappings with Applications, Topological Fixed Point Theory and Its Applications; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Osilike, M.O.; Aniagbosor, S.C. Weak and strong convergence theorems for fixed points of asymptotically nonexpansive mappings. Math. Comput. Model. 2000, 32, 1181–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinh, N.; Cholamjiak, P.; Suantai, S. A new CQ algorithm for solving split feasibility problems in Hilbert spaces. Bull. Malays. Math. Sci. Soc. 2018, 42, 2517–2534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauschke, H.H.; Combettes, P.L. A weak-to-strong convergence principle for fejér-monotone methods in Hilbert spaces. Math. Oper. Res. 2001, 26, 248–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.K. Iterative methods for solving the split feasibility in infinite-dimensional Hilbert spaces. Inverse Probl. 2010, 26, 105018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maingé, P.E. Convergence theorems for inertial KM-type algorithms. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 2018, 219, 223–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Jia, Z.; Li, Q. On inertial non-lipschitz stepsize algorithms for split feasibility problems. Comp. Appl. Math. 2024, 43, 431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tibshirani, R. Regression shrinkage and selection via the Lasso. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B 1996, 58, 267–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, B.; Qin, X.; Wang, X. Alternated inertial algorithms for split feasibility problems. Numer. Algor 2024, 95, 773–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okeke, C.C.; Okorie, K.O.; Nwakpa, C.E.; Mewomo, O.T. Two-step inertial accelerated algorithms for solving split feasibility problem with multiple output sets. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 2025, 141, 108461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Thang, T. Projection algorithms with adaptive step sizes for multiple output split mixed variational inequality problems. Comp. Appl. Math. 2024, 43, 387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kesornprom, S.; Cholamjiak, P. Proximal type algorithms involving linesearch and inertial technique for split variational inclusion problem in hilbert spaces with applications. Optimization 2019, 68, 2369–2395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Ling, C.; Xu, H.K. An Implementable Splitting Algorithm for the ℓ1-norm Regularized Split Feasibility Problem. J. Sci. Comput. 2016, 67, 281–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Liu, H.; Li, X. The iterative method for solving the proximal split feasibility problem with an application to LASSO problem. Comp. Appl. Math. 2022, 41, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
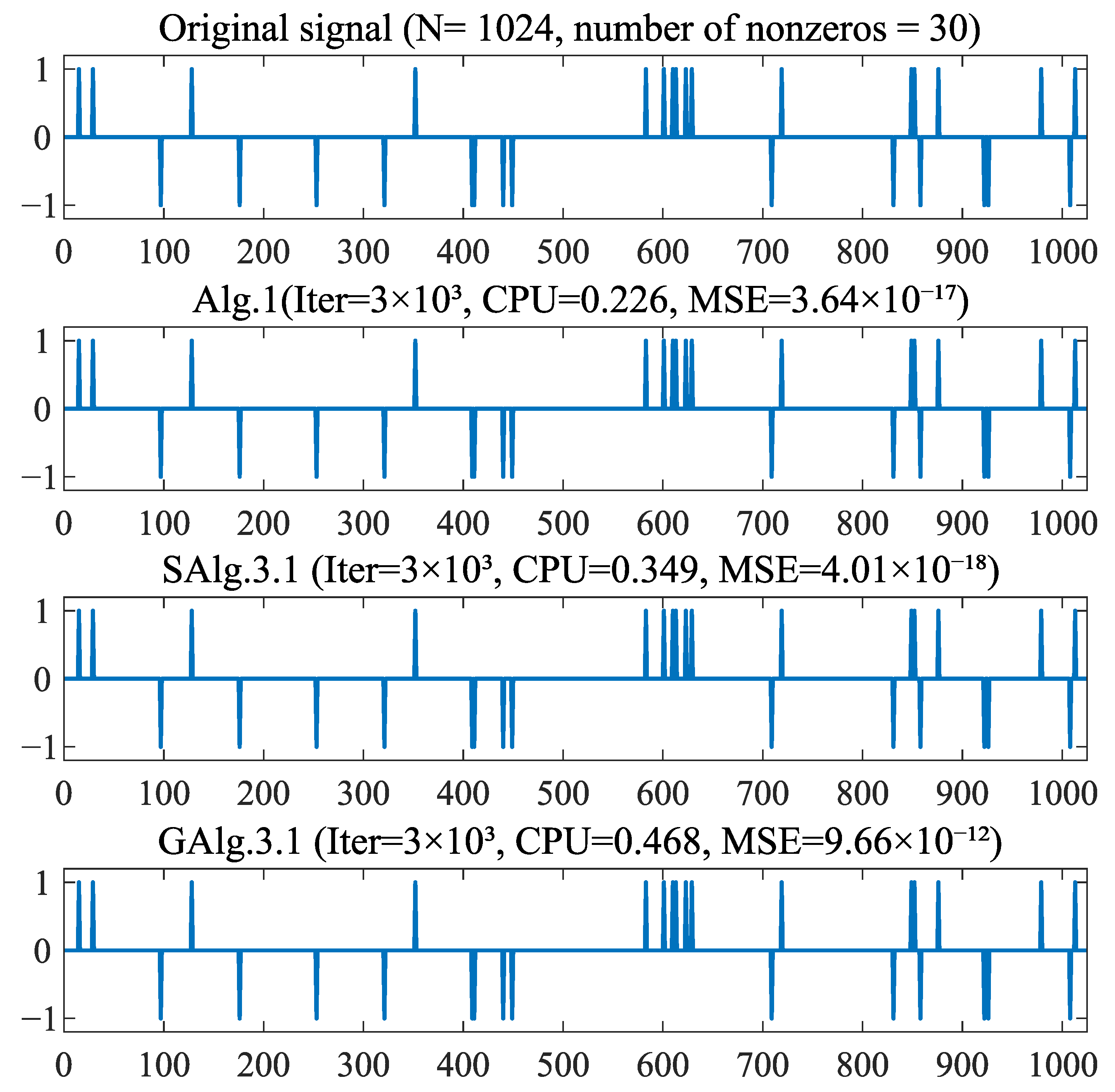
| Alg.1 | SAlg.3.1 | GAlg.3.1 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| time | time | time | ||||
| (240, 1024, 30) | 1.8479 × 10−10 | 0.9192 | 2.5269 × 10−9 | 1.3943 | 1.3316 × 10−5 | 1.8579 |
| (480, 2048, 60) | 1.1073 × 10−14 | 4.5840 | 6.8123 × 10−12 | 6.7324 | 3.3606 × 10−6 | 8.8775 |
| (720, 3072, 90) | 1.0120 × 10−14 | 27.5802 | 1.2631 × 10−12 | 40.6743 | 1.7002 × 10−6 | 53.7751 |
| (960, 4096, 120) | 1.0123 × 10−14 | 50.4016 | 4.7432 × 10−13 | 75.4683 | 7.8236 × 10−7 | 100.9057 |
| (1200, 5120, 150) | 9.1161 × 10−15 | 81.3778 | 3.0586 × 10−14 | 122.1031 | 6.1916 × 10−7 | 162.5137 |
| Cases | Alg. 2 | MLAlg. 3.1 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| iter. | time | iter. | time | ||
| Case 1 | 7 | 0.1751 | 7 | 0.2262 | |
| 9 | 0.2418 | 10 | 0.7618 | ||
| Case 2 | 7 | 0.1680 | 7 | 0.2330 | |
| 9 | 0.2610 | 9 | 0.2839 | ||
| Alg.3 | Alg.2 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| iter. | time | iter. | time | |
| (10, 20) | 19 | 7.5570 × 10−4 | 17 | 7.4960 × 10−4 |
| (20, 20) | 20 | 6.6100 × 10−4 | 19 | 4.3310 × 10−4 |
| (30, 20) | 20 | 0.0058 | 18 | 0.0061 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Y.; Ma, X. Accelerated Gradient-CQ Algorithms for Split Feasibility Problems. Symmetry 2025, 17, 1121. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17071121
Zhang Y, Ma X. Accelerated Gradient-CQ Algorithms for Split Feasibility Problems. Symmetry. 2025; 17(7):1121. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17071121
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Yu, and Xiaojun Ma. 2025. "Accelerated Gradient-CQ Algorithms for Split Feasibility Problems" Symmetry 17, no. 7: 1121. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17071121
APA StyleZhang, Y., & Ma, X. (2025). Accelerated Gradient-CQ Algorithms for Split Feasibility Problems. Symmetry, 17(7), 1121. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17071121







